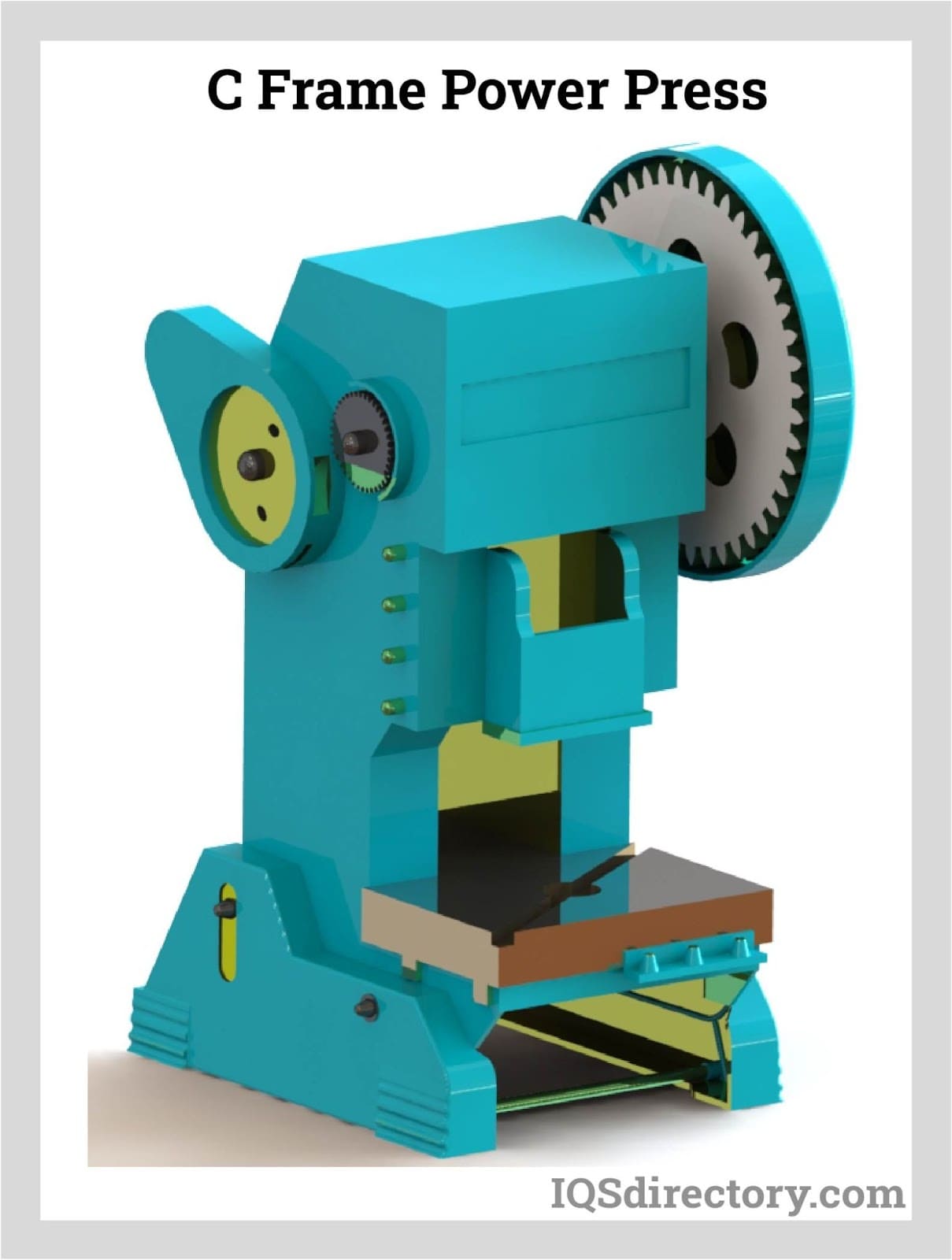
A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Power Presses: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for power presses
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, sourcing power presses that meet specific operational needs can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With diverse types such as hydraulic, forging, and portable power presses available, understanding which variant aligns best with your production requirements is crucial. This guide serves as an essential resource, offering a comprehensive exploration of power presses, including their applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
For businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including dynamic markets like Vietnam and Germany—navigating the global market for power presses requires careful assessment of local suppliers, technological advancements, and compliance with industry standards. By delving into the intricacies of power press machinery, this guide empowers decision-makers to make informed purchasing choices that enhance productivity and cost-efficiency.
With actionable insights on selecting reliable suppliers and evaluating the total cost of ownership, this resource aims to streamline your procurement process. Whether you’re looking to expand your manufacturing capabilities or upgrade existing equipment, understanding the nuances of power presses will position your business for success in an increasingly globalized market.
Understanding power presses Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forging Press | Utilizes a vertical ram for gradual pressure application. | Metal forming, automotive parts manufacturing. | Pros: High precision, excellent for thick materials. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Hydraulic Press | Uses hydraulic fluid to exert force; versatile. | Sheet metal forming, plastic molding, and assembly. | Pros: Greater force with compact design. Cons: Requires maintenance and hydraulic fluid management. |
| Mechanical Press | Operates via mechanical linkages; often less expensive. | Stamping, punching, and die-cutting applications. | Pros: Cost-effective, simpler operation. Cons: Limited force capacity compared to hydraulic presses. |
| Portable Power Press | Compact and versatile; designed for multiple functions. | Auto repairs, small-scale manufacturing, DIY projects. | Pros: Cost-effective, multifunctional. Cons: Lower capacity than larger industrial presses. |
| Pneumatic Press | Utilizes compressed air; ideal for lightweight tasks. | Assembly lines, light metal forming, and packaging. | Pros: Fast operation, lower energy costs. Cons: Limited force and not suitable for heavy materials. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Forging Presses?
Forging presses are characterized by their ability to apply controlled, gradual pressure through a vertical ram, making them ideal for forming metals into specific shapes. They are predominantly used in industries requiring high precision, such as automotive manufacturing and aerospace components. When considering a forging press, B2B buyers should evaluate the machine’s tonnage capacity and the types of dies compatible with their production needs.
How Do Hydraulic Presses Stand Out in Versatility?
Hydraulic presses are known for their ability to exert significant force through hydraulic fluid, making them versatile tools for various applications, including sheet metal forming and plastic molding. Their design allows for compact setups without sacrificing power, which can be a crucial factor for businesses with space constraints. Buyers should consider factors such as maintenance requirements and fluid management when investing in a hydraulic press.
What Makes Mechanical Presses a Cost-Effective Option?
Mechanical presses operate using a system of gears and linkages, making them a cost-effective choice for businesses focused on stamping, punching, or die-cutting. They are simpler to operate and maintain compared to hydraulic presses, appealing to smaller manufacturers or those with lower production volumes. However, potential buyers should be aware of their limitations in force capacity compared to hydraulic options.
Why Choose a Portable Power Press for Flexibility?
The portable power press is designed for versatility and ease of use in various applications, such as auto repairs and small-scale manufacturing. Its compact size allows it to be used in limited spaces, making it an excellent choice for small workshops or DIY enthusiasts. When purchasing, buyers should consider the range of functions it offers and its capacity compared to larger industrial presses.
In What Scenarios Are Pneumatic Presses Most Effective?
Pneumatic presses utilize compressed air to operate, making them ideal for lightweight tasks such as assembly lines and light metal forming. They are appreciated for their speed and efficiency, often leading to lower operational costs. However, buyers should evaluate the press’s force limitations and ensure it aligns with their production requirements, especially if heavier materials are involved.
Illustrative image related to power presses
Key Industrial Applications of power presses
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of power presses | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Pressing and forming metal components | Increased precision in component shapes and reduced waste | Need for high-tonnage presses; compatibility with specific metal types |
| Aerospace | Forging and shaping aircraft parts | Enhanced strength-to-weight ratio in components | Compliance with strict safety and quality standards; advanced technology requirements |
| Construction | Metal stamping for structural components | Cost-effective production of durable materials | Availability of custom dies; adaptability for various metal thicknesses |
| Electronics | Die stamping for circuit boards | High-volume production efficiency and reduced costs | Precision in tooling; ability to handle intricate designs |
| Consumer Goods | Bending and forming plastic parts | Streamlined manufacturing processes and reduced labor costs | Flexibility for small batch runs; support for diverse material types |
How Are Power Presses Utilized in Automotive Manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, power presses are vital for pressing and forming metal components such as body panels, brackets, and structural parts. These machines help achieve increased precision, ensuring that parts fit together seamlessly, which is crucial for vehicle safety and performance. For international buyers, sourcing high-tonnage presses that can handle various metal types is essential. Additionally, understanding the machine’s compatibility with local power supplies and maintenance services is crucial to avoid operational downtime.
What Role Do Power Presses Play in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, power presses are utilized for forging and shaping aircraft parts, such as wing structures and fuselage components. The ability to produce lightweight yet strong components is paramount in this industry, as it directly affects fuel efficiency and performance. Buyers in this field must consider presses that comply with stringent safety and quality standards. Advanced technology features, such as programmable controls and real-time monitoring, are also critical to meet the high demands of aerospace manufacturing.
How Are Power Presses Employed in the Construction Industry?
Power presses are extensively used in the construction industry for metal stamping of structural components like beams and connectors. This process enables cost-effective production of durable materials that can withstand heavy loads. When sourcing power presses for construction applications, buyers should focus on the availability of custom dies tailored for specific shapes and the ability to adapt to various metal thicknesses. Additionally, understanding local regulations and standards for construction materials is essential.
What Are the Applications of Power Presses in Electronics Manufacturing?
In the electronics industry, power presses are crucial for die stamping circuit boards and other electronic components. This process allows for high-volume production efficiency while reducing costs significantly. Buyers looking to invest in power presses for electronics must prioritize precision in tooling to handle intricate designs and ensure minimal waste. The ability to adapt to different materials, including plastics and metals, is also a key consideration for international buyers.
How Do Power Presses Benefit the Consumer Goods Sector?
Power presses are increasingly used in the consumer goods sector for bending and forming plastic parts, such as packaging and appliance components. This application streamlines manufacturing processes and significantly reduces labor costs, making production more efficient. For international buyers, sourcing presses that offer flexibility for small batch runs and support diverse material types is critical. Furthermore, understanding the local supply chain for parts and maintenance services can enhance operational efficiency.
Illustrative image related to power presses
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘power presses’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Pressing Results Leading to Waste
The Problem: B2B buyers frequently encounter issues with inconsistent pressing results when using power presses. This inconsistency can lead to defective parts that do not meet quality standards, resulting in material waste and increased production costs. For manufacturers in sectors like automotive or aerospace, where precision is critical, such variances can undermine the entire production line, leading to delays and potential losses in customer trust.
The Solution: To combat this issue, it is essential to invest in power presses equipped with advanced control systems that allow for precise adjustments in pressure and speed. Buyers should prioritize presses that offer programmable settings for different materials and thicknesses, enabling operators to maintain consistency across various production runs. Additionally, regular maintenance and calibration should be scheduled to ensure that the equipment remains in peak condition. Partnering with suppliers who provide comprehensive training and support on the machinery can further enhance operational efficiency and reduce the risk of human error.
Scenario 2: High Operational Costs Due to Inefficient Machinery
The Problem: Many companies face high operational costs associated with outdated or inefficient power presses. These machines often require excessive energy consumption and lead to higher utility bills, which can significantly affect the bottom line. In regions where energy costs are rising, this issue becomes even more pronounced, straining budgets and limiting the ability to invest in new technologies.
The Solution: To mitigate these costs, businesses should consider transitioning to energy-efficient power presses that utilize advanced hydraulic systems or alternative energy sources. When sourcing new equipment, buyers should look for energy labels or certifications that indicate lower energy consumption. Additionally, implementing a scheduled maintenance program can help ensure that existing machines operate at peak efficiency. This includes regular inspections of hydraulic fluid levels and seals, which can prevent leaks and reduce energy waste. Leveraging data analytics to monitor machine performance can also identify inefficiencies, allowing for targeted improvements and cost savings.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Finding Versatile Equipment for Diverse Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to find power presses that are versatile enough to handle a wide range of applications. Many machines are designed for specific tasks, leading to the need for multiple pieces of equipment to fulfill various production needs. This situation can lead to increased capital expenditures, wasted floor space, and logistical challenges in managing different machines.

Illustrative image related to power presses
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should seek out multi-functional power presses that offer interchangeable tooling and attachments. This adaptability allows one machine to perform various functions—such as pressing, bending, and clamping—thereby streamlining operations and reducing the need for multiple machines. When evaluating options, companies should conduct a thorough analysis of their production requirements and choose presses that can be easily customized or upgraded with new tooling. Establishing relationships with suppliers who offer modular equipment can provide long-term flexibility as business needs evolve, ensuring that the investment remains relevant and productive over time.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for power presses
What Are the Key Materials Used in Power Presses?
When selecting materials for power presses, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and how they align with international standards and buyer preferences. Below are analyses of four common materials used in the construction of power presses.
Steel: The Backbone of Power Presses
Key Properties: Steel is renowned for its high tensile strength and durability, withstanding significant pressure and temperature variations. It typically exhibits good corrosion resistance when treated with coatings or alloys.
Pros & Cons: Steel’s primary advantage is its strength, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, it can be costly due to the manufacturing processes involved, such as forging and heat treatment. Additionally, while it is highly durable, it may require additional treatments for corrosion resistance, especially in humid or corrosive environments.
Impact on Application: Steel’s compatibility with various media makes it ideal for applications requiring high pressure and temperature, such as hydraulic presses.

Illustrative image related to power presses
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards (e.g., ASTM, DIN) regarding material specifications. In Europe, particularly Germany, there is a strong preference for high-quality, certified steel, which may influence procurement decisions.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Versatile
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has excellent corrosion resistance. It can withstand moderate pressure and temperature levels, making it suitable for less demanding applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which allows for easier handling and reduced operational costs. However, it is not as strong as steel, which limits its use in high-pressure applications. Manufacturing complexity can also be a concern, as aluminum requires specialized techniques for welding and machining.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for applications that require portability and ease of use, such as smaller, mobile power presses.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should consider the availability of aluminum alloys that meet specific performance standards. Compliance with local regulations regarding aluminum sourcing and recycling is also essential.
Cast Iron: Stability and Vibration Damping
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its excellent vibration-damping properties and stability under load. It can handle high pressures but is less flexible than steel or aluminum.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of cast iron is its ability to absorb vibrations, making it suitable for precision applications. However, it is brittle and can crack under extreme stress, which limits its use in dynamic environments. Additionally, cast iron can be more expensive due to its casting processes.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is often used in stationary power presses where stability and precision are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe may prefer cast iron components that comply with specific EU standards for quality and safety. In regions with less stringent regulations, buyers should still prioritize quality to avoid long-term operational issues.
Composite Materials: Innovative and Adaptive
Key Properties: Composite materials combine different materials to achieve superior properties, such as enhanced strength-to-weight ratios and resistance to corrosion.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of composites is their adaptability, allowing for custom solutions tailored to specific applications. However, they can be expensive and require advanced manufacturing techniques, which may not be readily available in all regions.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly beneficial in applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in portable power presses.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from South America and Africa should assess the availability of composite materials and the necessary manufacturing capabilities. Compliance with international standards for composites is also crucial to ensure product reliability.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Power Presses
| Material | Typical Use Case for power presses | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty hydraulic presses | High tensile strength and durability | Costly and may require corrosion treatment | High |
| Aluminum | Portable and lightweight presses | Lightweight and easy to handle | Lower strength and manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Cast Iron | Stationary precision presses | Excellent vibration damping | Brittle and can crack under stress | Medium |
| Composite | Custom and portable applications | Superior strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive and requires advanced manufacturing | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for power presses, aiding international B2B buyers in making informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for power presses
What Are the Main Stages of Power Press Manufacturing?
Manufacturing power presses involves several key stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Power Presses?
Material preparation is critical in ensuring that the right materials are selected and treated before they undergo further processing. Typically, high-strength steel or specialized alloys are used, depending on the intended application of the power press. The raw materials undergo various processes such as cutting, shearing, and surface treatment to remove impurities and enhance their mechanical properties. Additionally, companies often utilize advanced software for material optimization, ensuring minimal waste and maximum efficiency.

Illustrative image related to power presses
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Power Presses?
The forming stage employs several techniques, primarily focusing on shaping and structuring the components of the power press. Key methods include:
-
Hydraulic Forming: This method uses hydraulic pressure to shape the metal into desired forms. It is particularly effective for complex shapes and heavy-duty applications.
-
Metal Stamping: This cold-forming process is essential for creating precise shapes from sheets of metal. It involves using dies to cut and shape the metal into components that will later be assembled into the power press.
-
Forging: This technique utilizes a vertical ram to apply controlled pressure to a die holding the workpiece, leading to a gradual deformation of the material. This method is preferred for producing strong and durable components.
Each of these techniques requires specialized equipment and skilled personnel to ensure the integrity and precision of the parts being manufactured.
How Is the Assembly of Power Presses Conducted?
The assembly stage is where all the individual components come together to form the complete power press. This process typically involves:
-
Precision Alignment: Components must be aligned accurately to ensure proper operation. Misalignment can lead to operational inefficiencies or mechanical failure.
-
Integration of Hydraulic Systems: For hydraulic power presses, the hydraulic system must be integrated carefully, ensuring that all connections are secure and leak-free.
-
Electrical Wiring: The power supply systems, including AC and DC configurations, need to be installed and tested to ensure safe and reliable operation.
The assembly process often employs jigs and fixtures to maintain component stability and alignment during assembly, thereby enhancing overall efficiency.
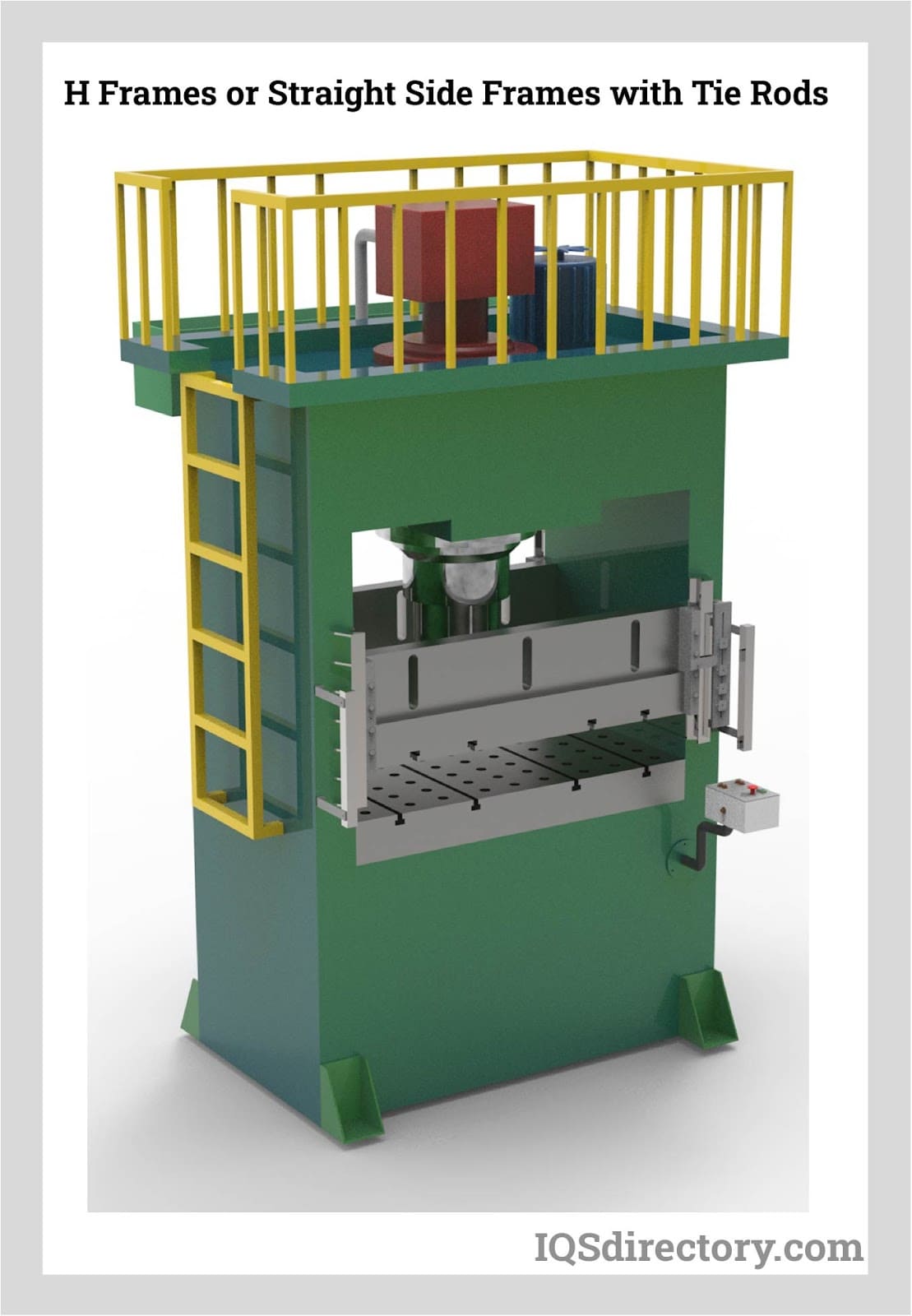

Illustrative image related to power presses
What Finishing Processes Are Commonly Used?
Finishing processes are critical for enhancing the durability and appearance of power presses. These processes include:
-
Surface Treatment: Techniques such as powder coating, galvanizing, or painting are used to protect the metal from corrosion and wear.
-
Quality Polishing: This process improves the aesthetic appeal and can also reduce friction on moving parts.
-
Final Assembly Inspection: Before the power press is deemed ready for shipment, a thorough inspection is conducted to ensure all components are functioning correctly and meet the specified tolerances.
How Is Quality Assurance Managed in Power Press Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral part of the manufacturing process, ensuring that the power presses produced meet international and industry-specific standards.
What International Standards Apply to Power Press Manufacturing?
For B2B buyers, understanding the applicable international standards is vital. ISO 9001 is the most recognized quality management standard, focusing on meeting customer expectations and delivering customer satisfaction. Compliance with ISO 9001 demonstrates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
In addition to ISO standards, power presses may also need to adhere to specific industry certifications such as:
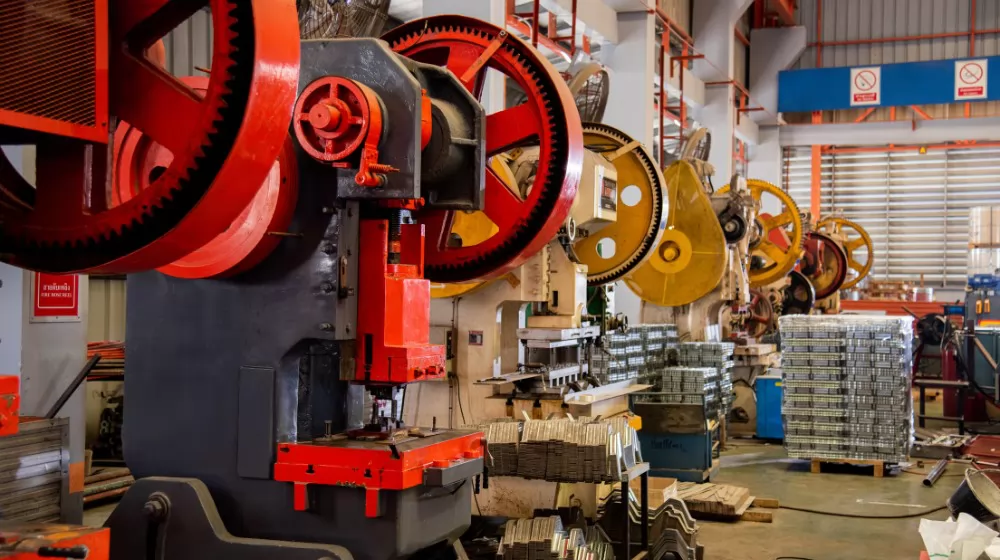

Illustrative image related to power presses
-
CE Marking: Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
-
API Certification: Relevant for companies manufacturing equipment for the oil and gas sector, ensuring compliance with specific industry standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Power Press Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are essential in the manufacturing process to ensure the final product meets all quality standards. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage checks the quality of raw materials and components before they enter the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process ensures that any deviations from the specified standards are caught early, preventing defects.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection phase includes testing the complete power press for functionality, safety, and compliance with all specifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Power Press Quality Assurance?
Several testing methods are employed to verify the performance and safety of power presses, including:
-
Hydraulic Testing: This checks for leaks and verifies the integrity of the hydraulic systems.
-
Load Testing: Ensures that the power press can handle its rated load without failure.
-
Functional Testing: Verifies that all operational features function correctly, including emergency stops and safety mechanisms.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international buyers, especially in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are some effective strategies:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits can help buyers assess the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality management systems, and compliance with international standards.
-
Request Quality Assurance Reports: Suppliers should be willing to provide documentation detailing their quality assurance procedures, including results from recent inspections and tests.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control measures and product integrity.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing power presses internationally, buyers should be aware of several nuances in quality control:
-
Cultural Differences: Different countries may have varying standards and practices for quality assurance. Understanding these can help buyers set realistic expectations.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with local and international regulations, which can vary significantly by region.
-
Communication Barriers: Language and time zone differences can complicate the verification process. Establishing clear communication channels is essential for effective collaboration.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with power presses, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source reliable and high-quality equipment that meets their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘power presses’
The procurement of power presses is a critical investment for businesses in various manufacturing sectors. This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers to ensure they make informed decisions while sourcing power presses that meet their operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before diving into the procurement process, clearly outline the technical requirements for the power press you need. Consider factors such as the type of press (e.g., hydraulic, mechanical, or forging), capacity, and specific applications (e.g., metal stamping, bending, or pressing). This clarity will streamline your search and help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers.
Step 2: Research Supplier Credentials
Engage in thorough research to identify reputable suppliers. Look for certifications that validate their manufacturing processes and quality standards, such as ISO 9001. Additionally, consider suppliers who have a strong presence in your region, as they may better understand local market conditions and regulations.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website; consider visiting their facilities if possible to assess their manufacturing capabilities and quality control processes.
Step 4: Assess Warranty and After-Sales Support
A robust warranty and reliable after-sales support are essential for minimizing downtime and ensuring long-term operational efficiency. Inquire about the warranty period and what it covers. Also, evaluate the supplier’s customer service responsiveness and availability of spare parts to support maintenance needs.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership
While price is a significant factor, consider the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, energy consumption, and the potential for productivity gains. Obtain detailed quotes from multiple suppliers, ensuring you understand what is included. Sometimes, a higher upfront cost can lead to lower operational costs in the long run.
Step 6: Examine Delivery Terms and Lead Times
Understand the delivery terms and lead times associated with your order. Delays in receiving machinery can disrupt production schedules. Confirm the supplier’s ability to meet your timeline and discuss any penalties for delays or options for expedited shipping if necessary.
Step 7: Seek Recommendations and Reviews
Finally, leverage your industry network to gather recommendations and feedback on potential suppliers. Online reviews and testimonials can provide insights into a supplier’s reliability, quality, and customer service. This information can help you avoid common pitfalls and choose a supplier that aligns with your business values.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing power presses effectively, ensuring they invest in equipment that enhances their manufacturing capabilities and supports their business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for power presses Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Power Press Manufacturing?
When sourcing power presses, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects the cost. High-strength steel or specialized alloys may increase the initial expense but can enhance durability and performance, ultimately reducing maintenance costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region. In countries with higher wages, like Germany, labor can account for a significant portion of production costs. Conversely, regions with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing, but potential trade-offs in quality and expertise should be considered.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility management. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower these overhead costs, leading to more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial setup for tooling can be a substantial investment, particularly for custom dies or molds. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs and whether they are included in the quoted price.
-
Quality Control: Quality assurance processes ensure that power presses meet industry standards and certifications. Implementing rigorous QC can increase costs but is essential for long-term reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely depending on the destination. International buyers should consider freight costs, customs duties, and potential delays that could affect delivery schedules.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build in a margin to cover risks and ensure profitability. Understanding the supplier’s pricing strategy can provide leverage during negotiations.
What Influences the Pricing of Power Presses?
Several factors can influence the pricing of power presses, including volume, specifications, materials, quality certifications, supplier factors, and Incoterms.
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to bulk discounts. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to optimize costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized features can significantly affect pricing. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Materials and Quality: The quality of materials used directly influences the durability and performance of the presses. Products that meet international standards may carry a premium price but offer enhanced reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, production capabilities, and location can impact costs. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge higher prices but can provide peace of mind.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial for cost management. Different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can affect the total cost of ownership, including insurance and customs fees.
How Can Buyers Negotiate Effectively for Power Press Pricing?
Effective negotiation strategies can lead to better pricing and terms for power presses. Here are some tips for international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct thorough market research to understand standard pricing and features. Use this information to benchmark offers from different suppliers.
-
Emphasize Total Cost of Ownership: Rather than focusing solely on the purchase price, consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, operational efficiency, and resale value.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Frequent communication can also provide insights into market trends and potential discounts.
-
Be Flexible: Being open to alternative solutions or suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations. Consider different configurations or models that may meet your needs at a lower cost.
-
Understand Payment Terms: Clarifying payment terms upfront can prevent misunderstandings. Consider negotiating favorable terms that align with your cash flow and financial planning.
Final Thoughts on Power Press Sourcing
When sourcing power presses, it is essential to consider the various cost components and pricing influencers. A well-informed approach can lead to significant savings and a better overall purchasing experience. Keep in mind that prices can vary widely, and what may be a fair price in one region might not apply in another. Always seek multiple quotes and be aware of the nuances involved in international transactions, especially regarding logistics and tariffs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing power presses With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Power Presses for Metalworking Solutions
In the world of metalworking, power presses are a popular choice for various applications such as forging, shaping, and stamping. However, there are alternative solutions that may better suit specific needs, depending on factors like budget, complexity, and application. This analysis compares power presses with two viable alternatives: hydraulic presses and mechanical stamping machines.
| Comparison Aspect | Power Presses | Hydraulic Presses | Mechanical Stamping Machines |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High force application; versatile | Excellent for heavy-duty tasks; slower than power presses | Fast production; ideal for high volume |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; ongoing operational costs | Generally lower upfront cost; varying maintenance costs | Higher initial investment; cost-effective for mass production |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators; installation may be complex | Easier to set up; user-friendly controls | Requires specialized knowledge; setup can be time-consuming |
| Maintenance | Regular upkeep needed; parts can be costly | Lower maintenance frequency; hydraulic fluid checks required | High wear on tooling; regular inspections needed |
| Best Use Case | Versatile applications; custom jobs | Heavy-duty tasks; automotive repairs | High-volume production; consistent part shapes |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Hydraulic Presses Compared to Power Presses?
Hydraulic presses utilize liquid pressure to perform tasks and are known for their ability to exert significant force. Their lower initial cost makes them attractive for small to medium-sized operations, especially in automotive repair where they can be used for bending and pressing tasks. However, hydraulic presses are generally slower than power presses and may not be suitable for high-volume production. The maintenance requirements are also relatively low, focusing primarily on the hydraulic fluid and seals, which can enhance long-term operational efficiency.
How Do Mechanical Stamping Machines Stack Up Against Power Presses?
Mechanical stamping machines are designed for high-volume production, utilizing mechanical energy to shape metal sheets quickly and efficiently. They excel in environments where consistent part quality and speed are paramount, making them ideal for industries like automotive manufacturing. However, the initial investment for mechanical stamping can be higher than that of power presses, and they may require specialized knowledge for setup and operation. Regular inspections are critical to maintain tooling performance, and any downtime can lead to significant production losses.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Metalworking Solution for Your Business Needs?
When deciding between power presses and alternative solutions like hydraulic presses and mechanical stamping machines, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and production goals. Power presses offer versatility and high force application, making them suitable for various applications, while hydraulic presses provide cost-effective solutions for heavy-duty tasks. Mechanical stamping machines, though requiring a higher investment, can significantly boost production efficiency for high-volume demands. By carefully evaluating these factors, businesses can select the right solution that aligns with their manufacturing needs and operational capabilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for power presses
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Power Presses?
Understanding the essential technical properties of power presses is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some of the critical specifications that buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade
Power presses are typically constructed from high-strength steel or alloys that offer durability and resistance to deformation. The material grade affects the machine’s overall strength, longevity, and ability to withstand heavy workloads. For buyers, selecting a power press made from reputable material grades ensures reliability, reducing the likelihood of costly breakdowns. -
Tonnage Capacity
Tonnage capacity refers to the maximum force that a power press can apply to a workpiece. This specification is critical for buyers to match the press with their specific applications, whether it’s metal stamping, bending, or forging. Insufficient tonnage can lead to ineffective operations, while excessive tonnage may result in unnecessary wear and tear on the equipment. -
Stroke Length
The stroke length is the distance the ram travels during operation. It is vital for determining the type of operations the press can perform. A longer stroke allows for deeper shaping or pressing, which can be advantageous for larger or thicker workpieces. Buyers should ensure that the stroke length aligns with their production requirements. -
Control System
Modern power presses often incorporate advanced control systems that allow for programmable settings and automated operations. This feature enhances precision and efficiency, making it easier for operators to manage complex tasks. For B2B buyers, investing in presses with sophisticated control systems can lead to improved productivity and reduced labor costs. -
Safety Features
Safety is paramount in manufacturing environments. Power presses equipped with features like emergency stop buttons, machine guards, and automatic shut-off mechanisms help protect operators from accidents. Buyers should prioritize safety certifications and features when selecting equipment to ensure compliance with industry regulations.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Power Presses?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication in the B2B marketplace. Here are some common terms that buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to the company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers looking for reliable components or machines, ensuring they purchase from reputable sources. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. This term is significant for buyers as it can affect inventory management and cash flow. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchasing strategies effectively. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent by buyers to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services. This term is crucial for initiating the procurement process and ensuring competitive pricing. Buyers should prepare detailed RFQs to receive accurate responses. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms helps buyers clarify shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, thus preventing misunderstandings during the procurement process. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. This term is essential for buyers to manage their production schedules and inventory levels. Shorter lead times can enhance operational efficiency and responsiveness to market demands.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the power press market more effectively, ensuring that their purchasing decisions align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the power presses Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing Power Presses?
The power presses market is experiencing robust growth driven by increasing demand for automation in manufacturing processes across various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Global industrialization and technological advancements are key factors propelling the market forward. Notably, regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing a surge in manufacturing activities, leading to a heightened demand for efficient and versatile power press machines.
Emerging trends in B2B sourcing highlight the shift towards digital platforms for procurement and supply chain management. International buyers are increasingly leveraging e-commerce and B2B marketplaces to streamline their sourcing processes. Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 technologies, including IoT-enabled machinery and predictive maintenance solutions, is reshaping the landscape of power presses. These innovations not only improve operational efficiency but also enhance the overall reliability of machinery, making them a preferred choice among manufacturers.

Illustrative image related to power presses
Furthermore, as competition intensifies, suppliers are focusing on offering customized solutions tailored to specific industry needs. The demand for multi-functional power presses that can perform various operations, such as bending, stamping, and forming, is on the rise. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers looking for cost-effective solutions that maximize productivity without compromising quality.
How Is Sustainability Reshaping Sourcing Practices for Power Presses?
In the current business environment, sustainability is a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the power presses sector. Companies are increasingly aware of their environmental impact and are seeking suppliers that prioritize ethical sourcing and sustainable practices. This includes selecting materials that are recyclable and minimizing waste throughout the manufacturing process.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Businesses that adopt sustainable sourcing practices not only enhance their brand reputation but also comply with regulatory requirements and meet consumer expectations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and adherence to international sustainability standards can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to responsible practices.
Moreover, the demand for ‘green’ materials and technologies is growing. Buyers are looking for power presses that utilize energy-efficient systems and eco-friendly lubricants to reduce their carbon footprint. Investing in machinery that meets these criteria not only contributes to sustainability goals but also leads to long-term cost savings through reduced energy consumption and maintenance needs.
Illustrative image related to power presses
What Is the Historical Context of Power Presses in Manufacturing?
The evolution of power presses can be traced back to the industrial revolution when the need for efficient metal forming and shaping processes became apparent. Initially, these machines were powered by steam and were primarily used in heavy industries. Over time, advancements in technology led to the development of hydraulic and mechanical presses, which allowed for greater precision and control in manufacturing processes.
The introduction of programmable power supplies in the late 20th century revolutionized the sector, enabling manufacturers to optimize their operations and enhance productivity. Today, power presses are integral to various industries, facilitating the mass production of components with consistent quality. As the market continues to evolve, the focus is shifting towards integrating smart technologies, ensuring that power presses remain at the forefront of manufacturing innovation.
By understanding these market dynamics, trends, and historical contexts, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing power presses, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and sustainability in their businesses.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of power presses
-
How do I choose the right power press for my manufacturing needs?
Selecting the right power press involves assessing your specific production requirements, such as the type of materials you’ll be working with, the desired output capacity, and the complexity of the operations (e.g., bending, stamping, or forging). Consider factors like the maximum tonnage, stroke length, and die compatibility. It’s also crucial to review the technical specifications and capabilities of different models from various suppliers to ensure they align with your operational goals. -
What is the best power press for high-volume production?
For high-volume production, hydraulic power presses are often the best choice due to their efficiency and ability to handle a wide range of materials. Look for models that offer programmable controls for automation, allowing for faster cycle times and consistent output. Additionally, consider the press’s reliability, maintenance requirements, and the availability of spare parts from the supplier to minimize downtime. -
What factors should I consider when vetting a power press supplier?
When vetting a supplier for power presses, assess their experience and reputation in the industry, as well as customer reviews and testimonials. Verify their manufacturing capabilities, quality control processes, and certifications (such as ISO). Request information about their after-sales support, warranty policies, and delivery times to ensure they can meet your operational needs effectively. -
Can I customize a power press for my specific application?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for power presses to cater to specific applications. Customizations can include modifications to the machine size, tonnage, control systems, and additional features like safety guards or specialized tooling. Be sure to communicate your requirements clearly to the supplier and obtain a detailed proposal outlining the costs and timelines for the customization. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for power presses?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for power presses can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of machine. Some suppliers may have no MOQ for standard models, while others might require a minimum order of several units for custom or specialized machines. It’s essential to discuss MOQs upfront during negotiations to ensure they align with your purchasing plans and budget. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing power presses internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of power presses typically involve a deposit upfront (often 30% to 50%) with the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer flexible payment options, including letters of credit or installment plans. Always clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., bank transfer, credit card) and confirm the currency used to avoid any unexpected costs. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for my power press order?
To ensure quality assurance for your power press order, request a detailed quality control plan from the supplier, including inspection protocols and testing methods. Many reputable manufacturers provide documentation of compliance with international standards and certifications. If possible, schedule a factory visit or request third-party inspections to verify quality before shipment, ensuring the machine meets your specifications. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for importing power presses?
When importing power presses, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs clearance processes. It’s crucial to work with a freight forwarder experienced in heavy machinery to navigate international shipping regulations and documentation. Additionally, factor in potential import duties and taxes, as well as storage and handling requirements upon arrival at your destination.
Top 6 Power Presses Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Power Presses
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Power Presses are machine tools designed for shaping, shearing, and punching metal through cold stamping. They are classified into hydraulic, mechanical, and servo types based on their power source. Hydraulic presses use pressurized hydraulic fluid, mechanical presses convert rotational to straight-line motion, and servo presses utilize a servo motor for precise control. Key components include the…
2. Portable Power Press – Hydraulic Multi-Function Press
Domain: portablepowerpress.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Portable Power Press is a Patent Pending design made in the USA, priced at $399.99, which is 85% cheaper than traditional shop presses. It functions as a hydraulic press for multiple uses including pressing, bending, clamping, spreading, jacking, and lifting. It is made with high strength American steel, has a 4-ton capacity cylinder, and is compact at only 4″ wide, making it suitable for both pro…
3. Britannica – Power Press
Domain: britannica.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: The power press is a machine used in tool and die making, specifically for cutting and forming sheet metal into predetermined shapes and configurations. It has led to a demand for press dies, which are essential for the fabrication process.
4. Safety and Health Magazine – Mechanical Power Presses
Domain: safetyandhealthmagazine.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Mechanical power presses are large equipment used in manufacturing to exert mechanical force for cutting or shaping materials. Key safety elements include: 1) Analyzing each process phase for risks, 2) Routine inspections and maintenance to ensure proper operation of clutches, brakes, and air lines, 3) Understanding regulatory standards, specifically OSHA’s updates and ANSI B11.1-2009, 4) Providin…
5. Harsle – Power Press
Domain: harsle.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Power press is a stamping press used in national production for its advantages in saving materials and energy, high efficiency, and low technical requirements for operators. It converts circular motion into linear motion through a main motor, flywheel, clutch, gear, crankshaft, and connecting rod. There are two main types of power presses based on driving force: mechanical and hydraulic. They can …
6. WorkSafe WA – Power Press Safety
Domain: worksafe.wa.gov.au
Introduction: Power presses are powered equipment used to stamp, cut or form materials using dies. They include equipment known as ‘croppers’ or ‘metal workers’. Injuries from power presses are common in metal machinery workplaces, often due to unguarded machines or malfunctioning guards, leading to serious injuries like amputated fingertips, particularly among young workers. Legally, all dangerous parts must b…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for power presses
As the global market for power presses continues to evolve, strategic sourcing remains a pivotal factor for businesses aiming to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. By understanding the diverse types of power presses—ranging from hydraulic to forging presses—buyers can tailor their procurement strategies to meet specific production needs. Additionally, incorporating modern technologies, such as programmable power supplies and versatile hydraulic systems, can significantly improve productivity and flexibility in manufacturing processes.
International buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize partnerships with reputable suppliers who offer not only high-quality machinery but also comprehensive support services. This approach ensures that investments in power presses yield long-term benefits and align with business growth objectives.
Looking ahead, the demand for innovative and cost-effective power press solutions will only increase. Companies that embrace strategic sourcing practices and leverage the latest advancements in technology will position themselves as leaders in their respective markets. Now is the time to explore new partnerships and invest in the right equipment to drive your business forward. Take the next step in your sourcing journey today to unlock the full potential of your manufacturing capabilities.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
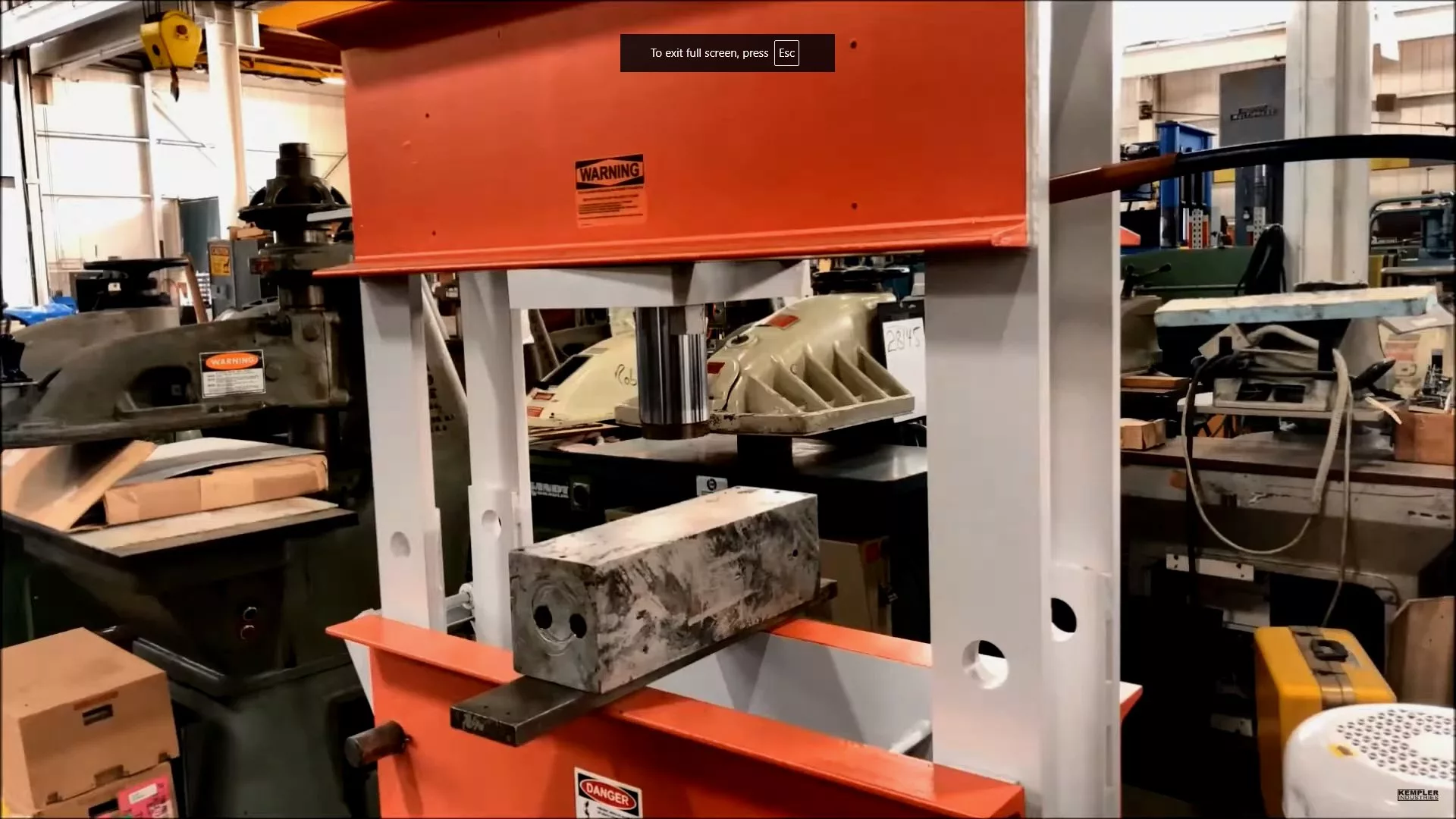

Illustrative image related to power presses
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.