A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Definition Of Electric Switch: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for definition of electric switch
In an increasingly interconnected global market, sourcing the right electric switch can present significant challenges for B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. An electric switch is more than just a component; it is a crucial element that dictates the efficiency and safety of electrical systems. Understanding the nuances of different switch types, such as Single Pole Single Throw (SPST) or Double Pole Double Throw (DPDT), is essential for making informed purchasing decisions that align with specific operational needs.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of electric switches, their applications across diverse industries, and key factors to consider when vetting suppliers. From evaluating environmental resistance to understanding circuit requirements, this resource equips international buyers with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of electric switch procurement. Additionally, we explore cost considerations and best practices for supplier engagement, ensuring that you can secure reliable products that meet both quality and budgetary expectations.
By leveraging the insights provided in this guide, B2B buyers can confidently approach the sourcing process, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and safety in their electrical systems. Whether you are in Brazil, Nigeria, or anywhere in between, this guide serves as your roadmap to making strategic, informed decisions in the electric switch market.
Understanding definition of electric switch Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPST-NO | Single circuit control, normally open contacts | Simple ON/OFF applications | Pros: Simple design, cost-effective. Cons: Limited functionality. |
| SPST-NC | Single circuit control, normally closed contacts | Safety applications, alarms | Pros: Ensures devices remain ON until switched off. Cons: Can lead to accidental activation. |
| SPDT | Changeover contacts, can switch between two circuits | Complex machinery, automation | Pros: Versatile, can control multiple circuits. Cons: More complex, potentially higher cost. |
| Double Pole Switch | Controls two circuits simultaneously, either NO or NC contacts | Industrial applications, lighting | Pros: Efficient for controlling multiple loads. Cons: Requires more space and installation effort. |
| Momentary vs. Alternate | Momentary switches activate only when pressed; alternate latches state | Control systems, machinery | Pros: Flexible operation modes. Cons: May not be intuitive for all users. |
What are the Characteristics of SPST-NO Switches?
SPST-NO (Single Pole Single Throw Normally Open) switches are designed for straightforward ON/OFF control of a single circuit. They remain open until activated, making them ideal for simple applications such as lighting or basic machinery. For B2B buyers, the main considerations include the switch’s voltage and current ratings, which must align with the specific application needs. While they are cost-effective and easy to install, their limited functionality means they may not be suitable for more complex systems.
How Do SPST-NC Switches Function in Safety Applications?
SPST-NC (Single Pole Single Throw Normally Closed) switches maintain a closed circuit until activated. This design is particularly useful in safety applications, such as alarm systems, where devices must remain operational until intentionally deactivated. B2B buyers should evaluate the switch’s durability and environmental resistance, especially for industrial settings. While they offer enhanced safety features, the risk of accidental activation can be a downside, necessitating careful placement and user training.
What Makes SPDT Switches Ideal for Complex Machinery?
SPDT (Single Pole Double Throw) switches allow for the control of two different circuits from a single switch, making them ideal for complex machinery and automation systems. They offer versatility by enabling a seamless transition between circuits. When purchasing, B2B buyers should consider the switch’s current and voltage ratings, as well as its mechanical life. Despite their advantages, SPDT switches can be more expensive and require careful installation due to their complexity.
Why Choose a Double Pole Switch for Industrial Applications?
Double pole switches can control two circuits simultaneously, making them ideal for industrial applications where efficiency is crucial. They can either feature normally open (NO) or normally closed (NC) contacts, providing flexibility in design. For B2B buyers, the key considerations include the switch’s ratings and compliance with industry standards. While they are effective for managing multiple loads, they require more space and can complicate installation, which may increase overall project costs.
What are the Differences Between Momentary and Alternate Switches?
Momentary switches are active only while pressed, whereas alternate switches maintain their state after being pressed. This distinction is critical for applications in control systems and machinery. B2B buyers should assess the operational requirements and user interface implications when selecting between these types. Momentary switches offer simplicity, while alternate switches provide greater control, but they may not be intuitive for all users. Understanding the operational context will guide the right choice for specific applications.
Key Industrial Applications of definition of electric switch
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of definition of electric switch | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Machine Control Systems | Enhances operational efficiency by automating processes and reducing manual errors. | Durability, environmental resistance, and compatibility with existing systems. |
| Renewable Energy | Solar Power Systems | Facilitates efficient energy management and distribution, optimizing energy use. | Compliance with international standards and ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions. |
| Transportation | Electric Vehicle Charging Stations | Improves user experience and safety by ensuring reliable power supply and circuit protection. | Load capacity, safety certifications, and ease of integration with various charging technologies. |
| Commercial Facilities | Lighting Control Systems | Reduces energy consumption and costs through automated lighting management. | Energy efficiency ratings, scalability, and adaptability to different lighting technologies. |
| Oil and Gas | Safety Shutdown Systems | Protects equipment and personnel by providing emergency shut-off capabilities. | Reliability under extreme conditions, quick response times, and compliance with industry safety standards. |
How is the definition of electric switch utilized in manufacturing applications?
In manufacturing, electric switches are integral to machine control systems, enabling operators to automate processes effectively. By facilitating the ON/OFF operation of machines, switches enhance operational efficiency and minimize manual errors. Buyers in this sector must consider switches that offer durability and environmental resistance, as manufacturing environments often involve exposure to dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures. Additionally, compatibility with existing systems is crucial to ensure seamless integration and functionality.
What role do electric switches play in renewable energy applications?
In renewable energy sectors, particularly solar power, electric switches are vital for managing energy distribution. They enable efficient control over energy flow, ensuring that systems operate optimally and safely. This application is essential for maximizing energy use and minimizing waste, which is particularly important in regions with high energy costs or limited resources, such as parts of Africa and South America. Buyers should prioritize switches that comply with international standards and can withstand harsh environmental conditions, ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
How do electric switches enhance electric vehicle charging stations?
Electric switches are critical in electric vehicle (EV) charging stations, where they manage the power supply to the charging units. This application not only improves user experience by providing reliable charging but also enhances safety by incorporating circuit protection features. For international buyers, especially in emerging markets, sourcing switches that have high load capacity and safety certifications is essential. Additionally, ease of integration with various charging technologies can influence the choice of switches, ensuring compatibility with a diverse range of electric vehicles.
How do electric switches contribute to energy efficiency in commercial facilities?
In commercial facilities, electric switches are utilized in lighting control systems to automate and optimize energy usage. By allowing for precise control over lighting, these switches help reduce energy consumption and operational costs. Buyers should look for switches that have high energy efficiency ratings and are scalable to accommodate future expansions or changes in lighting technology. The adaptability of the switches to different systems is also a key consideration, ensuring that businesses can maintain energy efficiency as their needs evolve.
What safety advantages do electric switches provide in the oil and gas industry?
In the oil and gas sector, electric switches are crucial for safety shutdown systems, which provide emergency shut-off capabilities to protect both equipment and personnel. These switches help mitigate risks associated with hazardous environments, ensuring quick response times in emergencies. Buyers should focus on sourcing switches that demonstrate reliability under extreme conditions and comply with industry safety standards. This focus on safety not only protects assets but also enhances compliance with regulatory requirements, crucial for operating in the oil and gas industry.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘definition of electric switch’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Type of Electric Switch for Specific Applications
The Problem: One common challenge faced by B2B buyers, especially those in sectors like manufacturing or construction, is the overwhelming variety of electric switches available. Buyers may struggle to identify which type—be it SPST, SPDT, or a specialized switch—best suits their specific applications. This confusion can lead to purchasing the wrong switch, resulting in operational inefficiencies or even safety hazards. For instance, a buyer might choose a switch that cannot handle the load requirements of an industrial machine, risking equipment failure and costly downtime.
The Solution: To overcome this problem, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their operational needs before making a purchase. This includes understanding the electrical load characteristics (inductive vs. non-inductive), the environment in which the switch will operate (temperature, humidity, exposure to dust or chemicals), and the switching mechanism required (momentary vs. alternate operation). Collaborating with suppliers who offer detailed product specifications and consultation services can also provide valuable insights. Creating a checklist that includes these considerations will ensure that buyers can confidently select a switch that meets their specific requirements, thus minimizing the risk of failure and enhancing operational reliability.
Scenario 2: Misunderstanding the Importance of Proper Installation and Maintenance of Electric Switches
The Problem: Many B2B buyers underestimate the significance of proper installation and maintenance of electric switches. This oversight can lead to malfunctioning switches, increased maintenance costs, and potential safety hazards such as electrical shocks or fires. For example, a buyer might install a switch on the wrong line, leading to dangerous voltage levels when the device is turned off, or neglect routine checks that could prevent wear and tear.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, buyers should prioritize training for their installation teams on best practices for switch installation and maintenance. This includes ensuring switches are placed on the hot line to minimize shock risks and regularly inspecting for signs of wear. Additionally, partnering with suppliers who provide installation guidelines, training materials, and even on-site support can greatly enhance safety and efficiency. Establishing a maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections and testing can also help identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring a longer lifespan for switches and a safer working environment.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Understanding the Regulatory Standards for Electric Switches
The Problem: International B2B buyers often face confusion regarding the various regulatory standards that govern electric switches in different regions. For instance, standards may vary significantly between Europe and Africa, impacting compliance and safety. A buyer unaware of these differences might import switches that do not meet local regulations, resulting in fines, project delays, or even the need for costly retrofits.
The Solution: To navigate these complexities, buyers should invest time in understanding the relevant standards and certifications required in their target markets. This could include IEC standards in Europe or local regulations in African countries. Engaging with industry associations, regulatory bodies, or compliance consultants can provide clarity on the necessary certifications. Additionally, buyers should collaborate with suppliers who are knowledgeable about international standards and can provide documentation ensuring that their products meet local compliance requirements. This proactive approach will help buyers avoid legal pitfalls and ensure that their projects proceed smoothly and within regulatory frameworks.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for definition of electric switch
When selecting materials for electric switches, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and how they align with specific applications. This analysis will focus on four common materials used in electric switch manufacturing: plastic, metal, ceramic, and rubber. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly impact performance and suitability in various environments.
What are the Key Properties of Plastic in Electric Switches?
Plastic is widely used in electric switches due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness. Common types include polycarbonate and nylon, which offer good electrical insulation, lightweight properties, and resistance to moisture and chemicals. The temperature rating for plastics can vary, but many can withstand temperatures up to 120°C (248°F).
Pros: Plastics are generally low-cost, lightweight, and easy to mold into complex shapes, making them suitable for high-volume production. They also provide good electrical insulation, reducing the risk of short circuits.
Cons: However, plastics can be less durable than metals and may degrade over time when exposed to UV light or extreme temperatures. They may also have lower mechanical strength, which can be a concern in heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application: In regions like Africa and South America, where humidity and temperature fluctuations can be significant, selecting high-quality plastics that can withstand these conditions is crucial.
How Does Metal Enhance the Performance of Electric Switches?
Metals, such as copper, brass, and stainless steel, are often used in the contacts of electric switches due to their excellent conductivity and durability. Metals can handle higher temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for industrial applications. For instance, copper has a high thermal and electrical conductivity, while stainless steel offers corrosion resistance.
Pros: Metals are robust, providing long-lasting performance and reliability. They are well-suited for applications requiring high current loads, such as in industrial machinery.
Cons: The primary drawback is the higher cost and weight compared to plastics. Additionally, metals can corrode if not properly treated, especially in humid environments.
Impact on Application: In regions such as the Middle East, where high temperatures can lead to corrosion, selecting corrosion-resistant metals is vital to ensure longevity.
What Role Does Ceramic Play in Electric Switch Applications?
Ceramic materials are often used for insulation in electric switches, particularly in high-voltage applications. They offer excellent thermal stability and electrical insulation properties, making them suitable for environments with extreme temperatures.
Pros: Ceramics are highly durable, resistant to wear, and do not degrade easily over time. They can withstand high temperatures, making them ideal for applications in heavy machinery and industrial settings.
Cons: The main limitation of ceramics is their brittleness, which can lead to breakage under mechanical stress. They are also more expensive and complex to manufacture compared to plastics and metals.
Impact on Application: In Europe, where strict compliance with safety standards (like DIN) is required, ceramics can provide the necessary reliability for high-voltage applications.
Why is Rubber Important in Electric Switch Design?
Rubber is commonly used in electric switches for sealing and insulation purposes. It provides excellent flexibility and can withstand a wide range of temperatures, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros: Rubber is effective in preventing moisture ingress and can enhance the durability of switches in outdoor applications. Its flexibility allows for easy installation and operation.
Cons: However, rubber can degrade over time due to exposure to UV light and extreme temperatures, which may limit its lifespan in certain environments.
Impact on Application: In regions like Nigeria, where humidity and temperature can fluctuate significantly, selecting high-quality rubber compounds that resist degradation is essential for ensuring the longevity of electric switches.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric Switches
| Material | Typical Use Case for definition of electric switch | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic | Housing and insulation for consumer switches | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable, may degrade over time | Low |
| Metal | Contacts in industrial switches | Excellent conductivity and durability | Higher cost, potential for corrosion | High |
| Ceramic | Insulation in high-voltage applications | High thermal stability and durability | Brittle, complex to manufacture | Med |
| Rubber | Sealing and insulation in switches | Flexible and moisture-resistant | Can degrade with UV exposure | Med |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the properties and applications of various materials used in electric switches. Understanding these factors will help international B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and environmental conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for definition of electric switch
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Electric Switches?
The manufacturing process of electric switches is a complex operation involving several stages, each critical to ensuring product quality and functionality.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Electric Switch Manufacturing?
The first stage in the manufacturing process involves selecting and preparing materials. Common materials include metals such as copper for electrical contacts, plastics for housings, and various alloys for durability and corrosion resistance.
- Copper: Often used for electrical contacts due to its excellent conductivity.
- Plastic Resins: Typically used for switch housings, these materials are chosen for their insulation properties and durability.
- Metal Alloys: Used for components that require strength and resistance to wear.
These materials undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet the specifications required for electrical performance and safety.
How Are Electric Switches Formed and Assembled?
The forming and assembly stages are where the components come together to create the final product.
-
Forming: This involves shaping the materials into specific components. Techniques such as stamping and molding are commonly used:
– Stamping: Used for creating metal contacts and frames from sheets of metal.
– Injection Molding: Utilized for producing plastic parts like housings and covers. -
Assembly: After forming, the components are assembled. This can be manual or automated, depending on the complexity of the switch. Key tasks include:
– Inserting contacts into the housing.
– Securing the components with screws or snap-fit techniques.
– Integrating additional features such as LED indicators or protective covers.
What Finishing Techniques Are Employed in Electric Switch Manufacturing?
Finishing processes enhance the performance and appearance of electric switches. Common techniques include:
- Plating: Applying a thin layer of metal to enhance conductivity and prevent corrosion. Nickel and gold plating are popular choices for electrical contacts.
- Surface Treatment: Methods like anodizing or powder coating can improve the durability and aesthetics of plastic components.
- Quality Testing: Before packaging, switches undergo functional testing to ensure they operate as intended.
What Are the Quality Assurance Standards Relevant to Electric Switches?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of electric switches to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance with international standards.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are essential for manufacturers aiming to demonstrate quality management principles. ISO 9001 focuses on meeting customer requirements and enhancing satisfaction through effective system implementation.
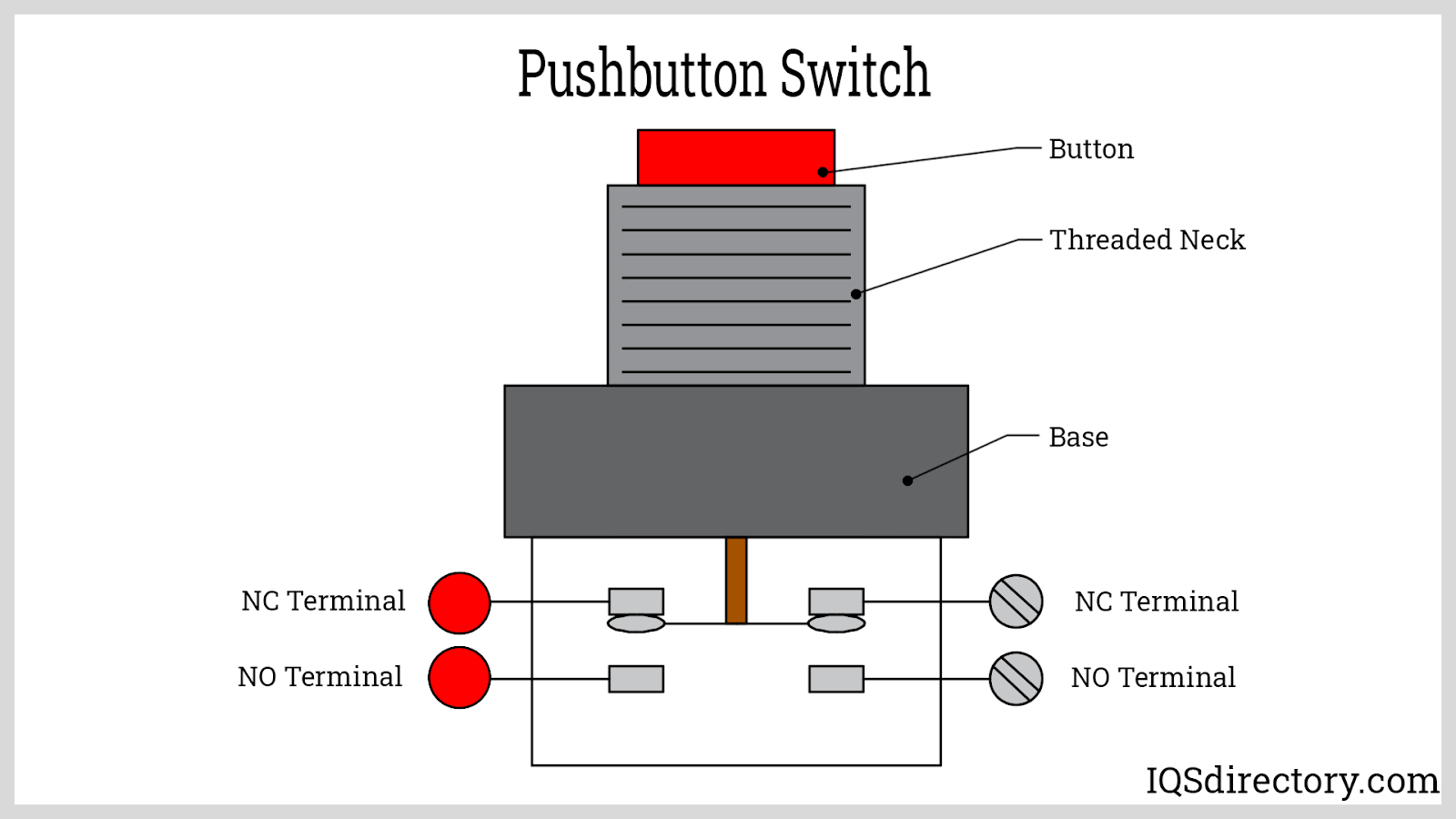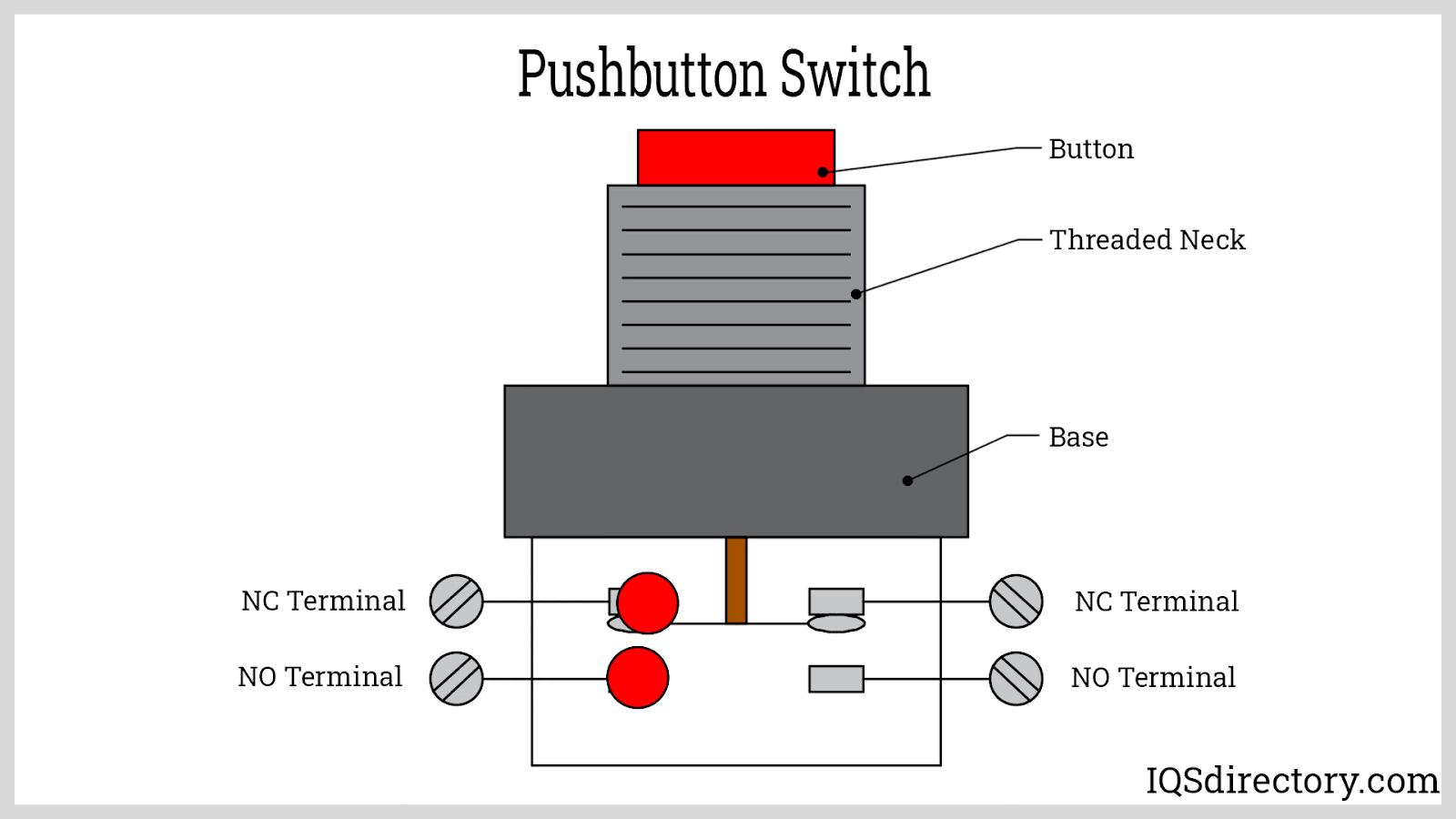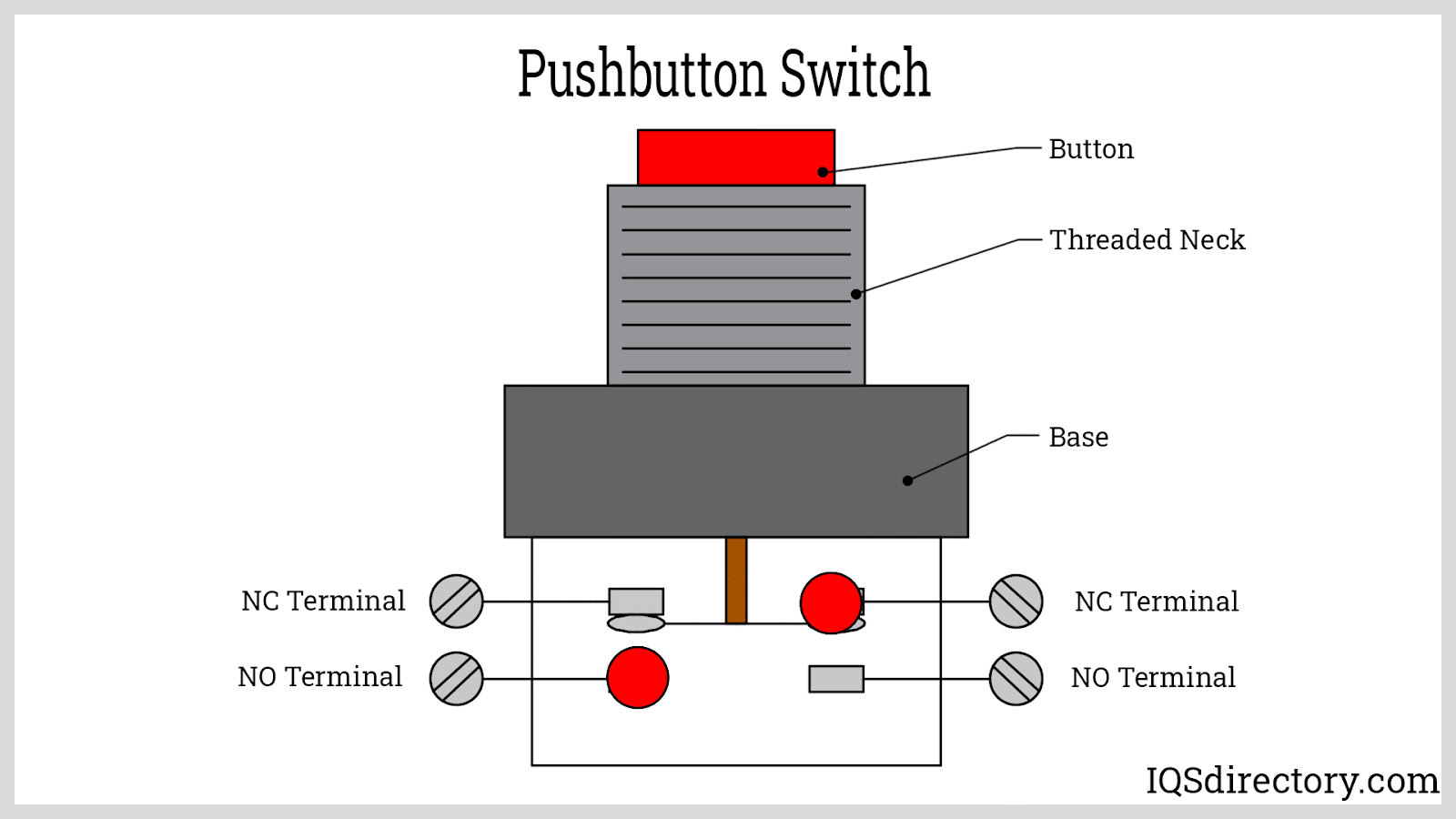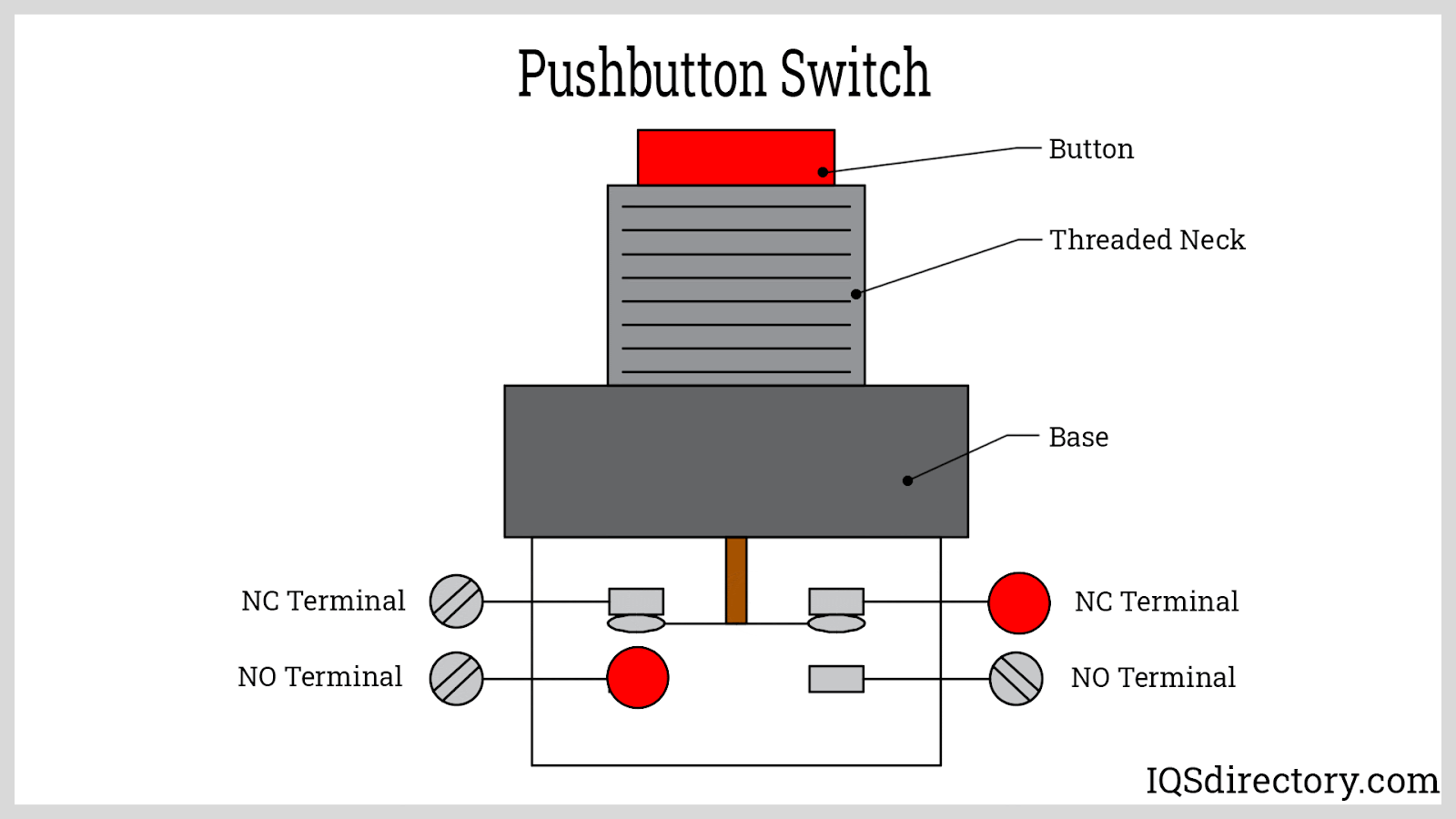
Illustrative image related to definition of electric switch
In addition to ISO, industry-specific standards can apply:
– CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
– API Standards: Particularly relevant for switches used in industrial applications, ensuring they meet safety and performance criteria.
What Quality Control Checkpoints Are Crucial in Electric Switch Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated at various stages of the manufacturing process to catch defects early.
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspects raw materials and components before they enter the production line, ensuring they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitors manufacturing processes to ensure compliance with operational standards. This can include checking dimensions, functional tests, and visual inspections during assembly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducts comprehensive testing on the finished product, including electrical performance, durability, and safety tests.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, especially those operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is vital for ensuring product reliability.
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This includes evaluating their adherence to international standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand the testing methods and results that suppliers use.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of product quality and compliance with relevant standards.
What Testing Methods Are Common in Electric Switch Quality Assurance?
Testing methods play a crucial role in the quality assurance process, ensuring that electric switches perform reliably under various conditions.
- Electrical Testing: Measures the switch’s electrical characteristics, including resistance, current rating, and response time.
- Mechanical Testing: Assesses the durability and physical integrity of switches through tests like actuation life cycles and environmental resistance (temperature, humidity).
- Safety Testing: Verifies that the switch meets safety standards, including insulation resistance and dielectric strength.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances when sourcing electric switches from different regions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Understanding local regulations and certifications can be challenging. Buyers should ensure that suppliers provide documentation verifying compliance with relevant international standards.
- Cultural Considerations: Different regions may have varying quality expectations and manufacturing practices. Buyers should be aware of these differences and communicate their requirements clearly.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: Delays in shipping or customs clearance can affect product quality. Establishing a reliable supply chain and maintaining open communication with suppliers can help mitigate these risks.
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for electric switches are critical components that B2B buyers must consider. By understanding these elements, buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source reliable and high-quality products for their needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘definition of electric switch’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a step-by-step checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure electric switches. Understanding the intricacies of electric switches is essential for making informed purchasing decisions that align with technical requirements and operational standards. This guide will help you navigate the complexities of sourcing electric switches effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Identifying your technical specifications is the foundation of a successful procurement process. Consider factors such as voltage ratings, current ratings, and the type of load (inductive or non-inductive) that the switch will control. This step ensures that the switches you select will meet the operational demands of your equipment and reduce the risk of failures.
Step 2: Determine the Required Switch Type
Electric switches come in various types, including SPST, SPDT, and multiple pole configurations. Understanding the differences between these types will help you choose the right one for your application. For example, SPST switches are ideal for simple on/off operations, while SPDT switches are useful for applications requiring circuit switching.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, thorough evaluation is crucial. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and references from previous clients in your region or industry. Assess their experience with international shipping and compliance with local regulations, as these factors can significantly impact your procurement process.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensuring that suppliers have the necessary certifications is critical for quality assurance. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, CE, or UL, which indicate adherence to industry standards. These certifications not only reflect the quality of the products but also enhance the reliability of your supply chain.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing your order, always request samples of the electric switches you intend to procure. Testing these samples in real-world conditions allows you to evaluate their performance, durability, and compatibility with your existing systems. This step can help prevent costly mistakes and ensure that the switches meet your operational needs.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a supplier, it’s essential to negotiate favorable terms and conditions. Discuss pricing, payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranty policies. Clear agreements in these areas will help mitigate risks associated with procurement and ensure a smooth transaction.
Step 7: Plan for After-Sales Support
Consider the after-sales support offered by your supplier, as this can be crucial for long-term operational efficiency. Inquire about warranty coverage, technical support, and return policies. A supplier that provides robust after-sales service can be a valuable partner in maintaining your electrical systems.
By following this checklist, you can streamline your sourcing process and ensure that you procure electric switches that meet your specific needs and standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for definition of electric switch Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Electric Switch Sourcing?
When considering the sourcing of electric switches, understanding the cost structure is essential. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margin.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as metals, plastics, and electronic components, can vary significantly based on global market conditions. High-quality materials often lead to enhanced performance and longevity, which is crucial for industrial applications.
-
Labor: Labor costs can fluctuate based on the geographical location of manufacturing. Regions with higher labor costs may affect the final price of electric switches. Additionally, skilled labor is essential for producing high-quality products, which can also influence pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with running production facilities, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these costs, allowing suppliers to offer competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The investment in specialized tooling for production can significantly impact the overall cost. Custom tooling may be necessary for unique switch designs, leading to higher initial costs but potentially lower unit costs at scale.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that switches meet industry standards and reduce the likelihood of defects. While this adds to the cost, it is vital for maintaining reputation and minimizing returns or replacements.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping, handling, and storage, can vary based on the distance from the manufacturer to the buyer. Additionally, the choice of Incoterms can affect who bears these costs.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on market positioning and competition. Understanding the typical margins in the industry can provide insight into pricing strategies.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Electric Switch Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of electric switches, which international B2B buyers should consider.
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders typically allow buyers to negotiate better pricing due to economies of scale. Manufacturers often have minimum order quantities (MOQs) that can affect the total cost per unit.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom switches tailored to specific applications can incur higher costs due to additional engineering, testing, and production processes. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the increased expenses.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards or possess specific certifications may come at a premium. However, these certifications can enhance trust and reliability in markets where compliance is critical.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer entrants may offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can significantly influence total costs, as they dictate who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms can help buyers calculate the full landed cost of products.
What Are Essential Buyer Tips for Sourcing Electric Switches?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost efficiency in sourcing electric switches.
-
Negotiation: Effective negotiation can lead to favorable terms. Buyers should be prepared to discuss volume commitments, payment terms, and delivery schedules to secure the best deal.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Rather than just considering the purchase price, buyers should evaluate the total cost of ownership, including installation, maintenance, and potential downtime costs. This holistic approach can reveal the true value of a switch.
-
Leverage Local Market Knowledge: Understanding local market conditions and supplier networks can provide insights into pricing trends and help identify cost-effective options.
-
Consider Long-term Partnerships: Building relationships with reliable suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to innovations in switch technology.
-
Stay Informed on Pricing Trends: Regularly monitoring market trends, material costs, and technological advancements can help buyers make informed decisions and anticipate price fluctuations.
Disclaimer
Prices discussed in this analysis are indicative and can fluctuate based on various factors, including market demand, material costs, and geopolitical conditions. Buyers should conduct thorough research and obtain quotes tailored to their specific needs and circumstances.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing definition of electric switch With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Electric Switches in Electrical Systems
In modern electrical systems, the electric switch plays a crucial role in controlling the flow of electricity. However, there are alternative solutions that can achieve similar objectives, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. This section will compare the definition of an electric switch against two viable alternatives: smart relays and programmable logic controllers (PLCs).
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Definition Of Electric Switch | Smart Relay | Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable ON/OFF control of circuits. | Offers flexibility with added features like timers and logic functions. | High performance with complex control capabilities for multiple circuits. |
| Cost | Generally low-cost, depending on type. | Moderate cost; higher than basic switches but less than PLCs. | Higher initial investment; long-term savings through efficiency. |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple to install and operate. | Requires some programming knowledge; installation is straightforward. | Complex setup; requires programming expertise and technical knowledge. |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance; durable with proper use. | Low maintenance, but programming may need updates. | Higher maintenance due to complexity and potential need for software updates. |
| Best Use Case | Simple applications where basic ON/OFF control is sufficient. | Ideal for applications needing logic functions and timer control. | Best suited for industrial automation where complex processes are managed. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Smart Relay
Smart relays serve as an advanced alternative to traditional electric switches. They provide the ability to program basic logic functions and incorporate timers, which makes them versatile for various applications. The pros include their ease of use in moderately complex setups and the added functionality they offer compared to standard switches. However, they can be costlier than traditional switches and may require some level of programming knowledge for effective use. For businesses looking for more than just ON/OFF control without diving into full automation, smart relays present a balanced choice.
Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)
PLCs are sophisticated devices designed for controlling complex processes and machinery. They can manage multiple inputs and outputs, making them ideal for industrial environments. The primary advantage of PLCs is their ability to handle intricate control tasks, which can lead to improved efficiency and productivity in operations. However, they come with a higher initial cost and require specialized knowledge for installation and programming. For companies with complex automation needs, the investment in a PLC can yield significant long-term benefits, but they may not be suitable for simpler applications due to their complexity and cost.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When evaluating which solution to implement, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and technical capabilities. For straightforward applications that require basic circuit control, traditional electric switches are often sufficient and cost-effective. However, if there is a need for more advanced functionalities, such as timing and logic operations, smart relays may provide the right balance of cost and capability. For organizations with complex automation requirements, investing in a PLC may be warranted despite the higher upfront costs. Ultimately, understanding the operational context and future scalability will guide buyers in selecting the most appropriate solution for their electrical control needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for definition of electric switch
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Electric Switches for B2B Buyers?
When considering electric switches for industrial or commercial applications, understanding specific technical properties is crucial. Here are six critical specifications that B2B buyers should evaluate:
-
Material Grade
Electric switches are typically made from materials like plastic, metal, or a combination of both. The choice of material affects durability, conductivity, and resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and temperature. For instance, switches made from high-grade thermoplastic are often used in harsh conditions, while metal switches may be preferred for their conductivity and robustness. Selecting the appropriate material ensures longevity and reliability, minimizing maintenance costs. -
Contact Rating
This specification indicates the maximum current and voltage that a switch can handle. It is essential to choose a switch with a contact rating that exceeds the operational requirements of the application to prevent overheating or failure. For example, a switch rated at 10A, 250V is suitable for devices that operate within these limits. Understanding contact ratings helps buyers avoid costly downtimes and enhances safety. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible variation in the switch’s dimensions and performance. High tolerance levels are critical in applications where precision is necessary, such as in automation and control systems. Variations can affect the switch’s ability to operate correctly, leading to inefficiencies or malfunctions. Buyers should ensure that the switches meet the tolerance standards required for their specific applications. -
Operating Temperature Range
The operating temperature range indicates the minimum and maximum temperatures at which a switch can function effectively. This is particularly important for applications in extreme climates, such as industrial settings in hot or cold regions. Selecting a switch that can withstand the operating environment helps avoid failures and prolongs the lifespan of the equipment. -
Switching Mechanism
Electric switches may utilize various mechanisms, such as toggle, push-button, or rotary. Each type has distinct operational characteristics, influencing how the switch interacts with the connected circuits. Understanding the switching mechanism can aid buyers in selecting switches that best suit their operational needs, whether for momentary or alternate operations. -
Environmental Resistance
Many electric switches are rated for resistance to factors like dust, water, and chemicals. For instance, IP (Ingress Protection) ratings indicate the level of protection against solids and liquids. In environments such as factories or outdoor settings, choosing switches with appropriate environmental resistance ensures reliability and reduces failure rates.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Electric Switches?
In addition to technical properties, familiarity with industry terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are six common terms that buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is essential for buyers looking to source switches that meet specific specifications for their machinery or equipment. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers assess whether a supplier can meet their needs without incurring excess inventory costs, which is especially important for businesses with varying demand levels. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and other information for specific products. This process is crucial for obtaining competitive pricing and ensuring that the specifications meet the buyer’s requirements. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade regarding shipping, risk, and costs. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand their obligations and rights, facilitating smoother transactions and reducing misunderstandings. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is critical for planning and inventory management, as it directly impacts project timelines and operational efficiency. -
Certification Standards
Many electric switches must comply with industry certification standards (e.g., ISO, CE, UL) to ensure safety and reliability. Knowing these standards helps buyers select switches that meet legal and operational requirements, thus enhancing their product’s credibility in the market.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing electric switches for their applications. This knowledge ultimately leads to better product performance, safety, and efficiency in operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the definition of electric switch Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Affecting the Electric Switch Sector?
The electric switch market is experiencing significant growth driven by several global factors, particularly in emerging economies across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. One of the primary drivers is the rapid expansion of the renewable energy sector, which requires robust and reliable switching solutions for applications in solar, wind, and other alternative energy sources. Additionally, the increasing demand for automation in industrial processes is propelling the need for more sophisticated electric switches that can handle complex circuits and high electrical loads.
Technological advancements are also reshaping the landscape. The integration of smart technologies, such as IoT-enabled switches, is providing B2B buyers with enhanced control and monitoring capabilities. These innovations not only improve operational efficiency but also offer data analytics, aiding in predictive maintenance and reducing downtime. Furthermore, the shift towards energy-efficient solutions is compelling manufacturers to develop switches that minimize energy loss during operation, thereby aligning with global sustainability goals.
As international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Brazil and Nigeria, seek to source electric switches, understanding these trends is crucial. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate adaptability to market changes, particularly in terms of technology and compliance with international standards. Additionally, being aware of local regulatory requirements can facilitate smoother procurement processes and ensure product reliability.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Electric Switch Market?
Sustainability is becoming an essential consideration in the electric switch market, influencing both sourcing decisions and product development. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and materials used in electric switches is under increasing scrutiny. B2B buyers are encouraged to look for suppliers who utilize sustainable practices, such as reducing waste and emissions during production. This not only helps in minimizing the carbon footprint but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
Ethical sourcing is equally critical. Buyers should ensure that their supply chains are transparent and adhere to ethical labor practices. The use of green certifications and materials, such as recyclable plastics and metals, can enhance a product’s marketability while appealing to environmentally-conscious consumers. Collaborating with manufacturers that prioritize ethical sourcing can mitigate risks associated with reputational damage and regulatory penalties, particularly in markets that are becoming more stringent about environmental compliance.
Furthermore, suppliers who adopt sustainable practices often benefit from reduced operational costs in the long run, enabling them to offer competitive pricing to B2B buyers. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, international buyers can not only fulfill their corporate social responsibility goals but also enhance their competitive edge in an increasingly eco-conscious marketplace.
What is the Brief Evolution and History of Electric Switch Technology?
The evolution of electric switch technology dates back to the late 19th century, with the introduction of the first mechanical switches. These early devices were primarily used in telegraph systems and rudimentary electrical circuits. As the demand for electricity surged with the advent of the industrial revolution, the design and functionality of switches evolved significantly. The introduction of toggle and rocker switches in the early 20th century brought greater convenience and safety to electrical control systems.
In the latter half of the 20th century, advancements in materials and manufacturing processes led to the development of more durable and versatile switches, catering to both industrial and consumer markets. The rise of electronics in the late 20th century further transformed the sector, with the introduction of micro-switches and push-button switches that paved the way for automation in various applications.
Today, electric switches are integral to numerous systems, from simple household appliances to complex industrial machinery. As technology continues to advance, the electric switch sector is poised for further innovation, particularly with the integration of smart technologies and IoT solutions, making it a dynamic area for B2B investment and sourcing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of definition of electric switch
-
How do I determine the right type of electric switch for my application?
Choosing the right type of electric switch depends on the specific requirements of your application, including the load type, voltage, and environmental conditions. For example, SPST (Single Pole Single Throw) switches are suitable for basic ON/OFF operations, while SPDT (Single Pole Double Throw) switches can control multiple circuits. Additionally, consider factors such as durability, resistance to dust or moisture, and the operational environment to ensure optimal performance. -
What are the common types of electric switches used in industrial applications?
In industrial settings, commonly used electric switches include toggle switches, push-button switches, and rotary switches. Toggle switches are often used for ON/OFF control, while push-button switches may serve momentary or alternate functions. Rotary switches are typically employed for multi-position control. Each type has specific applications and load capacities, so it’s essential to match the switch type to the operational demands of your equipment. -
How can I vet suppliers when sourcing electric switches internationally?
To vet suppliers effectively, begin by checking their certifications and compliance with international standards, such as ISO or IEC. Request references from previous clients, and evaluate their experience in your industry. Additionally, consider conducting site visits or audits if feasible. Utilizing third-party inspection services can also provide additional assurance regarding product quality and supplier reliability. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for electric switches from suppliers?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on the type of electric switch being purchased. Typically, MOQs may range from a few hundred to several thousand units. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you are testing a new product or entering a new market. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing electric switches internationally?
Payment terms can differ among suppliers and regions. Common terms include advance payment, letter of credit, or net 30/60 days after delivery. It’s crucial to establish clear terms upfront, including currency exchange considerations and any potential tariffs or duties. Be sure to review the supplier’s payment policies and negotiate terms that minimize your financial risk. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing electric switches?
To ensure quality assurance, establish a clear set of specifications and standards that the switches must meet. Request samples for testing before placing larger orders. Additionally, consider implementing a quality control process that includes inspections at various stages of production and before shipping. Collaborating with suppliers who have robust QA practices can further enhance product reliability. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing electric switches?
When importing electric switches, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations specific to your destination country. Evaluate freight options such as air or sea transport based on cost and urgency. Additionally, familiarize yourself with import duties, taxes, and any required documentation to ensure compliance and avoid delays at customs. -
What customization options are available for electric switches?
Many suppliers offer customization options for electric switches, including size, color, labeling, and functionality. Customization can help ensure that the switches fit specific operational requirements or branding needs. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore available options and any associated costs or lead times for customized products.
Top 8 Definition Of Electric Switch Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. OMRON – Electrical Switches
Domain: components.omron.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: OMRON offers a wide range of electrical switches including: Basic Switches (Miniature, Subminiature, Ultra Subminiature, Sealed), Detection Switches (Surface Mount, Door, Power), Tactile Switches (Standard, Illuminated, Sealed, SMD, Hinged), Rocker Switches, Pushbutton Switches (Small, Hand, Toggle), DIP Switches, Slide Types, Piano Types, Rotary Types, Automotive Switches, Limit Switches, and Saf…
2. Energy Education – Electric Switches
Domain: energyeducation.ca
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: An electric switch is an electrical component that breaks or closes an electric circuit. Opening the switch (breaking the circuit) turns off the electrical device, while closing the switch (completing the circuit) allows electrical current to flow, turning the device on. Switches should be placed on the hot line to reduce the risk of electric shock when the device is turned off.
3. IQS Directory – Electric Switches
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Electric switches are electromechanical devices that manage electrical circuits by opening or closing them, regulating the flow of electric current. Key details include: 1. **Current Rating**: Maximum electric current (in amperes) the switch can carry; exceeding this can cause damage or failure. 2. **Voltage Rating**: Maximum voltage (in volts) the switch can withstand; crucial for preventing arci…
4. Britannica – Electric Switches
Domain: britannica.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Electric switch is a device for opening and closing electrical circuits under normal load conditions, usually operated manually. Common types include toggle switches, mercury switches (used for home lighting), and oil switches (which have live parts immersed in oil to reduce arcing). The aggregate of switching or circuit-breaking equipment for power stations is referred to as switchgear.
5. Now Power Texas – Electrical Switches Guide
Domain: nowpowertexas.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Different types of electrical switches found in homes include: 1. Single-Pole Switch: A simple On/Off switch with two terminals, commonly used for controlling lights. 2. Three-Way Switch: Allows control of lights from two locations, typically used at staircases. 3. Double-Pole Switch: Used in high traffic areas, rated for 30 amps, suitable for high-demand appliances. 4. Four-Way Switch: Controls d…
6. SmartShop – Electric Switch Types
Domain: smartshop.lk-ea.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Electric Switch Types: 1. Basic Toggle Switches – Commonly used in homes, priced from a few to a couple hundred rupees based on quality and brand. 2. Smart Electrical Switch – Integrated into home automation, allowing control of lights and appliances via apps or voice commands. 3. Dimmer Switches – Regulate light illumination levels by controlling voltage, suitable for mood lighting. 4. Push-Butto…
7. ScienceDirect – Electric Switches
Domain: sciencedirect.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Electric switches are devices that control the flow of electricity in a circuit, serving as safety switches to prevent electric shock and ensure safe operation. They are important in communication and control systems, widely used in microwave and millimeter wave integrated circuits (MMICs) for telecommunication applications such as signal routing and impedance matching networks. State-of-the-art t…
8. Switch Components Inc – Switches and Accessories
Domain: switchcomp.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Switch Components Inc offers a variety of switches including Push Switches, Push Pull Switches, Toggle Switches, Rocker Switches, Battery Switches, Ignition Switches, Solenoids, Trailer Connectors, Accessories, and USB Charging Ports. Key terms related to their products include: Actuation Force, Actuator, Alternating Current (AC), Ampere (A), Arcing, Break-Before-Make (BBM), Capacitive load, Conta…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for definition of electric switch
In conclusion, understanding the definition and functionality of electric switches is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to enhance their procurement strategies. Electric switches serve as essential components in controlling electrical circuits, offering various configurations such as SPST and SPDT to meet diverse operational needs. By leveraging strategic sourcing, businesses can identify reliable suppliers that not only provide high-quality switches but also offer competitive pricing and robust support services.
For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the value of sourcing the right electric switches extends beyond mere functionality; it encompasses considerations of safety, efficiency, and compliance with regional standards. As industries evolve and the demand for innovative electrical solutions increases, establishing partnerships with reputable suppliers will be pivotal in driving operational excellence.
Looking ahead, now is the time for businesses to re-evaluate their sourcing strategies for electric switches. By prioritizing quality, reliability, and sustainability, companies can position themselves for success in an increasingly interconnected global market. Engage with suppliers who understand your unique challenges and can provide tailored solutions that drive your business forward.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.