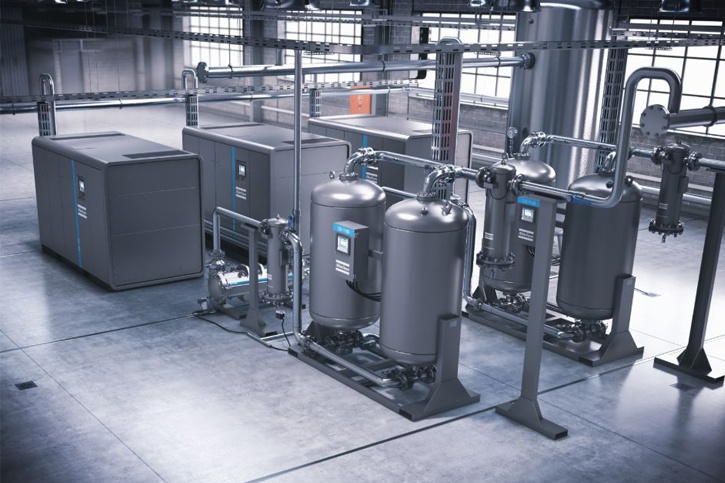
Everything You Need to Know About Air Dryers Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for air dryers
In the quest to enhance operational efficiency, sourcing the right air dryers can be a pivotal challenge for international B2B buyers. From Africa to South America and across Europe, companies are increasingly aware that the quality of compressed air directly impacts productivity and product integrity. This comprehensive guide delves into the global market for air dryers, addressing key considerations such as types, applications, supplier vetting, and cost analysis. By understanding the nuances of various air dryer technologies, businesses can make informed decisions that optimize their production processes and reduce downtime.
The air dryer market is multifaceted, encompassing refrigerated, desiccant, and membrane dryers, each suited for different industrial applications. Navigating this landscape requires insight into not only the technical specifications but also the reputability and reliability of suppliers. This guide empowers buyers by providing actionable insights and best practices for vetting suppliers, evaluating total cost of ownership, and understanding regional market dynamics, particularly in regions like Germany and Brazil, where regulations and standards may vary significantly.
By leveraging this guide, international B2B buyers can confidently source air dryers that meet their operational needs while ensuring compliance and efficiency, ultimately contributing to their bottom line.
Understanding air dryers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refrigerated Air Dryer | Uses refrigeration to cool air, condensing moisture. | Manufacturing, automotive, food processing | Pros: Cost-effective, reliable moisture removal. Cons: Limited efficiency in high humidity. |
| Desiccant Air Dryer | Utilizes desiccant materials to absorb moisture from the air. | Pharmaceuticals, electronics, textiles | Pros: Excellent for low dew points. Cons: Higher maintenance and operational costs. |
| Membrane Air Dryer | Employs membrane technology to separate moisture from compressed air. | Chemical processing, oil & gas | Pros: Compact design, low energy consumption. Cons: Limited capacity and dew point performance. |
| High-Temperature Air Dryer | Designed to handle elevated temperatures without degradation. | Heavy industry, metalworking | Pros: Durable, suitable for high heat applications. Cons: Typically more expensive. |
| Cycling Refrigerated Air Dryer | Features a cycling mechanism that optimizes energy use. | General manufacturing, automotive | Pros: Energy-efficient, adaptable to varying loads. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
What Are Refrigerated Air Dryers and Their Applications?
Refrigerated air dryers are among the most common types used in various industries. They function by cooling the compressed air, causing moisture to condense and be removed. Ideal for applications in manufacturing, automotive, and food processing, these dryers are cost-effective and reliable. However, they may struggle in high-humidity environments, which can impact their efficiency. Buyers should consider the local climate and application specifics when selecting a refrigerated dryer.
How Do Desiccant Air Dryers Work and Who Uses Them?
Desiccant air dryers utilize hygroscopic materials to absorb moisture from the air. They are particularly suitable for industries requiring low dew points, such as pharmaceuticals, electronics, and textiles. While they provide excellent moisture control, the operational and maintenance costs can be higher compared to other types. Buyers must evaluate their need for low humidity against the associated costs to determine if a desiccant dryer is the right choice.
What Advantages Do Membrane Air Dryers Offer?
Membrane air dryers employ a unique technology that separates moisture from compressed air through selectively permeable membranes. These units are compact and energy-efficient, making them suitable for applications in chemical processing and oil & gas. However, they may have limitations in capacity and dew point performance. B2B buyers should assess the specific moisture removal requirements of their application before investing in a membrane dryer.
Why Choose High-Temperature Air Dryers?
High-temperature air dryers are specifically designed to handle elevated temperatures without suffering from degradation. Industries such as heavy manufacturing and metalworking benefit from these dryers due to their durability and ability to function effectively in harsh conditions. While they are typically more expensive, their robustness can justify the investment for businesses operating under extreme temperatures. Buyers should weigh the operational environment against the cost to make an informed decision.
What Makes Cycling Refrigerated Air Dryers Energy Efficient?
Cycling refrigerated air dryers feature a mechanism that adjusts their operation based on the load, optimizing energy use. This flexibility makes them suitable for general manufacturing and automotive applications, where air demand can fluctuate. Although they come with a higher initial investment, the energy savings over time can be significant. Businesses should consider their air demand variability and long-term energy costs when evaluating cycling refrigerated dryers.
Key Industrial Applications of air dryers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Air Dryers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Compressed air systems for pneumatic tools | Enhances tool performance and lifespan | Reliability, energy efficiency, and maintenance support |
| Food and Beverage | Packaging and processing applications | Ensures product quality and compliance with safety standards | Hygiene certifications and moisture control capabilities |
| Pharmaceuticals | Laboratory and production environments | Maintains product integrity and prevents contamination | Precision in moisture removal and compliance with regulations |
| Automotive | Paint spray booths and assembly lines | Improves finish quality and reduces rework | Size and capacity to meet production demands |
| Electronics | Assembly lines for circuit boards | Protects sensitive components from moisture damage | Compatibility with existing systems and energy efficiency |
How Are Air Dryers Used in Manufacturing and What Problems Do They Solve?
In the manufacturing sector, air dryers are integral to compressed air systems, which power various pneumatic tools. They remove moisture from compressed air, preventing rust and corrosion in tools, which can lead to costly repairs and downtime. For international buyers, sourcing air dryers that offer reliability and energy efficiency is crucial, especially in regions where operational costs are a significant concern. Maintenance support is also a key consideration, as it ensures the longevity and performance of the air dryers.

Illustrative image related to air dryers
What Role Do Air Dryers Play in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage industry, air dryers are essential for packaging and processing applications. They help maintain product quality by ensuring that moisture does not compromise the integrity of packaging materials or the safety of food products. Compliance with hygiene standards is paramount, so buyers must consider air dryers that meet industry certifications and have effective moisture control capabilities. This is particularly vital in regions with varying climate conditions, where humidity levels can fluctuate significantly.
How Do Air Dryers Ensure Quality in Pharmaceuticals?
Pharmaceutical manufacturers rely on air dryers to maintain controlled environments in laboratories and production areas. By effectively removing moisture, these dryers prevent contamination that could compromise drug integrity. Buyers in this sector need to prioritize precision in moisture removal and compliance with stringent regulatory requirements. Investing in high-quality air dryers can enhance product reliability and reduce the risk of costly recalls or regulatory fines.
Why Are Air Dryers Important for the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, air dryers are crucial for paint spray booths and assembly lines, where they ensure that compressed air used in painting processes is free from moisture. Moisture can lead to defects in paint finishes, resulting in rework and increased production costs. When sourcing air dryers, businesses must consider the size and capacity to meet their specific production demands while ensuring that the equipment aligns with their operational workflows for optimal efficiency.
How Do Air Dryers Protect Electronics During Assembly?
In electronics manufacturing, air dryers are vital for protecting sensitive components during assembly, particularly circuit boards. Moisture can cause short circuits and other failures, which can be detrimental to product quality and reliability. Buyers should focus on sourcing air dryers that are compatible with existing systems and are energy-efficient, as this can significantly reduce operational costs. Ensuring that the air dryers can handle the specific moisture levels required for electronics assembly is essential for maintaining high standards in production.

Illustrative image related to air dryers
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘air dryers’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Air Quality Compromising Production Standards
The Problem: In many manufacturing environments, particularly in industries such as food processing or pharmaceuticals, maintaining a consistent air quality is crucial for product integrity. B2B buyers may face challenges with air dryers that fail to effectively remove moisture, leading to condensation that can contaminate products or damage equipment. This inconsistency can result in costly downtime, wasted materials, and potential regulatory compliance issues. Buyers may feel overwhelmed when attempting to choose the right air dryer that meets their specific humidity control needs while fitting within their budget.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should begin by conducting a thorough assessment of their operational requirements, including the specific humidity levels needed for their processes. Sourcing air dryers equipped with advanced moisture control technologies, such as heatless desiccant dryers or cycling refrigerated dryers, can greatly enhance performance. It’s also beneficial to consult with manufacturers or distributors who can provide insights based on industry-specific challenges. Implementing a scheduled maintenance program will ensure that air dryers operate at peak efficiency, preventing any unexpected failures. Additionally, investing in air quality monitoring systems can provide real-time data, enabling proactive adjustments before air quality issues arise.
Scenario 2: High Energy Costs and Inefficient Operation
The Problem: Many businesses are increasingly concerned about the rising costs associated with energy consumption from their air drying systems. Inefficient air dryers not only drive up energy bills but can also lead to excessive heat generation, which may require additional cooling solutions. B2B buyers may struggle to find a balance between performance and energy efficiency, leading to frustration and financial strain.

Illustrative image related to air dryers
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize energy-efficient air dryers that comply with international energy standards. Investing in variable-speed drive (VSD) technology can significantly reduce energy consumption by adjusting the dryer’s output based on demand. Additionally, opting for heat recovery systems allows businesses to reclaim energy that would otherwise be wasted, further lowering operating costs. Conducting a life cycle cost analysis (LCCA) before purchasing can provide a clearer picture of long-term savings versus initial investment. Buyers should also explore financing options or incentives for energy-efficient equipment that may be available in their region, thereby easing the upfront costs.
Scenario 3: Complex Installation and Integration Challenges
The Problem: Integrating new air dryers into existing systems can be a daunting task for many B2B buyers, especially in facilities with complex infrastructure. Buyers may encounter difficulties related to space constraints, compatibility with existing equipment, and the need for specialized installation expertise. This complexity can result in extended downtime during installation, leading to productivity losses.
The Solution: To mitigate these challenges, buyers should engage with suppliers who provide comprehensive support during the installation process. This includes pre-installation assessments to evaluate space and compatibility needs. Working closely with manufacturers to develop a tailored installation plan can streamline the process and ensure all components fit seamlessly. Additionally, considering modular air dryers can offer flexibility in installation and future upgrades. It’s also advisable to invest in training for staff on the new equipment to maximize operational efficiency right from the start. Establishing a clear communication line with the supplier throughout the process can help address any unexpected issues quickly, minimizing disruption to operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for air dryers
When selecting materials for air dryers, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, and disadvantages, particularly in relation to performance and compatibility with various applications. The following analysis focuses on four common materials used in the construction of air dryers: aluminum, stainless steel, carbon steel, and plastic composites. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly impact the performance and longevity of air dryers.
Illustrative image related to air dryers
What are the Key Properties of Aluminum in Air Dryers?
Aluminum is a lightweight material known for its excellent corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 200°C and can withstand moderate pressure levels. These properties make aluminum suitable for applications where weight reduction is crucial, such as portable air dryers.
Pros:
– Lightweight and easy to handle.
– Excellent resistance to corrosion, especially in humid environments.
– Good thermal conductivity enhances efficiency.
Cons:
– Lower strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-pressure applications.
– More expensive than carbon steel.
– Susceptible to scratching and denting.
Illustrative image related to air dryers
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is compatible with a wide range of media, including compressed air and gases. However, its lower strength may not be suitable for high-pressure systems.
International Considerations:
Buyers in regions such as Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with EU regulations regarding material safety and environmental impact. Common standards like ASTM and DIN may also apply.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Air Dryer Applications?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 400°C and can handle high-pressure applications effectively.
Pros:
– High durability and longevity, making it ideal for industrial applications.
– Excellent corrosion resistance, even in harsh environments.
– Can handle high-temperature and high-pressure conditions.
Illustrative image related to air dryers
Cons:
– Higher cost compared to aluminum and carbon steel.
– Heavier, which may not be ideal for portable units.
– Requires more complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is suitable for a variety of media, including aggressive gases and liquids. Its strength and durability make it a preferred choice for high-performance air dryers.
International Considerations:
Compliance with international standards such as JIS in Japan and ASTM in the U.S. is crucial. Buyers should also consider the environmental impact of stainless steel production.
What Role Does Carbon Steel Play in Air Dryers?
Carbon steel is a widely used material in air dryer construction due to its strength and cost-effectiveness. It can typically withstand temperatures up to 300°C and moderate pressure levels.
Pros:
– Cost-effective and readily available.
– High strength makes it suitable for various applications.
– Easy to manufacture and weld.
Cons:
– Prone to corrosion, requiring protective coatings.
– Heavier than aluminum and may not be suitable for portable applications.
– Limited temperature and pressure ratings compared to stainless steel.
Impact on Application:
Carbon steel is compatible with many media but may require additional treatment for corrosive environments.
International Considerations:
B2B buyers in Africa and South America should be aware of local standards for carbon steel, which may differ from those in Europe and the Middle East.

Illustrative image related to air dryers
How Do Plastic Composites Enhance Air Dryer Performance?
Plastic composites are increasingly used in air dryer construction due to their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. They typically have a temperature rating of up to 80°C and are suitable for low-pressure applications.
Pros:
– Lightweight and easy to handle.
– Excellent corrosion resistance, especially in humid environments.
– Cost-effective for low-pressure applications.
Cons:
– Limited temperature and pressure ratings.
– Not suitable for high-performance applications.
– May degrade over time when exposed to UV light.
Impact on Application:
Plastic composites are ideal for applications where weight is a concern, but their limitations in temperature and pressure make them unsuitable for industrial-grade air dryers.
International Considerations:
Buyers should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding plastic materials, especially in regions with stringent environmental policies.

Illustrative image related to air dryers
Summary Table of Material Selection for Air Dryers
| Material | Typical Use Case for air dryers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Portable air dryers | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Industrial air dryers | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost | High |
| Carbon Steel | General-purpose air dryers | Cost-effective and strong | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Plastic Composites | Low-pressure applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited temperature ratings | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for air dryers, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for air dryers
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Air Dryers?
The manufacturing process of air dryers involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets performance and quality standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Material Preparation: What Raw Materials Are Used?
The manufacturing process begins with the selection and preparation of raw materials. Common materials used in air dryer production include aluminum, stainless steel, and various plastics. Aluminum is often favored for its lightweight properties and resistance to corrosion, while stainless steel offers enhanced durability and strength. Suppliers must ensure that all materials comply with international standards, which can affect the longevity and efficiency of the air dryers.
Forming: How Are Air Dryer Components Shaped?
In the forming stage, the prepared materials are shaped into specific components using techniques such as extrusion, stamping, and machining. For instance, aluminum components may be extruded to achieve the desired profile, while steel parts are often stamped or machined to precise dimensions. The forming process is critical, as even minor deviations can lead to performance issues or inefficient operation of the air dryer.
Assembly: What Techniques Are Used to Assemble Air Dryers?
Once the components are formed, they move to the assembly stage. This process often employs both manual and automated techniques. Assembly lines may utilize robotic systems for high-volume production, ensuring consistency and reducing labor costs. Manual assembly may still be necessary for complex components, where skilled technicians can ensure proper fit and function. During assembly, quality checks are frequently integrated to catch any defects early in the process.
Finishing: How Is the Final Product Prepared for Market?
The finishing stage involves surface treatments such as painting, coating, or anodizing, which enhance the air dryer’s appearance and protect it from environmental factors. This stage is crucial for ensuring the durability of the product in various operational settings, particularly in harsh climates common in regions like Africa and the Middle East. Proper finishing not only adds aesthetic value but also extends the lifespan of the equipment.
Illustrative image related to air dryers
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Common in Air Dryer Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing of air dryers, ensuring that products meet both industry standards and customer expectations. B2B buyers should be familiar with the relevant international standards and specific quality checkpoints throughout the production process.
Which International Standards Apply to Air Dryer Manufacturing?
One of the most recognized quality standards is ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Adherence to ISO 9001 demonstrates a commitment to consistent quality and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking in Europe and API standards in the oil and gas sector, indicate compliance with safety and performance regulations.
What Are the Key Quality Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process, typically categorized into three main types: Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
- IQC: This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before they enter production.
- IPQC: During the assembly and manufacturing processes, ongoing checks are conducted to monitor quality and identify any issues that may arise.
- FQC: The final inspection occurs once the air dryers are fully assembled. This includes functional testing and verification against specifications to ensure optimal performance.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed for Air Dryers?
Testing methods for air dryers often include performance testing, pressure testing, and environmental testing. Performance testing measures how efficiently an air dryer operates under various conditions, while pressure testing ensures that the unit can withstand operational pressures without leaking. Environmental testing evaluates the product’s ability to function in extreme temperatures or humidity levels, which is particularly relevant for markets in Africa and South America.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should employ several strategies to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers.

Illustrative image related to air dryers
What Should Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits and Reports?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess the quality management practices in place. Buyers can request documentation regarding the supplier’s quality management systems, including reports from previous audits and certifications. This transparency allows buyers to gauge the supplier’s commitment to quality and compliance with international standards.
Why Are Third-Party Inspections Important?
Engaging a third-party inspection service can provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing process and quality assurance practices. Third-party inspectors can perform independent assessments of the products and processes, ensuring that they meet the required standards before shipment. This step is particularly critical for international buyers who may not have direct access to the manufacturing facility.
What Are the Quality Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must be aware of the specific certification requirements in their regions. For instance, while CE marking is essential for European markets, products sold in the Middle East might require compliance with local regulations. Buyers should communicate clearly with suppliers about these requirements to avoid complications during importation and ensure that products are compliant with local laws.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for air dryers is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on the stages of production, quality checkpoints, and verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and quality standards.

Illustrative image related to air dryers
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘air dryers’
Introduction
Sourcing air dryers for your business requires careful consideration and a strategic approach. This checklist is designed to guide B2B buyers through the essential steps to ensure a successful procurement process. By following these steps, you can identify the right air dryer for your needs while minimizing risks and maximizing value.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the specific technical requirements for your air dryer is crucial. Consider the airflow capacity (CFM), type of air dryer (refrigerated, desiccant, etc.), and the operating environment. Ensure that your specifications align with your application needs to avoid issues like insufficient drying or excess energy consumption.
- Airflow Capacity: Assess the CFM needed based on your system’s requirements.
- Type of Dryer: Choose between refrigerated and desiccant based on moisture removal efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Step 2: Research Regulatory Compliance and Standards
It’s imperative to ensure that the air dryers you consider meet local and international standards. Compliance with regulations can impact product safety and operational efficiency. Check for certifications such as ISO, CE, or others relevant to your region.

Illustrative image related to air dryers
- Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with the specific regulations that apply to air dryers in your country or region.
- Quality Standards: Look for suppliers that adhere to recognized quality management systems.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your needs. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Don’t just rely on their marketing materials; seek out third-party reviews or testimonials.
- Supplier Reputation: Investigate the supplier’s history and customer feedback.
- Experience in Your Industry: A supplier familiar with your specific requirements can provide valuable insights and support.
Step 4: Request and Analyze Quotes
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing, delivery terms, and warranty conditions. Be sure to request detailed information on what is included in the price to avoid hidden costs later.
- Breakdown of Costs: Ensure quotes include all potential costs such as shipping, installation, and maintenance.
- Warranty and Support: Assess the warranty terms and post-purchase support offered by the supplier.
Step 5: Conduct a Risk Assessment
Before finalizing your decision, perform a risk assessment related to your potential suppliers. Evaluate factors such as financial stability, production capacity, and lead times. This step is critical to avoid disruptions in your supply chain.
- Financial Health: Review financial reports or credit ratings to gauge stability.
- Production Capacity: Confirm the supplier can meet your order volume and timelines.
Step 6: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
Once you have selected a supplier, ensure that all terms and conditions are clearly outlined in a formal purchase agreement. This should include payment terms, delivery schedules, and service agreements.
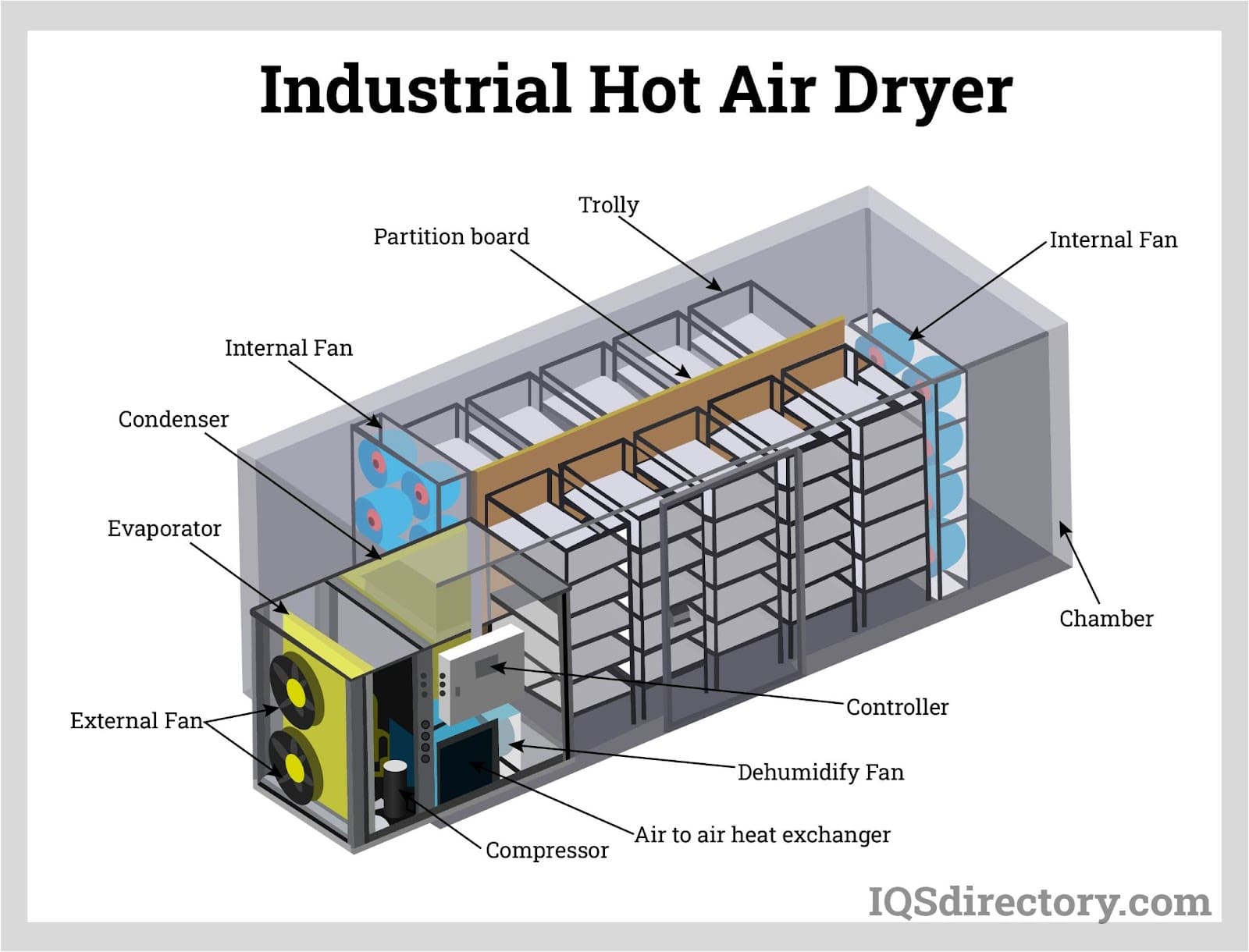
Illustrative image related to air dryers
- Clarity on Terms: Ensure that all parties understand their obligations to avoid misunderstandings.
- Legal Review: Consider having legal counsel review the agreement to protect your interests.
Step 7: Plan for Installation and Maintenance
Finally, prepare for the installation and ongoing maintenance of your air dryer. This includes training staff on operation and maintenance procedures to ensure longevity and optimal performance.
- Installation Support: Confirm if the supplier provides installation services or if you need to hire a third party.
- Maintenance Schedule: Establish a maintenance plan to prevent downtime and extend the life of the equipment.
By following this checklist, you can effectively navigate the sourcing process for air dryers, ensuring that you make informed decisions that align with your business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for air dryers Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Air Dryer Manufacturing?
When sourcing air dryers, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components typically include:

Illustrative image related to air dryers
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. High-quality metals, plastics, and electronic components can drive up expenses, but they also enhance durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is essential for quality assurance and assembly, particularly for custom or high-specification models.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these expenses.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for custom or specialized air dryers can be substantial. However, this is often amortized over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that air dryers meet international standards and certifications incurs costs but is essential for maintaining product reliability and safety.
-
Logistics: Transport costs can vary widely based on the destination and shipping methods. International buyers should factor in customs duties and potential delays.
-
Margin: The supplier’s profit margin is also a significant factor. Understanding the typical margins in your region can help in negotiating better pricing.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect Air Dryer Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing in the air dryer market:
-
Volume/MOQ: Manufacturers often provide discounts for larger orders. Understanding the minimum order quantities (MOQ) can help buyers negotiate better rates.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized air dryers with specific features or capacities typically cost more. It’s essential to balance the need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used will directly affect the price. High-performance materials may increase initial costs but offer long-term savings through reduced maintenance.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards often come at a premium. Certifications can also enhance marketability but should be weighed against costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge higher prices due to brand value but can also offer better support and warranty services.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, all of which can affect the final cost.
What Are Essential Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency in Air Dryer Sourcing?
B2B buyers can optimize their sourcing strategies by employing several best practices:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders or long-term contracts. Leverage multiple quotes to negotiate better terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also operational costs, maintenance, and potential downtime. A higher upfront cost may be justified by lower long-term operational expenses.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to labor costs, material availability, and demand fluctuations. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it’s essential to research local market conditions and supplier capabilities.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Regularly review market trends and price fluctuations to make informed purchasing decisions. This knowledge can help anticipate price changes and budget accordingly.
Conclusion
Understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics of air dryers is essential for international B2B buyers. By focusing on the key cost components, recognizing influential pricing factors, and applying effective sourcing strategies, buyers can secure optimal deals that align with their operational needs and budgetary constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing air dryers With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Air Dryers in Industrial Applications
In the realm of industrial applications, selecting the right drying technology is critical for optimizing efficiency and ensuring product quality. While air dryers are widely utilized for removing moisture from compressed air systems, various alternative solutions exist that can also effectively meet drying needs. This section explores a comparative analysis of air dryers against two prominent alternatives: desiccant dryers and membrane dryers.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Air Dryers | Desiccant Dryers | Membrane Dryers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Efficient for moderate moisture levels; typically achieves dew points of 35°F to 50°F | Can achieve lower dew points, often below 0°F, ideal for sensitive applications | Moderate performance, suitable for non-critical applications with dew points around 40°F |
| Cost | Generally lower initial investment; operational costs can rise with energy consumption | Higher upfront costs; lower energy costs due to lower operational temperatures | Moderate costs; may require additional investment in pre-treatment systems |
| Ease of Implementation | Typically straightforward installation with minimal site preparation | More complex installation due to additional components and space requirements | Simple installation, but requires careful integration with existing systems |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed to clean condensate traps and replace filters | Requires periodic replacement of desiccant material; maintenance can be intensive | Low maintenance; membranes can be cleaned but have limited lifespan |
| Best Use Case | Suitable for general industrial applications where air quality is important but not critical | Ideal for industries requiring ultra-dry air, such as pharmaceuticals and food processing | Best for applications where cost is a concern and air quality is moderately important |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Desiccant Dryers?
Desiccant dryers utilize hygroscopic materials to absorb moisture from compressed air, achieving very low dew points. This technology is particularly advantageous in industries where air quality is paramount, such as pharmaceuticals or food processing. However, the initial investment can be significant, and ongoing maintenance is required to replace desiccant materials, adding to the overall operational costs. Despite these drawbacks, their efficiency in moisture removal makes them a compelling choice for high-stakes applications.
How Do Membrane Dryers Compare to Air Dryers?
Membrane dryers operate by using selective permeation to separate moisture from compressed air. They are often favored for their simplicity and low maintenance requirements. While the initial setup is straightforward, membrane dryers are best suited for applications where air quality is not as critical. They typically achieve moderate dew points and can be a cost-effective solution for industries with less stringent moisture control needs. However, their performance may not be sufficient for applications requiring ultra-dry air.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Drying Solution?
Selecting the appropriate drying solution involves understanding the specific needs of your business. Consider factors such as the required air quality, budget constraints, and the complexity of installation and maintenance. For industries with stringent moisture control requirements, desiccant dryers might be the best fit despite their higher costs. Conversely, if simplicity and lower initial investment are paramount, air dryers or membrane dryers could be more advantageous. Ultimately, assessing your operational requirements and conducting a cost-benefit analysis will guide you in making the most informed decision.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for air dryers
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Air Dryers?
When evaluating air dryers for industrial applications, understanding their key technical properties is crucial. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
-
Air Flow Rate (CFM)
The air flow rate, measured in Cubic Feet per Minute (CFM), indicates the volume of air the dryer can process. This metric is essential for ensuring that the dryer can meet the demand of your specific application. Choosing a dryer with the appropriate CFM rating helps prevent moisture-related issues in compressed air systems, which can lead to equipment failures and increased maintenance costs. -
Operating Pressure
The operating pressure of an air dryer is typically measured in pounds per square inch (PSI). It defines the pressure range within which the dryer can efficiently operate. For B2B buyers, understanding the operating pressure is vital for compatibility with existing systems. An incorrect pressure specification can result in suboptimal performance and potential damage to both the dryer and connected equipment. -
Temperature Range
Air dryers are designed to operate within specific temperature ranges. This property is crucial for maintaining efficiency and preventing overheating. Buyers should ensure that the dryer can handle the ambient temperatures of the installation site, particularly in regions with extreme climates. A dryer that operates outside its temperature specifications may lead to reduced performance and a shorter lifespan. -
Refrigerant Type
The type of refrigerant used in a refrigerated air dryer can impact both efficiency and environmental compliance. Common refrigerants include R-134a and R-410A, with varying effects on ozone depletion and global warming potential. Understanding the refrigerant type is essential for buyers concerned with sustainability and regulatory compliance, especially in regions with stringent environmental laws. -
Dew Point
The dew point is the temperature at which moisture begins to condense out of the air. For air dryers, a lower dew point signifies a dryer that effectively removes moisture. This specification is critical for applications requiring dry air, such as in food processing or pharmaceutical manufacturing. Ensuring the dryer can achieve the desired dew point will safeguard product quality and operational efficiency.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know When Purchasing Air Dryers?
Understanding trade terminology is equally important for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some common terms used in the industry:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. When buying air dryers, knowing whether a product is OEM can assure you of its quality and compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for B2B buyers as it can affect inventory management and cash flow. Suppliers may impose an MOQ to ensure profitability, so negotiating terms that align with your purchasing needs is essential. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. For air dryer purchases, submitting an RFQ can help you gather competitive pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating better decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, insurance responsibilities, and the risk of loss during transit, which is crucial for budgeting and logistics planning. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to delivery. Understanding lead times is essential for project planning, especially in industries that rely on timely equipment installation to avoid production delays.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting air dryers, ensuring they meet operational needs while optimizing costs and efficiencies.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the air dryers Sector
What Are the Key Drivers and Trends in the Global Air Dryer Market?
The air dryer market is experiencing notable growth driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for high-quality compressed air in various industries, including manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and food processing, is a primary driver. As companies focus on enhancing operational efficiency, the need for effective moisture control in compressed air systems has become paramount. Additionally, technological advancements, such as energy-efficient models and automation capabilities, are shaping purchasing decisions among B2B buyers.
Emerging trends include the integration of smart technologies, allowing for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This shift towards the Internet of Things (IoT) enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime, making it an attractive feature for international buyers. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce platforms facilitates easier access to various air dryer models, enabling buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to compare products and pricing effortlessly.
Market dynamics are also influenced by regional factors, such as economic stability and infrastructure development. For instance, countries in Africa and South America are investing in industrial growth, which is anticipated to boost demand for air drying solutions. In Europe, particularly Germany, stringent environmental regulations are pushing businesses towards adopting energy-efficient and sustainable technologies.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Air Dryer Sourcing Decisions?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical factor in the sourcing of air dryers, reflecting a broader shift towards environmentally responsible business practices. The environmental impact of air dryers, particularly in terms of energy consumption and refrigerant use, is under scrutiny. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing products that meet or exceed energy efficiency standards, such as those set by the Energy Star program.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is becoming essential. Companies are expected to ensure that their supply chains are transparent and adhere to environmental regulations. This includes selecting suppliers who utilize sustainable materials and processes. Certifications, such as ISO 14001, which focuses on effective environmental management systems, are becoming increasingly important in supplier selection.
Buyers are also looking for air dryers that incorporate ‘green’ materials, such as recyclable components and low-impact refrigerants. By choosing these products, companies not only reduce their carbon footprint but also enhance their brand reputation in a market that values corporate social responsibility.

Illustrative image related to air dryers
What Is the Historical Context of Air Dryers in B2B Markets?
The evolution of air dryers can be traced back to the early 20th century when they were primarily used in industrial settings to remove moisture from compressed air systems. Initially, these systems were rudimentary, relying on basic refrigeration principles. However, as industries expanded and the demand for reliable, dry air increased, manufacturers began developing more sophisticated technologies.
By the late 20th century, the introduction of non-cycling and cycling refrigerated air dryers marked a significant advancement, improving energy efficiency and reliability. The ongoing development of digital technologies and IoT integration has further transformed the air dryer landscape, enabling enhanced monitoring and control, ultimately driving better operational outcomes for B2B buyers.
As the market continues to evolve, understanding the historical context provides valuable insights into current trends and future directions, allowing buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of air dryers
-
How do I choose the right air dryer for my business needs?
Choosing the right air dryer involves understanding your specific requirements, such as the volume of air processed, desired dew point, and operational environment. Consider the type of air dryer that best suits your application—refrigerated, desiccant, or membrane dryers. Evaluate the airflow capacity (CFM) needed for your operations and ensure the dryer can handle peak demand. Additionally, assess energy efficiency ratings and maintenance needs to minimize long-term costs. -
What is the best type of air dryer for humid climates?
For humid climates, refrigerated air dryers are generally more effective as they can efficiently reduce moisture in compressed air. However, if the humidity is exceptionally high, desiccant dryers may be necessary for achieving lower dew points. Always assess the specific requirements of your application, including the required air quality and downstream equipment needs, to determine the best option for your environment. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for air dryers?
Minimum order quantities for air dryers can vary significantly by supplier and product type. Typically, manufacturers may set an MOQ of one unit for standard models, while custom or specialized dryers might require larger quantities. It’s essential to negotiate with suppliers and clarify their terms to ensure that your procurement aligns with your operational needs and budget constraints. -
How can I vet suppliers for air dryers in international markets?
When vetting suppliers, conduct thorough background checks to assess their credibility and track record. Look for customer reviews, certifications, and industry reputation. Request references from other businesses that have purchased similar products. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s facility if possible, or utilize third-party inspection services to verify the quality and compliance of their products before placing a large order. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing air dryers internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include payment in advance, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that provide security for both parties, such as partial upfront payment and the remainder upon delivery. Always ensure that you understand the implications of currency exchange and international banking fees. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in air dryer suppliers?
Quality assurance measures are crucial in ensuring that the air dryers meet your operational standards. Look for suppliers that have ISO certification or equivalent quality management systems in place. Inquire about their testing procedures, warranty policies, and after-sales support. Request detailed documentation about compliance with international standards to ensure the product’s reliability and safety. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing air dryers?
Logistics play a vital role in international procurement. Consider shipping methods, lead times, and import/export regulations for your specific region. Evaluate the total landed cost, including shipping, tariffs, and handling fees. It’s beneficial to work with a freight forwarder who understands the complexities of international shipping and can provide guidance on customs clearance. -
How can I customize air dryers to meet my specific requirements?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for air dryers to suit specific industrial applications. Discuss your unique needs, such as size, capacity, or additional features like integrated filtration systems. Ensure that you communicate your requirements clearly during the initial discussions to avoid any misunderstandings. Request prototypes or detailed specifications to evaluate the proposed solutions before finalizing your order.
Top 6 Air Dryers Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Atlas Copco – Compressed Air Dryers
Domain: atlascopco.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Atlas Copco offers a complete range of compressed air dryers designed to efficiently remove moisture from compressed air systems, preventing corrosion, equipment damage, and product spoilage while optimizing energy use. Key features include:
1. **Dew Point Range**: Air dryers provide a wide range of dew points from +3 to -70 °C (37.4 to -94°F), ensuring precise air quality for specific applicatio…
2. PneumaTech – Compressed Air Dryers
Domain: pneumatech.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Compressed Air Dryers: 1. Refrigeration Dryers: Most commonly used, maintain a Pressure Dew Point (PDP) of +3 °C/37.4 °F, air-to-air and air-to-refrigerant heat exchangers, available in air-cooled or water-cooled, includes non-cycling, cycling, and VSD options. 2. Adsorption Dryers: Use hygroscopic materials like silica gel, achieve PDP from -10 °C/14 °F to -70 °C/-94 °F, consist of two drying ves…
3. Mikropor America – Energy-Efficient Air Dryers
Domain: mikroporamerica.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: MHOC Series: Heat of Compression Air Dryer, energy-efficient, zero-purge, designed for oil-free compressors, twin tower design, high energy efficiency. MK Series: Cost-effective compressed air dryer with advanced heat exchanger and refrigerant compressor. MCY Series: Cycling Dryers, cools liquid at 34 °F, energy-efficient at 5-95% air flow. MH Series: High Temperature Dryer with aftercooler for 24…
4. SMC – Air Dryers
Domain: smcusa.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, SMC – Air Dryers, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Donaldson – Compressed Air Dryers
Domain: donaldson.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Donaldson Compressed Air Dryers include several types designed to meet specific air quality requirements: 1. Heatless Adsorption: Prevents contamination and corrosion with clean, dry compressed air. 2. Oil-Free Adsorption: Safely removes hydrocarbons and other vapors for critical applications requiring oil and odor-free air. 3. Refrigeration: Utilizes a cooling system to create clean, dry air for …
6. Compressor World – Blower Purge Desiccant Air Dryers
Domain: compressorworld.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
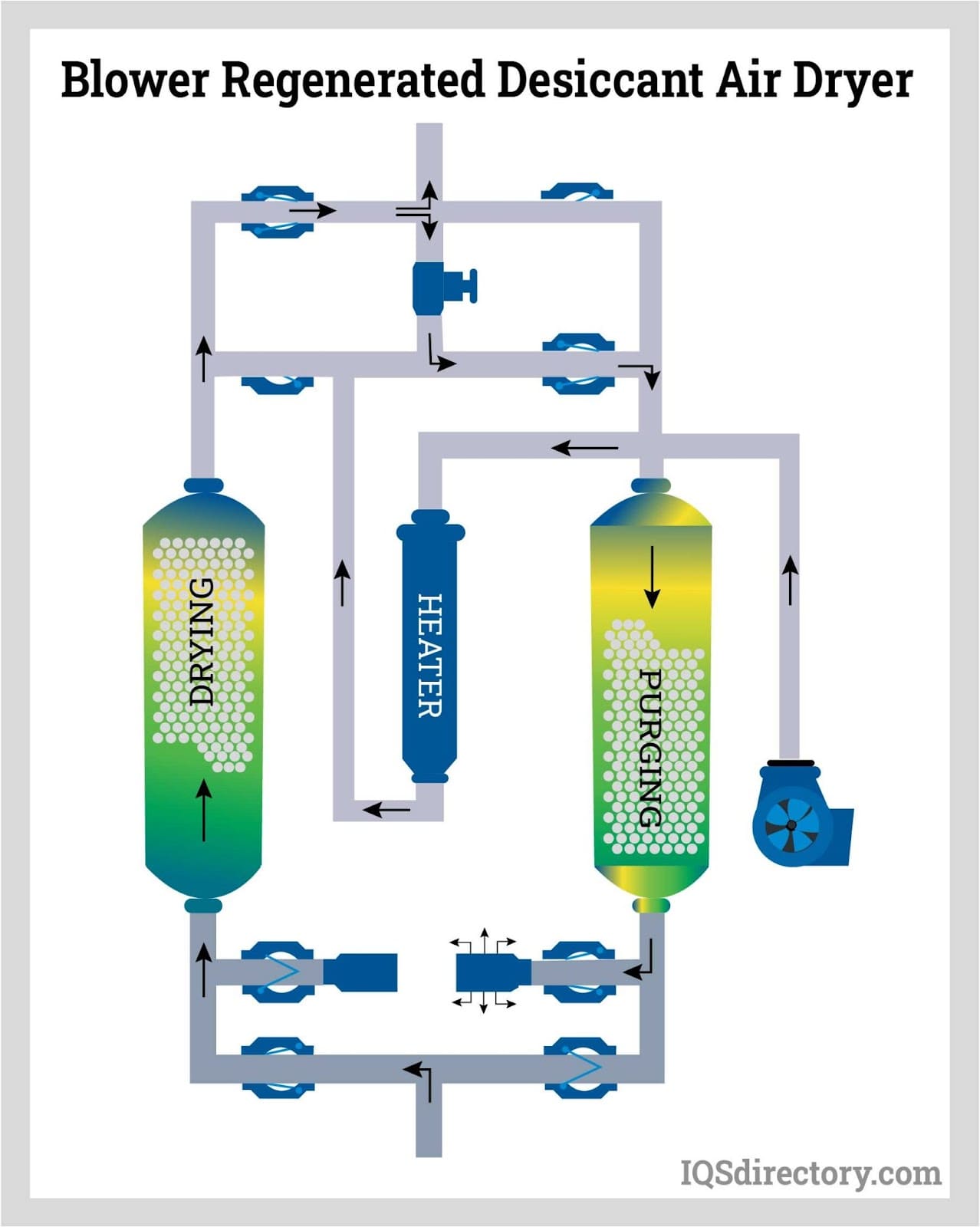
Introduction: Blower purge desiccant air dryers are a type of desiccant-based dryer that purges moisture to regenerate the desiccant. They use a combination of ambient air, heat, and compressed air for moisture removal. During regeneration, ambient air is heated and moved through the saturated desiccant, forcing moisture out, while compressed air cools the heated desiccant to increase its adsorptive capacity.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for air dryers
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Air Dryer Procurement?
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing is crucial for B2B buyers seeking to optimize their air dryer procurement. By carefully evaluating suppliers, understanding market trends, and leveraging technology, organizations can secure high-quality products while minimizing costs. The diverse range of air dryer options available—ranging from non-cycling refrigerated models to high-efficiency cycling variants—allows businesses to select solutions tailored to their specific operational needs.
Moreover, the value of establishing strong supplier relationships cannot be overstated. These partnerships can lead to better pricing, improved service levels, and access to the latest innovations. Buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should focus on suppliers that offer local support and flexibility to ensure seamless integration into their operations.
As we look ahead, the demand for energy-efficient and sustainable air dryers is likely to grow. Buyers are encouraged to stay informed about emerging technologies and regulatory changes that may impact their purchasing decisions. Embrace strategic sourcing as a proactive approach to enhance your procurement strategy, ensuring your business remains agile and competitive in an evolving market. Take the next step—evaluate your sourcing strategy today for a more sustainable and cost-effective future.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to air dryers
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.