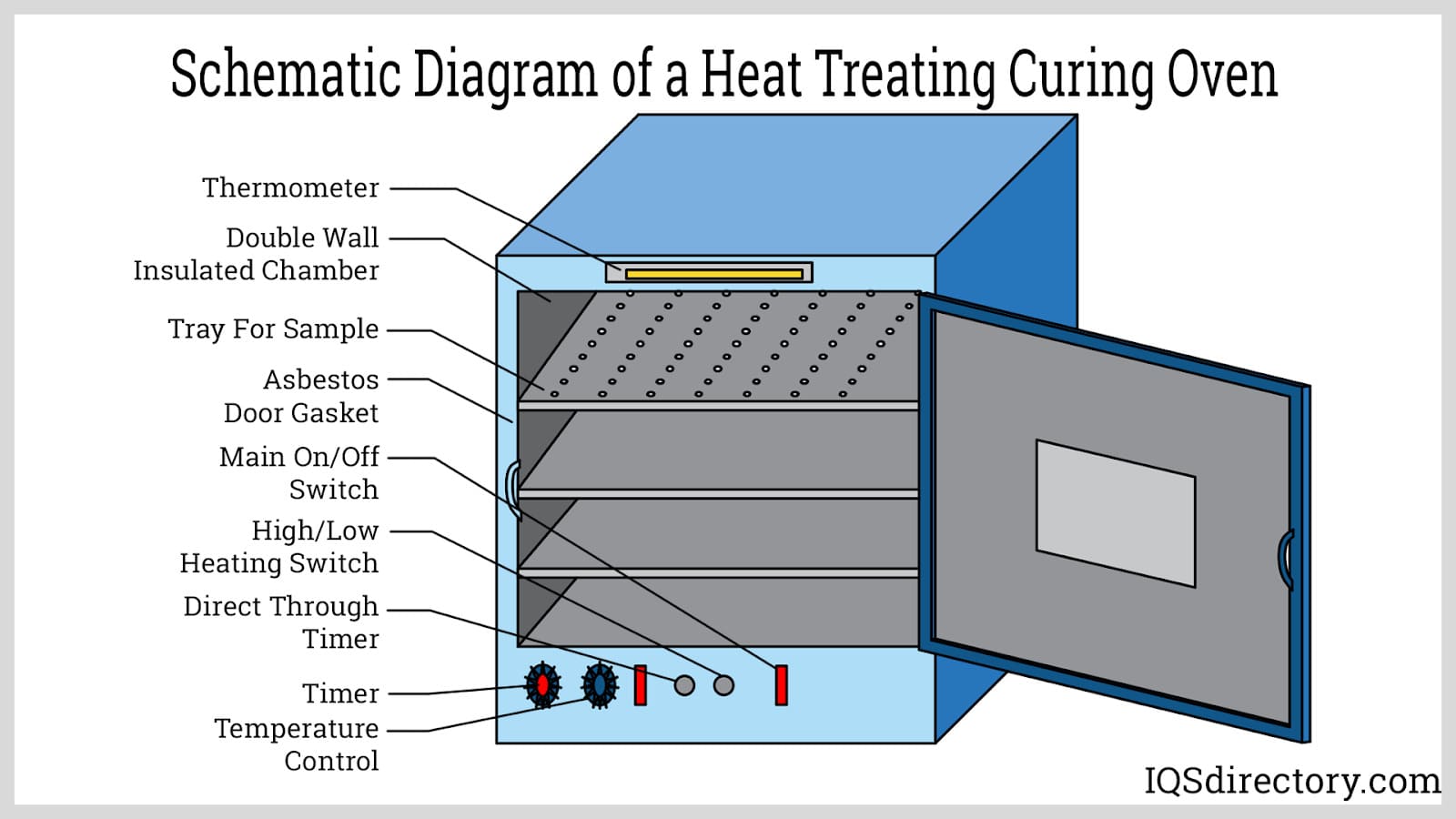
How to Source Diagram Of Oven Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for diagram of oven
In the increasingly competitive landscape of global commerce, international B2B buyers face the critical challenge of sourcing reliable and efficient appliances like the diagram of an oven. Understanding the intricate components and operational mechanics of ovens is essential for making informed procurement decisions that align with specific culinary needs and business objectives. This guide delves into the various types of ovens, their applications across different industries, and the essential parts that comprise these vital kitchen appliances.
We will explore the nuances of sourcing ovens suitable for diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, such as Vietnam and Saudi Arabia. Additionally, we will provide insights into effective supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and best practices for maintenance and replacement parts. By equipping B2B buyers with comprehensive knowledge about oven diagrams and functionalities, this guide empowers businesses to make strategic purchasing decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating the global market for ovens doesn’t have to be daunting; with the right information, you can ensure your investment meets your culinary requirements while adhering to local standards and preferences. This resource is designed to streamline your procurement process, helping you secure the best solutions for your business needs.
Understanding diagram of oven Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Oven | Standard heating elements, either gas or electric; simple design. | Restaurants, bakeries, catering | Pros: Versatile, cost-effective; Cons: Slower cooking times compared to convection. |
| Convection Oven | Includes a fan for even heat distribution; faster cooking times. | Commercial kitchens, food production | Pros: Reduces cooking time, even browning; Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Steam Oven | Uses steam for cooking, retaining moisture and nutrients. | Health-focused establishments, bakeries | Pros: Healthier cooking method, versatile; Cons: Requires regular maintenance. |
| Pizza Oven | High-temperature design for optimal pizza cooking; wood or gas-fired. | Pizzerias, food trucks | Pros: Authentic flavor, quick cooking; Cons: Limited use for other foods. |
| Industrial Oven | Heavy-duty, designed for large-scale operations; customizable options. | Manufacturing, large-scale baking | Pros: High capacity, durable; Cons: Significant investment, requires specialized knowledge. |
What Are the Characteristics of Conventional Ovens?
Conventional ovens are the most common type found in commercial kitchens. They operate using either gas or electric heating elements that provide consistent heat for baking, roasting, and broiling. Their straightforward design makes them easy to operate, which is ideal for establishments that require reliability without advanced features. B2B buyers should consider their space, budget, and cooking needs when selecting a conventional oven, as they are often more cost-effective but may have slower cooking times compared to other types.
How Do Convection Ovens Enhance Cooking Efficiency?
Convection ovens incorporate a fan that circulates hot air, allowing for faster and more even cooking. This technology is particularly beneficial in commercial kitchens where time efficiency is crucial. The ability to cook multiple dishes at once without compromising quality makes convection ovens a preferred choice for restaurants and catering services. Buyers should assess their volume needs and consider the initial investment, as convection ovens typically come at a higher price point but offer significant time savings.
Why Are Steam Ovens Gaining Popularity in B2B Settings?
Steam ovens utilize steam to cook food, preserving moisture and nutrients while enhancing flavor. This method is increasingly favored by health-conscious establishments, such as organic cafes and bakeries, as it allows for healthier cooking options. B2B buyers should evaluate the maintenance requirements and potential for versatility in menu offerings when considering steam ovens, as they may require more care than traditional models.
What Makes Pizza Ovens Unique for Commercial Use?
Pizza ovens are specifically designed to reach high temperatures necessary for optimal pizza cooking, often using wood or gas as fuel. Their unique design allows for quick cooking times and authentic flavors, making them essential for pizzerias and food trucks. However, buyers should be aware that pizza ovens are typically limited in their use for other types of food, which may impact their overall utility in a diverse menu setting.
How Do Industrial Ovens Cater to Large-Scale Operations?
Industrial ovens are built for heavy-duty use, suitable for large-scale food production and manufacturing. They can be customized to meet specific operational needs and are designed to handle high volumes of cooking. While they offer durability and capacity, the initial investment can be significant. B2B buyers must consider the long-term operational costs and the need for specialized knowledge to effectively use and maintain these ovens in their operations.
Key Industrial Applications of diagram of oven
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of diagram of oven | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Industrial baking ovens for large-scale production | Increased efficiency and consistency in baking processes | Energy efficiency ratings, size and capacity, ease of maintenance |
| Automotive | Burn-off ovens for cleaning automotive parts | Effective removal of paint and coatings, ensuring part integrity | Compliance with environmental regulations, temperature control capabilities, safety features |
| Construction & Manufacturing | Curing ovens for composite materials | Enhances durability and performance of materials | Temperature uniformity, material compatibility, energy source options |
| Electronics | Reflow ovens for soldering electronic components | Ensures quality and reliability in circuit assembly | Precision temperature control, cycle time efficiency, compatibility with various PCB sizes |
| Pharmaceutical | Sterilization ovens for medical equipment | Ensures safety and compliance with health regulations | Certification standards, material construction, automation features |
How is the ‘diagram of oven’ utilized in the food processing industry?
In the food processing sector, industrial baking ovens are crucial for large-scale production. The diagram of an oven helps manufacturers understand the layout and functionality of various components, such as heating elements and airflow systems. This knowledge aids in optimizing baking processes, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring consistent product quality. Buyers must consider energy efficiency ratings, the oven’s size and capacity, and ease of maintenance when sourcing equipment, especially in regions with varying energy costs and availability.
What role does the ‘diagram of oven’ play in the automotive industry?
Burn-off ovens are widely used in the automotive industry to clean parts by removing paint and coatings. The diagram of these ovens illustrates essential features like the primary heat input burner and explosion relief doors, which are critical for safe operation. These ovens help maintain the integrity of automotive parts during the cleaning process, making them indispensable in manufacturing. B2B buyers need to ensure compliance with environmental regulations, focus on temperature control capabilities, and prioritize safety features when sourcing these specialized ovens.
How do curing ovens benefit the construction and manufacturing sectors?
Curing ovens are integral in the construction and manufacturing industries for the treatment of composite materials. The diagram outlines how these ovens maintain uniform temperatures necessary for enhancing the durability and performance of materials. By using curing ovens, companies can produce stronger products that meet rigorous industry standards. Buyers should focus on temperature uniformity, material compatibility, and energy source options to ensure that the ovens can efficiently handle diverse manufacturing processes.
In what ways are reflow ovens essential for the electronics industry?
In the electronics sector, reflow ovens are essential for soldering electronic components onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). The diagram of the oven highlights critical components like temperature control systems and conveyor mechanisms, which are vital for achieving high-quality solder joints. Effective use of reflow ovens ensures product reliability and longevity. Buyers must consider precision temperature control, cycle time efficiency, and compatibility with various PCB sizes when selecting reflow ovens, especially in fast-paced manufacturing environments.
Why are sterilization ovens important in the pharmaceutical industry?
Sterilization ovens are crucial for ensuring that medical equipment is free from contaminants. The diagram of these ovens showcases features like temperature monitoring systems and insulation, which are vital for meeting health and safety regulations. These ovens help pharmaceutical companies maintain compliance and guarantee patient safety. Buyers should focus on certification standards, material construction, and automation features when sourcing sterilization ovens, particularly in regions with stringent health regulations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘diagram of oven’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Identifying Oven Component Failures for Efficient Maintenance
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter challenges when trying to identify which components of an oven may be malfunctioning. This issue can be especially prevalent in industrial settings where ovens are used for high-capacity cooking or manufacturing processes. For instance, if a bakery’s oven fails to maintain the right temperature, it can lead to inconsistent product quality, resulting in financial losses and customer dissatisfaction. Understanding the specific part responsible for the failure—be it the bake element, convection fan, or temperature sensor—can be daunting without a clear diagram or proper knowledge.
The Solution: To address this problem, it is crucial for B2B buyers to invest in detailed diagrams of their specific oven models that clearly label each component and its function. Such diagrams should be easily accessible, perhaps included in the user manual or available online from the manufacturer’s website. Additionally, conducting regular maintenance checks using these diagrams can help identify potential issues before they escalate. For instance, if the convection fan is not functioning, this can be diagnosed quickly by referencing the diagram, enabling swift repairs. Establishing a relationship with reliable suppliers for replacement parts is also advisable, as it ensures that buyers can procure authentic components that meet their oven specifications.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Understanding Oven Wiring Diagrams
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is grappling with complex wiring diagrams when troubleshooting electrical issues in ovens. For example, a restaurant that operates multiple ovens may face downtime if one of them malfunctions due to a wiring issue, causing delays in food preparation. The intricacies of the wiring can lead to confusion, particularly if the diagrams are not clearly labeled or if the buyer is not familiar with electrical components. This can result in improper repairs, further complications, or even safety hazards.
The Solution: To effectively navigate this challenge, B2B buyers should prioritize obtaining high-quality wiring diagrams from the manufacturer. These diagrams must be detailed and easy to interpret, providing clear visual guidance on connections and component locations. Buyers can also benefit from investing in training sessions for their maintenance teams, focusing on electrical troubleshooting and diagram interpretation. This proactive approach not only enhances the team’s capability to diagnose and fix issues quickly but also minimizes the risk of improper repairs. Furthermore, documenting common wiring issues and solutions can create a valuable reference guide for future troubleshooting.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compliance with Safety Standards in Oven Design
The Problem: Compliance with safety standards is a significant concern for B2B buyers, especially in industries such as food processing or manufacturing, where ovens are essential. Buyers may struggle with ensuring that their ovens meet local and international safety regulations, particularly when sourcing equipment from various suppliers. This lack of compliance can lead to legal repercussions, increased liability, and damage to the company’s reputation.
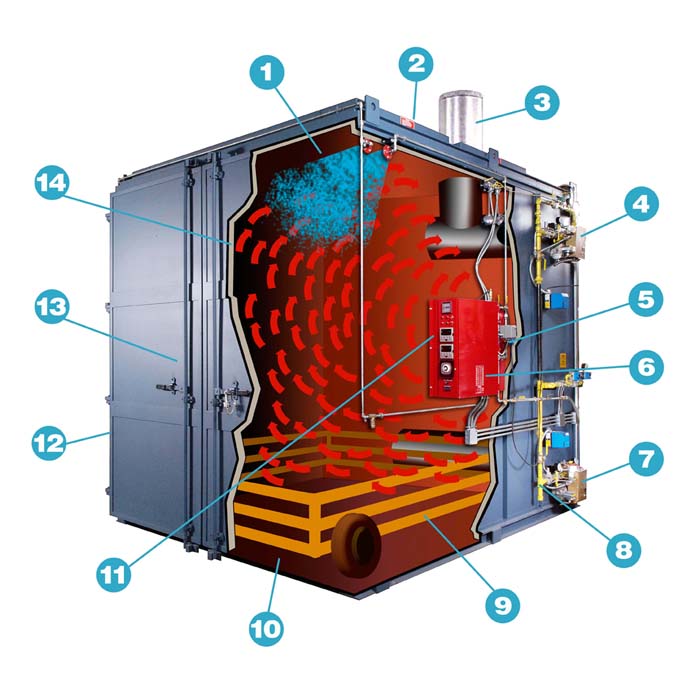
Illustrative image related to diagram of oven
The Solution: B2B buyers must conduct thorough research into the safety standards applicable to their specific industry and region. A comprehensive oven diagram should include safety features, such as explosion relief doors, proper insulation, and diagnostic panels that adhere to these regulations. Engaging with manufacturers that provide compliance documentation along with their diagrams can ensure that buyers are fully informed about safety features. Additionally, forming partnerships with industry experts or consultants can help buyers navigate compliance more effectively. Regular audits and updates of their equipment against evolving safety standards will further safeguard against potential risks, ensuring both employee safety and operational integrity.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for diagram of oven
What Are the Key Materials Used in Oven Manufacturing?
When selecting materials for the construction of ovens, several factors come into play, including thermal performance, durability, and manufacturing complexity. Understanding these materials is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Below, we explore four common materials used in oven manufacturing, examining their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international procurement.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Oven Applications?
Stainless steel is a widely used material in oven construction due to its excellent corrosion resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures. Key properties include a temperature rating of up to 1,200°F (650°C) and a strong resistance to rust and staining.
Pros: Stainless steel is durable, easy to clean, and aesthetically pleasing, making it a preferred choice for both commercial and residential ovens. Its strength allows for the construction of robust oven components, such as doors and racks.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, as stainless steel tends to be more expensive than other materials. Additionally, manufacturing processes can be complex, requiring specialized equipment for cutting and welding.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with various cooking media and is ideal for high-temperature applications. It is also compliant with international standards such as ASTM and DIN, making it suitable for global markets.
What Role Does Cast Iron Play in Oven Design?
Cast iron is another material often employed in oven manufacturing, particularly for stove tops and baking surfaces. It has a high thermal mass, allowing it to retain heat effectively.
Pros: The primary advantage of cast iron is its durability and ability to distribute heat evenly, which is essential for consistent cooking results. It is also relatively inexpensive compared to stainless steel.
Cons: However, cast iron is heavy and can be prone to rust if not properly maintained. It also requires a longer heating time compared to lighter materials.
Impact on Application: Cast iron can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for broiling and baking. Buyers should ensure compliance with local safety standards, especially in regions with stringent regulations.
Why Is Aluminum Used in Oven Manufacturing?
Aluminum is often used for oven components due to its lightweight nature and excellent thermal conductivity. It typically has a temperature rating of around 1,000°F (538°C).
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it easy to handle and install. Additionally, its thermal conductivity allows for rapid heating and cooling, which can improve cooking efficiency.
Cons: On the downside, aluminum is less durable than stainless steel and can warp under extreme temperatures. It is also more susceptible to corrosion unless treated with anodizing or other coatings.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various cooking methods makes it versatile, but buyers should consider the specific treatment required to enhance its durability. Compliance with standards like JIS may also be necessary in certain markets.
How Does Ceramic Coating Enhance Oven Performance?
Ceramic coatings are often applied to oven interiors and certain components to enhance thermal performance and ease of cleaning. These coatings can withstand temperatures up to 1,200°F (650°C).
Pros: The primary advantage of ceramic coatings is their non-stick properties, which facilitate easy cleaning and maintenance. They also provide a smooth surface that can improve heat distribution.
Cons: However, ceramic coatings can be prone to chipping and may require careful handling during manufacturing and installation. They can also be more expensive than traditional finishes.
Impact on Application: Ceramic coatings are ideal for high-heat applications and can improve energy efficiency. Buyers should ensure that the coatings meet local safety and health regulations, particularly in regions with strict environmental standards.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Oven Manufacturing
| Material | Typical Use Case for diagram of oven | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Oven exteriors, racks | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Cast Iron | Stove tops, baking surfaces | Durable and retains heat effectively | Heavy and prone to rust | Medium |
| Aluminum | Oven components, heat exchangers | Lightweight and good thermal conductivity | Less durable and may warp | Low |
| Ceramic Coating | Oven interiors, heating elements | Non-stick and easy to clean | Prone to chipping and higher cost | Medium |
This material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers looking to source ovens or components, enabling them to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for diagram of oven
What Are the Main Stages of Oven Manufacturing?
The manufacturing of ovens involves several key stages that ensure the final product meets both functionality and safety standards. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: The first step involves sourcing high-quality materials, such as stainless steel, aluminum, and various insulating materials. Suppliers must provide certifications to ensure that these materials meet international standards for durability and safety. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing local materials can also reduce costs and improve supply chain logistics.
-
Forming: This stage includes processes like stamping, bending, and cutting metal sheets to create various oven components, including the body, doors, and racks. Advanced techniques such as laser cutting and CNC machining are often employed to achieve precise dimensions. This precision is crucial for ensuring that components fit together seamlessly, which is essential for both aesthetic appeal and operational efficiency.
-
Assembly: During assembly, the various parts are brought together. Automated assembly lines may be used to enhance efficiency, but skilled labor is still essential for critical tasks such as wiring and installing components like heating elements and control panels. The assembly process also includes the installation of safety features, such as explosion relief doors and insulation, which are vital for user safety.
-
Finishing: The finishing stage involves applying coatings, such as enamel or powder finishes, to enhance the oven’s appearance and protect against corrosion. Quality control checks are conducted throughout this stage to ensure that the finishes meet the required standards for durability and aesthetic appeal.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into Oven Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of oven manufacturing, ensuring that each product meets stringent safety and performance standards. Various international standards, such as ISO 9001, provide frameworks for effective quality management systems.
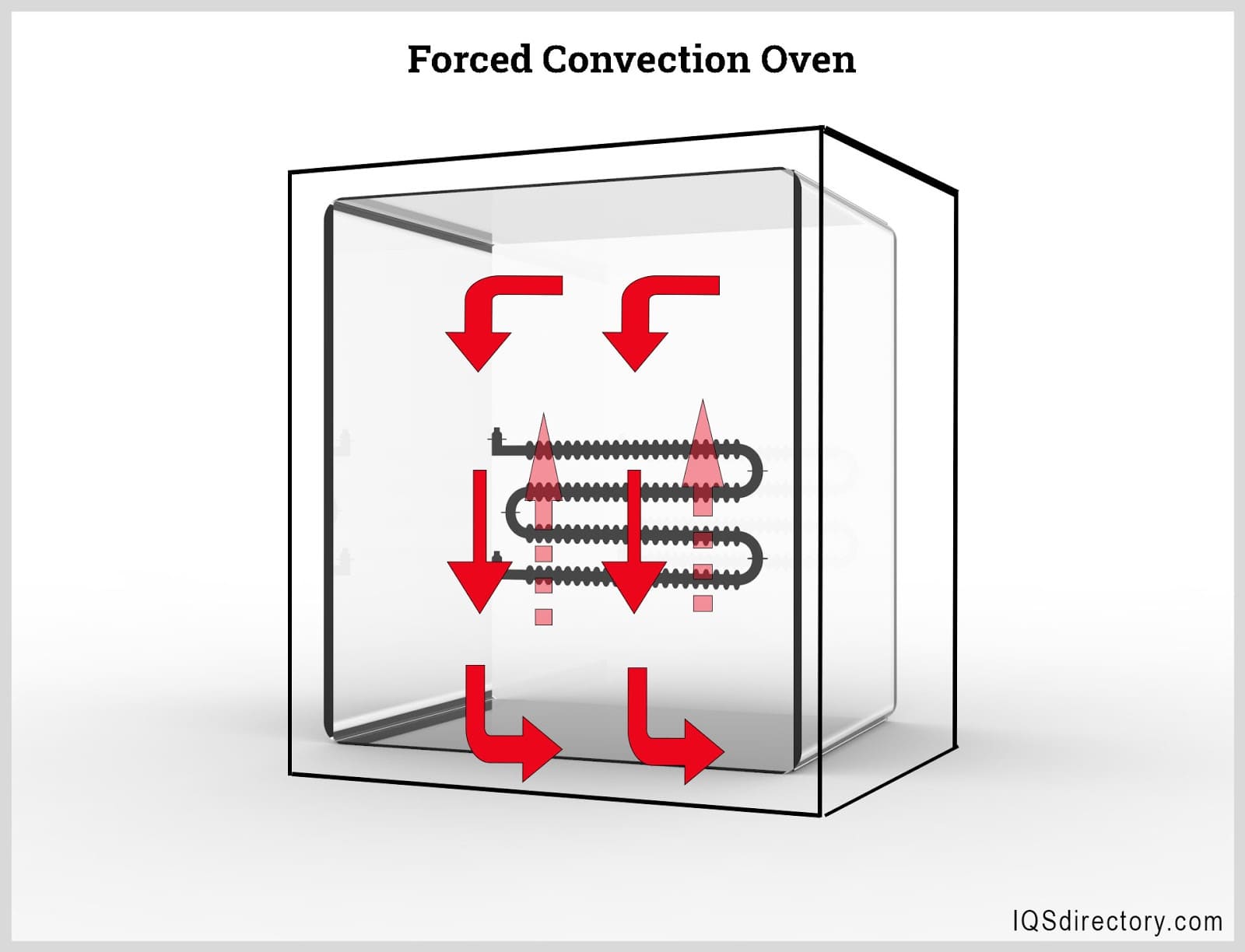
Illustrative image related to diagram of oven
-
International Standards: Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers have implemented quality management systems that focus on customer satisfaction and continuous improvement. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for European markets, indicate that the product meets essential health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: Quality control occurs at multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to verify compliance with specifications.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, regular checks are conducted to ensure that components are being produced to the correct specifications.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products leave the factory, they undergo a final inspection to confirm that they meet all necessary standards and function as intended.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Oven Manufacturing?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the performance and safety of ovens. These may include:
-
Thermal Performance Testing: This involves evaluating the oven’s ability to reach and maintain specified temperatures, crucial for ensuring cooking efficiency and safety.
-
Safety Testing: Ovens are subjected to rigorous safety tests to check for hazards such as overheating, electrical failures, and gas leaks. This is particularly important for gas ovens, where the risk of combustion must be meticulously managed.
-
Durability Testing: Ovens are tested for wear and tear through simulated long-term usage scenarios. This may include repeated heating and cooling cycles to assess the integrity of materials and components.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is crucial for ensuring product reliability. Here are some strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This can help identify potential risks and ensure compliance with international standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports and certificates of compliance can help buyers assess the manufacturer’s adherence to quality standards. These documents should include results from testing and inspections conducted at various stages of production.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturer’s quality control processes. This is particularly valuable for buyers unfamiliar with local suppliers, as it adds an additional layer of scrutiny.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Certification for International Buyers?
Navigating the complexities of quality certification can be challenging for international B2B buyers. Different regions may have varying requirements, and understanding these nuances is essential for successful procurement.
-
Regional Certifications: For example, while CE marking is crucial for products sold in Europe, other markets may require different certifications such as UL for the United States or SANS for South Africa. It is vital for buyers to understand these requirements to ensure compliance.
-
Cultural Differences: Buyers should also be aware of cultural differences that may affect quality perceptions. In some regions, personal relationships may play a significant role in business dealings, influencing trust and reliability.
-
Language Barriers: Communication can be a hurdle; therefore, it’s advisable for buyers to engage local experts or translators who understand both the technical and cultural aspects of the manufacturing process.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance mechanisms involved in oven production is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on these areas, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and standards.
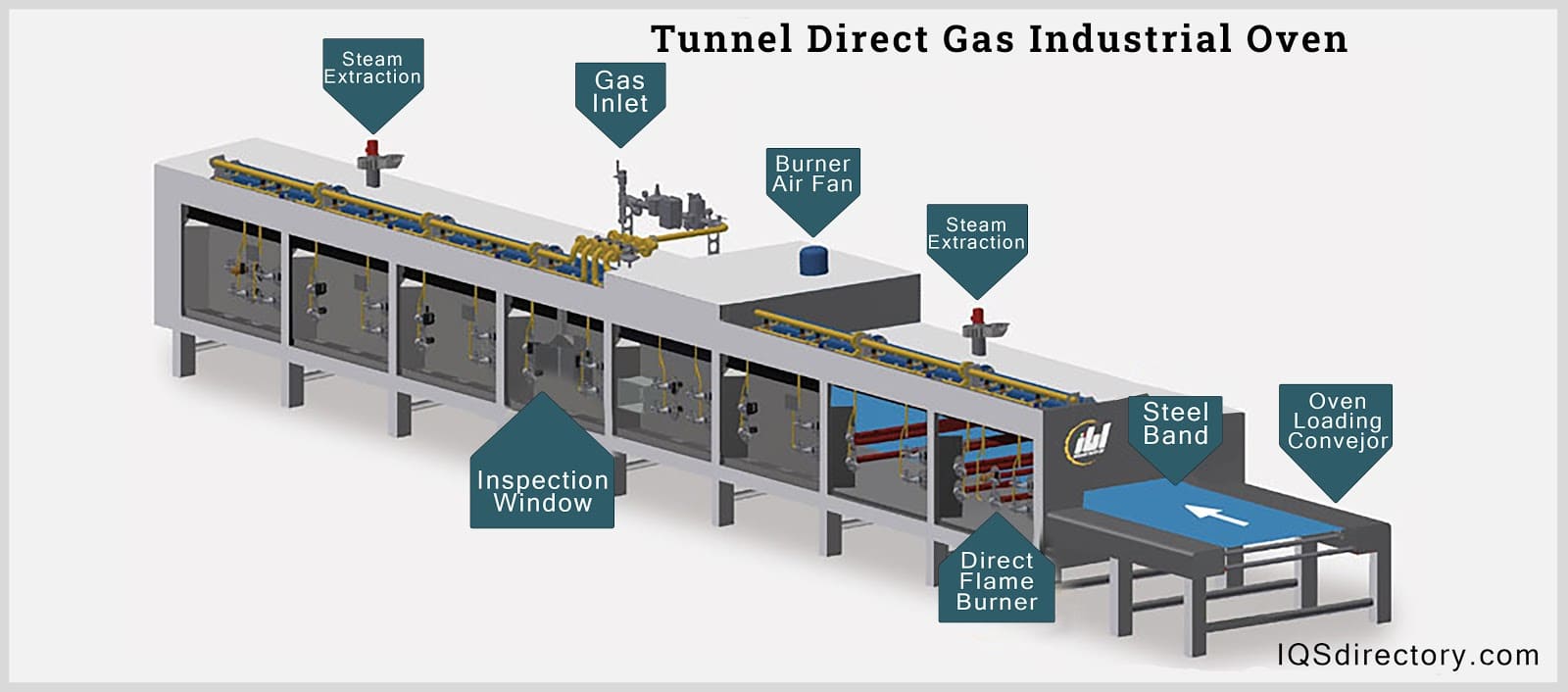
Illustrative image related to diagram of oven
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘diagram of oven’
When it comes to sourcing a diagram of an oven, understanding the intricate details of the components and functionality is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide provides a practical checklist to streamline your sourcing process, ensuring that you select the right diagrams that meet your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining the technical requirements of the oven diagram you need. Consider factors such as the type of oven (gas, electric, or specialized models) and the specific components you want to include, like heating elements, racks, and control systems. Defining these specifications upfront ensures that your sourcing aligns with your operational requirements and helps avoid unnecessary revisions later.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in oven diagrams. Look for companies with a strong reputation in the industry, as well as those that offer detailed diagrams that include all necessary components. Utilize platforms like industry directories, trade shows, and professional networks to gather a list of potential suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Credentials
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to assess their credentials. Request documentation such as certifications, quality control processes, and compliance with international standards. This step is vital to ensure that you are working with a reputable supplier who adheres to the necessary safety and quality regulations, particularly in diverse markets like Africa, South America, and the Middle East.
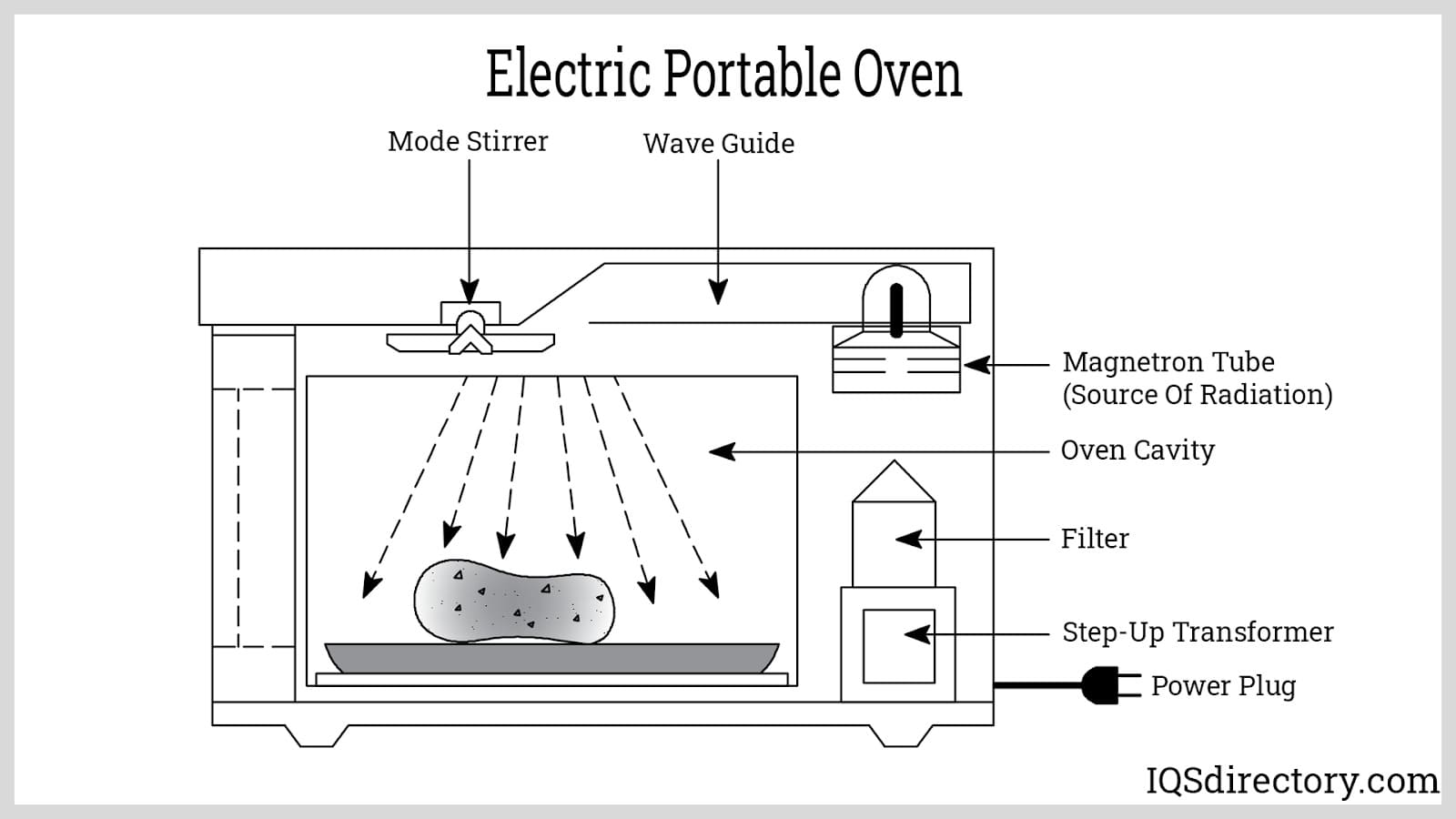
Illustrative image related to diagram of oven
Step 4: Review Sample Diagrams
Ask potential suppliers for sample diagrams to evaluate the quality and detail of their offerings. This review should focus on the clarity of the diagrams and the accuracy of the component representations. High-quality diagrams should not only be visually appealing but also technically precise, as they will serve as essential references for your projects.
Step 5: Inquire About Customization Options
Discuss customization capabilities with your suppliers. Depending on your specific needs, you may require modifications to standard diagrams or completely bespoke designs. Suppliers that offer flexibility in customization can better accommodate unique requirements, enhancing the overall utility of the diagrams for your applications.
Step 6: Assess Support and After-Sales Services
Evaluate the level of customer support and after-sales services provided by your suppliers. Reliable support can be crucial for troubleshooting and ensuring that you fully understand how to utilize the diagrams effectively. Look for suppliers who offer comprehensive documentation, technical support, and training resources.
Step 7: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Once you have narrowed down your options, request quotes from your shortlisted suppliers. Make sure to compare not only the pricing but also the value offered, including quality, customization, and support services. This step ensures that you make a cost-effective decision while also securing high-quality diagrams that meet your specifications.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for oven diagrams, ensuring that they select the most suitable options for their business needs while minimizing potential risks associated with procurement.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for diagram of oven Sourcing
When sourcing a diagram of an oven, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers. This section will delve into the key components of cost, factors influencing pricing, and practical tips for negotiating and optimizing procurement strategies.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Oven Manufacturing?
The primary cost components in the manufacturing of an oven diagram include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. High-quality metals, insulation materials, and electronic components contribute to the overall expense. Buyers should consider sourcing from suppliers who offer a balance between quality and cost-effectiveness.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region, with skilled labor often being more expensive in developed countries. In contrast, labor costs may be lower in emerging markets, which can affect the pricing of the final product.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient production processes can help lower these costs, which may be passed on to the buyer.
-
Tooling: The investment in tooling is crucial for producing high-quality oven components. Custom tooling for specialized designs can increase initial costs but may lead to better product fit and performance.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the reliability and safety of oven components requires robust QC processes. The costs associated with testing and certification can vary, and buyers should inquire about the quality assurance measures in place.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling fees can vary widely based on the distance and mode of transport. International buyers must consider additional costs related to customs clearance and tariffs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their risks and ensure sustainability. Understanding the market rates for similar products can aid in evaluating the fairness of quoted prices.
What Factors Influence Pricing for Oven Diagrams?
Several factors can influence the pricing of an oven diagram:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to lower unit costs due to economies of scale. Negotiating favorable terms based on anticipated order volumes can yield significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or unique specifications can increase costs. It’s essential to clarify requirements upfront to avoid unexpected price hikes later in the process.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., CE, ISO) can justify higher prices. Buyers should assess the value of certifications in relation to their market needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while new entrants might offer competitive rates to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) agreed upon can clarify who bears shipping costs, insurance, and risk during transport. This knowledge is critical for calculating the total landed cost.
How Can Buyers Negotiate and Optimize Costs Effectively?
-
Conduct Thorough Market Research: Understanding industry standards and competitor pricing can provide leverage during negotiations. It’s beneficial to gather quotes from multiple suppliers.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Rather than only considering the initial purchase price, evaluate the long-term costs associated with maintenance, energy efficiency, and durability. A higher upfront investment in quality may lead to lower operational costs over time.
-
Build Strong Relationships with Suppliers: Cultivating partnerships can lead to better pricing, terms, and support. Suppliers may offer discounts or incentives for repeat business or bulk orders.
-
Be Transparent About Needs: Clearly communicating specifications, timelines, and budget constraints can help suppliers provide more accurate quotes and potentially reduce costs.
-
Stay Informed About Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of fluctuations in material costs, currency exchange rates, and geopolitical factors that may influence pricing.
In conclusion, navigating the complexities of sourcing a diagram of an oven requires a thorough understanding of cost components and pricing influences. By employing strategic negotiation techniques and focusing on total cost considerations, B2B buyers can optimize their procurement processes and achieve better value.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing diagram of oven With Other Solutions
In the competitive landscape of commercial cooking solutions, understanding the various alternatives to a diagram of an oven is crucial for B2B buyers. This section compares the traditional oven diagram against two alternative cooking technologies: the convection oven and the microwave oven. Each of these solutions offers unique features that may better suit specific business needs.
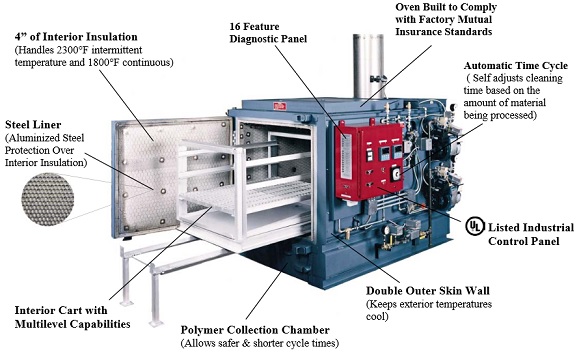
Illustrative image related to diagram of oven
| Comparison Aspect | Diagram Of Oven | Convection Oven | Microwave Oven |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable for baking and roasting; heat distribution can vary. | Even cooking and browning due to circulating hot air. | Rapid cooking with minimal browning; ideal for reheating. |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; maintenance costs can add up. | Generally higher upfront cost; energy-efficient in long run. | Lower initial cost; minimal maintenance. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires space and proper ventilation; installation may be complex. | Requires proper ventilation; may need additional space for air circulation. | Simple installation; minimal space requirements. |
| Maintenance | Regular cleaning and part replacements needed. | Less frequent maintenance; fan and heating element checks required. | Minimal maintenance; usually self-cleaning. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for baking, roasting, and slow cooking. | Best for baking, roasting, and cooking multiple dishes simultaneously. | Perfect for quick reheating and defrosting. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Convection Ovens?
Convection ovens utilize a fan to circulate hot air, ensuring even cooking and browning. This technology is advantageous for B2B buyers who prioritize efficiency and consistent results. The ability to cook multiple dishes at once can significantly increase productivity in a commercial kitchen. However, convection ovens typically come with a higher initial cost and require more space for installation compared to traditional ovens.
How Do Microwave Ovens Compare to a Diagram of Oven?
Microwave ovens excel in speed and convenience, making them ideal for reheating and defrosting food quickly. Their lower upfront costs and minimal maintenance requirements are attractive for businesses looking to save on initial investments. However, microwaves lack the browning and crisping capabilities of traditional ovens, which may limit their use in certain culinary applications. As such, they are best used as a supplementary cooking method rather than a complete replacement.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Cooking Solution?
When selecting the right cooking solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and space availability. If the primary focus is on baking and roasting, a traditional oven diagram or convection oven may be more suitable. For businesses prioritizing speed and efficiency in reheating, a microwave oven could be the optimal choice. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and limitations of each option will empower buyers to make informed decisions that enhance their culinary capabilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for diagram of oven
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Oven Diagrams?
When considering the specifications of an oven, various technical properties can impact performance, efficiency, and usability. Understanding these properties is essential for B2B buyers looking to invest in quality ovens for industrial or commercial use.
1. Material Grade
The material grade of an oven’s components, such as the body and heating elements, determines durability and heat resistance. Common materials include stainless steel for the outer casing, which provides corrosion resistance, and high-grade alloys for heating elements that can withstand high temperatures. Choosing the right material is crucial, as it affects the oven’s lifespan and maintenance needs.
2. Temperature Tolerance
Temperature tolerance refers to the maximum and minimum temperatures an oven can safely achieve and maintain. This specification is vital for applications requiring precise cooking conditions, such as baking or roasting. Ovens designed for high-temperature processes must be engineered to prevent overheating, which can lead to safety hazards or equipment failure.
3. Energy Efficiency Rating
Energy efficiency ratings indicate how effectively an oven converts energy into heat for cooking. Higher ratings suggest lower operational costs and reduced environmental impact. B2B buyers should prioritize energy-efficient models to minimize long-term expenses and comply with sustainability standards.
4. Capacity Measurement
The capacity of an oven, often measured in cubic feet or liters, indicates how much food it can accommodate. This property is particularly important for businesses with high-volume cooking needs. Selecting an oven with the appropriate capacity ensures optimal workflow and efficiency in food preparation.
5. Control Systems
Modern ovens come equipped with advanced control systems, including digital thermostats and programmable settings. These features allow precise temperature control and cooking times, enhancing usability. For B2B buyers, investing in ovens with sophisticated control systems can lead to improved consistency in cooking results and reduce the potential for human error.
6. Safety Features
Safety features such as automatic shut-off systems, cool-touch doors, and pressure relief mechanisms are crucial in industrial ovens. These elements not only protect operators but also minimize the risk of fire hazards. Understanding the safety specifications can help businesses comply with regulatory standards and ensure a safe working environment.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Oven Diagrams?
Navigating the procurement process for ovens involves familiarizing oneself with industry jargon. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of ovens, sourcing from reputable OEMs ensures that parts meet quality standards and are compatible with existing equipment.
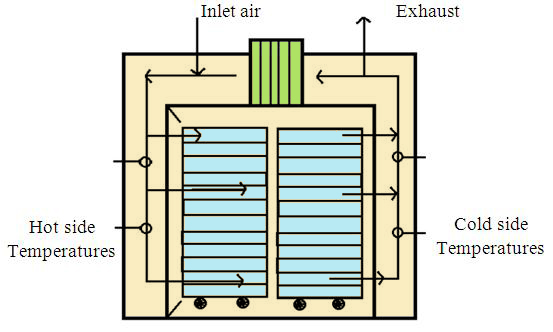
Illustrative image related to diagram of oven
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory effectively and avoid overstocking or stockouts.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. B2B buyers use RFQs to compare offers from multiple vendors, ensuring competitive pricing and favorable terms.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms used in international trade to clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, insurance, and liability during transportation.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the product. Understanding lead times is critical for effective supply chain management, allowing businesses to plan production schedules accordingly.
6. Warranty Terms
Warranty terms outline the coverage provided by manufacturers for defects or failures within a specified period. Knowing the warranty terms is crucial for B2B buyers as it impacts long-term operational costs and risk management.
In summary, understanding both the technical properties and trade terminology associated with oven diagrams is essential for informed decision-making in B2B procurement. This knowledge not only aids in selecting the right equipment but also enhances negotiation and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the diagram of oven Sector
What Are the Current Trends Influencing the Global Oven Market?
The global oven market is witnessing significant transformations driven by technological advancements, consumer preferences, and economic factors. Notably, the rise of smart ovens equipped with IoT capabilities is revolutionizing cooking experiences, enabling remote operation and precise temperature control. International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking suppliers who offer these innovations. Additionally, the demand for energy-efficient appliances is surging, prompted by rising energy costs and environmental concerns. This trend is particularly pertinent in regions with strict energy regulations, compelling manufacturers to adopt more efficient designs and materials.
Furthermore, an increased focus on multifunctional appliances is reshaping buyer preferences. Ovens that combine baking, roasting, and broiling functionalities, along with features like self-cleaning and steam cooking, are becoming more popular. This trend reflects a broader consumer desire for convenience and versatility in kitchen appliances, pushing B2B buyers to source products that meet these evolving needs. Emerging markets, especially in Africa and South America, are also witnessing a rise in middle-class consumers with disposable income, further driving demand for high-quality and technologically advanced ovens.
How Does Sustainability Shape Sourcing Decisions in the Oven Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are increasingly pivotal in the decision-making processes of B2B buyers in the oven market. As environmental regulations tighten and consumers demand greener products, manufacturers are compelled to adopt sustainable practices. This includes utilizing eco-friendly materials, reducing emissions during production, and ensuring that products are energy-efficient throughout their lifecycle. B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate commitment to sustainability, which can significantly influence their purchasing decisions.
Moreover, certifications such as Energy Star, EcoLabel, and ISO 14001 are becoming crucial benchmarks for assessing the environmental impact of oven products. Buyers are looking for suppliers who not only comply with these certifications but also actively pursue innovative methods to minimize their carbon footprint. The integration of recyclable materials in oven manufacturing and the development of energy-efficient models are essential components of this sustainable approach. As the global community increasingly values environmental stewardship, B2B buyers must be proactive in sourcing from manufacturers who align with these ethical standards, ensuring they contribute positively to the environment while meeting market demands.
How Has the Oven Market Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the oven market reflects broader technological advancements and changing consumer needs. Historically, ovens were simple heating devices primarily used for baking and roasting. However, the introduction of gas and electric ovens in the 20th century marked a significant shift, providing greater control over cooking temperatures and times. The latter part of the century saw the emergence of convection ovens, which utilized fans to circulate heat, improving cooking efficiency and quality.
In recent years, the integration of smart technology has further transformed the oven landscape. Modern ovens now come equipped with touch controls, Wi-Fi connectivity, and programmable settings, allowing users to monitor and control cooking remotely. This evolution is not just a technological upgrade; it reflects a shift in consumer behavior towards convenience and efficiency in cooking. As international B2B buyers navigate this dynamic market, understanding these historical shifts can provide valuable insights into current trends and future innovations, ensuring they make informed sourcing decisions that align with their business objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of diagram of oven
-
How do I troubleshoot common issues with oven diagrams?
To troubleshoot common issues with oven diagrams, first identify the specific problem, such as incorrect wiring or malfunctioning components. Consult the diagram to understand the connection of each part, like the heating elements, thermostat, or fan. Testing each component with a multimeter can help isolate the fault. If the problem persists, consider reaching out to the manufacturer or a qualified technician for expert assistance. Maintaining a detailed record of your troubleshooting steps can also be beneficial for future reference. -
What is the best type of oven diagram for commercial applications?
The best type of oven diagram for commercial applications typically includes detailed schematics that illustrate the layout and function of all components, such as heating elements, control panels, and ventilation systems. Look for diagrams that are specific to the type of oven you are using—whether it’s convection, electric, or gas—as this will ensure accuracy in repairs and maintenance. Additionally, a comprehensive diagram that includes safety features and troubleshooting tips will enhance operational efficiency. -
How can I ensure the quality of oven parts from international suppliers?
To ensure the quality of oven parts from international suppliers, start by verifying their certifications and compliance with international standards. Request samples to evaluate the material and workmanship quality before placing larger orders. Establishing clear quality assurance protocols, such as inspections and testing upon arrival, can further safeguard your investment. Additionally, consider conducting factory audits or utilizing third-party inspection services for added assurance. -
What customization options should I consider when sourcing oven diagrams?
When sourcing oven diagrams, consider customization options that align with your specific operational needs. This may include modifications to accommodate unique heating elements or control systems tailored for your market. Additionally, inquire about the possibility of integrating local safety standards or energy efficiency requirements into the design. Custom diagrams can enhance functionality and compliance, making them more suitable for your target audience. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for oven diagrams from suppliers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for oven diagrams can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the product. Typically, suppliers may set MOQs ranging from a few units to several hundred, depending on production capabilities and material costs. It is advisable to negotiate MOQs, especially if you are a smaller buyer, to ensure you can meet your needs without overcommitting resources. Always clarify the MOQ before entering into an agreement to avoid future complications. -
What payment terms are commonly accepted for international oven diagram purchases?
Common payment terms for international oven diagram purchases often include options such as wire transfers, letters of credit, or PayPal for smaller transactions. Suppliers may require partial payment upfront (30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or after inspection. Ensure that the payment terms are clearly outlined in your contract to prevent misunderstandings. Additionally, consider using escrow services for large transactions to add an extra layer of security. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping for oven diagrams from overseas suppliers?
Handling logistics and shipping for oven diagrams from overseas suppliers involves several key steps. First, choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling technical drawings and equipment. Ensure that you understand import regulations and customs duties in your country to avoid unexpected delays or costs. It’s also advisable to opt for insurance coverage during transit to protect against potential loss or damage. Finally, maintain open communication with your supplier throughout the shipping process for timely updates. -
What role does quality assurance (QA) play in sourcing oven diagrams?
Quality assurance (QA) plays a crucial role in sourcing oven diagrams by ensuring that the diagrams meet specified standards and function correctly. Implementing a QA process involves setting criteria for design accuracy, material quality, and compliance with safety regulations. Regular audits and inspections during production can help identify potential issues early, reducing the risk of costly errors. A robust QA strategy not only enhances the reliability of the diagrams but also builds trust with your buyers, ultimately leading to better customer satisfaction.
Top 3 Diagram Of Oven Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. KitchenAid – Essential Oven Components
Domain: kitchenaid.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: 1. OVEN DOOR: The gateway to the cooking process, essential for starting and ending cooking. 2. OVEN RACK: Used for placing food to be baked, broiled, or roasted; adjustable for cooking efficiency. 3. OVEN LIGHT BULB: Provides light inside the oven to monitor cooking; wattage details in the owner’s manual. 4. WARMING DRAWER: Keeps dishes warm, available in select models, some with a slow-cook opti…
2. Pinterest – Oven Parts & Repair Guides
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Oven parts diagram, Electric Wall Oven Repair Guide, Official GE ZET3058WH1WW electric wall oven parts, Bosch HBN5450UC/07 electric wall oven parts, Microwave Oven Installation Diagram, Microwave Oven Circuit Diagram, Commercial Bakery Ovens Collection, Industrial Oven Size Guide, Digital Industrial Oven, Standard Oven Size Guide, Oven Temperature Conversion Chart, Convection Oven Temperature Guid…
3. KitchenAid – Electric Oven Wiring Diagram
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Electric oven Wiring Diagram for KitchenAid Model KCO111OB, Series WFO3601110, 110 Volts.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for diagram of oven
In conclusion, understanding the intricate components of an oven is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance their product offerings. The key takeaway is that strategic sourcing of high-quality oven parts—such as heating elements, convection fans, and control systems—can significantly impact the efficiency and reliability of kitchen appliances. By prioritizing quality and compatibility, businesses can reduce maintenance costs and improve customer satisfaction.
Moreover, as the demand for advanced cooking technologies rises across diverse markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, companies must stay ahead of trends and innovations. Investing in sustainable sourcing practices not only meets regulatory requirements but also resonates with eco-conscious consumers.
Looking ahead, the global market for kitchen appliances is poised for growth, driven by innovation and evolving consumer preferences. International B2B buyers should leverage this momentum by forging strategic partnerships with reliable suppliers and manufacturers. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your product line and stand out in a competitive landscape by sourcing the best oven components that align with your business goals.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.