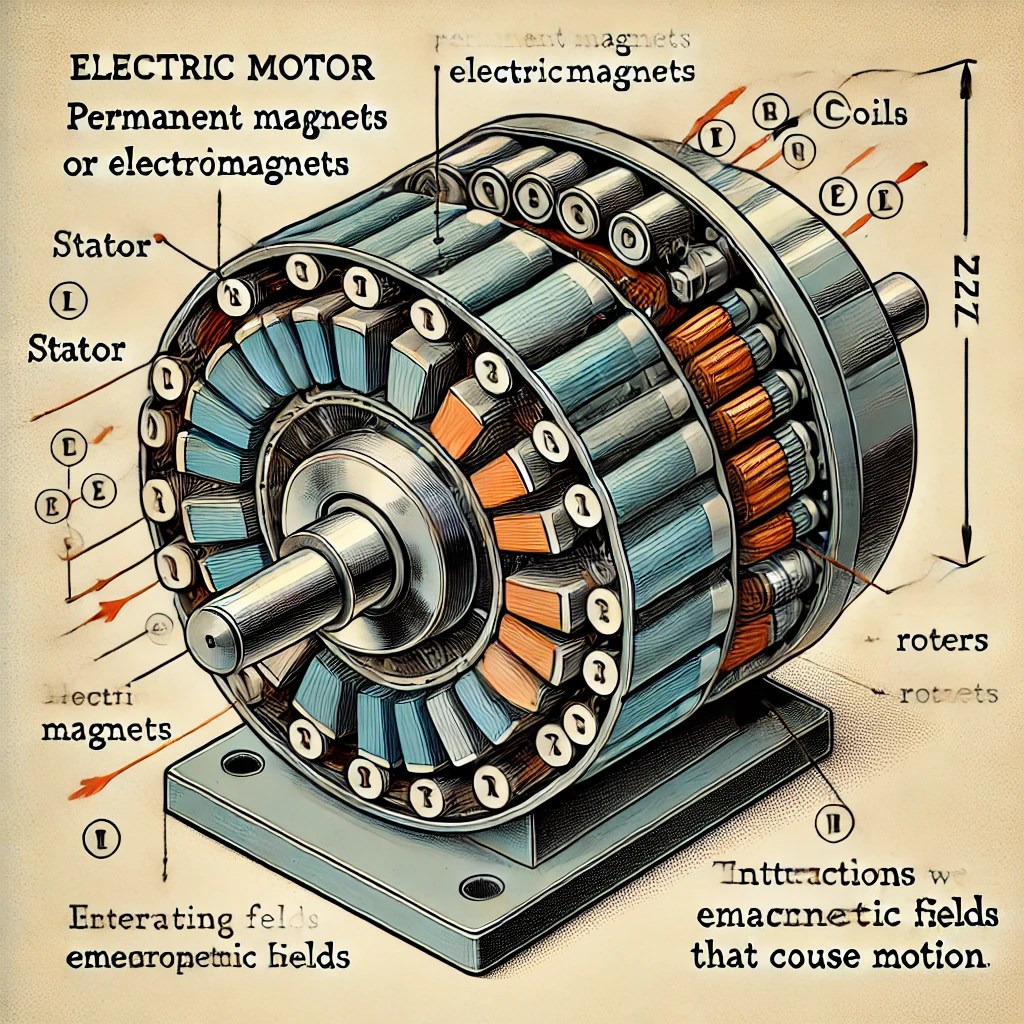
How to Source Stator Magnets Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for stator magnets
In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, sourcing high-quality stator magnets is a critical challenge for B2B buyers across the globe. Whether you’re operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, understanding the nuances of stator magnet procurement can significantly impact your operational efficiency and product performance. Stator magnets are integral components in electric motors and generators, responsible for generating the magnetic fields essential for energy conversion. As the demand for advanced electric machinery grows, so does the need for reliable suppliers who can meet diverse specifications and quality standards.
This comprehensive guide delves into various aspects of stator magnets, including types (such as ferrite and neodymium), applications in sectors like automotive and renewable energy, and effective supplier vetting strategies. We will also explore cost considerations and trends influencing the global market. By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable insights and best practices, this guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring that you select the right stator magnets for your specific applications.
Navigating the complexities of the global magnet market is no small feat, but with the right knowledge and resources at your fingertips, you can streamline your sourcing process, enhance product quality, and ultimately drive your business success.
Understanding stator magnets Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ferrite Stator Magnets | Cost-effective, corrosion-resistant, lower magnetic strength | Household appliances, low-power motors | Pros: Affordable; Cons: Lower efficiency compared to neodymium. |
| Neodymium Stator Magnets | High magnetic strength, compact size, and lightweight | Electric vehicles, drones, industrial motors | Pros: Superior performance; Cons: Higher cost and susceptibility to heat. |
| Samarium-Cobalt Stator Magnets | High resistance to demagnetization, stable at high temperatures | Aerospace, military applications | Pros: Excellent thermal stability; Cons: Expensive and brittle. |
| Alnico Stator Magnets | High temperature resistance, good magnetic stability | Specialty motors, sensors | Pros: Durable; Cons: Lower magnetic strength than rare-earth magnets. |
| Bonded Magnets | Flexible shapes, lower production costs, can be produced in complex geometries | Consumer electronics, small motors | Pros: Versatile design options; Cons: Generally lower performance. |
What Are Ferrite Stator Magnets and When Should B2B Buyers Consider Them?
Ferrite stator magnets are known for their cost-effectiveness and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for applications in household appliances and low-power motors. They are typically made from a mixture of iron oxide and strontium or barium carbonate. Buyers should consider these magnets when budget constraints are a priority, but they should also be aware that ferrite magnets have lower magnetic strength, which can limit their use in high-performance applications.
How Do Neodymium Stator Magnets Stand Out in Performance?
Neodymium stator magnets are recognized for their exceptional magnetic strength and compact size, making them suitable for high-efficiency applications like electric vehicles and drones. Their ability to generate a strong magnetic field allows for smaller and lighter designs. However, B2B buyers must consider the higher cost and the fact that neodymium magnets can lose their magnetic properties at elevated temperatures, necessitating careful thermal management in application design.
Why Are Samarium-Cobalt Stator Magnets Ideal for High-Performance Applications?
Samarium-cobalt stator magnets offer remarkable resistance to demagnetization and maintain their magnetic properties even at high temperatures. This makes them particularly well-suited for aerospace and military applications, where reliability and performance are critical. However, buyers should be prepared for a higher price point and the fragility of these magnets, which can complicate handling and installation.
In What Scenarios Should B2B Buyers Choose Alnico Stator Magnets?
Alnico stator magnets are favored for their high temperature resistance and good magnetic stability, making them suitable for specialty motors and sensors. They are composed of aluminum, nickel, cobalt, and iron, providing durability in demanding environments. While they are less powerful than rare-earth magnets, their robustness and stability can be advantageous in applications that experience extreme conditions.
What Are the Advantages of Using Bonded Magnets in Stator Applications?
Bonded magnets are made from a mixture of magnetic powder and a polymer binder, allowing for flexible shapes and lower production costs. They are particularly useful in consumer electronics and small motors, where design flexibility is essential. However, buyers should note that while bonded magnets offer versatility, they generally exhibit lower magnetic performance compared to other types of magnets, which may limit their application in high-demand scenarios.
Key Industrial Applications of stator magnets
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Stator Magnets | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Vehicles | Stator magnets in electric motors | Enhanced efficiency and performance of EVs | Need for high-grade neodymium magnets for optimal performance; consider local suppliers to reduce lead times. |
| Renewable Energy | Stator magnets in wind turbines | Increased energy conversion efficiency | Sourcing durable magnets that withstand harsh environmental conditions; focus on suppliers with proven reliability. |
| Industrial Machinery | Stator magnets in manufacturing equipment | Improved operational reliability and reduced downtime | Look for custom solutions that fit specific machinery requirements; evaluate suppliers for quality certifications. |
| Consumer Electronics | Stator magnets in appliances like refrigerators | Energy savings and improved performance | Ensure compliance with international safety standards; consider suppliers with a wide range of magnet options. |
| Aerospace & Defense | Stator magnets in aircraft systems | Enhanced reliability and safety in critical applications | Source high-performance magnets that meet aerospace standards; consider suppliers with experience in defense contracts. |
How Are Stator Magnets Used in Electric Vehicles?
In electric vehicles (EVs), stator magnets are crucial components of electric motors that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. The efficiency of these motors directly impacts the vehicle’s performance and range. Stator magnets, particularly high-grade neodymium magnets, are favored for their strength and compact size, enabling manufacturers to create lightweight and efficient systems. International buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers who can provide high-performance magnets tailored to specific motor designs, considering factors such as lead times and local availability to optimize their supply chain.
What Role Do Stator Magnets Play in Renewable Energy?
Stator magnets are integral to the functioning of wind turbines, where they contribute to the generation of electricity by creating a magnetic field that interacts with the rotor. This interaction enhances energy conversion efficiency, making wind energy more viable. Buyers in this sector must consider the durability of magnets, as they must withstand harsh environmental conditions. Sourcing from manufacturers with a reputation for quality and reliability is essential, especially for international buyers looking to ensure long-term operational success.
How Are Stator Magnets Utilized in Industrial Machinery?
In industrial machinery, stator magnets are used in electric motors that drive various manufacturing processes. Their reliable performance is critical for maintaining operational efficiency and minimizing downtime. Businesses should seek suppliers that can provide customized magnet solutions tailored to specific machinery requirements. Quality certifications and proven track records are key factors to consider when selecting a sourcing partner, especially for international buyers who need assurance of consistent performance and quality in diverse operational environments.
How Do Stator Magnets Enhance Consumer Electronics?
Stator magnets are found in household appliances, such as refrigerators and washing machines, where they help improve energy efficiency and overall performance. By generating a strong magnetic field, these magnets facilitate the efficient operation of motors within these appliances. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers comply with international safety standards and can offer a variety of magnet options to meet specific appliance designs. This consideration is particularly important for international buyers looking to maintain high-quality standards in competitive markets.
Why Are Stator Magnets Important in Aerospace and Defense?
In the aerospace and defense sectors, stator magnets are used in critical systems that require enhanced reliability and safety. These magnets are essential in electric motors for aircraft systems, where performance can directly impact safety and operational efficiency. Buyers should focus on sourcing high-performance magnets that meet stringent aerospace standards, ensuring that suppliers have experience in defense contracts. This focus on quality and reliability is vital for international buyers looking to fulfill regulatory compliance and maintain high operational standards in demanding environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘stator magnets’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Supply Chain Disruptions for Stator Magnets
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant challenges when sourcing stator magnets due to supply chain disruptions. Factors such as geopolitical tensions, raw material shortages, and fluctuating shipping costs can lead to delays in production timelines. This unpredictability can severely impact project deadlines, particularly for companies reliant on timely delivery of electrical components for motors and generators. Buyers may find themselves scrambling to find alternative suppliers, resulting in increased costs and potential project overruns.
The Solution: To mitigate supply chain risks, B2B buyers should establish relationships with multiple suppliers across different regions. Diversifying the supplier base can help create a more resilient supply chain. When sourcing stator magnets, it’s crucial to assess suppliers not just on price, but also on their ability to provide timely delivery, quality certifications, and customer support. Buyers should request detailed lead time estimates and consider placing bulk orders well in advance of projected needs to buffer against delays. Utilizing technology for real-time inventory tracking can also help in anticipating shortages and planning accordingly.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Compatibility of Stator Magnets with Motor Specifications
The Problem: Another common pain point is the compatibility of stator magnets with existing motor specifications. As electric motor technologies evolve, the requirements for stator magnets in terms of size, shape, and magnetic properties can vary significantly. Buyers may encounter issues if the magnets they purchase do not meet the precise specifications needed for their applications, leading to suboptimal motor performance or even failures.
The Solution: To ensure compatibility, B2B buyers should engage in thorough communication with their engineering teams before sourcing stator magnets. Providing suppliers with detailed specifications, including dimensions, magnetization direction, and performance requirements, is essential. Conducting tests with sample magnets before committing to larger orders can help verify that the chosen magnets will function as intended. Additionally, collaborating with suppliers who offer customization options for stator magnets can provide a tailored solution that aligns perfectly with the buyer’s unique motor designs.
Scenario 3: Managing Cost and Quality Trade-offs in Stator Magnet Sourcing
The Problem: Cost management is a perennial challenge for B2B buyers of stator magnets. While high-performance magnets like neodymium are often preferred for their efficiency, their higher price points can strain budgets, particularly for large-scale production runs. Buyers may feel pressured to compromise on quality to stay within budget, risking the reliability and longevity of their products.
The Solution: To effectively balance cost and quality, buyers should conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis of different magnet materials. Understanding the long-term implications of using lower-cost options versus investing in higher-quality magnets can inform better purchasing decisions. Buyers should also consider working closely with suppliers who can provide insights on material alternatives that offer similar performance at a lower cost. Additionally, establishing a quality assurance process to monitor performance post-purchase can help ensure that the chosen magnets meet operational standards without compromising on cost. Engaging in strategic partnerships with suppliers that allow for volume discounts or flexible payment terms can also alleviate budget constraints while maintaining quality.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for stator magnets
What Are the Key Materials Used for Stator Magnets?
When selecting materials for stator magnets, it is crucial to consider various factors that can impact performance, durability, and cost. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of stator magnets: ferrite, neodymium, samarium-cobalt, and aluminum-nickel-cobalt (AlNiCo). Each material has unique properties and applications, making them suitable for different industrial needs.
How Do Ferrite Magnets Perform in Stator Applications?
Ferrite magnets, made from iron oxide combined with barium or strontium, are widely used in stator applications due to their cost-effectiveness and decent magnetic properties. They typically operate at temperatures up to 250°C, making them suitable for various environments. However, ferrite magnets are less powerful than their neodymium counterparts, which can limit their use in high-performance applications.
Pros: Ferrite magnets are durable, resistant to corrosion, and inexpensive. They are easy to manufacture and can be molded into complex shapes, which is advantageous for diverse applications.
Cons: Their lower magnetic strength can necessitate larger sizes to achieve the desired performance, which may not be ideal for compact designs. Additionally, they are sensitive to high temperatures, which can affect their magnetic properties over time.
Impact on Application: Ferrite magnets are compatible with a wide range of media, making them suitable for general-purpose motors and generators. They are often preferred in cost-sensitive applications, such as household appliances.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or ISO, to guarantee quality and performance. Ferrite magnets are widely accepted globally, making them a safe choice for international procurement.
What Advantages Do Neodymium Magnets Offer for Stator Applications?
Neodymium magnets are known for their exceptional magnetic strength, making them ideal for high-performance applications. They can operate effectively at temperatures up to 80°C, with some high-temperature grades reaching up to 230°C. This makes them suitable for various environments, including industrial and automotive applications.
Pros: The primary advantage of neodymium magnets is their high magnetic energy density, allowing for smaller and lighter designs without sacrificing performance. They are also highly resistant to demagnetization.
Cons: Neodymium magnets are more expensive than ferrite magnets and can be prone to corrosion if not properly coated. Additionally, their high magnetic strength can complicate assembly and handling processes.
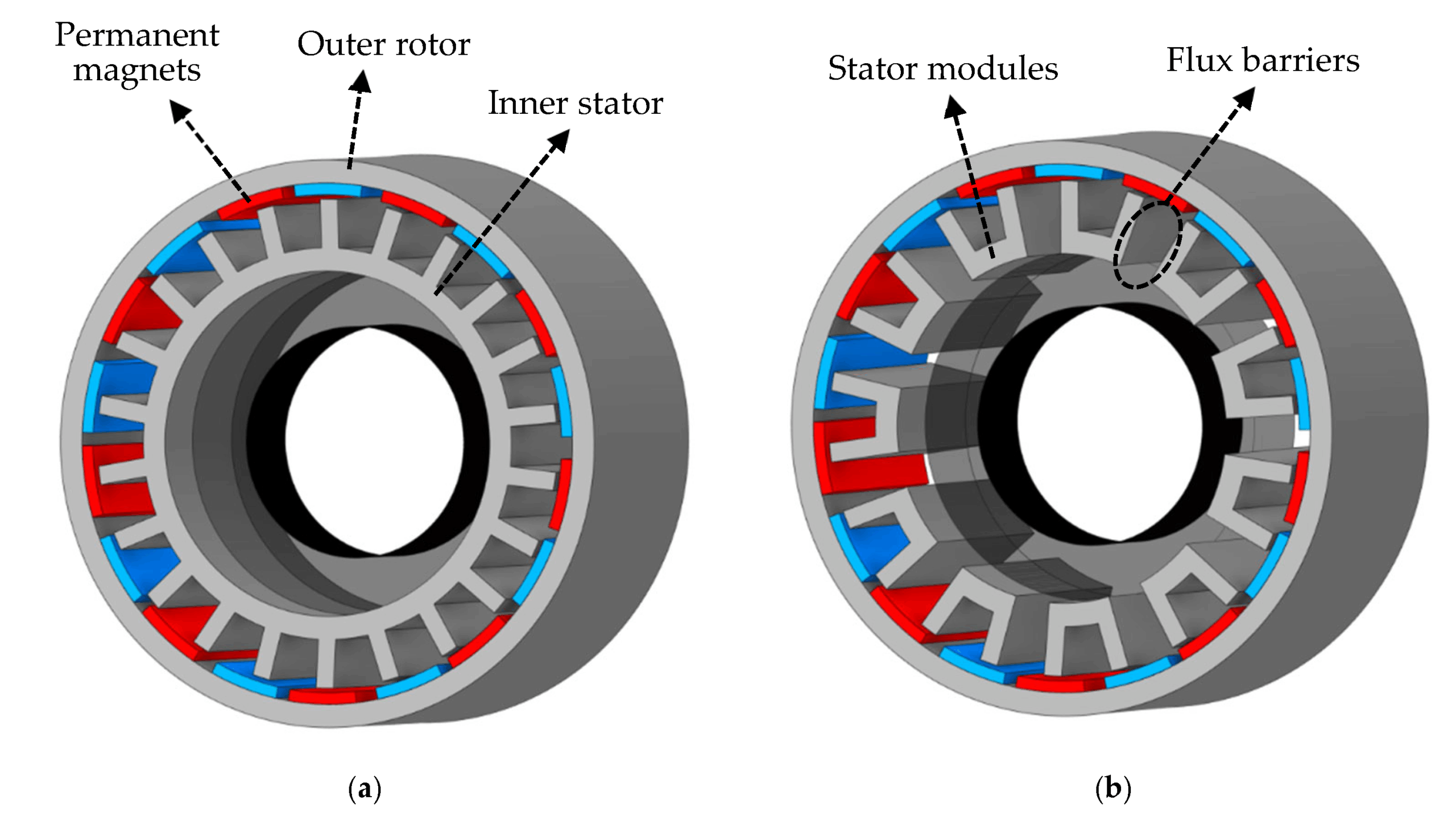
Illustrative image related to stator magnets
Impact on Application: Neodymium magnets are particularly effective in applications requiring compact designs, such as electric vehicles and high-efficiency motors. Their superior performance can lead to energy savings and improved overall efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the need for protective coatings to prevent corrosion, especially in humid environments. Compliance with international standards, such as JIS or DIN, is essential for ensuring product quality.
How Do Samarium-Cobalt Magnets Compare for Stator Use?
Samarium-cobalt (SmCo) magnets are known for their high-temperature stability and resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for demanding applications. They can operate in temperatures up to 300°C, which is advantageous in high-heat environments.
Pros: Samarium-cobalt magnets offer excellent magnetic stability and resistance to demagnetization. They are also less susceptible to corrosion compared to neodymium magnets.
Cons: The primary drawback is their high cost and brittleness, which can complicate manufacturing and handling. They are also less powerful than neodymium magnets, which may limit their use in certain applications.
Impact on Application: These magnets are ideal for aerospace and military applications, where high-temperature performance and reliability are critical. They are often used in precision instruments and high-performance motors.

Illustrative image related to stator magnets
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of SmCo magnets in their region, as they may not be as widely produced as ferrite or neodymium options. Compliance with international standards is also crucial for ensuring performance and reliability.
What Role Do Aluminum-Nickel-Cobalt Magnets Play in Stator Applications?
Aluminum-nickel-cobalt (AlNiCo) magnets are known for their excellent temperature stability and high magnetic strength. They can operate effectively at temperatures up to 550°C, making them suitable for high-temperature applications.
Pros: AlNiCo magnets are highly stable and resistant to demagnetization, making them ideal for precision applications. They also have a high resistance to temperature fluctuations.
Cons: The main disadvantages include their relatively high cost and the complexity involved in manufacturing. They are also less common than other magnet types, which may limit availability.
Impact on Application: AlNiCo magnets are often used in applications requiring high precision, such as sensors and instrumentation. Their stability makes them suitable for environments with fluctuating temperatures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that AlNiCo magnets meet local compliance standards and consider the potential challenges in sourcing these materials due to their specialized nature.
Summary of Material Selection for Stator Magnets
| Material | Typical Use Case for stator magnets | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferrite | General-purpose motors | Cost-effective and durable | Lower magnetic strength | Low |
| Neodymium | Electric vehicles, high-efficiency motors | High magnetic energy density | Higher cost, prone to corrosion | High |
| Samarium-Cobalt | Aerospace, military applications | High-temperature stability | High cost, brittle | High |
| Aluminum-Nickel-Cobalt | Precision instruments, sensors | Excellent temperature stability | Complex manufacturing, high cost | Med |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the strategic material selection for stator magnets, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.

Illustrative image related to stator magnets
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for stator magnets
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Stator Magnets?
The manufacturing of stator magnets is a meticulous process that involves several critical stages, each requiring precision and quality control to ensure optimal performance in electric motors and generators. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Stator Magnet Manufacturing?
The first step in producing stator magnets is the selection and preparation of raw materials. Common materials include:
- Ferrite: Known for its cost-effectiveness and good magnetic properties, ferrite is widely used in low-cost applications.
- Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB): This is a high-performance magnet material that offers superior magnetic strength, making it suitable for advanced applications.
- Samarium Cobalt (SmCo): This material is used for high-temperature applications due to its excellent thermal stability.
Once the materials are selected, they are processed into the required shapes through grinding and milling to achieve the desired magnetic properties.
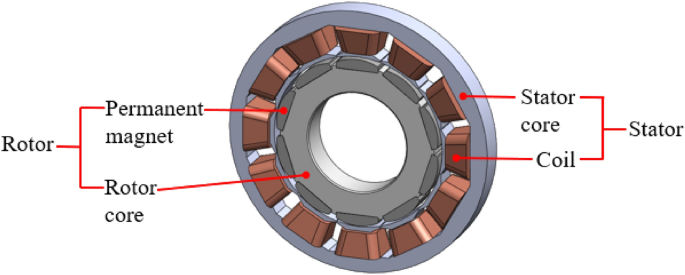
Illustrative image related to stator magnets
2. Forming: How Are Stator Magnets Shaped?
Forming involves several techniques to shape the prepared materials into magnets. Key methods include:
- Sintering: This is a widely used technique where powdered metal is heated to below its melting point, causing the particles to fuse together. Sintered magnets are known for their density and magnetic performance.
- Injection Molding: This technique allows for the production of complex shapes with precise dimensions. It is particularly useful for producing bonded magnets that combine magnetic powders with polymers.
- Casting: In this method, molten metal is poured into molds. It’s less common for stator magnets but can be used for specific applications.
The choice of forming method directly impacts the magnet’s performance, cost, and application suitability.
3. Assembly: How Are Stator Magnets Integrated into Products?
After forming, stator magnets are often assembled into larger components. This may involve:
- Coiling: The magnets are integrated with wire windings to create the stator assembly. The precise arrangement of coils is critical for generating the desired magnetic field.
- Lamination: To reduce energy losses due to eddy currents, laminating the stator core with thin layers of electrical steel is common. This enhances the efficiency of the stator in motor applications.
Effective assembly ensures that the magnets function optimally within the motor or generator, contributing to overall efficiency.
4. Finishing: What Quality Enhancements Are Applied?
Finishing processes enhance the performance and durability of stator magnets. These may include:
- Surface Treatment: Coatings such as nickel, epoxy, or zinc are applied to protect against corrosion and improve adhesion in bonded applications.
- Magnetization: The final magnets are magnetized to achieve the required magnetic strength. This step is crucial, as the orientation of the magnetic field will determine the efficiency of the stator.
Each finishing step is crucial for ensuring that the magnets meet the required specifications for performance and durability.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Stator Magnet Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing process of stator magnets, ensuring that the final products meet international standards and customer requirements.
Relevant International Standards: Which Certifications Should B2B Buyers Look For?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are essential indicators of a manufacturer’s commitment to quality management. Other relevant certifications include:
- CE Certification: Ensures that products meet EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For applications in the petroleum and natural gas industries, adherence to API specifications is crucial.
These certifications demonstrate a supplier’s reliability and adherence to quality benchmarks, which is particularly important for international buyers.
Quality Control Checkpoints: What Are the Key Stages of QC in Manufacturing?
Quality control in stator magnet manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage checks the quality of raw materials before production begins. It ensures that only materials that meet specifications are used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, various tests are conducted to monitor parameters such as temperature, pressure, and dimensions. This helps identify any deviations from quality standards early in the production cycle.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After manufacturing, the finished magnets undergo rigorous testing. This includes magnetic performance testing, dimensional checks, and surface quality evaluations to ensure they meet all specified requirements.
These checkpoints are critical to maintaining high-quality standards throughout the manufacturing process.
Common Testing Methods: How Are Stator Magnets Tested for Quality?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure that stator magnets meet quality requirements:
- Magnetic Testing: This assesses the strength and direction of the magnetic field produced by the magnets.
- Dimensional Inspection: Calipers and gauges are used to verify that the dimensions of the magnets meet specified tolerances.
- Thermal Cycling Tests: These evaluate the magnets’ performance under varying temperature conditions, ensuring they maintain their magnetic properties.
By employing these testing methods, manufacturers can ensure the reliability and performance of their stator magnets.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of the supplier’s manufacturing facilities can provide insights into their quality control practices.
- Request Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for documentation that outlines the quality control processes and results of testing conducted on the magnets.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality assurance processes.
Verifying these aspects can significantly reduce the risk of receiving subpar products and ensure that the magnets meet specific application needs.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the quality nuances is crucial:
- Cultural Differences: Be aware that quality expectations may differ across regions. It is essential to communicate clearly and align expectations with suppliers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have specific regulations regarding product safety and performance. Ensure that suppliers are compliant with local regulations in your target market.
- Logistics and Shipping: Quality can also be affected by transportation and handling. Discuss packaging standards and shipping methods with suppliers to mitigate risks of damage during transit.
By addressing these nuances, international buyers can foster better relationships with suppliers and ensure high-quality product delivery.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance of stator magnets are complex yet essential for ensuring performance in various applications. By understanding these processes and implementing thorough verification methods, B2B buyers can secure reliable and efficient products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘stator magnets’
In the dynamic landscape of B2B sourcing, procuring stator magnets requires a structured approach to ensure quality, performance, and cost-effectiveness. This guide outlines essential steps to help international buyers make informed decisions when sourcing stator magnets for various applications.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly articulating your technical requirements is the first step in the sourcing process. Stator magnets come in various materials, shapes, and sizes, which can significantly impact their performance in applications like electric motors or generators. Consider factors such as magnetic strength, dimensions, and thermal resistance to ensure compatibility with your machinery.
- Material Type: Decide between ferrite, neodymium, or other materials based on your application’s magnetic field requirements.
- Dimensions and Shape: Specify the exact size and shape needed for the stator to fit seamlessly into your design.
Step 2: Research and Shortlist Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers with a solid track record in manufacturing stator magnets. Look for companies that specialize in the type of magnet you need and have experience serving your specific industry.
- Industry Experience: Focus on suppliers with a proven history of delivering to sectors similar to yours.
- Geographical Considerations: Consider suppliers located in regions that can efficiently serve your market, reducing lead times and shipping costs.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. A supplier’s credibility can often be gauged through their existing client relationships and product quality.
- Quality Assurance: Inquire about their quality control processes and any certifications they hold (e.g., ISO 9001).
- Customer Feedback: Seek testimonials or reviews from other businesses that have sourced similar products.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, request samples of the stator magnets. This allows you to assess the quality and performance of their products firsthand before making a larger investment.
- Performance Testing: Evaluate samples under real-world conditions to ensure they meet your specifications.
- Material Analysis: Check for consistency in material quality, as variations can affect performance.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Engage in discussions with your selected suppliers regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. This step is crucial for ensuring that you receive competitive pricing while maintaining the quality you require.
- Volume Discounts: Inquire about bulk purchase discounts, especially if you plan to order large quantities.
- Lead Times: Discuss production and delivery timelines to align with your project schedules.
Step 6: Verify Logistics and Support Services
Assess the logistical capabilities of your suppliers. Efficient logistics are essential to ensure timely delivery and to mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
- Shipping Options: Understand the shipping methods available and the associated costs.
- After-Sales Support: Confirm the level of support available post-purchase, including warranty policies and customer service responsiveness.
Step 7: Finalize Your Order and Establish a Relationship
Once you are satisfied with the terms and conditions, finalize your order. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can lead to better service, pricing, and flexibility in future orders.
- Contractual Agreements: Ensure all agreements are documented to protect both parties’ interests.
- Feedback Loop: Maintain open communication for feedback and improvements in future transactions.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can confidently source high-quality stator magnets that meet their operational needs and enhance their product performance.
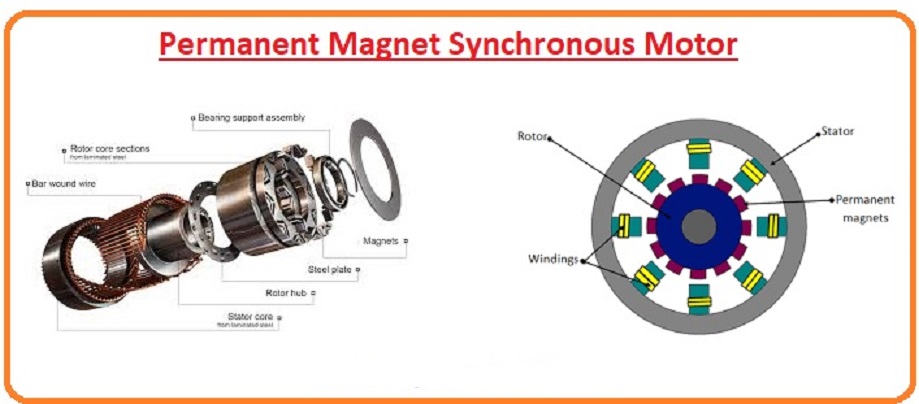
Illustrative image related to stator magnets
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for stator magnets Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Stator Magnets?
When sourcing stator magnets, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the cost. Common materials for stator magnets include ferrite and neodymium. Neodymium magnets, while offering superior performance, are typically more expensive than ferrite options. The global prices of rare earth materials can fluctuate, impacting overall costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and supplier. In countries with lower labor costs, such as some in South America and Africa, manufacturing expenses can be reduced. However, skilled labor is necessary for high-quality production, especially for custom specifications.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to utilities, maintenance, and factory operations. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower overhead costs, which can be passed on to buyers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront cost, particularly for specialized magnet shapes or sizes. Buyers should assess whether the tooling costs can be amortized over large orders to reduce per-unit expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the magnets meet industry standards and specifications requires investment in quality control processes. This is especially important for international buyers who may need to comply with specific certifications.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on distance, shipping methods, and Incoterms. For international buyers, understanding the logistics landscape is essential to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a markup to cover their costs and generate profit. This margin can vary based on competition, market demand, and the supplier’s operational efficiency.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Stator Magnet Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of stator magnets:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders typically lead to lower prices per unit. Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can affect pricing flexibility, so negotiating MOQs can be beneficial for cost savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized magnets often incur higher costs due to the need for specialized tooling and manufacturing processes. Buyers should clearly define specifications to avoid unexpected changes in pricing.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality magnets, especially those with certifications for specific applications (e.g., automotive or aerospace), will command higher prices. Ensuring that suppliers provide the necessary documentation is vital for maintaining compliance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and production capacity of suppliers can influence prices. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their experience and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can significantly impact the total landed cost. Buyers should understand terms like FOB (Free On Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) to optimize logistics costs.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Stator Magnet Prices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are some negotiation tips to ensure cost-efficiency:
-
Research and Compare: Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to establish a baseline for negotiations. Understanding market rates can provide leverage in discussions.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus not just on the initial purchase price but on the TCO, which includes logistics, maintenance, and replacement costs. A lower initial cost may lead to higher long-term expenses.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing, more favorable terms, and improved service. Long-term partnerships can result in more significant savings.
-
Flexibility on Specifications: If feasible, offer flexibility in specifications to allow suppliers to provide cost-effective solutions. This can include minor adjustments to design or materials.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing from local manufacturers can reduce shipping costs and support local economies, potentially leading to lower overall expenses.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost structure and price influencers of stator magnets is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. By leveraging negotiation strategies and focusing on TCO, B2B buyers can optimize their sourcing strategies to achieve the best possible outcomes. While indicative prices can provide a starting point, thorough market research and supplier evaluation are key to successful procurement in the global marketplace.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing stator magnets With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Stator Magnets in Electric Motors
As industries continue to innovate and seek efficient solutions for electric motors and generators, it’s essential to explore alternatives to stator magnets. While stator magnets are crucial for generating magnetic fields in these systems, various other technologies can also achieve similar objectives. This analysis compares stator magnets with two prominent alternatives: electromagnetic coils and reluctance motors, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their unique operational requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Stator Magnets | Electromagnetic Coils | Reluctance Motors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, consistent output | Variable performance based on current | Moderate efficiency, good torque |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost, ongoing energy costs | Moderate cost, low maintenance |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precise manufacturing | Easier to install, flexible design | Complex design, requires expertise |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Requires regular checks | Low maintenance, but complex setup |
| Best Use Case | High-performance applications | General-purpose motors | Cost-sensitive, moderate performance |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Electromagnetic Coils Compared to Stator Magnets?
Electromagnetic coils are a viable alternative to stator magnets. They utilize electric current to produce a magnetic field, allowing for variable output based on the current supplied. One of the primary advantages is their lower initial cost compared to permanent magnets, making them attractive for budget-conscious projects. However, they require continuous energy input, which can lead to higher operational costs over time. Additionally, electromagnetic coils can be easier to implement due to their adaptable designs, but they may necessitate regular maintenance to ensure optimal functionality.
How Do Reluctance Motors Compare with Stator Magnets?
Reluctance motors present another alternative, relying on the principle of magnetic reluctance to generate torque. These motors are typically less expensive and can be a suitable option for applications where cost is a significant consideration. The maintenance requirements are generally low, as they do not use permanent magnets. However, reluctance motors tend to have moderate efficiency and may not perform as well in high-demand situations compared to stator magnets. Their complex design may also require specialized expertise for installation, which could be a drawback for some buyers.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When deciding between stator magnets and their alternatives, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific application requirements, budget constraints, and long-term operational goals. Stator magnets excel in high-performance environments where efficiency and reliability are paramount. In contrast, electromagnetic coils may be more suited for projects with budget limitations but may incur higher energy costs over time. Reluctance motors can be a cost-effective option but might not deliver the same performance as stator magnets in demanding applications. Ultimately, understanding the operational context and aligning it with the right technology will enable buyers to make the most informed decision for their projects.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for stator magnets
What are the Key Technical Properties of Stator Magnets?
Understanding the technical properties of stator magnets is crucial for B2B buyers who aim to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Stator magnets are commonly made from materials such as ferrite, neodymium, and samarium-cobalt. Each material grade has distinct magnetic properties, including coercivity and energy product. For instance, neodymium magnets (often rated N35 to N52) provide higher magnetic strength compared to ferrite magnets. Selecting the appropriate material grade affects the performance, efficiency, and longevity of the electric motor or generator.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation in the dimensions of the magnets. Tight tolerances (e.g., ±0.1 mm) are critical in applications where precision is paramount, such as in high-speed motors. Poor tolerance can lead to misalignment, increased wear, and reduced efficiency. B2B buyers should prioritize manufacturers that can meet specific tolerance requirements for their applications.
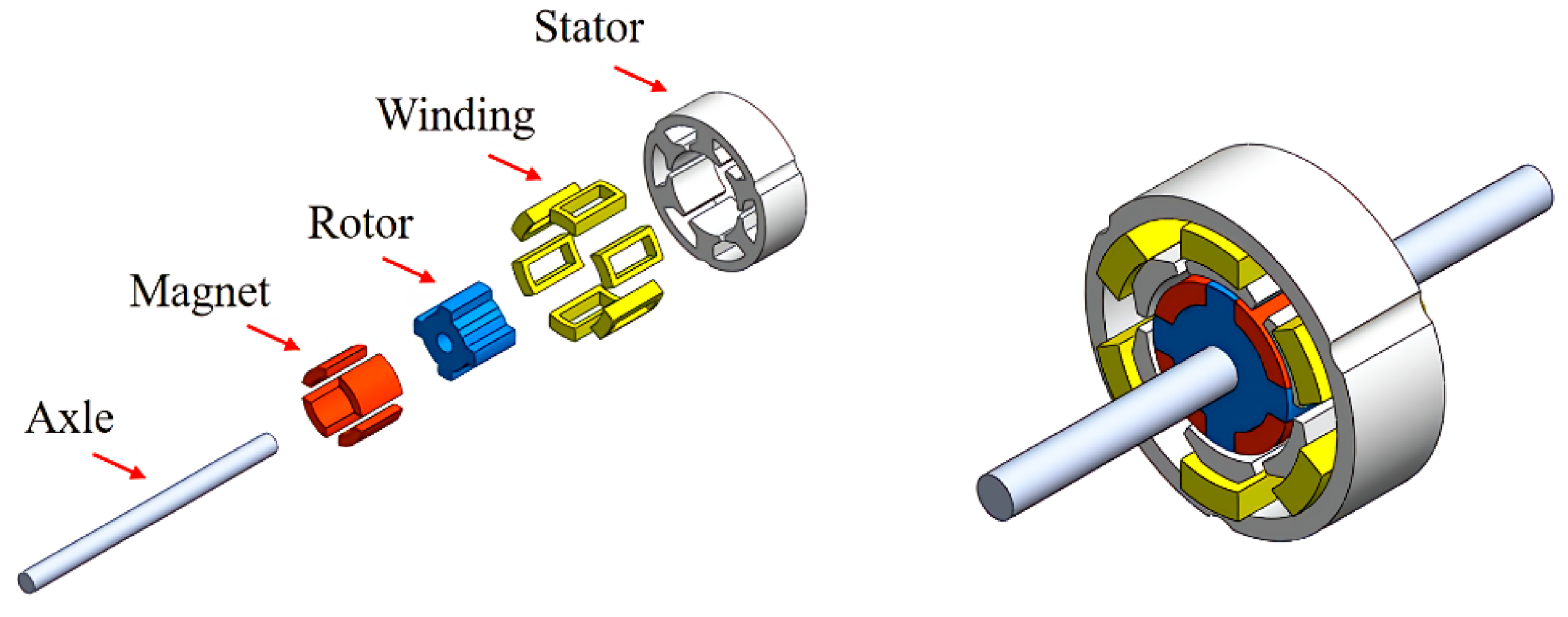
Illustrative image related to stator magnets
3. Magnetic Field Strength
Measured in Gauss or Tesla, magnetic field strength indicates the magnet’s ability to perform work in an electric motor or generator. Higher magnetic field strength correlates with improved efficiency and power output. Buyers need to assess the required magnetic strength based on the intended application to ensure optimal performance.
4. Coercivity
Coercivity is a measure of a magnet’s ability to withstand external magnetic fields without losing its magnetism. This property is crucial in environments exposed to high temperatures or fluctuating magnetic fields. Understanding the coercivity of stator magnets helps in selecting the right type for specialized applications, ensuring reliability and durability.
5. Operating Temperature
Every type of magnet has a maximum operating temperature, beyond which it may demagnetize or degrade. For instance, neodymium magnets typically operate well up to 80-120°C. Selecting magnets with appropriate temperature ratings is essential for applications in high-heat environments, such as motors in industrial machinery or automotive applications.
6. Surface Treatment
Surface treatments, such as nickel plating or epoxy coating, enhance the corrosion resistance and longevity of stator magnets. These treatments are particularly important for applications exposed to moisture or harsh chemicals. B2B buyers should inquire about surface treatment options to ensure the magnets will perform reliably over time.
What are Common Trade Terms in the Stator Magnet Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are several key terms B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are used as components in another company’s product. In the context of stator magnets, OEMs are often responsible for producing customized magnet solutions tailored to specific applications. Understanding OEM relationships can enhance supply chain efficiency.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for buyers to understand initial investment levels and inventory management strategies. Suppliers may have different MOQs based on the type of magnet or material grade.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and availability for specific products. This process is essential for B2B transactions, as it allows buyers to compare offers and negotiate better terms. Including detailed specifications in an RFQ can lead to more accurate and competitive quotes.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms helps mitigate risks associated with cross-border transactions. For example, terms like FOB (Free on Board) clarify when the responsibility for goods transfers from seller to buyer.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the products. Understanding lead times is vital for project planning and inventory management. Buyers should inquire about lead times during negotiations to ensure timely delivery of stator magnets.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that optimize their operations and drive success in their respective markets.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the stator magnets Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Stator Magnets Sector?
The stator magnets sector is experiencing dynamic shifts driven by several global factors. One of the primary drivers is the increasing demand for electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy solutions, particularly in regions like Europe, Africa, and the Middle East. Countries are investing heavily in infrastructure to support EV adoption, which in turn boosts the need for efficient stator magnets in electric motors and generators. Furthermore, advancements in magnetic materials, such as neodymium and ferrite, are enhancing the performance of stator magnets, leading to more compact and efficient motor designs.
Emerging B2B tech trends include the rise of automation and Industry 4.0, which require sophisticated and high-performance stator magnets in robotics and machinery. International buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide customized solutions tailored to specific applications, whether in automotive, industrial, or consumer electronics sectors. Additionally, the trend towards modular designs in machinery is pushing manufacturers to source stator magnets that can easily integrate with various systems, thereby reducing time-to-market.

Illustrative image related to stator magnets
In terms of sourcing dynamics, international buyers, especially from Africa and South America, are increasingly turning to suppliers in Asia and Europe for high-quality, cost-effective stator magnets. The competitive landscape is also shifting, with more companies seeking partnerships that offer not just products but comprehensive support in design and application. This trend highlights the importance of establishing strong relationships with suppliers who can provide ongoing technical assistance and customization capabilities.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influence the Stator Magnets Supply Chain?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal concern in the stator magnets sector, driven by growing awareness of environmental impacts and regulatory pressures. For international B2B buyers, understanding the environmental footprint of stator magnets is essential. The manufacturing processes for magnets, particularly those involving rare earth elements, can have significant ecological implications, including habitat destruction and pollution. Therefore, buyers must prioritize suppliers who adopt sustainable practices and minimize waste throughout the production cycle.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as consumers and businesses increasingly demand transparency in supply chains. Suppliers offering ‘green’ certifications and utilizing recyclable or less harmful materials can enhance their appeal to buyers concerned about their corporate social responsibility (CSR) commitments. For instance, opting for ferrite magnets, which are less environmentally damaging than neodymium magnets, can be a strategic choice for companies looking to mitigate their ecological impact.
Moreover, as buyers from regions like the Middle East and Europe emphasize sustainability, they should consider partnering with manufacturers who invest in renewable energy for their production processes. This alignment not only supports global sustainability goals but also positions companies favorably in a market that increasingly values ethical practices.
How Has the Stator Magnets Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the stator magnets sector reflects broader technological advancements and changing market demands. Initially, stator magnets were predominantly made from ferrite materials, which offered a cost-effective solution but limited performance. With the advent of neodymium magnets in the 1980s, significant improvements in magnetic strength and efficiency were realized, enabling the development of smaller and more powerful electric motors.
The 21st century has seen a surge in the application of stator magnets across various industries, driven by innovations in energy-efficient technologies and the push for electrification in transportation. As electric vehicles and renewable energy systems gain traction, the demand for high-performance stator magnets is set to increase further. Additionally, ongoing research into new materials and manufacturing techniques promises to enhance the capabilities of stator magnets, ensuring they remain at the forefront of technological advancements in the electric motor and generator markets.
In summary, international B2B buyers must navigate a complex landscape influenced by technological innovation, sustainability concerns, and evolving market dynamics to make informed sourcing decisions in the stator magnets sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of stator magnets
-
How do I choose the right stator magnets for my application?
Selecting the appropriate stator magnets involves considering several key factors, including the type of motor (AC or DC), the required magnetic performance (flux density, coercivity), and the operating environment (temperature, humidity). Additionally, evaluate the shape and size specifications that fit your design. Collaborating with suppliers who offer customization can help tailor the magnets to your specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency for your applications. -
What are the main types of stator magnets available in the market?
The most common types of stator magnets include ferrite magnets, neodymium magnets, and samarium-cobalt magnets. Ferrite magnets are cost-effective and suitable for a variety of applications but offer lower magnetic strength. Neodymium magnets provide high performance and efficiency, making them ideal for compact designs. Samarium-cobalt magnets are known for their excellent thermal stability and resistance to corrosion, suitable for high-temperature applications. Understanding the differences can help you select the best option for your project. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for stator magnets?
The MOQ for stator magnets can vary significantly between suppliers, often depending on the type of magnet and the level of customization required. Generally, standard products may have a lower MOQ, while custom designs may require higher minimums. When sourcing from international suppliers, it’s essential to clarify the MOQ to ensure it aligns with your production needs and budget. -
How can I ensure the quality of stator magnets before purchase?
To ensure the quality of stator magnets, request samples from potential suppliers to evaluate their performance in real-world applications. Additionally, inquire about certifications and quality assurance processes, such as ISO standards. Establishing a clear set of quality criteria and conducting audits or inspections can further guarantee that the magnets meet your specifications and industry standards. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing stator magnets internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, and balance payments before shipment. For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. Always clarify terms in advance and establish a contract that outlines payment schedules to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I vet potential suppliers of stator magnets?
When vetting suppliers, assess their reputation through customer reviews, industry certifications, and case studies. Request references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and service quality. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s manufacturing facilities, if possible, to evaluate their production capabilities and quality control measures. Engaging with trade associations and industry networks can also provide insights into reputable suppliers. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing stator magnets?
Logistics considerations include selecting reliable shipping methods, understanding customs regulations, and estimating lead times. Work with logistics partners who have experience in handling magnetic materials, as they may have specific shipping and handling requirements. Also, ensure that your supply chain can accommodate potential delays and that you have contingency plans in place for unforeseen circumstances. -
Can I customize stator magnets for specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for stator magnets, allowing you to tailor the size, shape, and material properties to meet your specific application needs. Customization can enhance performance and efficiency, especially for specialized industries like automotive, aerospace, or renewable energy. When discussing customization with suppliers, provide detailed specifications and requirements to facilitate the design process and achieve optimal results.
Top 5 Stator Magnets Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Courage Magnet – DC Motor Rotor & Stator Magnets
Domain: couragemagnet.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: DC Motor Rotor & Stator Magnets, available in various permanent materials and shapes including arc, rectangle, fan, wedge, and multi-pole ring. Key specifications include: Multipole radial ferrite rotor magnet ring (30mm x 21mm x 25mm), brushless motor skew arc neodymium magnet (custom supplier), curved bread loaf neodymium magnet (custom), injection molded one-piece arc segment ferrite rotor magn…
2. Essen Magnetics – Rotor and Stator Solutions
Domain: essenmagnetics.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Rotor and Stator are essential components of electric machines, such as motors and generators, creating a rotating magnetic field that produces mechanical or electrical energy.
Rotor:
– Rotating part of the machine, located inside the stator, attached to a shaft.
– Key Features:
– Rotation driven by magnetic interaction with the stator.
– Contains windings or permanent magnets for magnetic f…
3. CC Magnetics – Custom Neodymium Motor Magnets
Domain: ccmagnetics.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Custom Neodymium Motor Magnets available in various types including Sintered Arc Segment Magnets, Nickel Plated Magnetized Arc Magnets, Custom Epoxy Coated Arc Segment Magnets, OEM Arc Segment Magnets, ODM Arc Segment Magnets, Custom Bonded Stator Magnets, and Custom North on Outside Face Arc Segment Magnets. Price range: $9.95 – $299.00. Ratings range from 4.67 to 5 out of 5. Suitable for applica…
4. Britannica – Permanent-Magnet Motors
Domain: britannica.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Permanent-magnet motors utilize permanent magnets made of neodymium-boron-iron, samarium-cobalt, or ferrite on the rotor. These magnets can be mounted on the rotor core surface or inset into the rotor core. They are primarily used in variable-speed drives that allow for precise speed and position control, and they are highly efficient due to the absence of power losses in the rotor compared to ind…
5. Arnold Magnetics – Samarium Cobalt & Neodymium Iron Boron Magnets
Domain: arnoldmagnetics.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Permanent Magnets and Assemblies: High-performance permanent magnets for mission-critical applications. Key products include:
1. Samarium Cobalt Magnets: RECOMA® 35E, the most power dense samarium cobalt magnet, suitable for demanding environments.
2. Neodymium Iron Boron Magnets: Highest energy product available, used in various applications like motors and sensors.
3. Alnico Magnets: Economical…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for stator magnets
In summary, the strategic sourcing of stator magnets is pivotal for businesses aiming to enhance the efficiency and performance of their electric machines. By understanding the varying types of stator magnets—such as ferrite, neodymium, and custom configurations—buyers can optimize their procurement processes to meet specific operational needs. Establishing partnerships with reliable suppliers who offer customization, quality assurance, and competitive pricing will ensure that organizations remain at the forefront of technological advancements.
As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, the demand for high-performance electric motors and generators will only grow. Sourcing the right stator magnets is not just about cost; it’s about securing a competitive edge in a rapidly changing market landscape.
Moving forward, international B2B buyers are encouraged to explore strategic sourcing opportunities that align with their business goals. By collaborating with experienced manufacturers and leveraging innovative magnet technologies, companies can drive growth and sustainability in their operations. Let’s seize the potential of stator magnets to power the future of electric machinery.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.