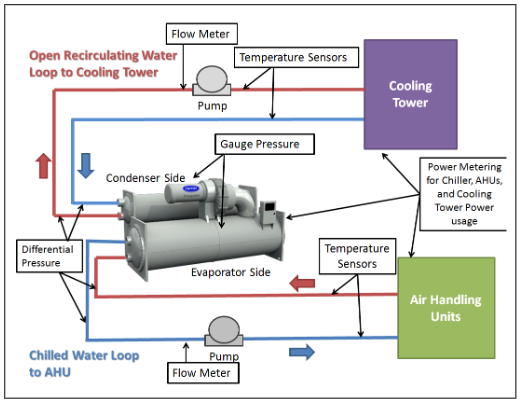
Is Your Condenser And Chiller Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read This 2025 Report
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for condenser and chiller
Navigating the complex landscape of the global market for condensers and chillers presents a formidable challenge for B2B buyers, especially those sourcing efficient HVAC solutions in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As the demand for reliable cooling systems grows, understanding the various types, applications, and technologies available becomes critical. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the world of condensers and chillers, providing insights into essential factors such as supplier vetting, cost considerations, and maintenance practices.
Through a detailed exploration of water-cooled and air-cooled systems, along with their specific applications in commercial and industrial settings, this guide equips international buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are operating in the bustling markets of Nigeria or the energy-rich sectors of Saudi Arabia, understanding the intricacies of these cooling systems will empower you to optimize operational efficiency and enhance your business’s sustainability.
By addressing key challenges, such as ensuring system reliability and minimizing operational costs, this guide serves as a valuable resource for decision-makers. Equip yourself with actionable insights that will streamline your procurement process and elevate your competitive edge in the global market for condensers and chillers.
Understanding condenser and chiller Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air-Cooled Chillers | Use ambient air for cooling; compact and easy to install. | Small to medium commercial buildings. | Pros: Lower initial costs; minimal water use. Cons: Less efficient in hot climates; higher operational costs. |
| Water-Cooled Chillers | Utilize water from cooling towers; higher efficiency rates. | Large industrial facilities and data centers. | Pros: High efficiency; better performance in large applications. Cons: Higher installation costs; requires water source. |
| Scroll Chillers | Use a scroll compressor; quieter operation and compact size. | Hospitals, hotels, and commercial spaces. | Pros: Energy-efficient; low maintenance. Cons: Limited capacity range; potentially higher upfront costs. |
| Centrifugal Chillers | Use centrifugal force; suitable for large cooling loads. | Large commercial and industrial applications. | Pros: High efficiency at large capacities; scalable. Cons: Complex installation; higher upfront investment. |
| Absorption Chillers | Utilize heat sources instead of electricity; eco-friendly. | Areas with waste heat or solar energy. | Pros: Reduced electricity costs; environmentally friendly. Cons: Lower efficiency; requires a heat source. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Air-Cooled Chillers?
Air-cooled chillers are designed to dissipate heat through ambient air, making them ideal for small to medium commercial buildings. Their compact design allows for easy installation, and they require minimal maintenance. However, their efficiency can decline in high-temperature environments, leading to increased operational costs. B2B buyers should consider their location and climate when evaluating air-cooled chillers, as they may not be the best choice for hotter regions where cooling demand is high.
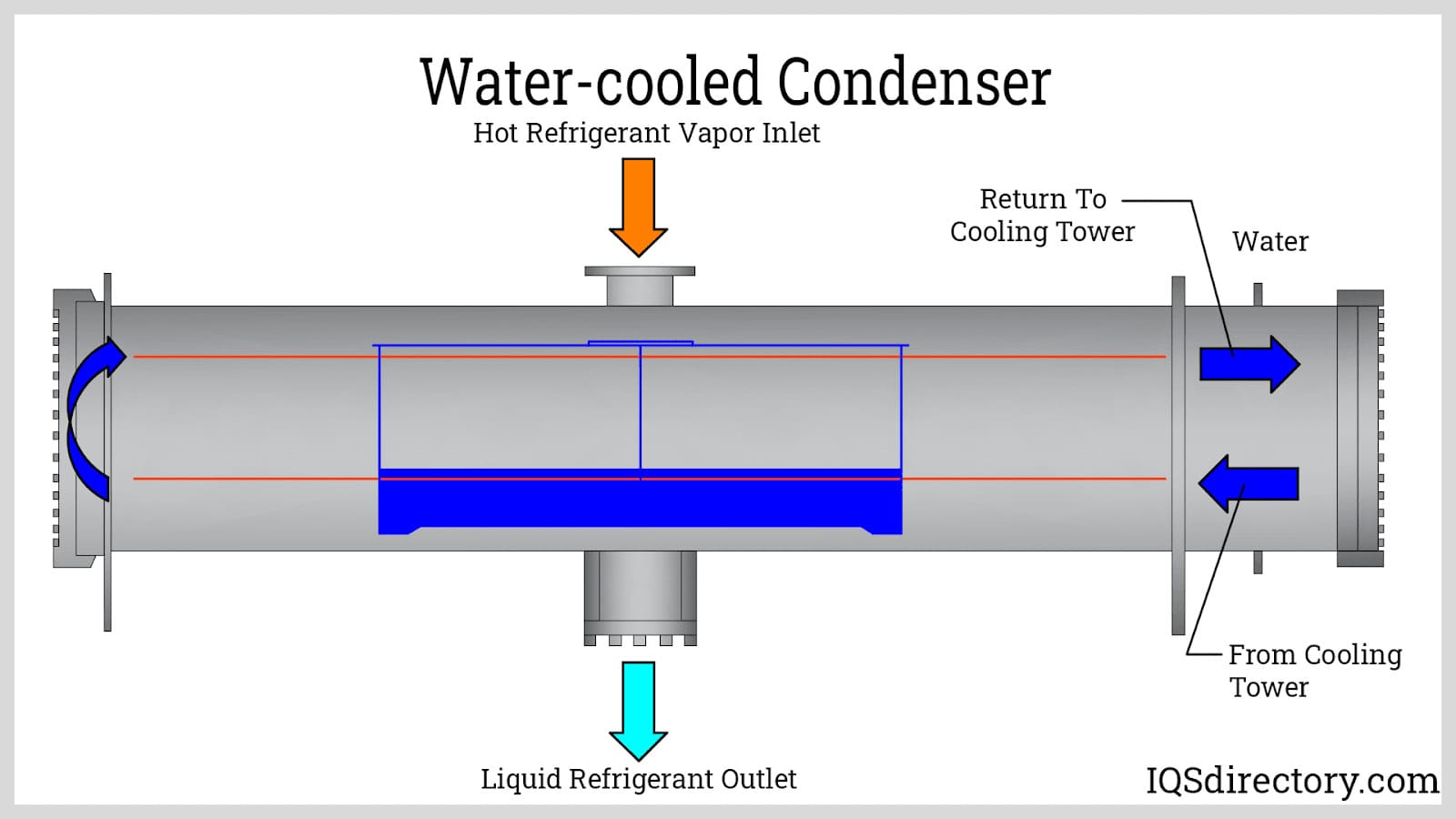
How Do Water-Cooled Chillers Stand Out in Efficiency?
Water-cooled chillers are distinguished by their reliance on water from cooling towers, which allows them to achieve higher efficiency levels compared to air-cooled models. They are particularly suitable for large industrial facilities and data centers where cooling demands are significant. While they offer superior performance, B2B buyers must factor in the higher installation costs and the need for a reliable water source. Understanding the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and water usage, is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
What Advantages Do Scroll Chillers Offer for Commercial Spaces?
Scroll chillers are characterized by their use of scroll compressors, leading to quieter operations and a more compact design. They are particularly well-suited for hospitals, hotels, and commercial spaces that prioritize noise reduction and energy efficiency. Although they may come with higher upfront costs, their low maintenance requirements and energy efficiency can result in long-term savings. Buyers should evaluate their specific cooling needs and budget constraints when considering scroll chillers.
Why Choose Centrifugal Chillers for Large Applications?
Centrifugal chillers utilize centrifugal force to achieve cooling, making them ideal for large commercial and industrial applications with significant cooling loads. They are known for their high efficiency at scale, allowing for cost-effective operation in large facilities. However, the complexity of their installation and higher initial investment can be a barrier for some buyers. Organizations should assess their cooling requirements and future scalability when considering centrifugal chillers.
What Makes Absorption Chillers an Eco-Friendly Option?
Absorption chillers operate using heat sources instead of electricity, making them an environmentally friendly option for areas with access to waste heat or solar energy. They are particularly beneficial in reducing electricity costs and can be a sustainable choice for businesses focused on green initiatives. However, absorption chillers typically have lower efficiency levels compared to traditional electric chillers and require a consistent heat source. B2B buyers should evaluate their energy sources and sustainability goals when considering this option.
Key Industrial Applications of condenser and chiller
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of condenser and chiller | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| HVAC & Building Services | Commercial building climate control | Enhanced occupant comfort and energy efficiency | Reliability, energy efficiency ratings, and maintenance services |
| Food & Beverage | Process cooling for production lines | Improved product quality and safety | Compliance with health regulations and efficiency standards |
| Petrochemical | Cooling in refining processes | Increased operational efficiency and safety | Durability under high-pressure conditions and material compatibility |
| Pharmaceuticals | Temperature control for sensitive products | Ensured product integrity and compliance | Precision in temperature management and regulatory compliance |
| Data Centers | Cooling for IT infrastructure | Enhanced equipment lifespan and performance | Scalability, energy efficiency, and redundancy features |
How is ‘Condenser and Chiller’ Used in HVAC & Building Services?
In the HVAC sector, condensers and chillers are essential for maintaining optimal indoor climates in commercial buildings. They work together to remove heat from the indoor environment, ensuring comfort for occupants while optimizing energy use. International buyers, particularly in regions with extreme climates like the Middle East or Africa, should prioritize energy efficiency ratings and reliability to mitigate operational costs and enhance system longevity.
What Role Do Condensers and Chillers Play in the Food & Beverage Industry?
In food and beverage production, condensers and chillers are crucial for process cooling, ensuring that products are maintained at safe temperatures throughout manufacturing. This application enhances product quality and extends shelf life, which is vital for compliance with health regulations. Buyers should consider equipment that meets local health standards and offers high efficiency to minimize energy costs, especially in regions like South America where energy prices may fluctuate.
Why Are Condensers and Chillers Important in the Petrochemical Sector?
In the petrochemical industry, condensers and chillers are employed in refining processes to manage heat and maintain the integrity of chemical reactions. This application not only increases operational efficiency but also enhances safety by preventing overheating. Buyers in this sector must focus on sourcing durable equipment capable of withstanding high-pressure conditions and corrosive environments, which is particularly relevant in regions with demanding operational requirements.
How Do Condensers and Chillers Benefit the Pharmaceutical Industry?
For the pharmaceutical sector, maintaining precise temperature control is critical for the integrity of sensitive products. Condensers and chillers ensure that products are stored and processed at the required temperatures, safeguarding efficacy and compliance with stringent regulations. Buyers should seek equipment that offers precise temperature management capabilities and robust compliance documentation, especially in regions like Europe where regulatory scrutiny is high.
What Advantages Do Condensers and Chillers Provide to Data Centers?
In data centers, condensers and chillers are vital for cooling IT infrastructure, preventing overheating that can lead to equipment failure. This application not only enhances the lifespan of critical hardware but also improves overall performance. Buyers should look for scalable solutions that offer energy efficiency and redundancy features, which are essential for maintaining uptime in increasingly data-dependent markets across Africa and the Middle East.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘condenser and chiller’ & Their Solutions
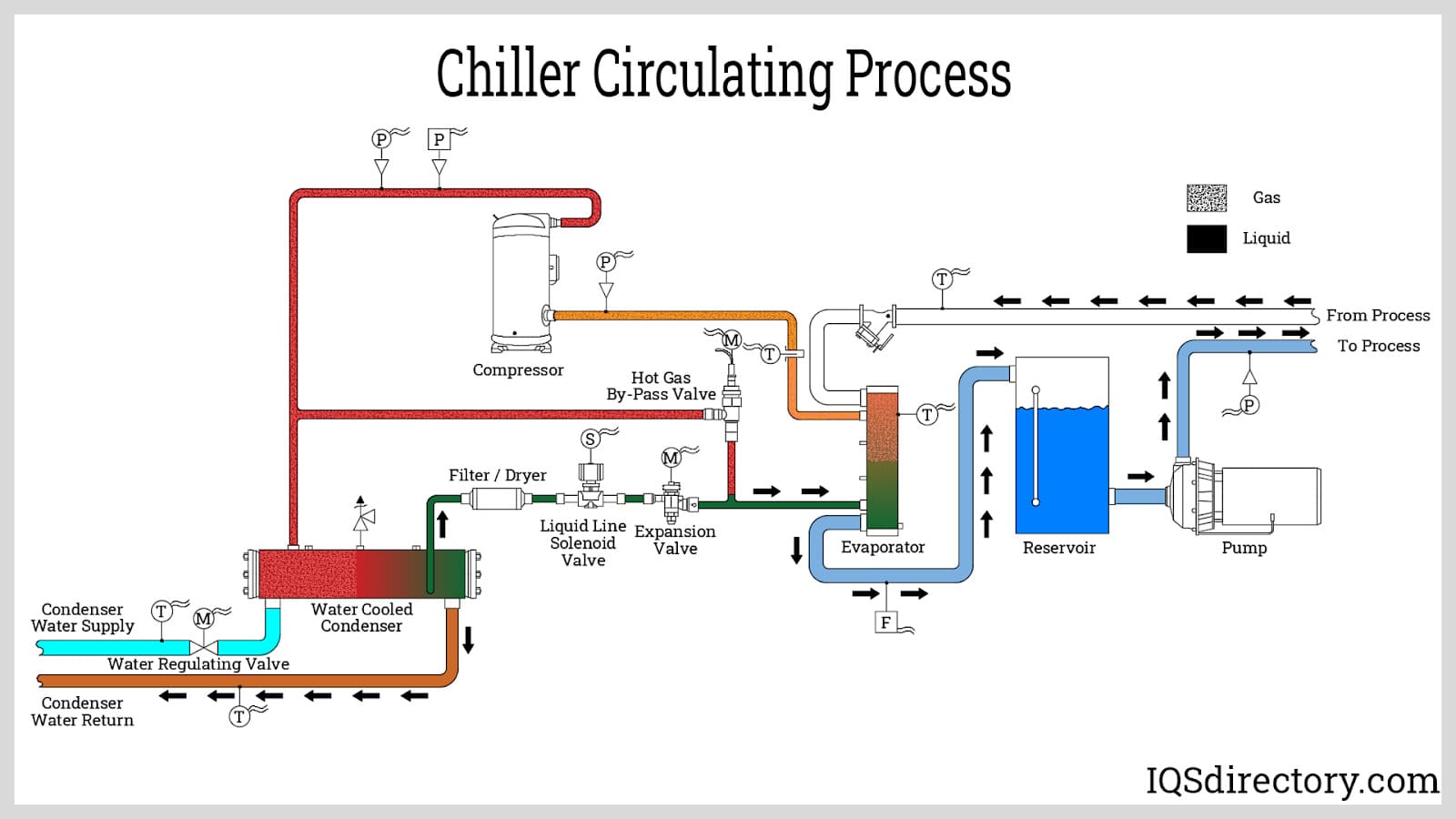
Scenario 1: Inefficient Heat Rejection Leading to Increased Operational Costs
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter significant challenges when their chillers and condensers fail to reject heat effectively. This inefficiency can arise from various factors, including fouling within the condenser tubes, incorrect installation, or inadequate system design. In regions with high ambient temperatures, such as the Middle East and Africa, the inability to efficiently dissipate heat can lead to higher energy consumption, resulting in increased operational costs. Moreover, prolonged inefficiencies can lead to equipment failures and costly repairs, disrupting business operations.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, it is essential to conduct regular maintenance and cleaning of condenser tubes to prevent fouling. Implementing a rigorous cleaning schedule, including chemical cleaning agents like Rydlyme, can help remove scale, dirt, and biological growth that impede heat transfer. Additionally, consider investing in a comprehensive thermal imaging analysis to identify hot spots and areas of poor heat exchange. This proactive approach allows for targeted maintenance and ensures optimal performance. When sourcing chillers and condensers, prioritize models that are designed for high ambient conditions and have efficient heat exchange capabilities. Collaborate with manufacturers or service providers who offer maintenance contracts that include regular inspections and cleanings to sustain efficiency over the long term.
Scenario 2: Complex Installation and Integration Challenges
The Problem: B2B buyers often face complexities during the installation and integration of chillers and condensers into existing HVAC systems. These challenges can stem from compatibility issues with existing equipment, misalignment in system specifications, or lack of skilled technicians for installation. In regions with emerging markets, such as Nigeria or South America, the lack of experienced professionals can exacerbate these issues, leading to delays and increased costs.
The Solution: To address these challenges, engage with suppliers early in the project to ensure that the selected chillers and condensers are compatible with existing systems. Detailed site assessments should be conducted to understand specific requirements and constraints. Moreover, consider employing a project manager with experience in HVAC systems to oversee the integration process. This individual can ensure that installation follows best practices and that the system is calibrated correctly. Investing in training programs for local technicians can also enhance installation efficiency and reduce reliance on external specialists. By preparing thoroughly and ensuring clear communication with suppliers, buyers can streamline the installation process and avoid costly pitfalls.
Illustrative image related to condenser and chiller
Scenario 3: Lack of Real-Time Monitoring Leading to Downtime
The Problem: In many industrial and commercial settings, the absence of real-time monitoring systems for chillers and condensers can lead to unanticipated downtimes. Without proper monitoring, businesses may not detect inefficiencies or malfunctions until they escalate into significant issues. This lack of oversight can be particularly detrimental in sectors like food processing and pharmaceuticals, where temperature control is crucial.
The Solution: To combat this issue, implement advanced monitoring solutions that provide real-time data on the performance of chillers and condensers. Invest in IoT-enabled sensors that can track temperature, pressure, and flow rates, alerting facility managers to any deviations from optimal performance. This technology enables proactive maintenance, allowing for quick interventions before minor issues escalate into major failures. Additionally, establish a routine review process for monitoring data to identify patterns and trends that may indicate underlying problems. By leveraging technology and data analytics, B2B buyers can enhance operational reliability and reduce the risk of unexpected downtimes, ultimately protecting their bottom line.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for condenser and chiller
What Are the Key Materials Used in Condensers and Chillers?
Selecting the right materials for condensers and chillers is crucial for optimizing performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of these systems: copper, stainless steel, aluminum, and carbon steel. Each material has unique properties, advantages, and limitations that can significantly impact application performance.
How Does Copper Perform in Condenser and Chiller Applications?
Copper is widely recognized for its excellent thermal conductivity, making it a preferred choice for heat exchangers. It can handle high temperatures and pressures, with a melting point of approximately 1,984°F (1,085°C). Copper is also resistant to corrosion, particularly in water-based applications, which is essential for maintaining efficiency over time.
Pros: Copper’s high thermal conductivity ensures efficient heat transfer, while its resistance to corrosion enhances longevity. It is relatively easy to fabricate, allowing for complex designs.
Cons: The primary drawback of copper is its cost, which is generally higher than that of other materials. Additionally, it can be susceptible to pitting corrosion in certain water conditions.
Impact on Application: Copper is highly compatible with refrigerants and water, making it suitable for a variety of cooling applications. However, users must consider water quality to avoid corrosion issues.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B280 for copper tubes is essential. Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should also consider local water quality and its effects on copper’s performance.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Condenser and Chiller Systems?
Stainless steel is favored for its strength and corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments. It can withstand high pressures and temperatures, making it suitable for both water-cooled and air-cooled systems. With a melting point of around 2,500°F (1,370°C), stainless steel is robust under extreme conditions.

Illustrative image related to condenser and chiller
Pros: Its durability and resistance to corrosion make stainless steel a long-lasting choice. It is also non-reactive, ensuring compatibility with various refrigerants and fluids.
Cons: The primary disadvantage is its higher cost compared to carbon steel and aluminum. Additionally, stainless steel can be more challenging to fabricate, leading to increased manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for applications requiring high durability and resistance to corrosive environments, such as coastal areas in Africa and the Middle East.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A312 for stainless steel pipes is crucial. Buyers should also be aware of the specific grades of stainless steel that best suit their application needs.
How Does Aluminum Compare for Condenser and Chiller Use?
Aluminum is lightweight and offers good thermal conductivity, making it a popular choice for certain chiller applications. It typically operates well in moderate temperature ranges, with a melting point of about 1,221°F (660°C).
Illustrative image related to condenser and chiller
Pros: Its lightweight nature reduces transportation costs, and it is generally less expensive than copper and stainless steel. Aluminum also resists corrosion, particularly when anodized.
Cons: While aluminum has decent thermal conductivity, it is not as effective as copper. It can also be less durable under high-pressure conditions.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications where weight is a concern, such as portable chillers. However, it may not be ideal for high-pressure systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. Local environmental conditions may also affect the choice of aluminum alloys.
What Advantages Does Carbon Steel Offer in Condenser and Chiller Systems?
Carbon steel is known for its strength and cost-effectiveness, making it a common choice for large-scale applications. It can handle high pressures and temperatures, with a melting point around 2,500°F (1,370°C).
Illustrative image related to condenser and chiller
Pros: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its low cost and high strength, making it suitable for large, industrial applications. It is also widely available and easy to fabricate.
Cons: Carbon steel is prone to corrosion, especially in humid or wet environments, which can lead to maintenance issues over time. It also has lower thermal conductivity compared to copper and aluminum.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is often used in applications where budget constraints are a primary concern, but users must implement effective corrosion protection measures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A106 for carbon steel pipes is important. Buyers should also consider local environmental factors that may affect corrosion rates.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Condensers and Chillers
| Material | Typical Use Case for condenser and chiller | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Heat exchangers in chillers | Excellent thermal conductivity | Higher cost; susceptible to corrosion | High |
| Stainless Steel | High-pressure applications | Durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost; complex fabrication | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight portable chillers | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower thermal conductivity; less durable | Medium |
| Carbon Steel | Large industrial applications | Cost-effective and strong | Prone to corrosion; lower thermal conductivity | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials used in condensers and chillers, enabling informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional considerations.
Illustrative image related to condenser and chiller
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for condenser and chiller
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Condensers and Chillers?
The manufacturing process for condensers and chillers involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets stringent performance and quality standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess the capabilities of potential suppliers.
1. Material Preparation
The first stage in manufacturing condensers and chillers is material preparation, where high-quality materials are sourced. Common materials include copper, aluminum, and stainless steel for tubing and components due to their thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. Suppliers often conduct rigorous material inspections to verify compliance with international standards such as ASTM or EN specifications. This phase may also involve the pre-treatment of metals to enhance adhesion for coatings or improve corrosion resistance.
2. Forming Techniques Used in Condenser and Chiller Manufacturing
Once materials are prepared, they undergo various forming techniques. These can include:
- Extrusion: For creating tubing and profiles with consistent cross-sections.
- Bending and Shaping: Tubes are bent to precise angles and shapes, often using CNC machines to ensure accuracy.
- Welding: Different components are joined using techniques such as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) or MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, particularly for joining the condenser tubes to the headers. This process is crucial for maintaining the integrity and efficiency of heat exchange.
Each forming technique must adhere to strict tolerances to ensure that the components fit together seamlessly during assembly.
3. Assembly Process for Efficient Heat Exchange
The assembly phase is where the individual components come together to form the final product. This process includes:
- Component Integration: The assembly of compressors, evaporators, and condensers into a cohesive unit. This may involve the use of jigs and fixtures to ensure proper alignment.
- Sealing and Insulation: Gaskets and insulation materials are added to minimize energy losses and prevent condensation. The choice of sealing materials is critical, as they must withstand various operating conditions.
Skilled technicians oversee the assembly to ensure that each unit meets the design specifications and operates efficiently.
4. Finishing Techniques to Enhance Durability
The final manufacturing stage involves finishing processes that enhance the durability and aesthetic appeal of the product. Common finishing techniques include:
- Coating: Applying protective coatings such as epoxy or powder coating to prevent corrosion and improve aesthetics.
- Painting: For outdoor units, weather-resistant paints are used to enhance durability against environmental factors.
- Quality Polishing: This may be done to improve the surface finish, particularly for visible components.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential in Manufacturing Condensers and Chillers?
Quality assurance is critical in the manufacturing of condensers and chillers to ensure reliability and efficiency. B2B buyers should be familiar with relevant quality control measures and international standards.
International Standards and Certifications
Manufacturers often adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems, and CE marking, which indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards within the European Economic Area. Additionally, standards set by the American Petroleum Institute (API) may apply for specific applications in industrial settings.
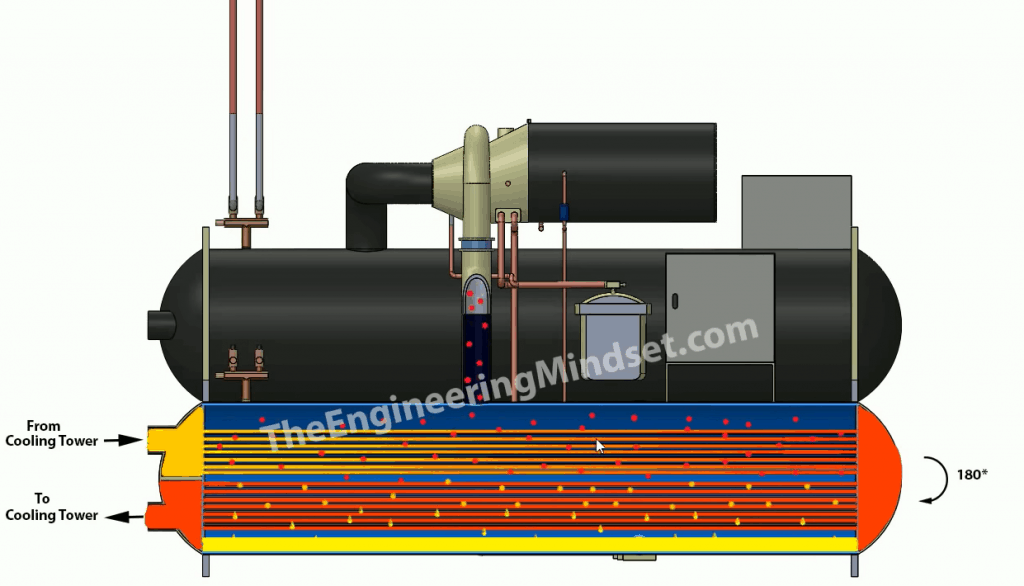
Illustrative image related to condenser and chiller
Key Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is integrated at various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before they enter the manufacturing process.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections are conducted to verify that processes are being followed and that products are being produced according to specifications.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, the final products undergo comprehensive testing, which may include:
-
Pressure Testing: To ensure that refrigerant systems can withstand operational pressures without leaks.
- Performance Testing: Chillers and condensers are tested for efficiency and cooling capacity under simulated operating conditions.
- Visual Inspections: For surface defects and assembly integrity.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are actionable steps buyers can take:
Supplier Audits and Inspections
Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into a manufacturer’s quality control processes. Buyers should look for:
- Documentation: Review quality control documentation, including inspection records and test results.
- Certifications: Verify that the supplier holds relevant certifications and adheres to international standards.
- Quality Management Practices: Assess the effectiveness of their quality management system, including employee training programs and process improvement initiatives.
Requesting Quality Reports and Certifications
Buyers should request copies of quality reports and certifications from suppliers. This may include:
- ISO Certification: Proof of compliance with ISO 9001 or other relevant standards.
- Test Reports: Documentation of performance tests and material certifications.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging a third-party inspection service can provide an unbiased assessment of the product quality.
What Are the Common Challenges in Quality Assurance for International Buyers?
International buyers may face unique challenges regarding quality assurance, especially when sourcing from different regions. These challenges include:

Illustrative image related to condenser and chiller
- Regulatory Differences: Variations in regulatory requirements across countries can complicate compliance.
- Cultural and Language Barriers: Misunderstandings in specifications or requirements can lead to quality issues.
- Logistical Challenges: Transporting equipment across borders may introduce risks of damage or quality degradation.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for condensers and chillers is essential for B2B buyers. By familiarizing themselves with the stages of manufacturing, international standards, and effective quality control practices, buyers can make informed decisions that ensure they source reliable, high-quality products suitable for their specific needs. This knowledge not only aids in supplier selection but also enhances the long-term performance and efficiency of their cooling systems.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘condenser and chiller’
Introduction
This guide provides a step-by-step checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure condensers and chillers. Understanding the complexities of these HVAC components is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This checklist will help streamline the sourcing process, ensuring that you select the right equipment and supplier for your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining your technical requirements. This includes the cooling capacity, type of refrigerant, and efficiency ratings relevant to your operational context. Knowing these specifications helps in narrowing down options and ensures compatibility with your existing systems.
- Cooling Capacity: Determine the required BTU/hr or kW for your application.
- Refrigerant Type: Choose between options like R-410A or R-134A based on regulatory requirements in your region.
Step 2: Assess Energy Efficiency Ratings
Evaluate the energy efficiency of the condensers and chillers under consideration. Look for models with high Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) or Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) ratings, as these can significantly reduce operating costs over time.
- Cost Savings: Higher efficiency often translates to lower energy bills, which is crucial for long-term budgeting.
- Environmental Impact: Energy-efficient units often align with sustainability goals, reducing your carbon footprint.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers before making a commitment. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and service quality.
- Supplier Reputation: Look for established suppliers with positive reviews and a strong track record in your industry.
- After-Sales Support: Assess their customer service and support options, including warranties and service agreements.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Local Regulations
Ensure that the condensers and chillers you consider comply with local and international regulations. This includes certifications like ISO, CE, or ASHRAE standards that guarantee product safety and performance.
- Regulatory Compliance: Non-compliance can lead to fines, operational delays, and increased liability.
- Market Acceptance: Products meeting recognized standards are more likely to be accepted in various markets, facilitating smoother operations.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, request detailed quotations that include pricing, delivery timelines, and installation costs. A comprehensive quote allows for better budget planning and aids in comparing different offers.
- Transparent Pricing: Ensure that the quote breaks down all costs to avoid hidden fees later.
- Lead Times: Confirm delivery times to align with your project schedules.
Step 6: Plan for Installation and Maintenance
Consider the logistics of installation and ongoing maintenance. Discuss installation services with your supplier and inquire about maintenance contracts that can keep your equipment operating efficiently.
- Installation Expertise: Ensure that the supplier can provide skilled technicians for proper setup.
- Maintenance Plans: Regular maintenance is essential for longevity; inquire about preventive maintenance options.
Step 7: Conduct a Final Review Before Purchase
Before finalizing your purchase, conduct a thorough review of all gathered information. Reassess your specifications against the proposed solutions to ensure alignment.
- Cross-Check Documentation: Verify that all necessary documentation, including warranties and service agreements, is in order.
- Decision-Making: Engage stakeholders to ensure consensus on the final decision, minimizing risks associated with the purchase.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed, strategic decisions when sourcing condensers and chillers, ensuring they select the best solutions for their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for condenser and chiller Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics for condensers and chillers is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis delves into the various cost components, influential pricing factors, and strategic tips for buyers seeking to optimize their procurement processes.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Chiller and Condenser Sourcing?
-
Materials: The primary materials used in manufacturing condensers and chillers include copper, aluminum, and various alloys, which are essential for thermal conductivity and structural integrity. The cost of these raw materials can fluctuate based on global market trends, affecting overall pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region and can be a major component of the total cost. Skilled labor is often required for manufacturing, assembly, and installation, particularly for customized solutions. Understanding local wage standards is essential for accurate cost forecasting.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility operations, utilities, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs, making it critical to assess suppliers’ operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling: Specialized tooling may be required for specific designs or customizations, impacting initial costs. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs, especially when considering custom specifications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are necessary to ensure product reliability and compliance with international standards. These processes incur additional costs, but they are crucial for maintaining product integrity and reducing long-term maintenance expenses.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary widely based on the distance from the manufacturer to the buyer, as well as the chosen Incoterms. Understanding these logistics costs is vital for total cost calculations.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on their market position, production capacity, and demand for specific products. Buyers should be aware of typical margins in the industry to gauge fair pricing.
What Pricing Influencers Should Buyers Consider?
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often attract discounts, making it essential for buyers to assess their purchasing strategy. Negotiating MOQs can lead to more favorable pricing structures.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-designed chillers and condensers usually come at a premium. Buyers should evaluate whether standard models can meet their needs to avoid unnecessary costs.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and products with recognized certifications (such as ASME, ISO, or CE) may command higher prices but can offer better performance and longevity, thus impacting the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and financial stability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers might have higher upfront costs but can offer better service and lower risks over time.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping (e.g., FOB, CIF) is critical as they determine who bears the risk and cost at various stages of transportation. Buyers should choose terms that align with their logistical capabilities and financial considerations.
What Negotiation and Cost-Efficiency Tips Can Buyers Use?
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: Buyers should consolidate orders to maximize volume discounts and negotiate better terms with suppliers.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the initial purchase price, but also installation, maintenance, and operational costs. A lower upfront cost may not result in long-term savings if quality is compromised.
-
Engage in Strategic Supplier Relationships: Building long-term relationships with reliable suppliers can lead to better pricing, improved service, and more favorable terms.
-
Be Aware of Regional Variations: Buyers should understand the economic conditions of their region, as these can affect pricing and availability. For example, international shipping costs may vary significantly between regions, impacting the final price.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: When sourcing, ask for itemized quotes that break down all cost components. This transparency can help in negotiations and in understanding where potential savings may lie.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure and pricing dynamics for condensers and chillers can empower international B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. By considering the key cost components, influential pricing factors, and effective negotiation strategies, buyers can optimize their sourcing processes and achieve better financial outcomes.

Illustrative image related to condenser and chiller
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing condenser and chiller With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Condensers and Chillers
In the realm of HVAC solutions, condensers and chillers are widely recognized for their effectiveness in managing heat and cooling environments. However, several alternative technologies can also achieve similar cooling objectives. Evaluating these alternatives can help B2B buyers determine the most suitable option for their specific operational needs and budget constraints.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Condenser and Chiller | Evaporative Cooling Systems | Heat Pumps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in large-scale cooling; ideal for commercial use. | Effective for moderate climates; performance drops in high humidity. | Versatile; provides both heating and cooling; efficient in moderate climates. |
| Cost | High initial investment; ongoing operational costs can be significant. | Lower initial costs; reduced energy costs, but may require water source. | Moderate initial investment; potential savings on energy bills over time. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional installation; complex integration with existing systems. | Simpler installation; can be added to existing systems with minimal disruption. | Installation can be complex depending on the system type; may require retrofitting. |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance for optimal performance; can be costly. | Minimal maintenance; occasional water treatment needed to prevent scaling. | Regular maintenance required; fewer issues if properly installed. |
| Best Use Case | Large commercial buildings, industrial applications, or data centers. | Suitable for warehouses, factories, and areas with dry climates. | Ideal for residential and commercial applications needing both heating and cooling. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Evaporative Cooling Systems
Evaporative cooling systems utilize the natural process of water evaporation to cool the air. These systems are particularly effective in hot, dry climates where humidity is low. The initial costs are generally lower than those associated with chillers and condensers, and they can significantly reduce energy consumption. However, their performance can decline in high-humidity environments, making them less effective in certain regions. Additionally, they require a consistent water supply and regular maintenance to prevent mineral buildup and ensure optimal performance.
Heat Pumps
Heat pumps are versatile systems that can provide both heating and cooling by transferring heat rather than generating it. This dual functionality makes them an attractive option for businesses looking to optimize energy efficiency throughout the year. While the initial investment for heat pumps can be moderate, they often lead to lower operational costs due to their energy efficiency. However, their effectiveness can diminish in extremely cold climates, and installation can be complex, particularly in retrofitting existing systems.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between condensers, chillers, and alternative cooling solutions, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including the specific cooling requirements of their operations, initial and ongoing costs, and the climate of their location. Understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each option can help businesses make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budget constraints. Engaging with HVAC professionals can also provide valuable insights tailored to specific applications, ensuring optimal system performance and efficiency.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for condenser and chiller
Understanding the technical properties and terminology associated with condensers and chillers is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse international markets. This knowledge not only aids in selecting the right equipment but also ensures effective communication with suppliers and partners. Below is a detailed exploration of critical specifications and common trade terms relevant to condensers and chillers.
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Condensers and Chillers?
-
Material Grade
The materials used in manufacturing condensers and chillers, such as copper, stainless steel, or aluminum, significantly impact their durability, thermal conductivity, and resistance to corrosion. For example, copper offers excellent thermal conductivity, making it ideal for heat exchange applications, while stainless steel provides enhanced resistance to environmental factors. Choosing the right material is essential for ensuring longevity and operational efficiency, particularly in varying climates across regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East. -
Cooling Capacity (BTU/hr or kW)
Cooling capacity, measured in British Thermal Units per hour (BTU/hr) or kilowatts (kW), indicates the amount of heat a chiller can remove from a space. This specification is critical for determining whether a unit can meet the cooling demands of a facility. Buyers should assess their specific cooling requirements to select a chiller with an appropriate capacity, ensuring efficient operation without excessive energy consumption. -
Operating Pressure
The operating pressure of a chiller system affects its performance and efficiency. It is typically specified in pounds per square inch (PSI) or bar. Understanding the maximum and minimum operating pressures helps in selecting compatible components and ensures safety during operation. For international buyers, especially in regions with varying regulatory standards, knowing the operating pressure is vital for compliance. -
Efficiency Ratings (EER, SEER)
Efficiency ratings such as Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) and Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) measure the cooling output relative to energy consumption. Higher ratings indicate more efficient units, which can lead to significant cost savings on energy bills. B2B buyers should prioritize high-efficiency models to enhance sustainability and reduce operational costs. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels define the acceptable range of variations in the manufacturing process and operational parameters. This specification is crucial for ensuring that condensers and chillers perform effectively under specific conditions. Understanding tolerances helps buyers assess the reliability and quality of the equipment, which is particularly important in regions with extreme temperatures.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Condenser and Chiller Industry?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of condensers and chillers, working with OEMs ensures that buyers receive high-quality products that meet specific standards and specifications, vital for maintaining system integrity. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum quantity of product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to ensure they can meet order requirements without over-committing resources, which is particularly important in markets with tight budgets or fluctuating demand. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document used by buyers to request price quotes from suppliers. It typically includes detailed specifications and quantities. Utilizing RFQs can streamline the procurement process and ensure that buyers receive competitive pricing and terms from multiple vendors. -
Incoterms
International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) are standard trade terms used in international sales contracts that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers, especially in international transactions, to avoid misunderstandings and ensure compliance with shipping regulations. -
Fouling
Fouling refers to the accumulation of unwanted materials on the heat transfer surfaces, which can reduce efficiency. Understanding fouling and its implications allows buyers to implement effective maintenance strategies, enhancing the longevity and performance of their chiller and condenser systems.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize procurement processes, and ensure successful operations in their respective markets.
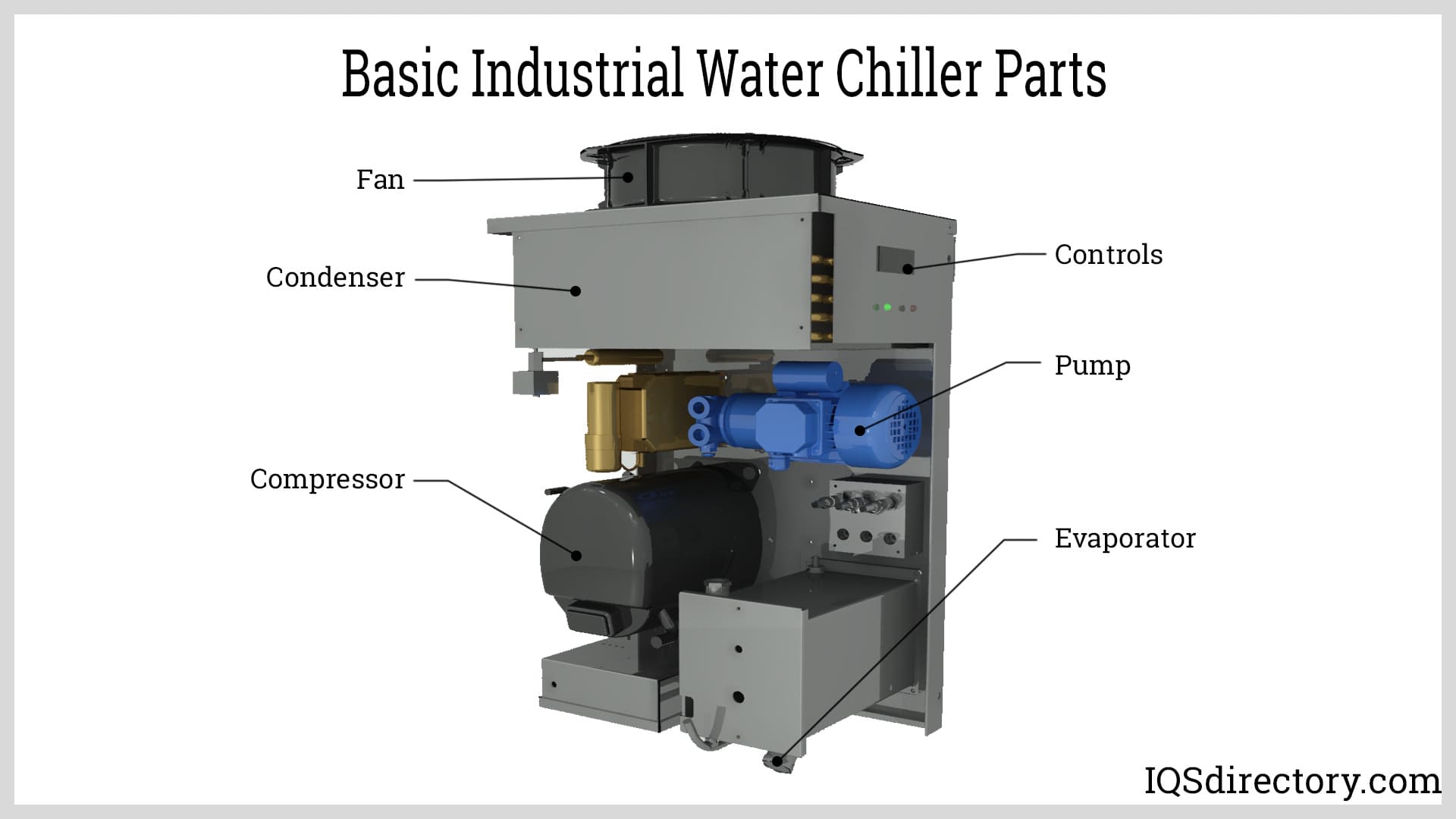
Illustrative image related to condenser and chiller
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the condenser and chiller Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing the Condenser and Chiller Sector?
The global condenser and chiller market is witnessing transformative changes driven by various factors such as urbanization, increased demand for energy-efficient HVAC systems, and the rising emphasis on environmental sustainability. In regions like Africa and South America, rapid urbanization is leading to a surge in construction activities, which in turn fuels the demand for cooling solutions. Meanwhile, the Middle East is focusing on energy efficiency due to extreme climate conditions, leading to innovations in chiller technology and condenser designs that optimize performance while minimizing energy consumption.
Emerging technologies, such as IoT-enabled chillers and advanced monitoring systems, are reshaping the sourcing landscape for international B2B buyers. These technologies enhance operational efficiency and facilitate predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs. Additionally, there’s a growing trend towards modular chillers and condensers, which offer flexibility in installation and scalability for businesses looking to expand their cooling capabilities without significant upfront investments.
Another critical market dynamic is the increasing regulatory pressure to comply with environmental standards. International buyers need to be aware of the refrigerants used in chillers and condensers, as many traditional refrigerants are being phased out due to their high global warming potential. This shift is prompting manufacturers to innovate and develop more environmentally friendly solutions that align with global sustainability goals.
How Is Sustainability Shaping Sourcing Decisions in the Condenser and Chiller Sector?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of sourcing decisions in the condenser and chiller sector. The environmental impact of HVAC systems is under scrutiny, prompting businesses to prioritize eco-friendly practices. This includes selecting suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing and sustainable manufacturing processes. For international B2B buyers, understanding the supply chain is crucial; it ensures that the products sourced not only meet regulatory requirements but also align with corporate sustainability goals.
The use of ‘green’ certifications, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and Energy Star, is increasingly influencing purchasing decisions. Buyers are now more inclined to choose condensers and chillers that incorporate environmentally friendly materials and manufacturing techniques. This trend is particularly relevant in regions like Europe, where stringent regulations on carbon emissions and energy efficiency drive demand for sustainable products.
Moreover, the adoption of alternative refrigerants, such as hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) and natural refrigerants, reflects the industry’s shift towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Suppliers that offer products with these advanced refrigerants are more likely to gain favor among international buyers seeking to enhance their sustainability profile.
How Has the Condenser and Chiller Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the condenser and chiller sector is marked by significant technological advancements and shifts in market demands. Initially, chillers relied heavily on traditional refrigerants and mechanical systems, which were less efficient and environmentally damaging. Over the decades, the industry has seen a transition towards more sophisticated systems, including water-cooled and air-cooled chillers, which provide enhanced energy efficiency and performance.
The introduction of microprocessor controls and smart technology has further revolutionized the sector, allowing for real-time monitoring and management of cooling systems. This evolution has not only improved the operational efficiency of chillers and condensers but has also paved the way for predictive maintenance strategies that minimize downtime and extend equipment lifespan.
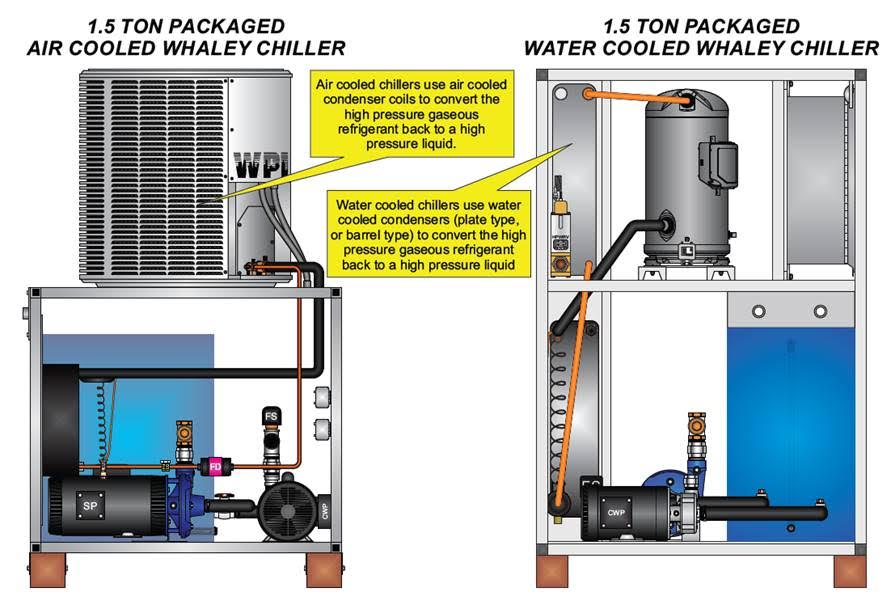
Illustrative image related to condenser and chiller
As global awareness of climate change has intensified, the focus on sustainability and energy efficiency has become paramount. This shift has driven manufacturers to innovate continuously, leading to the development of advanced chillers that utilize eco-friendly refrigerants and incorporate energy-saving technologies. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is essential to navigate the current landscape effectively and make informed sourcing decisions that align with future trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of condenser and chiller
-
How do I solve issues with condenser efficiency?
To address efficiency problems with your condenser, start by checking for fouling, which can insulate tubes and impede heat transfer. Regular cleaning, using chemical treatments or mechanical methods, can significantly enhance performance. Additionally, ensure that the cooling tower is functioning properly and not recirculating warm water back into the system. Monitoring the inlet and outlet temperatures can help identify inefficiencies. Consulting with a qualified HVAC technician for a thorough inspection can also provide targeted solutions to enhance condenser efficiency. -
What is the best chiller type for industrial applications?
The best chiller type for industrial applications largely depends on specific cooling needs, such as capacity, energy efficiency, and installation space. Water-cooled chillers are often preferred for large-scale operations due to their efficiency and reduced noise levels. In contrast, air-cooled chillers may be more suitable for smaller facilities or those with limited space. It’s essential to evaluate the application requirements and consult with suppliers to determine the most suitable chiller model that meets your operational goals. -
How can I vet suppliers for condensers and chillers?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize those with a solid reputation and experience in the HVAC industry. Request references and check customer reviews to gauge their reliability. Ensure they offer comprehensive warranties and after-sales support. Additionally, verify their compliance with international standards and certifications, especially if you’re sourcing from different regions. Engaging in direct communication with potential suppliers can help clarify their capabilities and responsiveness, ensuring a partnership that meets your procurement needs. -
What customization options are available for condensers and chillers?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for condensers and chillers to meet specific operational requirements. Common customizations include varying sizes, materials, and design configurations to enhance compatibility with existing systems. Additionally, options for enhanced energy efficiency, noise reduction, and advanced controls can be specified. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to explore available customization options that align with your operational goals and regulatory standards. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for condensers and chillers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for condensers and chillers can vary widely depending on the manufacturer and the complexity of the units. Generally, MOQs can range from a few units for standard products to larger quantities for custom designs. It’s advisable to discuss MOQs directly with suppliers during negotiations to understand their flexibility. Additionally, consider the impact of bulk purchasing on overall costs and whether it aligns with your budget and project timelines. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing internationally?
When sourcing condensers and chillers internationally, payment terms can vary significantly by supplier and region. Common arrangements include upfront payments, letters of credit, and installment payments based on delivery milestones. Ensure clarity on payment methods, currency exchanges, and any additional fees associated with international transactions. It’s advisable to negotiate favorable terms that protect your interests, especially in long-term contracts, and consider using escrow services for larger purchases to mitigate risks. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my chiller and condenser purchases?
To ensure quality assurance (QA), request detailed specifications and testing standards from suppliers before placing an order. Look for manufacturers with ISO certifications or other relevant quality standards. Conducting factory visits or third-party inspections can also provide insights into their production processes. Additionally, establish a clear QA protocol for receiving inspections upon delivery to verify that the products meet agreed-upon specifications and performance metrics. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing chillers and condensers?
When importing chillers and condensers, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations specific to your region. Collaborate with experienced freight forwarders who understand the complexities of international shipping and can handle necessary documentation. Evaluate the total landed cost, including shipping, duties, and taxes, to budget effectively. Additionally, plan for potential delays in customs clearance and ensure that your supply chain is adaptable to unforeseen circumstances.
Top 4 Condenser And Chiller Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. The Engineering Mindset – Chiller Condenser
Domain: theengineeringmindset.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Chiller Condenser for water cooled chillers; located between the compressor and expansion valve; hot, high pressure refrigerant vapor enters and liquid refrigerant exits; typically not insulated; collects unwanted heat from the building and transfers it to the condenser water loop; refrigerant and water are separated by a metal wall; condenser water flows at approximately 32°C (90°F) out and 27°C …
2. CCS Tubes – Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Services
Domain: ccs-tubes.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Condenser & Chiller Services provides complete shell and tube heat exchanger support, specializing in quality heat exchanger repairs, coatings, and non-destructive eddy current analysis since 1985. They have experience with centrifugal chillers up to 12,000 tons and small recip condensers of 20 tons. Services include retubing water tube boilers, ammonia evaporators, steam surface condensers, and l…
3. Drake Chillers – Water-Cooled Condensers
Domain: blog.drakechillers.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Water-cooled condensers are known for quick installation, long-lasting performance, quiet operation, and energy efficiency, making them ideal for industrial process cooling applications such as medical manufacturing, brewing, dairy production, and food processing. There are three primary types of water-cooled condensers: 1. Shell-and-tube: Common and efficient, easy to clean and repair, made of ca…
4. LinkedIn – Chillers
Domain: linkedin.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Chillers are available in two main types: air-cooled and water-cooled. Air-cooled chillers typically range from 7.5 to 500 tons, while water-cooled chillers can be packaged from 10 to nearly 4,000 tons. Air-cooled chillers utilize an air-to-refrigerant heat exchanger and fans for heat transfer, with options for finned tube coils or microchannel coils. Microchannel coils offer advantages such as hi…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for condenser and chiller
In the rapidly evolving landscape of HVAC solutions, strategic sourcing for condensers and chillers is paramount for international buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the intricate roles of condensers and chillers is essential, as these components are critical for efficient heat management and energy consumption in commercial and industrial applications. By prioritizing quality, reliability, and technological advancements in sourcing decisions, businesses can enhance operational efficiency and reduce long-term costs.
Investing in high-performance condensers and chillers not only mitigates maintenance issues—such as fouling and inefficiencies—but also promotes sustainability through reduced energy consumption. As global markets become increasingly interconnected, leveraging partnerships with reputable manufacturers and service providers can lead to improved supply chain resilience and innovation.
Looking forward, international B2B buyers are encouraged to stay abreast of emerging technologies and best practices in HVAC systems. By adopting a proactive approach to sourcing and maintenance, companies can position themselves for success in a competitive marketplace. Engage with trusted suppliers, explore new technologies, and foster collaborations that drive efficiency and sustainability in your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to condenser and chiller