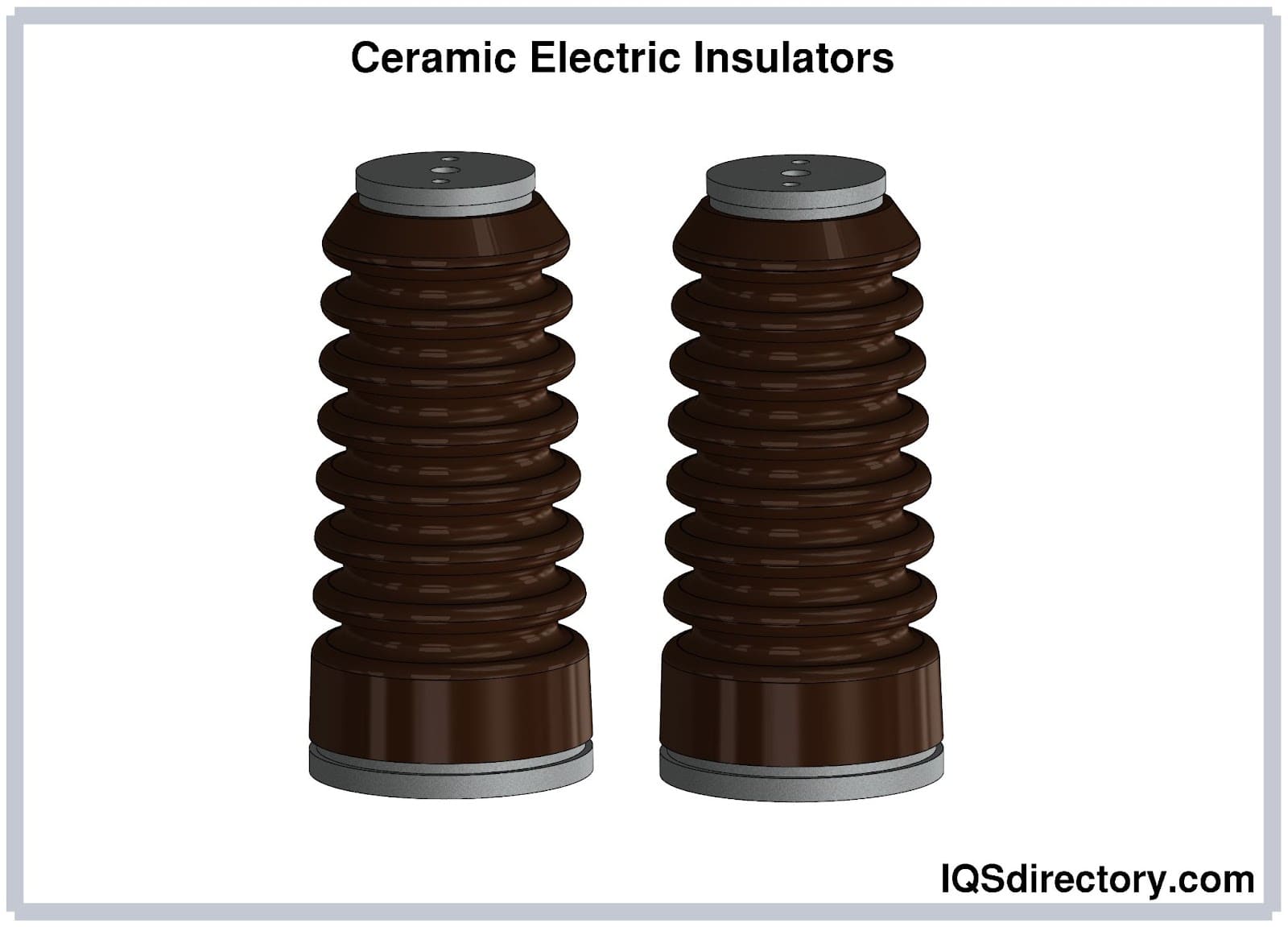
Ceramic Electrical Insulator Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for ceramic electrical insulator
In today’s interconnected world, sourcing reliable ceramic electrical insulators poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The demand for high-performance insulators that can withstand extreme conditions while ensuring electrical safety is ever-increasing. This guide aims to equip decision-makers with the insights necessary to navigate the complexities of the ceramic electrical insulator market, from understanding the various types available—such as alumina, cordierite, and steatite—to evaluating their specific applications across industries like power generation, electronics, and automotive sectors.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, buyers will discover essential information on supplier vetting processes, key factors influencing costs, and the latest technological advancements in ceramic materials. Each section is designed to empower stakeholders with the knowledge required to make informed purchasing decisions, reducing the risks associated with sourcing and ensuring compliance with regional standards. By addressing the unique needs of markets in countries such as Brazil and Germany, this guide offers tailored insights that can lead to more effective procurement strategies and long-term supplier partnerships. Whether you’re looking to enhance operational efficiency or meet stringent regulatory requirements, understanding the global landscape of ceramic electrical insulators is crucial for sustainable business growth.
Understanding ceramic electrical insulator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina | High strength, excellent thermal conductivity, low porosity | Electronics, aerospace, medical devices | Pros: High durability and thermal stability. Cons: Higher cost compared to other ceramics. |
| Cordierite | Exceptional thermal shock resistance, low thermal expansion | Electrical heating coils, automotive applications | Pros: Rapid heating and cooling. Cons: Lower mechanical strength than alumina. |
| Steatite | Economical, good dielectric strength, operates up to 2000°F | Power generation, electrical insulators | Pros: Cost-effective and decent performance. Cons: Limited to moderate temperatures. |
| Zirconia | High fracture toughness, excellent thermal insulation | High-temperature applications, specialized electronics | Pros: Extremely durable and resistant to wear. Cons: Higher weight and cost. |
| Wollastonite | Low thermal expansion, good electrical insulation properties | Insulation in high-voltage applications | Pros: Lightweight and effective insulator. Cons: May have limited availability. |
What Are the Characteristics and Suitability of Alumina Ceramic Insulators?
Alumina, or aluminum oxide, is renowned for its high mechanical strength and excellent thermal conductivity, making it suitable for applications requiring durability under high temperatures. With a porosity of 0-0.05%, it offers superior dielectric strength, ensuring reliable performance in electrical insulation. B2B buyers should consider alumina for industries such as electronics, aerospace, and medical devices, where reliability and performance are critical. However, its higher cost compared to other materials may be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers.
How Does Cordierite Compare in Thermal Shock Resistance?
Cordierite stands out due to its remarkable ability to withstand thermal shock and low thermal expansion. This makes it ideal for applications like electrical heating coils and automotive components, where rapid temperature changes are common. Its unique properties allow for quick heating and cooling, enhancing efficiency in manufacturing processes. Buyers should weigh the benefits of cordierite’s thermal stability against its slightly lower mechanical strength compared to alumina when selecting materials for demanding applications.
Why Choose Steatite for Cost-Effective Electrical Insulation?
Steatite ceramic insulators are favored for their economical pricing and decent dielectric strength, operating effectively at temperatures up to 2000°F. Their relatively low cost makes them an attractive option for power generation and other electrical applications. While steatite offers good performance, it is best suited for moderate temperature environments. B2B buyers should consider the balance of cost and performance when sourcing steatite insulators for their projects.
What Advantages Does Zirconia Provide in High-Temperature Applications?
Zirconia is known for its exceptional fracture toughness and thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for high-temperature and specialized electronic applications. Its durability and resistance to wear make it a preferred choice for industries requiring robust materials. However, buyers should be aware of its heavier weight and higher cost, which may impact budget considerations. Proper evaluation of application needs is essential when selecting zirconia for specific use cases.
How Does Wollastonite Function as an Insulator?
Wollastonite offers low thermal expansion and effective electrical insulation, making it suitable for high-voltage applications. Its lightweight nature contributes to its usability in various electrical components. While it provides significant insulation benefits, availability can sometimes be a concern for buyers. Ensuring a reliable supply chain is crucial for businesses looking to incorporate wollastonite into their products.
Key Industrial Applications of ceramic electrical insulator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of ceramic electrical insulator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Generation | Insulating components in turbines and generators | Enhances operational efficiency and safety by preventing electrical failures | Material durability, thermal resistance, and dielectric strength |
| Electronics Manufacturing | Insulators for circuit boards and electronic components | Ensures reliable performance and longevity of electronic devices | Precision machining capabilities and customization options |
| Automotive | Insulation for high-voltage systems in electric vehicles | Supports safety and performance in electric powertrain systems | Compliance with automotive standards and high-temperature performance |
| Heating Equipment | Insulating bushings for electric heating elements | Improves energy efficiency and reduces heat loss | Compatibility with heating applications and thermal shock resistance |
| Telecommunications | Insulators for RF and microwave components | Maintains signal integrity and system reliability | High-frequency performance and environmental resilience |
How Are Ceramic Electrical Insulators Used in Power Generation?
In the power generation sector, ceramic electrical insulators are essential for insulating components within turbines and generators. These insulators prevent electrical failures and enhance operational efficiency by ensuring that high voltages do not leak or cause short circuits. Buyers in this industry should prioritize materials with high dielectric strength and thermal resistance, as these properties are crucial for maintaining performance in extreme conditions. Additionally, sourcing from suppliers who can guarantee durability and reliability is vital, especially for installations in regions with fluctuating climates, such as Africa and South America.
What Role Do Ceramic Insulators Play in Electronics Manufacturing?
Ceramic electrical insulators are widely utilized in the electronics manufacturing sector, particularly in circuit boards and various electronic components. Their insulating properties help maintain the reliability and longevity of devices, which is critical in an industry that demands high performance and low failure rates. For international buyers, it’s important to consider suppliers that offer precision machining and customization capabilities to meet specific design requirements. Additionally, ensuring that the insulators comply with international standards can facilitate smoother supply chain processes across borders, especially in Europe and the Middle East.
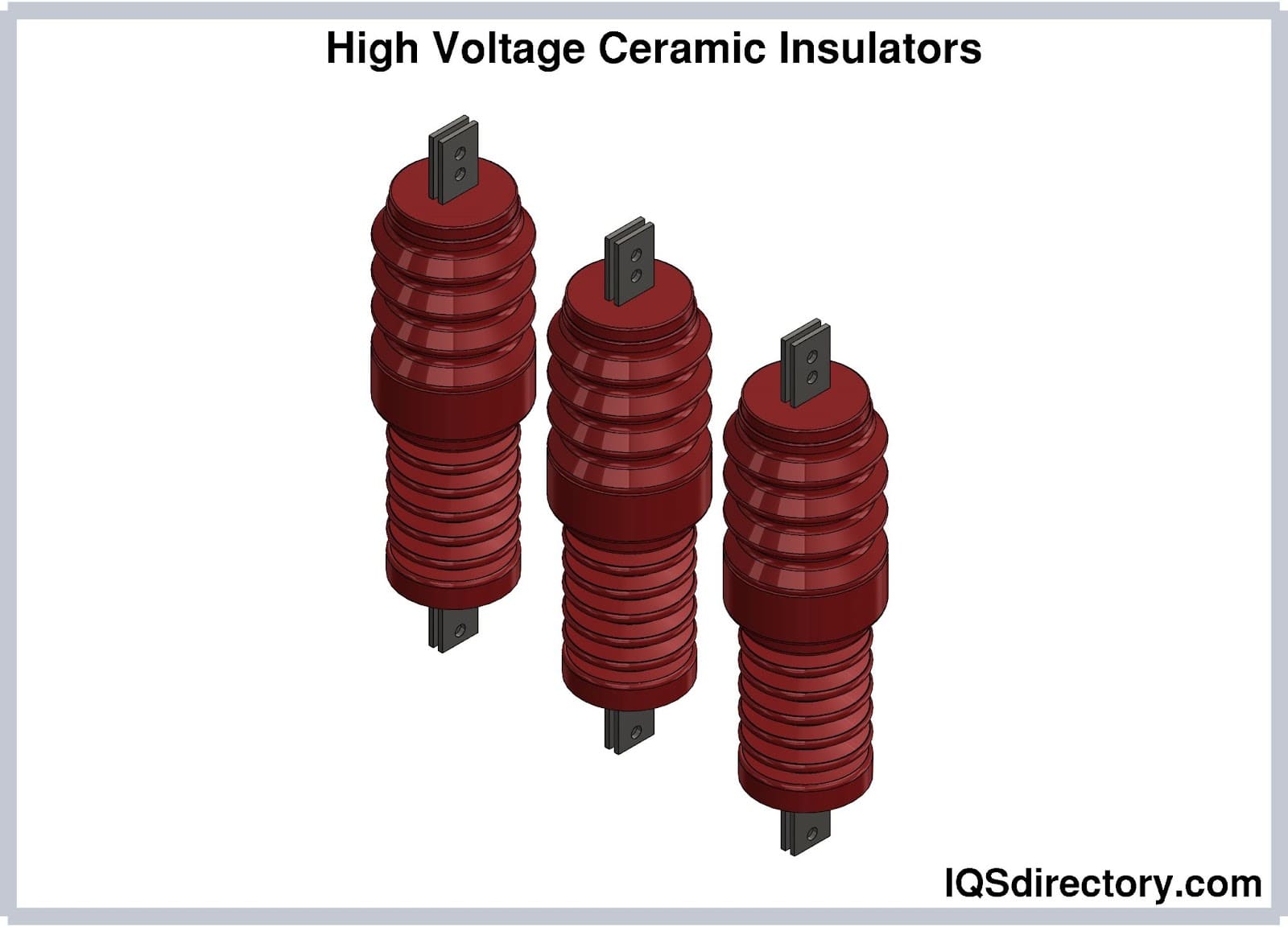
Illustrative image related to ceramic electrical insulator
How Are Ceramic Insulators Essential for Automotive Applications?
In the automotive industry, ceramic electrical insulators are crucial for insulating high-voltage systems found in electric vehicles. These insulators not only enhance safety by preventing electrical shorts but also contribute to the overall performance of electric powertrain systems. Buyers should focus on sourcing insulators that meet automotive standards for durability and thermal performance, particularly in regions with extreme temperature variations. Understanding the specific requirements for high-voltage applications can help buyers select the right materials, ensuring compliance and safety in their automotive designs.
What Benefits Do Ceramic Insulators Offer in Heating Equipment?
Ceramic electrical insulators are commonly used as insulating bushings for electric heating elements. These components enhance energy efficiency by minimizing heat loss and improving overall system performance. For businesses in the heating equipment sector, it is essential to source insulators that can withstand high temperatures and thermal shock. Suppliers that provide products designed for specific heating applications can significantly improve the reliability of heating systems. Additionally, considering the environmental conditions where the equipment will be used can guide buyers in selecting the most suitable materials.
How Do Ceramic Insulators Support Telecommunications?
In telecommunications, ceramic electrical insulators are vital for RF and microwave components, where they help maintain signal integrity and system reliability. The insulators ensure that high-frequency signals are transmitted without interference, which is critical for the performance of communication networks. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing insulators that exhibit high-frequency performance and resilience to environmental factors, such as humidity and temperature fluctuations. Engaging with suppliers who understand the specific challenges of telecommunications can lead to better product selection and long-term operational success.
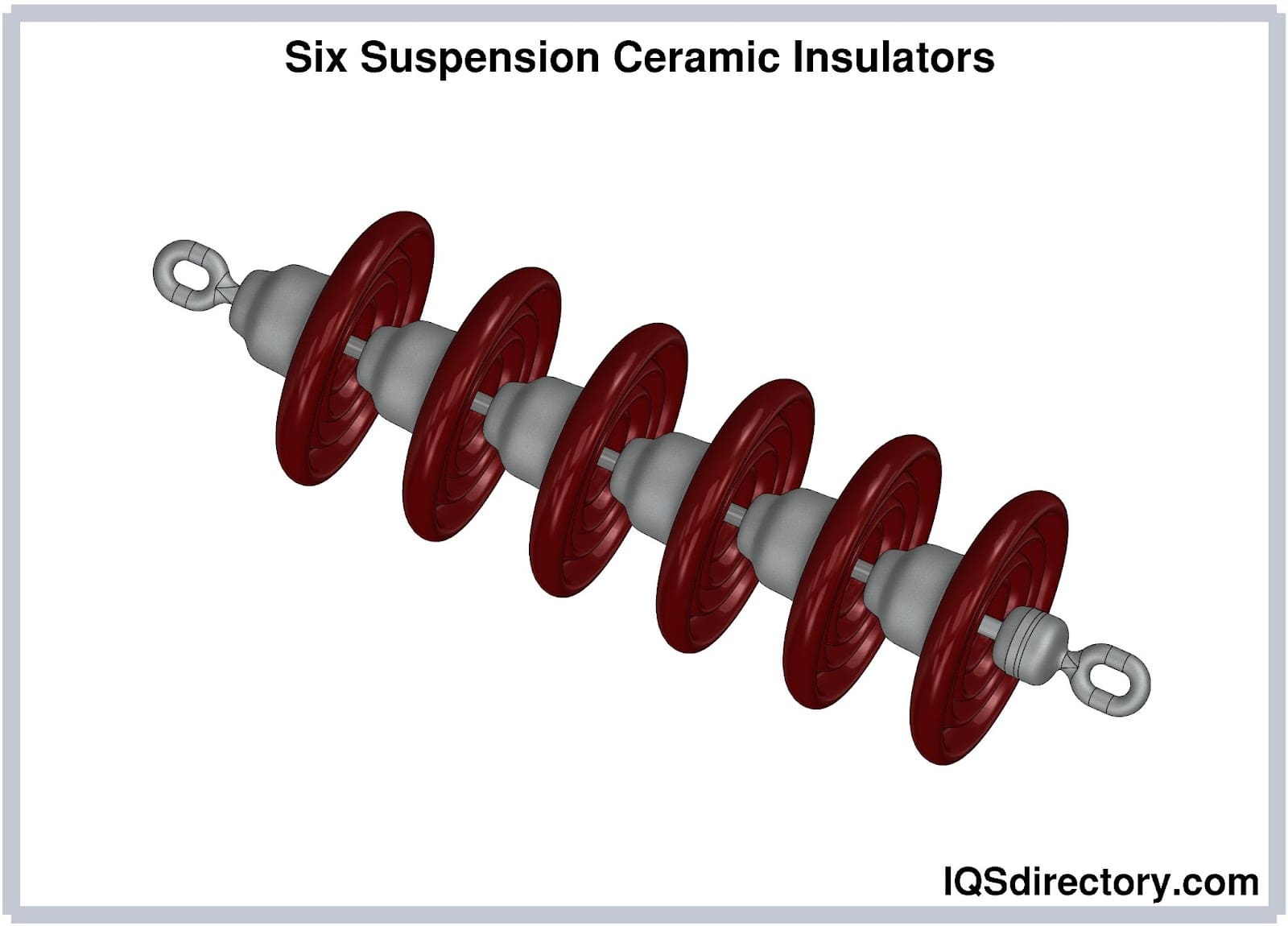
Illustrative image related to ceramic electrical insulator
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘ceramic electrical insulator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Material for Specific Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter challenges when selecting the appropriate ceramic electrical insulator material for their specific applications. The market offers a variety of materials such as alumina, cordierite, and steatite, each with distinct properties like dielectric strength, thermal conductivity, and chemical resistance. This diversity can lead to confusion, especially for buyers who may not be familiar with the technical specifications required for their electrical systems. Inadequate selection can result in system failures, reduced efficiency, and increased costs due to improper insulation.
The Solution: To navigate this complexity, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their application requirements. Start by evaluating the operating environment, including temperature ranges, exposure to chemicals, and mechanical stresses. For high-temperature applications, consider alumina for its exceptional dielectric strength and thermal conductivity. If thermal shock resistance is crucial, cordierite may be the ideal choice due to its low thermal expansion. When looking for a cost-effective solution for moderate temperatures, steatite can offer reasonable performance. Collaborating with suppliers who provide detailed technical data sheets and can offer expert guidance can streamline the selection process. Additionally, engaging in prototype testing can help ensure that the chosen material meets the performance criteria before full-scale implementation.
Scenario 2: Insufficient Understanding of Installation Techniques
The Problem: Buyers often face difficulties related to the installation of ceramic electrical insulators, which can lead to improper functioning and increased maintenance costs. The lack of knowledge about best practices for installation, including torque specifications and securing methods, can result in damage to the insulators or surrounding components. This not only affects the longevity of the insulators but also poses safety risks in electrical applications.
The Solution: To mitigate installation issues, it is crucial to provide comprehensive training for personnel involved in the installation process. Buyers should seek suppliers that offer detailed installation guidelines, including visual aids and step-by-step instructions. Implementing a standard operating procedure (SOP) for installation can ensure consistency and adherence to best practices. Additionally, consider using specialized tools designed for ceramic insulator installations, as these can help in applying the correct torque and reducing the risk of damage. Regular training sessions and workshops can further enhance the team’s understanding of installation techniques, leading to improved performance and reliability of the electrical systems.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Sourcing High-Quality Insulators
The Problem: Sourcing high-quality ceramic electrical insulators can be a significant pain point for B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where supply chains may be less established. Poor-quality insulators can lead to frequent failures and increased downtime, ultimately impacting the bottom line. Buyers often struggle with a lack of reliable suppliers, limited product availability, and variations in quality, which complicates their procurement processes.
The Solution: To address sourcing challenges, buyers should establish strong relationships with reputable manufacturers and distributors who specialize in ceramic electrical insulators. Conducting a thorough vetting process, including checking references, reviewing certifications, and analyzing previous projects, can help ensure the quality of the products. Joining industry associations or networks can also provide access to a wider range of trusted suppliers. Additionally, consider implementing a quality assurance program that includes incoming inspections and testing for critical specifications, which can help maintain standards across the supply chain. Engaging in long-term contracts with suppliers can also secure consistent product availability, reducing the risk of supply interruptions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for ceramic electrical insulator
What Are the Key Properties of Common Ceramic Materials for Electrical Insulators?
When selecting materials for ceramic electrical insulators, understanding the specific properties of each material is crucial. This analysis focuses on four common ceramic materials: Alumina, Cordierite, Steatite, and Zirconia, which are widely used in various applications.
Alumina: A High-Performance Insulator
Alumina, or aluminum oxide, is renowned for its exceptional mechanical strength and electrical resistance. It can withstand temperatures up to 2000°C and has high thermal conductivity, making it suitable for high-temperature applications. Alumina’s low porosity (0-0.05%) contributes to its durability and resistance to chemical corrosion.
Pros: Its high dielectric strength and thermal stability make it ideal for electrical applications, particularly in harsh environments.
Cons: However, the manufacturing process can be complex and costly, which may deter some buyers.
Impact on Application: Alumina is particularly effective in environments where high temperatures and chemical exposure are prevalent, such as power generation and aerospace.

Illustrative image related to ceramic electrical insulator
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards like ASTM and DIN is essential, especially in regions like Europe, where stringent regulations apply.
Cordierite: The Thermal Shock Resistant Material
Cordierite is known for its excellent thermal shock resistance and low thermal expansion. It can endure rapid temperature fluctuations, which is beneficial in applications involving heating elements. Cordierite typically operates effectively at temperatures up to 1400°C.
Pros: Its ability to withstand thermal cycling makes it suitable for applications in electric heating systems.
Cons: While it is less expensive than alumina, its mechanical strength is lower, which may limit its use in high-stress applications.

Illustrative image related to ceramic electrical insulator
Impact on Application: Cordierite is ideal for insulating electrical heating coils and other applications where rapid heating and cooling occur.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the material meets local standards and regulations, particularly in regions with specific thermal performance requirements.
Steatite: The Economical Insulator
Steatite is a cost-effective ceramic material that offers reasonable strength and durability. It can operate at temperatures up to 1100°C and has good dielectric properties, making it suitable for various electrical applications.
Pros: Its affordability and decent thermal and electrical performance make it a popular choice for many manufacturers.
Cons: However, it has lower mechanical strength compared to alumina and may not be suitable for high-stress environments.
Impact on Application: Steatite is commonly used in applications where cost is a primary concern, such as in consumer electronics and basic electrical components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying quality standards across regions, ensuring that the selected steatite meets the necessary compliance for their specific market.
Zirconia: The High-Performance Insulator
Zirconia is recognized for its high mechanical strength and toughness, along with excellent thermal stability. It can withstand temperatures exceeding 2500°C, making it suitable for extreme environments.
Pros: Its superior properties make it ideal for applications requiring high reliability under extreme conditions.
Cons: The cost of zirconia is relatively high, which may not be justified for all applications.
Impact on Application: Zirconia is often used in high-performance electrical insulators in industries such as aerospace and medical devices.

Illustrative image related to ceramic electrical insulator
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers need to consider the cost versus performance trade-off and ensure compliance with industry-specific standards in their region.
Summary Table of Ceramic Electrical Insulator Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for ceramic electrical insulator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina | High-temperature electrical applications | Exceptional mechanical strength | Complex and costly manufacturing | High |
| Cordierite | Electrical heating systems | Excellent thermal shock resistance | Lower mechanical strength | Medium |
| Steatite | Consumer electronics | Cost-effective and decent performance | Lower strength in high-stress areas | Low |
| Zirconia | Aerospace and medical devices | High performance in extreme conditions | Higher cost | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of various ceramic materials used in electrical insulators, assisting international B2B buyers in making informed decisions tailored to their specific applications and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for ceramic electrical insulator
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Ceramic Electrical Insulators?
The manufacturing of ceramic electrical insulators involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is critical to ensure the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards.
-
Material Preparation: The first step involves selecting high-quality raw materials, such as alumina, steatite, or cordierite. These materials are processed to remove impurities and ensure uniformity. The selected ceramics are then mixed with additives that enhance their properties, such as strength and thermal resistance. The mixture is finely ground to achieve the desired particle size, which is crucial for the subsequent forming process.
-
Forming: Once the materials are prepared, they are shaped into the desired forms using various techniques. Common methods include pressing, extrusion, and slip casting. In pressing, the powdered ceramic is placed in a mold and subjected to high pressure, creating a dense component. Extrusion involves forcing the material through a die to create long shapes, while slip casting uses a liquid mixture poured into molds to achieve intricate designs. The chosen method depends on the type of insulator being produced and the specific requirements of the application.
-
Assembly: For insulators that require multiple components, assembly is the next step. This may involve attaching various parts or integrating additional features such as metal fittings. It is essential to ensure that all components are properly aligned and securely bonded to prevent failures during operation.
-
Finishing: The final stage includes drying and firing the insulators in a kiln at high temperatures. This process not only hardens the ceramic but also enhances its electrical properties. After firing, the insulators undergo surface treatments, such as glazing or polishing, to improve their aesthetic qualities and resistance to environmental factors. Rigorous quality checks are performed to ensure dimensional accuracy and surface integrity.
How Do Quality Assurance Standards Impact Ceramic Insulator Production?
Quality assurance (QA) in the manufacturing of ceramic electrical insulators is paramount to ensure safety, reliability, and performance. Various international and industry-specific standards guide this process.
-
International Standards: Many manufacturers adhere to ISO 9001, which sets the criteria for a quality management system. This standard emphasizes customer satisfaction and continuous improvement. Compliance with ISO standards is often a prerequisite for B2B transactions, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East.
-
Industry-Specific Standards: In addition to ISO standards, there are specific certifications that may apply to ceramic electrical insulators, such as CE marking for products sold in the European Economic Area, and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for insulators used in the oil and gas industry. These certifications ensure that the products meet specific safety and performance criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Ceramic Insulator Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout the manufacturing process, with several critical checkpoints to ensure product integrity.
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected for quality and compliance with specifications. This includes verifying the chemical composition and physical characteristics of the ceramics. Any non-conforming materials are rejected to prevent defects in the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various parameters are monitored, such as temperature during firing and pressure during forming. Operators conduct regular inspections to ensure that processes remain within specified tolerances. This proactive approach helps identify potential issues before they escalate.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, finished insulators undergo comprehensive testing. This includes electrical insulation tests, mechanical strength assessments, and thermal shock resistance evaluations. These tests verify that the products meet the established performance criteria and are suitable for their intended applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial. Here are several methods to ensure confidence in supplier QC:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to international standards. This hands-on approach provides insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including testing results and compliance certifications, enables buyers to evaluate the supplier’s performance history. These documents should outline the methodologies used for testing and any corrective actions taken for non-conformities.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. These agencies often have expertise in specific industries and can offer detailed evaluations based on established standards.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Control?
International B2B buyers must navigate various nuances when dealing with quality control in different regions. Each market may have unique regulatory requirements, cultural expectations, and quality perceptions. Here are some considerations:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Understanding the regulatory landscape in the target market is essential. For instance, European buyers must ensure compliance with CE marking requirements, while South American and Middle Eastern markets may have different standards.
-
Cultural Expectations: Attitudes towards quality and reliability can vary significantly by region. Buyers should be aware of local expectations and norms regarding product quality, which may influence their supplier selection process.
-
Communication and Documentation: Clear communication regarding quality expectations and documentation requirements is vital for successful international transactions. Buyers should ensure that suppliers provide comprehensive documentation that meets both local and international standards.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for ceramic electrical insulators are intricate and critical for ensuring product reliability. By understanding these processes and verifying supplier quality controls, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘ceramic electrical insulator’
When sourcing ceramic electrical insulators, it’s vital to follow a structured approach to ensure you select the right products that meet your technical and operational needs. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to facilitate your procurement process, ensuring you make informed decisions while navigating the complexities of international sourcing.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for selecting the appropriate ceramic electrical insulator. Consider factors such as material type (e.g., alumina, cordierite, steatite), dielectric strength, thermal conductivity, and maximum operating temperature. This clarity will guide your interactions with suppliers and help you avoid mismatches in product capabilities.
Step 2: Identify Application Requirements
Different applications may demand specific insulator features. For instance, high-temperature applications may require insulators made from materials like alumina, while those needing rapid thermal shock resistance might benefit from cordierite. Understanding the precise requirements of your application will help you narrow down your options effectively.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s essential to conduct a thorough evaluation. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and references from other buyers in your industry. Look for suppliers with experience in your specific application area, as this can significantly impact the reliability and performance of the insulators you purchase.
- Check Certifications: Ensure that suppliers comply with international quality standards, such as ISO certifications, to guarantee product reliability.
- Assess Production Capabilities: Inquire about their manufacturing processes and technology to ensure they can meet your volume and quality demands.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the ceramic insulators you are considering. Testing samples in your specific application can provide valuable insights into performance, durability, and compatibility. This step is particularly important for insulators that will operate under extreme conditions.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have identified potential suppliers and tested their products, it’s time to negotiate terms and pricing. Discuss bulk purchase discounts, payment terms, and shipping logistics to ensure a favorable deal. Don’t hesitate to compare multiple quotes to ensure you are getting the best value for your investment.

Illustrative image related to ceramic electrical insulator
Step 6: Confirm Delivery and Lead Times
Effective project management relies on timely deliveries. Confirm the lead times for production and shipping with your chosen supplier to align with your project timelines. Ensure that they have reliable logistics partners, especially if you are sourcing internationally.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Assurance Process
After placing your order, set up a quality assurance process to monitor the insulators upon arrival. Inspect the products against your original specifications and test them in your applications to ensure they meet performance expectations. Establishing this process will help you maintain high standards in your operations and avoid costly disruptions.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing ceramic electrical insulators effectively, ensuring that they select products that meet their technical needs and business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for ceramic electrical insulator Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Ceramic Electrical Insulator Sourcing?
When sourcing ceramic electrical insulators, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of material significantly impacts the cost. Common materials such as alumina, cordierite, and steatite each have unique properties and pricing. For instance, while alumina offers high dielectric strength and thermal conductivity, it tends to be more expensive than steatite, which is a more economical option.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce required for manufacturing, assembling, and quality control. Skilled labor is essential for precision machining and ensuring that insulators meet strict specifications, particularly in high-temperature applications.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, maintenance of machinery, and facility costs. Efficient production processes can reduce overhead and contribute to competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for molds and specialized machinery can be significant, particularly for custom designs. These costs are often amortized over the production volume, making them a vital consideration in pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing and quality assurance processes ensure that insulators meet industry standards and specifications. Higher QC costs can lead to better product reliability, which is particularly important for critical applications.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs should not be overlooked, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and import duties can significantly affect total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their risks and operational costs. This margin can vary based on market conditions and the supplier’s positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Sourcing of Ceramic Insulators?
Several factors influence the pricing of ceramic electrical insulators:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Understanding a supplier’s MOQ can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs tailored to specific applications may incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential price increase.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Insulators meeting stringent quality standards or possessing certifications (e.g., ISO, RoHS) may command higher prices. Buyers must assess the necessity of these certifications based on their application requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer better quality and service but at a premium price.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international buyers. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) determine who bears the shipping costs and risks, affecting the overall price.
What Tips Can Buyers Use to Optimize Costs When Sourcing Ceramic Insulators?
B2B buyers can employ several strategies to ensure cost-effective sourcing:
-
Negotiation: Engaging in discussions about pricing, especially when placing large orders, can yield significant savings. Suppliers are often willing to negotiate terms to secure large contracts.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Conduct a thorough analysis of the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also logistics, maintenance, and potential failure costs. This holistic view can lead to better decision-making.
-
Market Research: Stay informed about market trends and pricing fluctuations. Understanding the competitive landscape can empower buyers in negotiations and help identify the best suppliers.
-
Consider Alternative Materials: Evaluate the need for high-end materials versus more economical options based on application requirements. This can lead to substantial cost savings without compromising performance.
-
Build Long-Term Relationships: Establishing long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers can lead to better pricing, improved service, and priority access to new products.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
The prices mentioned in various sources, such as $31.00 for a package of ceramic insulators or $86.70 for specific bushing models, are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier agreements, and specific buyer requirements. Always request up-to-date quotes and conduct thorough market research to ensure competitive sourcing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing ceramic electrical insulator With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Ceramic Electrical Insulators
In the realm of electrical insulation, ceramic insulators are often favored for their durability and high-temperature resistance. However, various alternatives exist that may better suit specific applications or budgetary constraints. This section will compare ceramic electrical insulators with two viable alternatives: polymer insulators and glass insulators, providing B2B buyers with insights to make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Ceramic Electrical Insulator | Polymer Insulator | Glass Insulator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High dielectric strength and excellent thermal resistance | Good dielectric properties but lower thermal resistance | High dielectric strength and good mechanical properties |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower | Moderate |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific mounting techniques | Easy to install; flexible designs available | Moderate; may require careful handling |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; durable | Moderate; can degrade over time | Low; resistant to weathering |
| Best Use Case | High-temperature applications in power generation | General electrical applications, especially in outdoor settings | Transmission lines and substations |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Polymer Insulators: Pros and Cons
Polymer insulators are made from materials like silicone rubber and offer a lighter alternative to ceramic insulators. Their flexibility allows for easier installation, particularly in outdoor applications where environmental factors can pose challenges. However, while they provide good electrical insulation, they may not withstand extreme temperatures as effectively as ceramic insulators. Over time, exposure to UV radiation and environmental pollutants can lead to degradation, necessitating more frequent replacements.
Glass Insulators: Pros and Cons
Glass insulators have been a long-standing choice in electrical applications due to their excellent dielectric strength and resistance to environmental factors. They are particularly effective in high-voltage transmission lines and substations, where mechanical stability is crucial. While they tend to be cost-effective, glass insulators are heavier and can be more fragile than ceramics, requiring careful handling during installation. They also provide low maintenance requirements, as they resist weathering and chemical damage.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Insulator for Your Needs
When selecting an electrical insulator, it’s essential for B2B buyers to consider the specific requirements of their applications. Ceramic insulators excel in high-temperature environments and provide long-term durability, making them ideal for power generation. Conversely, polymer insulators offer flexibility and ease of installation, making them suitable for various outdoor applications. Glass insulators, while heavier, provide robust performance for high-voltage lines. By weighing the pros and cons of each alternative against their unique operational needs, buyers can make an informed decision that aligns with their strategic objectives and budget.
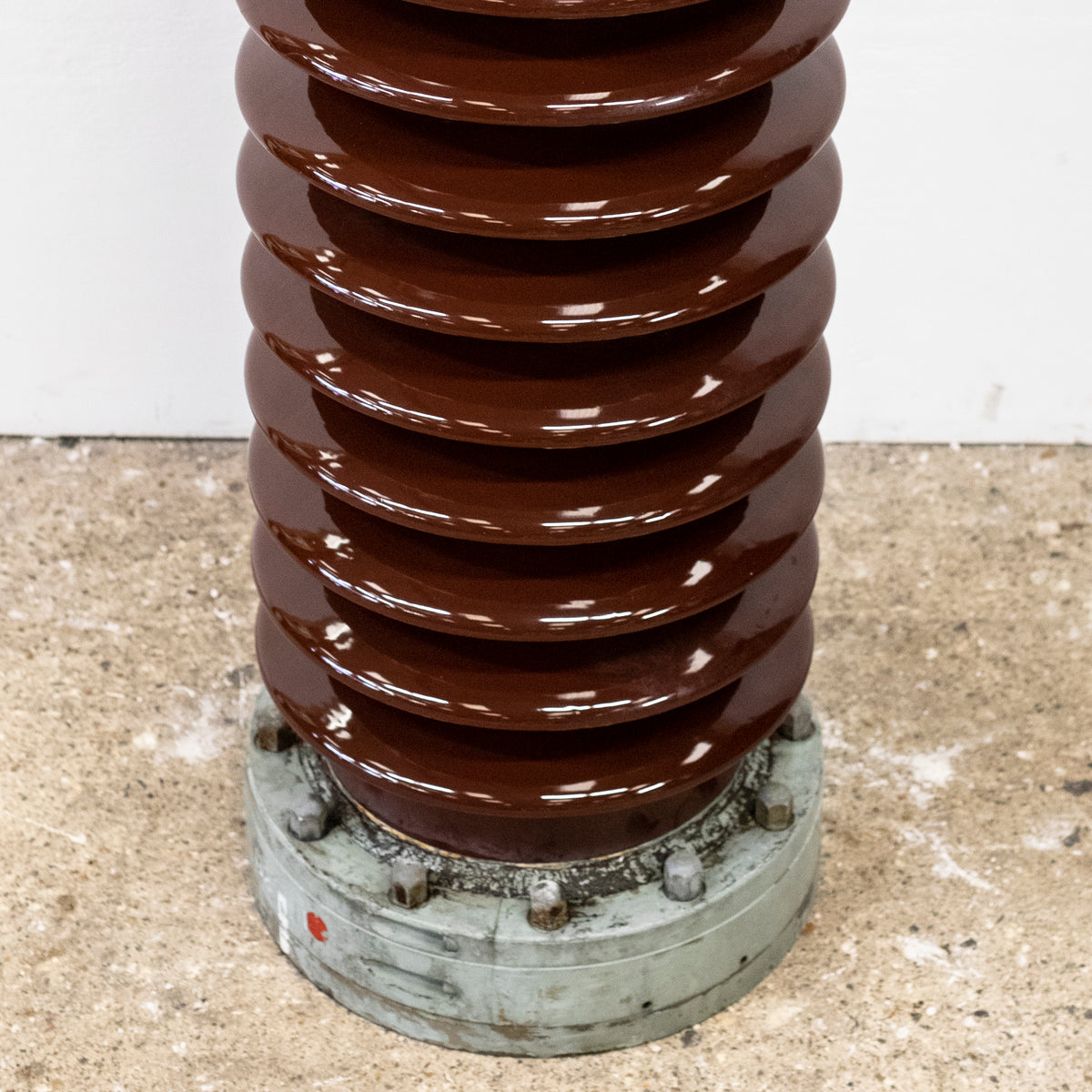

Illustrative image related to ceramic electrical insulator
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for ceramic electrical insulator
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Ceramic Electrical Insulators?
Ceramic electrical insulators are essential components in various industries, including power generation and electronics, due to their superior insulating properties and thermal resistance. Understanding the critical specifications is vital for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
1. Material Grade
The choice of material significantly impacts the performance of ceramic insulators. Common materials include Alumina, Cordierite, and Steatite. Each material has unique properties: Alumina offers high strength and thermal conductivity, Cordierite is known for its thermal shock resistance, while Steatite is a cost-effective option suitable for moderate temperature applications. Selecting the appropriate material grade aligns with operational requirements, ensuring durability and efficiency.
2. Dielectric Strength
Dielectric strength refers to the maximum electric field a material can withstand without breakdown. It is measured in volts per millimeter (V/mm). High dielectric strength is crucial for preventing electrical leakage and ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical systems. For B2B buyers, this property is vital as it directly correlates with the insulator’s performance in high-voltage applications.
3. Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity measures a material’s ability to conduct heat, typically expressed in watts per meter-kelvin (W/m·K). Insulators with low thermal conductivity are preferred as they minimize heat transfer, which is essential for maintaining system efficiency and protecting sensitive components. This specification is particularly important in high-temperature environments, such as electrical heating applications.
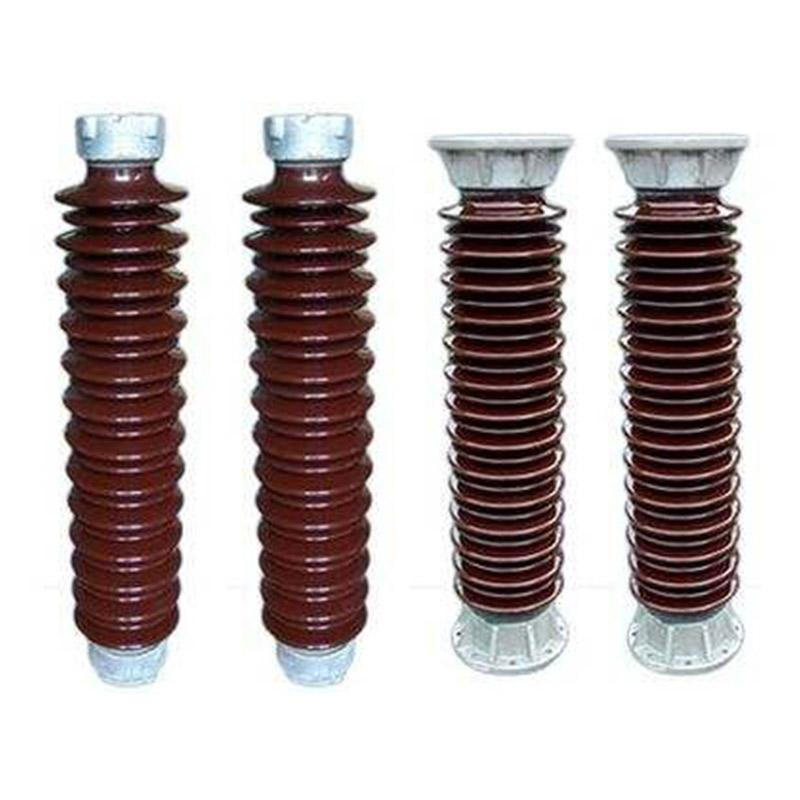

Illustrative image related to ceramic electrical insulator
4. Porosity
Porosity indicates the presence of voids within a material, affecting its mechanical strength and insulation properties. For ceramic insulators, a porosity of 0-0.05% is ideal, as lower porosity enhances strength and reduces moisture absorption, which can compromise electrical insulation. Buyers should evaluate porosity to ensure long-lasting performance in various environmental conditions.
5. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the permissible limits of variation in a product’s dimensions. In ceramic insulators, tight tolerances are critical for ensuring proper fit and function within electrical systems. Tolerance specifications can affect assembly processes and operational efficiency, making it essential for buyers to consider these limits in their procurement decisions.
6. Operating Temperature Range
The operating temperature range specifies the temperatures within which the insulator can function effectively. High-quality ceramic insulators can operate at temperatures exceeding 2000°F (1093°C). This specification is vital for buyers in industries like power generation, where extreme conditions are common, ensuring that the insulator can withstand the operational environment without failure.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Ceramic Insulator Industry?
Understanding industry terminology is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the procurement process.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of ceramic insulators, knowing whether a supplier is an OEM can help buyers assess product quality and compatibility with existing systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is important for buyers to understand as it can affect inventory management and cash flow. Buyers should inquire about MOQs to ensure they can meet their production needs without overcommitting resources.

Illustrative image related to ceramic electrical insulator
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request price quotes from suppliers. It typically includes detailed specifications for the desired product. For ceramic insulators, providing precise specifications in the RFQ ensures that suppliers can deliver accurate quotations and meet buyer expectations.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, including shipping, risk, and insurance. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to clarify their obligations and avoid disputes during the logistics process.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period from the placement of an order to the delivery of the product. It is critical for project planning and inventory management. Buyers should discuss lead times with suppliers to ensure timely delivery of ceramic insulators, especially in industries where downtime can be costly.

Illustrative image related to ceramic electrical insulator
In summary, understanding the essential technical properties and trade terminology related to ceramic electrical insulators empowers B2B buyers to make informed, strategic purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and business objectives.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the ceramic electrical insulator Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics in the Ceramic Electrical Insulator Sector?
The ceramic electrical insulator market is witnessing significant growth, driven by increasing demand across various industries, including power generation, electronics, and automotive sectors. The global shift towards renewable energy sources, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, has accelerated the need for reliable insulation solutions that can withstand high temperatures and harsh environments. Countries such as Brazil and Germany are investing heavily in infrastructure upgrades, further propelling the demand for advanced ceramic insulators.
Emerging trends in this sector include the adoption of advanced materials like alumina and cordierite, which offer superior thermal and electrical properties. International B2B buyers are increasingly looking for custom solutions that can meet specific application requirements. The rise of smart technologies and IoT applications is also influencing the demand for high-performance insulators that ensure reliable signal transmission while minimizing energy losses. Additionally, manufacturers are focusing on innovative designs, such as multi-hole ceramic insulators, to enhance functionality and reduce installation complexities.
How Is Sustainability Influencing B2B Sourcing Trends in Ceramic Electrical Insulators?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the sourcing of ceramic electrical insulators. As industries globally seek to reduce their environmental impact, buyers are prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. This includes using eco-friendly materials, implementing energy-efficient manufacturing processes, and ensuring that their supply chains are transparent and ethical.
The importance of certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and adherence to REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations is also on the rise. Buyers are increasingly looking for products made from recycled or sustainably sourced raw materials, which not only mitigate environmental impact but also enhance brand reputation. Furthermore, suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to sustainability may gain a competitive edge in attracting international clients, particularly in markets like Europe, where environmental regulations are stringent.
What Has Been the Evolution of Ceramic Electrical Insulators in the B2B Market?
The evolution of ceramic electrical insulators dates back to the early 20th century when they were primarily used in telecommunications and power distribution. Over the decades, advancements in material science have led to the development of high-performance ceramics that cater to diverse applications. Initially dominated by traditional materials like porcelain, the market has expanded to include advanced ceramics such as alumina, cordierite, and steatite, which offer enhanced durability and thermal resistance.
As industries continue to evolve with technological advancements, the ceramic electrical insulator market has adapted by introducing innovative designs and applications. This transformation reflects the growing need for insulators that can meet the demands of modern electrical systems, especially in the context of renewable energy and smart technology integration. Today, international B2B buyers benefit from a wide range of options, enabling them to select products that align with their specific operational needs and sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of ceramic electrical insulator
-
How do I choose the right ceramic electrical insulator for high-temperature applications?
Selecting the appropriate ceramic electrical insulator for high-temperature applications involves assessing material properties such as thermal resistance and dielectric strength. Alumina and cordierite are excellent choices, with alumina offering exceptional hardness and thermal stability, while cordierite is notable for its thermal shock resistance. Additionally, consider the specific voltage and environmental conditions your application will encounter to ensure optimal performance and longevity. -
What is the best material for ceramic electrical insulators in humid environments?
For humid environments, steatite and alumina are preferred materials due to their low porosity and high resistance to moisture absorption. Steatite offers good mechanical strength and thermal stability, making it suitable for various applications, while alumina provides superior electrical insulation and corrosion resistance. Ensure that the selected material meets the specific environmental requirements of your application to prevent degradation. -
How can I verify the quality of ceramic electrical insulators from suppliers?
To verify the quality of ceramic electrical insulators, request certification documents such as ISO 9001 and material test reports from potential suppliers. Conduct factory audits or third-party inspections if possible. Additionally, consider asking for samples to evaluate performance metrics like dielectric strength, thermal stability, and mechanical durability before placing a large order. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for ceramic electrical insulators?
Minimum order quantities for ceramic electrical insulators can vary significantly by supplier and the specific product type. Typically, MOQs can range from a few dozen to several hundred units. Discuss your requirements with suppliers to negotiate suitable terms, especially if you are looking for customized solutions or smaller trial orders. -
What are common payment terms for international transactions involving ceramic electrical insulators?
Common payment terms for international transactions may include options like a letter of credit, advance payment, or payment upon delivery. Many suppliers require a deposit (often 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due before shipping or upon receipt. Always clarify payment terms in your contract to avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction process. -
How do logistics and shipping impact the cost of ceramic electrical insulators?
Logistics and shipping can significantly impact the overall cost of ceramic electrical insulators. Factors such as shipping distance, mode of transport (air vs. sea), and customs duties can add to expenses. Collaborate with suppliers to explore the most cost-effective shipping options and consider bulk orders to reduce per-unit shipping costs. Additionally, factor in lead times when planning your supply chain. -
Can ceramic electrical insulators be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for ceramic electrical insulators to meet specific application requirements. Customizations can include variations in size, shape, material composition, and electrical properties. When discussing your project with potential suppliers, provide detailed specifications and application scenarios to ensure the final product meets your operational needs. -
What are the key applications for ceramic electrical insulators in various industries?
Ceramic electrical insulators are widely used across multiple industries, including power generation, electronics, and automotive sectors. They serve critical roles in applications such as electrical element supports, igniter insulators, and wiring board materials. Understanding the specific requirements of your industry can help you select the right insulator type, ensuring reliability and performance in your applications.
Top 6 Ceramic Electrical Insulator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. eBay – Ceramic Insulators for Sale
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Ceramic Insulator for sale on eBay includes various types and conditions such as:
– High Voltage Electric Insulators
– Vintage and Antique Ceramic Insulators
– Porcelain Insulators
– Different colors including brown, purple, khaki, and olive green
– Sizes ranging from small (2-1/2″) to large (10″ diameter)
– Prices ranging from under $15 to over $100
– Conditions: New, Used, Pre-Owned
– Fe…
2. AccuGlass – Ceramic Insulator 2 Hole Design
Domain: accuglassproducts.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: {‘product_name’: ‘Ceramic Insulator 2 Hole design – 0.020″ ID’, ‘part_number’: ‘112292’, ‘material’: ‘Steatite’, ‘rohs_compliant’: ‘Yes’, ‘max_bake_temperature’: ‘450ºC’, ‘max_operating_temperature’: ‘450ºC’, ‘min_operating_temperature’: ‘-200ºC’, ‘max_vacuum_level’: ‘1x10E-10 Torr’, ‘length’: ‘1.00″‘, ‘inner_diameter’: ‘0.020″‘, ‘wire_gauge’: ’24AWG nominal’, ‘quantity_per_package’: ’12’, ‘weight…
3. Associated Ceramics – Custom Electrical and Thermal Insulators
Domain: associatedceramics.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Associated Ceramics is a custom manufacturer of electrical ceramic insulators and thermal ceramic insulators for various industries including appliance, power generation, medical, and electronics. Key materials used include: 1. Alumina: High strength and hardness, excellent electrical resistance, high thermal conductivity, high resistance to chemical and corrosion, 0-0.05% porosity, high dielectri…
4. Kyocera – Fine Ceramics
Domain: global.kyocera.com
Registered: 1993 (32 years)
Introduction: Fine Ceramics, also known as advanced ceramics, are engineered materials that provide electrical insulation, inhibiting electricity from passing through. They are used in products such as packages for surface-mounted electronic components, including quartz crystal oscillators and surface acoustic wave (SAW) filters, which are common in mobile phones, automotive navigation systems, and portable mus…
5. Therm-Coil – Ceramic Insulators for Electrical Heating
Domain: therm-coil.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Ceramic Insulators made from Cordierite for insulating electrical heating coils. Available sizes include:
– 3/4″ O.D. x 5/16″ I.D. x 3/8″ thick
– 7/8″ O.D. x 13/32″ I.D. x 7/16″ thick
– 5/8″ O.D. x 19/64″ I.D. x 29/64″ thick.
Pricing examples:
– PI-3/4-1 Ceramic Insulators (50 Quantity Packs): Original price $102.00, Current price $86.70
– PI-7/8-1 Ceramic Insulator (25 Pack): Original price…
6. Zareba Systems – Ceramic Insulators
Domain: zarebasystems.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Ceramic Insulators:
– Made of red, brown, or white porous clay.
– Fired at temperatures between 2,100° to 2,300° Fahrenheit.
– Less expensive to produce than porcelain.
– Glazed only on the top layer.
– Can chip or break in cold weather.
– Excellent insulation quality.
– Stronger than plastic insulators.
– Standard return policy.
Porcelain Insulators:
– Made from refined white clay (kao…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for ceramic electrical insulator
As the demand for ceramic electrical insulators continues to rise across various industries, strategic sourcing has become a critical component for international buyers. By understanding the diverse materials available—such as alumina, cordierite, and steatite—buyers can select insulators that not only meet their technical specifications but also optimize cost and performance. The ability to leverage suppliers from different regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, allows for greater flexibility and competitive pricing in procurement strategies.
Investing in high-quality ceramic insulators ensures reliability and longevity in electrical applications, which is vital for maintaining operational efficiency and reducing maintenance costs. Moreover, buyers should consider suppliers that offer custom manufacturing capabilities, as this can lead to tailored solutions that enhance product performance.
Looking ahead, the global market for ceramic electrical insulators is poised for growth, driven by advancements in technology and increasing applications in sectors such as renewable energy and electronics. International buyers are encouraged to engage proactively with suppliers, explore innovative solutions, and stay informed about emerging trends to capitalize on this evolving landscape. By doing so, they can secure a competitive edge in their respective markets.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.