Thin Film Pressure Transducer Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for thin film pressure transducer
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, sourcing reliable thin film pressure transducers presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers across diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These sensors play a crucial role in various applications, from automotive to medical devices, ensuring precise pressure measurements that enhance product performance and safety. However, the myriad of options available can overwhelm buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the global market for thin film pressure transducers by exploring different types, applications, and key considerations for supplier vetting. It addresses essential factors such as performance specifications, cost implications, and the importance of compliance with international standards. By providing insights into the latest advancements and trends in sensor technology, this guide empowers international B2B buyers to navigate the complexities of the market confidently.
With a focus on actionable strategies, the guide not only helps buyers identify the most suitable products for their needs but also equips them with the knowledge to negotiate effectively with suppliers. Whether you are based in emerging markets like Vietnam or established regions such as Germany, this resource is designed to facilitate informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and drive business success.
Understanding thin film pressure transducer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capacitive Thin Film Sensors | High sensitivity, compact size, excellent linearity | Automotive, aerospace, medical devices | Pros: High accuracy, suitable for small spaces. Cons: Sensitive to temperature variations. |
| Resistive Thin Film Sensors | Cost-effective, simple construction, analog output | Industrial automation, HVAC systems | Pros: Affordable, easy integration. Cons: Limited durability under extreme conditions. |
| Piezoelectric Thin Film Sensors | Generates electrical charge under pressure, fast response | Robotics, dynamic pressure applications | Pros: High responsiveness, ideal for dynamic measurements. Cons: Less effective for static pressure measurements. |
| Optical Thin Film Sensors | Uses light reflection for pressure measurement, non-invasive | Medical diagnostics, wearable technology | Pros: Non-invasive, high precision. Cons: More complex and potentially higher costs. |
| Polymer-Based Thin Film Sensors | Flexible, lightweight, suitable for various substrates | Consumer electronics, smart textiles | Pros: Highly adaptable, can be integrated into diverse products. Cons: May have lower sensitivity compared to metal-based sensors. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Capacitive Thin Film Sensors?
Capacitive thin film sensors are distinguished by their high sensitivity and compact design, making them ideal for applications where space is limited. They operate by measuring changes in capacitance caused by pressure variations. These sensors are widely used in automotive and aerospace industries, particularly for applications that require precise pressure measurements. When considering capacitive sensors, buyers should evaluate their accuracy requirements and potential environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, that may affect performance.
How Do Resistive Thin Film Sensors Compare in Cost and Performance?
Resistive thin film sensors offer a cost-effective solution for pressure measurement, featuring a straightforward construction that allows for easy integration into various systems. They provide an analog output that is suitable for many industrial applications, including HVAC systems and automation. While they are generally more affordable than other types, buyers should be mindful of their limitations, particularly in extreme environmental conditions, which may impact durability and accuracy.
What Advantages Do Piezoelectric Thin Film Sensors Offer for Dynamic Measurements?
Piezoelectric thin film sensors are unique in their ability to generate an electrical charge in response to applied pressure, providing rapid response times crucial for dynamic pressure applications, such as in robotics. They excel in environments where quick measurement is vital, although they are less effective for static pressures. B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their application, including the need for fast response versus static pressure monitoring, when selecting piezoelectric sensors.
Why Choose Optical Thin Film Sensors for Non-Invasive Applications?
Optical thin film sensors utilize light reflection to measure pressure, making them non-invasive and suitable for sensitive applications like medical diagnostics and wearable technology. Their high precision and ability to avoid contact with the measured surface can be significant advantages in healthcare settings. However, the complexity and potential costs associated with optical sensors may be a consideration for buyers, who should assess the balance between precision and budget constraints.
How Do Polymer-Based Thin Film Sensors Enhance Flexibility in Design?
Polymer-based thin film sensors are characterized by their lightweight and flexible nature, allowing them to be integrated into a wide range of substrates, including textiles and consumer electronics. This adaptability makes them an attractive option for innovative applications in smart textiles and wearable devices. Buyers should weigh the benefits of flexibility against the potential trade-offs in sensitivity and performance when considering polymer-based options for their projects.
Key Industrial Applications of thin film pressure transducer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of thin film pressure transducer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) | Enhances safety and performance by ensuring optimal tire pressure. | Look for high durability and temperature resistance in sensors. |
| Healthcare | Patient monitoring in wearable medical devices | Provides real-time data for better patient outcomes and care. | Ensure compliance with medical standards and high sensitivity. |
| Aerospace | Structural health monitoring of aircraft | Increases safety by detecting pressure changes that indicate failure. | Focus on lightweight materials and high accuracy under varied conditions. |
| Manufacturing | Process control in hydraulic systems | Improves efficiency and reduces downtime by monitoring pressure levels. | Seek sensors with quick response times and robust data logging. |
| Consumer Electronics | Pressure sensing in smart textiles and wearables | Enhances user experience through accurate pressure mapping. | Look for compatibility with various materials and ease of integration. |
How Are Thin Film Pressure Transducers Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, thin film pressure transducers are integral to tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS). These sensors continuously measure tire pressure, alerting drivers when levels fall below optimal ranges, which can prevent blowouts and enhance fuel efficiency. For B2B buyers, sourcing transducers with high durability and temperature resistance is crucial, especially in regions with extreme weather conditions. The ability to withstand vibrations and environmental factors is essential for reliable performance.
What Role Do Thin Film Pressure Transducers Play in Healthcare?
In healthcare, thin film pressure transducers are used in wearable medical devices for patient monitoring. They provide real-time data on vital signs, such as blood pressure, enabling healthcare providers to respond swiftly to patient needs. Buyers in this field must ensure that the sensors comply with strict medical standards and offer high sensitivity for accurate readings. This is particularly important for international buyers who need to navigate varying regulations across regions.
How Are Thin Film Pressure Transducers Beneficial in Aerospace Applications?
The aerospace industry employs thin film pressure transducers for structural health monitoring of aircraft. By detecting pressure changes in critical components, these sensors help identify potential failures before they lead to catastrophic events. For B2B buyers, sourcing lightweight and highly accurate sensors is vital, as these factors directly impact aircraft performance and safety. The ability to operate under extreme conditions is also a significant consideration for suppliers in this sector.
In What Ways Do Thin Film Pressure Transducers Improve Manufacturing Processes?
In manufacturing, thin film pressure transducers are essential for process control in hydraulic systems. They monitor pressure levels to ensure systems operate efficiently, reducing the risk of downtime caused by pressure fluctuations. Buyers should prioritize sensors that offer quick response times and robust data logging capabilities, enabling effective monitoring and analysis. This is particularly important for manufacturers in regions like Africa and South America, where operational efficiency can significantly impact competitiveness.
How Are Thin Film Pressure Transducers Transforming Consumer Electronics?
Thin film pressure transducers are increasingly used in smart textiles and wearables within the consumer electronics sector. These sensors enable accurate pressure mapping, enhancing user experiences in products like fitness trackers and smart clothing. For B2B buyers, compatibility with various materials and ease of integration into existing systems are key sourcing considerations. As demand for innovative wearable technology grows globally, suppliers must provide solutions that meet diverse consumer needs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘thin film pressure transducer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Accurate Pressure Measurements in Harsh Environments
The Problem: Many industries, particularly those in manufacturing and oil & gas, require reliable pressure measurements under extreme conditions. Thin film pressure transducers can struggle with accuracy and stability when exposed to high temperatures, corrosive environments, or significant vibrations. This can lead to inaccurate data, resulting in poor decision-making, costly downtime, and potential safety hazards.
The Solution: To overcome these challenges, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing thin film pressure transducers specifically designed for harsh environments. Look for sensors that feature robust materials resistant to corrosion and high temperatures, such as stainless steel or specialized polymers. Additionally, consider transducers that come with built-in protective coatings to shield against environmental factors. Collaborating with manufacturers who offer customization options can ensure that the sensors meet the specific requirements of your application. Regular calibration and maintenance should also be established to guarantee ongoing accuracy and reliability in measurements, thereby ensuring operational efficiency and safety.
Scenario 2: Integration Challenges with Existing Systems
The Problem: Integrating new thin film pressure transducers into existing measurement systems can often be a daunting task for B2B buyers. Compatibility issues can arise from differing communication protocols, data formats, or physical dimensions. This integration difficulty can lead to project delays, increased costs, and frustration among engineering teams.

Illustrative image related to thin film pressure transducer
The Solution: To facilitate seamless integration, buyers should conduct thorough compatibility assessments before procurement. Engage with suppliers early in the process to understand the technical specifications and integration requirements of the thin film pressure transducers. It is crucial to ensure that the chosen sensors support the same communication protocols (e.g., analog, digital, or wireless) used by existing systems. Additionally, suppliers should be able to provide technical support, including detailed documentation and integration guides. Utilizing modular designs can also simplify integration, allowing for easier replacements or upgrades without overhauling the entire system. Training sessions for engineering teams on the new systems can further smooth the transition and enhance operational efficiency.
Scenario 3: Limited Understanding of Performance Specifications
The Problem: Buyers often face confusion regarding the performance specifications of thin film pressure transducers, such as sensitivity, range, and response time. Misunderstandings in these areas can lead to selecting inappropriate sensors for specific applications, resulting in suboptimal performance and costly mistakes.
The Solution: To address this issue, B2B buyers should invest time in understanding the key performance metrics that influence the effectiveness of thin film pressure transducers. Detailed conversations with suppliers can clarify how each specification aligns with the intended application. Buyers should also request detailed datasheets that outline the performance characteristics, including temperature ranges, accuracy levels, and response times. Participating in webinars or training offered by manufacturers can enhance understanding of these metrics. Furthermore, conducting pilot tests with selected sensors in real-world conditions can help validate performance before full-scale deployment. This thorough approach ensures that the selected pressure transducers will meet the required operational standards and enhance overall productivity.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for thin film pressure transducer
When selecting materials for thin film pressure transducers, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of the application, including environmental conditions, compatibility with media, and regulatory standards. Below are analyses of four common materials used in thin film pressure transducers, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Polyimide in Thin Film Pressure Transducers?
Polyimide is a high-performance polymer known for its excellent thermal stability and mechanical properties. It can withstand temperatures up to 300°C and has good chemical resistance, making it suitable for various harsh environments. Polyimide films are also flexible and can be easily integrated into different designs.
Pros: The durability and flexibility of polyimide allow for innovative designs in compact spaces. Its high-temperature rating makes it ideal for applications in automotive and aerospace industries.
Cons: Polyimide can be more expensive than other materials like polyester, and its manufacturing process may require specialized techniques, which can increase production costs.
Impact on Application: Polyimide is compatible with a wide range of media, including fuels and oils, making it suitable for applications in automotive and industrial settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure that polyimide materials comply with relevant standards such as ASTM and DIN. The higher cost may be justified in high-performance applications.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform as a Material for Thin Film Pressure Transducers?
Stainless steel is widely used in pressure transducers due to its excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. It can operate effectively in temperatures ranging from -200°C to 600°C, depending on the specific alloy used.
Pros: The robustness of stainless steel makes it suitable for harsh environments, including chemical processing and food industries. Its durability ensures a long lifespan for the transducer.
Cons: While stainless steel is durable, it is heavier than other materials, which may not be suitable for all applications. Additionally, the cost can vary significantly based on the alloy used.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel’s compatibility with a wide range of fluids makes it ideal for applications in the oil and gas sector, as well as in medical devices.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ISO and ASTM is crucial for buyers in regions like South America and Europe. The choice of alloy may also be influenced by local regulations regarding corrosion resistance.
What Advantages Does Silicon Offer in Thin Film Pressure Transducers?
Silicon is a semiconductor material commonly used in pressure transducers due to its excellent electrical properties and sensitivity. It can operate effectively in a range of temperatures and is often used in microelectromechanical systems (MEMS).
Pros: Silicon’s high sensitivity allows for precise measurements, making it suitable for applications requiring high accuracy, such as in aerospace and medical devices.
Cons: Silicon is brittle and can be susceptible to damage under mechanical stress. Its performance may also be limited in extreme environments.
Impact on Application: Silicon-based transducers are ideal for applications involving low-pressure measurements, such as in HVAC systems and consumer electronics.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that silicon components meet industry standards such as JIS and IEC, particularly in regions like Asia and Europe, where regulatory compliance is stringent.
Why Choose Polycarbonate for Thin Film Pressure Transducers?
Polycarbonate is a durable thermoplastic known for its impact resistance and clarity. It can withstand temperatures up to 120°C and has good chemical resistance, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros: The lightweight nature of polycarbonate makes it ideal for portable devices. Its transparency allows for easy visual inspection of the transducer.
Cons: Polycarbonate may not perform well in high-temperature applications compared to polyimide or stainless steel. It is also less rigid, which may affect the transducer’s performance under certain conditions.
Impact on Application: Polycarbonate is suitable for applications in consumer electronics and medical devices where weight and visibility are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that polycarbonate materials comply with relevant safety and performance standards, particularly in healthcare applications in regions like Africa and the Middle East.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Thin Film Pressure Transducers
| Material | Typical Use Case for thin film pressure transducer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyimide | Automotive and aerospace applications | High thermal stability | Higher manufacturing costs | High |
| Stainless Steel | Oil and gas, medical devices | Excellent corrosion resistance | Heavier than other materials | Medium |
| Silicon | HVAC systems, consumer electronics | High sensitivity | Brittle under mechanical stress | Medium |
| Polycarbonate | Consumer electronics, medical devices | Lightweight and impact-resistant | Limited high-temperature performance | Low |
This strategic material selection guide offers valuable insights for international B2B buyers, ensuring they make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with industry standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for thin film pressure transducer
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Thin Film Pressure Transducers?
The manufacturing of thin film pressure transducers involves several critical stages that ensure the performance and reliability of the final product. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to source high-quality sensors for their applications.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Thin Film Pressure Sensors?
The manufacturing process begins with the selection and preparation of materials. Thin film pressure transducers typically utilize materials such as silicon, polyimide, or other flexible substrates that provide the necessary mechanical and electrical properties. The choice of material is crucial as it affects the sensor’s sensitivity, durability, and performance under varying environmental conditions.
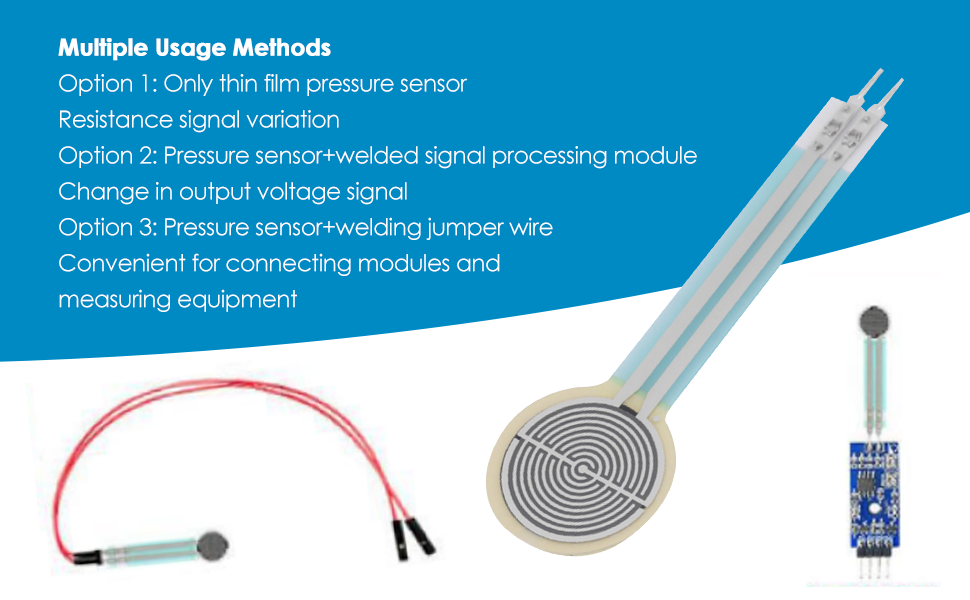
Illustrative image related to thin film pressure transducer
The initial step in material preparation involves cleaning and treating the substrate to ensure proper adhesion of the thin film layers. This may include chemical etching or plasma treatment to enhance surface properties. Following this, the deposition of the thin film itself can occur through techniques such as sputtering or chemical vapor deposition (CVD). These methods allow for precise control over the thickness and uniformity of the films, which are essential for accurate pressure measurements.
How Are Thin Film Pressure Sensors Formed?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage involves forming the sensors. This typically includes the following steps:
-
Thin Film Deposition: The thin films, often comprising metallic materials like gold or nickel, are deposited on the substrate. This layer acts as the sensing element, responding to pressure changes.
-
Patterning: A photolithography process is employed to define the sensor’s geometry. This involves applying a photoresist layer, exposing it to light, and developing it to create patterns that will guide the deposition of additional layers.
-
Etching: Unwanted material is removed through etching processes, which can be either wet (chemical) or dry (plasma). This step is critical in achieving the desired structure and functionality of the sensor.
-
Assembly: The sensors are then assembled with other components, such as electrical connections and protective casings. This may involve soldering or adhesive bonding, depending on the design requirements.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used to Ensure Quality?
Finishing techniques play a significant role in enhancing the performance and durability of thin film pressure transducers. After assembly, the sensors undergo several processes:
-
Encapsulation: To protect the sensitive components from environmental factors, sensors may be encapsulated in protective materials that are both durable and flexible.
-
Calibration: Each sensor is calibrated to ensure accurate pressure readings. This involves applying known pressures and adjusting the output accordingly.
-
Final Inspection: A thorough inspection is conducted to check for defects in materials and assembly. This includes visual inspections and functional testing to verify performance specifications.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Thin Film Pressure Transducer Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that the products meet both international standards and customer expectations.
What International Standards Guide Quality Assurance for Thin Film Pressure Sensors?
Manufacturers typically adhere to various international standards that govern quality management and product safety. One of the most recognized standards is ISO 9001, which outlines the criteria for a quality management system (QMS). Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers consistently produce products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking (for European markets) and API standards (for applications in oil and gas) may apply. These certifications often require rigorous testing and documentation to demonstrate compliance.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is integrated into the manufacturing process at various checkpoints, including:

Illustrative image related to thin film pressure transducer
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter the production process. Ensuring quality at this stage can prevent defects down the line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections and testing are performed to monitor the quality of the product in real-time. This includes checking for dimensional accuracy and functional performance.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the sensors are fully assembled, they undergo a final round of testing to verify that they meet specifications. This may include pressure testing, environmental testing, and calibration checks.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers. Here are some actionable strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols in place. This provides firsthand insight into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Review Quality Reports: Request detailed quality reports that outline testing methodologies, results, and compliance with international standards. These documents should also include any certifications held by the manufacturer.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s products and processes. This adds an additional layer of assurance regarding product quality.
-
Understanding QC Nuances for International Markets: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of specific regulatory requirements that may affect quality assurance. This includes understanding local certifications and standards that could impact product acceptance in their respective markets.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can mitigate risks and ensure they are sourcing high-quality thin film pressure transducers that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘thin film pressure transducer’
When sourcing thin film pressure transducers, it is essential to follow a systematic approach to ensure you select the right products that meet your specific needs. This guide outlines the critical steps to help international B2B buyers streamline their procurement process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing your technical requirements is the foundation of the sourcing process. Consider factors such as pressure range, sensitivity, size, and operating conditions. Clearly defined specifications will help you identify suitable transducers that can perform accurately in your application, whether it be in industrial automation, medical devices, or automotive testing.
Step 2: Research Supplier Options
Start by identifying potential suppliers that specialize in thin film pressure transducers. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in your industry. Utilize online platforms, trade shows, and industry networks to gather a list of reputable companies, ensuring they have experience with international shipping and compliance with regional regulations.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet your shortlisted suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies to understand their capabilities. Additionally, ask for references from other businesses in similar markets to gauge reliability and customer satisfaction. A supplier with a strong reputation will likely provide better support and quality assurance.
Step 4: Check for Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the suppliers you consider have the necessary certifications, such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards. Compliance with international quality and safety regulations is crucial, especially if the transducers are intended for sensitive applications like medical or aerospace. This step helps mitigate risks associated with product failures and legal liabilities.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the thin film pressure transducers you are considering. Testing samples in your specific application will provide insights into their performance, durability, and compatibility with your systems. Pay attention to how well they meet your defined specifications and consider factors like ease of integration and calibration.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have identified a suitable supplier and tested their products, engage in negotiations to finalize terms. Discuss pricing, payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranty conditions. Ensure that the terms align with your budget and project timelines, while also considering the total cost of ownership, which includes installation, maintenance, and potential downtime.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship
After procurement, work on building a collaborative relationship with your supplier. Regular communication can lead to better support and opportunities for future upgrades or innovations. A strong partnership can also facilitate quicker resolution of issues, ensuring that you have a reliable source for any future needs.
By following these steps, you can effectively navigate the sourcing process for thin film pressure transducers, ensuring that you select high-quality products that meet your operational requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for thin film pressure transducer Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Thin Film Pressure Transducers?
When sourcing thin film pressure transducers, understanding the cost structure is essential for informed decision-making. The total cost of these sensors comprises several components:
-
Materials: The primary costs involve raw materials like polymer substrates, conductive inks, and adhesives. High-quality materials can increase initial costs but may offer better performance and durability, reducing long-term expenses.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce involved in manufacturing, assembly, and testing. Skilled labor is necessary for quality control and precision in production, which can vary significantly by region.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: The cost of custom tooling can be significant, especially for specialized sensors. Initial tooling investments may be high, but they can be amortized over larger production runs, reducing per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that sensors meet specifications and certifications. Investing in quality assurance can prevent costly recalls and enhance customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely depending on the supplier’s location and the buyer’s destination. Choosing the right Incoterms can optimize logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their risks and operational costs. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market position and the competitive landscape.
What Influences Pricing for Thin Film Pressure Transducers?
Several factors can significantly influence the pricing of thin film pressure transducers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger order volumes usually lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers often offer discounts for minimum order quantities, making bulk purchasing a cost-effective strategy.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications, such as varying pressure ranges or unique dimensions, can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the added expense.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) can enhance the product’s reliability and marketability but also increase costs. Buyers should assess whether these factors align with their application requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, production capabilities, and geographic location can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge a premium, but they often provide better service and reliability.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can affect the final cost, as they dictate who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms is crucial for accurate budgeting.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for Thin Film Pressure Transducers?
To achieve cost-efficiency and better pricing when sourcing thin film pressure transducers, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage suppliers in discussions regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Many suppliers are open to negotiation, especially for larger orders or long-term partnerships.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial purchase price, but also the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A higher upfront cost may be justified by lower long-term expenses.
-
Leverage Regional Advantages: Buyers from different regions may benefit from varying pricing structures. For instance, sourcing from suppliers in emerging markets may provide cost advantages due to lower labor costs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local regulations that can affect the overall cost. Establishing a good relationship with a reliable freight forwarder can help mitigate logistics costs.
Conclusion
While sourcing thin film pressure transducers, it is crucial to consider the comprehensive cost structure and the various factors influencing pricing. By understanding these components and employing effective negotiation strategies, international B2B buyers can optimize their sourcing decisions, ensuring they achieve the best value for their investment. Always remember that prices can vary based on numerous factors, and it’s advisable to request indicative quotes tailored to specific needs and contexts.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing thin film pressure transducer With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Thin Film Pressure Transducers
In the realm of pressure measurement, thin film pressure transducers are known for their high sensitivity and compact design. However, various alternatives exist that may suit different applications and business needs. This section explores some of these alternatives, providing insights for B2B buyers in diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Comparison Table of Thin Film Pressure Transducer and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Thin Film Pressure Transducer | Strain Gauge Pressure Sensor | Capacitive Pressure Sensor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High accuracy and sensitivity; fast response time | Good accuracy; moderate response time | Excellent stability over time; good sensitivity |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost due to advanced technology | Moderate cost; widely available | Varies; can be cost-effective for high-volume applications |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific calibration and integration | Relatively easy to install with standard interfaces | Moderate complexity; requires proper handling of capacitance |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; durable under various conditions | Moderate maintenance; susceptible to environmental factors | Low maintenance; robust in stable environments |
| Best Use Case | Precision applications in aerospace, medical devices | Industrial applications, automotive testing | Applications requiring high stability, such as HVAC systems |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Strain Gauge Pressure Sensor
Strain gauge pressure sensors are widely utilized in industrial applications due to their balance of performance and cost. They operate by measuring the deformation (strain) of a material when subjected to pressure. The primary advantages of strain gauges include their affordability and ease of integration into existing systems. However, they may require calibration and can be sensitive to temperature changes, which can affect readings. For industries where cost is a primary concern, such as manufacturing, strain gauges offer a compelling option.
Capacitive Pressure Sensor
Capacitive pressure sensors leverage changes in capacitance caused by pressure variations to provide measurements. These sensors are known for their long-term stability and excellent linearity, making them ideal for applications that require consistent performance over time, such as in HVAC systems. While they can be more complex to implement than strain gauges, they often prove to be cost-effective in high-volume scenarios. However, they may be less suitable for environments with high humidity or contamination, which can impact their performance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Pressure Measurement Solution
When selecting a pressure measurement solution, B2B buyers must consider several factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and specific application needs. Thin film pressure transducers excel in precision and compactness, making them ideal for high-tech industries. In contrast, strain gauge and capacitive sensors provide viable alternatives that may offer advantages in cost and stability, respectively. Understanding the unique benefits and limitations of each option is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with organizational goals and operational demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for thin film pressure transducer
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Thin Film Pressure Transducers?
Thin film pressure transducers are vital components in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. Understanding their critical technical properties is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
1. Material Grade
Thin film pressure transducers are typically constructed from high-grade materials such as stainless steel, silicon, or polyimide. The choice of material impacts the sensor’s durability, resistance to corrosion, and performance in extreme temperatures. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade ensures reliability and longevity in demanding applications.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified measurement. In thin film pressure transducers, this can affect accuracy and sensitivity. A high tolerance level (e.g., ±0.1% of full scale) indicates precision, which is crucial in applications requiring stringent quality control. B2B buyers should prioritize manufacturers that offer low tolerance levels to ensure consistent performance.
3. Pressure Range
The pressure range of a transducer indicates the minimum and maximum pressures it can accurately measure. Typical ranges can vary from vacuum levels to several thousand psi. Understanding the required pressure range for specific applications helps buyers select suitable products, ensuring that they meet operational requirements without risking damage to the sensor.
4. Output Signal Type
Thin film pressure transducers can produce various output signals, including analog (voltage or current) and digital formats. The choice of output type affects compatibility with existing monitoring systems. B2B buyers must consider the integration capabilities of the transducer’s output signal to ensure seamless functionality with their applications.
5. Temperature Coefficient
This property measures how the output of the sensor changes with temperature variations. A lower temperature coefficient indicates better stability under fluctuating thermal conditions. Buyers should assess this specification, especially in environments with extreme temperature changes, to maintain measurement accuracy.
6. Response Time
Response time is the duration required for the sensor to react to a change in pressure. Fast response times (typically in milliseconds) are essential in applications requiring real-time monitoring. B2B decision-makers should consider response time as a critical factor for applications in dynamic environments, such as automotive testing or medical diagnostics.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Thin Film Pressure Transducers?
Understanding industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces components that are used in another company’s end products. In the context of thin film pressure transducers, OEMs may supply these sensors for integration into larger systems. Buyers should look for reputable OEMs to ensure quality and reliability.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is vital for buyers, particularly those in emerging markets, as it affects inventory management and initial investment costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing for specific quantities and specifications of products. This process is essential for B2B buyers to compare costs and terms from different manufacturers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms is crucial for B2B transactions, especially for international buyers, to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth logistics.
5. Calibration
Calibration involves adjusting the transducer to ensure its accuracy by comparing its output against a known standard. For B2B buyers, understanding calibration requirements is essential to maintain measurement integrity and compliance with industry standards.
6. Certification
Certification indicates that a product meets specific industry standards and regulations (e.g., ISO, CE). Buyers should prioritize certified products to ensure compliance and enhance credibility in their respective markets.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing thin film pressure transducers, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the thin film pressure transducer Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Thin Film Pressure Transducer Sector?
The global thin film pressure transducer market is witnessing significant growth driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand across various industries, including automotive, medical, and aerospace. With the rise of automation and Industry 4.0, the integration of smart sensors into manufacturing processes is becoming increasingly common. This trend emphasizes the need for precision and reliability, which thin film pressure transducers are well-suited to provide. Additionally, the push for miniaturization in devices has led to an increased preference for compact and lightweight sensors, further fueling market growth.
Emerging markets in Africa, South America, and the Middle East are particularly ripe for investment. The growing industrial sectors in these regions, such as renewable energy and healthcare, are driving demand for advanced pressure sensing technologies. European markets, including Germany, are also evolving, with a strong focus on innovation and quality standards. International B2B buyers must stay attuned to these regional dynamics, as local regulations and market maturity can significantly influence sourcing strategies.
Furthermore, digital transformation is reshaping sourcing trends. Buyers are increasingly favoring suppliers who offer integrated solutions, combining hardware and software for enhanced data analytics and operational efficiency. This shift towards digital solutions enables businesses to optimize processes and improve decision-making, underscoring the importance of selecting suppliers that can meet these evolving technological needs.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Thin Film Pressure Transducer Market?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor for B2B buyers in the thin film pressure transducer sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the lifecycle of products are under scrutiny, prompting companies to seek suppliers committed to ethical sourcing and sustainable practices. The pressure sensor industry is not exempt from these considerations, as the materials used and the manufacturing processes employed can significantly affect ecological footprints.
Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with environmental standards and certifications, such as ISO 14001 or RoHS. Furthermore, the demand for ‘green’ materials—those that are recyclable or made from renewable resources—is rising. Manufacturers that invest in sustainable practices not only enhance their brand reputation but also appeal to a growing segment of environmentally-conscious buyers.
Moreover, ethical supply chains are essential for mitigating risks associated with labor practices and environmental degradation. B2B buyers should evaluate potential suppliers based on their commitment to fair labor practices and transparency within their supply chains. By prioritizing suppliers with strong sustainability credentials, businesses can align their procurement strategies with broader corporate social responsibility goals while also meeting regulatory requirements.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Thin Film Pressure Transducers?
The evolution of thin film pressure transducers dates back to the late 20th century when the need for more accurate and reliable sensors became apparent across various industries. Initial developments focused on traditional piezoresistive sensors, which laid the groundwork for the emergence of thin film technology. By the early 2000s, advancements in materials science and microfabrication techniques enabled the production of thin film sensors that were not only more sensitive but also offered greater durability and flexibility.

Illustrative image related to thin film pressure transducer
Today, thin film pressure transducers are integral to numerous applications, from automotive systems that monitor tire pressure to medical devices that require precise pressure measurements. As technology continues to advance, these sensors are evolving further, incorporating features like wireless connectivity and real-time data analytics, which enhance their functionality and applicability across diverse sectors. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution can provide insights into the capabilities and future potential of thin film pressure transducers, guiding informed procurement decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of thin film pressure transducer
-
How do I select the right thin film pressure transducer for my application?
Choosing the right thin film pressure transducer involves assessing your specific application requirements, such as pressure range, accuracy, and environmental conditions. Start by determining the maximum and minimum pressure levels your sensor will encounter. Consider the sensor’s flexibility and size, especially if it’s to be integrated into confined spaces or dynamic environments. Additionally, review the sensor’s compatibility with your data acquisition systems to ensure seamless integration. Consulting with manufacturers or technical experts can also provide valuable insights tailored to your needs. -
What customization options are available for thin film pressure transducers?
Many suppliers offer customization options for thin film pressure transducers to meet specific project requirements. Customizations may include variations in size, shape, pressure range, and output signal types. Some manufacturers also provide tailored packaging solutions or specialized mounting features. When considering customization, communicate your precise specifications and intended application to the supplier early in the process to ensure they can accommodate your needs effectively. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for thin film pressure transducers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for thin film pressure transducers vary by supplier and can depend on the level of customization required. Generally, standard models may have a lower MOQ, while customized solutions might require larger orders to justify production costs. It’s advisable to discuss your needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and explore options for smaller trial orders, especially if you are testing a new application or market. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing thin film pressure transducers internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers and regions. Common practices include upfront payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods that provide buyer protection. Additionally, negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs, such as partial payments based on production milestones. Always clarify these terms before finalizing agreements to avoid misunderstandings. -
How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) for thin film pressure transducers?
To ensure quality assurance for thin film pressure transducers, request detailed information about the supplier’s QA processes. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Suppliers should provide documentation for testing methods, calibration procedures, and performance data. Consider asking for samples or conducting site visits to evaluate the manufacturing process. Establishing clear quality metrics and inspection protocols before production can also help maintain standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing thin film pressure transducers?
Logistics play a crucial role in the successful importation of thin film pressure transducers. Ensure you understand the shipping methods, lead times, and costs involved in transporting your products. Familiarize yourself with customs regulations and import duties in your country to avoid unexpected delays or fees. Collaborating with a freight forwarder experienced in your region can facilitate smoother logistics management and ensure compliance with all necessary documentation. -
How can I vet suppliers of thin film pressure transducers effectively?
When vetting suppliers for thin film pressure transducers, prioritize those with a solid reputation and proven track record in the industry. Research their history, client testimonials, and case studies to assess reliability. Request references and reach out to previous customers to gather firsthand feedback on their experiences. Additionally, consider suppliers who offer technical support and after-sales services, as these can be indicators of a commitment to customer satisfaction and product quality. -
What industry applications commonly use thin film pressure transducers?
Thin film pressure transducers are widely utilized across various industries, including automotive, medical devices, aerospace, and industrial automation. In automotive applications, they are used for tire pressure monitoring and engine control systems. In medical technology, they help monitor patient vitals and pressure in devices like ventilators. Their versatility and adaptability make them suitable for diverse applications, from wearables to robotics, ensuring precise pressure measurement in dynamic environments.
Top 6 Thin Film Pressure Transducer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Tekscan – Thin-Film Pressure Sensors
Domain: tekscan.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Thin-Film Pressure Sensors from Tekscan measure force and pressure distribution between two contacting surfaces. Key features include: 1. Minimally invasive high-resolution sensor that is thin (0.1 mm) and flexible. 2. Over 200 standard sensors with various shapes, sizes, resolutions, and pressure ranges. 3. Customizable to unique form factors and pressure ranges for specific applications. 4. Data…
2. Loomia – Thin Film Pressure Sensor
Domain: loomia.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Loomia Thin Film Pressure Sensor – Mega Soft Pressure Matrix
Price: $28.00
Key Features:
– Flexible, durable, and accurate for measuring pressure in wearables, robotics, and medical devices.
– 3×3 matrix with six leads for pressure mapping.
– Analog readout varying from 500K Ohms to 100 Ohms based on force applied.
– Compatible with microcontrollers like Arduino Nano and Teensy.
– C…
3. Mouser – RP High-Speed Pressure Sensors
Domain: mouser.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, Mouser – RP High-Speed Pressure Sensors, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. WIKA – Pressure Sensors
Domain: blog.wika.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: WIKA offers three common pressure sensor measuring principles: thin-film, thick-film, and piezoresistive sensors. Thin-film sensors utilize a Wheatstone bridge configuration with four resistors on a diaphragm to detect deformation under pressure, using a sputtering process for structuring. Thick-film sensors also employ a Wheatstone bridge with resistors printed on a ceramic base and burnt-in at h…
5. Setra – Model 3100 OEM Pressure Transducer
Domain: setra.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Model: 3100 OEM Pressure Transducer
Type: Thin Film Pressure Sensor
Accuracy: 0.25% FS
Pressure Range: 75 PSI to 32,000 PSI
Construction: All welded stainless steel
Environmental Protection: IP67 seal for moisture and humidity protection
Outputs: Variety of outputs including voltage, current, and ratiometric; dual pressure/temperature output available
Thermal Compensation: Less than 0.005%/°C
Fail…
6. DFRobot – Gravity Thin-film Pressure Sensor
Domain: dfrobot.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: {“name”: “Gravity: Thin-film Pressure Sensor for Pressure Science Course”, “SKU”: “SEN0616”, “price”: “$4.90”, “volume_discount”: {“3+ items”: “$4.80”, “5+ items”: “$4.70”, “10+ items”: “$4.50”}, “pressure_measurement_range”: “20g to 6kg”, “operating_voltage”: “3.3V to 5V”, “output_type”: “Analog”, “dimensions”: “57.5x22mm”, “weight”: “2.9g (14g including packaging and sensor wire)”, “applications…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for thin film pressure transducer
In summary, the strategic sourcing of thin film pressure transducers presents significant opportunities for international B2B buyers across diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By leveraging advanced technologies such as customizable sensor designs and integrated data acquisition systems, businesses can enhance product performance and streamline manufacturing processes. The ability to adapt these sensors for various applications—from automotive to medical devices—further underscores their versatility and value.
As global industries continue to evolve, the demand for precise and reliable pressure measurement solutions will only increase. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who not only offer high-quality products but also demonstrate a commitment to innovation and customer support. Engaging with manufacturers that provide comprehensive resources and technical assistance will be crucial in optimizing the integration of thin film pressure transducers into existing systems.
Looking ahead, now is the time for B2B buyers to explore partnerships with leading suppliers in the thin film pressure sensor market. By making informed sourcing decisions, businesses can position themselves at the forefront of technological advancement, ensuring they meet the future demands of their respective industries.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.