Rubber Tubes: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rubber tubes
In the complex world of global trade, sourcing high-quality rubber tubes can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With an array of materials, types, and applications available, making informed purchasing decisions is critical for ensuring the reliability and efficiency of industrial operations. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, delving into various types of rubber tubes, including seamless and specialty options, and their specific applications across industries like food processing, automotive, and construction.
Understanding the nuances of rubber tube sourcing, from supplier vetting to cost considerations, is essential for achieving competitive advantage. This guide empowers international buyers by providing actionable insights into evaluating suppliers, understanding material properties, and assessing compliance with regional regulations. Additionally, it highlights trends and innovations in rubber tube manufacturing that could impact procurement strategies.
By equipping B2B buyers with the knowledge to navigate this intricate market landscape, we aim to facilitate more informed purchasing decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product quality. Whether you’re in Saudi Arabia, Vietnam, or beyond, this guide is your key to unlocking the potential of rubber tube solutions tailored to your unique business needs.
Understanding rubber tubes Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber Tubes | High elasticity, excellent abrasion resistance | Material handling, vibration isolation | Pros: Great flexibility and durability; Cons: Poor resistance to oils and UV. |
| EPDM Rubber Tubes | Superior weather and chemical resistance | Automotive, construction, HVAC systems | Pros: Excellent longevity and versatility; Cons: Limited resistance to petroleum products. |
| Nitrile Rubber Tubes | Good oil and fuel resistance | Food processing, automotive, industrial machinery | Pros: Strong chemical resistance; Cons: Less elastic than natural rubber. |
| Silicone Rubber Tubes | High-temperature resistance and flexibility | Medical devices, food processing | Pros: Biocompatible and stable; Cons: Can be more expensive than other types. |
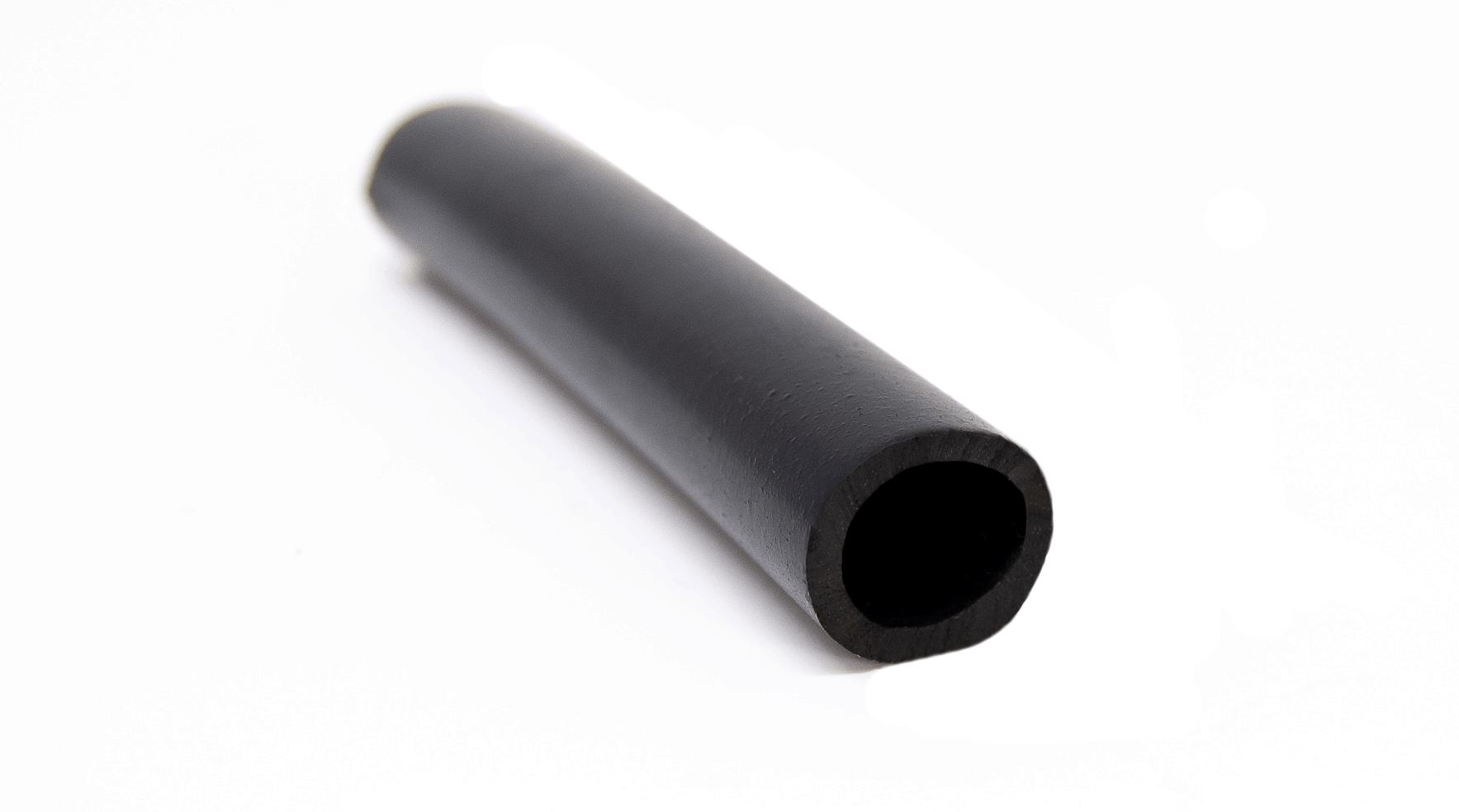
| Seamless Rubber Tubing | Smooth interior, customizable lengths and diameters | Bulk material handling, emergency repairs | Pros: Reduces stock variety; easy to customize; Cons: Requires careful handling to avoid damage. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Natural Rubber Tubes?
Natural rubber tubes are renowned for their exceptional elasticity and durability, making them suitable for a variety of applications such as material handling and vibration isolation. They exhibit excellent abrasion resistance, which is crucial in industries that require robust tubing solutions. However, buyers should be aware that natural rubber has poor resistance to oils, UV light, and extreme temperatures, which may limit its use in certain environments. When purchasing, consider the specific operational conditions to ensure the longevity of the product.
How Does EPDM Rubber Compare in Terms of Application Versatility?
EPDM rubber tubes stand out for their remarkable resistance to weather elements and chemicals, making them ideal for automotive, construction, and HVAC applications. Their durability allows them to withstand a wide range of temperatures and environmental conditions. However, while they excel in resisting water, steam, and UV exposure, they are less effective against petroleum-based products. Buyers should evaluate the environmental factors their tubing will encounter to select the appropriate EPDM formulation for their needs.
Why Choose Nitrile Rubber Tubes for Oil and Fuel Applications?
Nitrile rubber tubes are specifically designed for applications involving oils and fuels, offering excellent chemical resistance. These tubes are commonly used in food processing, automotive, and industrial machinery settings where exposure to oils is frequent. Although they provide strong protection against chemical degradation, nitrile rubber is generally less elastic than natural rubber, which can affect flexibility in certain applications. Buyers should consider the balance between chemical resistance and flexibility when selecting nitrile tubing.
What Are the Benefits of Using Silicone Rubber Tubes in Specialized Industries?
Silicone rubber tubes are known for their high-temperature resistance and flexibility, making them particularly valuable in medical devices and food processing applications. Their biocompatibility and stability under extreme conditions make them a preferred choice in environments where safety and reliability are paramount. However, silicone tubes can be more expensive than other types of rubber tubing. B2B buyers should weigh the cost against the benefits, especially in applications requiring stringent safety standards.
How Does Seamless Rubber Tubing Enhance Stock Management?
Seamless rubber tubing offers a smooth interior and the flexibility to be cut to customized lengths, which makes it an efficient choice for bulk material handling and emergency repairs. This adaptability reduces the need for a wide variety of stock lengths, thereby lowering inventory costs. While seamless tubing simplifies procurement and reduces waste, it requires careful handling to prevent damage during installation. B2B buyers should consider their operational needs and inventory strategies when selecting seamless rubber tubing.
Key Industrial Applications of rubber tubes
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of rubber tubes | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food & Beverage | Transfer of liquids and gases in processing plants | Ensures hygiene and compliance with food safety standards | Certifications (FDA, EU), material compatibility, seamless options |
| Agriculture | Irrigation systems and fluid transfer | Enhances efficiency in resource usage | UV resistance, flexibility, durability under varying temperatures |
| Automotive | Fuel and coolant hoses for vehicles | Improves engine performance and reliability | Temperature tolerance, chemical resistance, custom lengths |
| Construction | Vibration dampening in machinery | Reduces equipment wear and enhances operational efficiency | Tensile strength, elasticity, ease of installation |
| Mining & Quarrying | Transport of slurries and bulk materials | Increases operational efficiency and reduces downtime | Abrasion resistance, chemical compatibility, length options |
How Are Rubber Tubes Utilized in the Food & Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, rubber tubes are essential for the safe transfer of liquids and gases throughout processing plants. They are designed to meet stringent hygiene standards, ensuring that products remain uncontaminated. Buyers in this industry must prioritize sourcing tubes that comply with food safety regulations, such as FDA or EU certifications. Additionally, seamless rubber tubes are preferred as they minimize the risk of contamination, making them ideal for food-grade applications.
Why Are Rubber Tubes Important for Agriculture?
Rubber tubes play a vital role in agricultural irrigation systems, enabling efficient fluid transfer and resource management. Their flexibility and durability make them suitable for various environmental conditions, ensuring consistent water supply to crops. International buyers should consider sourcing tubes that offer UV resistance and can withstand varying temperatures to maximize longevity and performance in diverse climates, particularly in regions like Africa and South America.
What Role Do Rubber Tubes Play in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, rubber tubes are commonly used as fuel and coolant hoses, critical for maintaining optimal engine performance. These tubes must withstand high temperatures and exposure to various chemicals, necessitating careful selection based on material properties. Buyers should focus on sourcing hoses that offer superior temperature tolerance and chemical resistance to ensure reliability and reduce maintenance costs, particularly in high-performance vehicles.
How Do Rubber Tubes Contribute to Construction Equipment?
Rubber tubes are integral in construction for vibration dampening in machinery, significantly reducing wear and tear on equipment. This application enhances operational efficiency and extends the lifespan of costly machinery. Buyers should look for tubes with high tensile strength and elasticity to ensure they can absorb vibrations effectively. Ease of installation is also a key consideration, enabling quick replacement and minimizing downtime on job sites.
What Are the Benefits of Rubber Tubes in Mining & Quarrying?
In the mining and quarrying sectors, rubber tubes are utilized for the transport of slurries and bulk materials, playing a crucial role in operational efficiency. These tubes must be abrasion-resistant and compatible with various chemicals to withstand harsh environments. International buyers should focus on sourcing tubes that can handle heavy-duty applications while offering flexibility in terms of length and diameter options to suit specific operational needs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘rubber tubes’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing High-Quality Rubber Tubes for Diverse Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges when sourcing rubber tubes that meet specific application requirements. This includes not only the need for various diameters and lengths but also the necessity for specific material properties, such as chemical resistance or FDA compliance. For instance, a food processing company might require rubber tubes that can withstand high temperatures and are safe for food contact, while a construction firm may need tubes that can resist abrasion and extreme weather conditions. Misjudging these requirements can lead to costly delays, production downtime, or even safety hazards.

Illustrative image related to rubber tubes
The Solution: To effectively source high-quality rubber tubes, buyers should first conduct a thorough assessment of their application needs, considering factors such as temperature ranges, chemical exposure, and flexibility requirements. Collaborating closely with suppliers can provide insights into the material properties of different rubber types, such as EPDM for weather resistance or Nitrile for oil resistance. It is advisable to request samples for testing before making bulk purchases, ensuring that the selected rubber tubes meet the operational demands. Additionally, establishing a relationship with reputable manufacturers who can offer customized solutions can streamline the sourcing process and enhance product reliability.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Compatibility with Existing Equipment
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is ensuring that the rubber tubes they purchase are compatible with existing machinery and systems. In industries such as manufacturing and agriculture, where equipment configurations can vary widely, using the wrong type of rubber tube can lead to leaks, inefficiencies, or even equipment damage. For example, a factory utilizing pneumatic systems may find that certain rubber tubes fail under pressure or do not fit properly, leading to operational disruptions.
The Solution: To mitigate compatibility issues, buyers should begin by gathering precise specifications of their existing equipment, including the required inner and outer diameters, pressure ratings, and types of connections (such as barb or threaded). Consulting with equipment manufacturers or engineers can provide guidance on the best rubber tube options. Additionally, using standardized rubber tubing can simplify compatibility across different systems. It is also beneficial to invest in adjustable fittings and clamps that can accommodate slight variations in tubing dimensions, enhancing overall flexibility and reducing the risk of failure.
Scenario 3: Managing Inventory and Reducing Waste
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with inventory management of rubber tubes, which can lead to overstocking or shortages. This issue is particularly prevalent in industries with fluctuating demands, such as construction or automotive, where the need for rubber tubes can vary seasonally. Excess inventory ties up capital and storage space, while shortages can halt production or lead to rushed orders that compromise quality.
Illustrative image related to rubber tubes
The Solution: Implementing a just-in-time (JIT) inventory system can help manage rubber tube supplies more effectively. By analyzing historical usage data and forecasting future demands, businesses can better align their orders with actual needs. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers who offer flexible order quantities can also enhance responsiveness to market changes. Additionally, keeping a limited stock of standardized rubber tubes that can be cut to length as needed can minimize waste while ensuring that essential supplies are always on hand. Regular audits of inventory can also help identify slow-moving items, allowing for proactive adjustments to purchasing strategies.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rubber tubes
What Are the Key Properties of Common Rubber Tube Materials?
When selecting rubber tubes for various applications, understanding the properties of different materials is crucial. Here, we analyze four common materials used in rubber tube manufacturing: Natural Rubber, EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer), Nitrile (Buna-N), and Silicone. Each material has unique characteristics that influence their performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications.
How Does Natural Rubber Perform in Rubber Tubes?
Natural rubber is renowned for its elasticity and tensile strength, making it an excellent choice for applications requiring flexibility. It typically operates effectively within a temperature range of -40°C to 80°C (-40°F to 176°F) and can withstand pressures up to 3000 PSI. However, it has limitations in chemical resistance, particularly against oils and solvents, which can lead to degradation over time.
Pros: Natural rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and excellent elongation properties, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to synthetic alternatives.
Cons: Its susceptibility to environmental factors such as UV light and ozone can limit its longevity. This material is not suitable for applications involving petroleum-based products.
For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East, compliance with local standards such as ASTM is essential. Additionally, the availability of natural rubber can vary, impacting supply chain logistics.
Why Choose EPDM for Rubber Tubes?
EPDM is a synthetic rubber known for its excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and UV exposure. It can handle temperatures ranging from -40°C to 120°C (-40°F to 248°F) and is suitable for applications that require exposure to water and steam. EPDM is often used in automotive and HVAC applications due to its durability and flexibility.
Pros: Its chemical resistance to a wide range of substances, including acids and alkalis, makes it versatile for various industrial applications. It also maintains its properties over a broad temperature range.
Cons: EPDM has poor resistance to petroleum oils, which can limit its use in certain environments. Additionally, its manufacturing complexity can lead to higher costs.
International buyers should ensure that EPDM products meet local compliance standards and certifications, particularly in the food and beverage sector, where FDA compliance may be necessary.
What Are the Advantages of Nitrile Rubber Tubes?
Nitrile rubber, or Buna-N, is particularly favored for its oil and fuel resistance, making it ideal for applications in the automotive and aerospace industries. It operates effectively in temperatures ranging from -40°C to 120°C (-40°F to 248°F) and can withstand pressures up to 1500 PSI.
Pros: Nitrile’s excellent chemical resistance to oils and solvents makes it a go-to material for fuel lines and hydraulic applications. It also offers good abrasion resistance.
Cons: While it excels in oil resistance, nitrile rubber can be less effective in applications involving high temperatures or steam. Its cost may be higher than natural rubber.
For B2B buyers in regions such as South America and Europe, understanding the specific chemical compatibility of nitrile with various media is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and compliance with environmental regulations.
How Does Silicone Rubber Compare for Rubber Tubes?
Silicone rubber is known for its high-temperature stability, operating effectively between -60°C to 200°C (-76°F to 392°F). It is often used in applications requiring flexibility and resistance to extreme temperatures, such as in food processing and medical devices.
Pros: Silicone is non-toxic, making it suitable for food and pharmaceutical applications. Its ability to maintain performance in extreme conditions is unmatched.
Cons: The primary drawback of silicone rubber is its lower tensile strength compared to other materials, which may limit its use in high-pressure applications. Additionally, it tends to be more expensive.
International buyers should consider the stringent compliance requirements for silicone in food and medical applications, ensuring that products meet relevant standards such as FDA regulations.
Summary Table of Rubber Tube Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for rubber tubes | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber | Heavy-duty applications, bulk material handling | Excellent abrasion resistance, cost-effective | Poor chemical resistance, UV degradation | Low |
| EPDM | Automotive, HVAC, water applications | Great weather and chemical resistance | Poor resistance to petroleum oils | Medium |
| Nitrile | Fuel lines, hydraulic applications | Excellent oil and fuel resistance | Less effective in high-temperature applications | Medium |
| Silicone | Food processing, medical devices | High-temperature stability, non-toxic | Lower tensile strength, higher cost | High |
This detailed analysis equips B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed decisions regarding rubber tube material selection, ensuring optimal performance and compliance across various applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rubber tubes
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Rubber Tubes?
The manufacturing process of rubber tubes involves several critical stages, each essential for ensuring the final product meets industry standards and customer specifications.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing rubber tubes is the selection and preparation of raw materials. Common materials include natural rubber, EPDM, and nitrile, each chosen based on the specific application requirements. These materials undergo a rigorous quality check to ensure they meet predetermined specifications. The rubber is typically processed in bulk, which may involve mixing with additives such as curing agents, stabilizers, and pigments to enhance properties like elasticity, resistance to chemicals, and UV stability.
2. Forming Techniques
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This can be accomplished through various methods, including extrusion and molding:
-
Extrusion: In this method, the rubber compound is forced through a die to create a continuous tube of the desired cross-section. This technique is widely used for producing seamless tubes and allows for precise control over dimensions.
-
Molding: For applications requiring specific shapes or complex features, molding techniques such as compression or injection molding may be employed. This allows for the creation of rubber tubes with integrated fittings or other components.
3. Assembly Processes
After forming, the tubes may need to be assembled with additional components, such as end fittings or connectors. This assembly process may involve:
-
Adhesive Bonding: For components that need to be joined together without welding.
-
Mechanical Fastening: Such as clamps or screws, which provide a reliable connection without altering the material properties.
4. Finishing Touches
The final manufacturing stage involves finishing processes that enhance the tube’s performance and aesthetics. This may include:
-
Curing: The rubber is subjected to a heat treatment process to cross-link the polymer chains, improving strength and durability.
-
Surface Treatment: Additional coatings or treatments may be applied to enhance resistance to environmental factors like abrasion, UV rays, or chemicals.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into Rubber Tube Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of rubber tube manufacturing that ensures products meet regulatory and customer expectations. The process involves multiple checkpoints and adherence to international standards.
Relevant International Standards for Rubber Tubes
B2B buyers should be aware of several key standards that govern the quality of rubber tubes:
-
ISO 9001: This international standard outlines criteria for a quality management system (QMS). It focuses on meeting customer expectations and delivering customer satisfaction.
-
CE Marking: For products sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: For applications in the oil and gas sector, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is essential.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early and ensure compliance with standards. These checkpoints typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to verify that they meet specified quality standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, samples are taken at various stages to ensure ongoing compliance with specifications.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Completed products are subjected to rigorous testing before shipment. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspections, and performance testing.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Rubber Tubes?
To verify the quality and performance of rubber tubes, various testing methods are employed:
-
Tensile Strength Testing: Measures the maximum stress a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking.
-
Elongation Testing: Assesses how much a rubber tube can stretch before reaching its breaking point, which is critical for applications requiring flexibility.
-
Hardness Testing: Evaluates the resistance of rubber to indentation, often measured in Shore A units, which helps determine suitability for specific applications.
-
Chemical Resistance Testing: Determines how well rubber tubes perform when exposed to various chemicals, an essential factor for industrial applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers, particularly in international markets, must take proactive steps to verify supplier quality control measures. Here are some actionable strategies:
-
Conduct Audits: Schedule on-site audits of manufacturing facilities to assess quality control processes and compliance with standards. This firsthand evaluation can provide insights into the supplier’s capabilities.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports that outline testing results, certifications, and compliance with relevant standards. This documentation is crucial for confirming product reliability.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection agencies to conduct independent evaluations of the manufacturing process and final products. This adds an additional layer of assurance and objectivity.
What Are the Nuances of QC/Certifications for International Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various nuances in quality control and certifications, especially when sourcing from different regions. Key considerations include:
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Understanding local regulations and industry practices can help buyers assess the credibility of suppliers and their compliance with international standards.
-
Language Barriers: Ensuring that quality documentation is available in a language that the buyer understands is crucial for transparency and effective communication.
-
Supply Chain Transparency: Buyers should seek suppliers who are open about their sourcing and manufacturing processes, including the origin of materials and compliance certifications. This transparency fosters trust and mitigates risks associated with quality issues.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for rubber tubes is vital for B2B buyers. By engaging with suppliers who adhere to rigorous quality standards and implementing thorough verification strategies, buyers can ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘rubber tubes’
To assist international B2B buyers in effectively procuring rubber tubes, this guide provides a comprehensive checklist designed to streamline the sourcing process. By following these steps, buyers can ensure that they select the right products and suppliers to meet their specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the rubber tubes you need. This includes parameters such as diameter, length, material type (e.g., EPDM, nitrile, or natural rubber), and any specific performance characteristics like chemical resistance or temperature tolerances. Defining these specifications early on helps in avoiding miscommunication with suppliers and ensures that the products will meet operational needs.
- Material Properties: Consider the application of the tubes, such as whether they will be used in high-temperature environments or require resistance to certain chemicals.
- Standards Compliance: Ensure that the materials comply with relevant industry standards, such as FDA compliance for food-grade applications.
Step 2: Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to compile a list of potential suppliers. Look for manufacturers and distributors known for quality and reliability in the rubber tube industry. Utilize online resources, trade shows, and industry directories to find reputable suppliers.
- Regional Considerations: Focus on suppliers from regions that have a strong reputation for rubber manufacturing, such as Southeast Asia or Europe.
- Industry Networks: Engage with industry associations or forums to gather recommendations and insights on trusted suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. This evaluation process helps in assessing their credibility and reliability.
- Certifications and Compliance: Verify that suppliers have the necessary certifications (ISO, CE, etc.) and compliance with international standards relevant to your industry.
- Quality Assurance Processes: Inquire about their quality control measures to ensure product consistency and reliability.
Step 4: Request Samples and Test Quality
Always request samples before placing a bulk order. Testing these samples allows you to evaluate the quality, flexibility, and performance of the rubber tubes against your specifications.
- Performance Testing: Check for durability under the conditions they will face in your application, including pressure tests and resistance to environmental factors.
- Feedback from Technicians: Involve your technical team in the evaluation process to ensure the product meets operational standards.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified a suitable supplier and tested their products, proceed to negotiate pricing and terms. Be clear about your budget and ensure all costs, including shipping and tariffs, are accounted for.
- Volume Discounts: Discuss bulk order discounts or long-term contracts that might reduce costs.
- Payment Terms: Clarify payment options and any warranties or return policies that apply to your purchase.
Step 6: Finalize Contracts and Place Orders
After negotiations, finalize contracts with clear terms and conditions that protect both parties. Ensure that all specifications, delivery timelines, and payment terms are documented.
- Legal Review: Consider having a legal expert review the contract to ensure compliance with local and international laws.
- Order Confirmation: Confirm the order details and maintain open lines of communication with the supplier throughout the production and shipping process.
Step 7: Monitor Delivery and Quality Assurance
Upon receipt of your order, conduct a thorough inspection to ensure that the rubber tubes meet the agreed-upon specifications. This step is vital to avoid any operational disruptions.

Illustrative image related to rubber tubes
- Quality Control Checks: Implement a quality assurance process to verify that the delivered products align with your requirements.
- Supplier Feedback: Provide feedback to the supplier based on your experience to build a stronger partnership for future orders.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing rubber tubes efficiently, ensuring that their procurement process is both effective and aligned with their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rubber tubes Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Rubber Tubes Manufacturing?
When sourcing rubber tubes, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of rubber type—natural, EPDM, or nitrile—significantly affects costs. For instance, natural rubber tends to be less expensive than specialty formulations like nitrile, which offers superior oil resistance. Prices can fluctuate based on market demand for raw materials.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the manufacturing location. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing; however, these can be offset by potential quality issues.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the costs associated with running production facilities, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and general operational costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront cost, particularly for specialized designs or large-volume orders. Buyers should consider whether the tooling investment aligns with their production needs.
-
Quality Control: Implementing rigorous QC measures is essential for ensuring product reliability. The costs related to QC can vary based on certification requirements, such as FDA compliance for food-grade applications.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs are influenced by the distance between the manufacturer and buyer, as well as the chosen Incoterms. Buyers should account for both freight costs and potential delays in delivery.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and generate profit. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s positioning in the market and their operational efficiency.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Rubber Tube Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of rubber tubes, making it essential for buyers to understand these dynamics.
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often have Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) that can affect pricing. Larger orders typically lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale, while smaller orders may incur higher prices.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications, such as unique diameters or material compositions, can drive up costs. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against the potential increase in price.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet specific industry standards or certifications (e.g., ISO, FDA) generally command higher prices. Buyers should assess the importance of these certifications based on their application needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of a supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products due to proven quality and service.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can affect total landed costs. For instance, Cost, Insurance, and Freight (CIF) terms place more responsibility on the seller, potentially leading to higher prices than Free On Board (FOB) terms.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Rubber Tubes?
To maximize value and minimize costs in rubber tube sourcing, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Engage in open discussions with suppliers regarding pricing, MOQs, and lead times. Building a strong relationship can lead to better terms and pricing flexibility.
-
Focus on Cost Efficiency: Analyze the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also logistics, maintenance, and potential downtime costs. This comprehensive view can guide better sourcing decisions.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and trade agreements that may affect pricing.
-
Request Samples: Before committing to large orders, request samples to assess quality. This can help prevent costly mistakes and ensure that the product meets your specifications.
-
Stay Informed: Keep abreast of market trends and material costs. Awareness of changes in the rubber market can provide leverage during negotiations and help anticipate future pricing shifts.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for rubber tubes can vary significantly based on the factors discussed. The figures provided here are indicative and may not reflect actual market conditions. Always obtain current quotes from suppliers to ensure accurate budgeting for your sourcing needs.

Illustrative image related to rubber tubes
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing rubber tubes With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Rubber Tubes in Industrial Applications
When considering solutions for fluid transfer and other applications, rubber tubes stand out for their flexibility and durability. However, there are alternative materials and technologies that may also meet specific needs. In this analysis, we will compare rubber tubes with two viable alternatives: PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Tubing and Silicone Tubing. This comparison will help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and application suitability.
| Comparison Aspect | Rubber Tubes | PVC Tubing | Silicone Tubing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent flexibility and chemical resistance; suitable for various applications. | Good for low-pressure applications; limited chemical resistance. | High temperature and chemical resistance; excellent flexibility. |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on material type (natural vs. synthetic). | Generally low-cost and widely available. | Higher cost due to specialty applications and materials. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific fittings and sometimes clamps for secure connections. | Easy to cut and connect; often available in pre-formed shapes. | Flexible but may require specialized fittings. |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic inspection for wear and tear; some degradation over time. | Low maintenance; resistant to corrosion but can become brittle. | Minimal maintenance; excellent durability and longevity. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-pressure applications and scenarios needing chemical resistance. | Suitable for irrigation, drainage, and low-pressure applications. | Best for medical, food, and high-temperature environments. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of PVC Tubing?
PVC tubing is a cost-effective alternative to rubber tubes. It is lightweight and easy to handle, making it ideal for applications such as irrigation and drainage. However, its performance is limited in high-pressure situations and it may not withstand exposure to certain chemicals. While PVC is resistant to corrosion, it can become brittle over time, particularly when exposed to UV light or extreme temperatures, which may necessitate more frequent replacements.
How Does Silicone Tubing Compare?
Silicone tubing offers superior performance in high-temperature environments, making it an excellent choice for industries such as food processing and pharmaceuticals. It is flexible and maintains its integrity under stress, but it is generally more expensive than both rubber and PVC. Silicone’s chemical resistance is outstanding, but its higher cost can be a barrier for budget-sensitive projects. Additionally, it often requires specialized fittings, which can complicate implementation.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Selecting the appropriate tubing solution depends on specific application requirements, including environmental factors, pressure conditions, and chemical exposure. For high-pressure and chemically aggressive applications, rubber tubes are often the best choice. If cost-effectiveness and ease of installation are paramount, PVC may serve well, especially in low-pressure scenarios. Conversely, for high-temperature and sensitive applications, silicone tubing offers unparalleled performance, albeit at a higher price point. By carefully evaluating these factors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rubber tubes
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Rubber Tubes for B2B Buyers?
When considering rubber tubes for industrial applications, several technical properties are critical for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Understanding these specifications can help buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
1. Material Grade
The material grade of rubber tubes typically refers to the type of rubber used in their manufacturing, such as natural rubber, EPDM, or Nitrile. Each grade has distinct properties, such as chemical resistance, flexibility, and temperature tolerance. For instance, Nitrile rubber offers excellent oil resistance, making it suitable for applications involving petroleum products. Selecting the right material grade is vital for ensuring the tube performs effectively in specific environments and conditions.
2. Tolerance and Dimensional Specifications
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in the dimensions of the rubber tube, including its diameter, wall thickness, and length. Precision in these measurements is crucial for ensuring a proper fit with other components in a system, which can prevent leaks and enhance the efficiency of fluid transport. Buyers should be aware of the tolerances required for their applications to avoid costly mistakes or product failures.
3. Temperature Resistance
Temperature resistance indicates the range of temperatures that a rubber tube can withstand without degrading or losing performance. For example, some rubber tubes can operate effectively in temperatures ranging from -40°C to 120°C. Understanding the temperature limits is essential for applications that involve heat transfer or exposure to extreme conditions, as exceeding these limits can lead to premature failure.
4. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength measures the maximum amount of stress a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. It is expressed in pounds per square inch (PSI). High tensile strength is particularly important in applications where the rubber tube may be subjected to high pressure or mechanical stress. Selecting a tube with appropriate tensile strength ensures durability and reliability during operation.
5. Elongation at Break
Elongation at break refers to the percentage increase in length of a rubber tube before it fractures. This property indicates the material’s ability to stretch and absorb energy without permanent deformation. A higher elongation percentage can be advantageous in dynamic applications where movement or vibration occurs. Buyers should consider this property when selecting tubes for applications that require flexibility and resilience.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Rubber Tubes?
Familiarity with industry terminology can enhance communication between buyers and suppliers, ensuring smoother transactions and clearer expectations.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of rubber tubes, understanding if a supplier is an OEM can indicate the quality and compatibility of the products offered, especially for specific industrial applications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers as it can affect inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses plan their purchases more effectively and avoid excess stock.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process in which a buyer requests pricing and terms from suppliers. It is an essential tool for comparing offers and negotiating better deals. For rubber tubes, an RFQ should include specifications such as material grade, dimensions, and quantity to obtain accurate quotations.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers, as they dictate shipping costs, insurance, and risk management. Familiarity with relevant Incoterms can help buyers negotiate better shipping arrangements.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the product. In the context of rubber tubes, lead time can be influenced by factors such as manufacturing capabilities and shipping logistics. Awareness of lead times can assist buyers in planning their projects and ensuring timely delivery of components.
By understanding these essential technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make more informed purchasing decisions regarding rubber tubes, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the rubber tubes Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Rubber Tubes Sector?
The rubber tubes market is experiencing robust growth driven by several global factors, including increased industrialization, rising demand in the automotive and construction sectors, and advancements in manufacturing technology. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial. The shift toward automation and IoT technologies is reshaping sourcing strategies, allowing companies to leverage smart inventory management systems and predictive analytics for better supply chain efficiency.
Emerging trends highlight the growing preference for seamless rubber tubing due to its superior performance characteristics, such as flexibility and chemical resistance. Furthermore, the adoption of standardized diameters and customizable lengths is becoming increasingly popular, enabling manufacturers to minimize waste and enhance inventory management. Additionally, sustainability is gaining traction, with many companies seeking eco-friendly alternatives in rubber sourcing to meet regulatory requirements and consumer expectations.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions for Rubber Tubes?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the rubber tubes sector. The environmental impact of rubber production, particularly in terms of deforestation and carbon emissions, is prompting B2B buyers to prioritize suppliers who adopt sustainable practices. Companies are increasingly looking for rubber tubes made from recycled materials or natural rubber sourced from certified plantations.
Furthermore, certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) are essential for ensuring ethical supply chains. These certifications not only demonstrate a commitment to reducing environmental impact but also help companies build brand trust and loyalty among environmentally conscious consumers. By aligning with suppliers who prioritize sustainability, B2B buyers can enhance their own corporate responsibility profiles while mitigating risks associated with non-compliance and reputational damage.
What Is the Historical Context of the Rubber Tubes Industry?
The evolution of the rubber tubes industry can be traced back to the late 19th century, when the first commercial rubber products emerged. Initially, the production of rubber tubes was limited to basic applications in plumbing and irrigation. However, advancements in material science and manufacturing processes have dramatically transformed the industry. The introduction of synthetic rubbers in the mid-20th century expanded the range of applications and improved the performance characteristics of rubber tubes.
Today, the industry is characterized by a wide variety of formulations, including EPDM, Nitrile, and natural rubber, each tailored for specific applications across various sectors. This evolution has not only enhanced product durability and functionality but has also paved the way for innovations in design and manufacturing that meet the complex demands of modern industries. As the market continues to grow, understanding this historical context can provide valuable insights for B2B buyers navigating their sourcing strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rubber tubes
-
How do I select the right rubber tube for my application?
Choosing the right rubber tube depends on several factors including application type, temperature resistance, and chemical compatibility. Assess the working environment and the substances the tube will transport. For instance, if you require a tube for food-grade applications, ensure it meets FDA standards. Consider the diameter and length needed, as well as whether a seamless design is necessary for flexibility and reduced friction. Consulting with suppliers about your specific requirements can also yield tailored recommendations. -
What are the key properties to look for in rubber tubes?
Key properties to consider include chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, flexibility, and durability. Different materials, such as EPDM, Nitrile, and natural rubber, offer varied resistance to oils, UV exposure, and mechanical wear. Evaluate the specific conditions under which the tube will operate, including pressure levels and environmental factors. For applications requiring frequent movement or vibration absorption, prioritize tubes with high elasticity and tensile strength. -
How can I ensure the quality of rubber tubes from suppliers?
To ensure quality, vet suppliers by checking certifications and compliance with international standards like ISO 9001. Request samples to assess material quality and performance before placing larger orders. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes, including testing methods for durability and chemical resistance. Establishing a relationship with suppliers who have a good track record in your industry can also provide peace of mind regarding product reliability. -
What are common payment terms in B2B transactions for rubber tubes?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common options include net 30 or net 60 days, where payment is due within that timeframe after receiving the invoice. Some suppliers may offer a discount for upfront payments or larger orders. Be sure to clarify payment methods accepted, such as wire transfers or letters of credit, especially when dealing with international transactions to ensure a smooth process. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for rubber tubes?
Minimum order quantities can differ significantly among suppliers and depend on the type of rubber tube requested. Generally, MOQs can range from as low as 100 meters to several thousand, particularly for custom sizes or specifications. When negotiating, express your needs clearly, as some suppliers may be flexible with MOQs for first-time customers or bulk orders. Consider the potential for future orders to leverage better terms. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping for international orders of rubber tubes?
When sourcing rubber tubes internationally, factor in logistics from the outset. Choose suppliers who can facilitate shipping and have experience with customs regulations in your target markets. Determine whether the supplier offers Incoterms (like FOB or CIF) that clarify responsibility for shipping costs and risks. For timely delivery, consider air freight for urgent needs, although sea freight can be more economical for larger shipments. -
Can I customize rubber tubes for specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for rubber tubes, including variations in diameter, length, and material composition. Custom designs may also include specific features such as additional reinforcement or unique chemical resistance. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and intended applications to ensure the supplier can meet your requirements. This can lead to improved performance and longevity of the tubes in your specific use case. -
What certifications should I look for when sourcing rubber tubes?
Look for certifications that indicate compliance with industry standards and safety regulations. Common certifications include ISO 9001 for quality management systems, FDA compliance for food-grade applications, and RoHS for environmental safety. Depending on your region, additional certifications may be required for specific applications, such as UL for electrical components. Ensuring your suppliers maintain these certifications can help mitigate risks associated with product quality and safety.
Top 5 Rubber Tubes Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Treestuff – Latex Rubber Tubing
Domain: treestuff.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Latex Rubber Tubing, 5/8″ overall diameter, stretches to three times its length before returning to original size. Can be used as replacement tubing for Big Shot or cut into sections for rubber bands. Useful for controlling eye size in eye splices, tool handles, carabiners, loop runners, etc. Sold by the foot. Manufacturer Part Number: 5234K82. Country of Manufacture: US.
2. The Rubber Company – Rubber Tubing
Domain: therubbercompany.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Rubber tubing is used in both private and industrial applications due to its high versatility. The Rubber Company manufactures and supplies tubing in various rubber compounds, offering a vast selection of inner and outer diameter sizes. Rubber tubing is suitable for the safe transfer of solids, liquids, and gases, thanks to its high resistance. It can maintain functionality in a wide temperature r…
3. McMaster – Rubber Tubing Selection
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Rubber Tubing Selection, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Filcoflex – Seamless Rubber Tubing
Domain: filcoflex.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Seamless Rubber Tubing features a smooth inside surface and a wrapped, light textured outside finish. Made from gum rubber, EPDM, or nitrile, it is available in standardized diameters and can be cut to length. The tubing is suitable for various applications including flexible sleeves, bulk bag filling bladders, and vibration isolation. It is ideal for food contact applications due to its smooth in…
5. Siftex – Seamless Rubber Tubing
Domain: siftex.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Siftex – Seamless Rubber Tubing, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rubber tubes
As the global demand for rubber tubes continues to rise, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical element for B2B buyers seeking to optimize their procurement processes. Understanding the diverse applications and material properties of rubber tubes—such as the advantages of seamless construction and the unique characteristics of various rubber types like EPDM and Nitrile—can significantly enhance product selection and supply chain efficiency.
By leveraging strategic sourcing practices, companies can not only reduce costs but also ensure quality, compliance, and sustainability in their purchases. This approach is particularly vital for businesses operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where market dynamics and regulatory requirements can vary considerably.
Looking ahead, the rubber tube market is poised for innovation, driven by advancements in materials science and manufacturing technologies. Buyers are encouraged to stay informed about industry trends and emerging suppliers, fostering partnerships that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals. Embrace strategic sourcing today to secure a competitive edge and enhance your supply chain resilience in the evolving global marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.