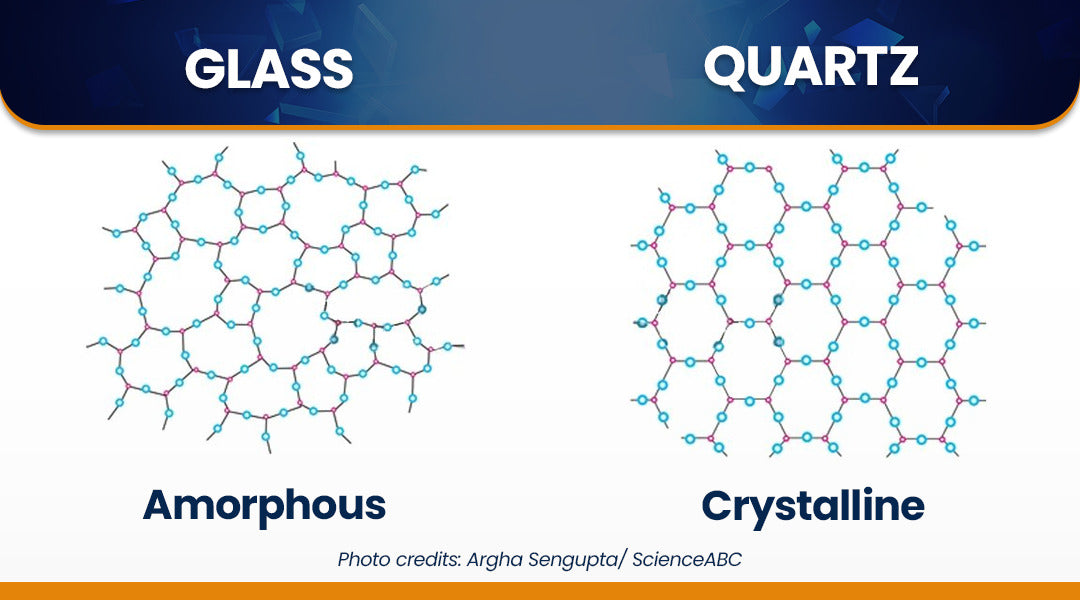
Crystal Quartz Glass Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for crystal quartz glass
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial materials, sourcing high-quality crystal quartz glass presents a unique challenge for B2B buyers across the globe. With its exceptional properties—such as thermal stability, optical clarity, and chemical inertness—crystal quartz glass is indispensable in various applications, from laboratory glassware to advanced optical instruments. However, navigating the complexities of suppliers, pricing, and quality assurance can be daunting, especially for international buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including nations like Germany and Saudi Arabia.
This comprehensive guide aims to illuminate the multifaceted world of crystal quartz glass, addressing key considerations for procurement. We will explore different types of quartz glass, their specific applications, and essential factors for supplier vetting to ensure you make informed purchasing decisions. Additionally, we will provide insights into cost structures and market trends, enabling you to understand the financial implications of your choices.
By equipping you with actionable insights and practical knowledge, this guide empowers international B2B buyers to confidently navigate the global market for crystal quartz glass, ensuring that your sourcing decisions align with your operational needs and standards of excellence. Whether you’re seeking suppliers for laboratory use or high-performance optical applications, this resource is your roadmap to successful procurement.
Understanding crystal quartz glass Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fused Quartz | High thermal stability, optical clarity, and chemical inertness | Laboratory glassware, optical components | Pros: Excellent durability and heat resistance. Cons: Higher cost compared to regular glass. |
| Fused Silica | Made from synthetic silica, very low thermal expansion | Semiconductor fabrication, optics | Pros: Superior purity and uniformity. Cons: Limited availability in bulk sizes. |
| Z-Cut Quartz Windows | Polished, precise optical properties | Laser optics, spectrophotometry | Pros: High precision and clarity. Cons: Requires careful handling to avoid scratches. |
| Quartz Tubing | Hollow form, customizable dimensions | Chemical processing, high-temperature applications | Pros: Versatile and customizable. Cons: May require specialized fittings. |
| Quartz Crucibles | High mechanical strength, withstands extreme temperatures | Material testing, sintering processes | Pros: Long lifespan and reliability. Cons: Heavier than alternatives, impacting transport. |
What are the Characteristics of Fused Quartz?
Fused quartz is a highly pure form of quartz glass made by melting silicon dioxide at high temperatures. Its key features include exceptional thermal stability, optical clarity, and chemical inertness, making it ideal for laboratory glassware and optical components. When purchasing, B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their applications, including temperature resistance and optical properties. The initial investment may be higher, but its durability and performance can lead to long-term savings.
Why Choose Fused Silica for Semiconductor Applications?
Fused silica is a synthetic variant of quartz glass known for its extremely low thermal expansion and high purity. This makes it particularly suitable for semiconductor fabrication and precision optics. B2B buyers in the tech sector should prioritize fused silica for applications requiring minimal distortion under heat. While it offers superior quality, the availability in bulk sizes can be a limiting factor, necessitating careful sourcing strategies.
How Do Z-Cut Quartz Windows Enhance Optical Performance?
Z-cut quartz windows are specifically polished to achieve precise optical properties, making them ideal for applications in laser optics and spectrophotometry. Their high precision and clarity are essential for accurate light transmission and analysis. Buyers should consider the handling and maintenance of these windows, as they require careful treatment to prevent scratches that could compromise performance. The investment in Z-cut quartz is justified by its superior optical quality.
What Makes Quartz Tubing Versatile for Industrial Use?
Quartz tubing is a hollow form of quartz glass that can be customized to various dimensions, making it highly versatile for chemical processing and high-temperature applications. B2B buyers should evaluate the specific dimensions and fittings required for their processes to ensure compatibility. While quartz tubing offers significant advantages in terms of chemical resistance and thermal stability, it may require specialized fittings, which could complicate procurement.
Why are Quartz Crucibles Essential for Material Testing?
Quartz crucibles are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, making them vital for material testing and sintering processes. Their high mechanical strength ensures longevity and reliability, which is crucial for laboratories conducting repetitive experiments. Buyers should consider the weight of quartz crucibles, as their heavier nature may impact shipping costs. However, the durability they offer often outweighs these considerations, providing a strong return on investment.
Key Industrial Applications of crystal quartz glass
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of crystal quartz glass | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laboratory and Analytical | Laboratory glassware (e.g., beakers, flasks) | Ensures high precision and reliability in scientific analysis | Look for high-purity quartz glass to avoid sample contamination. |
| Optical and Photonics | Optical components (e.g., lenses, windows) | Provides superior optical clarity and UV transmission | Verify optical specifications to ensure compatibility with applications. |
| Semiconductor Manufacturing | Quartz crucibles for melting and processing | High thermal stability supports advanced manufacturing processes | Source from suppliers with expertise in high-temperature applications. |
| Chemical Processing | Reactors and containment vessels | Resistant to corrosive substances and high temperatures | Ensure chemical compatibility and durability for specific applications. |
| Medical Devices | Components for diagnostic instruments | Enhances reliability and accuracy in medical testing | Assess biocompatibility and compliance with international standards. |
How is Crystal Quartz Glass Used in Laboratories and Why is it Essential?
In laboratory settings, crystal quartz glass is predominantly utilized for glassware such as beakers, flasks, and pipettes due to its exceptional thermal stability and chemical inertness. This material can withstand high temperatures, making it ideal for processes that require precise heating without risk of deformation. For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, and Europe, sourcing high-purity quartz glass is critical to prevent contamination that could compromise experimental results. Buyers should seek suppliers who can provide detailed specifications and certifications of purity.
What Role Does Crystal Quartz Glass Play in Optical and Photonics Industries?
In the optical and photonics sectors, crystal quartz glass is used to manufacture components like lenses and windows that require high optical clarity and the ability to transmit ultraviolet light. Its unique properties ensure minimal distortion and high transmission efficiency, which are crucial for applications such as spectroscopy and laser technology. International buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer a range of optical grades and can customize products to meet specific wavelength requirements.
How is Crystal Quartz Glass Beneficial in Semiconductor Manufacturing?
Crystal quartz glass is integral to semiconductor manufacturing, particularly in the form of quartz crucibles used for melting silicon and other materials. Its ability to withstand extreme temperatures without deforming is vital for maintaining the integrity of the manufacturing process. B2B buyers in this sector must consider sourcing from manufacturers who specialize in high-temperature applications and can ensure the material meets the stringent standards required for semiconductor production.
Why is Crystal Quartz Glass Preferred in Chemical Processing?
In the chemical processing industry, crystal quartz glass is favored for its resistance to corrosive chemicals and high thermal stability, making it ideal for reactors and containment vessels. This material minimizes the risk of reactions that could affect the integrity of the processes or the quality of the end products. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can provide detailed chemical compatibility data and are equipped to meet specific operational needs.
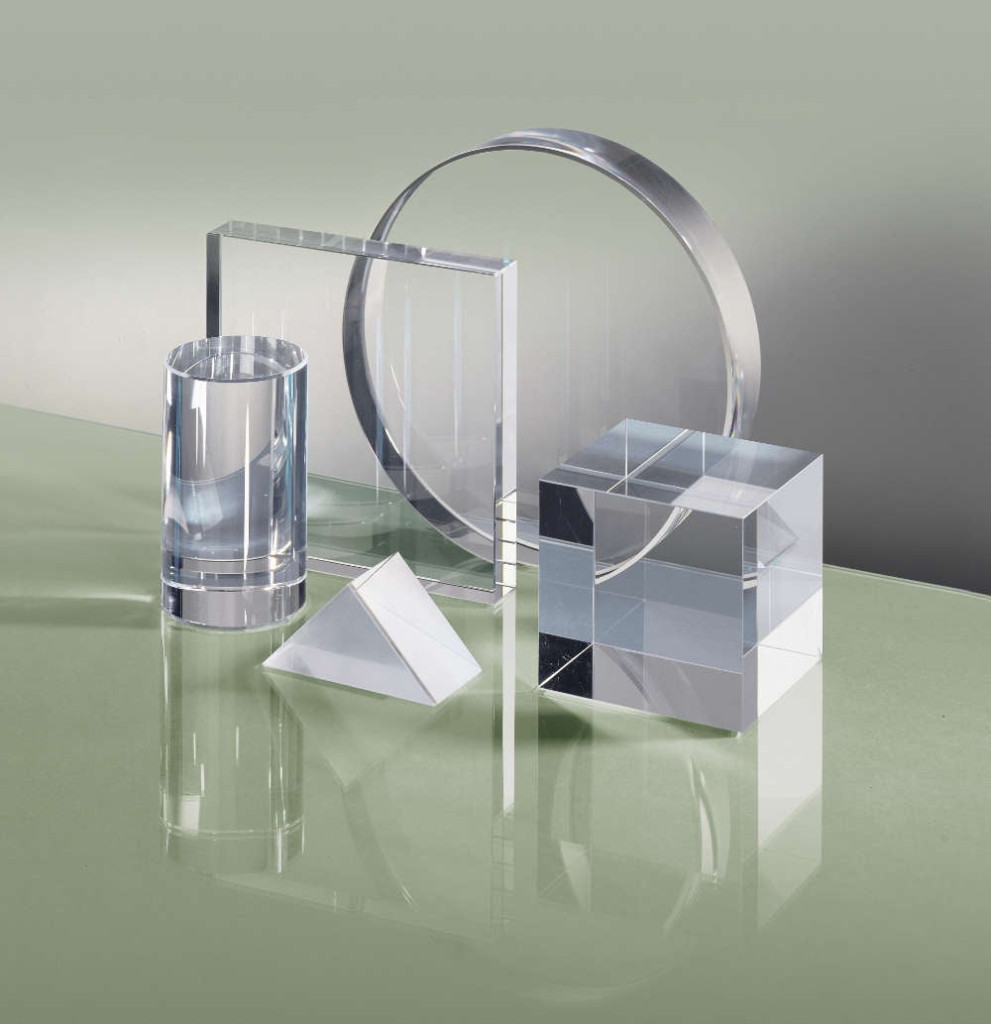

Illustrative image related to crystal quartz glass
What Advantages Does Crystal Quartz Glass Offer in Medical Devices?
Crystal quartz glass is increasingly used in the medical device industry for components in diagnostic instruments and laboratory equipment. Its high purity and chemical inertness enhance the reliability and accuracy of medical tests, which is critical for patient safety and treatment efficacy. B2B buyers in this field should look for suppliers that comply with international medical standards and can provide documentation on biocompatibility.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘crystal quartz glass’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sourcing High-Purity Quartz Glass for Laboratory Use
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with sourcing high-purity crystal quartz glass that meets specific laboratory standards. Many suppliers might offer quartz glass, but variations in purity levels can affect experimental results. Buyers may face challenges in identifying suppliers who can guarantee the absence of contaminants, which is critical when conducting sensitive experiments that require precision and accuracy.
The Solution: To ensure you source high-quality crystal quartz glass, establish a thorough vetting process for suppliers. Begin by requesting detailed product specifications and certifications that verify the purity levels of the quartz glass. Look for suppliers who provide transparency in their manufacturing processes and can demonstrate compliance with international standards, such as ISO 9001. Additionally, consider establishing a direct line of communication with potential suppliers to discuss your specific needs and expectations. Building a solid relationship can lead to better service, customized solutions, and potentially lower costs for bulk orders.
Scenario 2: Challenges with Thermal Stability in High-Temperature Applications
The Problem: In industries where crystal quartz glass is used for high-temperature applications, such as in laboratories or manufacturing, buyers often encounter issues with thermal stability. If the quartz glass is not adequately rated for the temperatures required, it may warp or break, leading to costly downtimes and losses in productivity. This becomes particularly problematic when precise temperature control is essential for experiments or production processes.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, it is crucial to accurately assess the thermal requirements of your specific applications before purchasing quartz glass. Consult technical data sheets from suppliers to understand the thermal limits of the products you are considering. Select quartz glass that can withstand temperatures beyond your maximum operational needs, providing a buffer for safety. Additionally, when placing orders, communicate clearly with your supplier about the conditions under which the glass will be used. This way, they can recommend the most suitable products and prevent potential issues arising from thermal stress.
Scenario 3: Inadequate Optical Clarity Affecting Experiment Outcomes
The Problem: B2B buyers often face difficulties with the optical clarity of quartz glass, especially when it comes to applications in spectroscopy or other optical analyses. Inconsistent quality can lead to poor light transmission, affecting the accuracy of readings and the integrity of experimental results. This can be particularly frustrating for laboratories that rely on precise measurements for research and development.
The Solution: To ensure optimal optical clarity, prioritize suppliers who specialize in optical-grade quartz glass. Request samples to evaluate the clarity and transmission properties before making a large purchase. Additionally, ask for data on the optical performance of the glass across different wavelengths, particularly if your applications involve ultraviolet (UV) light. Establishing long-term partnerships with reputable suppliers can also provide ongoing access to high-quality materials and technical support, which is invaluable for troubleshooting any optical issues that may arise in future projects. Regularly reviewing and assessing the performance of the quartz glass in your applications can help identify any discrepancies early, allowing for timely adjustments.
By addressing these common pain points with targeted solutions, B2B buyers can enhance their purchasing strategy for crystal quartz glass, ensuring they meet their operational needs effectively and efficiently.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for crystal quartz glass
What Are the Key Properties of Crystal Quartz Glass?
Crystal quartz glass, primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO₂), is renowned for its unique properties that make it suitable for a variety of industrial applications. Key properties include high thermal stability, allowing it to withstand temperatures exceeding 1,200°C, and exceptional optical transparency across ultraviolet, visible, and infrared spectra. These features make quartz glass ideal for applications requiring precise light transmission and high-temperature resistance.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Using Crystal Quartz Glass in B2B Applications?
1. Fused Quartz Glass
Key Properties: Fused quartz glass offers high thermal resistance and low thermal expansion. It can endure extreme temperatures without deforming, making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
Pros: Its durability and chemical inertness make it an excellent choice for laboratory glassware and optical components. Fused quartz is also highly transparent, allowing for effective light transmission.
Cons: The manufacturing process can be complex and costly, which may deter some buyers. Additionally, while it is robust, it can be brittle under certain conditions, necessitating careful handling.
Impact on Application: Fused quartz glass is particularly effective in high-temperature environments, such as semiconductor manufacturing and laboratory settings, where reliability is crucial.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN, which govern material quality and safety.

Illustrative image related to crystal quartz glass
2. Fused Silica Glass
Key Properties: Fused silica is synthetic and offers similar properties to fused quartz but with even higher purity levels. It is chemically inert and can withstand high temperatures.
Pros: Its high purity makes it ideal for sensitive applications, such as in the pharmaceutical and semiconductor industries. Fused silica also has excellent optical properties.
Cons: The cost of fused silica is typically higher than that of other materials, and its production may involve more complex processes.

Illustrative image related to crystal quartz glass
Impact on Application: This material is particularly suited for applications requiring high precision, such as optical components and laboratory equipment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of specific regional standards and certifications that may apply to high-purity materials, particularly in the pharmaceutical sector.
3. Quartz Glass Tubes
Key Properties: Quartz glass tubes are manufactured to withstand high temperatures and have excellent chemical resistance. They are often used in laboratory and industrial applications.
Pros: These tubes are versatile and can be used in a variety of settings, from laboratory experiments to industrial processes. Their durability ensures a long lifespan.
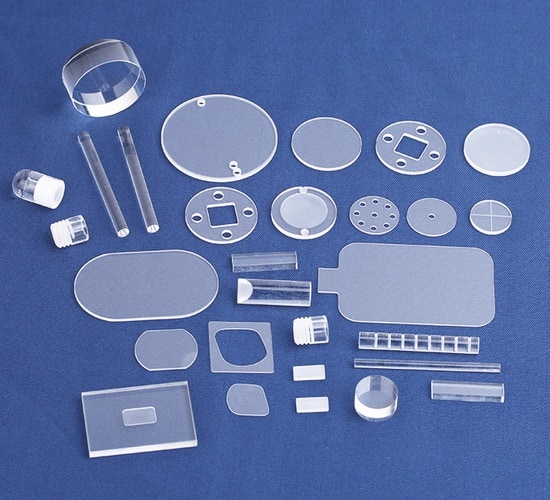

Illustrative image related to crystal quartz glass
Cons: The initial investment can be significant, especially for custom sizes or specifications. Additionally, they may require specialized fittings or supports.
Impact on Application: Quartz glass tubes are ideal for chemical processing and laboratory experiments, where high purity and thermal stability are essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider logistics and shipping costs, as quartz glass products can be fragile and require careful handling during transport.
4. Quartz Glass Windows
Key Properties: Quartz glass windows provide excellent optical clarity and thermal stability. They are commonly used in optical devices and laboratory equipment.
Pros: Their ability to transmit UV light makes them indispensable in spectroscopy and other optical applications. They are also resistant to thermal shock.
Cons: The cost can be prohibitive for large-scale applications, and they may not be suitable for all chemical environments.
Impact on Application: Ideal for spectroscopic analysis and high-precision optical applications, quartz glass windows enhance the performance of analytical instruments.

Illustrative image related to crystal quartz glass
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with optical standards and certifications is crucial, especially for buyers in Europe and North America.
Summary Table of Crystal Quartz Glass Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for crystal quartz glass | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fused Quartz Glass | Laboratory glassware, optical components | High thermal resistance and durability | Brittle under certain conditions | High |
| Fused Silica Glass | Semiconductor manufacturing, optical devices | High purity and excellent optical properties | Higher cost and complex production | High |
| Quartz Glass Tubes | Chemical processing, laboratory experiments | Versatile and durable | Significant initial investment | Medium |
| Quartz Glass Windows | Spectroscopy, high-precision optical applications | Excellent UV light transmission | Costly for large-scale applications | High |
This guide aims to equip international B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed decisions regarding the selection of crystal quartz glass materials, considering regional standards and application-specific requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for crystal quartz glass
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Crystal Quartz Glass?
The manufacturing of crystal quartz glass is a highly specialized process that involves several critical stages to ensure the highest quality and performance. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to source high-quality quartz glass products.

Illustrative image related to crystal quartz glass
Material Preparation: How Is Raw Quartz Processed?
The initial stage of manufacturing crystal quartz glass begins with the selection of high-purity quartz sand, primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO₂). This raw material undergoes a thorough purification process to eliminate any impurities that could affect the quality of the final product. Techniques such as chemical leaching, flotation, and high-temperature treatments are employed to achieve the necessary purity levels. The purity of the raw material is vital, as it directly influences the optical and mechanical properties of the finished glass.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Quartz Glass?
Once the raw material is prepared, it is subjected to high-temperature melting, typically exceeding 1,700°C. This process transforms the solid quartz into a molten state, allowing for various forming techniques. Common methods include:
- Blowing: Used to create hollow glass items.
- Pressing: Involves pressing molten glass into molds to form specific shapes.
- Casting: Pouring molten glass into molds for complex shapes.
- Drawing: A technique for producing thin sheets or fibers of quartz glass.
Each method offers different advantages depending on the intended application, such as optical components, laboratory glassware, or industrial parts.

Illustrative image related to crystal quartz glass
Assembly: How Are Different Components Joined?
For applications requiring multiple components, assembly becomes crucial. Techniques such as fusion bonding or adhesive bonding may be employed. Fusion bonding involves melting the edges of two glass pieces together, while adhesive bonding uses specialized adhesives designed for high-temperature and chemical resistance. Ensuring a strong and reliable bond is essential for maintaining the integrity of the final product, especially in high-stress applications.
Finishing: What Processes Enhance the Quality of Quartz Glass?
The finishing stage includes polishing, cutting, and coating processes that enhance the optical clarity and surface quality of quartz glass. Polishing removes any surface imperfections, while precise cutting ensures that components meet exact specifications. Additionally, surface treatments, such as anti-reflective coatings, can be applied to improve performance in optical applications. Quality control during this stage is critical, as it directly impacts the functionality and aesthetic appeal of the glass.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant to Crystal Quartz Glass?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of crystal quartz glass, particularly for B2B buyers who need to ensure that products meet stringent international standards.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Buyers should look for compliance with internationally recognized quality standards, such as:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines criteria for a quality management system, emphasizing customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
- ISO 14001: Focused on environmental management, this standard ensures that manufacturers minimize their environmental impact.
- CE Marking: Indicates that products meet European safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Specification: Particularly relevant for suppliers serving the oil and gas industry, ensuring products meet specific performance criteria.
Understanding these standards helps buyers assess the reliability and credibility of suppliers.
What Are Common Quality Control Checkpoints in Quartz Glass Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to verify compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing ensures adherence to established parameters.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished products undergo rigorous testing to confirm they meet the required standards before shipment.
These checkpoints help mitigate risks associated with defects and ensure that only high-quality products reach the market.
What Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure the Quality of Crystal Quartz Glass?
To guarantee the performance and reliability of crystal quartz glass, various testing methods are employed:
- Optical Testing: Measures light transmittance and clarity, ensuring that the glass meets optical standards.
- Thermal Cycling Tests: Evaluates thermal stability by subjecting the glass to extreme temperature fluctuations.
- Chemical Resistance Testing: Assesses how the glass interacts with various chemicals to ensure its suitability for laboratory applications.
- Mechanical Strength Tests: Determines the durability and resistance to breakage, which is critical for industrial applications.
These tests provide valuable data that manufacturers can use to refine their processes and improve product quality.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control practices is essential to mitigate risks and ensure product reliability.
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Ensure Supplier Credibility?
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their quality control processes and adherence to standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their QC processes, including results from testing and compliance with international standards.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices.
-
Evaluate Certifications: Ensure that suppliers hold relevant certifications that demonstrate their commitment to quality and compliance with industry standards.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing crystal quartz glass internationally, buyers must be aware of regional nuances in quality control. Different markets may have varying standards and expectations, which can impact product acceptance. For example, European markets may have stricter regulations compared to those in Africa or South America. Understanding these differences is crucial for establishing successful partnerships with suppliers and ensuring that the products meet local market requirements.
By focusing on comprehensive quality assurance practices, international B2B buyers can confidently source high-quality crystal quartz glass that meets their specific needs and applications.

Illustrative image related to crystal quartz glass
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘crystal quartz glass’
The following checklist is designed to guide B2B buyers in effectively sourcing crystal quartz glass. This material is essential for various applications in industries such as scientific research, manufacturing, and optics, and understanding the procurement process is crucial for ensuring quality and reliability.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating your sourcing process, clearly outline the specific technical requirements for your crystal quartz glass. Consider factors such as dimensions, purity levels, and thermal and optical properties. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure that the products meet your operational needs.
- Example Specifications:
- Diameter and thickness for windows.
- Desired optical clarity for optical applications.
- Temperature resistance for high-heat applications.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in crystal quartz glass. Focus on suppliers with a proven track record in your industry and region, as they will better understand your unique requirements and challenges.
- Key Considerations:
- Look for suppliers with experience in international shipping, especially if you are sourcing from different continents.
- Check for customer reviews and testimonials to gauge supplier reliability.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
It’s essential to verify that your potential suppliers hold the necessary certifications and adhere to industry standards. This step ensures that the products you receive meet quality and safety requirements.
- What to Look For:
- ISO certification for quality management.
- Compliance with relevant international standards (e.g., ASTM or DIN).
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the crystal quartz glass you intend to buy. This allows you to assess the material’s quality firsthand and verify that it meets your specifications.
- Testing Considerations:
- Evaluate the optical clarity and thermal resistance.
- Conduct chemical resistance tests if applicable to your use case.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. This step is crucial for ensuring that you receive the best value while establishing a solid business relationship.
- Negotiation Tips:
- Inquire about discounts for bulk orders or long-term contracts.
- Discuss payment terms to ensure they align with your cash flow needs.
Step 6: Confirm Logistics and Delivery Schedule
After finalizing the purchase agreement, confirm the logistics details, including shipping methods, delivery timelines, and any customs requirements for your region. Clear communication during this phase will help avoid delays and ensure timely receipt of your materials.
- Logistics Considerations:
- Consider suppliers who offer reliable tracking systems.
- Ensure that the packaging is suitable for protecting the glass during transit.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Assurance Process
After receiving your order, implement a quality assurance process to inspect the products against your initial specifications. This step is vital for maintaining operational integrity and ensuring that the materials meet your standards.
- Quality Control Measures:
- Conduct visual inspections for defects.
- Perform functionality tests based on your intended applications.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing crystal quartz glass, ensuring that they procure high-quality materials that meet their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for crystal quartz glass Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Crystal Quartz Glass?
When sourcing crystal quartz glass, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The base material, silicon dioxide (SiO₂), is a significant cost driver. High-purity quartz is essential for ensuring the quality of the final product, which can increase prices. Impurities can affect optical clarity and mechanical strength, making quality control a priority.
-
Labor: The labor costs associated with manufacturing quartz glass can vary significantly by region. Skilled labor is needed for processes like melting and shaping the glass, which can add to overall costs. In regions with higher wages, such as parts of Europe, this may be a more significant factor.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and machinery maintenance. Given the high temperatures required to produce quartz glass, operational costs can be substantial.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific shapes or sizes can be a considerable upfront investment. For B2B buyers looking for unique specifications, this cost must be factored into the overall pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that products meet required specifications involves rigorous QC processes. This can add costs but is essential for maintaining product integrity, especially for applications in scientific and industrial settings.
-
Logistics: Transporting quartz glass can be expensive, particularly for international shipments. Factors such as distance, shipping methods, and customs duties play a role in logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on supplier reputation, market demand, and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Sourcing of Crystal Quartz Glass?
Several factors can influence the pricing of crystal quartz glass:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchasing often leads to discounts. Suppliers may have minimum order quantities (MOQs), and buyers can negotiate better rates with higher volumes.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom sizes, shapes, and finishes can significantly affect pricing. Buyers should be clear about their specifications to receive accurate quotes.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO standards) can increase costs but are often necessary for applications in pharmaceuticals, optics, and other critical industries.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and production capabilities of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their reliability and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial. Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly impact the total cost.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Prices on Crystal Quartz Glass?
For B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation and cost management strategies can lead to better pricing:

Illustrative image related to crystal quartz glass
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider shipping, handling, and potential import taxes. A lower price may not always equate to a better deal when TCO is factored in.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If your organization regularly requires quartz glass, consider establishing a long-term relationship with a supplier to negotiate better rates based on consistent order volumes.
-
Be Transparent About Needs: Clearly communicate your requirements and any flexibility you may have regarding specifications. This can open up avenues for suppliers to propose cost-effective alternatives.
-
Research Market Trends: Stay informed about market trends and pricing fluctuations. Awareness of supply chain disruptions or changes in demand can give buyers leverage in negotiations.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a rapport with suppliers can lead to better terms. Suppliers are often more willing to negotiate with partners they trust.
Disclaimer Regarding Indicative Prices
Prices for crystal quartz glass can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. The figures provided are indicative and should be validated with suppliers for accurate quotations tailored to specific needs and market conditions. Always conduct thorough research and engage in detailed discussions to ensure the best possible sourcing outcomes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing crystal quartz glass With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternatives to Crystal Quartz Glass
In the realm of high-performance glass solutions, crystal quartz glass is renowned for its superior properties, including thermal stability, optical clarity, and chemical inertness. However, various alternatives exist that can meet specific needs across different industries. This analysis will compare crystal quartz glass with two viable alternatives: borosilicate glass and sapphire glass, providing B2B buyers with insights into their respective strengths and weaknesses.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Crystal Quartz Glass | Borosilicate Glass | Sapphire Glass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent thermal & optical properties; UV and IR transparency | Good thermal resistance; less optical clarity | Superior hardness; excellent thermal stability |
| Cost | Higher price point | Moderate cost | High cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized handling | Commonly available and easy to work with | Requires specialized manufacturing |
| Maintenance | Minimal; highly durable | Moderate; can be susceptible to thermal shock | Minimal; very durable and scratch-resistant |
| Best Use Case | High-temperature applications, spectroscopy | General laboratory use, chemical experiments | Optical devices, high-wear applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Borosilicate Glass
Borosilicate glass is a popular alternative due to its good thermal resistance and affordability. It is commonly used in laboratory glassware and is less prone to thermal shock compared to regular glass. However, while it offers decent optical clarity, it does not match the UV and IR transparency of crystal quartz glass. Additionally, borosilicate glass can be more susceptible to scratching and chemical interactions than quartz glass. Therefore, it is best suited for general laboratory applications where extreme conditions are not a primary concern.
Illustrative image related to crystal quartz glass
Sapphire Glass
Sapphire glass, known for its exceptional hardness and scratch resistance, provides superior durability in demanding environments. Its thermal stability is comparable to that of crystal quartz glass, making it suitable for high-temperature applications. However, sapphire glass comes with a higher price tag and requires specialized manufacturing processes, which can complicate sourcing and logistics. Its primary use cases include optical devices and high-wear applications where durability is paramount, but it may not be the best choice for applications requiring high optical clarity across the UV spectrum.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the right glass solution for your business, it is essential to consider the specific application requirements, budget constraints, and performance expectations. Crystal quartz glass excels in high-temperature and optical applications, making it ideal for scientific research and spectroscopy. Borosilicate glass serves well in general laboratory environments where cost-effectiveness is key, while sapphire glass is suited for high-durability needs in optical devices. By thoroughly evaluating these alternatives, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and enhance their product offerings.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for crystal quartz glass
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Crystal Quartz Glass?
Understanding the technical specifications of crystal quartz glass is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those involved in industries such as laboratories, optics, and manufacturing. Here are the essential properties to consider:

Illustrative image related to crystal quartz glass
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the purity and quality of the quartz glass, typically specified by its SiO₂ content. High-purity quartz glass, often exceeding 99.99% SiO₂, is crucial for applications in scientific research and optics where even minor impurities can affect results. Buyers should prioritize high-grade materials to ensure reliability and consistency in their applications.
2. Thermal Stability
Thermal stability indicates the ability of quartz glass to withstand high temperatures, often exceeding 1,200°C. This property is vital for applications involving high-temperature processes, such as those in laboratories and industrial settings. The low coefficient of thermal expansion ensures that the glass maintains its integrity under thermal stress, reducing the risk of breakage during critical operations.
3. Optical Transparency
Optical transparency is a measure of how well quartz glass transmits light across various wavelengths, including ultraviolet (UV), visible, and infrared spectrums. The exceptional clarity makes quartz glass ideal for optical instruments, such as lenses and cuvettes, where precise light transmission is necessary for accurate readings. For B2B buyers, this property is essential for applications in spectroscopy and photonics.
4. Chemical Inertness
Chemical inertness refers to the resistance of quartz glass to chemical reactions, making it suitable for handling corrosive substances and ensuring that the integrity of samples is preserved during analysis. This property is particularly important in laboratories where glassware must not react with acids, bases, or other chemicals. Buyers should ensure that the quartz glass they source is designed to withstand harsh chemical environments.
5. Mechanical Strength
Mechanical strength assesses the durability and robustness of quartz glass. With a Mohs hardness rating of around seven, quartz glass is significantly harder than ordinary glass, making it less prone to scratches and breaks. This durability is essential for applications requiring repeated use, such as laboratory equipment and industrial tools.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Crystal Quartz Glass?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some common terms that buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products or components that are marketed by another company under its brand name. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers who can provide customized quartz glass solutions tailored to specific applications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for buyers to understand pricing structures and inventory management, especially when sourcing quartz glass in bulk for large projects or production runs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price proposals from suppliers. It typically includes detailed specifications for the desired quartz glass products. This is an essential step for buyers to receive competitive quotes and evaluate different suppliers effectively.

Illustrative image related to crystal quartz glass
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand their obligations and the logistics involved in importing quartz glass from different regions, particularly when dealing with international suppliers.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the goods. For quartz glass, understanding lead time is essential for project planning and inventory management, particularly in industries where timely delivery can impact production schedules.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing crystal quartz glass, ensuring they select the right products for their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the crystal quartz glass Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends in the Crystal Quartz Glass Sector
The global market for crystal quartz glass is experiencing robust growth, fueled by a surge in demand across various industries, including electronics, telecommunications, and laboratory applications. Key drivers include the material’s unique properties, such as high thermal stability, optical clarity, and chemical inertness, which make it an ideal choice for high-performance applications. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions.
Emerging trends in the B2B landscape highlight the increasing integration of advanced technologies in the sourcing process. Digital platforms and e-commerce solutions are streamlining procurement, enabling buyers to access a wider array of suppliers and products. Additionally, the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, is enhancing supply chain efficiency and transparency, allowing businesses to better manage inventory and forecast demand.
Illustrative image related to crystal quartz glass
In regions like Germany and Saudi Arabia, there is a notable push towards innovative applications of crystal quartz glass, particularly in sectors such as renewable energy and advanced manufacturing. This shift is creating opportunities for suppliers to introduce new products tailored to specific industry needs. Furthermore, as global competition intensifies, buyers must prioritize quality and reliability to maintain a competitive edge, making supplier relationships critical in the sourcing process.
How is Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Crystal Quartz Glass Industry?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of modern B2B procurement strategies, particularly in the crystal quartz glass sector. The environmental impact of sourcing practices is under scrutiny, prompting buyers to seek suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. This includes evaluating the sourcing of raw materials, energy consumption during production, and waste management processes.
Ethical supply chains are gaining traction as businesses recognize the importance of social responsibility. Buyers are increasingly looking for partners that not only meet quality standards but also demonstrate commitment to ethical labor practices and environmental stewardship. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other ‘green’ certifications play a pivotal role in establishing credibility and trust among buyers.
Moreover, as consumers become more environmentally conscious, B2B buyers must align their sourcing practices with these values to enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty. This includes exploring recycled or sustainably sourced materials in the production of crystal quartz glass, which can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with manufacturing processes.
What is the Brief Evolution/History of Crystal Quartz Glass in B2B Applications?
The evolution of crystal quartz glass dates back to its early applications in scientific and industrial contexts, where its unique properties were first recognized. As technology advanced, particularly in the fields of optics and telecommunications, the demand for high-purity quartz glass surged. Innovations in production techniques have allowed for the creation of various forms, including fused quartz and fused silica, catering to specialized applications across different industries.
Over the years, the versatility of crystal quartz glass has expanded, finding applications in areas such as semiconductor manufacturing, laboratory equipment, and even renewable energy technologies. This evolution reflects not only advancements in material science but also the growing recognition of quartz glass as a critical component in achieving high-performance outcomes in modern applications. As industries continue to evolve, the role of crystal quartz glass is likely to expand, presenting ongoing opportunities for B2B buyers to leverage its unique properties.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of crystal quartz glass
-
How do I ensure the quality of crystal quartz glass when sourcing internationally?
To ensure quality, start by verifying supplier certifications, such as ISO standards, which indicate adherence to international quality management systems. Request detailed product specifications, including purity levels and thermal stability data. Additionally, consider arranging third-party inspections or sample testing to assess the material’s properties before placing a bulk order. Building a solid relationship with suppliers through regular communication can also help maintain quality control throughout the sourcing process. -
What is the best type of crystal quartz glass for high-temperature applications?
For high-temperature applications, fused quartz glass is recommended due to its exceptional thermal stability and ability to withstand temperatures exceeding 1,200°C. This type of quartz glass is ideal for laboratory equipment like crucibles and evaporating dishes, where heat resistance is crucial. Ensure that the supplier provides detailed specifications regarding the material’s thermal properties to confirm its suitability for your specific application. -
How can I customize my order of crystal quartz glass?
Most suppliers offer customization options, including specific dimensions, shapes, and finishes. To initiate the customization process, communicate your requirements clearly, including the intended application and any technical specifications needed. It’s also beneficial to discuss minimum order quantities (MOQ) for custom products, as these may differ from standard items. Ensure you receive a prototype or sample for approval before finalizing your order. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for crystal quartz glass?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the supplier and product type. Generally, MOQs for crystal quartz glass range from 10 to 100 units, depending on the complexity and customization of the product. When negotiating, inquire about any flexibility in the MOQ, especially if you are a new buyer or looking to test the market with smaller orders. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing crystal quartz glass internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region, but common practices include a 30% deposit upon order confirmation and the remaining balance prior to shipment. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or payment upon delivery. It’s advisable to clarify payment terms upfront and consider using secure payment methods to protect your transaction. Always review the terms of trade, including currency and potential fees, before finalizing the agreement. -
How do I vet suppliers of crystal quartz glass for reliability?
To vet suppliers, start by researching their business history, customer reviews, and industry reputation. Request references from previous clients and verify their experience in exporting to your region. Conduct background checks on their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Engaging in direct communication can also provide insights into their responsiveness and willingness to meet your needs. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing crystal quartz glass?
When importing crystal quartz glass, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations specific to your country. Work with a logistics partner experienced in handling fragile materials to ensure safe transportation. Understand the associated costs, including shipping, insurance, and customs duties, to avoid unexpected expenses. Additionally, confirm the supplier’s packaging standards to minimize the risk of damage during transit. -
How can I address potential issues with crystal quartz glass quality after purchase?
If you encounter quality issues after receiving your order, promptly document the discrepancies with photographs and detailed descriptions. Contact the supplier immediately to discuss your concerns and refer to the warranty or return policy outlined in your agreement. Most reputable suppliers will work with you to resolve the issue, whether through replacements, refunds, or further quality assurance measures. Maintaining open communication is key to addressing any post-purchase challenges effectively.
Top 3 Crystal Quartz Glass Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Crystran – Crystal Quartz Z-cut Window
Domain: crystran.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Crystal Quartz Z-cut Window”, “Dimensions”: “20mm diameter x 2mm thickness”, “Optical Finish”: “Polished”, “Product Code”: “QPZ20-2”, “Price”: “£39.90”, “Stock Level”: “15 in stock”, “Contact Information”: {“Phone”: “+44 (0) 1202 307650”, “Email”: “[email protected]”}, “Discount Information”: “Available for order quantities of 10 or more”, “Company Information”: {“Name”: “Crystr…
2. PGO Online – Fused Silica vs. Fused Quartz
Domain: pgo-online.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Fused Silica vs. Fused Quartz: Fused Silica is an optical-grade synthetic quartz glass made from high-purity silica powder, offering high light transmission (over 80% at 185 nm) and superior optical properties. Fused Quartz is made from natural quartz crystals, has moderate purity, lower light transmission in the UVC range, and is suitable for less demanding applications like sight glasses. Fused …
3. eBay – Handcrafted Clear Quartz Crystal Glass Knife
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Handcrafted Clear Quartz Crystal Glass Knife 10” – Black Thread Wrapped Athame, Brand New, $80.00 or Best Offer, Free delivery, Located in India; 10″ Clear Quartz Crystal Glass Arrowhead, Geometric Sculpture, Mystical Spearhead, Brand New, $68.00 or Best Offer, Free delivery, Located in India; OFFICIAL DICYANIN AURA GLASSES, reiki crystal hunting, ghost healing, evp psychic, Brand New, $59.99 or B…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for crystal quartz glass
As the demand for crystal quartz glass continues to rise across diverse industries, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical component for international B2B buyers. This material’s unparalleled properties—such as thermal stability, chemical inertness, and optical transparency—make it an indispensable choice for applications in laboratory glassware, semiconductor manufacturing, and optical devices.
For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of sourcing high-quality quartz glass can lead to significant competitive advantages. Establishing relationships with reliable suppliers not only ensures access to superior materials but also fosters innovation and enhances product reliability.

Illustrative image related to crystal quartz glass
Looking ahead, the global landscape for crystal quartz glass is poised for growth. Buyers are encouraged to leverage partnerships with manufacturers that prioritize quality and sustainability. By doing so, businesses can not only meet current demands but also position themselves at the forefront of technological advancements in their respective fields. Now is the time to act—invest in strategic sourcing of crystal quartz glass to unlock new opportunities and drive your business forward.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.