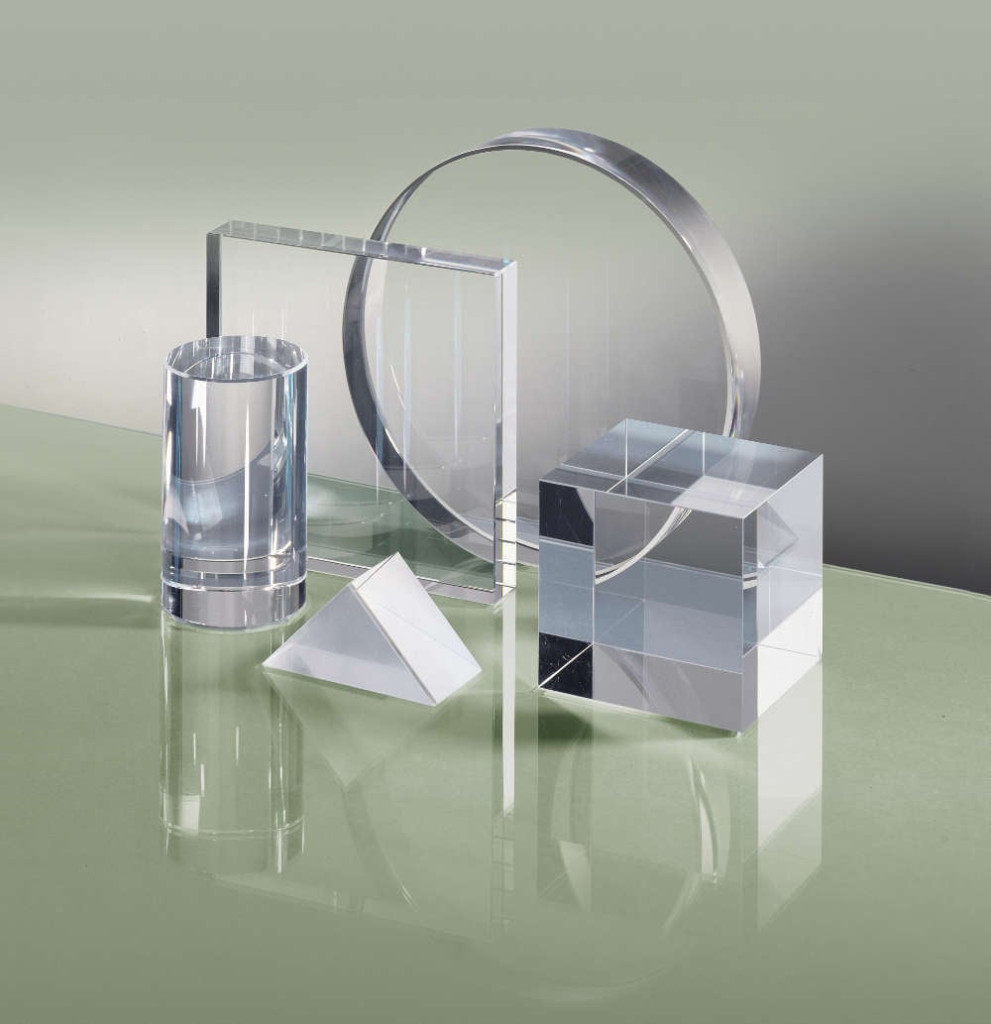
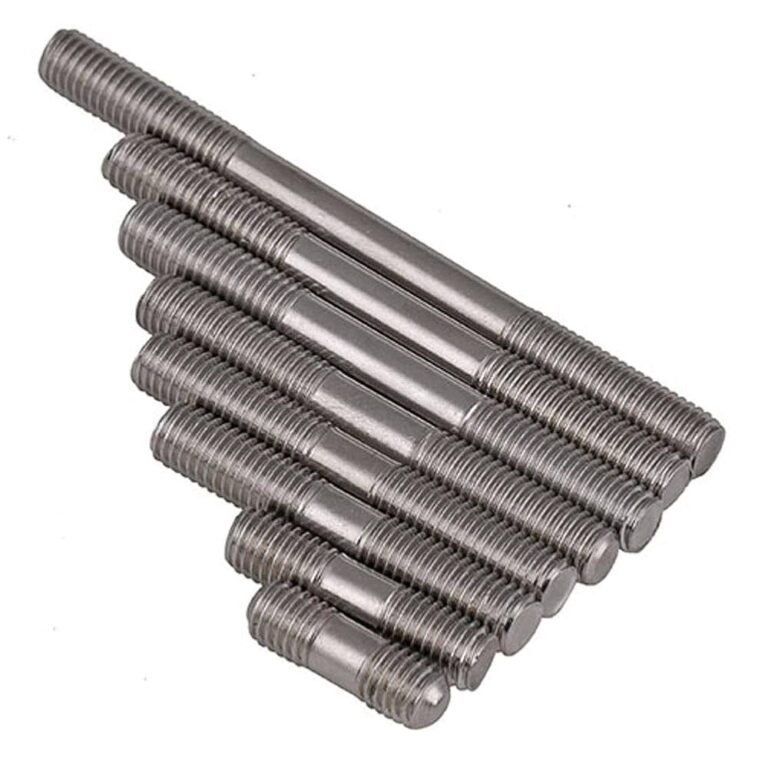
Is Your Quartz And Quartz Glass Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read This 2025 Report
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for quartz and quartz glass
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality quartz and quartz glass poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. As industries evolve and the demand for durable, versatile materials rises, understanding the distinctions between quartz and quartz glass becomes crucial. This guide delves into the multifaceted world of quartz products, covering types, applications, and supplier vetting processes, along with insights into pricing strategies. By providing a comprehensive overview, we aim to equip buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly in key markets like Saudi Arabia and Germany—with the necessary knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions.
Navigating the global market requires not only a grasp of product specifications but also an understanding of market trends and supplier reliability. This guide addresses essential questions such as, “What are the key differences between quartz and regular glass?” and “How can buyers ensure they select trustworthy suppliers?” By highlighting critical factors such as material properties, applications in various industries, and cost considerations, we empower B2B buyers to streamline their sourcing processes. Ultimately, this resource serves as a strategic tool, enabling companies to harness the unique properties of quartz and quartz glass to enhance their operations and drive business success.
Understanding quartz and quartz glass Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fused Quartz Glass | High purity silica, excellent thermal stability, low thermal expansion | Semiconductor manufacturing, optics | Pros: High performance, durability. Cons: Higher cost than regular glass. |
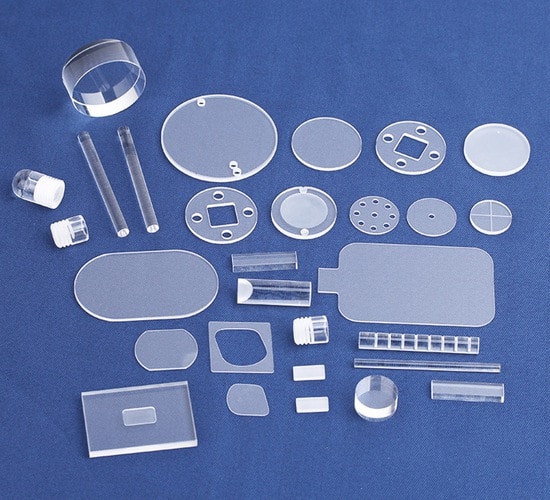
| Quartz Glass Plate | Transparent, available in various thicknesses, resistant to thermal shock | Laboratory equipment, electronics | Pros: Versatile, can be customized. Cons: Limited availability in some regions. |
| Fused Silica | Non-crystalline, extremely low impurity levels, high UV transmittance | Photovoltaics, fiber optics | Pros: Superior optical properties. Cons: More fragile than crystalline forms. |
| Quartz Tubes | Hollow structure, high thermal resistance, available in various diameters | Chemical processing, laboratory use | Pros: Excellent for high-temperature applications. Cons: Requires careful handling. |
| Colored Quartz Glass | Impurities or additives provide color, retains properties of quartz glass | Decorative applications, art glass | Pros: Aesthetic appeal, unique designs. Cons: May have reduced clarity. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Fused Quartz Glass?
Fused quartz glass is made from high-purity silica, making it an excellent choice for applications requiring thermal stability and low thermal expansion. Its unique properties allow it to withstand extreme temperatures and resist cracking under thermal stress. This type of glass is predominantly used in semiconductor manufacturing and optical applications, where precision and clarity are paramount. Buyers should consider the higher cost associated with fused quartz glass but can expect significant performance benefits in demanding environments.
How Does Quartz Glass Plate Meet B2B Needs?
Quartz glass plates are transparent and available in various thicknesses, making them highly versatile for numerous applications. They are particularly suited for laboratory equipment and electronics, where durability and resistance to thermal shock are critical. When purchasing quartz glass plates, businesses should evaluate their specific thickness and size requirements, as customization may be necessary. While they offer excellent performance, availability can be limited in certain regions, impacting procurement timelines.
What Advantages Does Fused Silica Offer in Industrial Applications?
Fused silica is characterized by its non-crystalline structure and extremely low impurity levels, resulting in high UV transmittance and exceptional optical clarity. This makes it ideal for applications in photovoltaics and fiber optics, where light transmission efficiency is crucial. B2B buyers should consider the superior optical properties of fused silica, though they should also be aware that it may be more fragile than its crystalline counterparts, necessitating careful handling during installation and use.
Why Choose Quartz Tubes for High-Temperature Applications?
Quartz tubes are hollow structures known for their high thermal resistance and ability to withstand extreme temperatures. These tubes are commonly used in chemical processing and laboratory environments, where they can endure harsh conditions. When evaluating quartz tubes for purchase, buyers should consider the required diameter and length, as well as handling protocols due to their fragility. While they excel in high-temperature applications, their delicate nature requires careful management to prevent breakage.

Illustrative image related to quartz and quartz glass
What Are the Unique Features of Colored Quartz Glass?
Colored quartz glass incorporates impurities or additives to achieve various colors while retaining the fundamental properties of quartz glass. This type of glass is particularly popular in decorative applications and art glass, where aesthetic appeal is essential. Buyers interested in colored quartz glass should assess the specific color and clarity requirements for their projects, as some variations may exhibit reduced transparency. While colored quartz offers unique designs, it may not be suitable for applications requiring high optical clarity.
Key Industrial Applications of quartz and quartz glass
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of quartz and quartz glass | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics | Semiconductor manufacturing using quartz wafers | High purity and thermal stability enhance device performance | Ensure high silica content and low impurity levels |
| Telecommunications | Fiber optics utilizing quartz glass | Exceptional light transmission for faster data rates | Verify material quality and compatibility with existing systems |
| Solar Energy | Quartz glass in photovoltaic cells | Improved efficiency and durability in solar panels | Focus on UV resistance and thermal stability |
| Medical Technology | Quartz glass in laboratory equipment and diagnostic tools | Enhanced accuracy and reliability in medical tests | Source from certified suppliers to ensure biocompatibility |
| Construction and Architecture | Quartz glass in high-performance windows and facades | Superior insulation and aesthetic appeal | Consider energy efficiency ratings and local regulations |
How is Quartz and Quartz Glass Used in Electronics Manufacturing?
In the electronics sector, quartz wafers are critical for semiconductor manufacturing. Their high purity and excellent thermal stability are essential for producing reliable electronic components. For international buyers, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East, sourcing quartz with a silica content exceeding 99% is crucial to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, suppliers must provide certifications confirming low impurity levels to meet stringent industry standards.
What Role Does Quartz Glass Play in Telecommunications?
Quartz glass is a key material in fiber optic technology, where its exceptional light transmission capabilities facilitate faster data transfer. Businesses in telecommunications benefit from the superior performance of quartz glass, which minimizes signal loss. When sourcing, companies should prioritize suppliers that can demonstrate compatibility with existing systems and provide detailed specifications on light transmittance and durability.
How is Quartz Glass Utilized in the Solar Energy Sector?
In solar energy applications, quartz glass is used in photovoltaic cells, enhancing their efficiency and longevity. The material’s ability to withstand high temperatures and UV exposure makes it ideal for outdoor installations. B2B buyers from regions with high solar energy potential, such as Africa and South America, should focus on sourcing quartz glass that meets specific thermal resistance and UV stability requirements to maximize energy production.
What are the Applications of Quartz Glass in Medical Technology?
Quartz glass is extensively used in medical laboratory equipment and diagnostic tools due to its chemical resistance and optical clarity. This ensures accurate measurements and reliable test results. For international buyers, particularly in Europe, sourcing from certified suppliers is essential to guarantee biocompatibility and compliance with health regulations. Additionally, suppliers should provide documentation to support the glass’s safety and efficacy for medical applications.
How Does Quartz Glass Enhance Construction and Architecture?
In the construction industry, quartz glass is employed in high-performance windows and facades, offering both aesthetic appeal and superior insulation properties. This not only enhances energy efficiency but also contributes to building aesthetics. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should consider local regulations regarding energy efficiency ratings and seek suppliers who can provide customized solutions that meet specific architectural needs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘quartz and quartz glass’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Choosing the Right Quartz Material for Industrial Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to select the appropriate type of quartz material for their specific industrial applications. With various forms available, such as fused quartz and quartz glass, the distinctions can be confusing. For instance, manufacturers in sectors like electronics, optics, and chemical processing may require materials with different thermal, chemical, and optical properties. Without a clear understanding of these differences, businesses risk purchasing subpar materials that lead to inefficiencies or product failures.
The Solution: To effectively choose the right quartz material, buyers should conduct a thorough needs assessment before sourcing. This involves identifying the specific application requirements, such as thermal resistance, chemical compatibility, and light transmittance. For example, if the application involves high-temperature processes, fused quartz, known for its superior thermal stability, would be a better choice. Conversely, for applications requiring high optical clarity, quartz glass may be more suitable due to its excellent light transmittance. Once the requirements are clearly defined, buyers should consult with reputable suppliers who can provide detailed technical specifications and samples for testing, ensuring that the selected material meets all operational criteria.
Scenario 2: Concerns Over the Durability and Longevity of Quartz Products
The Problem: Buyers frequently face concerns regarding the durability and longevity of quartz and quartz glass products, especially in demanding environments. Industries like aerospace and telecommunications require materials that can withstand harsh conditions, including extreme temperatures and exposure to chemicals. Buyers may fear that inferior products will lead to increased maintenance costs and downtime, impacting overall productivity and profitability.
The Solution: To mitigate these concerns, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing high-quality quartz products from established manufacturers with a proven track record. It’s essential to request certifications that validate the material’s performance under specified conditions, such as thermal shock resistance and chemical durability. Additionally, conducting field tests or pilot runs can provide valuable insights into how the materials will perform in real-world applications. Establishing a strong relationship with the supplier can also facilitate ongoing support, including advice on proper handling, installation, and maintenance practices to enhance the longevity of quartz products.
Scenario 3: Navigating Regulatory Compliance for Quartz Materials
The Problem: International buyers often encounter challenges regarding regulatory compliance when sourcing quartz and quartz glass. Different regions, such as the European Union and the Middle East, have varying regulations concerning material safety and environmental impact. This can create confusion and concern for businesses looking to ensure that their products meet local standards, as non-compliance can lead to significant penalties and reputational damage.
The Solution: To navigate regulatory compliance effectively, buyers should familiarize themselves with the specific regulations applicable to their target markets. This includes understanding guidelines related to material safety, environmental impact, and recycling. Engaging with legal experts or consultants specializing in material compliance can provide invaluable guidance. Moreover, buyers should seek suppliers who are transparent about their compliance certifications and can provide documentation that demonstrates adherence to local regulations. Regular audits and updates on regulatory changes will further help businesses stay compliant and avoid any potential disruptions in their supply chain.

Illustrative image related to quartz and quartz glass
Strategic Material Selection Guide for quartz and quartz glass
What Are the Key Properties of Quartz Glass?
Quartz glass, primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2), exhibits exceptional properties that make it suitable for various industrial applications. Its high purity (over 99% SiO2) contributes to its excellent thermal stability, allowing it to withstand temperatures exceeding 1,000°C without deforming. Additionally, quartz glass has superior light transmittance, enabling it to pass ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) light, which is crucial in applications like optics and photonics. Its hardness, rated at 7 on the Mohs scale, provides excellent scratch resistance, making it ideal for demanding environments.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Fused Silica?
Fused silica, a form of quartz glass, has unique advantages and disadvantages. One of its key advantages is its low thermal expansion coefficient, which minimizes the risk of thermal shock. This property is particularly beneficial in applications requiring precise temperature control, such as semiconductor manufacturing. However, the manufacturing process for fused silica can be complex and costly, which may deter some buyers. Additionally, while it offers excellent chemical resistance, it may not be suitable for all aggressive chemical environments, limiting its applications in certain industries.
How Does Quartz Impact Application Compatibility?
When selecting quartz materials, understanding their compatibility with specific media is essential. Quartz glass is highly resistant to most acids and bases, making it suitable for use in laboratories and chemical processing. However, it can be susceptible to hydrofluoric acid, which can etch the surface. For international buyers, it’s crucial to consider the specific chemicals and conditions under which the quartz will operate. Compliance with international standards, such as ASTM or DIN, is also vital to ensure product reliability and safety.
What Should International Buyers Consider When Sourcing Quartz Materials?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various compliance and regulatory standards when sourcing quartz materials. For instance, in Germany, adherence to DIN standards is critical, while buyers in Saudi Arabia may need to comply with local regulations that govern material safety and quality. Additionally, understanding the supply chain logistics, including shipping and customs regulations, is essential for timely delivery and cost management. Buyers should also evaluate the supplier’s ability to provide certification and documentation that meets their regional standards.
| Material | Typical Use Case for quartz and quartz glass | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz Glass | Optical components, laboratory equipment | High thermal stability and UV transmittance | Limited chemical resistance to hydrofluoric acid | High |
| Fused Silica | Semiconductor manufacturing, high-precision optics | Low thermal expansion, excellent durability | Complex and costly manufacturing process | High |
| Quartz Crystal | Electronics, resonators, timekeeping devices | Exceptional piezoelectric properties | Higher cost due to sourcing and purity | High |
| Quartz Sand | Glass manufacturing, construction materials | Abundant and cost-effective | Lower purity compared to quartz glass | Low |
This strategic material selection guide serves as a comprehensive resource for B2B buyers to make informed decisions about quartz and quartz glass. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material is crucial for optimizing application performance and ensuring compliance with international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for quartz and quartz glass
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Quartz and Quartz Glass?
The manufacturing of quartz and quartz glass involves several critical stages, each integral to ensuring the quality and performance of the final product. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing materials.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Selected and Processed?
The process begins with the selection of high-purity silica as the primary raw material. This silica must contain over 99% silicon dioxide to qualify as quartz glass. Various forms of silica are considered, including vein quartz, quartz sand, and fused silica, each selected based on the intended application.
Once the raw materials are sourced, they undergo thorough cleaning to eliminate impurities. This may involve mechanical sieving, chemical washing, or flotation processes to remove iron and other contaminants that could compromise the glass’s optical clarity and thermal resistance.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Quartz and Quartz Glass?
The next stage is forming, where the prepared silica is melted and shaped into desired forms. This can be achieved through various techniques, including:

Illustrative image related to quartz and quartz glass
- Fused Quartz Process: In this method, high-purity silica is melted at temperatures exceeding 1,700°C, resulting in a homogeneous liquid that can be molded into sheets, tubes, or custom shapes.
- Casting: This technique involves pouring molten silica into molds, allowing it to cool and solidify, which is particularly useful for creating complex geometries.
- Blowing: For hollow forms such as tubes or vessels, the blowing technique is employed, where the molten glass is inflated into shape.
Each of these methods requires precise temperature control and timing to ensure optimal material properties.
Finishing: How Is Quartz and Quartz Glass Refined for Quality?
After forming, the glass undergoes finishing processes to achieve the desired surface quality and dimensions. This may include grinding, polishing, and coating to enhance optical clarity and durability.
Finishing techniques are vital, especially for applications requiring high precision, such as optics or semiconductor manufacturing. The final product is often subjected to additional treatments like annealing, which helps relieve internal stresses formed during the cooling process.

Illustrative image related to quartz and quartz glass
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Quartz and Quartz Glass?
Quality assurance is critical in the manufacturing of quartz and quartz glass, particularly given the rigorous demands of industries such as electronics, optics, and aerospace. B2B buyers must be aware of the standards and checkpoints involved in ensuring product integrity.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Manufacturers of quartz and quartz glass often adhere to international quality management standards, such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for establishing a quality management system. Additionally, industry-specific certifications may apply, including:
- CE Marking: This indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- API Specification: Relevant for products used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring that materials meet specific performance standards.
For buyers in regions such as Africa and South America, understanding these certifications can be crucial for compliance and market entry.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Production?
Quality control (QC) is typically integrated into several stages of the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials for purity and consistency before they are used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the forming and finishing stages, regular checks are conducted to monitor parameters such as temperature, viscosity, and dimensional accuracy.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, the finished products undergo rigorous testing for optical quality, thermal resistance, and mechanical properties.
These checkpoints help ensure that any defects are identified and rectified before products reach the market.

Illustrative image related to quartz and quartz glass
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
Verifying the QC practices of potential suppliers is essential for B2B buyers to mitigate risks associated with product quality. Here are several strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insight into a manufacturer’s processes, equipment, and adherence to quality standards. This is particularly important for buyers from regions with specific regulatory requirements.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports can help buyers assess how manufacturers track and manage quality throughout the production process. These reports should include information on testing methods, results, and corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to evaluate products prior to shipment can offer additional assurance of quality. This is especially beneficial for international buyers who may not have direct oversight of the manufacturing process.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in the Quality Control of Quartz and Quartz Glass?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the quality and performance of quartz and quartz glass. These include:
- Optical Testing: This assesses the clarity, color, and light transmittance of the glass, which are critical for applications in optics and electronics.
- Thermal Shock Resistance Testing: This evaluates how well the glass can withstand rapid temperature changes, a vital property for industrial applications.
- Mechanical Testing: Hardness, tensile strength, and impact resistance are assessed to ensure the glass meets specific performance criteria.
Understanding these testing methods enables buyers to make more informed decisions regarding supplier capabilities and product suitability.
Conclusion: Why Is Quality Assurance Crucial for International B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for quartz and quartz glass is vital. By familiarizing themselves with these aspects, buyers can enhance their sourcing strategies, ensure compliance with international standards, and ultimately secure high-quality materials that meet their specific needs.
Illustrative image related to quartz and quartz glass
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘quartz and quartz glass’
The procurement of quartz and quartz glass requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure quality, compliance, and suitability for specific applications. This guide provides a practical checklist to assist B2B buyers in making informed decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining the technical requirements for your quartz or quartz glass needs. Consider aspects such as purity levels, hardness, thermal resistance, and specific dimensions. Knowing these details is crucial to avoid costly mistakes later on, as different applications may require different specifications.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Pricing
Conduct thorough research on current market trends and pricing for quartz and quartz glass. This knowledge will help you understand the average costs and identify any seasonal fluctuations. Utilize industry reports, trade publications, and supplier websites to gather pricing data.
Step 3: Identify Potential Suppliers
Create a list of potential suppliers that specialize in quartz and quartz glass. Look for companies with a proven track record in your industry. Utilize online directories, trade shows, and industry associations to find reputable suppliers.
Step 4: ✅ Verify Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding with any supplier, ensure they hold relevant certifications such as ISO 9001 or other quality management certifications. These certifications indicate a commitment to quality and compliance with international standards, reducing the risk of receiving subpar materials.
Step 5: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Assess the capabilities of each supplier, including their production capacity, technology used, and quality control processes. Understanding their capabilities will help you determine if they can meet your specific needs and maintain quality over time.
- Production Capacity: Ensure they can handle your order volume.
- Technology and Equipment: Advanced technology often leads to better quality products.
Step 6: Request Samples for Testing
Always request samples from shortlisted suppliers to evaluate the quality of their quartz and quartz glass. Testing samples will allow you to confirm their specifications and ensure they meet your application requirements. Pay attention to physical properties like clarity, hardness, and thermal resistance.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve selected a supplier, negotiate the terms of purchase, including price, delivery schedules, payment terms, and return policies. Clear communication at this stage can prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction. Make sure to include clauses that protect you in case of non-compliance with agreed specifications.

Illustrative image related to quartz and quartz glass
By following these steps, B2B buyers can ensure a well-informed and strategic approach to sourcing quartz and quartz glass, ultimately leading to successful procurement outcomes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for quartz and quartz glass Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Quartz and Quartz Glass?
When sourcing quartz and quartz glass, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The primary material for quartz glass is high-purity silica, with over 99% silicon dioxide content. The price can vary significantly based on purity levels and geographical sourcing. For quartz, the costs are influenced by the type of quartz (e.g., vein quartz, quartz sand) and its processing requirements.
-
Labor: Labor costs are variable and depend on the region where manufacturing occurs. Skilled labor is often required for quality assurance and handling specialized equipment, which can drive up costs in regions with higher wage standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations such as utilities, maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Overhead can vary based on local economic conditions and the scale of production.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific applications can significantly affect costs. The more intricate the tooling required, the higher the initial investment, which may be distributed over larger production volumes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous quality control measures are essential, especially for applications requiring high precision. The costs associated with QC can be substantial, particularly when certifications (like ISO or ASTM standards) are necessary.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs, influenced by distance and the mode of transport, play a critical role in the total cost. International shipments may incur additional fees such as tariffs and customs duties.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on competition and market demand.
What Factors Influence the Pricing of Quartz and Quartz Glass?
Pricing in the quartz and quartz glass market is influenced by several factors:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their needs while maximizing cost efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications (such as size, shape, and purity) can lead to increased costs. Suppliers may charge a premium for bespoke products that require specialized manufacturing processes.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and necessary certifications will elevate costs. Buyers should assess whether the additional investment in quality translates into tangible benefits for their applications.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality and service may charge higher prices but can offer assurances regarding product performance.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can impact costs significantly. Understanding who bears the cost of shipping, insurance, and risk during transport is essential for accurate budgeting.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Their Quartz and Quartz Glass Procurement Costs?
To secure the best pricing and terms, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also long-term costs associated with maintenance, potential failures, and the operational lifespan of the materials.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, especially for repeat orders. Long-term partnerships often result in favorable terms.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Conducting a thorough market analysis and soliciting quotes from multiple suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations and ensure competitive pricing.
-
Be Clear on Specifications: Clearly outline your specifications and requirements to avoid misunderstandings that could lead to additional costs.
-
Timing Purchases: Market conditions can fluctuate; being aware of seasonal trends or production cycles may allow for more strategic purchasing decisions.
Are There Any Pricing Nuances Specific to International Buyers from Regions Like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe?
International buyers must navigate unique challenges and opportunities based on regional factors. For instance, fluctuations in currency exchange rates can impact pricing. Additionally, buyers in regions with robust trade agreements may benefit from reduced tariffs, while those in emerging markets may face higher shipping costs. Understanding local regulations and compliance requirements is essential for effective sourcing.

Illustrative image related to quartz and quartz glass
Buyers should also consider logistics infrastructure, as regions with developed transport networks may reduce overall costs. Finally, cultural awareness and effective communication can enhance negotiation outcomes and supplier relationships.
Disclaimer on Pricing
The prices for quartz and quartz glass can fluctuate based on market dynamics and specific buyer requirements. This analysis provides a general overview; actual costs should be verified with suppliers to ensure accuracy and relevance to your purchasing needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing quartz and quartz glass With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Quartz and Quartz Glass
In the rapidly evolving landscape of materials used across various industries, quartz and quartz glass have established themselves as reliable options. However, businesses must evaluate alternative solutions that may offer similar benefits or even surpass them in specific applications. By analyzing the performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases, companies can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Quartz And Quartz Glass | Alternative 1 Name | Alternative 2 Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High thermal resistance, excellent optical clarity, and durability. | Borosilicate Glass | Soda-Lime Glass |
| Cost | Generally higher due to the purity of materials. | Moderate; cost-effective for many applications. | Low; widely available and inexpensive. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized handling and equipment for production. | Easier to work with, commonly available. | Simple manufacturing processes; familiar to most industries. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; resistant to thermal shock. | Requires careful handling to avoid breakage. | Moderate; can be prone to scratches and thermal stress. |
| Best Use Case | High-end applications like semiconductor manufacturing and optics. | Laboratory glassware, kitchenware, and scientific equipment. | General-purpose applications, windows, and containers. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Borosilicate Glass
Borosilicate glass is known for its superior resistance to thermal shock compared to standard glass, making it a popular choice in laboratory settings. Its composition allows it to withstand temperature fluctuations without cracking. However, while it offers good optical clarity and chemical resistance, borosilicate glass does not match the high-temperature performance of quartz glass. Its moderate cost and ease of handling make it suitable for applications like laboratory glassware and kitchen items.
2. Soda-Lime Glass
Soda-lime glass is the most common type of glass used in everyday applications, including windows, bottles, and jars. It is relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, which contributes to its widespread use. However, its thermal resistance and durability are significantly lower than that of quartz and quartz glass, making it less suitable for high-performance applications. While it is ideal for general-purpose usage, it may not be the best choice for environments requiring high optical clarity or extreme temperature resistance.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution
When selecting between quartz, quartz glass, and alternative materials, B2B buyers should consider their specific application requirements, budget constraints, and performance expectations. For high-end applications that demand exceptional durability and optical performance, quartz and quartz glass remain unmatched. However, for less demanding environments, borosilicate or soda-lime glass may provide a more cost-effective and easier-to-implement solution. Ultimately, the decision should be guided by a comprehensive understanding of the operational context and the inherent properties of each material.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for quartz and quartz glass
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Quartz and Quartz Glass?
When evaluating quartz and quartz glass for industrial applications, several technical properties are crucial. Understanding these specifications can significantly influence purchasing decisions and product performance.

Illustrative image related to quartz and quartz glass
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the purity and quality of the quartz or quartz glass. For quartz glass, the standard is typically over 99% silicon dioxide (SiO2). Higher grades are essential for applications requiring minimal impurities, such as in semiconductor manufacturing or optical components. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate grade ensures compatibility with specific industrial processes, thereby reducing the risk of product failure.
2. Hardness
Measured on the Mohs scale, quartz glass generally achieves a hardness of 7, while standard glass ranges from 5.5 to 6. This property is vital in applications where wear and tear are significant, such as in laboratory settings or high-traffic environments. A higher hardness translates to better scratch resistance, which is a key factor for durability and longevity in end products.
3. Thermal Shock Resistance
Quartz glass exhibits exceptional thermal shock resistance, able to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking. This quality is essential for applications involving high temperatures, such as in laboratory equipment or furnace windows. Understanding this property helps B2B buyers select the right materials for environments that experience extreme heat fluctuations.
4. Light Transmittance
The ability of quartz glass to transmit infrared and ultraviolet light is a distinct advantage over ordinary glass, which blocks these wavelengths. This property is particularly important in applications like optics, where clarity and transmission rates can significantly impact performance. Buyers in industries such as photonics or solar energy should prioritize this characteristic when sourcing materials.
Illustrative image related to quartz and quartz glass
5. Chemical Resistance
Quartz glass is highly resistant to chemical corrosion, making it suitable for use in laboratories and chemical processing environments. This property is crucial for ensuring the longevity of equipment and reducing maintenance costs. Understanding the chemical compatibility of quartz glass allows B2B purchasers to make informed choices, particularly in industries dealing with harsh chemicals.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon Related to Quartz and Quartz Glass?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology can enhance communication and negotiations between suppliers and buyers. Here are several key terms to know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the quartz industry, this term often applies to manufacturers who create specialized quartz components for use in larger systems. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable sources for high-quality materials tailored to their specific needs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management. This term is particularly relevant in industries where raw materials are needed in bulk, as it can affect overall project costs and supply chain logistics.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where a buyer requests price quotes from suppliers for specific quantities and types of products. For quartz and quartz glass, submitting an RFQ can help buyers compare prices, specifications, and lead times, enabling more informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. For B2B buyers in regions like Africa or South America, understanding Incoterms is crucial for navigating shipping costs, risk management, and delivery timelines.
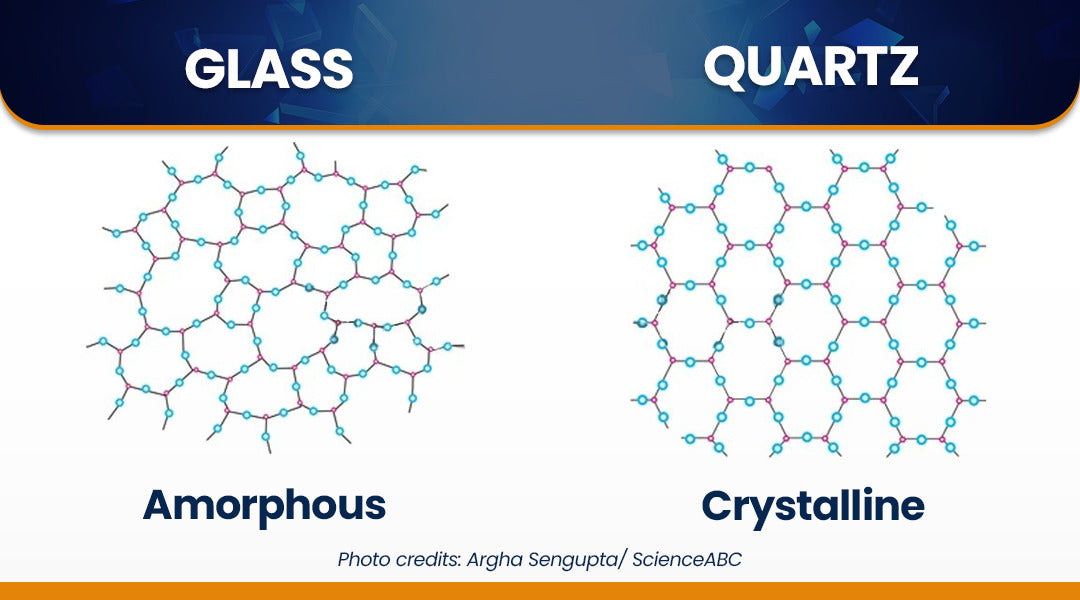
5. Fused Silica vs. Quartz Glass
While often used interchangeably, fused silica and quartz glass have distinct properties. Fused silica is created by melting silica sand, resulting in a non-crystalline form with excellent thermal stability. In contrast, quartz glass is derived from natural quartz crystals. Recognizing the differences can help buyers select the appropriate material for specific applications, particularly in high-tech industries.
By understanding these properties and terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing quartz and quartz glass, ensuring they meet the specific requirements of their industries.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the quartz and quartz glass Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics in the Quartz and Quartz Glass Sector?
The quartz and quartz glass market is experiencing robust growth driven by several global factors. Key applications in industries such as electronics, optics, and solar energy are propelling demand. For instance, quartz glass is essential for semiconductor manufacturing due to its high thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it a critical component in high-tech industries. Moreover, the increasing adoption of quartz in the manufacturing of photovoltaic cells has spurred growth in renewable energy sectors, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where solar energy solutions are becoming paramount.
Emerging B2B technologies are also reshaping sourcing trends. Advanced materials science is enabling the production of higher purity quartz and innovative manufacturing techniques such as 3D printing, which is gaining traction in Europe and the Middle East. International buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can provide tailored solutions, including customized quartz glass components. The shift towards digital supply chains facilitated by platforms that enhance transparency and efficiency is crucial for companies looking to optimize procurement processes.
Additionally, geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions have highlighted the importance of diversifying sourcing strategies. Buyers from regions such as Saudi Arabia and Germany are now prioritizing suppliers who offer reliability and flexibility in their supply chains, with an emphasis on minimizing lead times and enhancing product availability.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Practices in the Quartz Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a fundamental aspect of sourcing in the quartz and quartz glass sector. The environmental impact of quartz mining and glass production has prompted businesses to seek more sustainable practices. Ethical sourcing is not only about compliance with regulations but also about fostering a positive brand image and meeting consumer expectations for environmentally responsible products.
For B2B buyers, the importance of working with suppliers who adhere to sustainability standards cannot be overstated. Many companies are now pursuing ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001, which focuses on effective environmental management systems. Furthermore, suppliers who utilize recycled materials or implement energy-efficient manufacturing processes are gaining a competitive edge.
Investing in suppliers that prioritize sustainability can lead to long-term cost savings and risk mitigation, particularly as regulatory pressures increase globally. For instance, companies in Europe are facing stricter environmental regulations, making compliance an essential factor in supplier selection. Ultimately, the move towards sustainable practices will not only benefit the environment but also enhance the overall resilience and reputation of businesses in the quartz and quartz glass sector.
How Has the Quartz and Quartz Glass Industry Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the quartz and quartz glass industry is marked by significant technological advancements and changing market demands. Initially, quartz was primarily used in traditional glass-making applications. However, the late 20th century saw a shift as industries began to recognize the unique properties of quartz, such as its high thermal resistance and low expansion coefficient, leading to its widespread adoption in high-tech sectors.
In the early 2000s, the rise of the electronics industry further propelled quartz demand, especially in semiconductor and telecommunications applications. As industries became more digitized, the need for high-purity quartz glass became critical for manufacturing advanced components. Today, the market continues to innovate, with ongoing research into the potential of quartz in emerging technologies, including nanotechnology and advanced optics.
This historical context is vital for B2B buyers as it highlights the adaptability and longevity of quartz as a material, suggesting a stable future demand driven by technological advancements and sustainability considerations. Understanding these trends allows buyers to make informed sourcing decisions that align with their strategic objectives.

Illustrative image related to quartz and quartz glass
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of quartz and quartz glass
-
How do I determine the right grade of quartz glass for my application?
When selecting quartz glass, consider its intended use, required thermal resistance, and chemical stability. High-purity quartz glass, with over 99% silica content, is ideal for applications requiring high thermal stability and transparency, such as in semiconductor manufacturing or optical devices. Evaluate the specific properties needed, such as UV transmittance or resistance to thermal shock, and consult with suppliers to ensure they can meet those specifications. -
What is the best type of quartz glass for high-temperature applications?
Fused quartz glass is the best option for high-temperature applications due to its exceptional thermal resistance and low thermal expansion. It can withstand temperatures up to 1,200°C (2,192°F) without cracking or deforming. For industries like aerospace or semiconductor manufacturing, where high thermal stability is crucial, sourcing high-quality fused quartz from reputable suppliers is essential. -
How can I vet suppliers of quartz and quartz glass for international trade?
To vet suppliers, conduct thorough research, including checking their certifications and industry reputation. Look for suppliers with ISO certifications, as these indicate adherence to quality management standards. Request samples to assess product quality and seek references from other B2B buyers in your industry. Additionally, consider their experience in exporting to your region, as this can impact logistics and compliance with local regulations. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for quartz and quartz glass?
MOQs for quartz and quartz glass can vary significantly based on the supplier and product type. Generally, MOQs may range from 100 kg for raw materials to several hundred units for finished products like quartz tubes or plates. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and explore options for smaller or trial orders if you are uncertain about your requirements. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing quartz and quartz glass internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common practices include a 30% advance payment with the balance due upon shipment, or payment via letter of credit (LC) for larger orders. Always negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and risk tolerance. Ensure clarity on payment methods accepted, such as bank transfers or credit cards, and verify any additional fees related to currency exchange or international transactions. -
What quality assurance measures should be in place when sourcing quartz glass?
Quality assurance measures should include supplier audits, product certifications, and third-party testing. Request documentation proving compliance with relevant industry standards, such as ASTM or ISO. Implement a quality control process that includes inspecting samples upon receipt and conducting tests for properties like transparency, hardness, and thermal resistance to ensure the materials meet your specifications. -
How do logistics and shipping impact the cost of quartz and quartz glass?
Logistics can significantly affect the overall cost of sourcing quartz and quartz glass. Factors such as shipping distance, weight, and mode of transportation (air vs. sea) will influence freight costs. Additionally, consider customs duties, taxes, and insurance. Collaborating with experienced logistics providers can help streamline the shipping process and potentially reduce costs by consolidating shipments or optimizing routes. -
What customization options are available for quartz products?
Many suppliers offer customization options, including specific dimensions, shapes, and purity levels of quartz glass. Discuss your requirements directly with suppliers to explore possibilities such as cutting, polishing, or coating. Customization may also extend to packaging and labeling, which can be tailored to meet your branding or regulatory needs, ensuring that the final product aligns perfectly with your application.
Top 8 Quartz And Quartz Glass Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Quartz – Crystalline Excellence
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Quartz is a crystalline material with a well-defined structure where atoms occupy fixed positions in a periodic three-dimensional network (lattice). Glass is amorphous, lacking a well-defined structure, with atoms arranged randomly. Quartz is much harder than glass. Quartz is 100% pure silicon dioxide (SiO2), while common glass (Soda-lime glass) consists of approximately 72% SiO2, 14.2% sodium oxi…
2. Mo-Sci – Fused Silica Solutions
Domain: mo-sci.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Fused silica is a specialty material made from nominally pure silica (SiO2) that has been melted and cooled to form an amorphous solid. It has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion, making it highly resistant to thermal shock. Fused silica is transparent to a wide spectrum of light, from deep ultraviolet to far-infrared, and is chemically inert, resistant to most acids except hydrofluoric ac…
3. Continental Trade – Quartz Glass Solutions
Domain: continentaltrade.com.pl
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Quartz glass is a high-purity silica glass (SiO2 ≥ 99.9%) resistant to water and strong acids (except hydrofluoric acid) with low alkali resistance. It has a high melting point, low thermal expansion, and thermal shock resistance. It transmits ultraviolet and infrared light, with transmittance depending on additives. Types include natural quartz (suitable for high temperatures > 1000°C) and synthe…
4. Techinstro – ITO Coated Quartz Glass
Domain: techinstro.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “ITO Coated Quartz Glass”, “Manufacturer”: “Techinstro”, “Thickness”: “1mm”, “Molecular Formula”: “In2O3 (SnO2)x”, “Form”: “Solid”, “Color”: “Transparent”, “Transmittance”: “>83%”, “Resistivity”: “10 ohms/sq”, “Refractive Index”: “n20/D 1.517”, “Etching”: “d 250s”, “Thermal Shrinkage”: “126%”, “ITO Coating Thickness”: “180mm”, “Material Composition”: “Highly pure silica (SiO2 ≥ 99…
5. SQP – Quartz Glass Solutions
Domain: sqp.co.jp
Introduction: Quartz glass is a material characterized by high purity, superior high temperature stability, superior light transmittance, high chemical resistance, and a high level of homogeneity. It is used in semiconductor production processes, particularly in reaction chambers, furnace tubes, and optical devices. Key features include: (1) High purity with extremely low microscopic impurities, including ultra…
6. Azom – Fused Silica Solutions
Domain: azom.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Fused silica is nominally pure silica (SiO2) that has been melted and cooled to form a glassy, amorphous solid, without additives. Fused quartz refers to an amorphous solid formed by melting naturally occurring quartz, containing impurities based on the quartz used. Fused silica has high-performance applications due to its distinct electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties, including high res…
7. PGO Online – Fused Silica & Fused Quartz
Domain: pgo-online.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Fused Silica vs. Fused Quartz: Two distinct types of quartz glass with different properties and applications. Fused Quartz is made from natural quartz crystals and has moderate purity, suitable for sight-glass applications. Fused Silica is synthetic, high-purity, and ideal for optical applications requiring high imaging accuracy, low absorption in UV range (transmittance > 80% at 185 nm), and bett…
8. CureUV – Quartz Glass Plates
Domain: cureuv.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Collection: Quartz Glass Plates
52 products available
Made for various brands including Agfa, CET Color, ColorSpan, CureUV, Durst Rho, EFI, Gallus, Gandinnovations, Honle UV, HP, Inca.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for quartz and quartz glass
As the global demand for high-performance materials continues to grow, strategic sourcing of quartz and quartz glass emerges as a critical factor for businesses aiming to enhance their competitive edge. The unique properties of quartz glass—such as its superior hardness, high-temperature resistance, and exceptional light transmittance—make it indispensable across various industries, including electronics, optics, and construction. Understanding the differences between quartz and regular glass can help buyers make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right materials tailored to their specific applications.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, forging strong supplier relationships is essential. By engaging with reputable manufacturers and distributors, businesses can secure high-quality quartz products that meet stringent performance standards.
Looking ahead, the market for quartz and quartz glass is poised for growth, driven by advancements in technology and increasing applications in diverse sectors. Now is the time to evaluate your sourcing strategies and invest in sustainable partnerships that will enable your business to thrive in this evolving landscape. Embrace the opportunity to innovate and lead in your industry by prioritizing strategic sourcing of quartz and quartz glass today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.