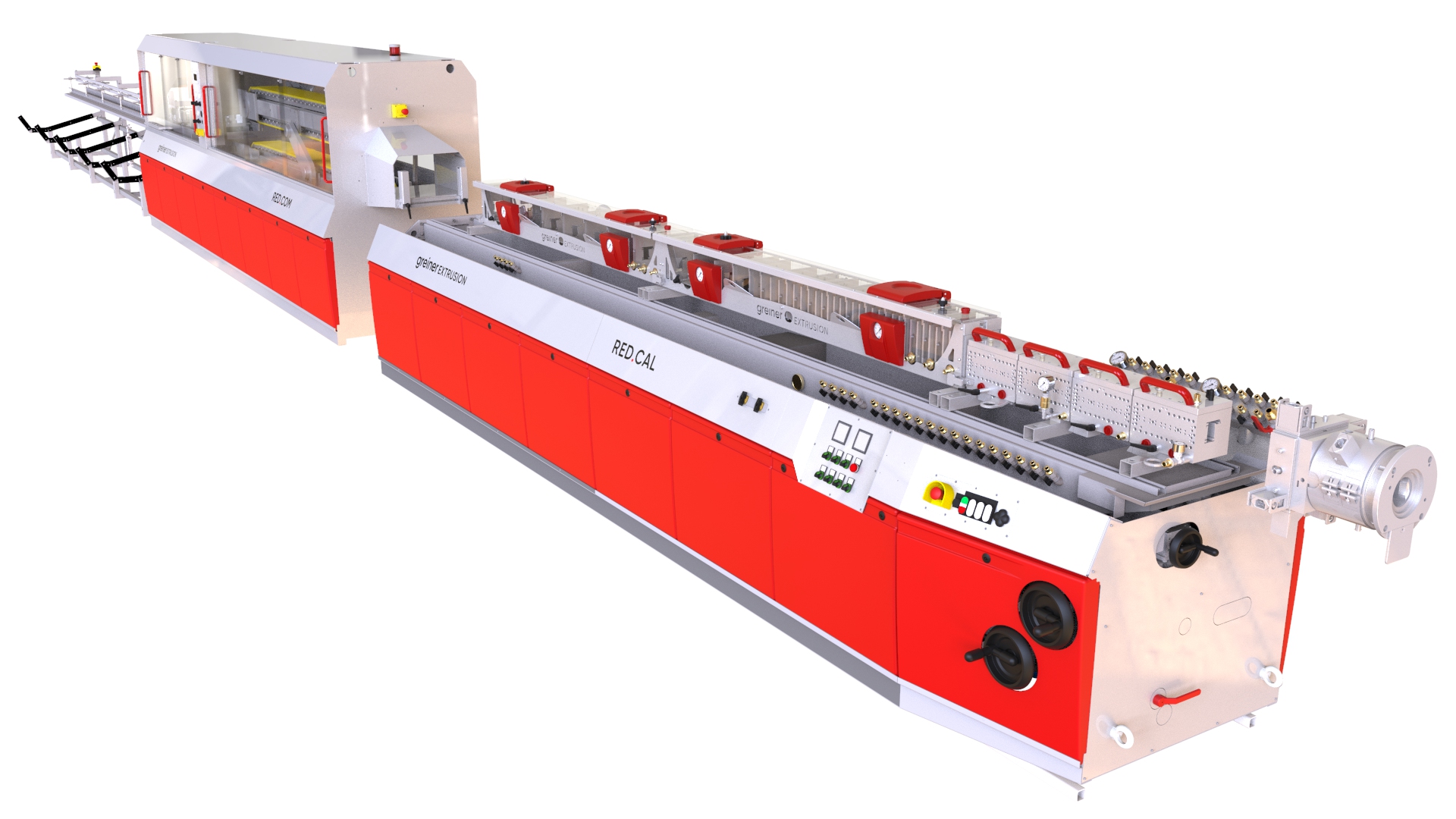
Extrusion Lines: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for extrusion lines
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, sourcing the right extrusion lines can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. With the demand for high-quality, continuous production of plastic products rising across diverse industries, understanding the intricacies of extrusion technology is essential. This guide aims to demystify the global market for extrusion lines, covering a comprehensive range of topics, including types of extrusion machinery, their applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
By delving into these critical aspects, this guide empowers buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Saudi Arabia—to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are looking to invest in advanced extrusion technology for packaging solutions or specialized machinery for medical applications, our insights will help you navigate supplier options and evaluate performance metrics effectively.
Moreover, we will explore the role of auxiliary equipment, the importance of material handling, and strategies for ensuring product quality, all designed to enhance your operational efficiency. This guide is your essential resource for optimizing your procurement strategy in the competitive extrusion market, ensuring you stay ahead of the curve in a globalized economy.
Understanding extrusion lines Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Screw Extrusion | Utilizes a single screw for material transport; ideal for uniform melting of pellets. | Plastic films, sheets, and profiles. | Pros: Simple design, lower cost. Cons: Limited to certain materials. |
| Twin-Screw Extrusion | Features two intermeshing screws for better mixing; suitable for both thermoplastics and thermosets. | Compounding, masterbatch production, and food applications. | Pros: Enhanced mixing, flexibility in formulations. Cons: Higher investment cost. |
| Co-Extrusion | Combines multiple materials in a single process to achieve varied properties. | Multi-layer films, composite materials, and packaging. | Pros: Cost-effective for specialized products. Cons: Complexity in setup and operation. |
| Sheet Extrusion | Focuses on producing thick sheets; often paired with downstream processes for shaping. | Construction materials, packaging, and automotive components. | Pros: High output, customizable thickness. Cons: Limited to sheet products. |
| Pipe Extrusion | Specializes in producing pipes of various diameters; often utilizes larger extruders. | Plumbing, drainage, and industrial applications. | Pros: High efficiency for large volumes. Cons: Requires significant space and investment. |
What are the Characteristics of Single-Screw Extrusion?
Single-screw extrusion is the most common type of extrusion line, characterized by its simplicity and cost-effectiveness. It operates using a single rotating screw that transports and melts plastic pellets, making it ideal for producing uniform products like films, sheets, and profiles. For B2B buyers, this type is suitable for operations requiring high volumes of consistent products. However, it may not be suitable for complex materials that require advanced mixing or processing capabilities.
How Does Twin-Screw Extrusion Enhance Material Processing?
Twin-screw extrusion features two intermeshing screws that work collaboratively to enhance material mixing and processing. This type is particularly effective for compounding and producing masterbatches, as it can handle both thermoplastics and thermosets. B2B buyers looking for versatility in material formulations will find twin-screw systems advantageous. However, the initial investment is higher compared to single-screw systems, which may be a consideration for budget-conscious operations.
Illustrative image related to extrusion lines
Why Choose Co-Extrusion for Specialized Products?
Co-extrusion is a unique process that allows for the simultaneous extrusion of multiple materials to create products with varied properties, such as multi-layer films. This method is particularly beneficial in packaging applications where barrier properties are crucial. Buyers should consider co-extrusion for projects that demand high-performance materials but be aware of the complexity and potential higher costs involved in setup and maintenance.
What Advantages Does Sheet Extrusion Offer for B2B Buyers?
Sheet extrusion focuses on producing thick plastic sheets, which can be further processed into various shapes. This method is often employed in industries like construction and automotive, where customized thickness and dimensions are critical. B2B buyers will appreciate the high output capabilities of sheet extrusion lines, but they should also consider that this type is limited to producing sheet products only, which may not meet all processing needs.
How Efficient is Pipe Extrusion for Large-Scale Production?
Pipe extrusion lines are designed specifically for producing pipes of varying diameters, making them essential in plumbing, drainage, and industrial applications. These systems are capable of high efficiency and output, making them ideal for large-scale production. However, B2B buyers should take into account the significant space and investment required for such equipment, as well as the specialized nature of the products produced.
Key Industrial Applications of extrusion lines
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of extrusion lines | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Packaging | Production of plastic films | High-volume production with consistent quality | Consideration for moisture control and material types |
| Construction | Manufacturing of plastic profiles | Lightweight, durable materials for various uses | Need for precise dimensions and tolerance specifications |
| Medical Devices | Creation of flexible tubing | Essential for medical applications requiring sterility | Compliance with health standards and material certifications |
| Plumbing and Infrastructure | Production of rigid plastic pipes | Long-lasting, corrosion-resistant solutions | Sourcing for large-scale output and material durability |
| Consumer Goods | Production of plastic components | Cost-effective production of diverse products | Flexibility in production scale and material options |
How are Extrusion Lines Used in the Packaging Industry?
Extrusion lines in the packaging sector are primarily employed for producing plastic films used in various applications, including food packaging and industrial wraps. These films are extruded continuously, allowing for high-volume production while maintaining consistency in quality. For international buyers, especially those in regions like Africa and South America, it is crucial to consider moisture control systems to ensure the integrity of the films, as humidity can significantly affect quality. Additionally, sourcing materials that comply with regional packaging regulations is essential.
What Role Do Extrusion Lines Play in the Construction Industry?
In the construction industry, extrusion lines are utilized to manufacture plastic profiles, such as window frames and siding. These profiles are valued for their lightweight nature and resistance to environmental factors, which enhances the durability of construction projects. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should focus on suppliers that can guarantee precise dimensions and tight tolerances, as these factors are critical for fitting and installation purposes. Moreover, sourcing materials that meet local building codes is vital for compliance and safety.
How are Extrusion Lines Essential in Medical Device Manufacturing?
Extrusion lines are integral to producing flexible tubing used in medical devices, which require strict adherence to hygiene and performance standards. The continuous nature of extrusion allows for the mass production of tubing that meets specific dimensional and material requirements essential for medical applications. Buyers, particularly in regions like Saudi Arabia, must prioritize suppliers that offer certified materials and processes that comply with health regulations, ensuring the safety and effectiveness of medical products.
In What Ways are Extrusion Lines Used for Plumbing and Infrastructure?
In plumbing and infrastructure, extrusion lines are used to create rigid plastic pipes that provide durable and corrosion-resistant solutions for water supply and drainage systems. The ability to produce large diameters and varying wall thicknesses is essential for meeting diverse infrastructure needs. Buyers from developing regions should consider sourcing extrusion lines capable of high-volume output while ensuring material strength and longevity. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding plumbing materials is crucial for compliance.
How Do Extrusion Lines Benefit the Consumer Goods Sector?
Extrusion lines are vital in the consumer goods sector for producing various plastic components, from packaging to household items. The cost-effective production capabilities of extrusion allow for a wide range of products to be manufactured efficiently. For international buyers, particularly in emerging markets, it is important to seek suppliers that offer flexible production scales and a variety of material options, enabling businesses to adapt to market demands and consumer preferences effectively.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘extrusion lines’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Struggles with Material Consistency and Quality Control
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant challenges with maintaining consistent material quality during the extrusion process. Variability in raw materials, such as moisture content or inconsistent pellet sizes, can lead to defects in the final products, resulting in increased scrap rates and customer dissatisfaction. This inconsistency can be particularly detrimental in industries such as medical supplies or food packaging, where precision and reliability are non-negotiable.
The Solution: To combat these issues, it is crucial to implement a robust material handling and quality assurance system. Buyers should prioritize sourcing high-quality raw materials from reputable suppliers who can provide consistent material specifications. Investing in advanced auxiliary equipment, such as centralized drying systems and gravimetric feeders, can help ensure that materials are uniformly dried and blended before entering the extruder. Additionally, integrating real-time monitoring systems that track moisture levels and material flow can provide valuable insights, enabling operators to make timely adjustments and maintain product quality.
Scenario 2: Downtime Due to Equipment Failures
The Problem: Unexpected downtime caused by equipment failures can cripple production lines and lead to significant financial losses. Buyers may experience challenges with the reliability of their extrusion lines, especially if they are using outdated machinery or lack proper maintenance protocols. This issue is compounded by the fact that sourcing replacement parts or specialized technicians can be difficult, particularly in regions with limited access to technical support.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, buyers should consider investing in modern, reliable extrusion technology with a proven track record for durability and performance. Conducting a thorough assessment of current equipment and identifying any aging components that may require upgrades can prevent failures before they occur. Establishing a comprehensive maintenance schedule that includes routine inspections, cleaning, and timely replacement of wear parts is essential. Additionally, partnering with equipment suppliers who offer extensive after-sales support and training can ensure that in-house staff are well-equipped to handle minor repairs and maintenance, reducing reliance on external service providers.
Scenario 3: Inefficient Production Processes Leading to High Costs
The Problem: B2B buyers frequently encounter inefficiencies in their production processes, which can lead to increased operational costs and reduced competitiveness. Factors such as slow production speeds, excessive waste generation, and poor material utilization can significantly inflate production costs. In regions where margins are already tight, such inefficiencies can threaten the viability of operations.
The Solution: To enhance production efficiency, buyers should conduct a thorough process audit to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement. Implementing a lean manufacturing approach can help streamline operations, reduce waste, and optimize workflow. Investing in advanced extrusion technologies, such as high-efficiency extruders and smart control systems, can significantly increase output while minimizing energy consumption. Furthermore, integrating in-line quality control measures can help detect issues early in the process, allowing for immediate corrections and reducing scrap rates. By focusing on these strategies, companies can not only improve their bottom line but also position themselves as leaders in their respective markets.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for extrusion lines
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Extrusion Lines?
When selecting materials for extrusion lines, it’s essential to consider their properties, manufacturing complexities, and suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in extrusion processes: Polyethylene (PE), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), Polypropylene (PP), and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS).
How Does Polyethylene (PE) Perform in Extrusion Applications?
Polyethylene is one of the most widely used thermoplastics in extrusion due to its excellent flexibility and chemical resistance. It has a temperature rating of up to 80°C (176°F) and exhibits good impact resistance.
Pros: PE is lightweight, cost-effective, and has a low density, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including films, bags, and containers. Its resistance to moisture and chemicals makes it ideal for packaging and agricultural films.
Cons: However, its lower temperature resistance limits its use in high-heat applications. Additionally, while it is durable, it may not perform well under extreme mechanical stress.
International Considerations: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding food safety and environmental impact, as PE is often used in food packaging.
What Are the Advantages of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) in Extrusion?
PVC is another popular choice for extrusion, particularly in construction applications. It has a temperature rating of approximately 60-80°C (140-176°F) and is known for its excellent durability and corrosion resistance.
Pros: PVC is highly versatile, making it suitable for pipes, profiles, and sheets. Its rigidity and strength make it ideal for structural applications, while its low cost adds to its appeal.

Illustrative image related to extrusion lines
Cons: The main drawback is its environmental impact, as PVC can release harmful chemicals during production and disposal. Additionally, it may require additional additives for specific applications, increasing manufacturing complexity.
International Considerations: Compliance with standards like ASTM and DIN is crucial, particularly in Europe, where regulations on construction materials are stringent. Buyers should also be aware of the growing preference for eco-friendly alternatives.
How Does Polypropylene (PP) Compare for Extrusion Processes?
Polypropylene offers a balance of strength and flexibility, with a temperature rating of around 100°C (212°F). It is known for its excellent fatigue resistance and low moisture absorption.

Illustrative image related to extrusion lines
Pros: PP is lightweight, chemical-resistant, and has a high melting point, making it suitable for automotive parts, packaging, and textiles. Its recyclability adds to its appeal in sustainable applications.
Cons: However, PP can be more expensive than PE and may require specific processing conditions to achieve optimal results. Its impact resistance can also be lower compared to other materials.
International Considerations: Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should consider the recyclability of PP, as there is a growing emphasis on sustainability and compliance with recycling standards.
What Makes Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) a Preferred Material?
ABS is a strong thermoplastic known for its impact resistance and toughness, with a temperature rating of around 80-100°C (176-212°F). It is commonly used in consumer goods and automotive applications.
Pros: ABS is easy to process and offers excellent aesthetic qualities, making it suitable for products requiring a high-quality finish. Its strength and rigidity make it ideal for structural applications.
Cons: The main limitation of ABS is its susceptibility to UV degradation, which can affect outdoor applications. Additionally, it can be more expensive than other materials like PE and PP.
International Considerations: Buyers should consider compliance with standards such as JIS in Japan and ASTM in the U.S. to ensure product quality and safety.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Extrusion Lines
| Material | Typical Use Case for extrusion lines | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | Packaging films, containers | Excellent flexibility and chemical resistance | Limited temperature resistance | Low |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Pipes, profiles, construction materials | High durability and corrosion resistance | Environmental concerns | Medium |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Automotive parts, packaging | High melting point and recyclability | Higher cost and specific processing needs | Medium |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Consumer goods, automotive applications | Strong impact resistance and aesthetic quality | Susceptible to UV degradation | High |
This strategic material selection guide aims to provide B2B buyers with actionable insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of commonly used materials in extrusion lines, ensuring informed decision-making for optimal application outcomes.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for extrusion lines
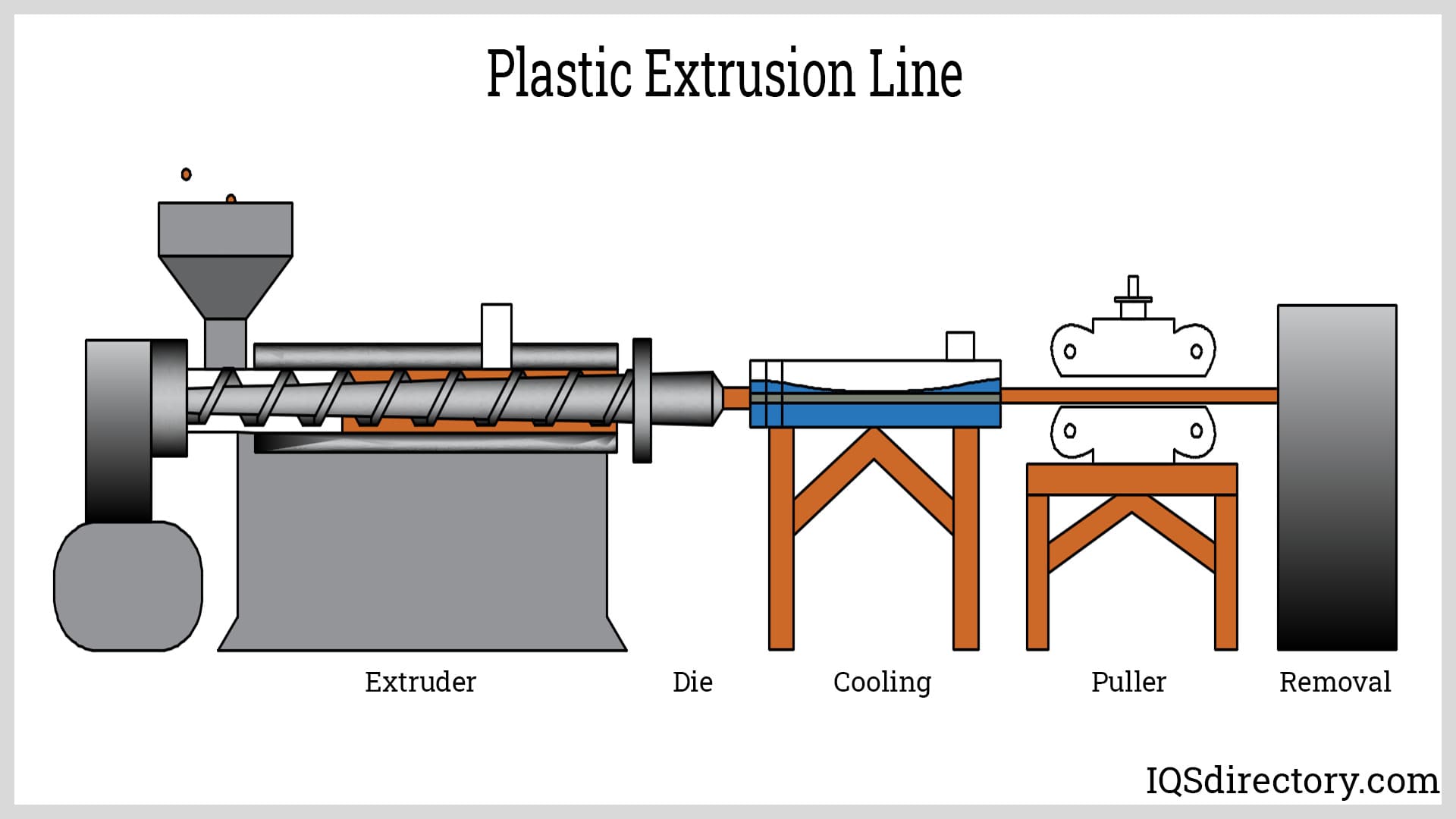
What Are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for Extrusion Lines?
The manufacturing process for extrusion lines consists of several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a vital role in ensuring the production of high-quality extruded products.

Illustrative image related to extrusion lines
How Is Material Prepared for Extrusion?
Material preparation is the first step in the extrusion process. It involves sourcing and handling raw materials, typically in the form of plastic pellets or powders. For optimal results, the materials must be properly dried and blended. This is particularly crucial for hygroscopic resins that can absorb moisture, which may lead to defects in the final product.
In practice, centralized drying systems or machine-side dryers are employed to ensure consistent moisture removal. Additionally, blending equipment is utilized to combine various materials, including additives and recycled materials, to achieve the desired properties in the final extrudate. The use of gravimetric feeders ensures precise measurements, enabling uniformity in production.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
The forming stage is where the actual extrusion occurs. The blended raw material is fed into an extruder, which melts the material and forces it through a die to create the desired shape. This process can vary significantly based on the type of extruder used—single-screw extruders are common for pellet processing, while twin-screw extruders are typically used for powders.
Temperature control is crucial during this stage to maintain the integrity of the material. The extruder must be equipped with advanced controls to monitor and adjust temperature and pressure, ensuring a homogeneous melt. After exiting the die, the extrudate may undergo cooling or shaping, depending on the final product requirements.
What Are the Key Assembly and Finishing Techniques in Extrusion?
Assembly and finishing processes follow the forming stage and are essential for achieving the final product specifications. During assembly, the extrudate is often cut, coiled, or otherwise processed into its final form. Downstream equipment, such as pullers and cutters, plays a crucial role in this stage, ensuring that the extrudate is shaped and sized correctly.
Finishing techniques can include surface treatments, coatings, or additional machining processes that enhance the product’s performance or aesthetic appeal. Quality assurance at this stage is critical, as any defects introduced during assembly or finishing can compromise product integrity.
What International Standards and Quality Control Measures Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Quality assurance in the extrusion manufacturing process is governed by various international standards, such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific certifications may apply, such as CE marking for products sold in Europe or API standards for oil and gas applications.
B2B buyers should pay close attention to the quality control (QC) checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the extrusion process allows for immediate corrections if deviations occur.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Finished products undergo rigorous testing to verify they meet the required specifications before shipment.
What Common Testing Methods Are Utilized in Extrusion Quality Control?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the quality of extruded products. These can include:
- Dimensional Inspection: Using calipers and gauges to verify that the dimensions of the extruded parts meet specified tolerances.
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing properties such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and flexibility through standardized tests.
- Visual Inspection: Checking for surface defects, color consistency, and overall appearance to meet aesthetic standards.
For B2B buyers, understanding these testing methods is crucial for verifying product quality and ensuring that suppliers adhere to industry standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
To ensure that suppliers maintain high standards of quality control, B2B buyers should consider several verification strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers’ facilities can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality assurance reports can help buyers understand the supplier’s QC practices and product performance history.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures and compliance with international standards.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
For international buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is essential. Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements and standards that must be met for products to be accepted in local markets.
Buyers should ensure that suppliers are not only compliant with international standards but also familiar with local regulations. This can prevent potential issues related to product acceptance and market entry, ensuring a smoother procurement process.

Illustrative image related to extrusion lines
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for extrusion lines is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing stages, alongside robust quality control measures, buyers can better assess potential suppliers and ensure the delivery of high-quality extruded products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘extrusion lines’
Introduction
Sourcing extrusion lines is a critical investment for businesses involved in plastic processing. This guide provides a practical checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the complexities of procurement, ensuring they select the right equipment that meets their operational needs and quality standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, outline the specific requirements for your extrusion line. Consider factors such as the type of material you will process, desired output capacity, and the product dimensions. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers and ensure they can meet your unique production needs.
- Material Types: Identify if you need to process rigid or flexible plastics, as this may influence the type of extruder required.
- Output Capacity: Determine the volume of production expected, as this will impact the size and configuration of the extrusion line.
Step 2: Research Supplier Experience and Reputation
Investigate the suppliers’ background in the extrusion industry. A vendor with a strong track record is more likely to provide reliable equipment and support. Look for testimonials, case studies, and reviews from existing customers.
- Industry Expertise: Ensure the supplier specializes in the type of extrusion line you need.
- Regional Presence: Consider suppliers with experience in your geographical area, as they may better understand local regulations and market conditions.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website; engage with previous clients to gauge their satisfaction levels.
- Site Visits: If possible, visit the supplier’s facility to assess their production capabilities and quality control processes.
- Customer Support: Inquire about post-sale support, including training, maintenance, and spare parts availability.
Step 4: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that the extrusion lines comply with international standards and regulations pertinent to your industry. This step is vital for maintaining product quality and safety.
- ISO Certifications: Look for ISO 9001 or other relevant certifications that demonstrate adherence to quality management practices.
- Local Regulations: Check compliance with local regulations, especially if you are operating in regions with stringent environmental or safety laws.
Step 5: Assess Total Cost of Ownership
Consider not just the initial purchase price but also the total cost of ownership (TCO) over the equipment’s lifespan. This includes operational costs, maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime.
- Energy Efficiency: Evaluate the energy consumption of the extrusion line, as high efficiency can lead to significant cost savings.
- Maintenance Requirements: Understand the maintenance schedule and costs associated with keeping the equipment in optimal condition.
Step 6: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed proposals that outline specifications, pricing, and delivery timelines. This will help you make a more informed comparison.
- Customization Options: Discuss any customizations that may be necessary to meet your production needs.
- Warranty and Service Agreements: Review the warranty terms and service agreements to ensure you have adequate support after purchase.
Step 7: Finalize Contract Terms
Before signing any agreements, carefully review all contract terms. Ensure that they align with your expectations and provide adequate protection for your investment.
- Payment Terms: Discuss flexible payment options that may be available.
- Liability Clauses: Pay attention to liability clauses to understand the supplier’s responsibilities in case of equipment failure or delays.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the sourcing process for extrusion lines and make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for extrusion lines Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Extrusion Lines?
When sourcing extrusion lines, buyers must consider several critical cost components that influence the overall pricing structure. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the supplier’s margin.
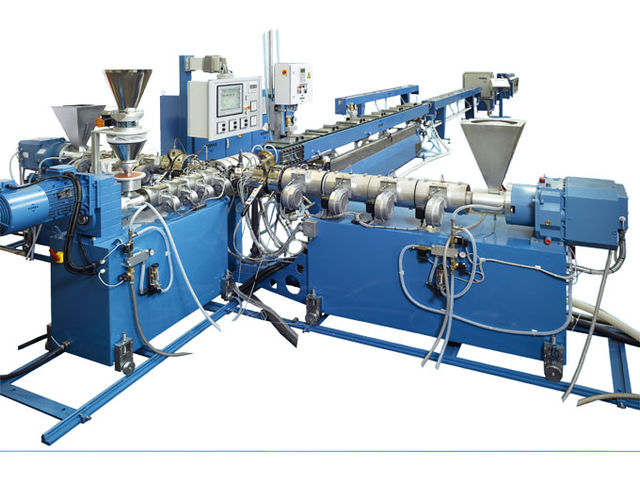
Illustrative image related to extrusion lines
-
Materials: The type and quality of raw materials, such as resin and additives, significantly affect costs. Bulk purchasing can yield savings, especially if the materials are sourced locally to minimize transportation expenses.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the region and complexity of the extrusion line. Skilled labor is essential for setup, maintenance, and operation, influencing total costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, facility costs, and other indirect expenses. Understanding the supplier’s operational efficiency can provide insights into how overhead impacts pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom dies and molds are often necessary for specific products, which can add significant costs. Buyers should evaluate the tooling requirements against their production needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Quality Control: Investing in robust QC processes ensures product consistency and reduces waste. However, it can also elevate costs, so buyers should assess the balance between quality and expense.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can vary widely based on distance and mode of transport. Understanding Incoterms and selecting favorable terms can help mitigate unexpected logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Supplier margins vary based on market conditions, competition, and the supplier’s reputation. Buyers should be aware of the standard margins in the industry to negotiate effectively.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Extrusion Line Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of extrusion lines, making it essential for buyers to understand their implications.
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can drive costs down. Larger orders typically yield better pricing, so buyers should consider their production forecasts and potential for scaling.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized equipment tailored to specific needs may incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential for increased pricing.
-
Quality and Certifications: Equipment meeting international standards often commands higher prices. Buyers in regions like Europe may prioritize certified machinery, impacting their budget.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s experience, reputation, and location can affect pricing. Established suppliers may offer better service and reliability, justifying higher costs.
-
Incoterms: The terms of trade can significantly impact total landed costs. Buyers should understand how Incoterms affect responsibilities and costs related to shipping and handling.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Extrusion Line Prices?
To ensure cost-efficiency and value in sourcing extrusion lines, international B2B buyers should adopt strategic negotiation practices.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on initial purchase prices, consider the TCO, which includes operational, maintenance, and end-of-life costs. This holistic view can reveal the true value of the equipment.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If possible, consolidate orders or collaborate with other companies to achieve higher volumes, thereby unlocking better pricing.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Solicit quotes from various suppliers to compare costs and services. This competitive approach can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances in Different Regions: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe may face unique challenges and opportunities. For instance, currency fluctuations and local tariffs can significantly impact pricing.
-
Build Long-Term Relationships: Establishing a rapport with suppliers can lead to better terms, responsiveness, and support, ultimately reducing costs over time.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
It is important to note that pricing for extrusion lines can vary widely based on numerous factors, including market conditions, supplier negotiations, and geographic location. The information provided serves as a general guideline and should not be considered definitive. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough research and engage in direct discussions with suppliers to ascertain accurate pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing extrusion lines With Other Solutions
When considering production methods for plastic and other materials, B2B buyers often seek alternatives to extrusion lines. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for selecting the most effective solution tailored to specific production needs. This analysis compares extrusion lines against two viable alternatives: injection molding and blow molding. Each method has distinct advantages and potential drawbacks depending on the application.
| Comparison Aspect | Extrusion Lines | Injection Molding | Blow Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High volume, continuous production; ideal for long products | Excellent for complex shapes; high precision | Suitable for hollow products; efficient for large volumes |
| Cost | Lower initial setup cost; high operational efficiency | Higher initial investment; cost-effective for high volume | Moderate initial costs; economical for large batches |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires significant space and setup time | Fast setup for small runs; complex for large systems | Requires specialized equipment; moderate complexity |
| Maintenance | Generally low; requires regular checks on auxiliary equipment | Moderate; requires regular calibration and maintenance | Low; mainly involves cleaning and occasional part replacement |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for films, pipes, and profiles | Best for detailed parts like automotive components | Perfect for bottles and containers |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mold. Its primary advantage lies in its ability to create complex geometries with high precision and excellent surface finishes. This method is particularly beneficial for producing small, intricate components, making it ideal for industries like automotive and consumer goods. However, the initial setup costs for molds can be significantly higher than extrusion lines, making it less economical for small production runs.
How Does Blow Molding Compare to Extrusion Lines?
Blow molding is another alternative that excels in producing hollow plastic parts, such as bottles and containers. This process involves inflating a heated plastic tube within a mold, resulting in lightweight and cost-effective products. Blow molding is advantageous for large-volume production, reducing the cost per unit significantly. However, it is less versatile than extrusion lines in terms of product variety and is limited primarily to hollow shapes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Production Needs
When deciding between extrusion lines and alternative methods like injection or blow molding, B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific production requirements. Considerations such as the type of product, volume needs, initial investment capabilities, and operational efficiency are crucial. For businesses focused on producing continuous, uniform products, extrusion lines may be the best fit. In contrast, if precision and complexity are paramount, injection molding could be the preferred choice. Blow molding, while limited in shape diversity, offers unparalleled efficiency for hollow products. Ultimately, aligning production technology with business goals will drive optimal outcomes and profitability.
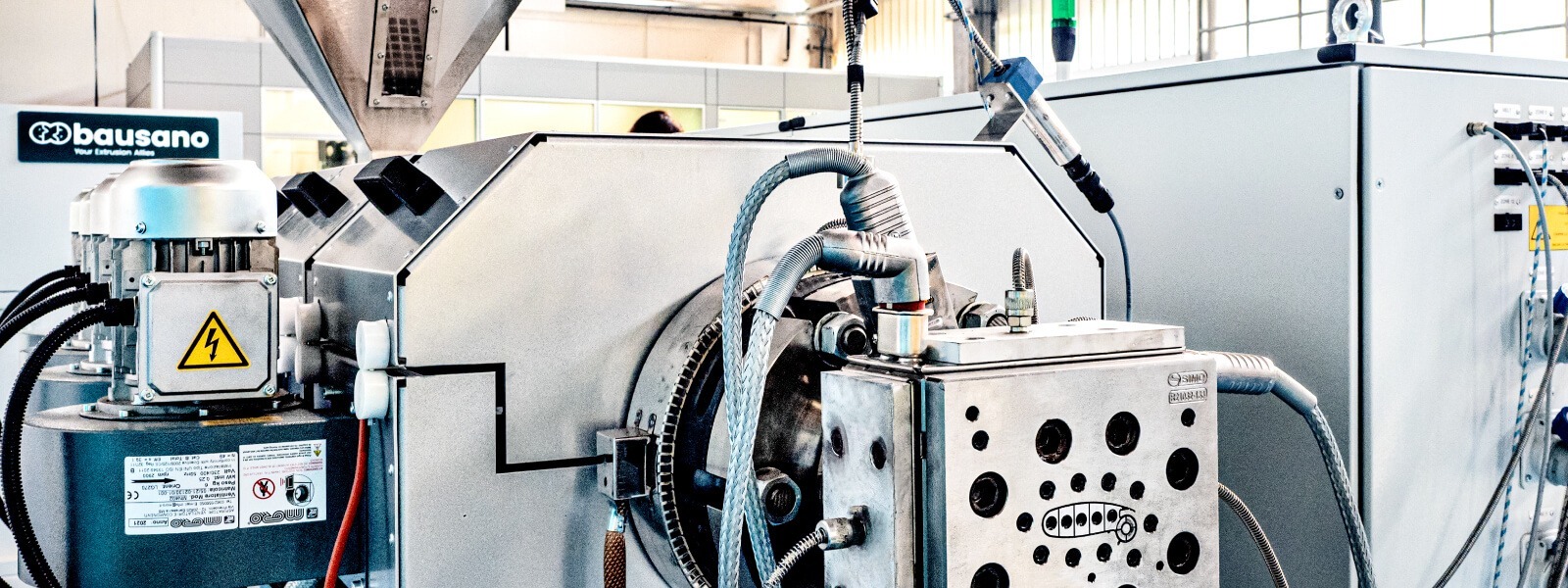
Illustrative image related to extrusion lines
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for extrusion lines
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Extrusion Lines?
Understanding the technical properties of extrusion lines is crucial for B2B buyers looking to invest in or upgrade their manufacturing capabilities. Here are several critical specifications that influence performance, quality, and cost-efficiency.
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific type of resin or polymer used in the extrusion process. Common grades include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Selecting the right material grade is essential as it affects product durability, chemical resistance, and suitability for specific applications. For example, medical-grade materials are necessary for healthcare applications, ensuring compliance with strict safety standards. -
Tolerance
Tolerance defines the permissible variation in dimensions of the extruded product. It is a critical parameter for ensuring that the final product meets the required specifications and fits with other components in assembly. Tighter tolerances are often necessary for high-precision applications, such as in automotive or aerospace industries. Understanding tolerance levels helps buyers assess the manufacturing capabilities of suppliers and ensure that the end product meets their quality standards. -
Output Capacity
Output capacity indicates the volume of material that an extrusion line can process within a specified timeframe, typically measured in pounds per hour (lbs/hr). This property is vital for businesses looking to meet production demands and optimize operational efficiency. A higher output capacity can reduce production costs per unit and improve profitability, making it an essential factor for scaling operations. -
Heat Transfer Efficiency
Heat transfer efficiency pertains to how effectively the extruder maintains the required temperature during processing. This property is crucial for achieving uniform melting and preventing material degradation. Efficient heat transfer contributes to product consistency and quality, thereby reducing scrap rates and ensuring that the final product meets performance standards. -
Screw Design
The design of the screw in the extruder affects the mixing, melting, and conveying of materials. Variations in screw geometry can optimize processing for different materials and applications. A well-designed screw enhances material flow and improves the quality of the extrudate, which is essential for maintaining high production standards.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Extrusion Lines?
Navigating the terminology in the extrusion industry is key for effective communication and negotiation. Here are several common trade terms that B2B buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable sources for components and machinery, ensuring that they are working with reputable suppliers who adhere to quality standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for buyers as it affects inventory management and initial investment. Understanding MOQs can help businesses plan their purchases effectively, especially when entering new markets or launching new products. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to invite suppliers to provide pricing and terms for specific products or services. This process is critical for comparing offers and negotiating better pricing, ensuring that buyers obtain the best possible deal for their extrusion line investments. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping, insurance, and liability aspects, facilitating smoother cross-border transactions. -
Extrudate
Extrudate is the final product that emerges from the extruder after processing. This term is important for buyers to understand as it relates to product quality, consistency, and specifications. Knowing the characteristics of the extrudate can guide quality control measures and application suitability.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product quality in the extrusion industry.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the extrusion lines Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing Extrusion Lines?
The global extrusion lines market is undergoing significant transformation, driven by various factors including technological advancements, increased demand for sustainable materials, and the rising need for efficient production processes. Emerging technologies such as Industry 4.0 and IoT are streamlining operations, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and enhanced efficiency. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions.
In regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia, the focus on local manufacturing capabilities is growing, prompted by government initiatives aimed at boosting domestic production and reducing reliance on imports. This trend is accompanied by an increased emphasis on automation, with many manufacturers investing in advanced extrusion lines that incorporate robotics for material handling and product finishing. Additionally, the demand for high-quality, customized products is leading to the adoption of flexible extrusion systems capable of processing a diverse range of materials.
Another notable trend is the integration of recycled materials into the extrusion process, as companies strive to meet both economic and environmental objectives. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in emerging markets, where cost efficiency and sustainability are increasingly prioritized. Overall, understanding these market dynamics allows B2B buyers to align their sourcing strategies with industry trends and demands.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Extrusion Lines Sector?
Sustainability has become a key consideration in the extrusion lines sector, influencing purchasing decisions and supply chain strategies. The environmental impact of plastic production is under scrutiny, prompting manufacturers to seek eco-friendly alternatives. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who prioritize ethical sourcing and offer ‘green’ certifications for their materials. This includes using recycled resins, biodegradable additives, and sustainable manufacturing practices.
Ethical supply chains not only enhance a company’s brand reputation but also contribute to regulatory compliance in various regions, particularly in Europe where stringent environmental laws are in place. Buyers from Africa and South America are similarly recognizing the importance of sustainability, as it becomes integral to gaining market access and consumer trust.

Illustrative image related to extrusion lines
In response to these trends, suppliers are investing in technologies that minimize waste and energy consumption during production. The use of auxiliary equipment that enhances material recovery and recycling is becoming standard practice. For buyers, partnering with manufacturers committed to sustainable practices not only fulfills corporate social responsibility goals but also positions them favorably in a competitive market increasingly defined by environmental consciousness.
What Is the Historical Context of Extrusion Lines and Their Evolution?
The extrusion process has its roots in the mid-19th century, primarily used for shaping metals and later adapted for plastics in the 1930s. The technology has evolved significantly since then, with advancements in machinery and materials leading to more efficient and versatile extrusion lines. Initially, the focus was on producing simple shapes and profiles, but today’s extrusion lines are capable of handling complex designs and a variety of materials, including composites and bioplastics.
Over the decades, the introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) and automation has revolutionized the extrusion landscape, allowing for greater precision and customization. The shift toward sustainability has also marked a significant turning point, as manufacturers begin to incorporate recycled materials and develop eco-friendly processes. As the industry continues to innovate, understanding its historical context helps B2B buyers appreciate the technological advancements that shape today’s extrusion lines and anticipate future trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of extrusion lines
-
1. How do I solve issues with extrusion line downtime?
To mitigate extrusion line downtime, first analyze the root causes, which may include mechanical failures, material inconsistencies, or inadequate auxiliary equipment. Implement a predictive maintenance schedule to regularly check and service machinery, focusing on wear components like screws and barrels. Additionally, ensure you have a robust supply chain for spare parts and consider investing in training for your operators to quickly address minor issues. Analyzing production data can also help identify patterns that lead to downtime, allowing for proactive measures. -
2. What is the best type of extrusion line for producing plastic profiles?
For producing plastic profiles, a twin-screw extruder is often recommended. This type of extruder offers superior mixing capabilities, which is essential for achieving consistent quality when blending various materials, including recycled content. Twin-screw extruders can handle diverse formulations and provide better control over the melting process. However, the best choice will depend on specific product requirements, including desired output capacity, material type, and end-use application. Consulting with equipment manufacturers can help you identify the most suitable configuration. -
3. What factors should I consider when sourcing extrusion lines internationally?
When sourcing extrusion lines internationally, consider the manufacturer’s reputation, experience, and certifications relevant to your industry standards. Evaluate their ability to provide localized support, spare parts availability, and customer service responsiveness. Additionally, assess the quality of the equipment through reviews, case studies, or referrals from other buyers in your region. Pay attention to logistics, including shipping costs and timelines, as well as any import regulations that may affect your procurement process. -
4. How can I customize an extrusion line to meet my production needs?
Customization of an extrusion line typically involves discussing your specific production requirements with the manufacturer. Key areas for customization include the type of extruder, die design, and auxiliary equipment tailored to your materials and product dimensions. You may also want to consider automation options for improved efficiency and quality control. Collaborating with a supplier experienced in custom solutions can ensure that your extrusion line is designed to enhance productivity and meet your unique specifications. -
5. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for extrusion lines?
Minimum order quantities for extrusion lines can vary widely depending on the manufacturer and the complexity of the equipment. Some suppliers may have a standard MOQ for complete lines, while others may allow for smaller orders, especially if you are purchasing auxiliary equipment or components. It is advisable to negotiate terms with your supplier, particularly if you are a new buyer or planning to establish a long-term relationship. Be sure to clarify whether the MOQ affects pricing, lead times, or customization options. -
6. What payment terms should I expect when purchasing extrusion lines?
Payment terms for extrusion lines can vary by supplier and region. Common arrangements include a deposit upon order confirmation (typically 30-50%), with the balance due before shipping or upon delivery. It is essential to discuss and negotiate these terms upfront to align with your cash flow. Some suppliers may offer financing options or installment plans, especially for larger orders. Always ensure that payment terms are documented in the purchase agreement to avoid any misunderstandings. -
7. How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my extrusion line purchases?
To ensure quality assurance for your extrusion line purchases, request detailed specifications and quality control procedures from the manufacturer. Look for suppliers who can provide certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to international quality management standards. Additionally, consider conducting factory visits or audits to observe production processes firsthand. It may also be beneficial to establish a quality assurance program that includes regular inspections and testing of equipment upon delivery. -
8. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing extrusion lines?
When importing extrusion lines, logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Understand the regulations and tariffs applicable to your specific equipment in your region to avoid unexpected costs. Partnering with a reliable freight forwarder can facilitate smooth transportation and compliance with international shipping standards. Additionally, ensure that you have a plan for installation and commissioning upon arrival, which may require specialized technical support from the manufacturer.
Top 7 Extrusion Lines Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Conair – Auxiliary Equipment for Extrusion Processing
Domain: conairgroup.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Conair offers a range of auxiliary equipment for extrusion processing, including: 1. **Blending**: Gravimetric batch blenders and blending accessories. 2. **Feeding**: Self-contained vacuum loaders, compressed air material loaders, and vacuum pumps/dust collectors. 3. **Drying**: Desiccant dryers and drying monitors. 4. **Extrusion Equipment**: Vacuum sizing equipment, cooling tanks, and pullers. …
2. Arlington Machinery – Key Components of Plastic Sheet Extrusion Lines
Domain: arlingtonmachinery.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Key Components of Plastic Sheet Extrusion Lines: 1. Extruder: Advanced screw design, precision temperature control, customizable configurations. 2. Die Head: Defines sheet width and thickness, ensures uniform material flow. 3. Calendering and Cooling Section: Automated thickness control, integrated cooling system. 4. Pull Rollers: Ensure steady tension and constant drawing of the sheet. 5. Cutting…
3. COLLIN – Pipe Extrusion Lines
Domain: collin-solutions.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: COLLIN pipe extrusion lines are designed for the production of mono or multi-layer pipes with diameters ranging from 1 to 50 mm, suitable for all thermoplastic materials. Key components include a mono or multi-layer pipe die capable of producing 1 to 7 layers, vacuum and cooling tanks, take-offs, winder, and cutting devices.
4. Exelliq – DIGI.LINE & RED.LINE
Domain: exelliq.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Exelliq offers a range of extrusion lines and systems tailored for various needs in the premium, mid, and economy segments. Key products include:
1. DIGI.LINE: Automated extrusion process with real-time optimization for maximum savings.
2. RED.LINE: Focuses on superior profile quality, productivity, process reliability, and energy savings.
– RED.LINE wide: Designed for large profiles, panels…
5. Davis-Standard – Blow Molding Extrusion Machinery
Domain: davis-standard.com
Introduction: Davis-Standard offers a range of extrusion systems including: 1. Blow Molding Extrusion Machinery – Custom-designed for automotive and consumer products, featuring closed-loop hydraulic and electronic controls, state-of-the-art screw design, and spiral head technology for faster color changes and efficient wall distribution. 2. Elastomer Extrusion Machinery – Supports global markets for tires, aut…
6. Boston Matthews – Turn-Key Extrusion Lines for Engineering Polymers
Domain: bostonmatthews.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Complete Turn-Key Extrusion Lines for Rod & Plate production of engineering polymers such as Polycarbonate, Polyurethane, Nylon, PEEK, and Acetal. Capable of extruding Acetal, PA, POM, PB, PE & PEEK Rod & Plate. Features include Void Free Extrusion Technology for high-quality surface finish, energy-efficient production, and total line control via a SMART control system with color touch-screen. Int…
7. Bomac Industries – Extrusion Lines for Plastics and WPC
Domain: bomac-industries.com
Introduction: Extrusion lines are used for continuous production of plastic or wood plastic composite (WPC) pellets, pipes, profiles, or sheets. They can process various types of plastics including PE, PP, PS, PET, ABS, WPC, and PVC. The extrusion process involves feeding plastic flakes or powder into a hopper, where a rotating screw forces the material through a heated barrel. The heat is generated by an elect…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for extrusion lines
Why is Strategic Sourcing Essential for Extrusion Lines?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of extrusion lines, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical component for maximizing operational efficiency and product quality. By investing in advanced auxiliary equipment and optimizing material handling processes, businesses can significantly reduce waste and enhance throughput. This approach not only mitigates risks associated with material contamination but also ensures that production lines operate smoothly, maintaining high-quality standards across diverse applications.
What Should International Buyers Consider for Future Investments?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market dynamics and technological advancements is crucial. As demand for sustainable and innovative plastic products grows, sourcing strategies must adapt to leverage both local and global supply chains. Engaging with reputable suppliers who offer cutting-edge extrusion technology and robust support services will be vital in maintaining a competitive edge.

Illustrative image related to extrusion lines
How Can You Prepare for the Future of Extrusion Processing?
Looking ahead, the future of extrusion processing promises exciting developments driven by automation and sustainability. By prioritizing strategic sourcing now, businesses can position themselves to capitalize on emerging trends and technologies. Embrace this opportunity to elevate your production capabilities and ensure long-term success in the global marketplace. Take action today by evaluating your sourcing strategies and exploring partnerships that align with your growth objectives.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.