How to Source Industries With Oems Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for industries with oems
In today’s rapidly evolving global market, sourcing high-quality components from Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) poses significant challenges for international B2B buyers. Whether you’re seeking reliable automotive parts or advanced electronic systems, understanding the complexities of the OEM landscape is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse industries that rely on OEMs, exploring the types of products available, their applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting processes.
As a B2B buyer from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, you face unique challenges, including fluctuating supply chain dynamics and varying regulatory standards. This guide empowers you by providing actionable insights into cost considerations, quality benchmarks, and the strategic importance of partnerships with leading OEMs. By navigating this landscape effectively, you can enhance your sourcing strategies, mitigate risks, and capitalize on opportunities for innovation and growth.
In this resource, we aim to equip you with the knowledge necessary to evaluate OEM capabilities, understand market trends, and leverage supplier relationships. Our focus on best practices and real-world applications ensures that you are well-prepared to make decisions that align with your business objectives, ultimately leading to a more competitive position in the global marketplace.
Understanding industries with oems Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive OEMs | Focus on vehicle manufacturing, including parts and systems. | Vehicle assembly, parts supply, aftermarket services. | Pros: Strong brand reliability; Cons: High competition. |
| Electronics OEMs | Specialize in consumer electronics, including components and devices. | Manufacturing of electronic devices and components. | Pros: Innovation-driven; Cons: Rapid technological changes. |
| Industrial Equipment OEMs | Produce machinery and equipment for various industries. | Construction, agriculture, and manufacturing. | Pros: Long-term durability; Cons: High initial investment. |
| Aerospace OEMs | Focus on aircraft and aerospace components, including systems. | Aircraft manufacturing, parts supply, maintenance. | Pros: High safety standards; Cons: Complex supply chains. |
| Medical Device OEMs | Specialize in medical equipment and devices. | Hospital supplies, diagnostics, and surgical instruments. | Pros: Regulatory compliance; Cons: High development costs. |
What are the characteristics of Automotive OEMs and their suitability for B2B buyers?
Automotive OEMs are characterized by their extensive supply chains and vertical integration, producing everything from engines to electrical systems. They cater to both internal brands and third-party manufacturers, ensuring a wide range of original parts. B2B buyers in this sector benefit from established reliability and innovation, especially in electric vehicle technologies. However, the competitive landscape can lead to price fluctuations, making it crucial for buyers to evaluate multiple suppliers to secure favorable terms.
How do Electronics OEMs drive innovation and what should buyers consider?
Electronics OEMs are at the forefront of technological advancement, producing components that power everything from smartphones to industrial machinery. They are distinguished by rapid innovation cycles and the need for constant adaptation to consumer trends. B2B buyers looking to partner with electronics OEMs should consider their R&D capabilities and responsiveness to market demands. While these OEMs offer cutting-edge solutions, buyers must also be wary of the fast-paced nature of the industry, which can lead to obsolescence of products.
What makes Industrial Equipment OEMs essential for construction and manufacturing sectors?
Industrial Equipment OEMs are vital for sectors like construction and agriculture, known for their robust machinery and equipment. Their offerings often include high-durability products designed for heavy use. B2B buyers in these industries should prioritize OEMs that provide comprehensive support services, including maintenance and training. Although these products can require significant upfront investment, their longevity and reliability often justify the cost, particularly in demanding operational environments.

Illustrative image related to industries with oems
How do Aerospace OEMs ensure safety and reliability in their products?
Aerospace OEMs specialize in manufacturing aircraft and components, adhering to stringent safety and regulatory standards. Their operations often involve complex supply chains and high levels of precision. B2B buyers in the aerospace sector must consider the OEM’s compliance with industry regulations and their experience in producing critical components. While partnering with established aerospace OEMs can enhance safety and reliability, the intricate nature of aerospace supply chains can pose challenges in terms of lead times and logistics.
What are the key considerations for buyers in the Medical Device OEM sector?
Medical Device OEMs focus on producing equipment and devices that meet rigorous health and safety standards. They are characterized by their commitment to innovation and compliance with regulatory requirements. B2B buyers in the healthcare sector should evaluate the OEM’s track record in regulatory compliance and product reliability. Although the costs associated with developing medical devices can be high, the potential for long-term partnerships and access to cutting-edge technology can provide significant value in this critical industry.
Key Industrial Applications of industries with oems
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of industries with oems | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of electric vehicle components | Enhanced product innovation and alignment with sustainability goals | Evaluate suppliers’ R&D capabilities and compliance with local regulations |
| Electronics | Manufacturing of consumer electronics parts | Improved product quality and enhanced market competitiveness | Consider the supply chain reliability and technological advancements of OEMs |
| Aerospace | Supply of aircraft engines and components | Increased operational efficiency and safety standards | Focus on certifications, quality control processes, and after-sales support |
| Industrial Machinery | Development of precision-engineered machinery parts | Higher productivity and reduced downtime | Assess OEMs’ capacity for customization and responsiveness to market needs |
| Renewable Energy | Production of solar panel components | Contribution to sustainable energy solutions and cost savings | Ensure OEMs have a track record in innovation and supply chain transparency |
How Do OEMs Enhance Automotive Production in Emerging Markets?
In the automotive sector, OEMs play a critical role in producing electric vehicle (EV) components. As demand for EVs grows, particularly in Africa and South America, OEMs provide essential parts that meet international quality standards. This enables local manufacturers to innovate and align with global sustainability goals. International buyers should focus on suppliers with strong R&D capabilities and a commitment to local regulatory compliance to ensure a smooth integration of OEM components.
Illustrative image related to industries with oems
What Role Do OEMs Play in Electronics Manufacturing?
In the electronics industry, OEMs supply critical components for consumer electronics, such as smartphones and home appliances. The partnership with OEMs allows businesses to enhance product quality and maintain competitiveness in fast-paced markets. For international buyers, evaluating the reliability of the supply chain and the technological advancements of OEMs is essential to mitigate risks associated with global sourcing.
How Are OEMs Transforming Aerospace Component Supply?
Aerospace OEMs are responsible for providing high-quality aircraft engines and critical components. Their expertise ensures increased operational efficiency and adherence to stringent safety standards, vital for international airlines operating in diverse regulatory environments. Buyers should prioritize OEMs that possess the necessary certifications and robust quality control processes to guarantee the reliability of aerospace components.
What Benefits Do OEMs Bring to Industrial Machinery?
In the industrial machinery sector, OEMs develop precision-engineered parts that enhance productivity and minimize downtime. This is particularly beneficial for manufacturers in emerging markets, where operational efficiency can significantly impact profitability. When sourcing from OEMs, businesses should assess their capacity for customization and responsiveness to evolving market demands to ensure they remain competitive.
How Do OEMs Contribute to Renewable Energy Solutions?
OEMs in the renewable energy sector produce components for solar panels and other sustainable technologies. By collaborating with these manufacturers, businesses can contribute to eco-friendly solutions while achieving cost savings. International buyers should ensure that OEMs have a proven track record in innovation and transparency in their supply chains, which is crucial for fostering trust and long-term partnerships in the renewable energy landscape.

Illustrative image related to industries with oems
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘industries with oems’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex Supply Chains
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant challenges when dealing with complex supply chains associated with OEMs. The intricacies of sourcing original parts can lead to delays and inconsistencies in production, especially in industries like automotive or electronics where timing and precision are critical. For example, a manufacturer in Nigeria may struggle to secure timely deliveries of components from a European OEM, leading to production halts and increased operational costs. This situation is exacerbated by fluctuating international shipping rates and regulatory hurdles, which can leave buyers feeling overwhelmed and uncertain about their supply chain stability.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, B2B buyers should develop strategic partnerships with local distributors or suppliers who have established relationships with OEMs. Building a robust network can facilitate quicker access to original parts and help navigate regulatory requirements more effectively. Implementing an inventory management system that integrates with OEM supply chains can also enhance visibility, allowing for better forecasting and planning. Moreover, buyers should engage in regular communication with their OEM partners to stay updated on lead times and potential disruptions, ensuring they can adapt their production schedules accordingly.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Quality Compliance Across Borders
The Problem: Quality assurance is a persistent pain point for B2B buyers working with OEMs, particularly when sourcing parts from different countries. Variations in manufacturing standards can lead to inconsistencies in product quality, which is especially concerning for industries like automotive and aerospace where safety and reliability are paramount. For instance, a buyer in Brazil might receive subpar components from a foreign OEM that do not meet local regulatory standards, resulting in costly recalls or legal repercussions.

Illustrative image related to industries with oems
The Solution: To address quality compliance issues, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence before entering partnerships with OEMs. This includes assessing their quality management systems and certifications to ensure they meet international standards such as ISO 9001. Additionally, buyers can implement a quality control protocol that includes regular audits and inspections of OEM facilities, even if conducted remotely. Collaborating with third-party quality assurance firms can also provide an added layer of scrutiny, ensuring that all components meet the required specifications before they enter the supply chain.
Scenario 3: Adapting to Rapid Technological Changes
The Problem: The fast pace of technological advancement poses a challenge for B2B buyers in industries with OEMs. As OEMs innovate and introduce new technologies—such as electric vehicle components or advanced manufacturing techniques—buyers may struggle to keep up with these changes. For example, a company in the Middle East looking to transition to electric vehicles might find it difficult to source compatible parts from traditional OEMs that have not yet fully adapted to this shift, leading to missed market opportunities.
The Solution: To stay ahead of technological changes, buyers should actively engage in ongoing education and industry networking. Attending trade shows, webinars, and industry conferences can provide insights into emerging technologies and trends. Buyers should also foster close relationships with OEMs that are committed to innovation, ensuring they receive timely information about new products and technologies. Additionally, investing in training for their teams on new technologies can facilitate smoother transitions and enable buyers to make informed decisions about which OEM partners to pursue for future projects.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for industries with oems
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in OEM Industries?
When selecting materials for OEM applications, understanding the properties and suitability of various materials is crucial. Here, we analyze four common materials used across industries with OEMs: aluminum, steel, plastics, and composites. Each material has distinct characteristics that influence their application in manufacturing processes.
How Does Aluminum Perform in OEM Applications?
Aluminum is widely favored in the automotive and aerospace industries due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. Key properties include a temperature rating up to 600°F and a low density, which contributes to fuel efficiency in vehicles.
Pros: Aluminum is durable, resistant to corrosion, and easy to fabricate, making it suitable for complex shapes. It also offers good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Cons: The primary drawback is its higher cost compared to steel, which can impact budget-sensitive projects. Additionally, while aluminum is strong, it may not withstand extreme pressure as effectively as some steel grades.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for components exposed to harsh environments, such as engine parts and body panels. However, international buyers must consider compliance with standards like ASTM B221 for extruded aluminum.
What Are the Advantages of Using Steel in OEM Manufacturing?
Steel remains a staple in OEM applications due to its strength and versatility. With a temperature rating that can exceed 1,500°F, steel is suitable for high-stress environments.
Pros: Steel is known for its durability, affordability, and ease of availability. It can be treated or alloyed to enhance specific properties, such as tensile strength or corrosion resistance.

Illustrative image related to industries with oems
Cons: Steel is heavier than aluminum and can be prone to rust if not properly coated. This can increase maintenance costs over time.
Impact on Application: Steel is commonly used in structural components, automotive frames, and machinery. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel.
How Do Plastics Contribute to OEM Solutions?
Plastics are increasingly used in OEM applications due to their lightweight and versatile properties. They can withstand temperatures from -40°F to 200°F, depending on the type.
Pros: Plastics are cost-effective, easy to mold into complex shapes, and resistant to many chemicals. They also provide good insulation properties.
Cons: The primary limitation of plastics is their lower mechanical strength compared to metals, which can restrict their use in high-stress applications. Additionally, some plastics may degrade under UV exposure.
Illustrative image related to industries with oems
Impact on Application: Plastics are widely used in consumer electronics and automotive interiors. International buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ISO 11469 for plastic identification and recycling.
Why Are Composites Gaining Popularity in OEM Industries?
Composites, particularly carbon fiber and fiberglass, are becoming increasingly popular in industries such as aerospace and automotive due to their high strength-to-weight ratio.
Pros: Composites are lightweight, incredibly strong, and resistant to corrosion. They can also be tailored for specific applications, enhancing performance.
Cons: The manufacturing process for composites can be complex and costly, often requiring specialized equipment and expertise.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for parts requiring high performance and low weight, such as aircraft components. Buyers from Europe may need to adhere to specific industry standards like EN 45545 for fire safety in rail transport.

Illustrative image related to industries with oems
Summary Table of Material Selection for OEM Industries
| Material | Typical Use Case for industries with oems | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Automotive body panels, aerospace components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost compared to steel | High |
| Steel | Structural frames, automotive chassis | Durable and cost-effective | Heavier and prone to rust | Medium |
| Plastics | Consumer electronics, automotive interiors | Cost-effective and easy to mold | Lower mechanical strength | Low |
| Composites | Aerospace parts, high-performance automotive | High strength-to-weight ratio | Complex and costly manufacturing process | High |
This guide provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, especially those in emerging markets such as Nigeria and Brazil, ensuring they make informed decisions in material selection for OEM applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for industries with oems
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes for OEMs?
In industries with Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), the manufacturing process typically encompasses several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is vital for ensuring that the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards.
How Is Material Prepared in OEM Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the foundational stage of manufacturing. It involves sourcing raw materials, which can include metals, plastics, and composites, depending on the product. This stage includes processes such as cutting, machining, and treating materials to ensure they meet the necessary specifications for strength, durability, and other performance criteria.
For instance, in the automotive sector, metals such as aluminum and steel undergo processes like forging and casting to achieve the desired dimensions and properties. Material preparation also involves rigorous quality checks to ensure that the materials comply with international standards like ISO 9001, which emphasizes quality management systems.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Processes?
The forming stage is where raw materials are shaped into components. Techniques vary widely based on the product type but typically include processes such as stamping, molding, and extrusion. For example, in the automotive industry, stamping is commonly used to create body panels, while injection molding is often employed for plastic parts.

Illustrative image related to industries with oems
Advanced forming techniques, such as hydroforming and 3D printing, are gaining traction, particularly for custom and lightweight components. These methods not only enhance efficiency but also reduce waste, aligning with the sustainability goals many OEMs are pursuing.
How Does Assembly Take Place in OEM Manufacturing?
Assembly is the stage where individual components come together to form the final product. This process can be manual or automated, depending on the complexity and scale of production. For high-volume products, such as vehicles, assembly lines are optimized for speed and efficiency, often employing robotics for tasks like welding and painting.
Quality control is particularly critical during assembly, as errors can propagate and result in significant defects. Techniques such as error-proofing (poka-yoke) are utilized to minimize human error and ensure that each component is correctly installed.
What Finishing Processes Are Commonly Used?
The finishing stage involves processes that enhance the product’s appearance and protect it from environmental damage. This can include painting, coating, polishing, and surface treatment. For example, automotive OEMs often use advanced paint technologies that not only provide aesthetic appeal but also offer corrosion resistance and durability.
Finishing processes must comply with various international regulations and standards, particularly in industries with strict environmental guidelines, such as automotive and aerospace.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in OEM Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the manufacturing process for OEMs, ensuring that products meet established standards and customer expectations. The QA process involves various international standards and industry-specific regulations.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
One of the most widely recognized international standards for quality management is ISO 9001. This standard provides a framework for organizations to improve their quality processes and ensure consistent product quality. Compliance with ISO 9001 signifies that an OEM has robust quality management systems in place.
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific standards such as CE marking for European markets, API for oil and gas, and automotive standards like IATF 16949 are also crucial. Understanding these standards can help B2B buyers assess the credibility of their suppliers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in OEM Manufacturing?
Quality control in OEM manufacturing involves several checkpoints throughout the production process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials before they enter the manufacturing process. IQC ensures that only materials meeting the required specifications are used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, IPQC monitors production activities to identify and rectify defects early. This is essential for maintaining quality and efficiency.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products leave the manufacturing facility, FQC involves a thorough inspection to ensure that the finished goods meet all specifications and standards.
These checkpoints are crucial for maintaining quality and minimizing defects, which is particularly important for international B2B buyers who may face significant costs from non-compliance.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure product quality in OEM manufacturing. Common techniques include:
-
Destructive Testing: This method evaluates the durability and performance of materials and components by subjecting them to extreme conditions until failure occurs.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing, radiography, and magnetic particle inspection allow for the assessment of materials and components without causing damage.
-
Functional Testing: This ensures that the product performs as intended under various conditions, validating its operational reliability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control measures of suppliers is essential to ensure product reliability and compliance. Here are several methods to consider:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control systems. This can be done through on-site visits or third-party audits.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand the supplier’s performance over time. These reports often include data on defect rates, compliance with standards, and corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes and product compliance. This is particularly useful for B2B buyers unfamiliar with local manufacturing practices.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
When dealing with suppliers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, B2B buyers should be aware of specific nuances related to quality control and certification:

Illustrative image related to industries with oems
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding local manufacturing practices and quality expectations can help buyers effectively communicate their requirements and establish strong partnerships.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulations concerning product standards and certifications. Buyers must ensure their suppliers comply with local laws and international standards.
-
Supply Chain Transparency: Buyers should seek suppliers who provide transparency in their supply chains, including sourcing and manufacturing practices. This can be critical for ensuring ethical and sustainable practices.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures employed by OEMs is crucial for international B2B buyers. By focusing on the key stages of manufacturing, relevant quality standards, and effective verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions that drive value and mitigate risks in their supply chains.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘industries with oems’
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure products from Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) across various industries. By following these steps, you can enhance your sourcing strategy, ensuring that you partner with reliable and innovative suppliers that meet your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, it is essential to clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes the specific components, materials, and performance standards that your OEM products must meet. Well-defined specifications help to streamline communication with potential suppliers and reduce the risk of misalignment later in the procurement process.
- Consider industry standards: Familiarize yourself with relevant regulations and quality benchmarks that apply to your industry, as these will inform your specifications.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Understanding the landscape of OEMs in your targeted industry is crucial. Research potential suppliers, their market positions, and their product offerings to identify those that align with your needs.
- Utilize industry reports: Leverage market analysis reports and industry publications to gather insights on leading OEMs and emerging players.
- Examine customer reviews: Look for testimonials and case studies from other businesses that have worked with these OEMs to gauge their reliability and product quality.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to any supplier, it’s vital to conduct a thorough evaluation. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions.

Illustrative image related to industries with oems
- Assess financial stability: Verify the financial health of potential suppliers to ensure they can fulfill your orders over the long term.
- Review certifications: Check for relevant industry certifications and quality standards that the OEMs adhere to, as this reflects their commitment to quality.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request samples or prototypes of their products. This step allows you to assess the quality and performance of the OEM parts firsthand.
- Test for compatibility: Ensure that the samples meet your specifications and are compatible with your existing systems or products.
- Evaluate lead times: Use this opportunity to discuss production timelines and delivery schedules to better understand their operational capabilities.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Effective negotiation can lead to favorable terms and pricing. Engage in discussions regarding payment terms, delivery schedules, and after-sales support.
- Consider total cost of ownership: When evaluating pricing, factor in not just the purchase price but also potential costs related to maintenance, logistics, and warranty services.
- Establish clear agreements: Ensure that all terms are documented in a formal agreement to protect both parties and provide clarity on expectations.
Step 6: Plan for Logistics and Supply Chain Management
A well-structured logistics plan is crucial for timely delivery and inventory management. Coordinate with your chosen OEM to establish effective shipping and handling processes.
- Discuss shipping options: Explore different shipping methods and timelines to find the most efficient and cost-effective solutions.
- Monitor supply chain risks: Stay informed about potential disruptions in the supply chain and collaborate with your OEM to develop contingency plans.
Step 7: Establish a Long-Term Relationship
Once you have successfully sourced OEM products, focus on building a strong, long-term relationship with your supplier. Regular communication and feedback can foster collaboration and innovation.
- Schedule regular reviews: Conduct performance evaluations to ensure the OEM continues to meet your quality and service expectations.
- Explore joint ventures: Consider opportunities for co-development or innovation projects that can benefit both parties in the long run.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing from OEMs, ultimately leading to successful partnerships that drive growth and innovation in their businesses.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for industries with oems Sourcing
In the realm of Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis dissects the fundamental components of OEM pricing and offers practical insights for effective procurement.
What Are the Key Cost Components Influencing OEM Pricing?
When evaluating the total cost structure associated with sourcing from OEMs, several key components come into play:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials constitutes a significant portion of the overall pricing. Fluctuations in commodity prices can greatly influence OEM costs, making it vital for buyers to stay informed about market trends.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on geographic location and the complexity of manufacturing processes. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this can also impact quality and lead times.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate overhead, but buyers should be aware of how these costs are factored into pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront investment, particularly for bespoke parts. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs and whether these are included in the unit price or charged separately.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure product reliability but can add to the cost. Certifications and testing protocols may also affect pricing, especially for industries with stringent regulatory requirements.
-
Logistics: Transportation, warehousing, and handling fees contribute to the final cost. International buyers should consider the impact of logistics on delivery timelines and overall pricing.
-
Margin: OEMs typically build in a profit margin that reflects their operational costs and market position. Understanding the margin expectations can help buyers negotiate more effectively.
What Influences Pricing Beyond the Basic Cost Structure?
Several factors can significantly influence the pricing of OEM products:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their purchasing needs and negotiate terms that align with their operational requirements.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized parts may incur additional costs for design and production. Clear communication about specifications can help avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Premium materials and certifications can elevate costs but often result in superior product performance. Buyers should weigh the benefits of higher-quality options against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, reputation, and past performance play a crucial role in pricing. Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects shipping responsibilities and costs. Understanding these terms can help buyers manage their logistics and financial liabilities effectively.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help B2B Buyers Secure Better Pricing?
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on initial pricing, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential savings over time. This perspective can strengthen your negotiating position.
-
Seek Long-term Partnerships: Building long-term relationships with OEMs can lead to favorable pricing structures and improved service levels. Consider negotiating for loyalty discounts or volume commitments.
-
Be Prepared for Price Fluctuations: Be aware that prices can fluctuate based on market conditions. Stay informed about industry trends and be ready to negotiate based on these insights.
-
Clarify Terms Early: Ensure all terms, including payment schedules, delivery timelines, and warranty conditions, are clearly defined before finalizing agreements. This clarity can prevent costly misunderstandings later.
-
Understand Cultural Nuances: When negotiating with international suppliers, cultural differences can influence business practices. Familiarize yourself with the norms in the supplier’s region to enhance communication and build rapport.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of OEM cost structures and pricing requires a strategic approach. By understanding the key cost components, price influencers, and negotiation tactics, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their organizational goals. Always remember to obtain indicative pricing and be prepared for variations based on market dynamics and supplier capabilities.

Illustrative image related to industries with oems
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing industries with oems With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Industries with OEMs: A Comparative Analysis
In the dynamic landscape of global manufacturing, Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) play a pivotal role in ensuring quality and innovation across various industries. However, businesses may consider alternative solutions that can achieve similar objectives, such as enhancing production efficiency and maintaining high standards. This section explores viable alternatives to industries with OEMs, comparing their performance, cost-effectiveness, ease of implementation, maintenance requirements, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Industries With OEMs | Alternative 1: Contract Manufacturing | Alternative 2: In-House Production |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-quality parts and systems | Variable quality, depending on the partner | Consistent quality, but dependent on resources |
| Cost | Typically high due to brand value | Potentially lower, but varies by contract | Can be high due to labor and material costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Established networks and processes | Relatively easy if a reliable partner is found | Complex setup and longer lead times |
| Maintenance | Robust support and service networks | Limited to the partner’s capabilities | Requires in-house expertise and resources |
| Best Use Case | Large-scale production with brand recognition | Startups or SMEs needing quick scalability | Businesses with specific needs or proprietary technology |
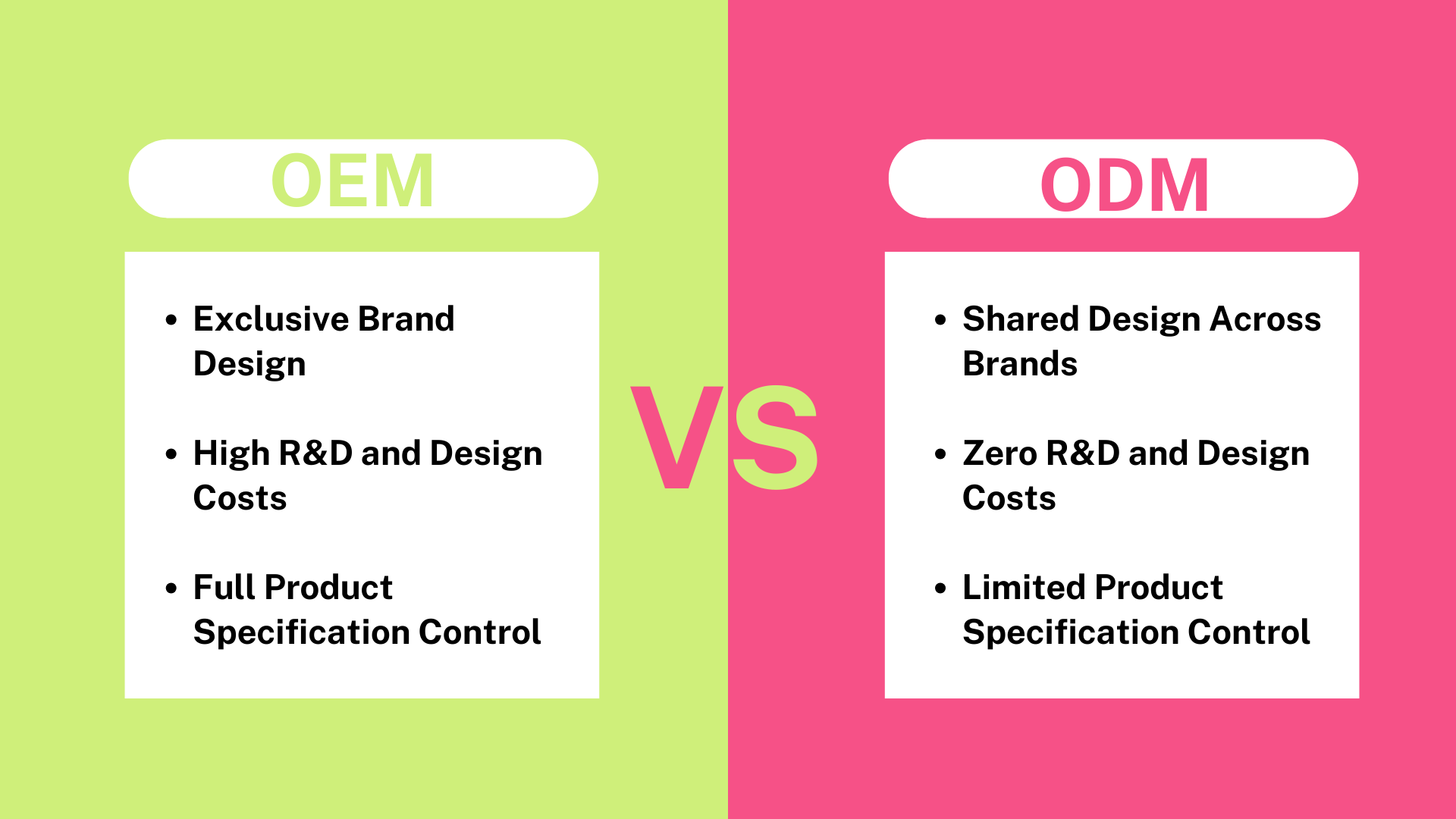
What are the Pros and Cons of Contract Manufacturing as an Alternative to OEMs?
Contract manufacturing allows companies to outsource their production needs to third-party manufacturers. This approach can significantly reduce costs, especially for startups and small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that may lack the resources to set up extensive manufacturing operations. The flexibility of contract manufacturing allows businesses to scale production quickly in response to market demands. However, quality control can be a significant concern, as the level of quality is often dependent on the capabilities and reliability of the chosen partner. Additionally, there may be limited control over the production process, which can lead to inconsistencies.
How Does In-House Production Compare to OEMs?
In-house production refers to companies managing their manufacturing processes internally. This method ensures complete control over quality and production timelines, which can be crucial for businesses with specific or proprietary technology. However, the initial setup costs can be substantial, and maintaining an in-house facility requires significant ongoing investment in labor, training, and equipment. Moreover, businesses may face challenges in scaling operations quickly, as they need to manage their resources effectively. For firms with unique manufacturing needs or those prioritizing confidentiality, in-house production may be the best approach.
Choosing the Right Solution: What Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Selecting the right solution depends on various factors, including the company’s size, production requirements, and strategic objectives. For organizations looking for high-quality, reliable parts and systems, partnering with established OEMs remains a strong choice due to their extensive networks and support systems. Conversely, businesses that prioritize cost efficiency and flexibility might benefit from contract manufacturing. Finally, firms with specific production needs or proprietary technologies may find that in-house production aligns best with their operational goals. Ultimately, B2B buyers should evaluate their unique needs and weigh the pros and cons of each alternative to make an informed decision that best supports their business objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for industries with oems
What Are the Key Technical Properties Critical for OEM Partnerships?
When engaging with Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), understanding specific technical properties is essential for ensuring compatibility, quality, and performance of parts and systems. Here are some critical specifications to consider:

Illustrative image related to industries with oems
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of materials based on their chemical composition, mechanical properties, and intended application. In the context of OEMs, specifying the correct material grade is vital for ensuring the durability and performance of components. For instance, automotive parts often require high-grade steel or aluminum to withstand stress and environmental factors. Buyers must verify that the materials meet industry standards to avoid costly failures and ensure compliance with regulations.
Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in manufacturing. It is crucial in ensuring that parts fit together correctly and function as intended. In B2B transactions, precise tolerances can prevent assembly issues, enhance product reliability, and minimize waste. For example, a tolerance of ±0.01 mm might be necessary for precision-engineered components, especially in the automotive and aerospace sectors.
Surface Finish
Surface finish describes the texture and smoothness of a component’s surface, which can affect its performance and aesthetic qualities. In many industries, particularly automotive and electronics, a specific surface finish is required to reduce friction, enhance adhesion, and prevent corrosion. Buyers should specify the desired surface finish to ensure that OEMs deliver parts that meet functional and visual standards.
Load Capacity
Load capacity refers to the maximum load a component can support without failure. This specification is particularly important in industries such as automotive and construction, where safety is paramount. Understanding the load capacity helps buyers select appropriate parts that will perform reliably under operational stresses, thereby minimizing risks associated with equipment failure.
Lifecycle and Reliability
Lifecycle refers to the expected operational lifespan of a component, while reliability assesses its performance consistency over time. These metrics are essential for B2B buyers to ensure that the components sourced from OEMs meet their operational demands without frequent replacements. OEMs with a strong reputation for lifecycle and reliability can offer peace of mind, leading to better overall business performance.

Illustrative image related to industries with oems
What Are the Common Trade Terms Used in OEM Industries?
Navigating the world of OEM partnerships requires familiarity with specific trade jargon that can significantly influence negotiations and operational efficiency. Here are some commonly used terms:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding this term is crucial for B2B buyers as it defines the relationship between suppliers and manufacturers. OEMs often provide the original parts necessary for product assembly, which can influence the quality and reliability of the final product.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for buyers as it can affect inventory management and cash flow. Understanding the MOQ helps businesses plan their procurement strategy effectively, particularly when dealing with specialized OEM components that may have higher production costs.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent by a buyer to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. This process is essential in B2B transactions, enabling buyers to compare offers and negotiate better terms with OEMs. A well-structured RFQ can lead to more competitive pricing and improved supplier relationships.

Illustrative image related to industries with oems
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers engaging with OEMs, as they govern shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, impacting overall procurement strategies.
Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving it. Understanding lead times is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory levels and production schedules effectively. OEMs with shorter lead times can provide a competitive advantage, allowing businesses to respond quickly to market demands.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can enhance their interactions with OEMs, ensuring better product quality, operational efficiency, and successful partnerships.

Illustrative image related to industries with oems
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the industries with oems Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Influencing OEM Industries?
The global landscape for Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) is shaped by several transformative trends that international B2B buyers should consider. One of the most significant drivers is the increasing demand for electric vehicles (EVs) and sustainable technologies. As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe move towards greener alternatives, OEMs are investing heavily in research and development for battery technology, hybrid systems, and energy-efficient components. This shift is not only addressing environmental concerns but also meeting consumer demand for sustainable products.
Another key trend is the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) into manufacturing processes. These technologies enhance supply chain transparency and operational efficiency, allowing OEMs to optimize production schedules and inventory management. For B2B buyers, this means access to more reliable and innovative products, as manufacturers leverage data analytics to predict trends and improve quality control.
Additionally, the ongoing disruptions caused by geopolitical events and the COVID-19 pandemic have prompted OEMs to rethink their supply chain strategies. This includes diversifying suppliers and investing in local manufacturing capabilities to mitigate risks. For international buyers, particularly in emerging markets, understanding these dynamics is crucial for securing reliable partnerships and ensuring a steady supply of original parts.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact OEM Industries?
The importance of sustainability in OEM industries cannot be overstated, particularly for B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Environmental impacts associated with manufacturing processes are under increasing scrutiny, prompting OEMs to adopt sustainable practices. This includes the use of renewable energy sources, waste reduction techniques, and the recycling of materials in production.
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing and sustainability. This is not just a moral imperative; it also aligns with consumer preferences for brands that prioritize environmental responsibility. Many OEMs are now seeking ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001, which validates their commitment to environmental management systems. These certifications can serve as a critical deciding factor for buyers when selecting OEM partners.
Furthermore, the demand for sustainable materials, such as recycled metals and bio-based plastics, is rising. OEMs that incorporate these materials into their product lines are likely to gain a competitive edge. For buyers, sourcing from OEMs that prioritize sustainability can enhance their own brand reputation and align with corporate social responsibility goals.
What Is the Historical Context of OEMs Relevant to Today’s B2B Landscape?
The role of Original Equipment Manufacturers has evolved significantly since their inception in the early 20th century. Initially focused on mechanical components for automobiles, OEMs have transformed into leaders of innovation across various industries, including electronics, aerospace, and consumer goods. The automotive sector, in particular, has seen a dramatic shift, with OEMs now investing heavily in technology and sustainability.
Historically, the rise of globalization has allowed OEMs to expand their reach, establishing production facilities and supply chains worldwide. This evolution has enabled manufacturers to respond more flexibly to regional demands while benefiting from lower production costs in emerging markets. For today’s B2B buyers, understanding this history helps contextualize current sourcing strategies and the importance of innovation and sustainability in the OEM landscape.
As the industry continues to navigate the complexities of market dynamics and sourcing trends, international B2B buyers must stay informed and adaptable to leverage opportunities effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of industries with oems
-
How do I source OEM parts effectively for my business needs?
Sourcing OEM parts involves thorough research and strategic selection of suppliers. Begin by identifying reputable OEM manufacturers that align with your industry requirements. Utilize platforms like trade shows, industry directories, and B2B marketplaces to find potential suppliers. It’s vital to assess their certifications, production capabilities, and previous client feedback. Establish clear communication regarding your specifications, lead times, and quality standards. Lastly, consider forming partnerships with logistics providers to streamline the import/export process, especially if you’re sourcing internationally. -
What is the best strategy for vetting OEM suppliers?
To vet OEM suppliers, start by checking their industry certifications and quality management systems, such as ISO 9001. Request references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and service quality. Conduct on-site visits if feasible, or utilize third-party inspection services to evaluate their manufacturing processes. Additionally, assess their financial stability and capacity to meet your production demands. Establishing a clear agreement on terms, including quality assurance protocols and penalties for non-compliance, will further safeguard your interests. -
What customization options should I consider when working with OEMs?
When collaborating with OEMs, explore customization options that align with your product requirements. Discuss the potential for bespoke designs, material specifications, and performance enhancements that cater to your target market. Understand the implications of customization on lead times and costs, as these can vary significantly based on complexity. Ensure that the OEM has the necessary capabilities and technologies to deliver your custom requests. It’s also advisable to request prototypes before full-scale production to ensure the final product meets your expectations. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for OEM parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for OEM parts can vary widely depending on the manufacturer, part type, and production processes. Generally, MOQs range from a few hundred to thousands of units. When negotiating with OEMs, clarify their MOQ policies and explore options for trial orders or smaller batches, especially if you are a new buyer. Keep in mind that higher MOQs often lead to lower per-unit costs, so balance your budget and inventory needs when discussing order sizes. -
What payment terms are common when sourcing from OEMs?
Payment terms with OEMs can vary based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation skills. Common arrangements include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, and balance payments prior to shipment. For international transactions, consider utilizing letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. Ensure that the payment terms are clearly outlined in your contract, including any penalties for late payments or conditions for refunds. Understanding the currency exchange rates and transaction fees is also essential for budgeting. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing OEM parts?
To ensure quality assurance, work closely with your chosen OEM to establish clear quality standards and inspection processes. Implement a comprehensive quality control plan that includes regular inspections at various production stages. Request samples and prototypes before mass production to assess quality. Additionally, consider third-party quality assurance services for independent verification. It’s crucial to communicate your quality expectations upfront and include these standards in your contractual agreements to hold the supplier accountable. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing OEM parts?
Logistics is a critical aspect of importing OEM parts, especially when dealing with international suppliers. Assess shipping methods, lead times, and costs associated with different transport options, such as air freight versus sea freight. Understand customs regulations and duties that may apply to your shipments, as these can significantly impact your overall costs. Collaborating with a reliable freight forwarder can help navigate these complexities and ensure timely delivery. Additionally, consider warehousing options to manage inventory effectively upon arrival. -
What are the key trends in the OEM industry that buyers should be aware of?
Current trends in the OEM industry include a strong focus on sustainability, with many manufacturers adopting eco-friendly practices and materials. The shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) is reshaping demand for OEM parts, particularly in automotive sectors. Digital transformation is also prevalent, with increased use of automation and data analytics to enhance production efficiency. As a buyer, staying informed about these trends can help you align your sourcing strategies with market demands and capitalize on emerging opportunities within the OEM landscape.
Top 6 Industries With Oems Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Bosch – Automotive Parts
Domain: mach1services.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: 1. Bosch: Provides a range of automotive parts, including brakes and electronics.
2. Denso: Supplies air conditioning, heating, exhaust, and engine cooling parts.
3. Magna International: Offers drivetrain, body, chassis, and engineering solutions.
4. Continental: Known for tires, brake systems, interior electronics, automotive safety, powertrain, and chassis components.
5. ZF Friedrichshafen: Prov…
2. IQS Directory – OEM Manufacturing Solutions
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: OEM Manufacturers, OEM Manufacturing Companies, Manufacturing Site Categories, 55 Gallon Drums, Automation Equipment, Automated Guided Vehicles, Air Pollution Control, Aluminum Extrusions, Balers, Blowers, Blow Molding, Boilers, Brushes, Cardboard Tubes, Carrying Cases, Ceramic Machining, Chillers, Clean Rooms, Conveyors, Corrugated Boxes, Crane Manufacturers, Deburring Equipment, Die Castings, Di…
3. Volkswagen – Beetle, Golf, Passat; Toyota – Hybrid Technology
Domain: emag.directindustry.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: 1. Volkswagen: Founded in 1937, headquartered in Wolfsburg, Germany. Known for vehicles like Beetle, Golf, and Passat. Revenue: $284.21 B. 2. Toyota: Founded in 1937, headquartered in Toyota City, Aichi, Japan. Manufactures 10 million vehicles annually, known for hybrid technology with Toyota Mirai. Revenue: $260.13 B. 3. Mercedes-Benz: Founded in 1926, German luxury automaker. Offers a range of v…
4. FDI – Comprehensive Supply Chain Solutions
Domain: fdi.us.com
Introduction: Federal Defense Industries (FDI) offers a comprehensive supply chain program that includes active business relationships with over 4,500 OEMs, contract manufacturing facilities, distributors, and suppliers across the United States and Europe. FDI specializes in various components including: Aircraft Components, Electronic Components, Vehicle Components, Electro-Mechanical Components, and Mechanica…
5. OEMs – Automotive & Electronics
Domain: indeed.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, OEMs – Automotive & Electronics, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. Zinfi – OEM Solutions
Domain: zinfi.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: OEM, or Original Equipment Manufacturer, refers to companies that produce parts, components, or complete products used by other companies in their final products. OEMs provide specialized expertise, advanced technology, and cost-effective manufacturing solutions, allowing companies to focus on core activities like design and marketing. They are vital to industry-specific supply chains, supplying e…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for industries with oems
In conclusion, the landscape of Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) presents immense opportunities for international B2B buyers. By leveraging strategic sourcing, businesses can optimize their supply chains, enhance product quality, and foster innovation. The top OEMs, like Volkswagen and Toyota, exemplify how vertical integration and strategic partnerships can lead to resilient operations and superior product offerings. These companies not only set industry standards but also drive the transition towards sustainability and electrification, which is increasingly essential in today’s market.

Illustrative image related to industries with oems
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, aligning with reputable OEMs can be a pivotal factor in ensuring reliable supply chains and accessing cutting-edge technology. As the global economy shifts towards digitization and eco-friendly solutions, now is the time to engage with OEMs that prioritize innovation and quality.
Explore partnerships with these leading manufacturers to unlock competitive advantages and future-proof your business. The journey towards strategic sourcing is not just about procurement; it’s about building long-term relationships that drive mutual growth and success. Take the next step and connect with OEMs that align with your business goals.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to industries with oems