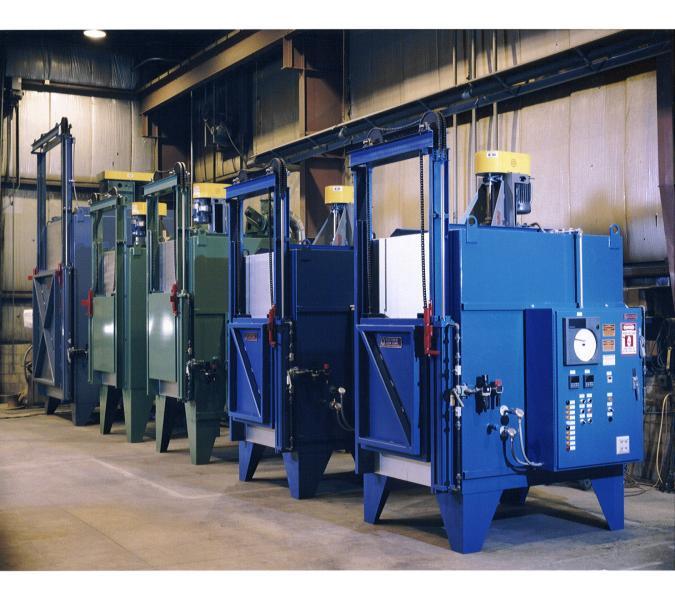
Choosing Your Industrial Heat Treatment Furnaces: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for industrial heat treatment furnaces
In the ever-evolving landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing the right industrial heat treatment furnaces can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The demand for precision-engineered heat treatment solutions is increasing as industries strive to enhance the durability and performance of their products. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, addressing the various types of heat treatment furnaces, their specific applications across different sectors, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
From dual chamber furnaces designed for high-temperature processing to versatile single chamber ovens, the options available can be overwhelming. Additionally, understanding the cost implications, including shipping and installation, is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide empowers international B2B buyers by offering actionable insights into the latest advancements in heat treatment technology and best practices for selecting the right equipment for their unique operational needs.
By navigating through the complexities of the industrial heat treatment furnace market, you will gain the knowledge necessary to enhance your procurement strategy and ultimately improve your product offerings. Whether you are operating in automotive manufacturing, aerospace, or metal fabrication, this resource will equip you with the expertise to make confident, informed decisions that drive your business forward.
Understanding industrial heat treatment furnaces Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Chamber Furnaces | Compact design, uniform heating, versatile use | Aerospace, automotive, metal fabrication | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to operate. Cons: Limited capacity for larger batches. |
| Dual Chamber Furnaces | High-temperature processing with controlled cooling | Hardening, tempering, specialized applications | Pros: Efficient space usage, versatile. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Bench Top Furnaces | Compact, ideal for small-scale operations | Laboratory R&D, small production runs | Pros: Space-efficient, precise control. Cons: Limited batch size, less rugged. |
| Continuous Ovens | Automated, allows for uninterrupted processing | Mass production, automotive, electronics | Pros: High throughput, consistent results. Cons: Higher maintenance, complex setup. |
| Pit Furnaces | Deep design for large components, high capacity | Aerospace, large metal components | Pros: Suitable for large parts, efficient. Cons: Requires significant floor space. |
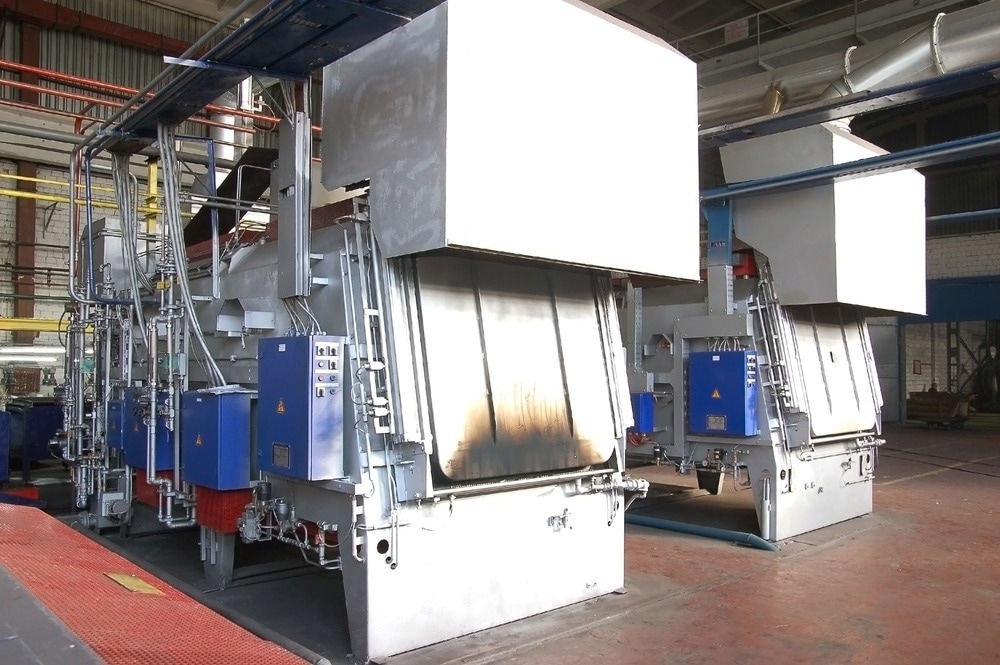
What Are the Characteristics of Single Chamber Furnaces?
Single chamber furnaces are designed for versatility and ease of use, making them a popular choice in industries such as aerospace and automotive. They provide uniform heating for processes like hardening and brazing, ensuring consistent results. Buyers should consider their production scale, as these furnaces are ideal for smaller batches but may not accommodate larger operations effectively.

Illustrative image related to industrial heat treatment furnaces
Why Choose Dual Chamber Furnaces for Heat Treatment?
Dual chamber furnaces combine high-temperature processing with controlled cooling in one unit, making them efficient for applications like hardening and tempering. Their compact design saves space while offering flexibility in processing. Buyers should weigh the initial investment against the potential for increased efficiency and versatility, especially for specialized heat treatment needs.
How Do Bench Top Furnaces Serve Industrial Applications?
Bench top furnaces are compact and designed for small-scale operations, making them ideal for laboratory research and development as well as small production runs. Their precise temperature control ensures reliable results, crucial for metallurgical processes. While they are space-efficient and user-friendly, buyers should note their limitations in batch size and robustness compared to larger furnaces.
What Are the Advantages of Continuous Ovens in Mass Production?
Continuous ovens facilitate automated, uninterrupted processing, making them suitable for mass production environments such as automotive and electronics manufacturing. Their design allows for high throughput and consistent heat treatment results. However, buyers must consider the complexity of setup and maintenance, which can be higher than traditional batch processing methods.
When Should You Consider Pit Furnaces?
Pit furnaces are designed for large components, offering high capacity and efficient heat treatment. Their deep design allows for the processing of sizable parts, making them ideal for industries like aerospace. While they provide significant benefits for large-scale operations, buyers should be mindful of the substantial floor space required for installation and operation.
Key Industrial Applications of industrial heat treatment furnaces
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of industrial heat treatment furnaces | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Heat treatment of turbine blades and structural components | Enhances performance and safety of critical components | Precision temperature control, compliance with industry standards |
| Automotive | Hardening of gears and shafts | Increases durability and lifespan of automotive parts | Customization for specific part sizes and heat-treat cycles |
| Oil & Gas | Stress relief of drill bits and valves | Improves reliability and reduces failure rates | Ability to handle large components and high temperatures |
| Tool Manufacturing | Heat treatment of cutting tools | Enhances hardness and wear resistance | Accurate temperature uniformity and quick turnaround times |
| Electronics | Sintering of ceramic components | Ensures high-quality, reliable electronic parts | Compatibility with various materials and temperature settings |
How Are Industrial Heat Treatment Furnaces Used in Aerospace?
In the aerospace sector, industrial heat treatment furnaces are essential for processing turbine blades and structural components. These components undergo specific heat treatments to enhance their performance and safety, which is critical given the high-stakes nature of aviation. Buyers in this industry must ensure that the furnaces provide precise temperature control and comply with stringent aerospace industry standards, which can vary by region.
What Role Do Industrial Heat Treatment Furnaces Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
Automotive manufacturers rely on industrial heat treatment furnaces to harden gears and shafts, significantly increasing the durability and lifespan of these critical parts. Heat treatment processes such as quenching and tempering are commonly employed to improve mechanical properties. Buyers should consider sourcing furnaces that offer customization options for various part sizes and specific heat-treat cycles to meet their unique production needs.
How Are Industrial Heat Treatment Furnaces Beneficial in the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, industrial heat treatment furnaces are utilized for stress relief processes on drill bits and valves, enhancing their reliability and reducing the likelihood of failures during operation. The ability to handle large components and maintain high temperatures is crucial for this application. Buyers should prioritize furnaces that can accommodate the specific dimensions and material types prevalent in oil and gas equipment.
What Applications Exist for Industrial Heat Treatment Furnaces in Tool Manufacturing?
Tool manufacturers use industrial heat treatment furnaces for the heat treatment of cutting tools, which is vital for enhancing hardness and wear resistance. This process ensures that tools can withstand the rigors of manufacturing environments. Sourcing considerations for buyers include the need for accurate temperature uniformity and the ability to deliver quick turnaround times to keep production schedules on track.
How Do Industrial Heat Treatment Furnaces Support the Electronics Industry?
In the electronics industry, industrial heat treatment furnaces are employed for the sintering of ceramic components, ensuring high-quality and reliable electronic parts. The specific temperature settings and compatibility with various materials are critical factors for buyers in this sector. Furnaces that provide flexibility in temperature management and can accommodate diverse material types will be advantageous for electronics manufacturers looking to maintain competitive quality standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘industrial heat treatment furnaces’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Temperature Control Leads to Defective Products
The Problem: A manufacturer of precision tools faces significant challenges due to inconsistent temperature control in their industrial heat treatment furnaces. Variations in temperature can lead to defects in the treated metal, affecting hardness and strength, ultimately resulting in product recalls and loss of customer trust. This inconsistency often stems from outdated equipment that lacks modern temperature control technology or from improper maintenance routines that fail to identify calibration issues before they affect production.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing modern heat treatment furnaces equipped with advanced temperature control systems. Look for models that offer features such as programmable temperature profiles and real-time monitoring capabilities, which can help ensure uniform heating and cooling processes. Additionally, implementing a rigorous maintenance schedule is essential. Regular calibration checks and preventive maintenance can identify issues before they disrupt production. Partnering with a reputable manufacturer that provides ongoing support and training can also ensure that your team is well-equipped to operate and maintain the equipment effectively.
Scenario 2: High Operating Costs Due to Inefficient Energy Use
The Problem: A company in the aerospace sector is facing escalating operating costs due to the inefficient energy use of their aging heat treatment furnaces. The high energy consumption not only affects the bottom line but also raises concerns about sustainability and compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. This scenario is particularly pressing for international buyers in regions where energy costs are rising rapidly.
The Solution: To address high operating costs, businesses should consider investing in energy-efficient heat treatment furnaces that utilize the latest insulation and heating technology. Look for furnaces that offer features such as advanced thermal insulation, which minimizes heat loss, and energy recovery systems that repurpose excess heat. Conducting an energy audit can also identify specific inefficiencies in your current system, guiding you to make informed decisions about upgrading or retrofitting existing equipment. Additionally, explore financing options for energy-efficient upgrades, as many manufacturers offer incentives or leasing programs that can alleviate upfront costs while promoting long-term savings.
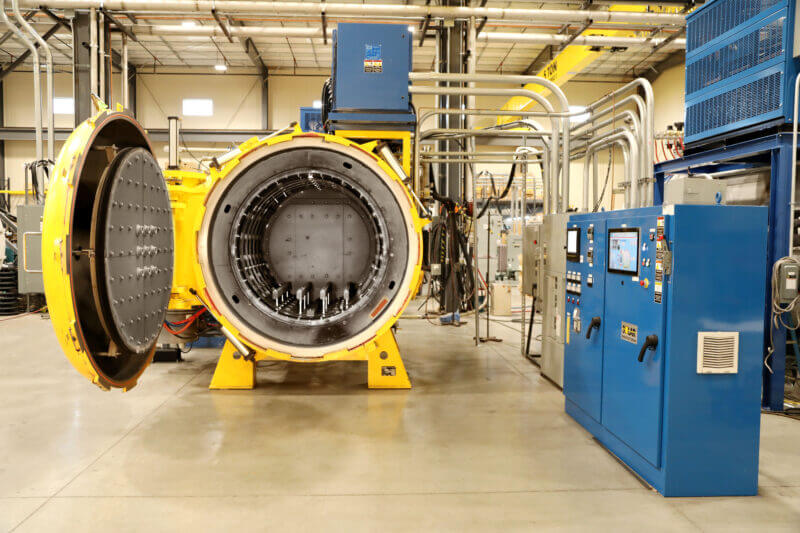
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Meeting Custom Specifications
The Problem: A metal fabrication company frequently struggles to meet the unique heat treatment specifications required by various clients, leading to missed deadlines and dissatisfied customers. The existing furnaces are not versatile enough to handle the wide range of materials and processes needed for different projects, resulting in bottlenecks and extended lead times.
The Solution: To overcome these challenges, businesses should seek out customizable heat treatment furnaces that can adapt to a variety of processes and materials. Engaging with manufacturers that specialize in bespoke solutions can be beneficial. Requesting a consultation can help identify specific needs and ensure that the furnace design aligns with your operational requirements. Additionally, consider investing in dual-chamber furnaces that allow for simultaneous processing of different materials or treatments. Training staff on best practices for operating these versatile systems can also enhance efficiency and flexibility, enabling your company to respond more swiftly to changing client demands.

Illustrative image related to industrial heat treatment furnaces
Strategic Material Selection Guide for industrial heat treatment furnaces
What Are the Key Materials Used in Industrial Heat Treatment Furnaces?
When selecting materials for industrial heat treatment furnaces, it’s crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The right material can significantly affect the furnace’s performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these furnaces.
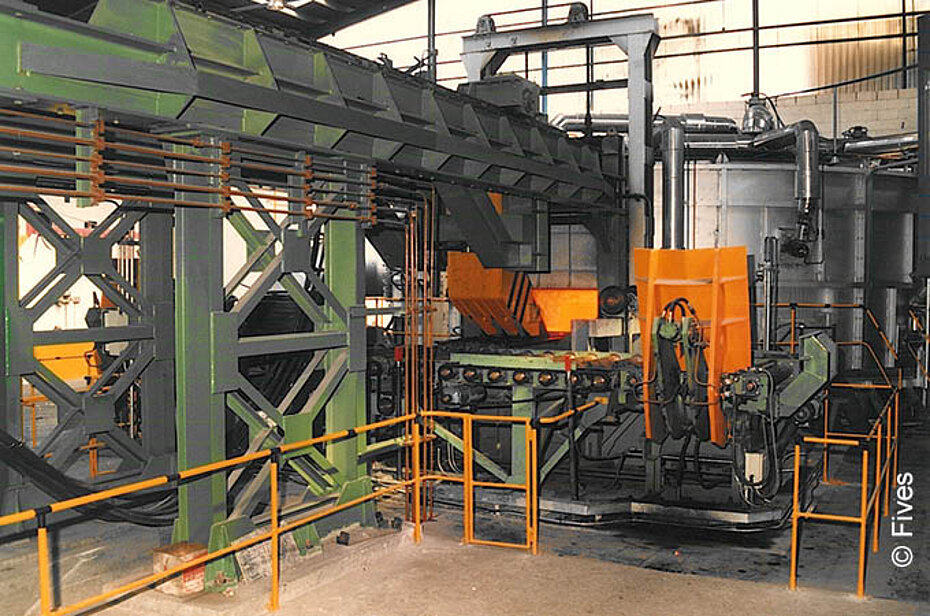
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Heat Treatment Furnaces?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength. It can withstand temperatures up to 1,600°F (870°C) without losing structural integrity, making it suitable for various heat treatment processes.
Pros & Cons: One of the main advantages of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to oxidation, which prolongs the life of the furnace. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, and its manufacturing complexity can lead to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including air and inert gases, making it versatile for different heat treatment processes. Its non-reactive nature is beneficial when treating sensitive materials.

Illustrative image related to industrial heat treatment furnaces
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN. Local availability of stainless steel can also affect costs and lead times.
Why Is Carbon Steel a Popular Choice for Heat Treatment Furnaces?
Key Properties: Carbon steel offers good strength and heat resistance, typically rated for temperatures up to 1,200°F (650°C). It is less expensive than stainless steel and is widely used in various industrial applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its cost-effectiveness, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers. However, it is less resistant to corrosion, which can lead to a shorter lifespan in humid or corrosive environments.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is suitable for applications where high corrosion resistance is not critical. However, it may not be ideal for processes involving reactive gases or fluids.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding carbon emissions and material standards. Ensuring compliance with ASTM or JIS standards can enhance product acceptance in international markets.
What Role Does Refractory Material Play in Heat Treatment Furnaces?
Key Properties: Refractory materials are designed to withstand high temperatures, often exceeding 2,500°F (1,370°C). They are critical for insulation and protecting the furnace structure from extreme heat.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of refractory materials is their ability to maintain structural integrity at high temperatures, enhancing energy efficiency. However, they can be brittle and may require careful handling during installation.
Impact on Application: Refractory materials are essential in applications requiring prolonged exposure to extreme temperatures, such as in high-temperature sintering processes.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of refractory materials that meet local standards. Compliance with international quality standards can also be a deciding factor in procurement.
How Do Ceramics Enhance Performance in Heat Treatment Furnaces?
Key Properties: Ceramics are known for their exceptional heat resistance and low thermal conductivity. They can withstand temperatures of up to 3,000°F (1,650°C) and are often used in specialized applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of ceramics is their ability to maintain performance at very high temperatures without deformation. However, they can be more expensive and fragile compared to metals, which may complicate installation and maintenance.
Impact on Application: Ceramics are particularly useful in applications involving high-temperature processes, such as the treatment of advanced materials. Their low thermal mass also contributes to energy efficiency.

Illustrative image related to industrial heat treatment furnaces
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should evaluate the availability of high-quality ceramics that comply with international standards. The cost and sourcing of these materials can vary significantly across different regions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Industrial Heat Treatment Furnaces
| Material | Typical Use Case for industrial heat treatment furnaces | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | General-purpose heat treatment applications | High corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Carbon Steel | Economical solutions for less corrosive environments | Cost-effective | Lower corrosion resistance | Medium |
| Refractory Material | High-temperature insulation and protection | Excellent heat resistance | Brittle and requires careful handling | Medium |
| Ceramics | Specialized high-temperature applications | Maintains performance at extreme temps | Expensive and fragile | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials used in industrial heat treatment furnaces, assisting international B2B buyers in making informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for industrial heat treatment furnaces
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Industrial Heat Treatment Furnaces?
The manufacturing process for industrial heat treatment furnaces involves several key stages, each crucial for ensuring that the final product meets the high standards required for effective heat treatment.
-
Material Preparation: This initial stage involves sourcing high-quality raw materials, typically metals and alloys that can withstand extreme temperatures and thermal cycling. Suppliers must provide materials that meet specific mechanical and chemical properties, ensuring they align with industry standards. Buyers should verify the material specifications through certificates of compliance to ensure they are sourcing from reputable suppliers.
-
Forming: During this phase, the prepared materials are shaped into the components of the furnace. Techniques such as laser cutting, CNC machining, and welding are commonly used. Precision is critical in this stage to ensure that all parts fit together correctly and can withstand operational stresses. B2B buyers should inquire about the machinery and techniques used in forming to assess the potential for precision and durability.
-
Assembly: The assembly stage involves integrating all the components into a cohesive unit. This process often requires skilled technicians who can ensure that all parts are correctly aligned and secured. It’s beneficial for buyers to understand the assembly process, as this can impact the furnace’s overall performance and reliability. Asking for assembly quality checklists or protocols can provide insights into the thoroughness of this stage.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves applying protective coatings, insulation, and any necessary electrical components. This finishing touches not only enhance the aesthetic appeal but also improve the furnace’s efficiency and safety. Buyers should inquire about the finishing techniques used, as well as any environmental compliance measures taken during this stage.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of Heat Treatment Furnaces?
Quality assurance (QA) is essential in the manufacturing of industrial heat treatment furnaces, ensuring that each unit meets the required performance and safety standards.
-
International Standards and Certifications: Many manufacturers adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines a framework for consistent quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking for compliance with European safety directives or API standards for oil and gas applications are also relevant. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with these certifications, as they indicate a commitment to quality and safety.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: Quality control (QC) is typically integrated into several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified requirements.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Quality checks are conducted during the manufacturing process to monitor compliance with specifications and tolerances.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the furnace is assembled, a final inspection is performed to ensure the product is functioning correctly and meets all performance standards. -
Testing Methods for Quality Assurance: Various testing methods are employed to validate the performance and safety of heat treatment furnaces. Common tests include thermal cycling tests to assess temperature uniformity, pressure testing to ensure integrity, and safety system tests. B2B buyers should ask for detailed reports of these tests as part of their procurement process.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
Verification of a supplier’s quality control practices is vital for B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.

Illustrative image related to industrial heat treatment furnaces
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols. Buyers should establish a clear audit framework and frequency to ensure ongoing compliance with quality standards.
-
Quality Assurance Reports: Requesting detailed QA reports can help buyers understand the quality processes employed by the supplier. These reports should outline the testing methods used, results obtained, and any corrective actions taken in case of deviations from standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These independent assessments can verify that the furnaces meet all specified standards before shipment, reducing the risk of receiving subpar equipment.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers?
International buyers face unique challenges when sourcing industrial heat treatment furnaces, particularly in verifying quality standards and compliance.
-
Understanding Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying standards for industrial equipment. Buyers must familiarize themselves with the local regulations and compliance requirements in their respective countries. This knowledge will help ensure that the equipment meets all necessary legal and operational standards upon arrival.
-
Logistical Considerations: Shipping industrial furnaces internationally can pose risks, such as damage during transit. Buyers should discuss packaging and shipping methods with suppliers to ensure that the equipment is adequately protected.
-
Post-Purchase Support and Warranty: Understanding the warranty and post-purchase support offered by suppliers is crucial. Buyers should inquire about the terms of warranties, availability of replacement parts, and support services, especially for international operations where access to immediate support may be limited.
By focusing on these aspects of manufacturing processes and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when purchasing industrial heat treatment furnaces, ensuring they invest in reliable and efficient equipment tailored to their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘industrial heat treatment furnaces’
To assist B2B buyers in procuring industrial heat treatment furnaces effectively, this guide provides a practical step-by-step checklist. Following these steps will ensure that you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and long-term goals.

Illustrative image related to industrial heat treatment furnaces
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, it’s essential to clearly define the technical specifications of the heat treatment furnace required for your applications. Consider factors such as temperature range, chamber size, and heating methods (e.g., convection, radiant). These specifications will help narrow down your options and ensure that the equipment meets your production requirements.
Step 2: Identify Your Budget
Establishing a budget is critical to avoid overspending and to ensure that the selected furnace aligns with your financial capabilities. Include not only the initial purchase price but also consider installation costs, maintenance, and any necessary upgrades. This comprehensive view will help you to make a more informed decision without compromising on quality.
Step 3: Research and Shortlist Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a proven track record in manufacturing industrial heat treatment furnaces. Look for companies that have been in the industry for a significant period and offer warranties or guarantees on their products. Create a shortlist based on their reputation, product offerings, and customer feedback, especially from businesses in your region.

Illustrative image related to industrial heat treatment furnaces
Step 4: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
It’s crucial to verify that potential suppliers hold the necessary certifications and comply with industry standards. Check for ISO certifications or other relevant quality assurance certifications that indicate reliability and safety in manufacturing. Compliance with local regulations is also essential, particularly if your operations are subject to specific environmental or safety laws.
Step 5: Request and Analyze Quotes
Once you have a shortlist of potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that include specifications, pricing, and delivery timelines. Analyze these quotes not only based on price but also on the value offered, such as after-sales support, warranty conditions, and installation services. Comparing these elements will help you identify the best overall deal.
Step 6: Check Customer References and Case Studies
Before finalizing a supplier, reach out to previous customers to gather insights about their experiences. Ask for case studies that demonstrate the supplier’s capability to meet specific heat treatment needs and how they handled any challenges. This information can provide a more realistic expectation of the supplier’s reliability and product performance.

Illustrative image related to industrial heat treatment furnaces
Step 7: Plan for Post-Purchase Support and Maintenance
Consider the supplier’s post-purchase support, including training, technical assistance, and maintenance services. Establishing a solid support structure can significantly impact the longevity and performance of your furnace. Ensure that the supplier offers accessible resources for troubleshooting and spare parts to minimize downtime in your operations.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing industrial heat treatment furnaces, ensuring that they invest in equipment that meets their specific needs while providing long-term value.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for industrial heat treatment furnaces Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Industrial Heat Treatment Furnaces?
Understanding the cost structure of industrial heat treatment furnaces is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions. The primary components influencing the total cost include:

Illustrative image related to industrial heat treatment furnaces
-
Materials: The choice of materials is fundamental, as high-grade metals and specialized alloys often drive up costs. For example, furnaces designed for high-temperature applications may utilize advanced refractory materials, which can significantly increase the price.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the complexity of the furnace design and the location of manufacturing. Skilled labor is essential for precision engineering, particularly in custom units, and can influence overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these expenses, but they are often reflected in the final pricing.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are incurred when producing custom parts or unique designs. Buyers should consider whether the supplier has the necessary tooling available or if new tooling must be developed, which could increase lead times and costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are essential for ensuring that furnaces meet industry standards. This can add to the cost but is a necessary investment for reliability and safety.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary significantly based on the destination. International shipping, particularly to regions such as Africa or South America, may incur additional tariffs and customs fees.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market conditions and competition.
What Factors Influence Pricing for Industrial Heat Treatment Furnaces?
Several factors can influence the pricing of heat treatment furnaces, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often qualify for bulk discounts. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-built furnaces tailored to specific operational needs tend to be more expensive. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements to avoid unforeseen costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Furnaces constructed from higher-grade materials or those that adhere to strict quality certifications (like ISO standards) will command higher prices. Verify these certifications to ensure product reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and experience of the supplier can affect pricing. Established manufacturers with a history of quality may charge a premium but offer better reliability and support.
-
Incoterms: The terms of delivery can significantly impact final costs. Understanding Incoterms will clarify who bears responsibility for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can influence overall expenditure.
How Can Buyers Negotiate for Better Pricing on Industrial Heat Treatment Furnaces?
Negotiation is key when sourcing industrial heat treatment furnaces. Here are some actionable tips:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A furnace with a higher upfront cost may offer lower operating expenses in the long run.
-
Leverage Multiple Quotes: Obtain quotes from several suppliers to compare pricing structures. This will provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Discuss Payment Terms: Flexible payment terms can ease cash flow concerns. Discussing options such as extended payment plans or financing can create a win-win scenario.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a long-term relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time. Trust can result in favorable negotiations and support.
-
Monitor Market Trends: Stay informed about market conditions and pricing trends in the heat treatment industry. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations and help them recognize fair pricing.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of pricing for industrial heat treatment furnaces requires a comprehensive understanding of cost components and pricing influencers. By employing strategic negotiation techniques and focusing on the total cost of ownership, international buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. It is essential to remember that prices may fluctuate based on market conditions, so staying proactive and informed is key to successful sourcing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing industrial heat treatment furnaces With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Industrial Heat Treatment Furnaces
In the realm of metallurgical processes, industrial heat treatment furnaces are a cornerstone for altering the mechanical properties of metals. However, several alternative solutions exist that can achieve similar outcomes. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and specific operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Industrial Heat Treatment Furnaces | Induction Heating Systems | Salt Bath Heat Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and uniform heating across various materials. | Rapid heating with localized control, suitable for specific applications. | Excellent heat transfer, ideal for uniform heating of complex shapes. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment with long-term durability. | Moderate to high, depending on the system’s complexity. | Generally lower capital cost, but operational costs can vary significantly. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires significant installation and setup time, often needing specialized infrastructure. | Easier setup with less space required; portable models available. | Requires specific materials and safety measures; setup complexity can vary. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed to ensure efficiency and safety; parts can be costly. | Lower maintenance needs but requires skilled personnel for optimal operation. | Maintenance is critical to prevent contamination and ensure safety; can be labor-intensive. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for large-scale operations requiring consistent and repeatable results across diverse materials. | Best for small to medium operations focusing on specific metal treatments. | Suitable for operations needing precise control over temperature and uniform heating of complex geometries. |
Understanding Induction Heating Systems
Induction heating systems utilize electromagnetic fields to heat conductive materials directly. This method is especially beneficial for processes requiring rapid heating, such as hardening or tempering of specific components. The advantages of induction heating include energy efficiency and minimal heat loss, making it a cost-effective choice for smaller operations. However, its effectiveness can be limited by the size and shape of the items being heated, and it may require a higher level of operator expertise to manage the process effectively.

Illustrative image related to industrial heat treatment furnaces
Analyzing Salt Bath Heat Treatment
Salt bath heat treatment involves submerging metals in a heated salt solution, providing uniform heating and excellent thermal conductivity. This method is advantageous for intricate components, as it ensures consistent temperature distribution and minimizes oxidation. While the initial capital costs are often lower than those of industrial furnaces, operational expenses can escalate due to the need for regular maintenance of the salt bath and adherence to safety protocols. This method is ideal for specialized applications where precision is paramount.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate heat treatment method hinges on several factors, including the scale of production, the specific materials involved, and the desired mechanical properties of the finished product. B2B buyers should assess their operational requirements, budget constraints, and the technical expertise available within their teams. By comparing industrial heat treatment furnaces against alternatives like induction heating and salt bath methods, decision-makers can determine the most effective solution tailored to their unique business needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for industrial heat treatment furnaces
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Industrial Heat Treatment Furnaces?
When evaluating industrial heat treatment furnaces, understanding specific technical properties is vital for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical specifications to consider:

Illustrative image related to industrial heat treatment furnaces
-
Temperature Range
The temperature range indicates the maximum and minimum temperatures the furnace can achieve. Most industrial furnaces are designed to operate between 1,200°F to 2,500°F, depending on the application. A wider temperature range allows flexibility in treating various materials, making it essential for B2B buyers to select a furnace that meets their operational requirements. -
Material Grade
The construction materials used in a heat treatment furnace significantly impact its durability and performance. Common materials include high-grade stainless steel and refractory bricks. Selecting the right material grade ensures that the furnace can withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments, which is crucial for long-term operational efficiency. -
Cooling Rate
The cooling rate refers to how quickly the furnace can lower the temperature after a heat treatment cycle. This specification is particularly important for processes requiring rapid quenching, as it affects the mechanical properties of the treated metals. Understanding this property can help buyers optimize their heat treatment processes for desired outcomes. -
Chamber Size and Capacity
The internal chamber size directly influences the volume of material that can be processed at one time. Buyers should consider their production needs and space constraints when selecting a furnace. A properly sized chamber can enhance efficiency and reduce energy costs, making it a crucial factor in purchasing decisions. -
Energy Efficiency Rating
Energy efficiency is increasingly important in industrial operations. Furnaces with higher efficiency ratings consume less energy, reducing operational costs and environmental impact. Buyers should look for models that feature advanced insulation and energy-saving technologies to maximize their investment. -
Control Systems
Modern heat treatment furnaces often come equipped with sophisticated control systems that allow for precise temperature regulation and monitoring. Features such as programmable logic controllers (PLC) and touchscreen interfaces enhance usability and ensure consistent results. Understanding these control capabilities can help buyers choose a furnace that aligns with their technical expertise and operational needs.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Industrial Heat Treatment Furnaces?
Familiarizing oneself with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms related to industrial heat treatment furnaces:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that may be marketed by another company under its brand name. In the heat treatment industry, buyers often work directly with OEMs for custom furnace solutions. Understanding OEM relationships can aid buyers in sourcing high-quality equipment tailored to their specifications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for buyers, especially when budgeting for new equipment or spare parts. It can also impact inventory management and production scheduling, making it a key consideration in procurement strategies. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. A well-structured RFQ can streamline the procurement process and ensure that all necessary specifications are communicated, leading to more accurate quotes and better decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms can prevent misunderstandings regarding shipping, insurance, and risk, which is essential for B2B buyers operating across different regions. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. In the context of heat treatment furnaces, understanding lead times can help buyers plan their operations and manage production schedules effectively.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of purchasing industrial heat treatment furnaces, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their business needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the industrial heat treatment furnaces Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends in the Industrial Heat Treatment Furnaces Sector?
The global industrial heat treatment furnaces market is experiencing a dynamic transformation influenced by several key factors. A significant driver is the increasing demand for high-performance materials in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing. As these sectors push for enhanced product quality and durability, the need for advanced heat treatment technologies grows. Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing practices is leading to the integration of IoT and automation in heat treatment processes, enabling real-time monitoring and improved operational efficiency.
Emerging trends also highlight the importance of customization and flexibility in furnace design. Manufacturers are increasingly offering tailored solutions that cater to specific customer requirements, whether for small-scale operations or large-scale production. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where market needs can vary significantly. Furthermore, the push for quick turnaround times has prompted suppliers to enhance their logistics capabilities, ensuring that furnaces can be delivered and installed rapidly to meet the demands of global supply chains.

Illustrative image related to industrial heat treatment furnaces
How Does Sustainability Influence Sourcing in the Industrial Heat Treatment Furnaces Market?
Sustainability has become a critical consideration in the procurement of industrial heat treatment furnaces. With growing awareness of environmental impacts, buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices. This includes the use of energy-efficient technologies, which not only reduce operational costs but also minimize carbon footprints. Additionally, many manufacturers are now exploring the use of eco-friendly materials and processes, contributing to a circular economy.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, as companies seek to ensure that their supply chains are transparent and responsible. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and LEED for energy-efficient buildings are becoming essential criteria for suppliers. Buyers should look for manufacturers who can provide evidence of their sustainability initiatives, including lifecycle assessments and reports on resource consumption. This focus on sustainability not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but can also enhance brand reputation in increasingly eco-conscious markets.
How Has the Industrial Heat Treatment Furnaces Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of industrial heat treatment furnaces dates back to the early 20th century when basic furnace designs were primarily used for metal hardening and tempering. As industrial processes advanced, so too did the technology behind heat treatment. The introduction of electric furnaces in the mid-20th century marked a significant turning point, providing greater temperature control and uniformity, which became essential for high-quality metal treatment.
Over the years, manufacturers have continuously innovated to meet the changing demands of the industry. The shift towards automation and the integration of digital technologies have further revolutionized the sector, allowing for more precise control over heat treatment processes and improved energy efficiency. Today, the market is characterized by a diverse range of products, from compact benchtop models to large-scale dual-chamber furnaces, reflecting the industry’s response to both technological advancements and evolving customer needs. This historical context is vital for B2B buyers to understand the capabilities and innovations available in the current market landscape.

Illustrative image related to industrial heat treatment furnaces
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of industrial heat treatment furnaces
1. How do I determine the right specifications for an industrial heat treatment furnace?
To select the right specifications for an industrial heat treatment furnace, begin by assessing your specific heat treatment processes, including the types of materials you will treat and the desired properties (e.g., hardness, strength). Consider factors like the maximum temperature required, chamber size, and heating rate. It’s also essential to evaluate the furnace’s energy efficiency and operational safety features. Engaging with manufacturers to discuss your needs can help clarify which furnace models and configurations will best meet your production goals.
2. What is the best type of heat treatment furnace for my manufacturing needs?
The best type of heat treatment furnace depends on your specific applications. For small-scale operations or research and development, bench-top furnaces offer flexibility and ease of use. For larger manufacturing needs, dual chamber furnaces are ideal for processes that require both heating and controlled cooling. If you are dealing with high-temperature applications, consider heavy-duty box furnaces. Always consult with suppliers to match the furnace type with your intended heat treatment processes.
3. How can I ensure the quality of the heat treatment furnace I purchase?
To ensure quality, source your heat treatment furnace from reputable manufacturers with established histories in the industry. Request detailed specifications, including performance metrics and warranties. It’s advisable to review customer testimonials and case studies to gauge reliability. Additionally, inquire about the quality assurance processes that the manufacturer employs, including testing protocols and certifications that comply with international standards.

Illustrative image related to industrial heat treatment furnaces
4. What customization options are available for industrial heat treatment furnaces?
Customization options for industrial heat treatment furnaces can include modifications in chamber size, temperature range, and control systems. Many manufacturers offer tailored solutions to meet specific operational requirements, such as integrating quench tanks or enhancing safety features. When discussing customization, provide detailed information about your process needs to ensure the manufacturer can deliver a solution that optimally fits your production environment.
5. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for industrial heat treatment furnaces?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for industrial heat treatment furnaces can vary significantly by manufacturer and model. Some suppliers may have no MOQ for standard models, while custom-built furnaces may require larger orders. It’s crucial to discuss MOQs upfront with potential suppliers, especially if you are planning for large-scale projects or ongoing production needs. This conversation will help you align your purchasing strategy with the supplier’s capabilities.
6. What payment terms should I expect when purchasing industrial heat treatment furnaces?
Payment terms for industrial heat treatment furnaces typically involve a deposit upfront, with the balance due upon delivery or installation. Some suppliers may offer flexible financing options or payment plans, particularly for larger orders. It’s important to clarify payment terms during negotiations, as well as any penalties for late payments or discounts for early settlement. Ensure that all terms are documented in your purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings.
7. How do I navigate international shipping and logistics for heat treatment furnaces?
Navigating international shipping and logistics requires careful planning. First, confirm that the supplier can handle shipping to your location, including customs clearance. Understand the shipping costs, delivery timelines, and responsibilities for both parties. It’s advisable to engage a logistics provider experienced in handling industrial equipment to ensure compliance with regulations and to mitigate potential shipping risks. Having a clear communication channel with your supplier throughout the process is also crucial.
8. What post-purchase support and maintenance services should I expect?
Post-purchase support and maintenance services should include installation assistance, operator training, and access to customer service for troubleshooting. Many manufacturers offer maintenance contracts that cover routine inspections and repairs. Ensure you understand the warranty terms, including what is covered and for how long. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can facilitate ongoing support and ensure your furnace operates efficiently throughout its lifespan.

Illustrative image related to industrial heat treatment furnaces
Top 7 Industrial Heat Treatment Furnaces Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Keith Company – Bench Top Hardening Heat Treat Furnaces
Domain: keithcompany.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Bench Top Hardening Heat Treat Furnaces rated up to 2250°F. Designed for hardening tool steels (e.g., 17-4 PH, D2, A2, A6, H13, S7, M2, AISI 4140) with operating temperatures between 1500°F and 2000°F. Features include a vertical rising door for operator safety, quick configuration options, and accessories such as quench tank, audible alarm, bench stand, and various temperature controllers. Known …
2. Lucifer Furnaces – Dual Chamber Furnaces & Ovens
Domain: luciferfurnaces.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Lucifer Furnaces specializes in manufacturing high-quality heat-treating equipment designed for precision, reliability, and long-term performance. Key product offerings include: 1. **Dual Chamber Furnaces + Ovens**: Combine high-temperature processing and controlled cooling in one compact unit, ideal for hardening, tempering, and space-saving efficiency. 2. **Single Chamber Furnaces**: Box furnace…
3. Azom – Heat Treatment Furnaces
Domain: azom.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Types of Heat Treatment Furnaces: 1. Salt Bath Furnaces: – Use molten salt as the heating medium. – Suitable for carburizing, carbonitriding, and nitrocarburizing. – Advantages: Rapid and uniform heating, reduced oxidation, suitable for small parts, even temperature distribution. – Disadvantages: Limited temperature range, salt residue cleaning required, high maintenance. 2. Box Furnaces: – Also k…
4. Lindberg Furnace – Heat Treat Furnaces
Domain: lindbergmph.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Lindberg Furnace offers a wide range of heat treat furnaces including: Hot Stamping Furnace, Press Hardening Furnace, Industrial Box Furnaces (Rod Overbend Box, Cyclone Box, Silicon Carbide Element Box, Car Bottom Box, Corrtherm Element Electric Box, Gas-Fired Radiant Tube Box, Polymer Burn Off Box, Investment Cast Burn Out Box), Pit Furnaces (Corrtherm Carburizing, Steam HOMO® Pit, HOMO® Temperin…
5. Knights Furnace – Dual Chamber Heat Treat Furnaces
Domain: knightsfurnace.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”DKMT-242436 Dual Chamber Heat Treat Furnace”,”price”:”$0″},{“name”:”DKMTG-242436 Dual Chamber Heat Treat Furnace”,”price”:”$0″},{“name”:”KMTG-242436 Heat Treat Furnace”,”price”:”$0″},{“name”:”DKMTG-36 Dual Chamber Heat Treat Furnace”,”price”:”$0″},{“name”:”DKMTG-27 Dual Chamber Heat Treat Furnace”,”price”:”$0″},{“name”:”DKMTG-21 Dual Chamber Heat Treat Furnace”,”price”:”$0″},…
6. Cress Furnaces – C122012
Domain: heattreatnow.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: [{‘name’: ‘Cress Furnaces – C122012’, ‘price’: ‘$6,555.00’, ‘original_price’: ‘$6,900.00’}, {‘name’: ‘Cress Furnaces – C122012DW’, ‘price’: ‘$8,730.50’, ‘original_price’: ‘$9,190.00’}, {‘name’: ‘Cress Furnaces – C1228DW’, ‘price’: ‘$8,056.00’, ‘original_price’: ‘$8,480.00’}, {‘name’: ‘Cress Furnaces – C1240 / PM3T’, ‘price’: ‘$9,175.10’, ‘original_price’: ‘$9,658.00’}, {‘name’: ‘Cress Furnaces – G…
7. Ipsen USA – Vacuum Furnaces & Aftermarket Services
Domain: themonty.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: 1) Ipsen USA: Vacuum furnace builder with 2023 sales over $110 million USD; 50% new equipment, 50% aftermarket (parts, service, hot zones). 2) AFC-Holcroft: Largest manufacturer of atmosphere heat treating furnaces in North America; known for batch IQ furnaces and pushers; serves automotive, industrial bearings, gears, and more. 3) Surface Combustion: Known for Allcase® Batch Integral Quench Furna…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for industrial heat treatment furnaces
In summary, strategic sourcing of industrial heat treatment furnaces is essential for international buyers seeking to enhance operational efficiency and product quality. By focusing on high-quality manufacturers with a proven track record, such as those offering customization and innovative solutions, businesses can secure equipment that meets their unique specifications. Understanding the diverse range of products—from dual chamber furnaces to bench top models—allows buyers to select the right technology for their specific applications, whether in aerospace, automotive, or metallurgical processes.
Moreover, investing in reliable and durable heat treatment equipment not only improves performance but also ensures long-term savings through reduced maintenance costs and increased operational uptime. As global markets evolve, the importance of sourcing equipment that aligns with local regulations and market demands becomes paramount.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are encouraged to engage with reputable manufacturers to explore tailored solutions that drive growth and innovation. By taking proactive steps in strategic sourcing, companies can position themselves for success in an increasingly competitive landscape. Now is the time to invest in the future of your operations—begin your sourcing journey today.
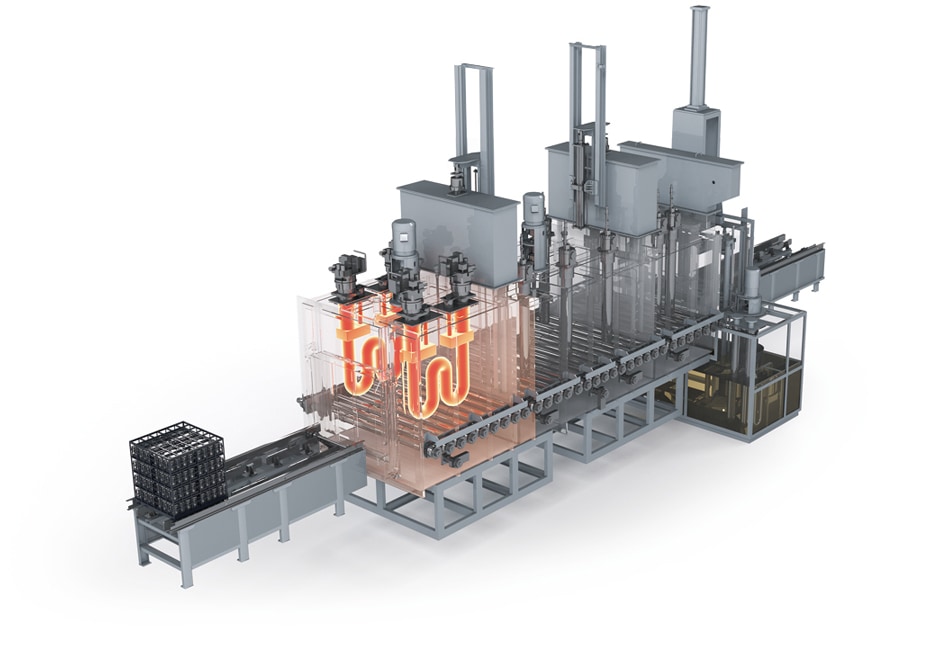
Illustrative image related to industrial heat treatment furnaces
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.