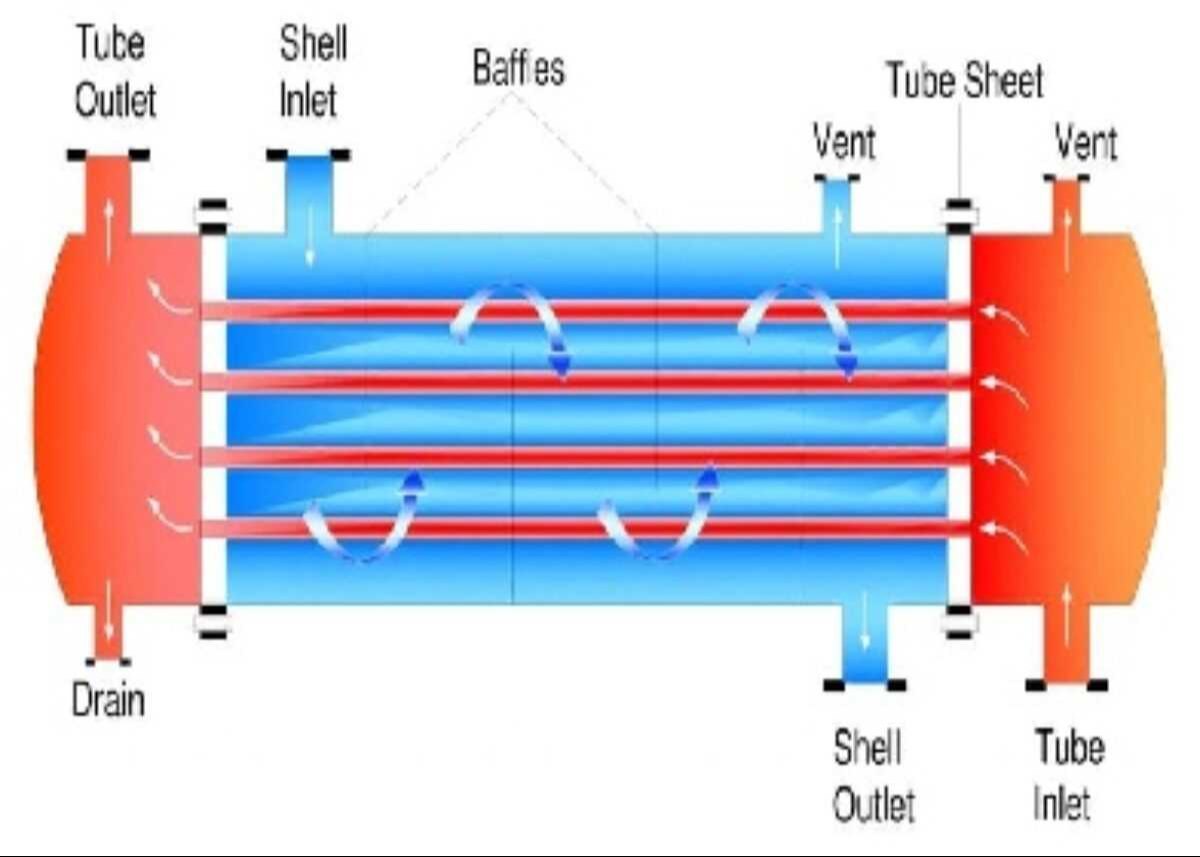
Top 4 Shell Side Tube Side Heat Exchanger Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for shell side tube side heat exchanger
In the dynamic landscape of international trade, sourcing a reliable shell side tube side heat exchanger presents a unique set of challenges for B2B buyers. With intricate considerations such as fluid allocation, fouling potential, and maintenance strategies, understanding these systems is crucial for optimizing thermal efficiency and operational reliability. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of shell and tube heat exchangers, their applications across industries, and the critical factors influencing supplier selection.
Our aim is to equip businesses from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Saudi Arabia—with the insights needed to make informed purchasing decisions. By exploring essential elements like cost analysis, maintenance practices, and performance evaluations, this guide empowers you to navigate the complexities of the global market with confidence. Whether you’re focused on enhancing energy efficiency or minimizing operational downtime, the information provided here will serve as a valuable resource to streamline your procurement process.
Let this guide be your roadmap in selecting the right shell side tube side heat exchanger that not only meets your operational needs but also aligns with your strategic business objectives.
Understanding shell side tube side heat exchanger Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| U-Tube Heat Exchanger | Flexible design, easy to maintain, compact | Oil & gas, chemical processing | Pros: Compact design, ease of cleaning. Cons: Limited to lower pressure applications. |
| Straight Tube Heat Exchanger | Straight tubes, higher efficiency | HVAC, power generation | Pros: High thermal efficiency, easier cleaning. Cons: More space required, potential for higher fouling. |
| Multi-Stream Heat Exchanger | Multiple fluids in one unit, space-saving | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Efficient for multiple processes. Cons: Complex design, higher initial cost. |
| Double-Pipe Heat Exchanger | Simple design, low maintenance | Water heating, refrigeration | Pros: Low cost, easy installation. Cons: Less efficient for large-scale applications. |
| Shell and Plate Heat Exchanger | Combination of shell and plate designs | Petrochemical, energy recovery | Pros: High efficiency, versatile. Cons: More complex maintenance, potentially higher costs. |
What Are U-Tube Heat Exchangers and When to Use Them?
U-tube heat exchangers feature a design that allows for flexible tube arrangements. This configuration is particularly advantageous in applications where space is limited, such as in oil and gas or chemical processing industries. They are easier to clean and maintain, making them a practical choice for operations that prioritize uptime. However, their design limits them to lower pressure applications, which buyers must consider when evaluating their needs.
How Do Straight Tube Heat Exchangers Enhance Efficiency?
Straight tube heat exchangers are characterized by their straightforward tube arrangement, which promotes high thermal efficiency. They are commonly used in HVAC systems and power generation facilities. The design allows for easier cleaning, reducing maintenance downtime. Buyers should be aware that while they offer excellent performance, they require more physical space and can be susceptible to fouling if not properly managed.
What Advantages Do Multi-Stream Heat Exchangers Offer?
Multi-stream heat exchangers are designed to handle multiple fluids within a single unit, making them ideal for applications in food processing and pharmaceuticals. Their space-saving design allows for efficient heat transfer among various processes. However, the complexity of their design can lead to higher initial costs and maintenance challenges. Buyers should weigh the benefits of efficiency against the potential for increased operational complexity.
When Should You Consider Double-Pipe Heat Exchangers?
Double-pipe heat exchangers are known for their simplicity and low maintenance requirements. They are often used in water heating and refrigeration applications. Their straightforward design makes installation easy and cost-effective. However, they may not provide the efficiency required for larger-scale operations, which buyers should consider when assessing their thermal management needs.
Why Choose Shell and Plate Heat Exchangers?
Shell and plate heat exchangers combine the advantages of shell and tube designs with plate technology, offering high efficiency and versatility. They are particularly well-suited for petrochemical applications and energy recovery systems. While they deliver excellent thermal performance, the complexity of maintenance and potentially higher costs can be a deterrent for some buyers. Understanding the specific operational requirements is essential for making an informed purchase decision.
Key Industrial Applications of shell side tube side heat exchanger
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of shell side tube side heat exchanger | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Crude oil cooling and processing | Enhances thermal efficiency, reduces operational costs | Material compatibility, fouling resistance, and maintenance needs |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Heat recovery in exothermic reactions | Optimizes energy use, minimizes waste, and improves process efficiency | Design flexibility, corrosion resistance, and cleaning accessibility |
| Food & Beverage | Pasteurization and cooling of liquids | Ensures product safety, quality, and compliance with health standards | Hygiene standards, ease of cleaning, and thermal performance |
| Power Generation | Waste heat recovery systems | Increases overall plant efficiency and reduces emissions | Pressure ratings, fluid compatibility, and installation space |
| HVAC & Refrigeration | Chilled water systems for building climate control | Improves energy efficiency, lowers operating costs | Size, capacity, and adaptability to varying fluid types |
How is the Shell Side Tube Side Heat Exchanger Used in the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, shell side tube side heat exchangers are vital for cooling crude oil during processing. These units enhance thermal efficiency, which is crucial for maintaining optimal operating temperatures and reducing energy consumption. Buyers must consider material compatibility with corrosive fluids and fouling resistance, as well as the ease of maintenance, to ensure long-term operational reliability.
What Role Does the Shell Side Tube Side Heat Exchanger Play in Chemical Manufacturing?
In chemical manufacturing, these heat exchangers are often employed for heat recovery during exothermic reactions. They help optimize energy use by reclaiming heat from processes that would otherwise be wasted. For international buyers, it is essential to evaluate the design flexibility of the exchanger to accommodate various chemical properties and the need for corrosion-resistant materials to extend service life.
Why is the Shell Side Tube Side Heat Exchanger Important for the Food & Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage industry, shell side tube side heat exchangers are crucial for processes like pasteurization and cooling of liquids. They ensure product safety and compliance with health standards while maintaining quality. Buyers should focus on hygiene standards, ease of cleaning, and thermal performance to meet stringent regulatory requirements and consumer expectations.
How Does the Shell Side Tube Side Heat Exchanger Enhance Power Generation?
In power generation, these heat exchangers are essential for waste heat recovery systems. By capturing and reusing waste heat, they significantly increase overall plant efficiency and reduce emissions. When sourcing for this application, buyers must consider pressure ratings and fluid compatibility to ensure the exchanger can handle the specific operational demands of their power plants.
What Are the Benefits of Using Shell Side Tube Side Heat Exchangers in HVAC & Refrigeration?
In HVAC and refrigeration systems, shell side tube side heat exchangers are used to manage chilled water for building climate control. They enhance energy efficiency and lower operating costs, making them a valuable investment for facility management. Key sourcing considerations include size, capacity, and the exchanger’s adaptability to varying fluid types to ensure optimal performance in diverse environmental conditions.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘shell side tube side heat exchanger’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Managing Fouling and Maintenance
The Problem: One of the most prevalent challenges faced by B2B buyers of shell side tube side heat exchangers is fouling. Fouling occurs when unwanted materials accumulate on heat transfer surfaces, leading to reduced efficiency and increased maintenance costs. This issue is particularly critical for industries in warmer climates, such as those in Africa and South America, where biological growth and mineral scaling are more pronounced. Buyers often experience increased pressure drops and diminished heat transfer effectiveness, resulting in costly downtime and inefficient operations.
The Solution: To effectively manage fouling, buyers should prioritize the design phase of their heat exchanger selection. It’s essential to understand the properties of the fluids involved and their fouling tendencies. For fluids known to foul easily, placing them on the tube side, which is generally easier to clean, can significantly reduce maintenance time and costs. Additionally, implementing a robust cleaning schedule with both chemical and mechanical methods can help maintain performance. Buyers should also consider investing in advanced monitoring technologies, such as pressure sensors, to detect fouling early and schedule maintenance proactively, minimizing unexpected downtime.
Scenario 2: Corrosion and Material Selection Concerns
The Problem: Corrosion is a critical issue for many industries using shell side tube side heat exchangers, particularly those handling aggressive fluids. B2B buyers often grapple with the challenge of selecting the right materials to withstand corrosion while maintaining cost-effectiveness. For instance, in the Middle East, where oil and gas operations frequently involve corrosive substances, improper material selection can lead to catastrophic failures and costly replacements.
The Solution: To combat corrosion, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of the fluids used in their processes before selecting materials. It’s advisable to place more corrosive fluids on the tube side, where tubes can be made from more corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel, without the need to over-engineer the entire system. Engaging with suppliers who offer customized solutions tailored to specific fluid characteristics can also help. Regular inspections and maintenance, including the use of sacrificial anodes, can further extend the lifespan of the heat exchanger and ensure reliable operation.
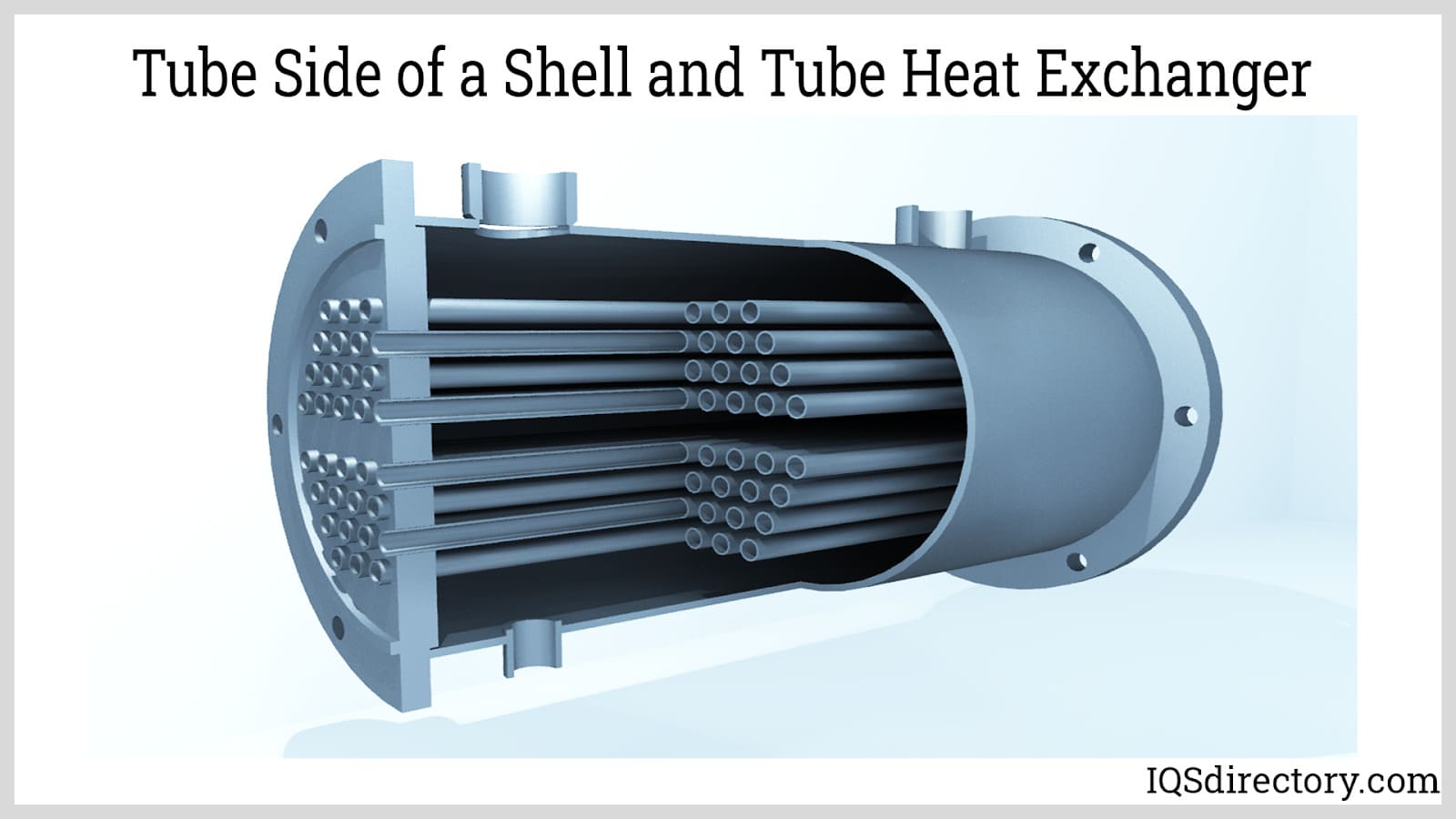
Illustrative image related to shell side tube side heat exchanger
Scenario 3: Managing High-Pressure Operations Effectively
The Problem: B2B buyers in industries that deal with high-pressure fluids often face challenges related to the structural integrity of their shell side tube side heat exchangers. High-pressure operations demand thicker walls for tubes and shells, leading to higher costs and complexity in maintenance. Buyers in regions like Europe, where industries such as chemicals and pharmaceuticals operate under strict safety standards, must ensure that their heat exchangers can handle these pressures without compromising efficiency or safety.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize a thorough understanding of their operating pressures when selecting a heat exchanger. It is generally more cost-effective to allocate high-pressure fluids to the tube side, as it allows for the use of thinner shells while maintaining safety. Collaborating with manufacturers who specialize in high-pressure designs can also yield better solutions. Additionally, implementing regular pressure testing and maintenance protocols can help identify potential weak points before they lead to failures. Investing in training for operational staff on handling high-pressure systems can further enhance safety and operational reliability.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for shell side tube side heat exchanger
What Are the Key Materials for Shell Side Tube Side Heat Exchangers?
When selecting materials for shell side tube side heat exchangers, it is essential to consider various factors such as temperature and pressure ratings, corrosion resistance, and overall compatibility with the fluids involved. Below, we analyze four common materials used in these heat exchangers, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high strength and durability, with a temperature rating up to 400°F (204°C) and moderate pressure capabilities. It has a lower corrosion resistance compared to stainless steel but can be treated with coatings.
Pros & Cons: Carbon steel is cost-effective and easy to manufacture, making it a popular choice for many applications. However, its susceptibility to corrosion limits its use in harsh environments, requiring careful consideration of the media it will be in contact with.
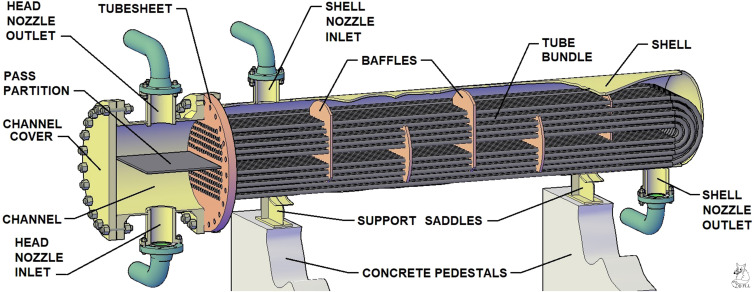
Illustrative image related to shell side tube side heat exchanger
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is suitable for non-corrosive fluids and applications where cost is a significant factor. However, in regions with high humidity or corrosive media, its longevity may be compromised.
International Considerations: Buyers from regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia should be aware of local standards such as ASTM A106 and the need for protective coatings to enhance durability.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, with temperature ratings often exceeding 800°F (427°C). It is particularly suitable for high-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for a wide range of fluids, including aggressive chemicals. However, it comes at a higher cost and can be more complex to manufacture.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a variety of media, including corrosive fluids, making it a preferred choice in industries such as petrochemicals and pharmaceuticals.
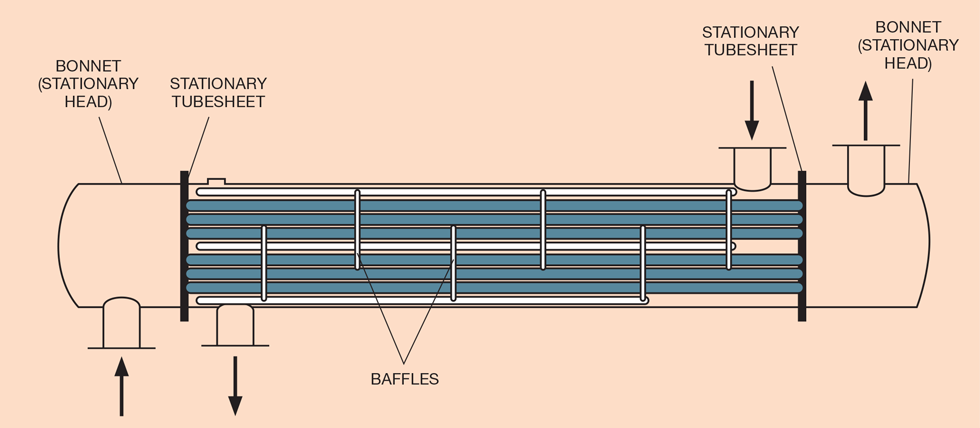
Illustrative image related to shell side tube side heat exchanger
International Considerations: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A312 and DIN 17440 is crucial for buyers in Europe and the Middle East, where stringent regulations on material quality are enforced.
3. Copper-Nickel Alloys
Key Properties: Copper-nickel alloys exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in seawater applications, with temperature ratings up to 400°F (204°C). They also have good thermal conductivity.
Pros & Cons: These alloys are highly resistant to biofouling, making them suitable for marine applications. However, they are more expensive than carbon steel and may require specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application: Ideal for applications involving seawater or other corrosive environments, copper-nickel alloys can enhance the longevity of heat exchangers in marine and offshore applications.
International Considerations: Buyers in coastal regions should consider compliance with standards like ASTM B171, especially in countries with significant marine industries.
4. Titanium
Key Properties: Titanium boasts exceptional corrosion resistance and can withstand extreme temperatures, often rated above 1000°F (538°C). It is lightweight yet strong, making it suitable for high-performance applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of titanium is its unmatched resistance to corrosion, particularly in aggressive environments. However, it is one of the most expensive materials and can be challenging to machine and weld.
Impact on Application: Titanium is ideal for highly corrosive fluids and applications requiring high strength-to-weight ratios, such as aerospace and chemical processing.
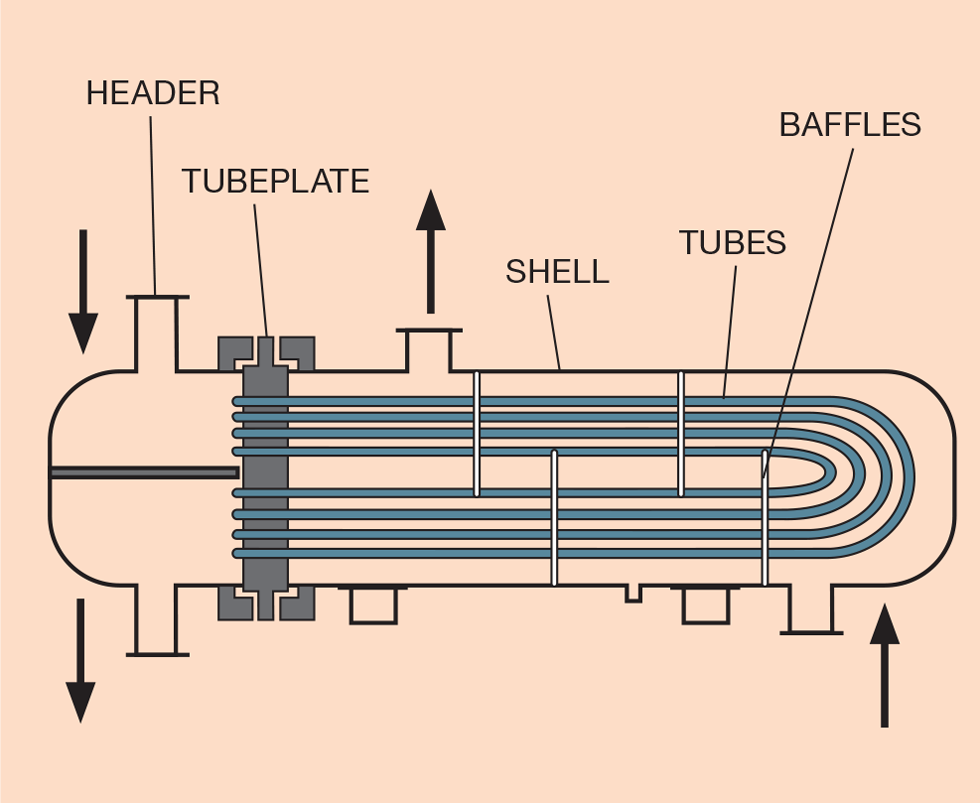
Illustrative image related to shell side tube side heat exchanger
International Considerations: Buyers should be aware of compliance with ASTM B338 and the high costs associated with titanium, which may limit its use to specialized applications in regions like Europe and the Middle East.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for shell side tube side heat exchanger | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Non-corrosive fluids in general applications | Cost-effective and durable | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosive fluids in various industries | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Copper-Nickel Alloys | Marine and seawater applications | Resistant to biofouling | More expensive and specialized welding | Medium |
| Titanium | Highly corrosive and extreme temperature applications | Unmatched corrosion resistance | Very high cost and difficult to machine | High |
This material selection guide aims to provide B2B buyers with a comprehensive understanding of the options available for shell side tube side heat exchangers, enabling informed decisions that align with operational needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for shell side tube side heat exchanger
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Shell Side Tube Side Heat Exchangers?
The manufacturing of shell side tube side heat exchangers involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure product quality and efficiency. Understanding these processes helps B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
How Is Material Prepared for Heat Exchanger Production?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. High-quality materials, typically stainless steel, carbon steel, or specialized alloys, are selected based on the specific application and fluid characteristics.
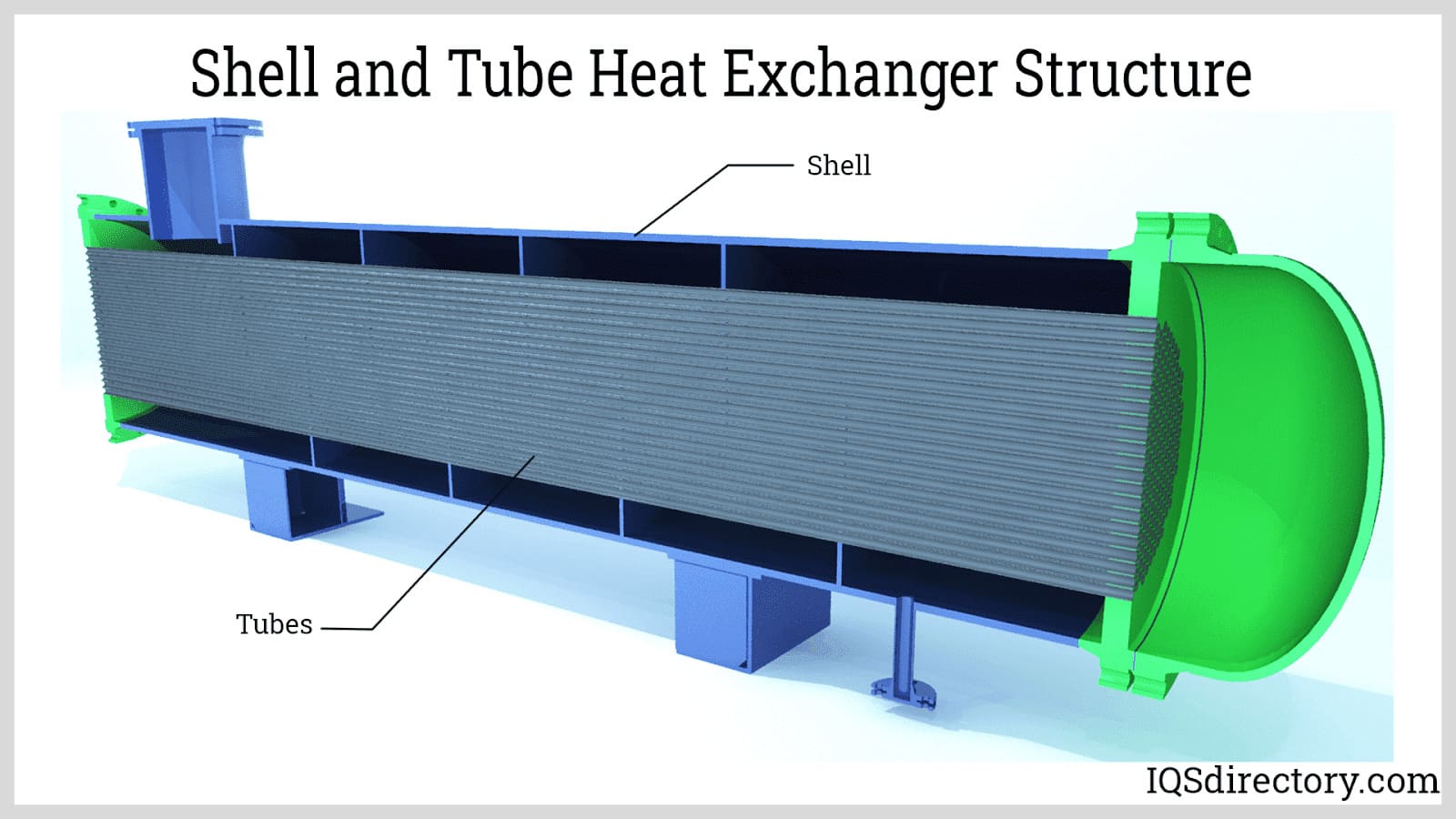
Illustrative image related to shell side tube side heat exchanger
-
Material Selection: Engineers assess the corrosiveness, pressure, and temperature of the fluids involved to choose appropriate materials. For instance, more corrosive fluids often necessitate the use of stainless steel tubes.
-
Material Inspection: Incoming materials undergo rigorous inspection to ensure compliance with international standards (such as ASTM) and specifications. This includes checking for defects, composition, and mechanical properties.
What Techniques Are Used for Forming Heat Exchanger Components?
Forming is the next crucial stage, where raw materials are shaped into functional components.
-
Tube Formation: Tubes are typically manufactured through processes such as extrusion or seamless pipe production. The choice of method impacts the mechanical strength and corrosion resistance of the tubes.
-
Shell Fabrication: The shell is formed using techniques like rolling and welding. This stage often involves bending plates into cylindrical shapes and welding the seams to create a robust structure.
-
Baffle Design: Baffles are critical for enhancing turbulence and heat transfer efficiency. They are cut and shaped from flat sheets of metal, then installed within the shell to direct fluid flow appropriately.
How Are Components Assembled in Heat Exchangers?
Assembly is where the individual components come together to create the final product.
-
Tube Bundle Assembly: The tubes are inserted into the shell and secured using tube sheets. Proper alignment and spacing are critical to ensure optimal heat transfer.
-
Welding and Sealing: Various components, such as tube sheets and end caps, are welded to create a leak-proof assembly. The quality of welding is crucial; any defects can lead to leaks or structural failures.
-
Final Assembly Checks: A thorough inspection is conducted to ensure that all components are correctly installed and secure before moving on to the finishing stage.
What Finishing Techniques Are Employed for Heat Exchangers?
The finishing stage enhances the heat exchanger’s durability and aesthetic appeal.
-
Surface Treatment: Processes like pickling, passivation, or coating may be applied to improve corrosion resistance. These treatments help maintain the integrity of the exchanger over time.
-
Final Inspection: After finishing, each unit undergoes a final inspection to verify that it meets specified standards and customer requirements. This includes checking surface finishes and confirming that all dimensions are within tolerance.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Heat Exchanger Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that the final product meets stringent standards.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For B2B buyers, it’s important to understand the quality certifications that manufacturers should possess.
-
ISO 9001: This international standard for quality management systems ensures that manufacturers consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. Compliance indicates a commitment to continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
-
CE Marking: In Europe, CE marking is required for products to demonstrate compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards. This is particularly important for buyers in the European market.
-
API Standards: For buyers in the oil and gas sector, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is essential, especially when heat exchangers are used in critical applications.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Production?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically integrated throughout the manufacturing process.
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections are conducted during the manufacturing process, focusing on critical stages such as forming and assembly. This includes monitoring weld quality and dimensional accuracy.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final product undergoes comprehensive testing and inspection before shipping. This may involve pressure testing, leak testing, and performance evaluations to ensure the unit meets all specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
Verifying the quality control practices of potential suppliers is essential for B2B buyers, particularly when sourcing internationally.
What Steps Can Buyers Take for Supplier Audits?
-
Conducting Supplier Audits: Buyers should perform regular audits of suppliers to assess their quality management systems and manufacturing processes. This provides insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality and compliance with international standards.
-
Reviewing Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports and certifications from suppliers can help buyers understand their quality control measures. This includes documentation of testing methods and results.
How Do Third-Party Inspections Enhance Assurance?
- Engaging Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturer’s quality practices. These inspectors can verify compliance with industry standards and ensure that the products meet specified requirements.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of specific nuances in quality assurance.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local standards and ensure that their suppliers comply with both international and regional regulations.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences can enhance communication and collaboration with suppliers, leading to better quality outcomes.
In summary, comprehending the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for shell side tube side heat exchangers is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, along with robust quality control measures, buyers can ensure they select reliable suppliers that meet their operational needs and standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘shell side tube side heat exchanger’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure a shell side tube side heat exchanger. Given the complexities and critical nature of these systems, this guide will help you make informed decisions, ensuring efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness in your operations.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes understanding the fluids involved, their temperatures, pressures, and potential fouling or corrosive characteristics. Accurate specifications will guide your selection process and ensure the heat exchanger meets your operational needs.
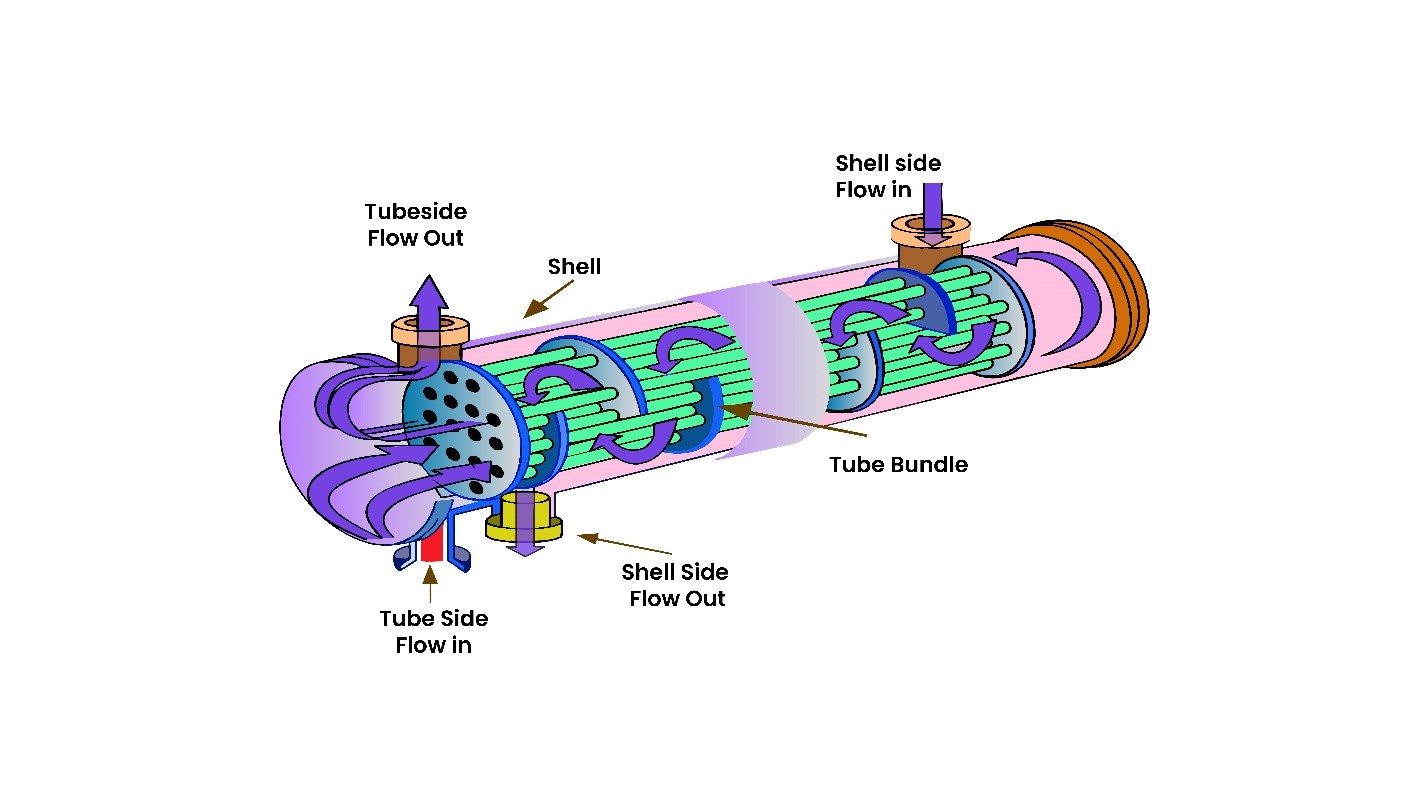
Illustrative image related to shell side tube side heat exchanger
Step 2: Assess Fluid Allocation Needs
Determine which fluid should be placed on the tube side versus the shell side. Consider factors such as fouling potential, viscosity, and corrosion rates. For instance, fluids that are prone to fouling should generally go on the tube side, where cleaning is more manageable, while more corrosive fluids should also be placed in the tubes to simplify maintenance and replacement.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they meet your quality and reliability standards. Request documentation such as company profiles, case studies, and references from clients in similar industries or regions. Evaluate their experience with shell and tube heat exchangers, and consider their reputation for customer service and support.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that your chosen suppliers comply with relevant industry standards and certifications. This may include ISO certifications, ASME codes, and other local or international standards. Compliance not only guarantees quality but also reduces the risk of future operational issues and legal liabilities.
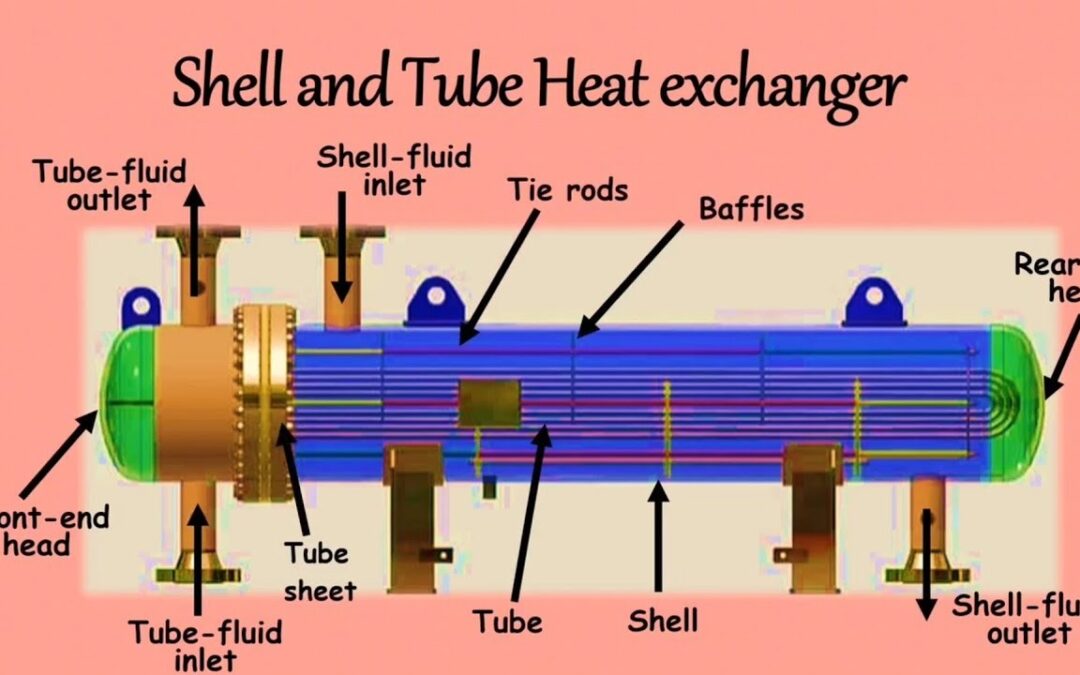
Illustrative image related to shell side tube side heat exchanger
Step 5: Analyze Maintenance and Support Services
Inquire about the maintenance and support services provided by the supplier. Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity of heat exchangers. Look for suppliers who offer comprehensive service packages, including cleaning, repairs, and emergency support, to minimize downtime and optimize efficiency.
Step 6: Request Detailed Quotations
Obtain detailed quotations from shortlisted suppliers, ensuring they include all necessary components and services. Pay attention to pricing structures, delivery timelines, and warranties. Comparing multiple quotes will provide insights into market rates and help you negotiate better terms.
Step 7: Conduct a Final Review and Selection
Before making a final decision, review all gathered information and assess how each supplier aligns with your needs. Consider factors such as total cost of ownership, lead times, and after-sales support. This final review will help ensure that you select a supplier that not only meets your technical specifications but also supports your long-term operational goals.
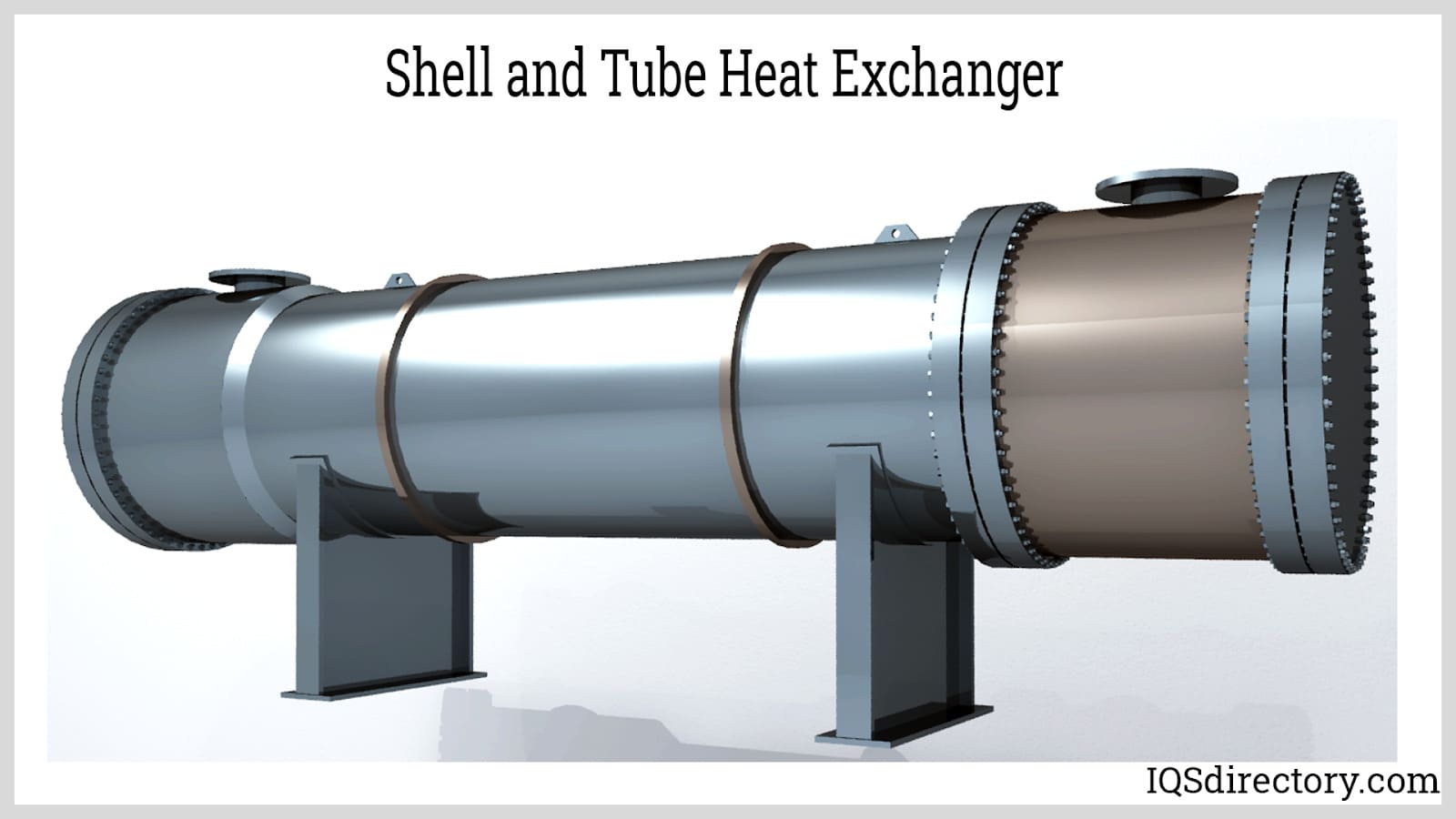
Illustrative image related to shell side tube side heat exchanger
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for shell side tube side heat exchanger Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Shell Side Tube Side Heat Exchangers?
When evaluating the cost structure for shell side tube side heat exchangers, several key components must be considered. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margin.
Materials typically account for the largest portion of the total cost, especially when considering the choice of corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel versus carbon steel. The selection of materials is critical not only for durability but also for the efficiency of heat transfer.
Labor costs vary based on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is often required for precise assembly and quality checks. Manufacturing overhead encompasses factory utilities, equipment depreciation, and administrative expenses, which can fluctuate based on production scale.
Tooling costs are essential for custom designs, particularly when unique specifications are required. This is especially relevant for international buyers looking for tailored solutions to meet specific operational needs.
Quality Control is another significant cost factor; rigorous testing and certification processes ensure that the heat exchangers meet industry standards and performance metrics.
Logistics costs can vary greatly depending on the distance from the supplier to the buyer, shipping methods, and customs duties, particularly for international transactions. Finally, the supplier margin represents the profit markup added to the total cost, influenced by supplier reputation and market demand.
How Do Volume and Customization Influence Pricing?
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) play critical roles in determining pricing for shell side tube side heat exchangers. Higher volume orders generally lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers are often willing to negotiate better rates for bulk purchases, which can significantly benefit buyers looking to equip multiple facilities or projects.
Customization also impacts pricing. Unique specifications or design changes can lead to increased costs due to additional engineering and manufacturing requirements. Buyers should consider the trade-off between customization and cost, focusing on essential features that provide the best value.
What Are the Key Influencers on Pricing for International Buyers?
Several factors influence pricing for international buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The choice of materials, quality certifications, and supplier reputation can significantly affect costs. For instance, sourcing from suppliers with recognized quality certifications may come at a premium but can ensure reliability and efficiency.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) also play a crucial role in determining total costs. These terms specify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting the overall budget for heat exchanger procurement.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help Achieve Cost-Efficiency?
When negotiating for shell side tube side heat exchangers, buyers should be well-prepared with market research to understand prevailing prices and supplier capabilities. Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Consider negotiating for longer payment terms or bulk discounts, which can improve cash flow.
Buyers should also evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the upfront price. This includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs associated with fouling and corrosion. By focusing on long-term performance and reliability, buyers can justify higher initial investments if they lead to lower operational costs over time.
Why Is It Important to Understand Pricing Nuances in Different Regions?
Understanding pricing nuances in different regions is essential for successful procurement. Economic conditions, supply chain dynamics, and regional demand can lead to significant price variations. For example, buyers in emerging markets may encounter higher logistics costs or tariffs, while those in more developed regions may benefit from established supply chains and competitive pricing.
By staying informed about regional trends and supplier capabilities, international buyers can make strategic decisions that align with their operational goals and budget constraints. Always keep in mind that indicative prices may fluctuate based on market conditions, so continuous monitoring and flexibility in sourcing strategies are advisable.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing shell side tube side heat exchanger With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Shell Side Tube Side Heat Exchangers
In the field of thermal management, selecting the right heat exchanger technology is crucial for optimizing performance and cost-efficiency. While shell side tube side heat exchangers are a popular choice, various alternatives exist that may better suit specific applications. This analysis will compare shell side tube side heat exchangers with plate heat exchangers and air-cooled heat exchangers, highlighting their respective advantages and disadvantages.
| Comparison Aspect | Shell Side Tube Side Heat Exchanger | Plate Heat Exchanger | Air-Cooled Heat Exchanger |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, suitable for large flow rates | Excellent heat transfer, compact design | Good for ambient cooling, variable flow |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment, higher maintenance | Generally lower upfront cost, easy to expand | Low operating cost, high initial setup |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires significant space, complex installation | Easier to install, smaller footprint | Requires space for air circulation, limited by ambient conditions |
| Maintenance | Can be challenging due to fouling; requires regular cleaning | Easier to clean and maintain | Minimal maintenance, but relies on clean air |
| Best Use Case | Heavy industrial applications with high thermal loads | Food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, HVAC | Process cooling in remote areas or where water is scarce |
In-Depth Look at Alternative Solutions
What Are the Advantages of Plate Heat Exchangers?
Plate heat exchangers consist of multiple thin plates that create channels for fluid flow, allowing for efficient heat transfer. Their compact design makes them ideal for operations with limited space. Additionally, the lower upfront cost and ease of maintenance are significant advantages. However, they may not handle high-pressure applications as effectively as shell and tube exchangers, and their performance can decrease if not properly maintained, especially in fouling-prone environments.
How Do Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers Operate?
Air-cooled heat exchangers use ambient air to dissipate heat from process fluids. They are particularly advantageous in regions where water resources are limited or expensive, as they require no water for cooling. Their low operating costs make them attractive for long-term applications. However, their performance can be significantly affected by environmental conditions, and they may require additional space for adequate air circulation. This reliance on ambient conditions can also make them less efficient than liquid-cooled systems.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Heat Exchanger Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate heat exchanger technology is a critical decision for B2B buyers, particularly those in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. When considering shell side tube side heat exchangers versus alternatives like plate or air-cooled heat exchangers, factors such as performance requirements, cost constraints, ease of maintenance, and specific application scenarios should guide your choice. Conducting a thorough analysis tailored to your operational needs and conditions will ultimately lead to improved efficiency and reduced total costs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for shell side tube side heat exchanger
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Shell Side Tube Side Heat Exchangers?
When evaluating shell and tube heat exchangers, several critical specifications can greatly influence performance, maintenance, and costs. Understanding these properties is essential for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
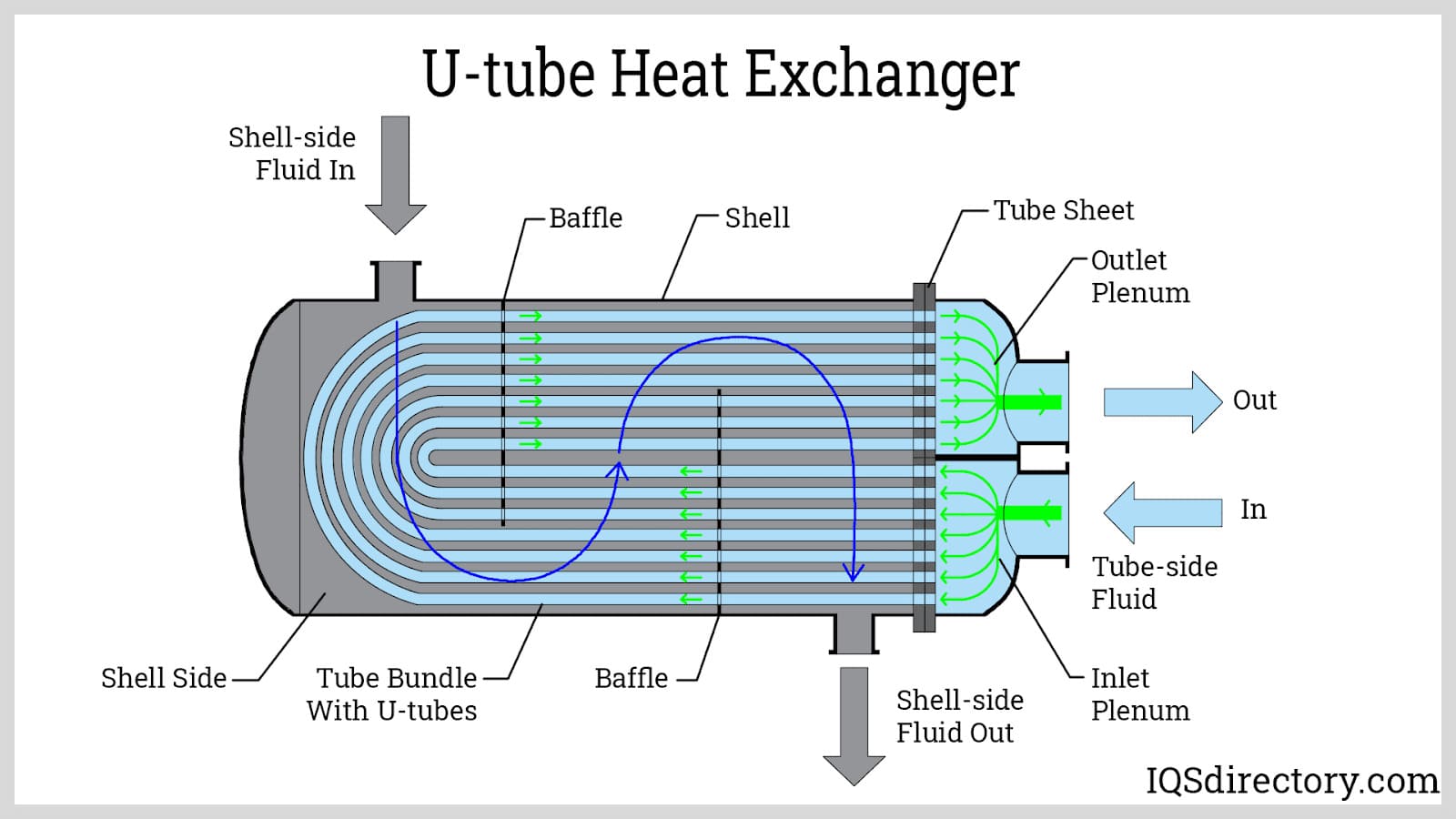
Illustrative image related to shell side tube side heat exchanger
1. Material Grade
The choice of material for both the tubes and the shell is crucial. Common materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, and alloys. Stainless steel is often preferred for its corrosion resistance, especially when handling aggressive fluids. Selecting the right material not only extends the lifespan of the heat exchanger but also reduces maintenance costs, making it a vital consideration for buyers.
2. Tube Diameter and Wall Thickness
The diameter and wall thickness of the tubes directly impact the heat transfer efficiency and pressure drop within the system. Thicker walls can withstand higher pressures, which is essential for high-pressure applications. However, they also increase the cost and weight of the exchanger. Buyers must balance these factors based on the specific requirements of their processes.
3. Heat Transfer Area
This property is determined by the number of tubes, their length, and diameter. A larger heat transfer area typically leads to better heat exchange efficiency, which is critical in applications requiring precise temperature control. Buyers should assess their operational needs to ensure the heat exchanger has sufficient capacity for optimal performance.
4. Fouling Resistance
Fouling can significantly reduce heat transfer efficiency. When selecting a heat exchanger, it is essential to consider the fouling potential of the fluids involved. Some designs incorporate features to minimize fouling, such as enhanced surface areas or specific baffle arrangements. Understanding the fouling characteristics can help buyers choose a model that minimizes maintenance needs and downtime.
5. Design Configuration
The configuration of the heat exchanger, such as U-tube or straight tube designs, affects cleaning and maintenance processes. U-tube designs can be more challenging to clean, making it essential for buyers to consider how often maintenance will be required. This choice can have long-term implications for operational efficiency and overall costs.
What Are Common Trade Terminologies Used in Shell Side Tube Side Heat Exchangers?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the procurement process. Here are some key terms every B2B buyer should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of heat exchangers, buyers should consider whether they are sourcing from OEMs to ensure quality and compatibility with existing systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ defines the smallest order a supplier is willing to process. Understanding MOQ is critical for buyers, especially when planning inventory and budget allocations. It can also impact cash flow and storage considerations.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. For heat exchangers, a well-defined RFQ can help ensure that suppliers understand the technical specifications and requirements, leading to more accurate pricing and proposals.
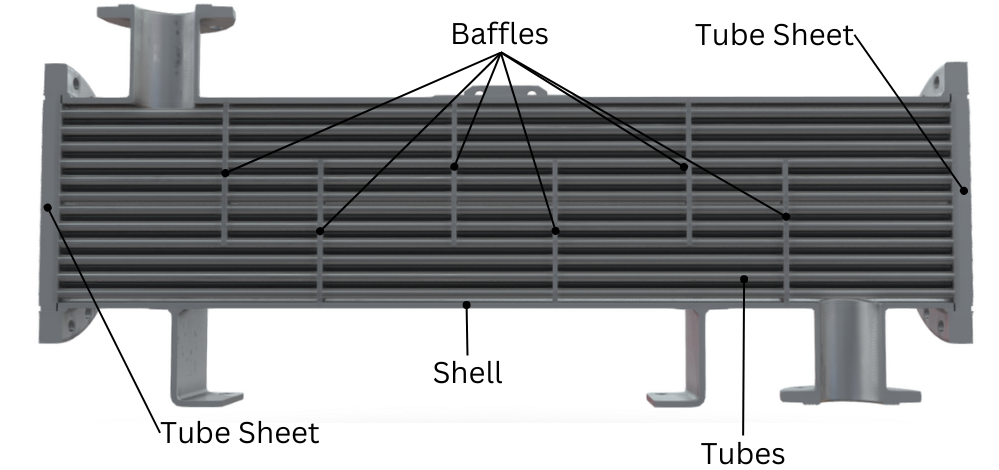
Illustrative image related to shell side tube side heat exchanger
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B transactions, as they clarify shipping responsibilities, insurance, and risk management.
5. Baffles
Baffles are internal components used to direct fluid flow and increase turbulence, thereby enhancing heat transfer efficiency. Knowing about baffles can help buyers assess the design and efficiency of different heat exchanger models.
6. Thermal Fatigue
This term refers to the weakening of materials due to repeated thermal cycling. Buyers should be aware of thermal fatigue when selecting materials and designs, as it can impact the longevity and reliability of the heat exchanger.
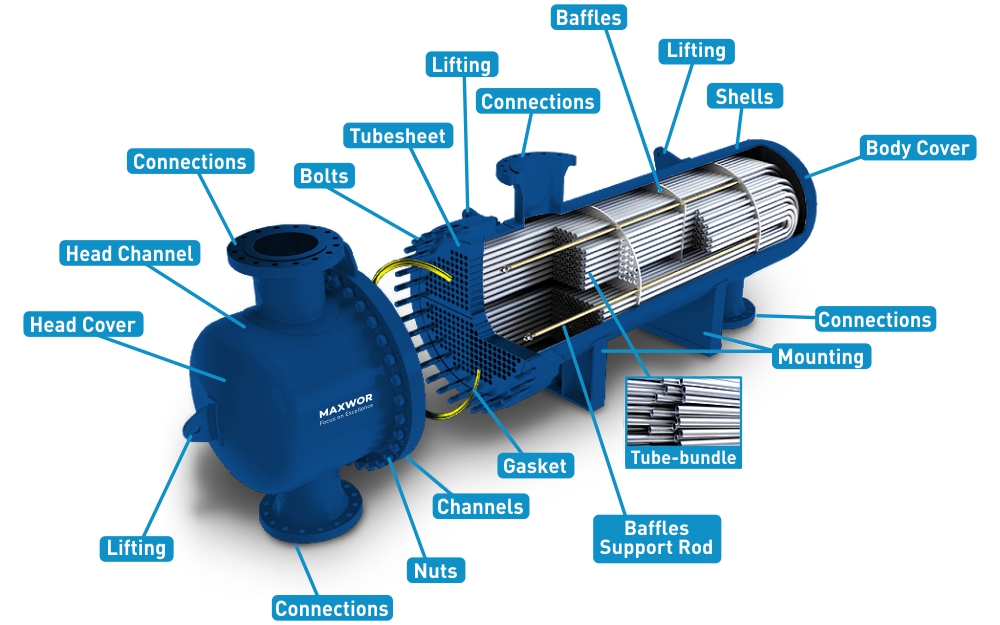
Illustrative image related to shell side tube side heat exchanger
By understanding these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when investing in shell side tube side heat exchangers, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness for their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the shell side tube side heat exchanger Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Shell Side Tube Side Heat Exchanger Sector?
The global shell side tube side heat exchanger market is witnessing significant growth driven by rising energy demands and the need for efficient thermal management across various industries, including petrochemicals, power generation, and food processing. Key trends shaping the market include the increasing adoption of advanced materials that enhance corrosion resistance and thermal efficiency, as well as the integration of digital technologies such as IoT for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. These innovations not only improve operational efficiency but also reduce downtime and maintenance costs, which are critical considerations for international B2B buyers.
Emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly influential in this sector. Countries like Brazil and Saudi Arabia are investing heavily in industrial infrastructure, creating a surge in demand for reliable heat exchange solutions. Additionally, the emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability is prompting manufacturers to innovate, leading to the development of customized solutions tailored to specific operational needs. Buyers in these regions must stay abreast of these trends to ensure they are sourcing products that not only meet current needs but also align with future regulatory requirements and market shifts.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Shell Side Tube Side Heat Exchanger Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a central pillar in the decision-making process for B2B buyers in the shell side tube side heat exchanger sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the lifecycle of heat exchangers are under increasing scrutiny. Buyers are encouraged to consider suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly materials and processes. Utilizing corrosion-resistant alloys and coatings can enhance the longevity of heat exchangers while minimizing the environmental footprint associated with frequent replacements.
Moreover, ethical sourcing practices are gaining traction as companies strive to create transparent supply chains. Buyers should seek out manufacturers that demonstrate responsible sourcing of raw materials, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and ethical labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other green certifications can help buyers identify suppliers committed to sustainability. By aligning with these practices, businesses not only contribute positively to the environment but also enhance their brand reputation, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and stakeholders.
What Has Been the Evolution of Shell Side Tube Side Heat Exchangers in the B2B Market?
The evolution of shell side tube side heat exchangers can be traced back to their inception in the early 20th century when they were primarily used in steam power plants. Over the decades, advancements in materials science and engineering have led to significant improvements in their design and efficiency. Initially, these heat exchangers were primarily constructed from carbon steel, but the introduction of stainless steel and other alloys has greatly enhanced their durability and resistance to corrosion.
The increasing complexity of industrial processes and the need for higher efficiency have spurred further innovation, leading to the development of specialized designs such as U-tube and fixed tube sheet configurations. These advancements have allowed for better maintenance practices and reduced operational costs. As industries continue to evolve, the shell side tube side heat exchanger remains a critical component, adapting to new technologies and sustainability requirements, thereby ensuring its relevance in modern manufacturing and processing environments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of shell side tube side heat exchanger
-
How do I solve fouling issues in my shell and tube heat exchanger?
Fouling is a common challenge in shell and tube heat exchangers. To mitigate fouling, first, ensure the fluid with a higher fouling potential is placed in the tube side, as it is generally easier to clean. Implement regular maintenance routines that include visual inspections and cleaning schedules using hydro blasting or mechanical methods for stubborn deposits. Additionally, consider using chemical cleaners compatible with your materials. Monitoring pressure drops and performance metrics will help you detect fouling early, allowing for timely intervention. -
What is the best fluid allocation strategy for my heat exchanger?
The best fluid allocation strategy depends on several factors, including the fouling potential, corrosiveness, and physical states of the fluids involved. Generally, place fluids with higher fouling or corrosive properties on the tube side for easier maintenance. For vapors, allocate them to the shell side to prevent stagnation, while fluids with high viscosity should also go on the shell side to enhance heat transfer efficiency. Consulting with an engineering expert during the design phase can help tailor the system to your specific process needs. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for heat exchangers?
When vetting suppliers, assess their industry experience and reputation, particularly in your region. Check for certifications that ensure compliance with international standards, such as ASME or ISO. Additionally, inquire about their manufacturing capabilities, lead times, and customer service responsiveness. Request references or case studies from previous clients, especially those in similar industries or geographical areas, to gauge reliability. Finally, evaluate their after-sales support and warranty terms to ensure they align with your expectations. -
How can I customize my shell and tube heat exchanger to suit my needs?
Customization options for shell and tube heat exchangers include selecting materials that resist corrosion or fouling, adjusting tube diameters, and configuring tube arrangements for optimal flow. Work closely with your supplier to discuss your specific process requirements, such as temperature, pressure, and fluid characteristics. Additionally, consider features like baffle designs and insulation for energy efficiency. A well-defined specification will help the manufacturer create a heat exchanger that meets your operational needs. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for heat exchangers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly among suppliers, influenced by factors such as manufacturing capacity and material availability. Generally, larger orders may yield better pricing and shorter lead times, while smaller orders may incur higher per-unit costs. It’s crucial to communicate your needs clearly and inquire about flexible options. Some suppliers may accommodate lower MOQs for custom designs, especially if you establish a long-term partnership or demonstrate potential for repeat business. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing internationally?
Payment terms for international transactions can vary widely based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation. Common terms include upfront deposits (often 30-50%) with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Letter of Credit (LC) is also a secure option for both parties. Be sure to clarify the currency used for transactions and any additional costs such as taxes, tariffs, or shipping fees that may apply. Establishing clear payment terms upfront can prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smoother transaction. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for my heat exchanger?
Quality assurance (QA) can be ensured by selecting suppliers with robust quality management systems certified by recognized standards like ISO 9001. Request detailed documentation of their QA processes, including material certifications, inspection reports, and testing protocols. It may also be beneficial to arrange for third-party inspections during manufacturing. Establishing a clear communication channel with the supplier regarding quality expectations and receiving regular updates can further enhance the QA process. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for international shipping?
When planning logistics for international shipping of heat exchangers, consider factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in both the exporting and importing countries. Ensure that your supplier provides detailed shipping documentation to facilitate customs clearance. Discuss packaging options to prevent damage during transit, and consider insurance to mitigate risks. Collaborate with experienced freight forwarders who understand the intricacies of international shipping to streamline the process and avoid delays.
Top 4 Shell Side Tube Side Heat Exchanger Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. The Chemical Engineer – Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Domain: thechemicalengineer.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Shell and tube heat exchangers consist of tubes secured in tubeplates within a cylindrical shell. Key features include:
– Tube diameters: 3/4 inch or 1 inch OD.
– Tube arrangements: triangular (most economical), square (easier cleaning), and rotated-square (better coefficients).
– Standard tube length: often 20 ft (6.1 m), with lengths ranging from 8 ft (2.4 m) to 40 ft (12 m).
– Types of exchange…
2. Reddit – Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Multiple tubes in shell and tube heat exchangers are used instead of a single pipe primarily to increase the surface area for heat transfer. More tubes provide a greater boundary area for the transfer of heat between the two media. Additionally, using multiple smaller tubes allows for better flow dynamics, reducing the distance cold media has to travel to be heated effectively. This design also he…
3. Thermopedia – Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Domain: thermopedia.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers are popular due to their flexibility for various pressures and temperatures. They are categorized into two main types: petrochemical industry exchangers (TEMA standards) and power industry exchangers (feedwater heaters, condensers). Key components include: Front Header (fluid entry), Rear Header (fluid exit), Tube Bundle (tubes, tube sheets, baffles), and Shell (cont…
4. Flodraulic – Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Domain: flodraulic.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Shell and tube heat exchangers are common in industrial facilities for cooling or heating process fluids. They are inexpensive to manufacture, require no external energy, and are reliable due to the absence of moving parts. They can handle both liquid and gas, making them versatile. Key components include:
– Shell: The outer portion that holds the process fluid.
– Tubes/tube bundle: Contain the …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for shell side tube side heat exchanger
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Shell Side Tube Side Heat Exchanger Procurement?
In the competitive landscape of shell side tube side heat exchangers, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal component for optimizing procurement processes. By carefully evaluating fluid allocation, maintenance needs, and material compatibility, B2B buyers can significantly enhance the efficiency and longevity of their heat exchangers. Key considerations, such as the potential for fouling, corrosion resistance, and the physical state of fluids, should guide your decision-making, ensuring that your system operates at peak performance.
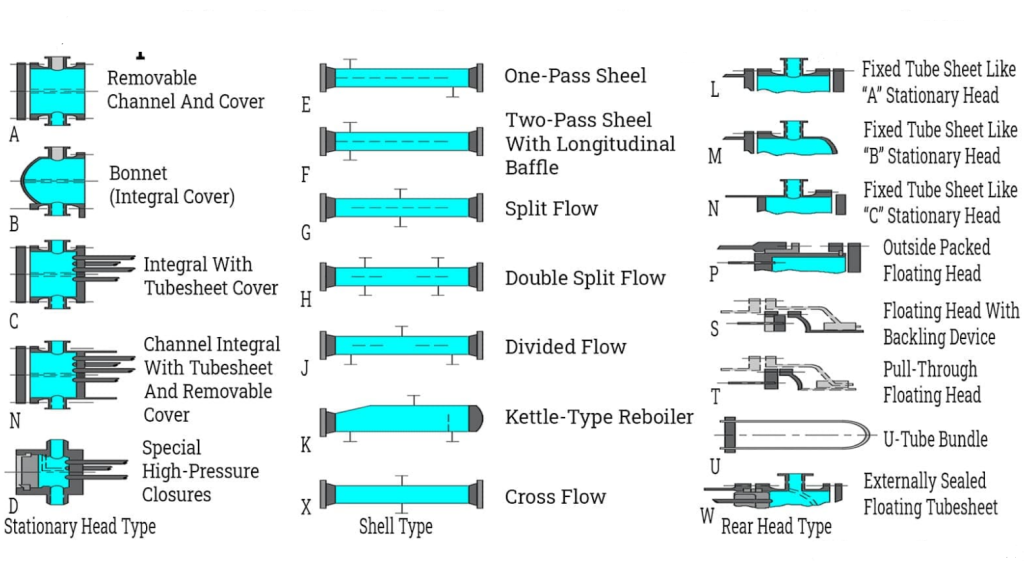
Illustrative image related to shell side tube side heat exchanger
Moreover, understanding the unique operational conditions in diverse regions—such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—allows for tailored solutions that address specific market challenges. By leveraging strategic sourcing, buyers not only reduce operational costs but also enhance their supply chain resilience.
Looking ahead, the demand for innovative and efficient heat exchange solutions is set to rise globally. Now is the time for international B2B buyers to engage with trusted suppliers who can provide customized solutions designed for your unique processes. Embrace the opportunity to optimize your operations and achieve sustainable growth in your markets. Reach out today to explore how strategic sourcing can transform your heat exchanger procurement strategy.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.