A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Closed Cell Insulating Foam: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for closed cell insulating foam
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing closed cell insulating foam can present significant challenges for international B2B buyers. As companies strive to enhance energy efficiency and reduce operational costs, the importance of selecting the right insulation material cannot be overstated. This comprehensive guide addresses the critical aspects of closed cell insulating foam, from understanding its various types and applications to navigating supplier vetting processes and evaluating cost-effectiveness.
By delving into factors such as R-value, moisture resistance, and fire retardant properties, this guide empowers businesses, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—such as Nigeria and Brazil—to make informed purchasing decisions. With a focus on practical insights, we will explore the nuances of the global market, including the latest trends and innovations that can influence your choices.
Furthermore, this guide serves as a valuable resource for identifying reputable suppliers and understanding pricing structures, ensuring that you can secure high-quality products that meet your specific needs. Whether you are involved in construction, manufacturing, or energy efficiency projects, our insights will help you navigate the complexities of the closed cell insulating foam market with confidence.
Understanding closed cell insulating foam Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Closed Cell Spray Foam | High R-value, moisture resistance, quick application | Construction, HVAC, refrigeration | Pros: Excellent thermal performance; Cons: Requires professional installation. |
| Rigid Foam Board | Solid panels, high compressive strength | Insulation for walls, roofs, and floors | Pros: Easy to cut and install; Cons: Limited flexibility in design. |
| Polyurethane Foam | Versatile, can be applied in various environments | Pipeline insulation, marine applications | Pros: Strong adhesion; Cons: Can be expensive compared to alternatives. |
| Polyisocyanurate Foam | Higher R-value than standard polyurethane | Industrial insulation, cold storage | Pros: Superior thermal resistance; Cons: More sensitive to moisture during installation. |
| Spray Foam Kits | Convenient DIY options, varying sizes available | Small-scale projects, home insulation | Pros: Easy to use; Cons: Limited coverage compared to professional kits. |
What Are the Characteristics of Closed Cell Spray Foam?
Closed cell spray foam is renowned for its high R-value, typically around 7 per inch, and exceptional moisture resistance. It expands upon application, filling gaps and creating a tight seal, which makes it ideal for a variety of applications in construction, HVAC, and refrigeration. For B2B buyers, the speed of application is a significant advantage, enabling quicker project completion. However, it often requires professional installation, which can add to overall costs.
How Does Rigid Foam Board Compare in Insulation?
Rigid foam board insulation is characterized by its solid panels, which provide high compressive strength and are easy to cut and install. This type is commonly used in insulating walls, roofs, and floors, making it a versatile choice for various construction projects. B2B buyers appreciate the straightforward installation process, although the lack of flexibility in design can be a limitation for some applications. Proper sealing is essential to maximize the insulation’s effectiveness.

Illustrative image related to closed cell insulating foam
Why Choose Polyurethane Foam for Industrial Applications?
Polyurethane foam is favored for its versatility and strong adhesion properties, making it suitable for applications such as pipeline insulation and marine environments. It can effectively insulate against both heat and cold, which is crucial for maintaining temperature control in industrial settings. While it offers excellent performance, buyers should consider the higher price point compared to other foam types, which may impact budget constraints.
What Are the Advantages of Polyisocyanurate Foam?
Polyisocyanurate foam stands out due to its higher R-value compared to standard polyurethane, making it an excellent choice for industrial insulation and cold storage facilities. Its superior thermal resistance can significantly enhance energy efficiency. However, B2B buyers must be cautious during installation, as this foam is more sensitive to moisture, which can affect its performance if not handled correctly.
Are Spray Foam Kits a Good Option for Small-Scale Projects?
Spray foam kits offer a convenient solution for small-scale projects, providing varying sizes that cater to DIY enthusiasts. These kits are user-friendly and allow for quick application, making them ideal for home insulation or smaller commercial projects. However, the coverage limitations compared to professional-grade products may lead to higher costs for larger applications, making it essential for buyers to assess their specific needs before purchasing.
Key Industrial Applications of closed cell insulating foam
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of closed cell insulating foam | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Insulation in commercial buildings | Enhances energy efficiency and reduces heating/cooling costs | Compliance with local building codes and regulations |
| HVAC | Duct insulation | Prevents energy loss and improves system efficiency | Material durability in high-temperature environments |
| Marine | Insulation for boats and ships | Provides buoyancy and thermal insulation | Resistance to moisture and marine conditions |
| Refrigeration | Insulation for cold storage facilities | Maintains optimal temperatures, reducing energy costs | Compliance with food safety and environmental standards |
| Automotive | Insulation in vehicle components | Reduces noise and enhances thermal management | Lightweight materials for improved fuel efficiency |
How is Closed Cell Insulating Foam Utilized in the Construction Industry?
In the construction sector, closed cell insulating foam is extensively used for insulating walls, roofs, and foundations in commercial buildings. Its high R-value per inch ensures superior thermal resistance, significantly lowering energy costs for heating and cooling. For international buyers, especially in regions with extreme climates like Africa and the Middle East, sourcing foam that meets local building codes and regulations is crucial. Additionally, the foam’s moisture resistance helps prevent mold growth, an essential factor in humid environments.
What Role Does Closed Cell Insulating Foam Play in HVAC Systems?
In HVAC applications, closed cell insulating foam is employed to insulate ducts, ensuring minimal energy loss and improved system efficiency. This insulation not only helps maintain desired temperatures but also reduces noise, contributing to a more comfortable environment. For businesses in South America and Europe, it is vital to consider the material’s durability in high-temperature settings and its compliance with energy efficiency standards when sourcing.

Illustrative image related to closed cell insulating foam
How is Closed Cell Insulating Foam Beneficial in Marine Applications?
In the marine industry, closed cell insulating foam is used to insulate boats and ships, providing essential thermal insulation while also contributing to buoyancy. This dual functionality is particularly important for vessels operating in varying water conditions. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should prioritize sourcing foam that offers resistance to moisture and marine environments to ensure longevity and performance.
In What Ways Does Closed Cell Insulating Foam Support Refrigeration Needs?
Closed cell insulating foam is critical in refrigeration applications, particularly in cold storage facilities. It helps maintain optimal temperatures, thereby reducing energy costs associated with refrigeration. Businesses in the food industry must consider compliance with food safety standards when sourcing insulation materials. Additionally, the foam’s ability to act as a vapor barrier is essential in preventing condensation, which can lead to spoilage.
How is Closed Cell Insulating Foam Applied in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, closed cell insulating foam is used in various vehicle components, including doors, hoods, and dashboards. This insulation aids in noise reduction and enhances thermal management within the vehicle, contributing to a more comfortable ride. For international buyers, especially in Brazil and the Middle East, sourcing lightweight materials is vital for improving fuel efficiency while still meeting stringent safety and performance standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘closed cell insulating foam’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges with Coverage Calculations for Projects
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter difficulties in accurately estimating the amount of closed cell insulating foam required for their projects. This can lead to over-purchasing, resulting in unnecessary costs and wasted materials, or under-purchasing, which can delay project timelines and affect budgets. Buyers may struggle with understanding the concept of board feet and how it translates to their specific insulation needs, particularly in different environmental conditions or application methods.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, it is crucial for buyers to familiarize themselves with the concept of board feet and how to calculate the required coverage accurately. A reliable approach involves using the manufacturer’s guidelines, which typically outline the coverage per kit based on thickness. Buyers should conduct a detailed assessment of the project area, considering the dimensions and any unique architectural features. Furthermore, it is advisable to consult with insulation experts to clarify uncertainties regarding product specifications. Implementing a systematic approach to measuring and estimating can help ensure the right amount of foam is purchased, thus optimizing both costs and time.
Scenario 2: Concerns Over Mold Growth in Insulation Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers worry about the potential for mold growth in closed cell insulating foam, particularly in humid or moisture-prone environments. This concern is exacerbated by the fact that improper application or product selection can lead to moisture retention, ultimately compromising the integrity of the insulation and the structures they are meant to protect. Buyers need to ensure that the products they choose are not only effective insulators but also resistant to mold and mildew.
The Solution: To address these concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing closed cell foam that has been treated with anti-microbial properties. Products that meet ASTM G21 standards indicate resistance to mold growth. It is also essential to ensure proper installation techniques are followed, such as maintaining recommended temperature ranges and ensuring that surfaces are adequately prepped to minimize moisture entrapment. Additionally, conducting routine inspections and implementing moisture control strategies within buildings can significantly reduce the risk of mold issues, ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of the insulation.
Scenario 3: Navigating Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
The Problem: B2B buyers face challenges when it comes to understanding and adhering to various regulatory compliance and safety standards associated with closed cell insulating foam. These regulations can differ significantly across regions, particularly in international markets, leading to confusion and the risk of non-compliance. Buyers may struggle with the certifications required for fire safety, environmental impact, and health concerns, which can complicate purchasing decisions and project execution.
The Solution: To navigate these complexities, it is essential for buyers to engage with suppliers who are knowledgeable about local regulations and can provide documentation for compliance. Buyers should conduct thorough research on applicable standards in their specific market regions, focusing on certifications such as ASTM E84 for fire retardancy and compliance with local environmental regulations. Establishing a relationship with a reputable supplier who can offer guidance on these matters will not only streamline the procurement process but also ensure that all purchased materials meet necessary safety and regulatory requirements. Additionally, keeping abreast of changes in regulations through industry associations can help buyers remain compliant and informed.

Illustrative image related to closed cell insulating foam
Strategic Material Selection Guide for closed cell insulating foam
When selecting closed cell insulating foam materials, B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, cost, and suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in closed cell insulating foam, highlighting their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international markets.
What Are the Key Properties of Polyurethane Closed Cell Foam?
Polyurethane closed cell foam is one of the most widely used materials due to its excellent thermal insulation properties. It typically has an R-value of about 6 to 7 per inch, making it highly effective for energy efficiency. Its temperature resistance ranges from -40°F to 180°F (-40°C to 82°C), which is suitable for various climates. Additionally, polyurethane foam exhibits good chemical resistance, making it compatible with a range of media.
Pros: The durability of polyurethane foam is notable, as it can withstand moisture and prevent mold growth. It is also relatively lightweight, which can reduce shipping costs.
Cons: However, polyurethane can be more expensive than other materials, and its production process may involve complex chemical reactions, requiring specialized equipment.

Illustrative image related to closed cell insulating foam
How Does Polystyrene Compare in Terms of Performance and Cost?
Polystyrene, particularly in its extruded form (XPS), is another common choice for closed cell insulation. It has a similar R-value to polyurethane but is generally more affordable. Polystyrene is resistant to moisture, making it suitable for applications in humid environments.
Pros: The cost-effectiveness of polystyrene makes it appealing for large-scale projects. It also has good compressive strength, which is beneficial for structural applications.
Cons: On the downside, polystyrene is less durable than polyurethane in extreme temperatures and can be more susceptible to damage from UV exposure.
What Are the Advantages of Using Phenolic Foam?
Phenolic foam is known for its low thermal conductivity and excellent fire resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring stringent fire safety standards. Its R-value can exceed that of polyurethane and polystyrene, reaching up to 8 per inch.
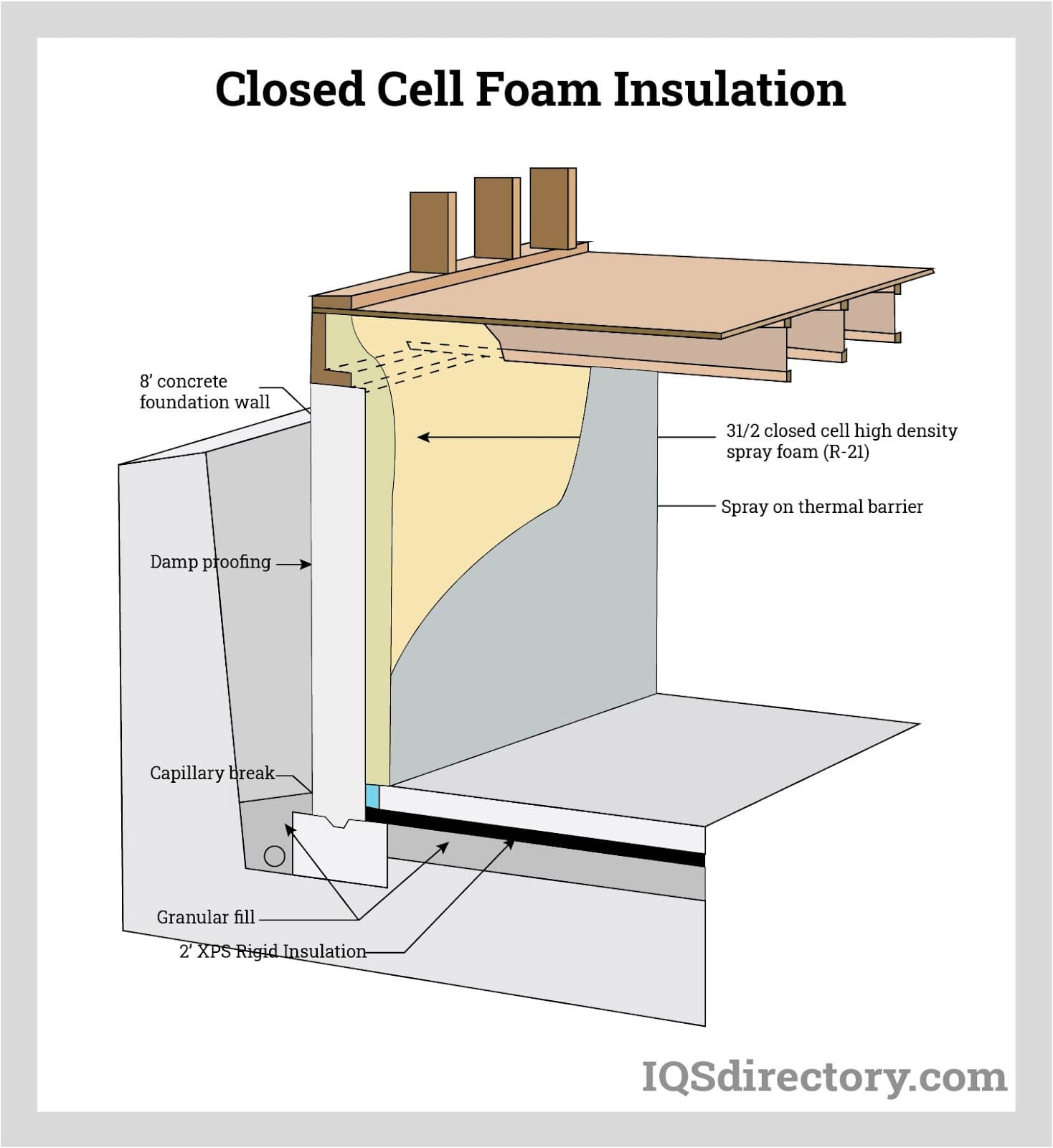
Illustrative image related to closed cell insulating foam
Pros: The fire-resistant properties of phenolic foam make it ideal for commercial buildings and industrial applications. It also has a low environmental impact due to its reduced greenhouse gas emissions during production.
Cons: However, phenolic foam can be more expensive and may require specialized handling during installation, which could increase labor costs.
What Should Buyers Consider Regarding International Standards?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, compliance with local standards such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials), DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung), or JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards) is crucial. Buyers should also consider the availability of materials locally, as shipping costs can significantly impact overall expenses.
Summary Table of Closed Cell Insulating Foam Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for closed cell insulating foam | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane | Residential and commercial insulation | Excellent thermal insulation | Higher production complexity | High |
| Polystyrene | Large-scale construction projects | Cost-effective and moisture-resistant | Less durable in extreme conditions | Medium |
| Phenolic | Industrial and commercial buildings | Superior fire resistance | Higher cost and installation complexity | High |
| Polyethylene | Refrigeration and HVAC applications | Flexibility and moisture resistance | Lower R-value compared to others | Medium |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into selecting the right closed cell insulating foam materials based on performance, cost, and compliance with international standards. By considering these factors, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their project requirements and regional regulations.

Illustrative image related to closed cell insulating foam
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for closed cell insulating foam
The manufacturing of closed cell insulating foam involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets stringent performance and quality standards. Understanding these processes can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing materials, especially in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
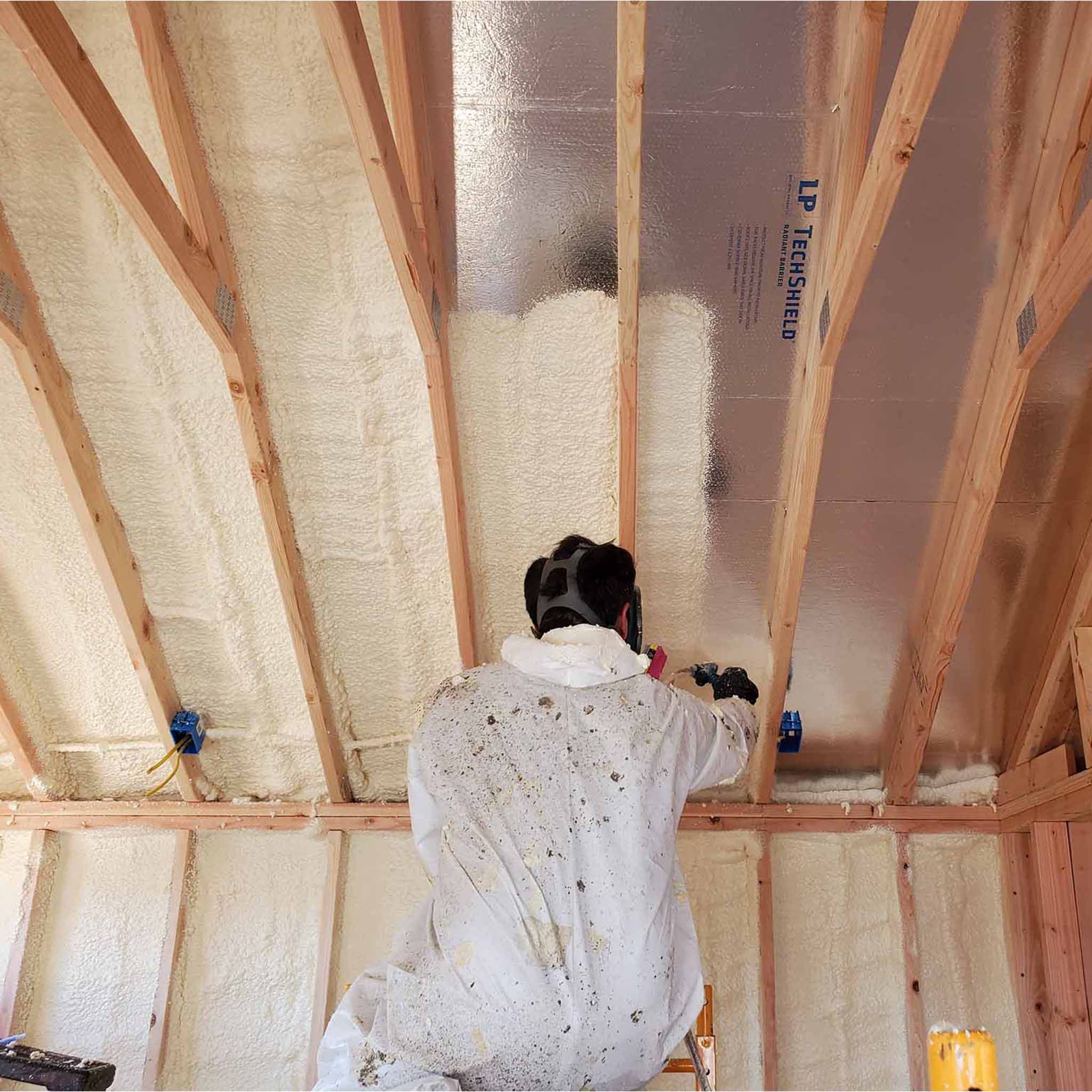
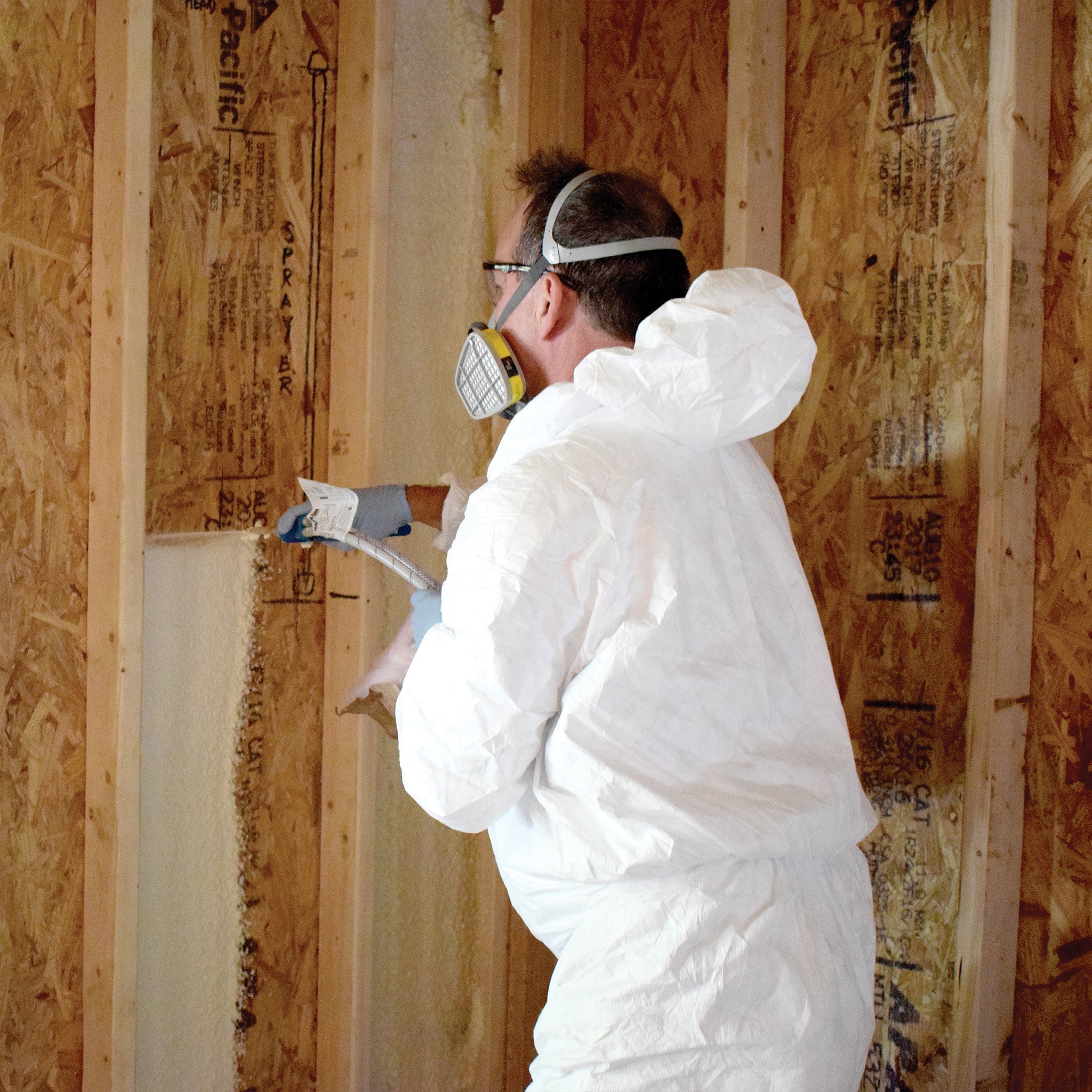
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Closed Cell Insulating Foam?
1. Material Preparation: What Raw Materials Are Used?
The primary ingredients for closed cell foam are polyol and isocyanate. These components are mixed in specific ratios to produce a chemical reaction that generates foam. Suppliers often utilize additives to enhance properties such as fire resistance, thermal insulation, and antimicrobial effects. Proper material storage and handling are critical, as moisture contamination can adversely affect the foam’s performance.
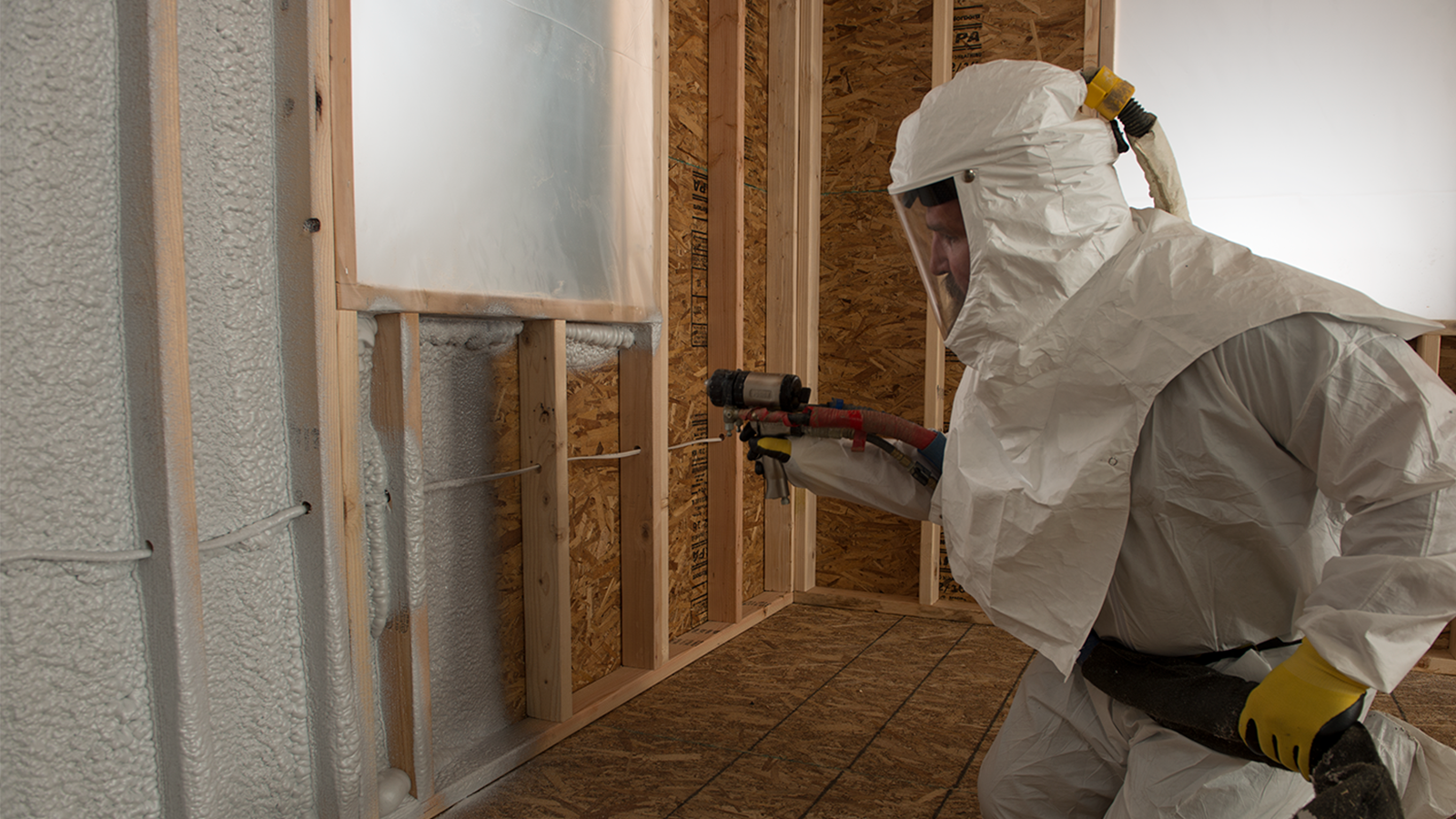
2. Forming: How Is Closed Cell Foam Shaped?
The forming stage involves the application of the mixed components into molds or using spray techniques. For spray foam, specialized equipment ensures even distribution and controlled application thickness. The foam expands and solidifies within seconds, forming a closed cell structure that provides superior insulation. Precision in this stage is vital to avoid defects that could compromise the material’s integrity.
3. Assembly: Are There Additional Steps After Forming?
Once the foam has set, it may undergo additional processing, such as cutting or shaping to meet specific customer requirements. This stage can also involve layering different types of foam or integrating the material into composite structures. For B2B buyers, understanding the assembly capabilities of a supplier can provide insights into customization options for unique applications.
4. Finishing: What Final Treatments Are Applied?
The finishing process can include surface treatments to improve adhesion or aesthetics. Some manufacturers apply coatings that enhance the foam’s resistance to environmental factors, such as UV light or moisture. Quality checks during this phase ensure that the foam meets the required specifications for density, weight, and thermal resistance.
What Quality Control Standards Are Relevant for Closed Cell Foam?
International Standards: How Do They Ensure Product Quality?
Closed cell insulating foam manufacturers often adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines quality management system requirements. Compliance with these standards indicates a commitment to consistent quality, customer satisfaction, and continuous improvement.
Industry-Specific Certifications: What Should Buyers Look For?
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications like CE marking in Europe or API certification for oil and gas applications provide further assurances of product quality. These certifications signify that the foam meets specific safety and performance criteria relevant to its intended use.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
1. Incoming Quality Control (IQC): How Are Raw Materials Inspected?
Before production begins, suppliers conduct rigorous inspections of incoming materials to verify their quality. This includes checks for consistency in chemical composition and physical properties. Establishing a reliable IQC process helps prevent defects in the final product.

Illustrative image related to closed cell insulating foam
2. In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): What Checks Are Performed During Production?
During manufacturing, IPQC measures ensure that processes are performed correctly and that any deviations are addressed promptly. This may involve monitoring temperature, pressure, and mixing ratios in real-time, ensuring that the foam is produced under optimal conditions.
3. Final Quality Control (FQC): How Is the Finished Product Tested?
FQC involves comprehensive testing of the finished foam to ensure it meets all specifications. Common tests include density measurement, thermal resistance (R-value), fire performance, and moisture resistance. The results of these tests are often documented in quality assurance reports, which can be shared with B2B buyers.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Supplier Audits: What Should Buyers Consider?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way for B2B buyers to assess the quality control measures in place. Audits should focus on the manufacturing process, documentation practices, and adherence to relevant standards. Buyers may also consider engaging third-party inspection services for an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s capabilities.
Quality Assurance Reports: How Can They Be Used?
Requesting quality assurance reports from suppliers can provide insight into their testing processes and results. These reports should detail the methodologies used, compliance with industry standards, and any corrective actions taken in response to quality issues. Transparent reporting is a sign of a trustworthy supplier.
Third-Party Inspections: What Are the Benefits?
Utilizing third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of assurance for B2B buyers. Independent inspectors can verify that the manufacturing processes align with the agreed-upon standards and specifications, thus minimizing the risk of sourcing subpar materials.

Illustrative image related to closed cell insulating foam
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware Of?
For international buyers, particularly from diverse regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, understanding local regulations and standards is crucial. Different regions may have varying requirements for product safety and performance, which can affect the usability of closed cell foam in specific applications.
Moreover, some suppliers may only possess certifications recognized in their home country, which may not be valid in other regions. Buyers should conduct thorough due diligence to ensure that the products meet the standards required in their markets. This includes verifying that suppliers can provide the necessary documentation and certifications for their products.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for closed cell insulating foam is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on the main stages of production, relevant quality control standards, and effective verification methods, businesses can ensure they source high-quality materials that meet their specific needs. This diligence not only enhances product performance but also fosters long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers across the globe.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘closed cell insulating foam’
In the evolving landscape of construction and insulation materials, sourcing high-quality closed cell insulating foam is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to enhance energy efficiency and performance in their projects. This guide offers a step-by-step checklist to facilitate informed purchasing decisions, ensuring that you acquire the best materials for your needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by determining the specific requirements for your project. This includes assessing the R-value, density, and application method of the closed cell foam. Understanding these parameters is essential, as they dictate the foam’s thermal resistance and suitability for your application.
- R-Value Consideration: Aim for a higher R-value for better insulation performance.
- Density Requirements: Identify the density that aligns with your project’s structural and thermal needs.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Stay updated with the latest advancements in closed cell foam technologies. Innovations in formulations can lead to improved performance characteristics, such as fire resistance or lower environmental impact.
- Sustainability Features: Look for products that offer low Global Warming Potential (GWP) options, which can enhance your project’s eco-friendliness.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the products meet local and international standards, which may vary by region.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a purchase, it is crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. This due diligence ensures that you are partnering with reliable vendors who can meet your quality and service expectations.
- Supplier Certifications: Verify that the supplier holds relevant certifications, such as ASTM or ISO, to ensure product quality.
- Customer Reviews: Consider feedback from other clients to gauge supplier reliability and product performance.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Obtaining samples allows you to evaluate the foam’s performance in real-world conditions. Testing samples can help you assess factors such as adhesion, ease of application, and insulation effectiveness.
- Application Trials: Conduct tests in various conditions to ensure the foam meets your expectations under different environmental factors.
- Performance Metrics: Measure the foam’s performance against your technical specifications to confirm its suitability.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, engage in negotiations to secure favorable pricing and terms. Bulk purchasing can often lead to significant cost savings, so consider your order volume carefully.

Illustrative image related to closed cell insulating foam
- Volume Discounts: Inquire about pricing structures that reward larger orders.
- Payment Terms: Clarify payment conditions, including deposit requirements and payment schedules.
Step 6: Confirm Delivery and Logistics
Ensure that the supplier can meet your delivery timelines and logistical needs. This is especially important for international shipments, where delays can impact project timelines.
- Shipping Options: Discuss shipping methods and timelines to avoid unexpected delays.
- Customs and Duties: Be aware of any import regulations, tariffs, or duties that may apply to your shipment.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Agreements
Before proceeding with the order, finalize all contracts and agreements. Clearly outline terms regarding warranties, returns, and support to protect your interests.
- Warranty Coverage: Confirm the length and scope of warranty coverage for the products.
- Support and Service: Ensure that the supplier offers technical support and assistance for installation if needed.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for closed cell insulating foam, ensuring they select the best materials for their projects while fostering strong supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for closed cell insulating foam Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Closed Cell Insulating Foam Sourcing?
When sourcing closed cell insulating foam, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The base materials, such as polyols and isocyanates, significantly affect pricing. Fluctuations in raw material costs can impact the final price, making it crucial to stay updated on market trends.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the location of manufacturing. Regions with higher labor costs, such as Western Europe, may reflect this in the product pricing compared to regions like South America or Africa, where labor might be more affordable.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs such as utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overheads, thereby lowering the overall cost.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling and equipment can be substantial, especially for custom formulations. Buyers should inquire about these costs as they may be amortized over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the foam meets industry standards involves additional costs. Products with certifications (e.g., ASTM, ISO) may come at a premium, but they ensure quality and safety.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping and customs duties, can add significant expenses, especially for international buyers. Understanding Incoterms is crucial to clarify who bears the risk and costs during transit.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins can vary significantly. It’s advisable to compare multiple suppliers to gauge reasonable pricing structures.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Closed Cell Insulating Foam?
Several factors can influence the pricing of closed cell insulating foam, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically qualify for bulk discounts. Negotiating MOQs can yield more favorable pricing, making it worthwhile to consolidate purchases.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions or specific performance criteria can lead to increased costs. Buyers should evaluate whether the additional expense aligns with their project requirements.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials or those with specific certifications can elevate costs. However, these investments often lead to better performance and longevity.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation and reliability can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a track record may charge more but offer greater assurance of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of trade can help buyers manage logistics costs effectively. Different Incoterms (like FOB, CIF) dictate who is responsible for shipping costs and risks, directly affecting the total landed cost.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing Closed Cell Insulating Foam?
To maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing closed cell insulating foam, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating prices, especially for larger orders. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can also result in better terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but the total cost of ownership, including installation, maintenance, and potential energy savings. Higher upfront costs for better-performing foam can lead to lower long-term costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local taxes, which can affect the overall cost. Engaging with local suppliers can mitigate some of these challenges and provide logistical advantages.
-
Market Research: Stay informed about market trends and competitor pricing. This knowledge can empower you during negotiations and help identify the best sourcing options.
-
Trial Orders: Before committing to large orders, consider placing trial orders to assess product quality and supplier reliability. This can prevent costly mistakes and ensure the foam meets your specifications.
By understanding these components and strategies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that optimize costs while ensuring they receive high-quality closed cell insulating foam tailored to their specific needs.
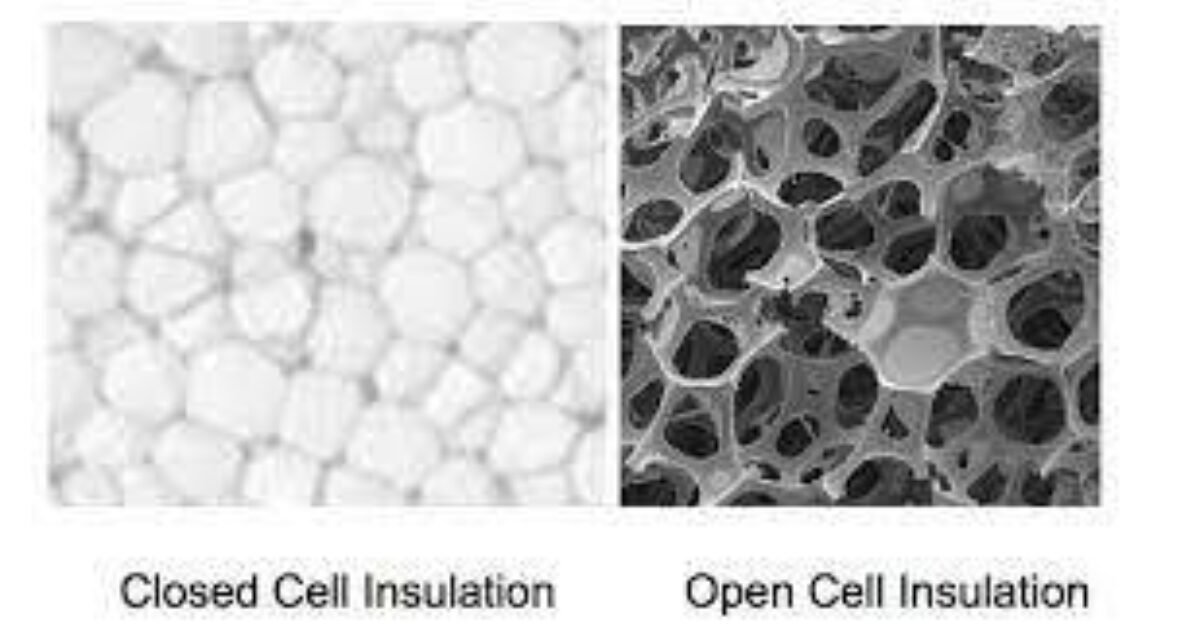
Illustrative image related to closed cell insulating foam
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing closed cell insulating foam With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Closed Cell Insulating Foam
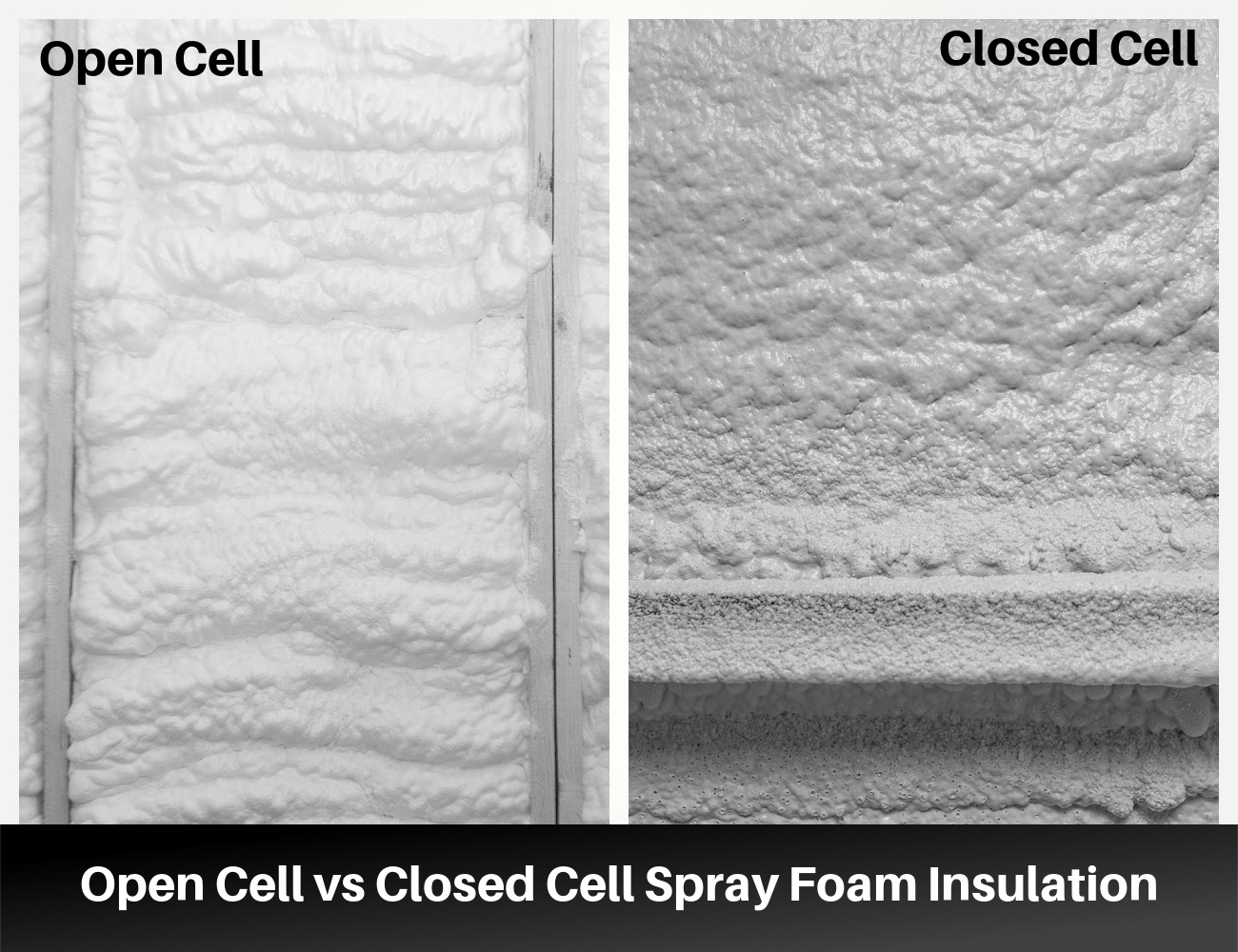
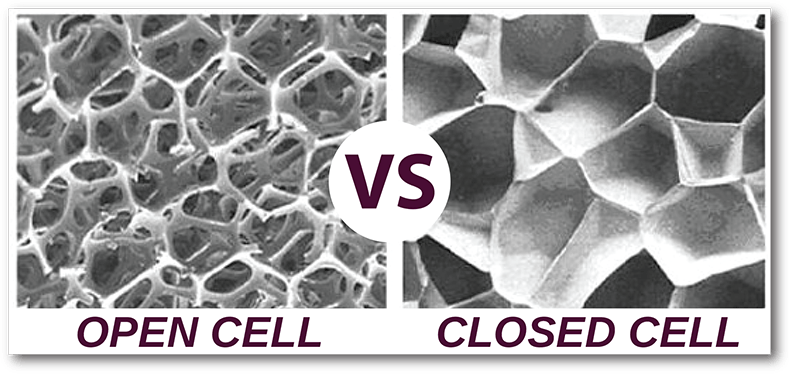
In the world of insulation, closed cell insulating foam is a popular choice due to its superior thermal resistance and moisture control. However, it’s essential for B2B buyers to consider alternative solutions that may better suit specific project requirements or budget constraints. This section will compare closed cell insulating foam with two viable alternatives: fiberglass insulation and open cell spray foam.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Closed Cell Insulating Foam | Fiberglass Insulation | Open Cell Spray Foam |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High R-value (~7 per inch), excellent air and moisture barrier | Moderate R-value (~2.9 to 4.3 per inch), effective but less air-tight | Good R-value (~3.5 to 4 per inch), effective air barrier but less moisture resistant |
| Cost | Higher upfront costs ($0.50 – $1.50 per board foot) | Lower costs ($0.30 – $0.70 per square foot) | Moderate costs ($0.45 – $1.00 per board foot) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional application for best results | Can be installed DIY or by professionals | Requires professional application for optimal performance |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance once applied; durable | Susceptible to moisture, may require replacement | Low maintenance; can settle and lose effectiveness over time |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for areas needing superior insulation and moisture control (e.g., basements, roofs) | Suitable for walls and attics in dry climates | Best for interior applications where soundproofing is a priority |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Fiberglass Insulation
Fiberglass insulation is one of the most traditional insulation materials. It consists of fine glass fibers and is well-regarded for its cost-effectiveness. While it offers a moderate R-value, it does not provide the same level of air sealing or moisture resistance as closed cell foam. A significant advantage of fiberglass is its ease of installation, making it suitable for DIY projects. However, it can be susceptible to moisture damage, which may necessitate replacement or additional treatments in humid environments.
Open Cell Spray Foam
Open cell spray foam is another alternative that provides good thermal insulation and air sealing properties. It has a lower R-value compared to closed cell foam but offers excellent soundproofing capabilities, making it ideal for interior spaces. One of the primary benefits of open cell foam is its lower cost compared to closed cell options. However, it is less effective at moisture control and can absorb water, which may lead to mold growth if not properly managed. Like closed cell foam, it typically requires professional installation for optimal performance.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Insulation Solution
Selecting the right insulation solution depends on several factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and specific application needs. Closed cell insulating foam is often preferred for its superior insulation and moisture control, making it ideal for challenging environments. On the other hand, fiberglass insulation may be a more economical choice for dry areas, while open cell spray foam is excellent for soundproofing in interior applications. B2B buyers should assess their unique project specifications and consult with insulation professionals to determine the most effective solution for their needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for closed cell insulating foam
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Closed Cell Insulating Foam?
Closed cell insulating foam is a versatile and effective material commonly used in construction and manufacturing. Understanding its technical properties is crucial for B2B buyers who need to make informed purchasing decisions.
R-Value: What Does It Indicate?
The R-value measures the thermal resistance of insulation materials. For closed cell foam, the R-value typically ranges from 6 to 7 per inch. This high R-value indicates superior insulation properties, making it ideal for energy efficiency in buildings. For B2B buyers, selecting materials with a high R-value can significantly reduce heating and cooling costs, offering long-term savings on energy bills.
Density: Why Is It Important?
Density is a critical property that influences the foam’s strength and insulation performance. Closed cell foams usually have a density between 1.5 to 3.0 pounds per cubic foot. Higher density foams generally provide better insulation and structural support. For businesses, selecting the appropriate density is essential to ensure that the foam meets specific application requirements, such as load-bearing capacity and durability.

Illustrative image related to closed cell insulating foam
Water Vapor Permeability: How Does It Affect Performance?
Water vapor permeability refers to the foam’s ability to resist moisture penetration. Closed cell foams typically have low permeability, acting as effective vapor barriers. This property is vital for preventing mold and moisture-related damage in buildings. Understanding this characteristic helps B2B buyers choose products that enhance indoor air quality and structural integrity.
Fire Resistance: What Standards Should You Look For?
Closed cell insulating foams are often rated for fire resistance according to ASTM E-84 standards. A Class I rating indicates the best performance in terms of fire safety. For businesses, ensuring that the insulation complies with fire safety regulations is not only crucial for safety but also for meeting industry standards and avoiding liability issues.
Thermal Expansion: Why Does It Matter?
Thermal expansion refers to how much the foam expands or contracts with temperature changes. Closed cell foams typically exhibit minimal thermal expansion, which helps maintain their integrity over time. For B2B buyers, this property is essential for applications in environments with fluctuating temperatures, as it ensures consistent performance and longevity of the insulation.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Closed Cell Foam Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiations in B2B transactions involving closed cell insulating foam.
What Does OEM Stand For?
OEM, or Original Equipment Manufacturer, refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of closed cell foam, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure product compatibility.

Illustrative image related to closed cell insulating foam
MOQ: What Does Minimum Order Quantity Mean?
MOQ, or Minimum Order Quantity, is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for B2B buyers to understand, as it can impact inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchases effectively.
How Is RFQ Used in Procurement?
RFQ, or Request for Quotation, is a document that companies send to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. In the context of closed cell foam, utilizing RFQs can help buyers compare prices, quality, and delivery terms from different manufacturers, facilitating better procurement decisions.
What Are Incoterms and Why Are They Important?
Incoterms, or International Commercial Terms, are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. These terms clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, reducing misunderstandings in international trade. For B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, understanding Incoterms is essential for successful cross-border transactions.
What Does Lead Time Imply?
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. In the closed cell foam industry, lead times can vary based on product availability and shipping logistics. Understanding lead times is crucial for B2B buyers to manage project timelines effectively and avoid delays in construction or manufacturing processes.

Illustrative image related to closed cell insulating foam
In conclusion, being well-versed in the essential technical properties and trade terminology of closed cell insulating foam empowers B2B buyers to make informed decisions, ensuring quality, compliance, and cost-effectiveness in their projects.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the closed cell insulating foam Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends: What Drives the Closed Cell Insulating Foam Sector?
The closed cell insulating foam market is experiencing robust growth, driven by several global factors. Increasing energy efficiency regulations, particularly in Europe and North America, are pushing industries to adopt superior insulation solutions to reduce energy consumption. In regions like Africa and South America, rapid urbanization and infrastructure development are spurring demand for effective insulation materials in both residential and commercial constructions.
Emerging technologies, such as advanced spray foam systems that enable better application and coverage, are also reshaping the sourcing landscape. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for high-performance products that offer superior thermal resistance (R-value) while being easy to install. This trend aligns with the growing preference for user-friendly kits that come with comprehensive mixing and application tools.

Illustrative image related to closed cell insulating foam
Another key market dynamic is the rising competition among suppliers, which leads to price fluctuations and bulk purchasing incentives. Buyers from diverse markets, including Nigeria and Brazil, should be prepared to leverage these competitive pricing structures, particularly for bulk orders. Understanding local market conditions and supplier capabilities can significantly enhance sourcing strategies.
Furthermore, there is a shift towards digital platforms for procurement, allowing buyers to easily compare products, access reviews, and evaluate suppliers based on their certifications and product offerings. This digital transformation is critical for buyers seeking to make informed decisions in a rapidly evolving market.
How Can Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing Impact Your Sourcing Strategy for Closed Cell Insulating Foam?
Sustainability is becoming a core consideration for B2B buyers in the closed cell insulating foam sector. The environmental impact of insulation materials is under scrutiny, particularly regarding greenhouse gas emissions from production processes. As such, buyers are increasingly inclined to choose products with low Global Warming Potential (GWP) and those that comply with environmental regulations.
Ethical sourcing is equally crucial. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate transparency in their supply chains and adhere to ethical labor practices. Certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
Moreover, the market is witnessing a rise in ‘green’ certifications for closed cell foams, which highlight eco-friendly attributes such as being free from harmful chemicals and being recyclable. For international buyers, especially in emerging markets, aligning procurement strategies with sustainability goals not only enhances brand reputation but also meets the growing demand for environmentally responsible products.
What is the Brief Evolution and History of Closed Cell Insulating Foam in the B2B Context?
The evolution of closed cell insulating foam can be traced back to the mid-20th century, when the need for more efficient insulation solutions became apparent amid rising energy costs. Initially developed for industrial applications, closed cell foam gained popularity in the construction sector due to its superior insulation properties, moisture resistance, and structural integrity.
Over the decades, technological advancements have significantly improved the formulation and application of closed cell foams. Innovations such as spray foam technology have made it easier to apply these materials in a variety of settings, from residential homes to large commercial projects. Today, the focus has shifted towards enhancing product performance while minimizing environmental impacts, with a growing emphasis on sustainability and ethical sourcing practices.

Illustrative image related to closed cell insulating foam
As the market continues to evolve, international buyers are encouraged to stay informed about technological advancements and regulatory changes that could affect their sourcing strategies. Understanding the historical context of closed cell insulating foam can provide valuable insights into current trends and future developments in the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of closed cell insulating foam
-
How do I determine the right thickness of closed cell insulating foam for my project?
Selecting the appropriate thickness of closed cell insulating foam depends on various factors, including the climate of the project location, intended use, and building codes. Generally, a thickness of 1 to 3 inches is common, providing an R-value of approximately 7 per inch. For extreme climates, thicker insulation may be required to ensure optimal thermal performance. Consult with local building regulations and consider conducting a thermal analysis to ascertain the necessary thickness for your specific application. -
What is the best closed cell foam insulation for industrial applications?
For industrial applications, the best closed cell foam insulation is typically one that offers high R-values, moisture resistance, and fire retardant properties. Look for products that meet ASTM E-84 Class I fire-retardant standards and ASTM G21 anti-microbial specifications to prevent mold growth. Brands like Foam it Green provide robust solutions with a high-density formula suitable for demanding environments. Always evaluate the specific requirements of your industry, such as temperature extremes and exposure to chemicals. -
How can I vet suppliers of closed cell insulating foam for international trade?
Vetting suppliers is crucial when sourcing closed cell insulating foam internationally. Start by reviewing their certifications, such as ISO or ASTM compliance, which assure quality and safety standards. Request references and case studies from existing clients to gauge reliability. Additionally, assess their production capabilities, lead times, and customer service responsiveness. Online platforms and trade shows can also provide insights into the supplier’s reputation within the industry. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for closed cell insulating foam?
Minimum order quantities for closed cell insulating foam can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific product. Some manufacturers may require MOQs as low as 50 to 100 board feet, while others may have higher thresholds, especially for custom formulations. Always inquire about MOQs during the negotiation process to ensure they align with your project needs and budget. Consider the potential for bulk purchasing discounts as well. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing closed cell foam internationally?
Payment terms can differ widely among suppliers in international trade. Common arrangements include upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, or letters of credit for larger transactions. It is advisable to negotiate terms that provide both parties with security, such as staggered payments based on milestones or delivery schedules. Always clarify currency exchange rates and any associated fees to avoid unexpected costs. -
How do I ensure quality assurance when purchasing closed cell insulating foam?
To ensure quality assurance when purchasing closed cell insulating foam, request detailed product specifications and certifications from your supplier. Establish a clear inspection process, including pre-shipment inspections and third-party testing if necessary. Additionally, consider asking for samples before committing to a larger order to evaluate the product’s performance firsthand. Maintaining open communication with the supplier throughout the production process can also help mitigate quality issues. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing closed cell insulating foam?
Importing closed cell insulating foam involves several logistical considerations, including shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Determine the most efficient shipping option based on cost and delivery timelines, whether by air or sea. Familiarize yourself with import regulations in your country, including necessary documentation and compliance with safety standards. Collaborating with a freight forwarder or logistics expert can streamline the process and help navigate any complexities. -
Can closed cell insulating foam be customized for specific applications?
Yes, closed cell insulating foam can often be customized to meet specific application requirements. Many suppliers offer tailored formulations that can include varying densities, R-values, and additional features like fire retardancy or anti-microbial properties. When seeking customization, provide detailed specifications and discuss your project needs with the supplier to ensure they can meet your expectations. Custom solutions may involve longer lead times and minimum order quantities, so plan accordingly.
Top 5 Closed Cell Insulating Foam Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Huntsman Building Solutions – Closed-Cell Spray Foam Insulation
Domain: huntsmanbuildingsolutions.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: CLOSED-CELL INSULATION: HBS closed-cell spray foam insulation provides an air, water, and vapor barrier in a single component, adhering to most surfaces and expanding to create a seamless, airtight building envelope. Suitable for commercial, residential, institutional, industrial, or agricultural applications.
1. HEATLOK HFO Pro: Continuous insulation solution with superior adhesion and compress…
2. Tiger Foam – TF600FR Fast Rise E-84 Fire Rated Spray Foam Insulation Kit
Domain: tigerfoam.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Professional Grade Spray Foam Insulation by Tiger Foam offers high R-values, energy savings, and comfort. Key products include: TF600FR Fast Rise E-84 Fire Rated Spray Foam Insulation Kit, TF600SR Slow Rise Board Foot Spray Foam Insulation Kit, and TF1350 Open Cell Formula Spray Foam Insulation Kit. The closed cell foam provides over R18 insulation value with just 3 inches applied. It is designed …
3. Fine Homebuilding – Spray Foam Insulation
Domain: finehomebuilding.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Closed-cell spray foam has an R-value of up to R-6.5 per inch. Open-cell spray foam has an R-value of about R-3.7 per inch. Closed-cell foam is dense and difficult to trim, typically filled to a maximum depth of 3 inches in a 2×4 wall, leaving a gap to the drywall. Open-cell foam can fill a 3-1/2 inch cavity completely and is easier to trim. Closed-cell foam insulation is more expensive and less e…
4. Profoam – JM Corbond IV 2# HFO Closed Cell Spray Foam
Domain: profoam.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: JM Corbond IV 2# HFO Closed Cell Spray Polyurethane Foam is a next generation HFO blown, two component, Class 1 rated, medium density SPF insulation system. It is designed for insulating commercial, residential, and industrial buildings. The foam is produced with low Global Warming Potential (GWP) and has an Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP) of zero. It offers high yield, superior thermal and moistu…
5. JM – Corbond IV Spray Foam Insulation
Domain: jm.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: JM Corbond IV closed-cell spray polyurethane foam (SPF) is a high-yield, medium-density insulation system designed for commercial, residential, and industrial buildings. It features HFO technology, resulting in low Global Warming Potential (GWP) and zero Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP). The product is Class 1 rated and provides superior thermal energy efficiency, advanced air and sound control, an…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for closed cell insulating foam
In summary, strategic sourcing of closed cell insulating foam offers B2B buyers a pathway to enhanced efficiency, cost savings, and superior product performance. By leveraging bulk pricing and evaluating supplier capabilities, companies can optimize their insulation strategies while ensuring compliance with international standards. The significant R-value and moisture resistance of closed cell foam make it an invaluable asset in construction and manufacturing sectors across diverse climates.
As international markets evolve, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for high-quality insulating materials is projected to increase. Buyers are encouraged to prioritize suppliers who demonstrate innovation, sustainability, and exceptional customer support. Engaging with suppliers that offer transparent communication and robust product information will facilitate informed purchasing decisions.
Illustrative image related to closed cell insulating foam
Looking ahead, the closed cell insulating foam market is set to expand, driven by advancements in technology and growing environmental awareness. By embracing strategic sourcing practices today, B2B buyers can position themselves for success in a competitive landscape. Start your sourcing journey now and unlock the potential of closed cell insulating foam to enhance your projects and bottom line.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to closed cell insulating foam
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.