Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the Rubber Injection Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rubber injection
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality rubber injection components poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With varying production processes like injection, transfer, and compression molding, understanding the right method for your specific application is crucial. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the complexities of rubber injection by exploring the different types of molding processes, their applications across diverse industries, and essential factors for supplier vetting.
As you navigate the global market, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key players like Vietnam and Brazil—this guide serves as a vital resource. It empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions by providing insights into cost considerations, material specifications, and the importance of customizing solutions to fit unique operational requirements.
By leveraging the information presented here, you can effectively identify reliable suppliers, streamline your procurement process, and ultimately enhance the efficiency of your operations. Embrace this opportunity to elevate your sourcing strategy and ensure your business remains competitive in a rapidly evolving marketplace.
Understanding rubber injection Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber Transfer Molding | Uses a closed mold; ideal for complex geometries and multi-cavity parts | Automotive components, seals, gaskets | Pros: High dimensional accuracy, reduced cycle times. Cons: Higher material waste, longer setup time. |
| Rubber Compression Molding | Traditional method; utilizes open molds; suited for low to medium volumes | O-rings, gaskets, bulkier parts | Pros: Strong materials, low setup costs. Cons: Longer curing times, limited to specific shapes. |
| Organic Rubber Injection | Efficient material prep; no pre-forms required; preheating process | High precision components in automotive and aerospace | Pros: Reduced labor, faster cycle times. Cons: Higher initial costs, complex machinery requirements. |
| Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection | Closed system; uses liquid silicone; ideal for medical applications | Medical devices, consumer goods | Pros: Minimal contamination risk, high precision. Cons: Limited to specific applications, higher cost. |
| Thermoplastic Rubber Injection | Processes elastomers like plastic; recyclable; colored easily | Consumer products, automotive parts | Pros: Fast production, no curing time. Cons: Limited thermal resistance, not suitable for all applications. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Rubber Transfer Molding?
Rubber transfer molding is characterized by its ability to handle intricate designs and multiple cavities. This method employs a closed mold system, making it suitable for parts that require precise dimensional tolerances. Industries such as automotive frequently utilize this technique for components like seals and gaskets. B2B buyers should consider the balance between setup costs and material waste, as the process can generate excess rubber that must be discarded.
How Does Rubber Compression Molding Work and When Should it be Used?
Rubber compression molding is a traditional method that involves placing rubber pre-forms into open molds. This technique is particularly effective for low to medium production volumes and larger parts. Common applications include O-rings and gaskets. Buyers should be mindful of longer curing times and the limitations on part geometry, as this method is not as versatile as others. However, it offers strong materials and lower tooling costs, making it a viable option for certain projects.

Illustrative image related to rubber injection
What are the Benefits of Organic Rubber Injection for B2B Buyers?
Organic rubber injection stands out for its efficient material preparation and the elimination of pre-forms, which can significantly reduce labor costs. This method preheats the rubber, enhancing flow and curing speed, making it ideal for high-precision components in sectors like automotive and aerospace. Buyers should weigh the benefits of reduced cycle times against the potentially higher initial machinery costs, ensuring that the investment aligns with their production needs.
Why Choose Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection for Medical Applications?
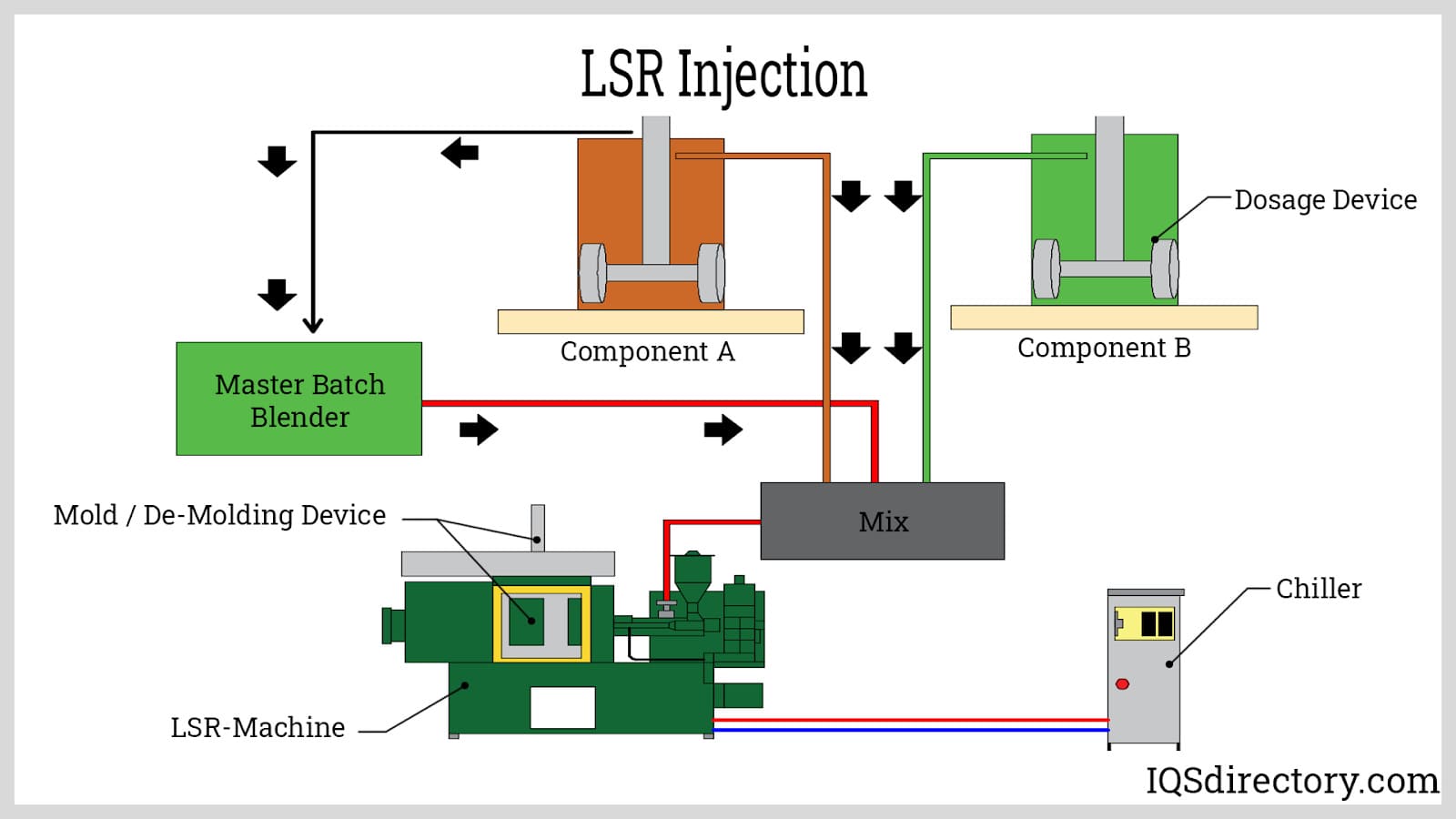
Liquid silicone rubber (LSR) injection is renowned for its closed system that minimizes contamination risks, making it an excellent choice for medical devices and consumer goods. This method allows for high precision and consistency in production. B2B buyers in the medical field should consider the benefits of reduced contamination and faster production cycles, while also noting the higher costs associated with LSR materials and machinery.
What Advantages Does Thermoplastic Rubber Injection Offer in Manufacturing?
Thermoplastic rubber injection combines the properties of rubber with the processing ease of plastics, allowing for rapid production without the need for curing. This method is well-suited for consumer products and automotive parts, offering flexibility in design and coloration. However, buyers should be cautious of its limitations in thermal resistance and ensure it fits the specific application requirements. The absence of lengthy curing times can be a significant advantage in fast-paced manufacturing environments.
Key Industrial Applications of rubber injection
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of rubber injection | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Seals and gaskets for engines and transmissions | Enhanced durability and performance, leading to reduced maintenance costs | Quality of materials, precision in molding, and compliance with automotive standards |
| Medical Devices | Custom silicone components for surgical instruments | Improved patient safety and device reliability | Regulatory compliance, biocompatibility of materials, and customization capabilities |
| Consumer Electronics | Vibration dampening pads for electronic devices | Reduced noise and improved user experience | Material properties, environmental resistance, and design flexibility |
| Construction | Rubber flooring and matting solutions | Increased safety and comfort in work environments | Durability, ease of installation, and resistance to wear and tear |
| Aerospace | Engine mounts and vibration isolators | Enhanced performance and safety in critical applications | High-temperature resistance, lightweight materials, and precision engineering |
How is Rubber Injection Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, rubber injection is crucial for producing seals and gaskets that ensure engine and transmission integrity. These components must withstand extreme temperatures and pressures while maintaining a reliable seal. Buyers in this industry need to prioritize sourcing from manufacturers who can provide high-quality materials that comply with automotive standards, as well as precision in molding to ensure dimensional accuracy. The right rubber injection process can significantly enhance the durability and performance of these critical components, ultimately reducing maintenance costs and improving overall vehicle reliability.
What Role Does Rubber Injection Play in Medical Devices?
Rubber injection molding is extensively used in the medical industry to create custom silicone components for surgical instruments and devices. These components must meet stringent regulatory standards for biocompatibility and safety. International buyers should consider suppliers that can demonstrate compliance with medical regulations and offer customization capabilities to meet specific design requirements. The benefits of using rubber injection in this context include improved patient safety and the reliability of medical devices, which are paramount in healthcare applications.
How Does Rubber Injection Benefit Consumer Electronics?
In consumer electronics, rubber injection is employed to manufacture vibration dampening pads that enhance the user experience by reducing noise and vibrations. These pads are essential for maintaining the performance and longevity of electronic devices. When sourcing these components, buyers should focus on the material properties, such as resilience and environmental resistance, as well as the flexibility of design to accommodate various device shapes. By investing in high-quality rubber injection molded parts, companies can significantly improve product performance and customer satisfaction.
What Are the Applications of Rubber Injection in Construction?
Rubber injection is increasingly used to produce flooring and matting solutions in the construction industry. These products provide safety and comfort in work environments, particularly in industrial and commercial settings. Buyers should prioritize sourcing durable materials that can withstand heavy foot traffic and resist wear and tear. Additionally, ease of installation is a key consideration, as it can impact project timelines and costs. By leveraging rubber injection technology, construction companies can enhance the safety and functionality of their workspaces.
Illustrative image related to rubber injection
How is Rubber Injection Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, rubber injection is critical for manufacturing engine mounts and vibration isolators that ensure the safety and performance of aircraft. These components must be lightweight yet robust, able to withstand high temperatures and stresses. Buyers in this industry should seek suppliers with expertise in high-precision engineering and materials that meet aerospace specifications. The use of rubber injection in these applications not only improves performance but also enhances safety in critical aerospace operations, making it a vital consideration for industry stakeholders.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘rubber injection’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Material Selection Challenges in Rubber Injection Molding
The Problem: B2B buyers often face difficulties in selecting the right type of rubber material for their injection molding needs. With various options available—such as organic rubber, liquid silicone rubber (LSR), and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE)—the nuances of material properties can create confusion. Buyers may struggle to determine which material best suits their specific application, leading to potential production delays, increased costs, and suboptimal product performance.
The Solution: To effectively navigate material selection, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their project requirements. Start by defining the mechanical properties needed, such as elasticity, temperature resistance, and chemical compatibility. Engaging with suppliers who offer expert consultation can provide insights into which material aligns best with your specifications. It is also beneficial to request sample parts to evaluate their performance in real-world conditions before committing to large-scale production. This proactive approach ensures that the chosen material enhances product functionality and reduces the risk of costly revisions later.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Production Efficiency Hurdles in Rubber Injection
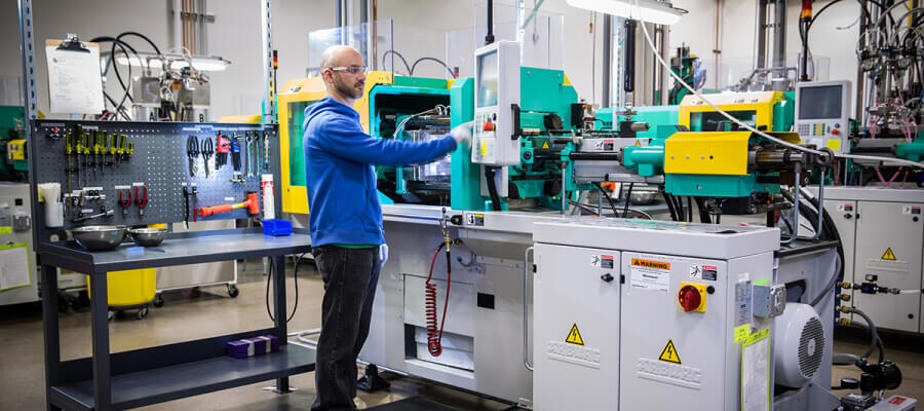
The Problem: Many manufacturers encounter inefficiencies in their rubber injection processes due to inadequate tooling or outdated machinery. These inefficiencies can result in longer cycle times, increased waste, and ultimately, higher production costs. B2B buyers may also face challenges in scaling production to meet demand, as older equipment may not be capable of handling higher volumes without sacrificing quality.
The Solution: To enhance production efficiency, buyers should consider investing in modern injection molding technology that incorporates advanced features like flashless tooling and automated material handling systems. Conducting an equipment audit can identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement. Collaborating with manufacturers who provide customized tooling solutions tailored to specific production requirements can significantly reduce cycle times and waste. Additionally, implementing lean manufacturing principles can streamline operations, improve workflow, and boost overall productivity. This strategic investment not only optimizes current operations but also positions the company for scalable growth in the future.
Illustrative image related to rubber injection
Scenario 3: Addressing Quality Control Issues in Rubber Injection Parts
The Problem: Ensuring consistent quality in rubber injection molded parts can be a persistent challenge for B2B buyers. Variability in production processes, material inconsistencies, and improper curing can lead to defects that compromise product integrity. Buyers often face the dilemma of managing quality assurance while balancing cost constraints, which can result in subpar components that affect end-user satisfaction.
The Solution: Implementing a robust quality control system is essential to mitigate these risks. Buyers should establish clear quality standards and work closely with their suppliers to ensure adherence throughout the production process. This includes performing regular inspections and utilizing advanced testing methods such as tensile strength testing and dimensional analysis. Investing in real-time monitoring systems can also provide immediate feedback on production quality, allowing for quick corrective actions. Furthermore, fostering open communication with suppliers about quality expectations can help in building a reliable partnership that prioritizes product excellence. By taking these steps, buyers can significantly enhance the quality of their rubber injection molded parts, thereby improving customer satisfaction and reducing return rates.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rubber injection
What Are the Key Materials Used in Rubber Injection and Their Properties?
When selecting materials for rubber injection, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of various types is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. Below, we analyze four common materials used in rubber injection, focusing on their applications, benefits, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Natural Rubber (NR)
Natural rubber is derived from the latex of rubber trees and is known for its excellent elasticity and resilience.

Illustrative image related to rubber injection
Key Properties:
– High tensile strength and flexibility.
– Good abrasion resistance and resilience.
– Temperature range: -50°C to 80°C.
Pros & Cons:
Natural rubber is cost-effective and offers outstanding performance in dynamic applications. However, it has limited resistance to oils, solvents, and UV exposure, which can lead to degradation over time.
Impact on Application:
Natural rubber is ideal for applications requiring flexibility and shock absorption, such as seals and gaskets. However, it may not be suitable for environments with exposure to harsh chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with ASTM D2000 and other local standards is essential. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider the availability of natural rubber and potential supply chain challenges.

Illustrative image related to rubber injection
2. Synthetic Rubber (SBR, EPDM, NBR)
Synthetic rubbers, including Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR), Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM), and Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR), are engineered to provide specific properties.
Key Properties:
– Varying temperature ratings: SBR (up to 100°C), EPDM (up to 150°C), NBR (up to 120°C).
– Excellent resistance to oils and chemicals (especially NBR).
Pros & Cons:
Synthetic rubbers offer tailored properties for specific applications, such as oil resistance in automotive parts. However, they can be more expensive than natural rubber and may require more complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application:
These materials are suitable for a wide range of applications, including automotive seals, hoses, and gaskets. The choice of synthetic rubber depends on the specific media compatibility required.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards such as DIN and JIS. Additionally, understanding local market preferences for synthetic versus natural rubber is crucial, especially in regions with diverse industrial needs.
3. Silicone Rubber (LSR)
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) is a high-performance material known for its thermal stability and flexibility.
Key Properties:
– Operating temperature range: -60°C to 200°C.
– Excellent chemical resistance and UV stability.
Pros & Cons:
Silicone rubber is ideal for high-temperature applications and offers superior durability. However, it tends to be more expensive than other rubber types and may not be suitable for high-stress applications.

Illustrative image related to rubber injection
Impact on Application:
Silicone is commonly used in medical devices, food processing equipment, and automotive applications where high temperature and chemical resistance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with FDA and other health regulations is vital for medical applications. Buyers should also consider the availability of LSR in their region and any associated costs.
4. Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)
Thermoplastic elastomers combine the properties of rubber with the processing advantages of plastics.
Key Properties:
– Temperature range: -40°C to 120°C.
– Good chemical resistance and flexibility.
Pros & Cons:
TPEs are easy to process and can be recycled, making them environmentally friendly. However, they may not provide the same level of durability as traditional rubber materials in extreme conditions.

Illustrative image related to rubber injection
Impact on Application:
TPEs are suitable for consumer goods, automotive parts, and medical devices where flexibility and ease of processing are essential.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Understanding local recycling regulations and market demand for eco-friendly materials can influence the choice of TPEs. Compliance with relevant standards is also necessary.
Summary Table of Rubber Injection Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for rubber injection | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber (NR) | Seals, gaskets, shock absorbers | Excellent elasticity and cost-effectiveness | Limited chemical and UV resistance | Low |
| Synthetic Rubber (SBR, EPDM, NBR) | Automotive seals, hoses, gaskets | Tailored properties for specific applications | Higher cost and complexity in manufacturing | Medium |
| Silicone Rubber (LSR) | Medical devices, food processing equipment | High thermal stability and chemical resistance | Higher cost, limited high-stress applications | High |
| Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) | Consumer goods, automotive parts | Easy processing and recyclability | Lower durability in extreme conditions | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of common rubber injection materials, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rubber injection
What Are the Key Stages in the Rubber Injection Manufacturing Process?
The manufacturing process for rubber injection involves several critical stages that ensure the production of high-quality rubber components. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing rubber products.
Material Preparation: How Is Rubber Prepared for Injection Molding?
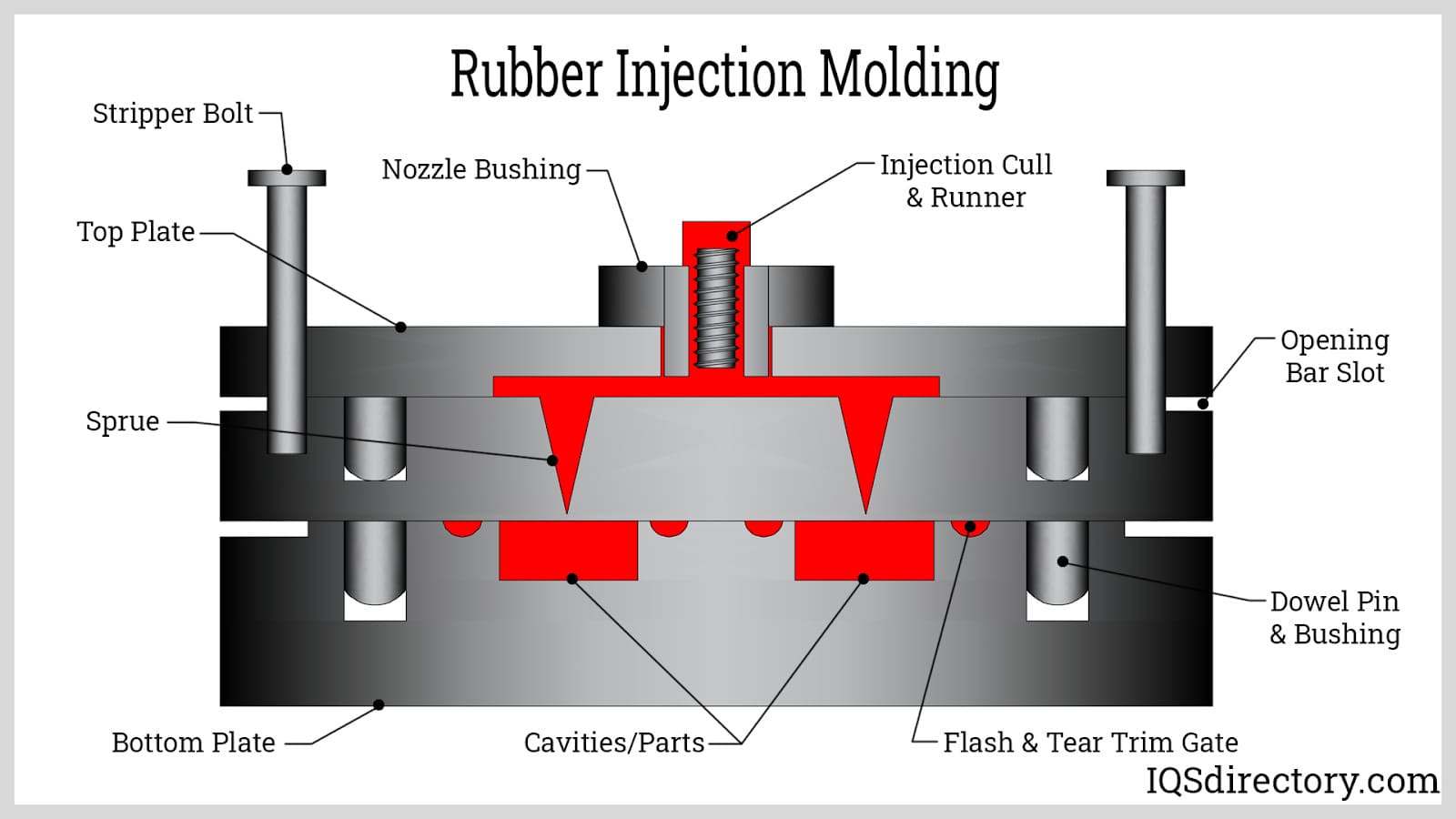
The first step in the rubber injection process is material preparation. This involves mixing rubber compounds to achieve the desired properties, such as hardness and elasticity. The materials are typically combined with additives to enhance performance characteristics. Once mixed, the rubber is formed into continuous strips, generally measuring about 1.25 inches wide and 0.375 inches thick. These strips are then fed into a screw that fills a barrel with a predetermined amount of rubber material. Pre-heating the rubber during this stage reduces its viscosity, allowing for easier flow into the mold cavities.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Rubber Injection?
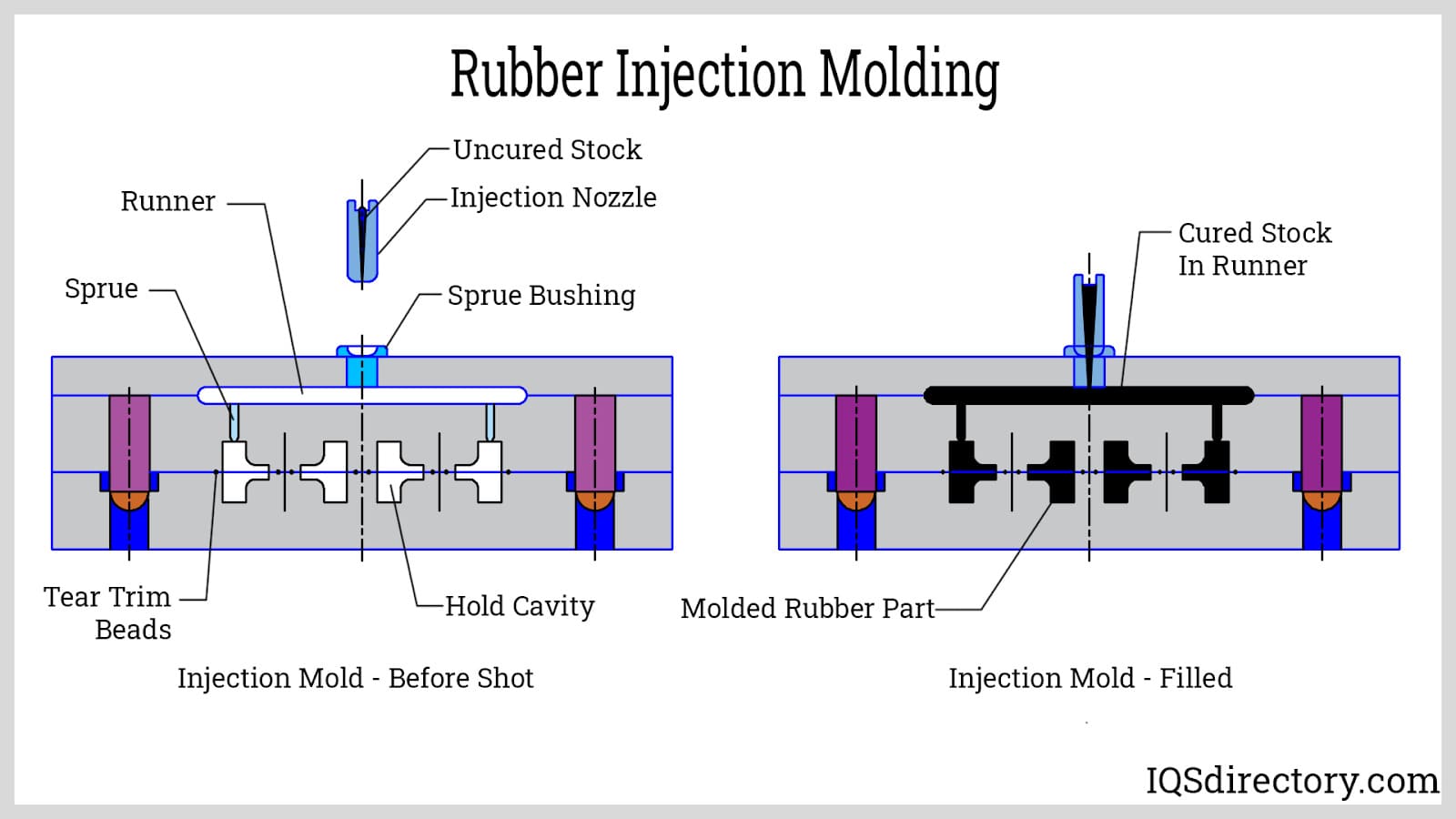
The forming stage is where the prepared rubber material is injected into molds. This is typically done using an injection molding machine that applies high pressure to ensure the rubber fills all cavities completely. The primary techniques used in this stage include:
- Organic Rubber Injection: This method allows for efficient material handling by eliminating the need for pre-forms. The rubber is injected directly into the mold where it cures.
- Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) Injection: Ideal for applications requiring high precision, this method involves two-part liquid silicone that is injected into the mold, minimizing contamination.
- Thermoplastic Rubber Injection: This technique combines the characteristics of rubber and plastic, allowing for quick production cycles without the need for curing.
Each method has its specific advantages and is chosen based on the requirements of the final product.
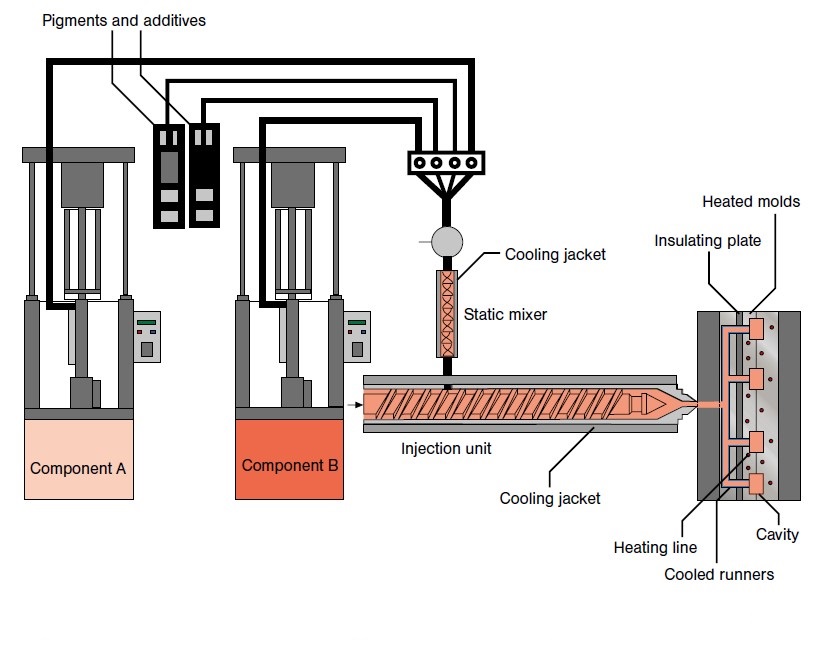
How Are Rubber Products Assembled and Finished?
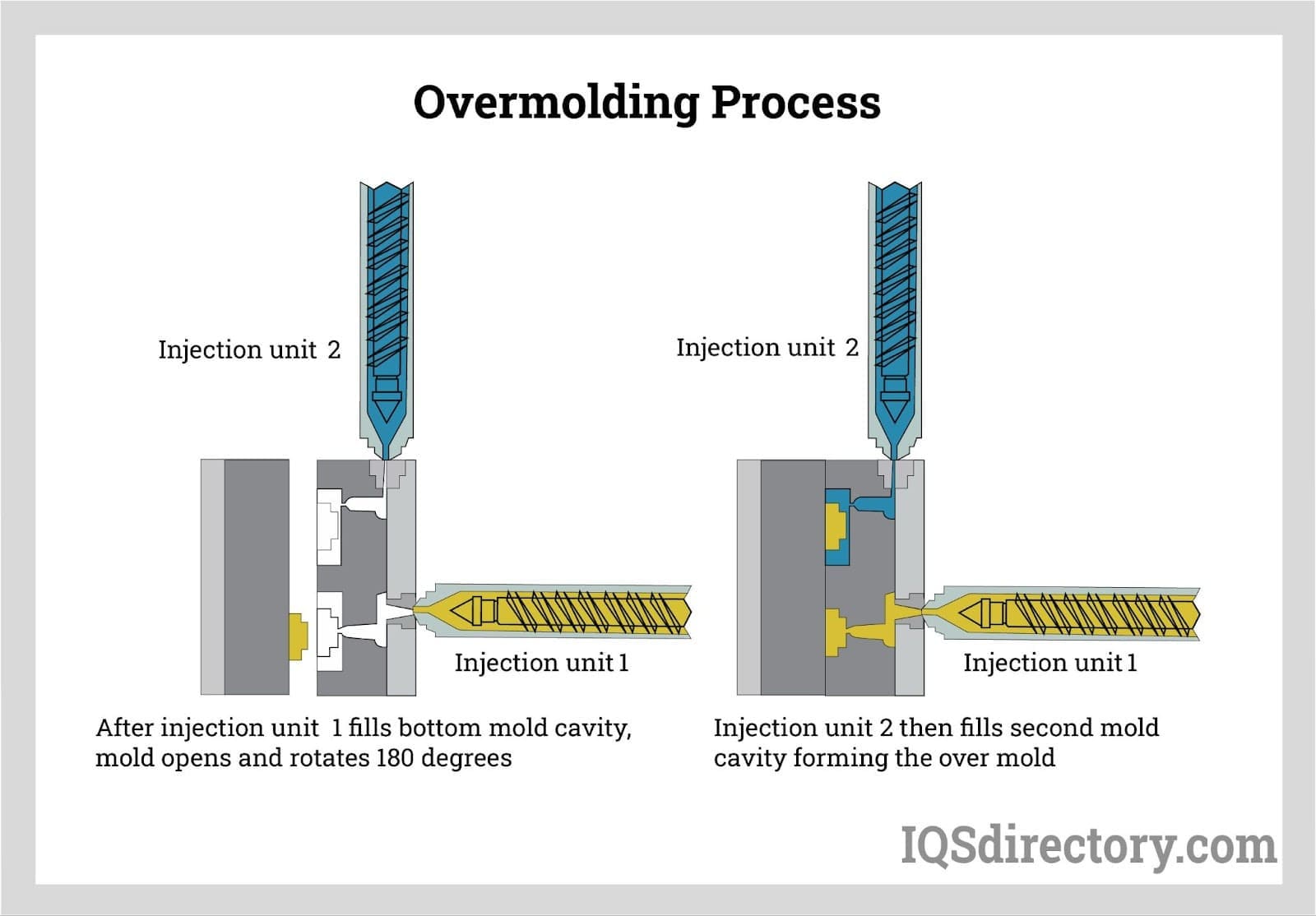
After the molding process, the next stage involves assembly and finishing. This can include trimming excess material, assembling multiple components, or applying surface treatments such as coatings or colors. The assembly may also involve overmolding, where additional layers of rubber are added to existing parts for enhanced functionality.
Illustrative image related to rubber injection
The finishing touches ensure that the final product meets the aesthetic and functional expectations of the client. This stage is crucial for components that will be used in visible applications or require specific surface properties.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential in Rubber Injection Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital part of the rubber injection process, ensuring that products meet international standards and client specifications. For B2B buyers, understanding these measures can help in selecting reliable suppliers.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Look For?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are essential for any manufacturer to demonstrate their commitment to quality management. ISO 9001 outlines the requirements for a quality management system, helping organizations ensure they meet customer and regulatory requirements consistently. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking for European markets and API standards for petroleum-related applications are critical for ensuring compliance in specialized sectors.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Rubber Injection Process?
Quality control checkpoints are integral to maintaining product integrity throughout the manufacturing process. These checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the production process to ensure they meet specified quality standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify any deviations from quality standards in real-time, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection ensures that the finished products meet all specifications and are free from defects before shipping.
These checkpoints help maintain high standards and minimize the risk of defects in the final product.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Rubber Injection Quality Control?
Several testing methods are employed to assess the quality and performance of rubber products, including:
- Mechanical Testing: This includes tensile strength, elongation, and hardness tests to evaluate the physical properties of rubber.
- Thermal Testing: Assessing the thermal stability and performance of rubber under various temperature conditions is crucial, especially for applications in extreme environments.
- Chemical Resistance Testing: Determining how well rubber withstands exposure to different chemicals is vital for applications in industries such as automotive and medical.
These tests provide valuable data that can help buyers understand the reliability and suitability of rubber products for their specific applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control practices is critical to ensuring reliable product delivery.
What Should Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits and Reports?
Buyers should request and review quality control reports and audits from potential suppliers. This documentation should detail the quality management systems in place, results of past quality audits, and any corrective actions taken for non-conformance. Suppliers with robust QA documentation demonstrate a commitment to maintaining high standards and transparency.
Why Is Third-Party Inspection Important for Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can further enhance the verification process. Independent inspectors can provide unbiased assessments of the manufacturing processes and finished products. This is particularly important for buyers entering new markets or working with suppliers for the first time.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements and standards that impact quality control practices. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of these nuances to ensure compliance and avoid potential pitfalls.
For instance, regulatory frameworks may differ significantly between the EU and other regions, necessitating a thorough understanding of local standards. Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences may affect communication regarding quality expectations. Therefore, establishing clear lines of communication and understanding local regulations is essential for successful international partnerships.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in rubber injection is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing stages, along with rigorous quality control measures, buyers can ensure they select the right suppliers for their needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘rubber injection’
Introduction
This guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in effectively sourcing rubber injection services. Whether you are seeking components for automotive applications, industrial machinery, or specialized products, understanding the procurement process for rubber injection is essential. Following this checklist will help you navigate the complexities of supplier selection, ensuring you find a partner that meets your technical and operational requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical specifications is the first step in the sourcing process. This includes determining the size, geometry, weight, and material requirements for your rubber components. A well-defined specification will not only streamline the design process but also assist suppliers in providing accurate quotes and timelines.
Illustrative image related to rubber injection
- Consider the volume of production needed.
- Identify any specific performance requirements (e.g., temperature resistance, elasticity).
Step 2: Research Different Rubber Injection Molding Processes
Understanding the various rubber injection molding processes available is crucial for selecting the right method for your application. The three primary types—organic rubber injection, liquid silicone rubber (LSR) injection, and thermoplastic rubber injection—each have unique advantages and limitations.
- Assess which method best aligns with your product requirements and production volume.
- Keep in mind that some processes may offer faster cycle times or lower material waste.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a decision, it’s vital to conduct a thorough evaluation of potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from clients within your industry. This will provide insight into their experience, capabilities, and reliability.
- Look for suppliers with a proven track record in rubber injection.
- Verify their certifications and compliance with industry standards.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Once you have narrowed down your list of suppliers, request samples or prototypes of the rubber components you need. This step is essential to assess the quality of their work and ensure that the materials and manufacturing processes meet your specifications.
- Evaluate the samples for consistency, durability, and adherence to your design.
- Use this opportunity to provide feedback and gauge the supplier’s responsiveness to your needs.
Step 5: Discuss Lead Times and Production Capabilities
Understanding the lead times and production capabilities of your selected suppliers will help you plan your project timelines effectively. Inquire about their production capacity, turnaround times, and any potential bottlenecks they may face.
- Ensure the supplier can meet your delivery schedules without compromising quality.
- Discuss options for scaling production if demand increases.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have selected a supplier, enter into negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Clear communication is key to establishing a mutually beneficial agreement that protects both parties’ interests.

Illustrative image related to rubber injection
- Be open about your budget constraints while seeking competitive pricing.
- Ensure that all terms are documented to avoid misunderstandings later.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Finally, establish a clear communication plan with your chosen supplier to ensure ongoing collaboration throughout the production process. Regular updates and check-ins can help address any issues that arise and maintain alignment on project goals.
- Set up scheduled meetings or reports to monitor progress.
- Foster an open line of communication to facilitate swift problem resolution.
By following this practical sourcing checklist, you can streamline the process of procuring rubber injection services and ensure that your needs are met efficiently and effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rubber injection Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Rubber Injection Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of rubber injection molding is essential for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The total cost of sourcing rubber injection products can be broken down into several key components:
-
Materials: The type of rubber used—be it natural, synthetic, or thermoplastic—significantly influences costs. Premium materials or specialized compounds, such as liquid silicone rubber (LSR) or thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), can drive up prices. Buyers should consider the long-term durability and performance of these materials against their initial costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. In regions with higher wages, such as Europe, the cost of skilled labor for operating injection molding machinery can be substantial. Conversely, labor costs in countries like Vietnam or Brazil might be lower, which can influence overall pricing strategies.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. High-quality manufacturers often invest in advanced technology and automation, which can increase overhead but also enhance production efficiency and product quality.
-
Tooling: The design and manufacturing of molds are critical to rubber injection molding. Tooling costs can be high, particularly for custom molds. The complexity of the mold design, the materials used, and the required precision all factor into tooling expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality is paramount, especially for industries like automotive or medical where standards are stringent. Implementing robust QC processes incurs additional costs but is necessary to avoid costly recalls and ensure compliance with international certifications.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on location, volume, and Incoterms. International shipping often involves additional fees such as customs duties, insurance, and handling charges. Understanding these logistics costs is crucial for accurate budgeting.
-
Margin: Supplier margins typically account for their profit and can vary widely based on market competition, product demand, and the supplier’s positioning. Negotiating favorable terms is essential to ensure a competitive price.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Rubber Injection Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of rubber injection products:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can affect unit costs significantly. Higher volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs carefully and negotiate MOQs that balance cost with inventory management.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom rubber parts generally come at a premium. The complexity of design, specific material requirements, and unique performance characteristics will all impact pricing. Buyers should be clear about their specifications to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards or certifications (e.g., ISO, FDA) may incur higher costs. However, these certifications can be essential for market entry in certain regions, making it a necessary investment.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more but can provide assurance of product consistency and service reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipment can greatly affect the total cost. Incoterms determine who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and customs duties, which can lead to significant differences in pricing.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help Buyers Achieve Cost-Efficiency?
International B2B buyers should employ strategic negotiation techniques to optimize costs:
-
Leverage Volume: Use projected order volumes to negotiate better pricing. Suppliers are often willing to offer discounts for larger, consistent orders.
-
Clarify Specifications: Clearly articulate your requirements to avoid scope creep and additional costs. Consider standard parts over custom designs to reduce expenses.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial costs, assess the TCO, which includes maintenance, durability, and potential downtime. A higher upfront investment in quality materials may yield savings in the long run.
-
Research Regional Variations: Understand the local market dynamics in different regions. Prices can vary based on local demand and competition, allowing you to negotiate effectively.
Why Is It Important to Note Pricing Nuances for International Buyers?
For international buyers, it’s crucial to be aware of the nuances in pricing structures. Currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and regional market conditions can all impact final costs. Always request indicative pricing and be prepared for variations based on changing economic conditions. Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers and maintaining open communication can also help in navigating these complexities and securing favorable terms.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing rubber injection With Other Solutions
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, businesses often seek the most effective methods to produce rubber parts. Rubber injection molding is a popular choice due to its efficiency and precision; however, other methods may also serve specific needs effectively. This analysis compares rubber injection molding with two alternative solutions: compression molding and transfer molding. Each method presents unique advantages and limitations, making it essential for B2B buyers to understand which solution aligns best with their operational requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Rubber Injection | Compression Molding | Transfer Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, capable of intricate designs | Good for low to medium volumes; less precise | Excellent for multi-cavity molds; high precision |
| Cost | Economical for high volume production | Lower initial cost, but higher per unit for low volumes | Moderate costs; waste can increase expenses |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized machinery and setup | Simple setup, but longer cycle times | More complex setup than compression, but efficient for specific designs |
| Maintenance | Requires regular upkeep of machinery | Lower maintenance; simpler tools | Higher maintenance due to complexity of molds |
| Best Use Case | High volume, intricate components | Low to medium volume, simple designs | Parts needing multiple cavities or intricate designs |
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Compression Molding?
Compression molding is a traditional method that works well for low to medium production volumes. It utilizes pre-formed shapes that are loaded into open molds, where heat and pressure cure the rubber. The primary advantage of this method is its cost-effectiveness for small batches, as the initial tooling costs are lower than those for injection molding. However, the process is slower, as it involves lengthy curing times and the potential for less precision in parts compared to rubber injection.
How Does Transfer Molding Compare to Rubber Injection?
Transfer molding is ideal for producing complex parts with multiple cavities. This method involves loading rubber into a pot and using pressure to transfer it into closed molds, which allows for high precision and reduced risk of air entrapment. The downside is that it can generate more waste, as uncured rubber must be discarded after the process. While it can be more efficient for certain designs, the initial setup can be more complex than that of compression molding.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Rubber Processing Method?
Selecting the appropriate rubber molding method depends on several factors, including production volume, part complexity, and cost considerations. For high-volume, intricate components, rubber injection is often the best choice due to its efficiency and precision. In contrast, if a company requires low to medium volumes or simpler designs, compression molding may be more suitable. Transfer molding serves specialized needs where precision is critical, particularly for parts with multiple cavities. Ultimately, understanding the specific requirements of the application will guide B2B buyers in making the right decision, ensuring optimal production efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rubber injection
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Rubber Injection?
When engaging in rubber injection processes, it is essential to understand the specific technical properties that influence product quality and production efficiency. Here are critical specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific formulation of rubber used in the injection molding process. Different grades, such as silicone, EPDM, or Nitrile, have distinct properties, including temperature resistance, chemical compatibility, and durability. Selecting the appropriate material grade is crucial for ensuring the final product meets performance requirements in its intended application, whether in automotive, medical, or industrial settings.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the permissible limit of variation in a product’s dimensions. In rubber injection molding, tighter tolerances are often required for precision applications. High tolerances can lead to better fitting parts, reducing the need for post-processing and ensuring that components work seamlessly in assemblies. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance requirements helps in assessing manufacturing capabilities and quality assurance processes.
3. Cycle Time
Cycle time is the total time required to complete one production cycle, from the start of the injection process to the removal of the finished part. Shorter cycle times enhance production efficiency and lower costs, making them a crucial consideration for businesses aiming to optimize manufacturing processes. Buyers should inquire about cycle times to ensure that suppliers can meet production schedules without compromising quality.
4. Viscosity
Viscosity refers to the thickness or flow characteristics of the rubber material before it is injected into the mold. Lower viscosity allows for easier flow into intricate mold designs, reducing the risk of defects and improving the overall quality of the molded parts. Understanding viscosity helps buyers select the right material and processing conditions to achieve the desired product characteristics.
5. Shore Hardness
Shore hardness measures the material’s resistance to indentation, which correlates to its softness or hardness. Different applications require specific hardness levels; for instance, automotive seals may need a softer rubber, while industrial components might require harder materials. Buyers must specify the required hardness to ensure product performance and longevity.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Rubber Injection?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the rubber injection market. Here are key terms every B2B buyer should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that manufactures products or components that are sold to another company under that company’s brand name. In rubber injection, OEMs often require customized parts that meet specific design and performance criteria. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers seeking reliable sourcing options.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant in rubber injection as it can affect cost structures and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs and budget constraints to avoid excess inventory or underutilization of resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document used by buyers to solicit pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products or services. In the rubber injection industry, an RFQ typically outlines the required specifications, quantities, and delivery timelines. Crafting a detailed RFQ helps ensure accurate and competitive pricing from potential suppliers.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in global trade. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs during the transportation of goods. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers engaged in international transactions, as it impacts cost and logistics planning.
5. Custom Molding
Custom molding refers to the tailored production of rubber parts to meet specific client requirements. This service allows businesses to create unique components that fit particular applications or machinery. For buyers, understanding the custom molding process ensures they can obtain specialized products that enhance operational efficiency.
Illustrative image related to rubber injection
In summary, knowing the essential technical properties and trade terminology related to rubber injection can significantly impact decision-making and supplier selection for B2B buyers across various industries.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the rubber injection Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Global Rubber Injection Market?
The rubber injection molding market is witnessing significant growth driven by diverse global factors. One of the primary drivers is the increasing demand for high-performance rubber products across various industries, such as automotive, medical, and consumer goods. The shift towards automation and advanced manufacturing technologies, including Industry 4.0 practices, is enhancing production efficiency and precision. This is particularly important for international B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where quality and cost-effectiveness are paramount.
Emerging trends in sourcing include the adoption of digital platforms for procurement, allowing buyers to connect with multiple suppliers, compare offerings, and streamline the purchasing process. Moreover, the trend towards customization is becoming more prominent, as businesses seek tailored solutions that meet specific application requirements. Sustainable practices are also gaining traction, with suppliers increasingly offering eco-friendly materials and processes, reflecting a broader global shift towards sustainability.
The growing importance of supply chain resilience is another market dynamic that international B2B buyers must navigate. Recent disruptions have highlighted the need for diversified sourcing strategies to mitigate risks. Companies are now more inclined to source from suppliers with robust contingency plans and transparent operations, ensuring continuity and reliability in their supply chains.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Rubber Injection Industry?
Sustainability has become a critical focus in the rubber injection sector, driven by increasing regulatory pressures and consumer demand for environmentally responsible products. The environmental impact of rubber production, including deforestation and pollution, necessitates that companies adopt more sustainable practices. This is particularly relevant for B2B buyers who are increasingly scrutinizing their suppliers’ environmental policies and practices.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as businesses strive to ensure that their supply chains are free from exploitation and promote fair labor practices. Buyers should seek suppliers who adhere to recognized sustainability certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade certifications, which ensure ethical sourcing practices. Additionally, the use of ‘green’ materials, such as bio-based elastomers or recycled rubber, is gaining popularity, allowing companies to reduce their carbon footprint while maintaining product quality.
For B2B buyers, partnering with suppliers committed to sustainability can enhance brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. It can also lead to cost savings in the long term, as sustainable practices often result in greater efficiency and reduced waste.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Rubber Injection Molding?
The history of rubber injection molding dates back to the mid-20th century when innovations in material science enabled the adaptation of plastic injection molding techniques to rubber. Originally, rubber molding processes were labor-intensive and less efficient, relying heavily on manual operations. As technology progressed, the introduction of automated systems and advanced materials transformed the industry.
Today, rubber injection molding stands as a highly efficient process, characterized by precise material preparation and reduced cycle times. The evolution has allowed for greater customization, enabling manufacturers to produce complex shapes and designs that meet specific market demands. This evolution reflects the industry’s response to the growing need for high-quality, reliable rubber products in an increasingly competitive global marketplace.
In conclusion, understanding these market dynamics, sustainability initiatives, and the evolution of rubber injection molding will empower international B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational goals and ethical standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rubber injection
-
How do I select the right rubber injection molding process for my needs?
Choosing the appropriate rubber injection molding process—such as transfer, compression, or injection molding—depends on several factors. Consider the complexity of your part design, production volume, and material properties. For intricate designs or multi-cavity parts, transfer molding may be ideal. Compression molding suits low to medium production volumes, while injection molding excels in high-volume scenarios with precise tolerances. Assess your project specifications, including size, geometry, and material requirements, to determine the best fit for your application. -
What are the advantages of rubber injection molding compared to other methods?
Rubber injection molding offers numerous advantages, including reduced labor costs due to the elimination of pre-forms, decreased cycle times through efficient material heating, and minimal material waste. This method allows for high-volume production of complex parts with tight tolerances, making it economically viable for large-scale manufacturing. Additionally, it supports overmolding and can utilize advanced materials, ensuring the final product meets specific performance standards across various industries. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQs) should I expect when sourcing rubber injection parts?
MOQs for rubber injection parts can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the complexity of the parts. Generally, you may find MOQs ranging from 500 to 1,000 units for standard components. For custom parts, MOQs might be higher due to the setup costs involved in creating molds and tooling. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms that align with your production requirements. -
How can I vet potential suppliers for rubber injection molding?
To effectively vet suppliers, consider their industry experience, manufacturing capabilities, and quality assurance processes. Request samples of previous work to assess their product quality and ask for references from other clients. It’s also beneficial to review certifications, such as ISO standards, which indicate adherence to international quality norms. Engaging in direct communication about your specifications and timelines can provide insight into their responsiveness and reliability. -
What payment terms are common when purchasing rubber injection parts internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases can vary based on supplier policies and your negotiation. Common arrangements include payment in advance, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s essential to clarify terms such as deposit amounts, payment methods (wire transfer, credit card), and any applicable taxes or duties. Establishing clear terms in a contract can help mitigate risks associated with international transactions. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from rubber injection suppliers?
Reputable suppliers should have robust quality assurance protocols in place, including material inspections, in-process quality checks, and final product testing. They should provide documentation of quality standards, such as test reports and certifications, to ensure compliance with your specifications. Additionally, inquire about their capability for corrective actions and handling returns or defects, as these processes are vital for maintaining product integrity. -
How does logistics work for shipping rubber injection parts internationally?
Logistics for shipping rubber injection parts involves several steps, including packaging, customs clearance, and transportation. Suppliers should provide options for shipping methods, such as air freight for expedited delivery or sea freight for cost-effective solutions. Ensure that the supplier is familiar with international shipping regulations and can assist with necessary documentation to facilitate smooth customs processing. Discuss lead times and delivery schedules to align with your operational needs. -
What should I consider when customizing rubber injection parts?
When customizing rubber injection parts, focus on design specifications, material selection, and production capabilities. Collaborate closely with your supplier to create detailed drawings and prototypes, ensuring that all functional requirements are met. Consider the performance characteristics of different rubber materials, such as temperature resistance and elasticity, to select the best fit for your application. Finally, factor in the costs and lead times associated with customization to align with your budget and project timelines.
Top 4 Rubber Injection Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Timco Rubber – Rubber Injection Molding Process
Domain: timcorubber.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Rubber Injection Molding Process: Developed in the mid 1960s, it involves heating rubber and applying high pressure for efficient molding. Advantages include elimination of pre-forms, reduced cycle time, flashless tooling, and minimal material waste. Transfer Molding: Requires pre-forms placed in a pot, offering high cavity count and tighter dimensional control. Compression Molding: Involves creat…
2. Da/Pro Rubber – Precision Rubber Injection Molding
Domain: daprorubber.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Da/Pro Rubber specializes in rubber injection molding, offering high precision, tolerance, and low flash in the industry. Their expertise includes plastic injection and liquid silicone rubber injection molding. Key features include:
– Lower operating costs compared to other rubber molding methods due to automation and continuous operation.
– Custom molding of components using various materials suc…
3. Repinjection – Rubber Injection Moulding Machines
Domain: repinjection.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Rubber Injection Moulding Machines include: G10 Performance Range, Multistation Presses (CMX), Horizontal Presses, Vertical Standard Presses, Custom-Built Presses, G10 Lean Range, Entry Range, RT9, G9A India Compression Molding Presses, Composite Molding Presses, HSR Devulcanizing Machine. Key models include: V410-Y1000 (1600 kN), V510-Y2000 (3050 kN), V710-Y5000/L5000 (5100 kN), CMX1 (1540 kN), C…
4. Reddit – Silicone Rubber Injection Moulding
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rubber injection
In the rapidly evolving landscape of rubber injection molding, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal element for international B2B buyers. Understanding the various molding processes—such as transfer, compression, and injection molding—enables businesses to select the most appropriate method tailored to their unique specifications and production needs. Key factors like material choice, part geometry, and production volume must guide your sourcing decisions to ensure both quality and cost-effectiveness.
Moreover, leveraging custom rubber solutions can significantly enhance operational efficiency, offering tailored designs that meet specific application requirements. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to innovate, the demand for high-quality molded rubber products will only grow.
Looking ahead, international buyers are encouraged to engage with experienced suppliers who can provide comprehensive support, from prototyping to production. Establishing strong partnerships will not only streamline your sourcing process but also position your business to capitalize on future advancements in rubber technology. Reach out today to explore the possibilities and drive your business forward in this dynamic market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.