Choosing Your Infrared Cookers: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for infrared cookers
In today’s fast-paced culinary landscape, sourcing high-quality infrared cookers presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers. These innovative appliances are revolutionizing cooking efficiency and energy consumption, making them an essential consideration for businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Germany and Saudi Arabia. As global demand for energy-efficient and safe cooking solutions rises, understanding the nuances of infrared cookers becomes paramount for informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into various types of infrared cookers, their applications across different sectors, and critical factors for supplier vetting. We will explore the cost implications and potential return on investment, ensuring buyers can evaluate options effectively. Furthermore, this guide offers insights into market trends and consumer preferences, empowering businesses to make strategic choices that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals.
By equipping B2B buyers with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of the infrared cooker market, this resource aims to facilitate smarter procurement processes. Whether you are a distributor looking to expand your product line or a restaurant owner seeking efficient cooking solutions, understanding the infrared cooker landscape will help you stay competitive and responsive to market demands.
Understanding infrared cookers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infrared Cooktops | Flat surface, quick heat-up, compatible with various cookware | Restaurants, catering, food trucks | Pros: Fast cooking, energy-efficient. Cons: Limited to flat surfaces. |
| Infrared Burners | Portable, single or double plate, often used for outdoor cooking | Small kitchens, events, outdoor catering | Pros: Versatile and portable. Cons: Limited cooking capacity. |
| Conveyor Infrared Ovens | Continuous cooking process, even heat distribution | Food processing, bakeries, industrial | Pros: High efficiency, consistent results. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
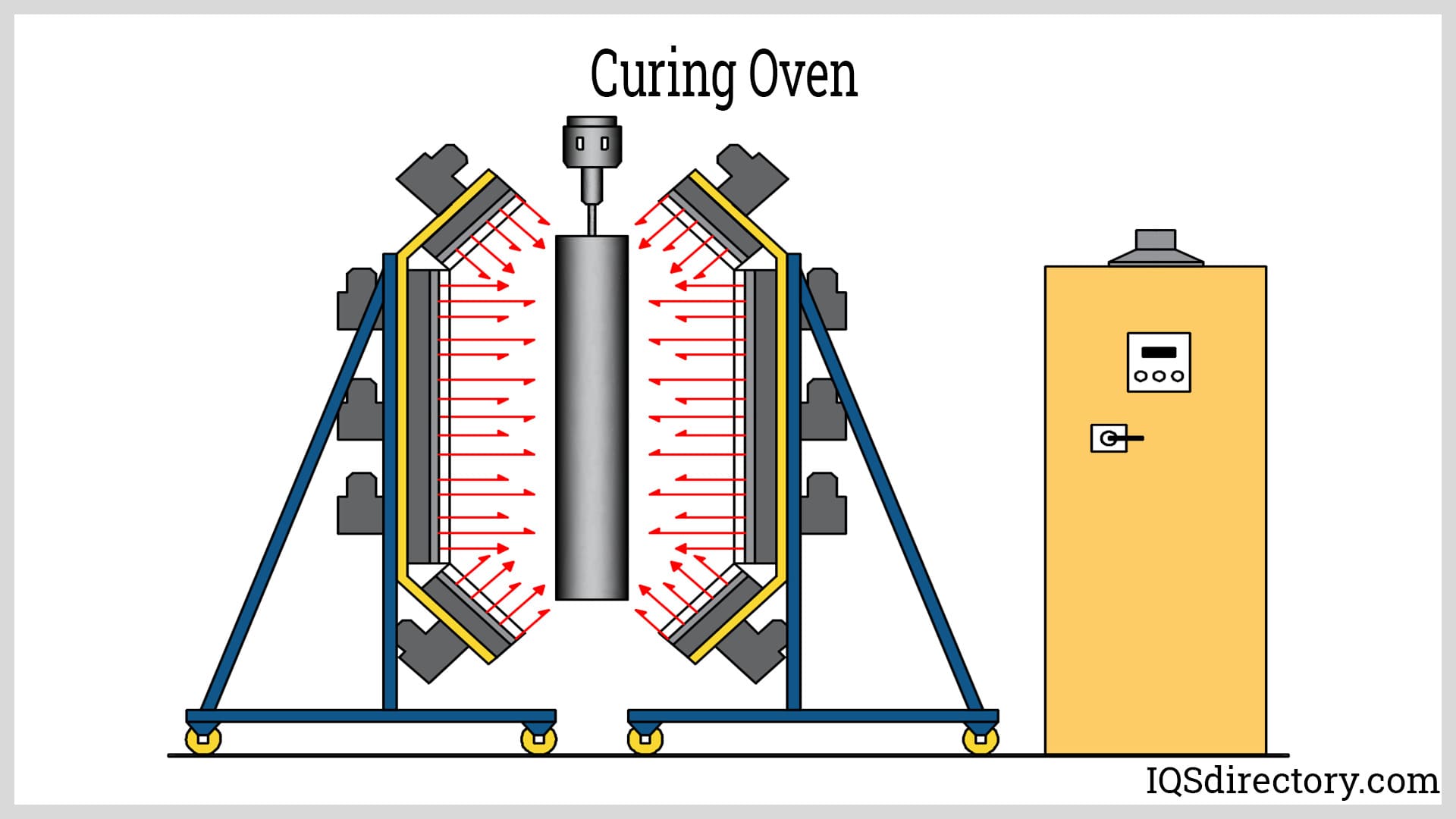
| Industrial Curing Ovens | Designed for material strengthening, high-temperature capabilities | Manufacturing, automotive, aerospace | Pros: Excellent for curing and drying. Cons: Requires specialized knowledge. |
| Infrared Grills | Direct heat source, ideal for grilling and searing | Restaurants, food service, outdoor kitchens | Pros: Quick grilling, retains moisture in food. Cons: Limited to grilling applications. |
What Are the Key Features of Infrared Cooktops and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Infrared cooktops are designed with a flat surface and utilize infrared radiation to deliver rapid and even heating. They are suitable for various commercial settings, such as restaurants and catering services, where quick meal preparation is essential. B2B buyers should consider energy efficiency and the ability to work with multiple types of cookware, making these cooktops versatile for diverse culinary applications. Additionally, their sleek design facilitates easy cleaning, which is a significant advantage in high-volume kitchens.
How Do Infrared Burners Differ and What Are Their Applications?
Infrared burners are portable cooking appliances that come in single or double plate configurations, making them ideal for small kitchens or outdoor events. Their lightweight design allows for easy transport, making them a popular choice among food trucks and catering businesses. When purchasing, B2B buyers should evaluate the burner’s power output and portability, as these factors influence cooking speed and convenience during events or in limited kitchen spaces.
What Are the Advantages of Conveyor Infrared Ovens for Industrial Use?
Conveyor infrared ovens are designed for continuous cooking processes, making them highly efficient for food processing and industrial applications. These ovens provide consistent heat distribution, ensuring uniform cooking results, which is crucial for maintaining product quality. B2B buyers should weigh the initial investment against long-term operational efficiency, as these ovens can significantly increase production rates in bakeries and other food manufacturing settings.
Why Are Industrial Curing Ovens Essential in Manufacturing Processes?
Industrial curing ovens are specialized equipment used to enhance the strength and durability of materials through thermal processing. They are widely used in sectors like automotive and aerospace, where precise material properties are critical. B2B buyers must consider the specific temperature requirements and the materials being processed, as well as the need for specialized knowledge in operating these ovens effectively. Their investment can lead to improved product quality and reduced production times.
How Do Infrared Grills Enhance Cooking in Commercial Settings?
Infrared grills utilize direct heat to cook food quickly while retaining moisture, making them an excellent option for restaurants and outdoor kitchens. They offer the advantage of rapid cooking times, which is beneficial in high-demand environments. B2B buyers should assess the grill’s size, heating capabilities, and ease of use to ensure it meets the operational needs of their food service business. While ideal for grilling, buyers should also consider their specific menu offerings to determine if an infrared grill aligns with their culinary goals.
Key Industrial Applications of infrared cookers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Infrared Cookers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Cooking and drying food products in industrial kitchens | Faster cooking times and reduced energy consumption | Ensure compliance with food safety regulations and energy efficiency standards. |
| Hospitality | Preparing meals in restaurants and catering services | Enhanced cooking precision and reduced labor costs | Look for models with rapid heating capabilities and easy maintenance features. |
| Manufacturing | Preheating and curing materials in production lines | Improved product quality and consistency | Assess the temperature control accuracy and durability of the cookers. |
| Retail | Cooking demonstrations in supermarkets | Increased customer engagement and product visibility | Consider the cooker’s portability and ease of use for staff. |
| Home Appliances | Residential kitchen installations for energy-efficient cooking | Lower energy bills and improved cooking speed | Evaluate compatibility with various cookware and warranty options. |
How are Infrared Cookers Used in Food Processing and What Problems Do They Solve?
In the food processing industry, infrared cookers are employed for cooking, drying, and sterilizing food products. They provide a significant advantage by reducing cooking times by up to 50% and ensuring even heat distribution, which enhances food quality. International buyers, especially those in Africa and South America, must prioritize energy efficiency and compliance with food safety standards when sourcing infrared cookers to optimize their production processes.
What Role Do Infrared Cookers Play in the Hospitality Sector?
In the hospitality sector, infrared cookers are utilized for preparing meals in restaurants and catering services. Their ability to heat up quickly and cook food evenly allows chefs to serve high-quality dishes promptly, thus improving customer satisfaction. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should focus on models that offer ease of maintenance and precise temperature control to meet the high demands of the culinary environment.
How are Infrared Cookers Beneficial in Manufacturing?
Manufacturers use infrared cookers for preheating and curing materials as part of their production lines. This application enhances product consistency and quality while reducing processing times. B2B buyers in industries such as automotive or electronics manufacturing should evaluate the durability and temperature control features of infrared cookers to ensure they meet the specific requirements of their production processes.
Why are Infrared Cookers Valuable for Retail Cooking Demonstrations?
In retail environments, infrared cookers are employed for cooking demonstrations in supermarkets, attracting customers and enhancing product visibility. Their rapid heating capabilities and ease of use make them ideal for engaging shoppers. Retailers should consider the portability and user-friendliness of infrared cookers to facilitate effective demonstrations and maximize consumer interest.
How Do Infrared Cookers Contribute to Home Cooking Efficiency?
Infrared cookers are increasingly popular in residential kitchens for their energy efficiency and quick cooking times. They can reduce energy bills while providing consistent cooking results, making them an attractive option for eco-conscious consumers. Buyers in the home appliance sector should ensure that the cookers are compatible with a variety of cookware and come with reliable warranty options to cater to diverse customer needs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘infrared cookers’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Limited Cooking Capacity for Large Orders
The Problem: B2B buyers in the food service industry often face the challenge of cooking large quantities of food efficiently. Infrared cookers, while excellent for individual meals, may not have the capacity or speed required for catering events, large restaurants, or food production facilities. This limitation can lead to delays in service, increased labor costs, and potential loss of business during peak hours.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should consider investing in commercial-grade infrared cookers with multiple heating zones and larger cooking surfaces. When sourcing these units, look for models specifically designed for high-volume cooking, with features such as adjustable power settings and rapid heat-up capabilities. Additionally, integrating infrared cookers into a well-planned kitchen layout can optimize workflow. Training staff on efficient cooking techniques can also maximize the benefits of infrared technology, allowing for quicker meal preparation and consistent output during busy periods.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Cooking Results
The Problem: A common pain point for buyers is the inconsistency in cooking results, which can arise from varying cookware compatibility and incorrect heat settings. This inconsistency can lead to customer dissatisfaction, especially in businesses where food quality is paramount, such as restaurants and catering services. The challenge is exacerbated in international markets, where cookware materials may differ significantly.
The Solution: To ensure uniform cooking results, buyers should prioritize infrared cookers that offer precise temperature control and compatibility with a wide range of cookware materials, including glass, ceramic, and metal. When purchasing, opt for models that feature built-in sensors to monitor cooking temperatures and adjust heat output automatically. Additionally, developing a standardized cooking protocol can help staff achieve consistent results. Regular training sessions focusing on the use of different cookware types can also empower kitchen teams to adapt their techniques for optimal performance.
Scenario 3: High Energy Costs and Sustainability Concerns
The Problem: Energy efficiency is a critical concern for B2B buyers, particularly in regions with high energy costs or where sustainability is a significant factor. Infrared cookers are often marketed as energy-efficient, but the initial investment and operating costs can still be a barrier for many businesses, especially in developing markets.
The Solution: Buyers should conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis before investing in infrared cookers, considering both upfront costs and long-term savings on energy bills. Seek models that have been certified for energy efficiency by recognized organizations. Additionally, implementing energy management practices, such as scheduling cooking during off-peak energy hours and using infrared cookers alongside other energy-efficient appliances, can further reduce costs. Collaborating with suppliers who offer financing options or energy rebates can also alleviate the financial burden, making the switch to infrared cooking more feasible and appealing. Engaging in sustainable practices can enhance a brand’s reputation, appealing to eco-conscious consumers and partners.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for infrared cookers
What Are the Key Materials Used in Infrared Cookers?
When selecting materials for infrared cookers, it is essential to consider properties that directly impact performance, durability, and safety. The most common materials used in the construction of infrared cookers include ceramic glass, stainless steel, aluminum, and cast iron. Below is a detailed analysis of each material, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Ceramic Glass Perform in Infrared Cookers?
Ceramic glass is a popular choice for the surface of infrared cookers due to its excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal shock. It can withstand high temperatures, typically up to 1000°F (538°C), making it suitable for rapid heating applications. The smooth surface is easy to clean and does not retain food odors, which is advantageous for maintaining hygiene.
Pros: Ceramic glass is highly durable and resistant to scratches and stains. It also provides a sleek, modern appearance that appeals to consumers.
Cons: The primary limitation is its brittleness; while it can handle high temperatures, it can crack under sudden impacts or thermal shock. Additionally, ceramic glass can be more expensive than other materials.
Impact on Application: Ceramic glass is compatible with various cooking media, including liquids and solids. However, care must be taken to avoid sudden temperature changes.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with safety standards such as ASTM C158 and DIN EN 14428 is crucial. Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East may prioritize materials that meet these standards for safety and reliability.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Infrared Cookers?
Stainless steel is often used in the construction of the body and components of infrared cookers due to its strength and corrosion resistance. It can withstand high temperatures and is less prone to warping compared to other metals.
Pros: The durability of stainless steel makes it suitable for heavy-duty applications. It is also easy to clean and maintain, which is a significant advantage for commercial settings.

Illustrative image related to infrared cookers
Cons: Stainless steel can be more expensive than aluminum and may have lower thermal conductivity, which can affect cooking efficiency. It may also require additional insulation to maintain heat.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with various cooking methods and media, making it versatile for different culinary applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the stainless steel used complies with international standards, such as JIS G4303 for stainless steel bars and rods. This is particularly relevant for markets in Germany and Saudi Arabia, where quality standards are stringent.
How Does Aluminum Compare in Infrared Cookers?
Aluminum is often used in infrared cookers for its lightweight nature and excellent thermal conductivity. It heats up quickly, making it efficient for cooking applications.
Pros: The low weight of aluminum makes it easy to handle and install. Its thermal properties allow for rapid cooking, which is ideal for fast-paced environments.
Cons: Aluminum is less durable than stainless steel and can warp or scratch more easily. It is also prone to corrosion if not properly coated or anodized.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for cooking a wide range of foods, but its susceptibility to corrosion can limit its use in environments with high humidity or acidic foods.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for anodized aluminum options to enhance durability. Compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 is essential, especially for buyers in regions with strict material regulations.
Why Is Cast Iron a Consideration for Infrared Cookers?
Cast iron is known for its excellent heat retention and even cooking capabilities. While less common in modern infrared cookers, it is still used in some applications where high heat retention is required.
Pros: Cast iron can withstand very high temperatures and provides excellent heat distribution, making it ideal for slow cooking and frying.
Cons: The weight of cast iron can be a disadvantage for portability. It also requires more maintenance to prevent rust and maintain seasoning.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is particularly suited for heavy-duty cooking applications but may not be ideal for all infrared cooker designs due to its weight.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that cast iron products meet relevant standards for food safety and durability, particularly in markets like Africa and South America, where local regulations may vary.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Infrared Cookers
| Material | Typical Use Case for infrared cookers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Glass | Cooktop surface | High thermal resistance | Brittle and prone to cracking | High |
| Stainless Steel | Body and components | Durable and corrosion-resistant | Lower thermal conductivity | Medium |
| Aluminum | Cooking vessels | Lightweight and efficient | Prone to warping and corrosion | Low |
| Cast Iron | Heavy-duty cooking applications | Excellent heat retention | Heavy and requires maintenance | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers looking to source infrared cookers, ensuring they make informed decisions based on material properties, performance, and compliance with international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for infrared cookers
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Infrared Cookers?
The manufacturing of infrared cookers involves several critical stages that ensure high-quality output and efficiency. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Infrared Cookers?
The process begins with the selection and preparation of materials. Infrared cookers typically utilize high-grade ceramics, metals (like stainless steel), and specialized heat-resistant glass. Each material is chosen for its thermal conductivity, durability, and safety features. The materials undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet industry standards for heat resistance and safety, especially in regions with specific regulatory requirements.
Forming: How Are Components Shaped for Infrared Cookers?
Once materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This involves several techniques, including:
- Injection Molding: Used primarily for creating plastic components such as knobs and housing.
- Die Casting: Commonly used for metal parts, ensuring precise shapes and strength.
- Glass Molding: For the ceramic or glass surfaces that are essential for infrared cooktops.
Advanced technologies like CNC machining may also be employed to achieve high precision in component shapes, ensuring seamless assembly later on.

Illustrative image related to infrared cookers
Assembly: What Are the Key Steps in Assembling Infrared Cookers?
The assembly of infrared cookers is a meticulous process that integrates all formed components. Key steps include:
- Component Assembly: This includes placing the heating elements, wiring, and control systems into the cooktop structure.
- Quality Checks During Assembly: Regular inspections are conducted to identify any defects immediately, ensuring that only components meeting quality standards progress to the next stage.
- Final Assembly: Once all parts are assembled, the cookers undergo final checks to ensure that all features work correctly and meet the design specifications.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Infrared Cookers?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of infrared cookers, as it ensures safety, reliability, and performance. Buyers should be aware of the various QA measures that suppliers implement.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Consider?
International standards play a crucial role in quality assurance. For infrared cookers, the following certifications are particularly relevant:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: Essential for products sold in Europe, it indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: While more common in industrial applications, some manufacturers may adhere to these standards to ensure high performance in cooking appliances.
Understanding these standards helps buyers assess the credibility of manufacturers and their commitment to quality.

Illustrative image related to infrared cookers
What Are the QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated into the manufacturing process to maintain product integrity. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During assembly, random samples are tested to identify defects early in the production cycle.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, finished products undergo comprehensive testing, including functionality tests, safety checks, and compliance verifications.
These checkpoints provide a systematic approach to maintaining high standards throughout the manufacturing process.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers. Here are some effective strategies:
What Audit Practices Should Buyers Implement?
Conducting regular audits of suppliers is a vital practice. Buyers can consider:
- On-site Audits: Visiting manufacturing facilities to observe processes and quality control measures firsthand.
- Supplier Self-Audits: Requesting suppliers to provide self-audit reports, which can offer insights into their internal quality practices.
How Do Third-Party Inspections Add Value?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. These inspections typically include:
- Random Sampling: Inspecting a set number of products from a batch to ensure consistency in quality.
- Detailed Reporting: Providing comprehensive reports that outline findings, helping buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
What Specific QC Considerations Exist for International Buyers?
International buyers face unique challenges and considerations regarding quality control. Understanding these nuances can help in selecting reliable suppliers.

Illustrative image related to infrared cookers
How Do Cultural and Regulatory Differences Affect Quality?
Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe may encounter diverse regulatory environments. It’s essential to:
- Research Local Regulations: Understanding specific safety and quality regulations in each region can guide buyers in assessing supplier compliance.
- Communicate Expectations Clearly: Clear communication regarding quality expectations and standards can help bridge any cultural gaps.
What Are the Implications of Certification Nuances?
Different certifications may hold varying significance in different markets. For instance, while CE marking is vital for European markets, other regions may prioritize local certifications. Buyers should ensure that suppliers possess the necessary certifications relevant to their target market.
Conclusion: How to Ensure Quality in Your Supply Chain for Infrared Cookers?
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for infrared cookers is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on the stages of manufacturing, relevant quality standards, and effective verification methods, buyers can confidently select suppliers that meet their needs. Prioritizing these factors not only enhances product quality but also builds long-term partnerships that contribute to business success in a competitive global market.

Illustrative image related to infrared cookers
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘infrared cookers’
This guide aims to assist international B2B buyers in sourcing infrared cookers effectively. By following these steps, you can ensure that you make informed decisions, select high-quality products, and establish reliable partnerships with suppliers.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before you start sourcing, it’s essential to outline the technical requirements for the infrared cookers you need. Consider factors such as wattage, size, and cooking technology (e.g., halogen vs. radiant). Clearly defined specifications will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure the products meet your operational needs.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Requirements
Understanding the market landscape in your target regions (Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe) is critical. Research consumer preferences, local regulations, and energy efficiency standards. This knowledge will help you identify the best product features and ensure compliance with regional guidelines, which can impact sales and operational efficiency.

Illustrative image related to infrared cookers
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies to understand their capabilities. Look for suppliers with experience in your industry and region, as they will be more adept at meeting specific challenges and requirements.
- Check References: Contact other businesses that have sourced from them, especially those in similar markets.
- Review Certifications: Ensure the supplier holds relevant quality and safety certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) that are recognized in your target market.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Obtaining product samples is a crucial step in the sourcing process. By evaluating samples, you can assess the quality, performance, and usability of the infrared cookers firsthand. This will also help you gauge whether the product aligns with your specifications and expectations.
- Test Performance: Evaluate heating efficiency, cooking times, and evenness.
- Inspect Build Quality: Ensure the materials used are durable and suitable for your intended use.
Step 5: Analyze Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership
While initial pricing is important, understanding the total cost of ownership (TCO) is critical for long-term planning. Assess not only the purchase price but also factors like shipping costs, warranties, and energy efficiency.
- Calculate Energy Savings: Compare the energy consumption of different models to identify potential savings.
- Consider Maintenance Costs: Evaluate the ease of maintenance and the availability of spare parts.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, it’s time to negotiate terms. Discuss pricing, payment terms, delivery timelines, and after-sales support. Clear agreements on these aspects can prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smooth procurement process.
- Establish Clear SLAs: Service Level Agreements (SLAs) should outline expected performance and support timelines.
- Discuss Return Policies: Understand the supplier’s policies on returns and warranties to mitigate risks.
Step 7: Plan for Logistics and Distribution
Finally, consider the logistics of transporting the infrared cookers to your location. Plan the distribution channels and timelines to ensure timely delivery and minimize disruptions to your operations.

Illustrative image related to infrared cookers
- Choose Reliable Shipping Partners: Work with logistics companies experienced in handling kitchen appliances.
- Factor in Customs Regulations: Be aware of import duties and regulations in your target market to avoid unexpected delays.
By adhering to this checklist, you can streamline your sourcing process, reduce risks, and enhance the chances of a successful procurement of infrared cookers.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for infrared cookers Sourcing
When sourcing infrared cookers, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. The cost components, price influencers, and buyer tips outlined below will provide valuable insights for making informed purchasing decisions.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Infrared Cooker Manufacturing?
The primary cost components for infrared cookers include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects the overall cost. High-quality ceramic, glass, and stainless steel components are common in infrared cookers. Prices can fluctuate based on market demand and availability.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region. In countries with lower labor costs, such as certain parts of Africa and South America, manufacturers may offer more competitive pricing. However, the expertise required for quality assembly can drive costs up in regions with higher labor standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, which is essential for maintaining competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in molds and machinery for producing infrared cookers can be substantial. However, these costs are amortized over production runs, making it crucial for buyers to consider minimum order quantities (MOQs) when sourcing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality through rigorous QC processes adds to costs but is necessary for maintaining standards, especially for buyers in regions with stringent safety regulations.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs can vary significantly depending on the geographical location of suppliers and buyers. Incoterms play a critical role in defining who bears these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build a profit margin into their pricing, which can vary based on market positioning and competitive landscape.
What Factors Influence Pricing for Infrared Cookers?
Several factors can influence the pricing of infrared cookers in the B2B market:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger volumes often leads to discounted pricing. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to ensure they receive favorable rates.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected price hikes.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (such as CE, RoHS) can justify a premium price. Buyers should assess whether these certifications are essential for their market.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their reputation and reliability. Evaluating supplier history and customer reviews can help in choosing the right partner.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for determining who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and customs duties, which can affect the total landed cost.
What Are the Best Negotiation Strategies for International Buyers?
When negotiating prices for infrared cookers, buyers should consider the following strategies to enhance cost-efficiency:

Illustrative image related to infrared cookers
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO beyond just the purchase price. This includes maintenance, energy consumption, and potential warranty claims. Infrared cookers often have lower energy consumption, which can result in long-term savings.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Frequent communication and transparency about your needs can foster trust and collaboration.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough research on market prices and trends. This knowledge empowers buyers during negotiations and can help in identifying the best sourcing options.
-
Timing: Consider the timing of purchases. Off-peak seasons may yield better pricing as manufacturers seek to increase sales volume.
What Should International Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Pricing Nuances?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must be aware of specific pricing nuances:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Changes in exchange rates can impact the final cost. Buyers should factor in currency risks when negotiating contracts.
-
Import Duties and Taxes: Understand the import regulations and potential tariffs in your region to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Cultural Considerations: Different regions have varying negotiation styles and expectations. Understanding these cultural nuances can facilitate smoother negotiations and stronger partnerships.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for infrared cookers can vary significantly based on multiple factors. The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and should be validated with suppliers for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing infrared cookers With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Infrared Cookers
In the ever-evolving kitchen technology landscape, businesses seeking efficient cooking solutions must consider various alternatives to infrared cookers. Infrared cooking technology is recognized for its rapid heating capabilities and energy efficiency, but other methods also offer unique benefits tailored to different operational needs. This analysis will compare infrared cookers against two viable alternatives: induction cooktops and traditional gas stoves.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Infrared Cookers | Induction Cooktops | Gas Stoves |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Fast heating, even cooking, energy-efficient | Instant heat, precise temperature control | Variable heat, slower heating time |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment, low operating costs | Higher upfront costs, efficient long-term | Lower initial cost, variable costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation, compatible with various cookware | Requires specific cookware, installation may be complex | Easy installation, widely available |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy to clean surfaces | Low maintenance, but needs specific care | Higher maintenance due to grease and soot |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-volume cooking and energy-conscious environments | Best for precise cooking and high-end culinary applications | Suitable for traditional kitchens and diverse cooking styles |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Induction Cooktops
Induction cooktops utilize electromagnetic energy to directly heat pots and pans, offering precise temperature control and rapid heating capabilities. They are known for their safety features, as the cooktop remains cool to the touch, reducing the risk of burns. However, induction cooktops can be more expensive initially and require specific magnetic cookware, limiting their compatibility with existing kitchen equipment. They are particularly beneficial for commercial kitchens where precision and safety are paramount.
Gas Stoves
Gas stoves are a traditional cooking method that uses an open flame to heat cookware. They are favored for their versatility, allowing chefs to control the heat level instantly and providing a more familiar cooking experience for many. However, they can be less energy-efficient compared to infrared or induction options and may require more maintenance due to grease buildup and soot. Gas stoves are ideal for environments where diverse cooking techniques are employed, and the preference for flame-based cooking remains strong.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Cooking Solution for Your Business
When selecting a cooking solution, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific needs, including budget constraints, cooking volume, and desired cooking precision. Infrared cookers offer a balanced approach with energy efficiency and ease of use, making them suitable for high-volume environments. Induction cooktops provide unmatched precision and safety, ideal for high-end culinary applications. In contrast, gas stoves cater to traditional cooking practices, ensuring versatility across various culinary styles. By aligning the chosen cooking technology with operational requirements, businesses can enhance efficiency and culinary quality in their food preparation processes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for infrared cookers
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Infrared Cookers?
When considering infrared cookers for commercial use, understanding their essential technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some key specifications:
1. Wattage
Wattage indicates the power output of an infrared cooker, typically ranging from 750W to 2200W. Higher wattage means faster cooking times, which can significantly enhance operational efficiency in a commercial kitchen. For B2B buyers, wattage is a critical factor as it directly impacts the appliance’s performance and energy consumption.
2. Material Grade
The materials used in infrared cookers, such as ceramic glass or stainless steel, affect durability, heat distribution, and ease of maintenance. High-grade materials ensure longevity and resistance to corrosion, which is essential for businesses looking to minimize replacement costs. Buyers should prioritize cookers with robust materials that can withstand rigorous use in professional kitchens.
3. Temperature Control Range
A broad temperature control range allows for versatile cooking options, from simmering to searing. Infrared cookers typically feature precise temperature settings, enabling chefs to achieve consistent results. For B2B buyers, the ability to control cooking temperatures can lead to improved food quality and customer satisfaction.
4. Size and Portability
Infrared cookers come in various sizes, from single-plate models to larger double-plate versions. Portability is another factor, as some models are designed for easy transportation. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for businesses that may need to move equipment for catering events or in different kitchen setups.
5. Safety Features
Modern infrared cookers incorporate safety features such as cool-touch surfaces and automatic shut-off mechanisms. These safety enhancements are vital for reducing the risk of accidents in busy kitchen environments. B2B buyers should consider the safety features as part of their procurement process to ensure a secure working environment for staff.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know When Purchasing Infrared Cookers?
Understanding industry jargon is equally important for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some essential trade terms related to infrared cookers:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another company. Buyers often engage with OEMs for customized infrared cookers tailored to their specific needs. Familiarity with OEM relationships can help businesses source products that meet unique requirements.

Illustrative image related to infrared cookers
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for B2B buyers as it can affect inventory levels and purchasing decisions. Understanding MOQ helps businesses plan their orders effectively and manage cash flow.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process used to invite suppliers to bid on specific products or services. In the context of infrared cookers, an RFQ allows businesses to compare pricing, features, and terms from various suppliers, ensuring they secure the best deal.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. For B2B transactions involving infrared cookers across borders, understanding Incoterms is essential for clarifying liability and costs associated with shipping.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. This term is particularly important for businesses with tight operational timelines. Knowing the lead time for infrared cookers helps buyers plan their inventory and avoid disruptions in service.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can navigate the procurement process more effectively, ensuring they select the right infrared cookers for their operational needs.

Illustrative image related to infrared cookers
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the infrared cookers Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Infrared Cookers Sector?
The infrared cookers market is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing consumer demand for energy-efficient and safer cooking options. Global trends indicate a shift towards modern cooking technologies, with infrared cookers becoming popular for their ability to provide faster and more even heating compared to traditional gas or electric stoves. This trend is particularly evident in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where urbanization and rising disposable incomes are influencing consumer preferences.
International B2B buyers should note that the adoption of infrared cooking technology is also being supported by a growing emphasis on sustainable cooking solutions. As manufacturers innovate to improve energy efficiency—showing reductions in energy consumption by up to 40%—there is an increasing focus on the environmental impact of these appliances. The integration of smart technologies, such as IoT-enabled features for monitoring energy use, is emerging as a key trend. Additionally, sourcing trends are shifting towards manufacturers that prioritize quality and reliability, ensuring that products meet the stringent standards of diverse international markets, including Germany and Saudi Arabia.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Transforming the Infrared Cookers Market?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration in the sourcing of infrared cookers. As global awareness of environmental issues rises, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing products that minimize ecological footprints. Infrared cookers are recognized for their energy efficiency, which not only reduces electricity costs for consumers but also contributes to lower carbon emissions.

Illustrative image related to infrared cookers
Moreover, ethical sourcing practices are gaining traction, with buyers keen to ensure that their supply chains are transparent and responsible. This includes sourcing materials that have been certified as ‘green’ or eco-friendly, such as recyclable components and non-toxic materials used in the manufacturing process. Certifications like Energy Star or EcoLabel are becoming essential for manufacturers to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
Buyers in emerging markets should also consider the importance of local sourcing to support regional economies and reduce transportation emissions. Establishing relationships with suppliers who share these values can enhance brand reputation and align with the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
What is the Brief Evolution and History of Infrared Cookers?
The evolution of infrared cookers can be traced back to advancements in heating technology that began in the mid-20th century. Initially, infrared technology was primarily used in industrial applications, but over the years, it has transitioned into residential cooking appliances. The first consumer infrared cookers emerged in the 1990s, offering a safer alternative to gas stoves with no open flames and minimal heat waste.
As technology progressed, the development of ceramic and glass cooktops allowed for more versatile and efficient designs. Today, infrared cookers are recognized for their unique ability to deliver rapid, even heating while being compatible with a wide range of cookware. This evolution has not only enhanced cooking experiences but has also positioned infrared cookers as a key player in the modern kitchen, appealing to both consumers and B2B buyers seeking innovative solutions.
In summary, the infrared cookers sector presents a dynamic landscape for international B2B buyers, characterized by emerging technologies, sustainability initiatives, and a rich history of innovation. Understanding these trends can empower businesses to make informed sourcing decisions that align with market demands and consumer expectations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of infrared cookers
1. How do I select the right infrared cooker for my business needs?
When selecting an infrared cooker, consider factors such as wattage, size, and cooking capacity. Evaluate the specific needs of your business, such as the volume of food you plan to prepare and the types of dishes you will cook. Look for models that offer energy efficiency and even heat distribution, which can reduce cooking times significantly. Additionally, check for compatibility with various cookware types, as some infrared cookers can work with all materials, unlike induction cookers. Consulting with suppliers about your requirements can also help you make an informed decision.

Illustrative image related to infrared cookers
2. What are the benefits of using infrared cookers in a commercial kitchen?
Infrared cookers offer numerous advantages for commercial kitchens, including faster cooking times and enhanced energy efficiency—up to 40% more efficient than traditional stoves. They heat cookware directly, resulting in even cooking and reduced energy wastage. Safety features, such as cooler surfaces, minimize burn risks, making them ideal for busy kitchen environments. Additionally, the easy-to-clean surfaces simplify maintenance, allowing staff to focus more on food preparation rather than cleaning up. These benefits can lead to improved operational efficiency and lower overhead costs for your business.
3. What should I look for in a supplier of infrared cookers?
When vetting suppliers for infrared cookers, prioritize those with a proven track record in quality and reliability. Check their certifications, customer reviews, and industry experience. It’s also crucial to inquire about their manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols to ensure consistent product standards. Additionally, assess their ability to provide after-sales support, warranty options, and replacement parts. A responsive supplier that understands the specific needs of your market can significantly enhance your procurement experience.
4. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for infrared cookers?
Minimum order quantities for infrared cookers can vary widely depending on the supplier and the specific model. Generally, MOQs can range from 10 to 100 units for standard models, while customized or specialized products may have higher MOQs. It is essential to discuss your order volume upfront to negotiate favorable terms. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or larger contracts, allowing you to scale your orders as your business grows.
5. What payment terms are commonly offered for international purchases of infrared cookers?
Payment terms for international purchases typically include options such as advance payment, letter of credit, or net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days). Many suppliers may require a deposit upfront, especially for larger orders, with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. It’s crucial to clarify payment methods, currency, and any additional fees associated with international transactions. Establishing clear payment terms can help prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smooth purchasing process.
6. How can I ensure the quality of infrared cookers I import?
To ensure the quality of infrared cookers, conduct thorough supplier audits and request product samples before placing a bulk order. You may also consider third-party quality assurance services that can perform inspections during production and pre-shipment. Ensure that the products meet relevant international standards and regulations for safety and performance. Additionally, reviewing warranty policies and return terms can provide further assurance of the product’s quality and reliability.
7. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing infrared cookers?
When importing infrared cookers, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs clearance procedures. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling kitchen appliances to navigate international shipping regulations efficiently. Additionally, factor in potential tariffs, taxes, and insurance to budget accurately for your total landed cost. Clear communication with your supplier regarding shipping schedules and packaging requirements can help minimize delays and ensure the safe arrival of your products.
8. Are there customization options available for infrared cookers?
Many suppliers offer customization options for infrared cookers, allowing you to tailor features such as size, wattage, color, and branding to meet your specific business needs. Customization can enhance your brand identity and ensure that the cookers align with your operational requirements. Discuss your customization preferences with potential suppliers early in the negotiation process to determine feasibility and associated costs. Keep in mind that custom orders may have longer lead times and higher MOQs compared to standard products.
Top 3 Infrared Cookers Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Ovente – Electric Infrared Burners
Domain: ovente.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Ovente Electric Infrared Burner, Single-Plate 7.5” (1000W) Ceramic Glass Cooktop, Silver (BGI201S) – $42.99; Ovente Electric Double-Plate Burner, 7″ (750W) + 7″ (750W) Infrared Ceramic Glass Cooktop, Silver (BGI202S) – $60.99; Ovente Electric Infrared Burner, Double-Plate 7″ (1000W) + 6.5″ (700W) Ceramic Glass Cooktop, Silver (BGI102S) – $64.99; Ovente Electric Infrared Burner, 7” Single-Plate, 10…
2. Reddit – Infrared vs Induction Cooktops
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Infrared cooktops are marketed as resistive-coil stoves with a glass top. They can warp, crack, or break with moderate use, especially if used frequently. Induction cooktops, on the other hand, have a glass top that withstands thermal shocks better, making them more durable. Induction cooktops are generally more powerful and efficient, requiring compatible pots that can be tested with a magnet. In…
3. IQS Directory – Infrared Ovens
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Infrared ovens utilize infrared radiation to heat or cook items, differing from traditional conduction and convection ovens. They are used in commercial kitchens, residential spaces, and industrial settings. Infrared ovens heat food directly without heating the surrounding air, making them more energy-efficient and quieter than convection ovens. They operate using electromagnetic radiation with wa…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for infrared cookers
The strategic sourcing of infrared cookers presents a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance their culinary offerings while prioritizing efficiency and safety. As outlined, infrared cookers offer significant advantages, including up to 40% greater energy efficiency and faster cooking times compared to traditional methods. This makes them an attractive choice for businesses aiming to reduce operational costs while improving service delivery.
For buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is crucial to consider suppliers who not only provide high-quality products but also understand the specific market dynamics and regulatory environments of their respective regions. Building relationships with manufacturers that emphasize innovation and sustainability will be key to staying competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
Looking ahead, the demand for energy-efficient and safe cooking solutions will only grow, driven by increasing consumer awareness and regulatory pressures. Now is the ideal time to invest in infrared cookers to meet these demands and position your business for future success. Embrace this transformative technology and elevate your kitchen operations today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.