Industrial Surface Treatment Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for industrial surface treatment
In the dynamic realm of industrial surface treatment, sourcing the right solutions can be a daunting task for B2B buyers, particularly those operating across diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Companies face the critical challenge of ensuring their products achieve optimal adhesion and durability, which directly impacts performance and safety. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the complexities of industrial surface treatment by exploring various methodologies, applications, and best practices.
From plasma and flame treatments to chemical etching and laser ablation, we will delve into the intricacies of each method, highlighting their respective benefits and limitations. Additionally, we will provide actionable insights on supplier vetting, cost considerations, and the importance of selecting the right treatment for specific materials and applications. By equipping international B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions, this guide empowers them to enhance their manufacturing processes and achieve superior product quality.
As markets evolve, understanding the nuances of industrial surface treatment not only fosters operational efficiency but also positions businesses for competitive advantage in a global landscape. Whether you are based in Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, or beyond, this guide serves as a vital resource for navigating the multifaceted world of surface treatment solutions.
Understanding industrial surface treatment Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma Treatment | Utilizes ionized gas to create reactive surfaces; atmospheric and vacuum variants available. | Electronics, automotive, medical devices | Pros: High precision, adaptable to various materials. Cons: Equipment can be costly; requires expertise for operation. |
| Flame Treatment | Employs a controlled flame to remove contaminants and activate surfaces; effective on low-energy materials. | Plastics, composites, packaging | Pros: Effective for challenging surfaces. Cons: Risk of overheating and damaging materials; less control than plasma. |
| Chemical Etching | Involves using chemical baths to selectively remove material, providing precise surface activation. | Microelectronics, aerospace, medical devices | Pros: High precision and reliability. Cons: Risk of chemical contamination; requires strict process control. |
| Vapor Degreasing | Uses solvent vapor to clean surfaces; economical and reusable solvents possible. | Automotive, manufacturing, electronics | Pros: Cost-effective, effective cleaning. Cons: Environmental regulations on solvents; requires careful monitoring. |
| Laser Ablation | Uses focused laser beams to remove surface material with high precision; suitable for micro/nano applications. | Semiconductor manufacturing, coatings, medical devices | Pros: Extremely precise, versatile applications. Cons: High initial investment; risk of micro-debris contamination. |
What Are the Characteristics and Suitability of Plasma Treatment?
Plasma treatment leverages ionized gas to modify surface properties, enhancing adhesion for various applications. The two main types, atmospheric and vacuum plasma, allow for flexibility in processing different materials. This method is particularly suitable for industries such as electronics and automotive, where high precision is crucial. B2B buyers should consider the upfront costs of plasma equipment and the need for skilled operators, as the technology requires careful calibration for optimal results.
How Does Flame Treatment Work and Where is it Used?
Flame treatment employs a controlled flame to oxidize and activate surfaces, making it ideal for low-energy materials like plastics and composites. This method effectively prepares surfaces for coatings and adhesives, especially in packaging applications. Buyers should weigh the benefits of effective surface activation against the risk of damaging materials due to excessive heat. Understanding the specific requirements of the materials being treated is essential for successful implementation.
What Are the Advantages of Chemical Etching for Surface Activation?
Chemical etching is a precise method that involves immersing materials in temperature-regulated chemical baths to clean and activate surfaces. This technique is commonly used in sectors that demand high reliability, such as microelectronics and aerospace. While it offers exceptional precision, B2B buyers must be aware of the potential for chemical contamination and the need for stringent process controls to maintain quality.

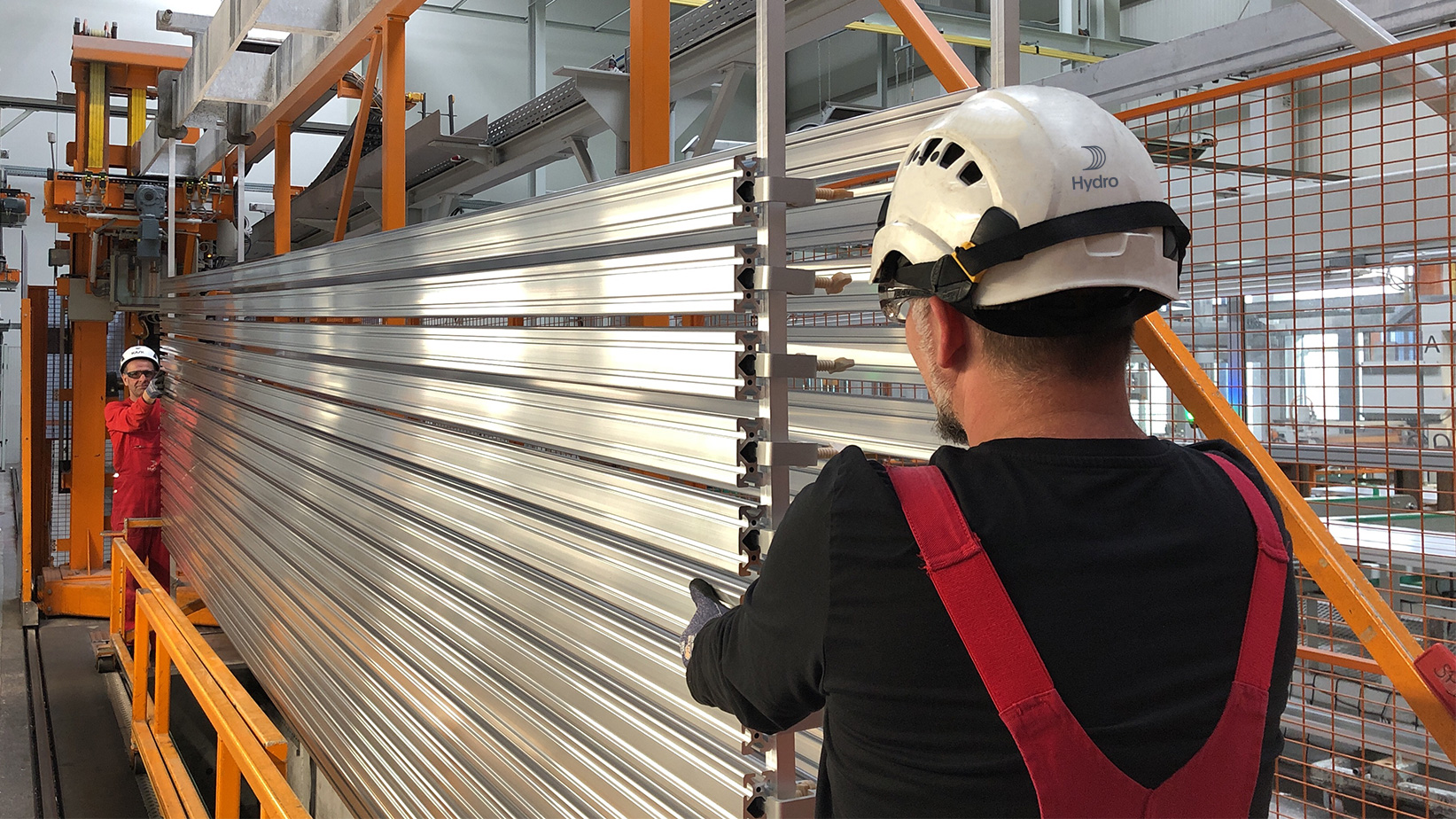
Illustrative image related to industrial surface treatment
Why Choose Vapor Degreasing for Surface Cleaning?
Vapor degreasing utilizes solvent vapors to effectively remove contaminants from surfaces, making it a cost-effective cleaning method for various industries, including automotive and electronics. The ability to recycle solvents can enhance sustainability efforts. However, buyers should be mindful of environmental regulations regarding solvent use and ensure that the cleaning process is closely monitored to prevent contamination.
What Makes Laser Ablation a Precise Surface Treatment Option?
Laser ablation employs focused laser beams to remove material from surfaces with remarkable precision, making it suitable for applications in semiconductor manufacturing and medical device coatings. This method allows for micro and nano-level control but comes with a high initial investment and the risk of creating micro-debris that can affect surface quality. Buyers should assess their specific application needs and budget constraints when considering this advanced technology.
Key Industrial Applications of industrial surface treatment
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of industrial surface treatment | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Coating of metal components for corrosion resistance | Enhances durability and extends the lifespan of parts | Need for high-performance coatings that meet local regulations |
| Electronics | Surface preparation for microelectronics | Ensures reliable adhesion of components, reducing failures | Precision in surface treatment to prevent contamination |
| Medical Devices | Surface treatment for biocompatibility | Improves patient safety and device performance | Compliance with strict health regulations and standards |
| Packaging | Treatment of polymer films for printing and coating | Enhances product appearance and shelf life | Compatibility with various printing technologies |
| Aerospace | Surface finishing of aircraft components | Reduces weight and improves fuel efficiency | Adherence to rigorous safety and performance standards |
How is Industrial Surface Treatment Applied in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, surface treatment is primarily utilized for coating metal components to enhance corrosion resistance. This process is critical for extending the lifespan of parts exposed to harsh environmental conditions. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East, sourcing high-performance coatings that comply with local regulations is essential. This ensures not only durability but also compliance with safety standards, which can vary significantly by region.
What Role Does Surface Treatment Play in Electronics?
Surface preparation in the electronics sector is vital for microelectronics, where precise adhesion of components is crucial for device functionality. Industrial surface treatment methods, such as plasma and chemical etching, are employed to create clean, reactive surfaces that promote reliable bonding. For B2B buyers in South America and Europe, ensuring that the chosen surface treatment methods prevent contamination is paramount, as even minor defects can lead to significant product failures.
Why is Surface Treatment Important for Medical Devices?
In the medical device industry, surface treatment is essential for ensuring biocompatibility. This involves modifying the surface properties of devices to enhance interaction with biological tissues, thereby improving patient safety and device performance. Buyers from regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia must consider suppliers who adhere to stringent health regulations and quality standards, as the consequences of non-compliance can be severe.

Illustrative image related to industrial surface treatment
How Does Surface Treatment Enhance Packaging Solutions?
In packaging, surface treatment is applied to polymer films to prepare them for printing and coating. This process enhances both the visual appeal and the shelf life of products, making them more attractive to consumers. For international B2B buyers, it is crucial to ensure that the treatments used are compatible with various printing technologies, as this can affect the overall quality and effectiveness of the packaging solutions.
What Benefits Does Surface Treatment Provide in the Aerospace Industry?
Surface finishing of aircraft components through industrial surface treatment plays a significant role in reducing weight and improving fuel efficiency. This is particularly important in the aerospace sector, where even minor improvements can lead to substantial cost savings over time. Buyers must ensure that their sourcing decisions comply with rigorous safety and performance standards, which are critical in this highly regulated industry.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘industrial surface treatment’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Adhesion Quality Across Different Materials
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the challenge of achieving consistent adhesion quality when using industrial surface treatment across a variety of materials. For instance, a manufacturer may need to bond metal with plastic, but the chemical properties of these substrates can differ significantly. This inconsistency can lead to adhesion failures, resulting in product defects and increased production costs. Buyers often feel overwhelmed by the need for specialized treatments tailored to each material, which can complicate their production processes and increase turnaround times.
The Solution: To address this issue, it’s essential to implement a comprehensive surface treatment strategy that includes a detailed analysis of the materials being used. Start by conducting thorough surface energy tests for each substrate, which will inform you about the appropriate surface treatment method to use. For example, plasma treatment may be ideal for plastics, while chemical etching can enhance the surface of metals. Collaborating with surface treatment experts can provide insights into the most effective methods tailored to your specific materials. Additionally, investing in real-time surface quality monitoring equipment can help ensure that the surface treatments are achieving the desired adhesion levels consistently.
Scenario 2: Inefficient Surface Preparation Leading to Contamination
The Problem: Contamination during the surface preparation phase is a common pain point for B2B buyers in the industrial sector. Many manufacturers encounter issues where the surfaces of their components are contaminated with oils, dust, or residues from previous processes. This contamination can severely compromise adhesion quality, leading to costly rework and delays in production. Buyers often struggle to find efficient cleaning methods that ensure surfaces are adequately prepared for bonding or coating.
The Solution: To mitigate contamination issues, it is crucial to establish standardized cleaning protocols that include both pre-treatment and post-treatment checks. Utilizing methods like vapor degreasing or laser ablation can effectively remove contaminants without damaging the substrate. Ensure that your cleaning processes are integrated into the production line, allowing for seamless transitions between stages. Furthermore, consider implementing a cleanliness verification step using tools like contact angle measurement devices to assess surface readiness before proceeding to the adhesion phase. Regular training for staff on contamination risks and best practices will also bolster the effectiveness of these measures.
Scenario 3: High Costs Due to Over-treatment or Under-treatment
The Problem: Buyers often encounter financial strain due to the high costs associated with either over-treatment or under-treatment of surfaces during the industrial surface treatment process. Over-treatment can lead to the degradation of the material, while under-treatment may result in inadequate adhesion. Both scenarios can cause increased scrap rates and rework, significantly impacting the bottom line. Buyers may feel frustrated as they navigate the complexities of optimizing treatment levels for different applications.
The Solution: To avoid the pitfalls of over-treatment and under-treatment, it’s vital to implement a controlled surface treatment process that utilizes advanced monitoring technologies. Employing surface analysis tools can help assess the effectiveness of treatment and ensure that the correct parameters are being used. For example, utilizing a Surface Analyst can provide real-time feedback on surface energy levels, allowing for adjustments before the final adhesion process. Additionally, developing a clear standard operating procedure (SOP) that outlines optimal treatment durations and conditions for various materials can help standardize practices across your production team. This systematic approach will not only reduce costs but also enhance the overall quality of your products.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for industrial surface treatment
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Industrial Surface Treatment?
When selecting materials for industrial surface treatment, understanding their properties is crucial for ensuring product performance and longevity. Below, we analyze four common materials used in surface treatment processes, focusing on their key properties, pros and cons, impact on applications, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.

Illustrative image related to industrial surface treatment
1. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has a high strength-to-weight ratio. It can withstand temperatures up to 600°C (1112°F) and is non-magnetic, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The durability of aluminum is commendable, especially in environments prone to oxidation. However, it can be more expensive than other metals like steel. The manufacturing complexity is moderate, as it requires specific techniques for surface treatment, such as anodizing or chemical etching, to enhance its properties.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is widely used in the aerospace and automotive industries due to its excellent weight-to-strength ratio. It is compatible with various media, including water and oils, but may not perform well in highly acidic environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should be aware of compliance with standards such as ASTM B580 for anodizing. Additionally, the availability of aluminum may vary, necessitating local sourcing strategies.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures (up to 800°C or 1472°F). Its mechanical properties are robust, making it suitable for high-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to rust and staining. However, it tends to be more expensive than carbon steel, and its surface treatments, such as passivation or electropolishing, can add to manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical industries due to its hygienic properties. It is compatible with a wide range of media, including harsh chemicals, making it versatile.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe should consider compliance with EN 10088 standards for stainless steel. Additionally, understanding local market preferences for specific grades (e.g., 304 vs. 316) is crucial for ensuring suitability.
3. Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high tensile strength and ability to withstand high pressures. However, it is susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its low cost and ease of manufacturing. However, it requires surface treatments like galvanization or powder coating to improve corrosion resistance, which can complicate the manufacturing process.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is commonly used in construction and heavy machinery. Its compatibility with various media is good, but it can corrode quickly in moist or corrosive environments without proper treatment.

Illustrative image related to industrial surface treatment
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from South America should be aware of ASTM A123 for hot-dip galvanizing standards. Local regulations regarding environmental impact and safety standards must also be considered.
4. Plastics (Polymer Materials)
Key Properties: Plastics are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can be engineered for specific properties such as flexibility or rigidity. They can withstand temperatures up to 120°C (248°F) depending on the type.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of plastics is their versatility and low weight. However, they may not be suitable for high-temperature applications and can be less durable than metals. Surface treatments like corona or plasma treatment are often required for effective adhesion.

Illustrative image related to industrial surface treatment
Impact on Application: Plastics are widely used in consumer goods, packaging, and electronics. Their compatibility with various media is generally good, but they can degrade under UV exposure or extreme temperatures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East should consider compliance with ISO 9001 for quality management systems. Understanding local preferences for specific plastic grades and treatment methods is essential for successful applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Industrial Surface Treatment
| Material | Typical Use Case for industrial surface treatment | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost compared to other metals | High |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing equipment, chemical tanks | Excellent corrosion resistance | More expensive and complex to treat | High |
| Carbon Steel | Construction, heavy machinery | Low cost and high tensile strength | Susceptible to corrosion without treatment | Low |
| Plastics | Consumer goods, packaging | Versatile and lightweight | Limited high-temperature performance | Medium |
This table provides a concise overview of the materials analyzed, allowing international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for industrial surface treatment
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Industrial Surface Treatment?
The manufacturing process for industrial surface treatment involves several critical stages, each designed to optimize the surface properties of materials. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to ensure product quality and performance.
How Does Material Preparation Influence Surface Treatment?
Material preparation is the first and arguably the most crucial stage in the surface treatment process. This phase involves cleaning and conditioning the surface of the materials to remove contaminants such as oils, dust, and oxides that can hinder adhesion. Techniques such as chemical etching, vapor degreasing, and mechanical cleaning are commonly employed.
-
Chemical Etching: This method utilizes temperature-regulated chemical baths to selectively remove contaminants and prepare metal surfaces. Precision is key, as improper control can lead to chemical residues that affect adhesion.
-
Vapor Degreasing: By generating solvent vapors that condense on the material’s surface, this method effectively removes contaminants. It’s a cost-effective approach, especially when solvents can be recovered and reused.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
Once materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This process shapes the materials into their desired forms, often using techniques like stamping, molding, or machining. The choice of technique can significantly influence the effectiveness of subsequent surface treatments.
-
Molding and Casting: These techniques are used for producing complex shapes and can incorporate surface treatments during the process to enhance adhesion properties.
-
Machining: Precision machining can create surfaces that are ideal for bonding or coating, especially when paired with advanced surface treatment methods like laser ablation.
How Is Assembly Conducted in Surface Treatment Processes?
The assembly stage involves joining treated surfaces together. This is where the effectiveness of the surface treatment is put to the test. Various bonding methods, including adhesives, welding, and fastening, are applied based on the materials and intended application.
-
Adhesive Bonding: This method requires rigorous surface preparation to ensure strong adhesion. The surface must be treated to promote chemical bonding between the adhesive and the substrate.
-
Welding: For metals, welding can be an effective assembly method, but surfaces must be clean and free from oxidation to ensure strong joints.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used?
Finishing techniques enhance the surface’s appearance and functionality. This stage can include coating, painting, or applying protective films.

Illustrative image related to industrial surface treatment
-
Coating: Techniques such as powder coating or liquid painting provide protective layers that improve durability and resistance to environmental factors.
-
Surface Modifications: Additional treatments, like anodizing or galvanizing, may be applied to enhance corrosion resistance, which is particularly important in harsh environments common in industries across Africa, South America, and the Middle East.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Industrial Surface Treatment?
Quality assurance is paramount in industrial surface treatment to guarantee that products meet international standards and customer expectations.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers adhere to relevant international quality standards. ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard for quality management systems, focusing on meeting customer requirements and enhancing satisfaction. Industry-specific standards such as CE marking for safety and API standards for the oil and gas sector are also crucial.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) in surface treatment involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint examines raw materials and components upon arrival. Ensuring that materials meet specified standards helps prevent issues later in the process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during manufacturing monitor the treatment processes and ensure adherence to specifications. This stage is critical for identifying and rectifying any issues before they escalate.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection involves testing the finished product against predetermined criteria to ensure that it meets all quality standards before delivery.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers maintain rigorous QC processes, B2B buyers can implement several verification strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their QC processes and adherence to standards. This proactive approach helps identify potential issues before they impact the supply chain.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can offer transparency into their QC measures and outcomes. These documents should outline testing results, process validations, and any corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s QC processes and product quality. This step is particularly beneficial for international buyers concerned about varying standards across regions.
What Are the Nuances of QC and Certification for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of QC and certification is vital.

Illustrative image related to industrial surface treatment
-
Regional Standards: Different regions may have specific regulations and standards that must be adhered to. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local compliance requirements to avoid legal and logistical challenges.
-
Certification Validity: Buyers should verify the validity of certifications provided by suppliers, ensuring they are up to date and recognized internationally. This diligence can prevent reliance on outdated or irrelevant certifications that may not reflect current practices.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices and quality expectations can enhance communication and foster stronger supplier relationships.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in industrial surface treatment, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance product quality, reliability, and performance. This knowledge empowers buyers to choose suppliers who align with their quality standards and operational needs, ultimately driving business success.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘industrial surface treatment’
In the competitive landscape of industrial manufacturing, sourcing effective surface treatment solutions is essential for enhancing product performance and longevity. This guide serves as a practical checklist to assist B2B buyers in evaluating and procuring industrial surface treatment services and technologies.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before beginning the sourcing process, it’s critical to outline your technical requirements. This includes identifying the materials you will be treating, the desired surface properties (e.g., adhesion, corrosion resistance), and any industry-specific standards that must be met. Clear specifications help streamline supplier selection and ensure compatibility with your manufacturing needs.
Step 2: Research Available Surface Treatment Methods
Familiarize yourself with various surface treatment techniques, such as plasma, flame, corona treatments, and chemical etching. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each method will enable you to choose the most suitable option for your application. Consider factors such as material type, treatment scale, and environmental impact in your evaluation.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they meet your quality and service expectations. Request detailed company profiles, including certifications and compliance with relevant industry standards. Additionally, seek references or case studies from other clients, particularly those in similar industries or regions, to gauge reliability and performance.

Illustrative image related to industrial surface treatment
Step 4: Assess Equipment and Technology
Examine the equipment and technology utilized by suppliers for surface treatment processes. Advanced technologies, such as laser ablation or vacuum plasma systems, often yield superior results. Ensure that the supplier’s capabilities align with your technical specifications and inquire about their process monitoring systems to maintain quality control.
Step 5: Verify Quality Control Procedures
Quality assurance is paramount in surface treatment. Investigate the supplier’s quality control measures, including testing protocols and surface readiness assessment tools. A reputable supplier should provide documentation of their quality assurance processes, demonstrating their commitment to consistent performance and reliability.
Step 6: Request Sample Treatments
Before finalizing your supplier choice, request sample treatments to evaluate their capabilities firsthand. This step allows you to assess the effectiveness of the treatment on your materials and the supplier’s adherence to your specifications. Analyze the results meticulously, considering factors like adhesion strength and surface finish.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, lead times, and service terms. Ensure that all agreements are documented clearly to avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, discuss potential for scalability in treatment processes should your production needs evolve in the future.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for industrial surface treatment, ensuring they select the right suppliers and methods to meet their manufacturing goals.

Illustrative image related to industrial surface treatment
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for industrial surface treatment Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Industrial Surface Treatment?
When evaluating the cost structure of industrial surface treatment, several critical components must be considered. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences costs. Different surface treatment methods, such as plasma or chemical etching, require specific consumables that can vary in price based on quality and availability. For example, high-purity chemicals for etching may be more expensive but are crucial for industries like microelectronics.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for operating complex surface treatment equipment and ensuring quality outcomes. Labor costs can fluctuate based on regional wage standards, particularly in emerging markets in Africa and South America where skilled labor may be less costly compared to Europe or the Middle East.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs related to production, including utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient processes can reduce overhead, but initial setup costs for advanced technologies can be significant.
-
Tooling: Investment in specialized tools and equipment is necessary for precision surface treatments. The initial costs can be high, but they can be amortized over time based on production volume.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring adherence to quality standards is critical, particularly in sectors such as aerospace and medical devices. Implementing robust QC processes incurs costs but ultimately mitigates the risk of adhesion failures and product recalls.
-
Logistics: Transporting raw materials and finished products adds another layer of cost. Geographic location plays a role; suppliers in regions with well-developed logistics networks may offer more competitive shipping rates.
-
Margin: The profit margin varies by supplier and is influenced by market demand, competition, and the perceived value of the treatment provided.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Industrial Surface Treatment Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing in the industrial surface treatment market:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Suppliers often provide discounts for bulk orders. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers negotiate better pricing based on their purchasing capacity.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom treatments or specifications can lead to higher costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in surface treatment directly affect pricing. High-quality materials may come at a premium but can enhance performance and durability.
-
Quality Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards or certifications may command higher prices due to the assurance of reliability and safety.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but can provide better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of delivery (Incoterms) can influence overall costs. Different terms dictate who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly affect the total price.
What Are the Best Practices for Buyers in Negotiating Surface Treatment Prices?
-
Negotiate Smartly: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating prices, especially for larger orders. Establish long-term relationships with suppliers to secure better deals.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher maintenance or operational costs down the line.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers must understand local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and import duties that can affect pricing. Countries like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia may have specific regulations that influence costs.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure that quotes include a breakdown of all costs to avoid surprises. This transparency allows for better comparison between suppliers.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Being aware of shifts in the market, such as material shortages or technological advancements, can provide leverage in negotiations.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for industrial surface treatment can vary widely based on numerous factors including supplier, location, and specific requirements. The figures mentioned in this analysis are indicative and should be confirmed with suppliers for accurate quotes tailored to specific needs and circumstances.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing industrial surface treatment With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Industrial Surface Treatment
In the manufacturing sector, achieving optimal adhesion and surface performance is critical. While industrial surface treatment is widely utilized, various alternative methods exist, each with its unique advantages and drawbacks. This analysis provides a comparative overview of industrial surface treatment against alternative solutions such as chemical etching and laser ablation, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Industrial Surface Treatment | Chemical Etching | Laser Ablation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High adhesion reliability; versatile across materials | Excellent for metals; precise cleaning | Extremely precise; effective for micro-level applications |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; ongoing operational costs | Generally low-cost, but chemical disposal can be expensive | High initial investment; operational costs depend on technology used |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled personnel; setup can be complex | Relatively easy to set up; requires chemical handling knowledge | High expertise required; complex machinery |
| Maintenance | Regular calibration needed; ongoing monitoring essential | Low maintenance; chemical bath management necessary | Requires maintenance of laser systems; risk of debris |
| Best Use Case | Broad applications in manufacturing; ideal for coatings and bonding | Best for cleaning and activating metal surfaces | Ideal for microelectronics and precision applications |
Pros and Cons of Alternatives
Chemical Etching
Chemical etching is a process that utilizes temperature-controlled chemical baths to clean and activate metal surfaces. Its primary advantage lies in its cost-effectiveness and simplicity of setup compared to other methods. However, it demands careful handling of chemicals and can lead to environmental concerns related to chemical disposal. While it provides excellent adhesion for metals, it is less versatile for non-metal substrates.

Illustrative image related to industrial surface treatment
Laser Ablation
Laser ablation employs focused laser beams to precisely remove material from surfaces, ideal for applications requiring micro-level precision. The primary strength of this method is its ability to achieve intricate surface modifications without the need for contact. However, the high initial investment in laser technology and the required expertise for operation can be a barrier for some organizations. Additionally, if not monitored closely, laser ablation can produce debris that complicates adhesion processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
Choosing the right surface treatment method depends on various factors, including the materials being used, the desired performance characteristics, and budget constraints. Industrial surface treatment offers a balance of versatility and reliability, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. Chemical etching is an excellent choice for metal surfaces where cost efficiency is a priority, while laser ablation is the go-to for precision applications in high-tech industries. By carefully evaluating these alternatives against specific operational needs, B2B buyers can select the most effective solution to enhance their manufacturing processes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for industrial surface treatment
What Are the Key Technical Properties in Industrial Surface Treatment?
In the realm of industrial surface treatment, several technical properties are crucial for ensuring the efficacy and reliability of the processes involved. Understanding these properties enables buyers to make informed decisions when selecting materials and methods for their specific applications.

Illustrative image related to industrial surface treatment
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of a substrate based on its chemical composition and mechanical properties. Different grades are suited for various treatments and applications, impacting adhesion, corrosion resistance, and overall durability. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade is vital to ensure compatibility with the intended surface treatment and to meet industry standards.
2. Surface Roughness
Surface roughness measures the texture of a surface, which can significantly influence adhesion and coating performance. It is quantified using parameters like Ra (average roughness) and Rz (average maximum height of the profile). A rougher surface can enhance mechanical interlocking for adhesives, while a smoother finish may be required for aesthetic coatings. Understanding surface roughness helps manufacturers optimize adhesion processes and improve product quality.
3. Chemical Cleanliness
Chemical cleanliness assesses the absence of contaminants such as oils, dust, and residues on a surface prior to treatment. It is critical for achieving effective adhesion and preventing failures. B2B buyers must ensure that their chosen surface treatment methods effectively clean the substrates to maintain high-quality standards and product reliability.
4. Coating Thickness
Coating thickness is a vital specification that dictates the durability and protective capabilities of surface treatments. Too thin a coating may not provide adequate protection, while an overly thick layer can lead to issues like cracking or peeling. Buyers need to specify coating thickness requirements to align with performance expectations and regulatory compliance.
5. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels define the permissible limits of variation in dimensions and properties of treated surfaces. This specification is essential for ensuring that components fit correctly and function as intended. Buyers should communicate their tolerance requirements clearly to prevent costly rework or product failures.

Illustrative image related to industrial surface treatment
6. Adhesion Strength
Adhesion strength measures the force required to separate a coating from a substrate. It is a critical property that determines the longevity and effectiveness of the treatment. Understanding the expected adhesion strength helps B2B buyers select appropriate treatments for their specific applications, ensuring long-term performance and reducing the risk of failures.
What Are Common Terms in Industrial Surface Treatment?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some common terms you may encounter:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In surface treatment, OEMs often require specific standards and specifications for surface preparation to ensure compatibility with their products.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cost-effectiveness. Understanding MOQs helps businesses plan their purchases and manage budgets effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. It often outlines detailed specifications, quantities, and delivery requirements. Crafting a comprehensive RFQ can streamline the procurement process and ensure competitive pricing.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify aspects such as shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers involved in cross-border transactions to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth logistics.
5. Surface Energy
Surface energy is a measure of the thermodynamic work required to create a new surface. It influences how liquids spread on a surface and is critical in determining adhesion properties. Buyers should consider surface energy when selecting treatments to ensure optimal bonding characteristics.
6. Passivation
Passivation is a chemical treatment that enhances the corrosion resistance of metals by forming a protective oxide layer. This process is especially important for stainless steel and other alloys. Understanding passivation is crucial for buyers seeking to improve the longevity and performance of their products in challenging environments.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complex landscape of industrial surface treatment with confidence, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the industrial surface treatment Sector
What are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing the Industrial Surface Treatment Sector?
The industrial surface treatment sector is witnessing a transformative phase driven by several global factors. One of the primary drivers is the increasing demand for advanced materials and coatings that enhance durability and performance across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. As international trade expands, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers are seeking innovative surface treatment solutions that offer superior adhesion and longevity.
Emerging technologies such as automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics are reshaping sourcing strategies. For instance, companies are increasingly adopting surface quality monitoring equipment that utilizes AI to predict adhesion failures before they occur. This proactive approach not only minimizes waste but also enhances product reliability, making it a compelling selling point for suppliers targeting B2B buyers. Additionally, the integration of Industry 4.0 practices in manufacturing processes is driving efficiencies, allowing businesses to optimize their supply chains and reduce lead times.
As buyers navigate these market dynamics, they should also consider the shift towards localized sourcing. The disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities in global supply chains, prompting companies to seek regional suppliers who can deliver quality surface treatment solutions without the long lead times associated with international shipping. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in emerging markets, where establishing partnerships with local suppliers can lead to significant cost savings and enhanced agility.

Illustrative image related to industrial surface treatment
How Does Sustainability Influence Sourcing Decisions in Industrial Surface Treatment?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in sourcing decisions for industrial surface treatment. Buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of their procurement choices, pushing for solutions that minimize waste and reduce carbon footprints. This shift is reflected in the growing demand for eco-friendly surface treatment methods, such as plasma and flame treatments, which often require fewer chemicals and generate less hazardous waste compared to traditional methods.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, including responsible sourcing of raw materials and adherence to environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems or specific ‘green’ certifications for materials used in surface treatments are becoming essential criteria in the selection process. These certifications not only provide assurance of compliance but also enhance a company’s reputation in a competitive marketplace.
Moreover, as regulations around environmental standards tighten globally, particularly in regions like Europe, companies that proactively adopt sustainable practices can gain a competitive edge. This trend is particularly pertinent for international buyers who must navigate varying regulatory landscapes, making it essential to partner with suppliers that can provide compliant and sustainable surface treatment solutions.
What is the Historical Context of Industrial Surface Treatment in the B2B Sector?
The evolution of industrial surface treatment can be traced back to the early 20th century when manufacturers began to recognize the significance of surface preparation in enhancing product performance. Initially, methods such as galvanization and basic coating techniques were employed primarily for corrosion resistance. However, as technology advanced, so did the complexity and variety of surface treatment processes.

Illustrative image related to industrial surface treatment
The introduction of chemical etching and laser ablation in the late 20th century marked a significant leap forward, allowing for precise control over surface properties. This evolution was driven by the increasing demands of high-tech industries, such as electronics and aerospace, where the performance of materials is critical. Today, the sector continues to innovate, integrating sophisticated technologies that not only improve adhesion but also focus on sustainability, making it a dynamic field ripe with opportunities for international B2B buyers.
In summary, understanding the current market dynamics and trends in the industrial surface treatment sector is essential for international buyers. By focusing on sustainability and leveraging technological advancements, companies can enhance their sourcing strategies, ensuring they remain competitive in an ever-evolving landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of industrial surface treatment
-
How do I solve adhesion issues in surface treatment?
To resolve adhesion problems, start by analyzing the surface preparation methods being used. Ensure that the surfaces are adequately cleaned and treated to enhance their chemical reactivity. Consider employing techniques such as plasma, flame, or corona treatments, which are designed to prepare surfaces for better bonding. Conduct regular quality checks with surface readiness tools to monitor surface cleanliness and treatment effectiveness. Additionally, collaborate with surface treatment experts who can provide insights tailored to your specific materials and applications. -
What is the best surface treatment method for polymers?
For polymers, corona and flame treatments are generally the most effective surface treatment methods. Corona treatment is ideal for enhancing surface energy and improving adhesion for printing and coating applications. It utilizes high-voltage electricity to treat the surface without significant heat, making it suitable for sensitive materials. Flame treatment, while effective for low-energy surfaces, requires careful control to avoid damage. Evaluate the specific characteristics of your polymer to determine which method aligns best with your adhesion goals. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in surface treatment processes?
Implementing a robust quality assurance (QA) program involves several key steps. First, establish clear specifications and standards for surface preparation, treatment methods, and adhesion performance. Regularly monitor and document processes using surface analysis tools to ensure consistency and identify potential issues early. Training staff on best practices and the importance of cleanliness in surface treatment is essential. Finally, consider third-party audits or certifications to validate your processes and ensure adherence to international quality standards. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for surface treatment services?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for surface treatment services can vary significantly based on the supplier, treatment method, and material involved. Generally, MOQs can range from small batches (e.g., 100 pieces) for specialized treatments to larger quantities (e.g., 1,000 pieces) for bulk processing. It’s crucial to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers and understand how their MOQs align with your production requirements. Negotiating MOQs may also be possible, especially if you are a long-term customer. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing surface treatment services internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier’s policies and the nature of your agreement. Common terms include advance payment, net 30 or net 60 days, and letters of credit for larger orders. For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods that offer buyer protection, such as PayPal or escrow services. Always clarify payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings and ensure that they fit within your budget and cash flow constraints. -
How do I vet suppliers for surface treatment services?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize those with a proven track record and expertise in industrial surface treatment. Request references and case studies to assess their experience with similar projects. Evaluate their certifications and compliance with international quality standards, such as ISO. Conduct site visits if possible, or use virtual audits to inspect their facilities and equipment. Additionally, consider their ability to provide customization options and their responsiveness to inquiries, as these factors can indicate their commitment to customer service. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when sourcing surface treatments?
Logistics plays a critical role in sourcing surface treatment services, particularly in international transactions. Assess shipping options, lead times, and customs regulations for your specific regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Ensure that your supplier has experience in handling international shipping and can provide reliable tracking and documentation. Additionally, consider the potential for delays due to customs clearance and factor in these timelines when planning your production schedule. -
Can surface treatment services be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many surface treatment suppliers offer customization options tailored to specific applications and materials. This may include adjusting treatment parameters, selecting appropriate methods based on the substrate, or developing proprietary solutions for unique adhesion challenges. Engage in detailed discussions with potential suppliers about your specific needs and applications to ensure they can accommodate your requirements. Custom solutions often enhance performance and reduce the risk of adhesion failures, making them a worthwhile investment.
Top 6 Industrial Surface Treatment Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Aalberts Surface Technologies – Heat and Surface Treatments
Domain: aalberts-st.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Aalberts Surface Technologies specializes in heat and surface treatments, offering a range of services including:
1. **Heat Treatment**: Processes such as vacuum hardening, carbonitriding, and hydrogen annealing.
2. **Surface Treatment**: Galvanic surface treatment including electroless nickel plating, electroplating, hard anodizing, and zinc flake coating.
3. **Polymer Coatings**: Applied using …
2. Impro – Electroplating Services
Domain: improprecision.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Impro provides surface treatment services primarily through electroplating, which is a widely-used technique for altering the surface properties of metal parts. Electroplating involves immersing a metal part in a salt solution containing metallic ions that are deposited onto the surface through electric currents. The services are categorized into functional electroplating, which enhances conductiv…
3. Syensqo – Surface Treatment Solutions
Domain: syensqo.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Syensqo offers versatile and high-performing surface treatment solutions for various industries, focusing on optimizing production processes and enhancing the longevity and performance of finished products. Their surface treatment formulations provide benefits such as corrosion resistance, improved lubrication, optimized glass etching and cleaning, and odor control. Key product brands include Addi…
4. CAPLINQ – Surface Treatments
Domain: caplinq.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Surface Treatments are coatings applied to improve surface properties, made from nanoparticles designed to be hydrophobic, oleophobic, and/or anti-fouling. They enhance performance in electronics, textiles, and industrial equipment, providing protection against wear and corrosion. CAPLINQ partners with Aculon, Inc. to offer easy-to-apply nanotech surface-modification technologies, allowing for dur…
5. Curtiss-Wright Surface Technologies – Metal Surface Treatments
Domain: cwst.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Curtiss-Wright Surface Technologies offers a range of metal surface treatments and protective coatings, including: 1. Shot Peening – A cold working process using small spherical media to improve surface strength. 2. Laser Peening – Available at facilities in the US and UK, with mobile options for on-site applications. 3. Engineered Coatings – Custom coatings to enhance performance, reduce costs, a…
6. Henkel – Surface Treatment Solutions
Domain: henkel-adhesives.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Surface Treatment Solutions by Henkel include a range of conversion coating solutions designed for advanced manufacturing. Key features include:
– Preparation of metal surfaces for painting, welding, and bonding.
– In-house testing for corrosion performance with access to over 130 analytical methods.
– Modern surface analytical and spectroscopic methods.
– Process testing capabilities for small sa…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for industrial surface treatment
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Industrial Surface Treatment Needs?
In the evolving landscape of industrial surface treatment, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal factor for B2B buyers aiming to optimize operational efficiency and product quality. By carefully selecting suppliers and treatment methods—such as plasma, flame, and chemical etching—buyers can significantly enhance adhesion performance, minimize production failures, and reduce long-term costs. Understanding the unique requirements of various materials and their interactions with different surface treatments is crucial in making informed decisions that drive success.
As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to expand, the demand for advanced surface treatment solutions is expected to rise. International buyers are encouraged to leverage partnerships with experienced suppliers who can provide cutting-edge technologies and insights tailored to specific regional needs. Emphasizing quality assurance and surface readiness will be essential in maintaining competitiveness.

Illustrative image related to industrial surface treatment
Looking ahead, organizations that invest in strategic sourcing for surface treatment will not only improve their product offerings but also position themselves as leaders in innovation. Now is the time to reassess your sourcing strategies and explore new opportunities for collaboration, ensuring your business is prepared to meet the challenges of tomorrow. Engage with experts in the field and elevate your surface treatment processes to achieve unparalleled results.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.