Everything You Need to Know About Do It Yourself Closed Cell Foam Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for do it yourself closed cell foam
Navigating the global market for do-it-yourself closed cell foam presents a unique challenge for B2B buyers looking to enhance insulation solutions in their projects. As energy efficiency becomes a paramount concern across various industries, sourcing the right closed cell foam can significantly impact both operational costs and compliance with local regulations. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of DIY closed cell foam, covering a range of products, their specific applications, and essential factors such as supplier vetting and cost analysis.
International buyers from regions including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, such as Vietnam and Brazil, will find valuable insights tailored to their unique market dynamics. Understanding the differences between various foam types, such as fast-rise versus slow-rise formulations, can aid in making informed purchasing decisions that align with project specifications and budget constraints. Additionally, the guide addresses logistical considerations, including shipping, handling, and training requirements for effective application.
By empowering decision-makers with actionable information and best practices, this guide aims to streamline the procurement process for DIY closed cell foam. Buyers will be better equipped to evaluate suppliers, negotiate costs, and ultimately select the products that best meet their insulation needs, ensuring a successful outcome for their projects.
Understanding do it yourself closed cell foam Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2-Component Spray Foam Kits | Requires mixing of two components; delivers high insulation value | Construction, retrofitting, insulation projects | Pros: High R-value, effective sealing; Cons: Requires training for safe use. |
| HFO Fast Rise Spray Foam | Quick expansion and curing; ideal for new builds | New construction, large area insulation | Pros: Fast application, good for open surfaces; Cons: Higher cost than alternatives. |
| HFO Slow Rise Spray Foam | Expands slowly for controlled application; versatile | Retrofitting, filling cavities | Pros: Better for precision applications; Cons: Longer curing time. |
| HandiFoam Disposable Kits | Pre-packaged, no calibration needed; portable | Small jobs, mobile contractors | Pros: Easy to use, no return logistics; Cons: Limited coverage per kit. |
| Canned Closed Cell Foam | Available in aerosol cans; user-friendly for small applications | DIY projects, minor repairs | Pros: Convenient, accessible; Cons: Limited insulation value, may not pass inspections. |
What are the Characteristics of 2-Component Spray Foam Kits?
2-component spray foam kits are a popular choice for B2B buyers due to their high insulation value and effectiveness in sealing air leaks. These kits require mixing two components—usually an isocyanate and a polyol resin—before application. They are ideal for a variety of projects, including new construction and retrofitting existing structures. Buyers should consider the need for training and safety precautions, as improper handling can lead to health risks and suboptimal results.
How Does HFO Fast Rise Spray Foam Differ from Other Types?
HFO Fast Rise Spray Foam is designed for rapid expansion, making it suitable for new builds where speed is essential. This type of foam quickly fills large areas and adheres well to various surfaces, providing a robust thermal barrier. While its quick application time is a significant advantage, the higher cost may deter some buyers. It is particularly beneficial for contractors looking to complete projects efficiently without sacrificing quality.
What Makes HFO Slow Rise Spray Foam a Versatile Option?
HFO Slow Rise Spray Foam is ideal for applications where precision is crucial, such as retrofitting older buildings. Its slower expansion rate allows for better control during application, ensuring that cavities are filled without damaging existing structures. This versatility makes it a favorite among contractors who work on a variety of projects. However, buyers should be aware that its longer curing time may affect project timelines.
Why Choose HandiFoam Disposable Kits for Smaller Jobs?
HandiFoam Disposable Kits are designed for convenience, providing a ready-to-use solution without the need for calibration. These kits are portable and perfect for small jobs or mobile contractors who require flexibility. The primary downside is their limited coverage compared to larger kits, which may necessitate multiple purchases for extensive projects. Nonetheless, their ease of use and no-return logistics make them an attractive option for many B2B buyers.
Are Canned Closed Cell Foams a Viable Option for DIY Projects?
Canned closed cell foams are gaining popularity among DIY enthusiasts for their convenience and accessibility. Available in aerosol cans, they are easy to apply for minor repairs and small-scale insulation tasks. However, their insulation value may not meet building codes for larger projects, and buyers should check for R-value listings to ensure compliance with local regulations. While they offer a quick fix, they may not be suitable for all applications, particularly those requiring professional-grade performance.
Key Industrial Applications of do it yourself closed cell foam
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of do it yourself closed cell foam | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction & Renovation | Insulating walls, roofs, and attics in new builds or retrofits | Reduces energy costs, enhances thermal performance, and improves indoor comfort | Ensure compliance with local building codes and regulations; consider climate-specific insulation needs. |
| Automotive | Soundproofing and insulation for vehicle interiors | Enhances passenger comfort and reduces noise, improving overall vehicle quality | Evaluate material durability under varying temperatures and moisture levels; ensure compatibility with existing materials. |
| Marine & Transportation | Insulating and sealing hulls and cabins of boats | Increases energy efficiency and prevents condensation and mold growth | Assess marine-grade certifications and resistance to saltwater and UV exposure; consider weight restrictions. |
| HVAC & Refrigeration | Insulating ductwork and refrigeration lines | Improves energy efficiency and reduces operational costs | Verify compatibility with various refrigerants and adherence to safety standards; consider ease of application in confined spaces. |
| Packaging & Shipping | Protective packaging for delicate goods during transport | Minimizes damage and loss, enhancing customer satisfaction | Consider the foam’s cushioning properties and environmental impact; ensure compliance with international shipping regulations. |
How is Do It Yourself Closed Cell Foam Used in Construction and Renovation Projects?
In the construction and renovation sectors, do-it-yourself closed cell foam is primarily used for insulating walls, roofs, and attics. This foam expands upon application, filling gaps and creating an airtight seal that significantly improves thermal performance. For international buyers, especially in regions with diverse climates like Africa and Europe, it is crucial to ensure that the foam complies with local building codes and addresses specific insulation requirements, such as R-value standards. This application not only reduces energy costs but also enhances indoor comfort, making it a valuable investment for builders and homeowners alike.
What Role Does Closed Cell Foam Play in Automotive Applications?
In the automotive industry, do-it-yourself closed cell foam is utilized for soundproofing and insulating vehicle interiors. By applying this foam, manufacturers can enhance passenger comfort by reducing road noise and vibrations. For B2B buyers in automotive sectors across South America and the Middle East, it is essential to evaluate the foam’s durability under varying temperatures and moisture levels, ensuring it can withstand the rigors of different driving conditions. This application not only improves the quality of vehicles but also contributes to higher customer satisfaction.
How Can Marine and Transportation Industries Benefit from Closed Cell Foam?
Closed cell foam is used extensively in the marine and transportation industries for insulating and sealing hulls and cabins of boats. This application increases energy efficiency and prevents condensation and mold growth, which can be detrimental in marine environments. Buyers in these sectors should assess the foam’s marine-grade certifications, ensuring resistance to saltwater and UV exposure, which are critical for longevity. This ensures that vessels remain comfortable and energy-efficient, reducing operational costs over time.
Why is Closed Cell Foam Important for HVAC and Refrigeration?
In HVAC and refrigeration applications, do-it-yourself closed cell foam is employed to insulate ductwork and refrigeration lines. This insulation improves energy efficiency by minimizing heat loss or gain, which can lead to significant operational cost reductions. For buyers in regions with extreme temperatures, it is crucial to verify the foam’s compatibility with various refrigerants and adherence to safety standards. By optimizing HVAC systems, businesses can enhance performance while reducing energy consumption.
How Does Closed Cell Foam Enhance Packaging and Shipping?
In the packaging and shipping industry, closed cell foam serves as protective packaging for delicate goods during transport. Its cushioning properties minimize damage and loss, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction. For international buyers, particularly in regions with strict shipping regulations, it is vital to consider the foam’s environmental impact and compliance with international standards. This ensures that products arrive safely at their destinations while maintaining eco-friendly practices.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘do it yourself closed cell foam’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Application and Performance Issues
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter issues with inconsistent application when using do-it-yourself closed cell foam kits. The foam may expand unpredictably, leading to gaps, uneven coverage, or even overexpansion that compromises structural integrity. This problem is particularly pronounced in regions with varying temperatures and humidity levels, which can affect the curing process and overall effectiveness of the insulation. Buyers may find that their insulation does not meet energy efficiency standards, resulting in potential regulatory issues and increased costs.
The Solution: To address these application inconsistencies, it is crucial to choose a high-quality closed cell foam kit that comes with comprehensive instructions and user support. Buyers should consider investing in kits designed for specific climates, as these products are formulated to perform optimally under local conditions. Additionally, proper training on the equipment and application techniques can significantly improve results. Training sessions can be arranged with the supplier, ensuring that personnel understand how to calibrate the spray equipment correctly and apply the foam evenly. Utilizing temperature-controlled environments during application can also help achieve uniform curing, enhancing overall performance.
Scenario 2: Safety Concerns and Compliance Challenges
The Problem: Another significant concern for B2B buyers is the safety hazards associated with applying closed cell foam. The chemicals involved can pose health risks if not handled properly, and many buyers may not be aware of the necessary personal protective equipment (PPE) or safety protocols required during application. Moreover, compliance with local building codes and safety regulations can be daunting, particularly for international buyers navigating different regulatory landscapes.
The Solution: To mitigate safety concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing closed cell foam kits that include comprehensive PPE packages, such as respirators, gloves, and protective suits. Suppliers should provide clear safety guidelines, including necessary training on equipment usage and chemical handling. Buyers should also conduct a thorough review of local regulations regarding spray foam insulation to ensure compliance. Partnering with local experts or consultants familiar with regional regulations can help streamline this process and ensure that all safety measures are adhered to, ultimately protecting workers and the business from potential liabilities.
Scenario 3: Limited Technical Support and Guidance
The Problem: Many B2B buyers experience frustration due to the lack of technical support when using do-it-yourself closed cell foam products. When issues arise—such as equipment malfunctions or application challenges—buyers often find themselves without adequate resources or guidance. This lack of support can lead to project delays, increased costs, and subpar insulation performance, which can affect customer satisfaction and repeat business.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, it is essential for buyers to choose suppliers who offer robust technical support services. This could include online resources, such as detailed FAQs, instructional videos, and troubleshooting guides. Additionally, buyers should inquire about the availability of live technical support via phone or chat during project hours. Establishing a partnership with suppliers that provide on-site training or consultation can also be beneficial, especially for complex projects. By ensuring that a reliable support system is in place, buyers can enhance their confidence in using closed cell foam products and achieve better project outcomes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for do it yourself closed cell foam
What Are the Key Materials for Do It Yourself Closed Cell Foam?
When selecting materials for do-it-yourself closed cell foam applications, it is essential to consider the properties, advantages, and limitations of various options. Here, we analyze four common materials used in closed cell foam formulations, focusing on their performance characteristics and implications for international B2B buyers.
1. Polyurethane
Key Properties: Polyurethane closed cell foam exhibits excellent thermal insulation properties with an R-value ranging from 6 to 7 per inch. It is also resistant to moisture and can withstand a wide temperature range, making it suitable for various climates.
Pros & Cons: The durability of polyurethane is noteworthy, as it can last for decades without significant degradation. However, the manufacturing process can be complex and requires precise calibration, which may increase costs. Additionally, it may not be suitable for all end products due to its chemical sensitivity.
Impact on Application: Polyurethane foam is compatible with many substrates, including wood and metal. However, it is essential to ensure proper surface preparation to achieve optimal adhesion.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM E84 for fire safety is crucial. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should also consider local regulations regarding chemical emissions during application.

Illustrative image related to do it yourself closed cell foam
2. Polyisocyanurate
Key Properties: Polyisocyanurate foam offers high thermal resistance, with an R-value of approximately 7.2 per inch. It is also known for its fire-resistant properties, making it a preferred choice for certain applications.
Pros & Cons: This material is relatively lightweight and easy to handle, which can reduce installation time and labor costs. However, its higher cost compared to polyurethane may deter some buyers. Additionally, it has a lower compressive strength, which may limit its use in load-bearing applications.
Impact on Application: Polyisocyanurate is particularly effective in roofing applications and can be used in both residential and commercial settings. It is essential to ensure compatibility with roofing membranes and other materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with local building codes and fire safety regulations, particularly in regions like the Middle East where fire resistance is critical.

Illustrative image related to do it yourself closed cell foam
3. Expanded Polystyrene (EPS)
Key Properties: EPS is a lightweight, cost-effective option with decent thermal insulation properties (R-value of about 4.0 per inch). It is also resistant to moisture, although not as effectively as closed-cell polyurethane or polyisocyanurate.
Pros & Cons: The low cost and ease of handling make EPS a popular choice for many DIY projects. However, its lower thermal performance and susceptibility to UV degradation can be significant drawbacks, particularly in outdoor applications.
Impact on Application: EPS is suitable for various applications, including insulation panels and packaging. However, it may require additional protective coatings when exposed to sunlight.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local environmental regulations is essential, especially in regions with strict waste management policies. Buyers should also consider the availability of EPS in their local markets.
4. Phenolic Foam
Key Properties: Phenolic foam offers excellent thermal insulation (R-value of around 5.0 per inch) and is known for its low smoke generation and flame spread characteristics.

Illustrative image related to do it yourself closed cell foam
Pros & Cons: Its fire-resistant properties make it an ideal choice for applications requiring stringent safety standards. However, phenolic foam can be more expensive and may require specialized handling during installation.
Impact on Application: This material is particularly effective in industrial applications, such as refrigeration and HVAC systems. Proper installation techniques are crucial to ensure optimal performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with international standards such as ISO 9705 for fire testing. Additionally, local regulations regarding the handling of phenolic materials should be reviewed.
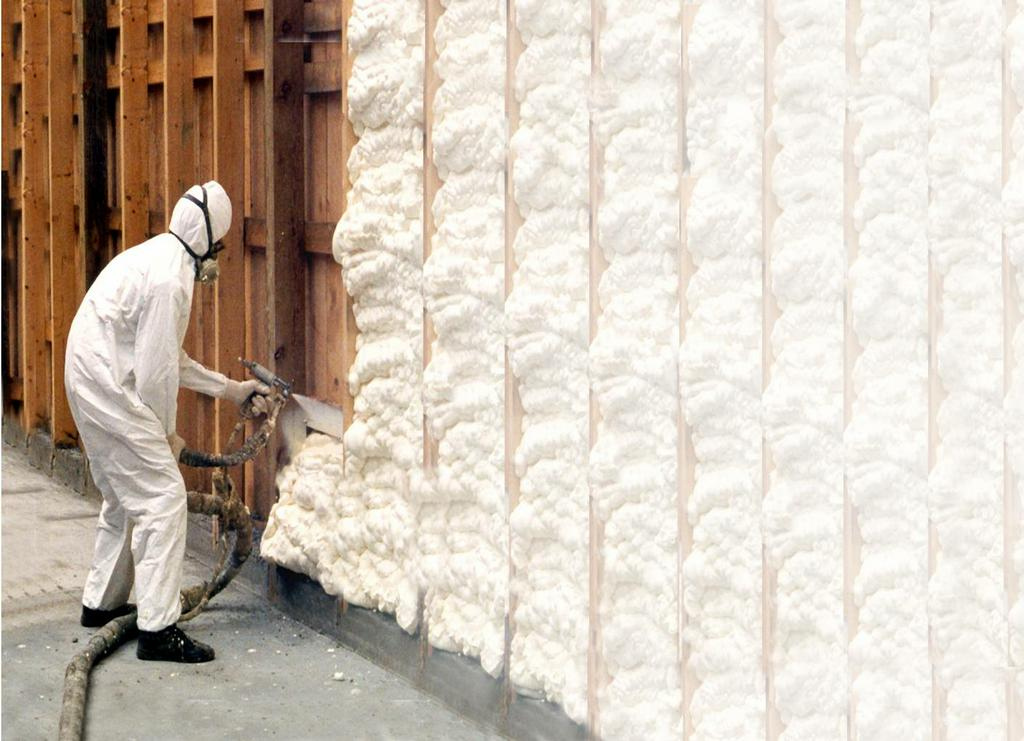

Illustrative image related to do it yourself closed cell foam
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for do it yourself closed cell foam | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane | Insulating walls and roofs in residential projects | High durability and thermal resistance | Complex manufacturing process | Medium |
| Polyisocyanurate | Roofing and commercial insulation applications | Excellent fire resistance | Higher cost compared to alternatives | High |
| Expanded Polystyrene | Insulation panels and packaging | Cost-effective and lightweight | Lower thermal performance | Low |
| Phenolic Foam | Industrial insulation in HVAC and refrigeration | Low smoke generation and flame spread | Higher cost and specialized handling | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers in diverse international markets, helping them make informed decisions when sourcing closed cell foam materials for DIY applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for do it yourself closed cell foam
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Do It Yourself Closed Cell Foam?
The manufacturing process for do it yourself closed cell foam involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: This initial stage includes sourcing high-quality raw materials such as polyols and isocyanates, which are the main components of closed cell foam. Suppliers often conduct rigorous testing of these materials to ensure they meet specific standards before they are used in production. Additionally, the materials must be stored in controlled environments to prevent degradation.
-
Forming: The next step is mixing the prepared materials in precise ratios. This is typically done in a controlled environment to ensure consistency and quality. Advanced mixing techniques, such as high-shear mixing, may be employed to achieve a uniform blend. The mixture is then injected into molds or sprayed onto surfaces, depending on the product design.
-
Assembly: In cases where the foam is part of a kit, components such as spray guns, hoses, and safety gear are assembled alongside the foam product. This assembly process must be meticulously executed to ensure that all parts function correctly when delivered to the end-user.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves curing the foam to achieve its desired properties. This can include heating or cooling processes, depending on the formulation. After curing, products are visually inspected, and any surface imperfections are addressed to ensure aesthetic quality.
What Key Techniques Are Employed in the Manufacturing of Closed Cell Foam?
Manufacturers utilize various advanced techniques to enhance the quality and efficiency of foam production. These may include:
-
Chemical Blending: Precise chemical blending ensures optimal foam characteristics such as density, R-value, and expansion rate. Automated systems often control this process to minimize human error.
-
Temperature Control: Maintaining specific temperatures during the mixing and curing stages is crucial. Temperature fluctuations can affect the foam’s properties, so manufacturers invest in advanced temperature monitoring systems.
-
Quality Control Automation: Automated systems for monitoring production processes help maintain consistency. Sensors can detect variations in density or chemical ratios, triggering alerts for corrective actions.
How is Quality Assurance Integrated into the Manufacturing Process?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the production of do it yourself closed cell foam, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations.

Illustrative image related to do it yourself closed cell foam
-
International Standards: Many manufacturers adhere to ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with these standards is essential for international B2B transactions, as they provide a framework for consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
-
Industry-Specific Certifications: Products may also require certifications such as CE marking for European markets or API standards for specific industrial applications. These certifications validate that the products meet regulatory requirements and performance standards.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: Several checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are tested upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during production helps identify and rectify issues in real time.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Finished products undergo rigorous testing for performance metrics, including density, thermal resistance, and expansion characteristics.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Closed Cell Foam Quality Assurance?
Testing methods for closed cell foam typically include:
-
Density Testing: This determines the weight per unit volume of the foam, which is crucial for insulation performance.
-
Thermal Conductivity Testing: Often measured using a heat flow meter, this test assesses the R-value of the foam, ensuring it meets energy efficiency standards.
-
Expansion Rate Testing: This evaluates how well the foam expands upon application, which is vital for achieving effective insulation.
-
Adhesion Testing: To verify that the foam adheres correctly to various substrates, manufacturers conduct adhesion tests, which are crucial for ensuring long-term performance.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control processes of suppliers:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help ensure that they are adhering to quality management systems and international standards. Buyers should request access to audit reports and corrective action plans.
-
Request Certification Documentation: Buyers should ask for copies of certifications such as ISO 9001 or CE marking. This documentation can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspections: Utilizing third-party inspectors can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control processes. These inspectors can perform their tests and verify compliance with relevant standards.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification:
-
Regional Regulations: Different regions may have distinct regulatory requirements for construction materials. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regulations to ensure compliance.
-
Language Barriers: Documentation and certifications may be in different languages. Buyers should ensure they can understand the quality standards and product specifications.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding the cultural context of suppliers can facilitate better communication regarding quality expectations and standards.
By focusing on these elements, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing do it yourself closed cell foam, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their specifications and compliance requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘do it yourself closed cell foam’
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in procuring ‘do it yourself’ closed cell foam. The process requires careful consideration of technical specifications, supplier reliability, and product quality to ensure optimal performance and compliance with local regulations. Follow these steps to streamline your procurement process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Identifying your project requirements is critical. Establish the necessary R-value, coverage area, and application method for the closed cell foam. This will help narrow down suitable products and ensure compliance with local building codes.
– Considerations:
– What is the intended use (e.g., insulation, soundproofing)?
– Are there specific environmental conditions (e.g., humidity, temperature) to consider?
Step 2: Research Product Options
Explore available products to find the best fit for your needs. Investigate different formulations and performance characteristics of closed cell foam, such as fast rise vs. slow rise options.
– Key Factors:
– Look for products that offer bulk discounts for larger orders.
– Evaluate the ease of use and safety features included in the kits, such as PPE and application tools.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet suppliers to ensure reliability and product quality. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from previous buyers within your region or industry. This will provide insight into their operational standards and customer satisfaction levels.
– What to Ask:
– Can they provide testimonials or case studies demonstrating successful past projects?
– What is their track record for on-time delivery and responsiveness?
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the products meet local and international standards. Check for certifications that demonstrate compliance with safety and environmental regulations, which is particularly crucial in markets with stringent building codes.
– Important Certifications:
– Look for ISO certifications or regional equivalents.
– Ensure products have been tested for fire resistance and thermal performance.
Step 5: Request Samples
Before finalizing a purchase, obtain samples of the foam. Testing small quantities can provide insight into the application process and product performance. This step is vital to avoid costly mistakes with large orders.
– Testing Criteria:
– Assess the foam’s expansion and adhesion capabilities.
– Evaluate ease of application and cleanup.

Illustrative image related to do it yourself closed cell foam
Step 6: Clarify Shipping and Handling Terms
Understand the logistics involved in shipping and handling your order. Verify shipping costs, lead times, and any additional fees for bulky items. This clarity will help in budgeting and planning for your project timeline.
– Key Questions:
– Are there minimum order quantities that affect shipping costs?
– What are the shipping timelines for international orders?
Step 7: Establish Support and Training Options
Look for suppliers that offer training and technical support. Proper training can significantly reduce the risk of application errors and enhance the quality of the installation. Ensure that training is accessible and covers safety protocols.
– Support Features:
– Does the supplier provide on-site training or virtual sessions?
– What ongoing support options are available for troubleshooting?
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for ‘do it yourself’ closed cell foam, ensuring they select the right products and suppliers for their projects.

Illustrative image related to do it yourself closed cell foam
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for do it yourself closed cell foam Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Do It Yourself Closed Cell Foam?
When sourcing do-it-yourself closed cell foam, understanding the cost structure is critical for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The raw materials for closed cell foam typically consist of polyurethane or similar polymers. The quality of these materials directly influences the foam’s thermal resistance (R-value), durability, and performance. Higher-quality materials may incur higher costs but offer better long-term savings in energy efficiency.
-
Labor: Although DIY kits minimize labor costs, training and safety measures are still essential. Companies often provide training sessions, which can add to the initial outlay. Additionally, if the foam application requires specialized skills or additional workforce, these labor costs should be factored into the total expenditure.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to the production process, such as facility costs, utilities, and equipment maintenance. For suppliers, economies of scale can reduce these overheads, allowing them to offer competitive pricing on bulk orders.
-
Tooling and Quality Control (QC): Custom tooling for unique applications can add significant costs, especially if a buyer requires specific shapes or sizes. Quality control measures ensure that the product meets industry standards, which can increase costs but ultimately benefits the buyer by reducing potential failures.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on location and order size. International buyers should consider tariffs, customs fees, and freight charges. Efficient logistics can reduce costs, so selecting suppliers with robust distribution networks is advisable.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to their base costs to ensure profitability. Understanding the margin structure can help buyers negotiate better deals, especially when purchasing in larger quantities.
What Influences Pricing for Closed Cell Foam?
Several factors can significantly influence the pricing of closed cell foam products:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Suppliers often offer discounts for bulk purchases. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers optimize their orders to achieve better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom formulations or specific performance characteristics (like fire resistance or environmental certifications) can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against budget constraints.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Certifications (e.g., LEED, ISO) can affect pricing. Higher-quality materials that meet stringent standards may cost more but can enhance the product’s reputation and marketability.
-
Supplier Factors: Reputation, reliability, and the supplier’s location can impact pricing. Sourcing from established suppliers may yield better service and product reliability.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipment (e.g., FOB, CIF) affect the total landed cost. Understanding these terms can help buyers assess their overall expenses more accurately.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Closed Cell Foam Internationally?
-
Negotiation Strategies: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing and terms. Leverage bulk purchasing power to negotiate better deals. Building long-term relationships can lead to more favorable terms over time.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): While initial costs are important, consider the long-term savings from energy efficiency and durability. A higher upfront cost may be justified if the product provides significant savings over its lifespan.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and their impact on pricing. For buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, understanding local market conditions can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Research and Due Diligence: Prioritize suppliers with positive reviews and proven track records. Request samples to evaluate quality before committing to larger orders.
-
Consider Local Regulations: Different regions may have varying building codes and insulation requirements. Ensure that the products sourced comply with local regulations to avoid costly modifications or penalties.
By understanding these cost components, pricing influencers, and effective sourcing strategies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing do-it-yourself closed cell foam products.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing do it yourself closed cell foam With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Do It Yourself Closed Cell Foam
When considering insulation options, B2B buyers are often faced with various alternatives to do it yourself (DIY) closed cell foam. Each solution has its unique advantages and drawbacks, making it crucial to evaluate them based on performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases. This analysis will help international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Do It Yourself Closed Cell Foam | Alternative 1: Spray Foam Insulation Kits | Alternative 2: Fiberglass Insulation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High R-value, moisture barrier | High R-value, versatile applications | Moderate R-value, less effective moisture barrier |
| Cost | Moderate ($410 – $950) | Higher ($875 – $7,717) | Lower ($0.50 – $1.00 per square foot) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires some training; DIY-friendly | Requires professional training; easy to use | Simple installation; no special skills needed |
| Maintenance | Minimal, long-lasting | Minimal; requires proper handling | Moderate; may require replacement over time |
| Best Use Case | Retrofits, small projects | New builds, large jobs | Attics, walls, and floors in low-budget applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Spray Foam Insulation Kits?
Spray foam insulation kits, such as those offered by Tiger Foam and SFS PRO, provide a professional-grade solution that combines high R-values with ease of application. They are ideal for larger projects and new constructions, providing excellent coverage and insulating capabilities. However, these kits often come at a higher price point, ranging from $875 to over $7,700, depending on the size and complexity of the job. While they offer a quick setup and are user-friendly, they require professional training for safe and effective use, which may add to the overall project timeline and cost.
How Does Fiberglass Insulation Compare to Closed Cell Foam?
Fiberglass insulation is a traditional and widely used alternative that offers a lower upfront cost, typically ranging from $0.50 to $1.00 per square foot. It is relatively easy to install, making it a popular choice for DIY projects. However, its R-value is generally lower than that of closed cell foam, and it does not provide the same level of moisture resistance, which can lead to issues in humid environments. Fiberglass also requires more maintenance and may need replacement over time, particularly in areas prone to moisture exposure.

Illustrative image related to do it yourself closed cell foam
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Insulation Solution for Your Needs
In summary, selecting the right insulation solution hinges on understanding the specific requirements of your project. Do it yourself closed cell foam offers high performance and durability, making it suitable for retrofitting smaller areas. Conversely, spray foam insulation kits present a robust option for larger or new constructions but come with higher costs and require professional training. Fiberglass insulation is a budget-friendly alternative, albeit with lower performance in moisture resistance. B2B buyers should carefully assess their project scope, budget, and expertise to choose the most suitable insulation solution that aligns with their operational goals and environmental conditions.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for do it yourself closed cell foam
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Do-It-Yourself Closed Cell Foam?
When considering closed cell foam for DIY applications, several technical properties are crucial for ensuring performance, durability, and compliance with industry standards. Understanding these specifications can greatly impact purchasing decisions.
-
R-Value: This is a measure of thermal resistance. In the context of closed cell foam, a higher R-value indicates better insulation performance. For B2B buyers, knowing the R-value helps assess whether the foam meets building codes and energy efficiency standards required in various regions.
-
Density: The density of closed cell foam is typically expressed in pounds per cubic foot (pcf). Higher density foam generally offers superior insulation and structural integrity. B2B buyers should consider the density based on the application—lighter foams are often suitable for residential projects, while heavier densities may be necessary for commercial applications requiring greater durability.
-
Tensile Strength: This refers to the foam’s ability to withstand tension without breaking. It is measured in pounds per square inch (psi). For businesses, a higher tensile strength indicates the foam can endure various stresses and loads, making it suitable for more demanding applications.
-
Expansion Rate: Closed cell foam expands upon application, which is critical for filling gaps and voids. The expansion rate can be a determining factor in how efficiently the foam can be applied. B2B buyers should ensure that the product’s expansion rate aligns with their project requirements to avoid wastage and ensure a proper seal.
-
Fire Rating: The fire resistance of closed cell foam is categorized by various standards, such as ASTM E84. Understanding the fire rating is essential for compliance with safety regulations in construction projects, especially in commercial settings where fire safety is paramount.
-
Shelf Life: This refers to the period during which the foam maintains its properties before use. It is typically noted in months from the date of manufacture. For B2B buyers, a longer shelf life can reduce costs associated with disposal of expired materials and ensure flexibility in project scheduling.
What Are Common Terms Used in the Do-It-Yourself Closed Cell Foam Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology can significantly enhance communication and negotiation processes in B2B transactions. Here are some essential terms to understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and manufacturers for closed cell foam products.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): This is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budget planning and ensures that buyers can meet their project needs without incurring unnecessary costs.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): This is a standard business process in which a buyer requests pricing and other details from suppliers. An RFQ is essential for B2B buyers looking to compare options and secure competitive pricing for closed cell foam products.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation.
-
BFT (Board Feet): This unit of measurement is commonly used to quantify the volume of foam products. Understanding BFT is vital for estimating how much material will be needed for a project and ensuring accurate pricing.
-
PPE (Personal Protective Equipment): This refers to safety gear required when handling spray foam products, such as gloves, goggles, and respirators. Awareness of PPE requirements is essential for maintaining safety standards in both DIY and professional applications.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed purchasing decisions regarding do-it-yourself closed cell foam products, ultimately leading to successful project outcomes.
Illustrative image related to do it yourself closed cell foam
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the do it yourself closed cell foam Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Do It Yourself Closed Cell Foam Sector?
The global do-it-yourself (DIY) closed cell foam market is witnessing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient insulation solutions across various sectors. A key driver is the rising awareness of energy conservation and the need for sustainable building practices, particularly in emerging markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These regions are experiencing a surge in construction activities, pushing the demand for effective insulation materials that provide superior thermal resistance and moisture barriers.
Emerging technologies are reshaping the sourcing landscape for closed cell foam. Innovations such as portable spray foam kits allow contractors and DIY enthusiasts to undertake insulation projects with ease and efficiency. For instance, kits that include all necessary components—such as guns, nozzles, and safety gear—are increasingly popular among B2B buyers seeking convenience and effectiveness. Additionally, there is a notable trend towards customization, with suppliers offering various formulations tailored for specific applications, from small DIY jobs to large-scale construction projects.
International B2B buyers are also prioritizing suppliers who can provide comprehensive support, including training and technical assistance, to ensure proper application and compliance with local building codes. As the market evolves, understanding these dynamics will be crucial for buyers looking to optimize their sourcing strategies and capitalize on emerging opportunities within the DIY closed cell foam sector.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Important in the Do It Yourself Closed Cell Foam Market?
Sustainability is becoming a central theme in the sourcing of do-it-yourself closed cell foam products, as both consumers and businesses increasingly prioritize environmentally responsible materials. The production of closed cell foam can have significant environmental impacts, particularly in terms of greenhouse gas emissions associated with traditional manufacturing processes. As a result, manufacturers are shifting towards more sustainable practices, including the use of eco-friendly blowing agents and raw materials sourced from renewable resources.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers are now more aware of the supply chain’s transparency and the environmental and social implications of their purchases. Companies that can demonstrate a commitment to ethical practices—such as fair labor conditions and responsible sourcing of raw materials—are likely to gain a competitive advantage. Additionally, certifications such as GreenGuard and LEED can enhance a product’s appeal, offering assurance to buyers that the materials used are safe and environmentally friendly.

Illustrative image related to do it yourself closed cell foam
For B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where regulatory frameworks may be evolving, sourcing from suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices can mitigate risks and enhance brand reputation. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, businesses can not only meet regulatory requirements but also cater to the growing consumer demand for eco-conscious products.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Do It Yourself Closed Cell Foam Sector?
The do-it-yourself closed cell foam sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades, transitioning from traditional insulation methods to advanced spray foam technologies. Initially, closed cell foam was primarily used in commercial applications, but innovations have made it accessible for residential and DIY projects. The introduction of user-friendly spray foam kits has empowered homeowners and small contractors to undertake insulation tasks without needing specialized equipment.
In recent years, the market has shifted towards greater customization and performance, with manufacturers developing specialized formulations that cater to specific applications, such as retrofitting and new constructions. This evolution has not only enhanced the product’s versatility but also its appeal to a broader audience, including international B2B buyers looking for efficient and effective insulation solutions. As the sector continues to grow, ongoing innovations in technology and materials will likely shape its future, making it an exciting area for investment and development.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of do it yourself closed cell foam
-
How do I ensure the quality of closed cell foam products before purchasing?
To ensure the quality of closed cell foam products, conduct thorough supplier vetting. Request product samples and technical data sheets to assess the foam’s specifications, such as density and R-value. Additionally, check for certifications that meet international standards, such as ISO or ASTM compliance. Engaging with customer reviews and case studies can provide insights into the product’s performance in real-world applications. Establishing clear communication with the supplier about quality assurance processes can also help mitigate risks. -
What is the best closed cell foam option for insulation in humid climates?
For humid climates, closed cell foam with a high R-value and moisture resistance is optimal. Products designed specifically for high humidity applications will prevent moisture accumulation and mold growth. Look for foams that provide excellent air sealing properties and are rated for exterior use to withstand environmental stressors. Consulting with suppliers on product specifications and real-world performance can help you select the best option tailored to your specific project needs. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for closed cell foam kits?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for closed cell foam kits can vary significantly among suppliers. Some manufacturers may offer MOQs as low as one kit, while others may require larger bulk orders to achieve competitive pricing. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about their flexibility on MOQs, especially if you are testing the market or starting a new project. Consider discussing your long-term purchasing plans, as this may incentivize suppliers to accommodate smaller orders initially. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing closed cell foam internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing of closed cell foam typically range from 30% upfront deposit with the balance due upon shipment, to net 30 or net 60 terms after delivery. It’s essential to clarify payment methods, such as wire transfers, letters of credit, or online payment platforms. Additionally, be aware of currency fluctuations and potential fees associated with international transactions. Establishing a clear agreement in your purchase contract will help avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I customize closed cell foam products for my specific needs?
Customizing closed cell foam products often involves discussing specific requirements with your supplier, such as density, size, and formulation. Many manufacturers offer tailored solutions, including variations in R-value, color, or additional properties like flame resistance. Providing detailed specifications and understanding the production capabilities of the supplier will facilitate a smoother customization process. Be prepared to discuss lead times and any additional costs associated with custom orders. -
What are the shipping options and logistics considerations for closed cell foam products?
Shipping options for closed cell foam products vary based on weight, volume, and destination. Most suppliers can provide shipping via air or sea freight, with air being faster but often more expensive. Ensure you understand the logistics involved, including customs regulations, import duties, and potential delays. Collaborate with suppliers who can assist in navigating these complexities, and consider using freight forwarders with expertise in handling foam products for smooth delivery. -
How do I assess the environmental impact of closed cell foam products?
To assess the environmental impact of closed cell foam products, inquire about the materials used in production and their sustainability certifications. Products that utilize eco-friendly blowing agents and have low global warming potential (GWP) are preferable. Additionally, consider the lifecycle assessment of the foam, including its energy efficiency in application and disposal options at the end of its life. Engaging with suppliers on their sustainability practices can provide valuable insights into the environmental footprint of their products. -
What safety measures should I take when using closed cell foam?
When using closed cell foam, safety is paramount. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and respiratory protection, as the application process can release harmful chemicals. Ensure the workspace is well-ventilated to minimize inhalation risks. Familiarize yourself with the material safety data sheets (MSDS) provided by the supplier and follow all recommended safety guidelines during application. Consider completing a training session if available, to understand proper handling and emergency procedures.
Top 3 Do It Yourself Closed Cell Foam Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Tiger Foam – Closed Cell Spray Foam Insulation
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: DIY closed cell spray foam insulation for a cathedral ceiling in a garage. Required amount: approximately 1,000 board feet (330 sq ft at 3 inches thick). Brands considered: Tiger Foam, Foam It Green, Froth-Pak, Kraken. Desired outcome: decent appearance for potential painting.
2. Green Building Advisor – Canned Closed Cell Spray Foam
Domain: greenbuildingadvisor.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Canned closed cell spray foam is a DIY product that can be used for insulation, but it is not equivalent to professional two-part spray foam. It requires a specific foam gun for application and is easier to use for smaller areas rather than large spaces. The product needs to list an R-value to pass inspection. It is noted that while it can seal larger areas, it may not provide the same insulating …
3. Facebook – DIY Closed Cell Spray Foam Guide
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – DIY Closed Cell Spray Foam Guide, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for do it yourself closed cell foam
Why is Strategic Sourcing Crucial for Do It Yourself Closed Cell Foam?
In the competitive landscape of do it yourself closed cell foam, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical element for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their procurement processes. By establishing strong relationships with reliable suppliers, businesses can ensure consistent quality and availability of materials, thus enhancing project efficiency and performance. This is especially vital in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where market dynamics may fluctuate, and local suppliers might offer unique advantages.
How Can International Buyers Leverage Opportunities in the Foam Market?
As international buyers explore the expanding market for do it yourself closed cell foam, they should consider factors such as price competitiveness, product specifications, and supplier reliability. Engaging with manufacturers that offer bulk purchasing options or specialized kits tailored for specific applications can lead to significant cost savings. Additionally, understanding the unique needs of local markets will enable buyers to tailor their offerings effectively.
What Lies Ahead for the Do It Yourself Closed Cell Foam Sector?
Looking forward, the demand for closed cell foam solutions is expected to rise, driven by increasing awareness of energy efficiency and sustainable building practices. This presents a lucrative opportunity for B2B buyers to invest in innovative products and technologies that meet evolving market needs. By prioritizing strategic sourcing and staying informed about industry trends, international buyers can position themselves for success in this growing sector. Embrace these opportunities and elevate your procurement strategy to capitalize on the future of closed cell foam.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.