Is Your Rubber Plastic Molding Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read This 2025 Report
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rubber plastic molding
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing reliable rubber plastic molding solutions can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to optimize their production processes, understanding the intricacies of rubber molding becomes crucial. This guide delves into the various types of rubber plastic molding, including transfer, compression, and injection molding, highlighting their specific applications and advantages.
By exploring the nuances of each method, buyers will be equipped to select the most suitable approach for their unique needs, whether it’s for automotive components, medical devices, or industrial applications. Additionally, we will cover essential considerations for supplier vetting, ensuring that businesses can identify trustworthy partners that meet quality and compliance standards.
Cost analysis, material specifications, and production volume requirements will also be addressed, empowering buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals. Ultimately, this comprehensive resource serves as a roadmap for navigating the global market for rubber plastic molding, enabling businesses to enhance their supply chain efficiency and drive innovation in their respective sectors.
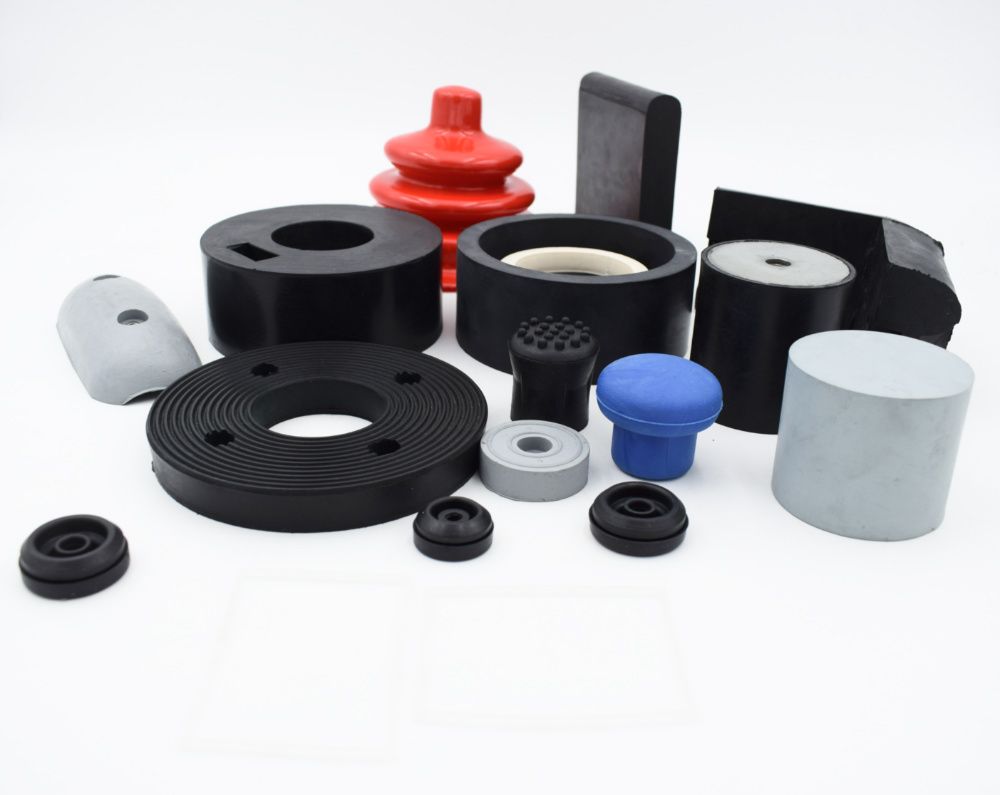
Understanding rubber plastic molding Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber Transfer Molding | Utilizes closed molds; suitable for intricate designs; piston-driven | Automotive parts, seals, gaskets | Pros: High precision; Cons: Potential material waste |
| Rubber Compression Molding | Open molds; uses pre-formed rubber; ideal for low to medium volumes | Seals, O-rings, larger parts | Pros: Simple process; Cons: Longer curing times |
| Rubber Injection Molding | High pressure; eliminates pre-forms; suitable for high volumes | Consumer goods, medical devices | Pros: Fast production; Cons: Higher initial setup costs |
| Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) | Uses liquid silicone; closed systems; excellent for complex shapes | Medical, automotive, electronics | Pros: Reduced contamination; Cons: Requires specialized molds |
| Thermoplastic Rubber Injection | Processes elastomers like plastic; recyclable; color options | Toys, automotive components | Pros: Efficient production; Cons: Limited to high-temperature applications |
What Are the Characteristics of Rubber Transfer Molding?
Rubber transfer molding is characterized by its use of closed molds, making it ideal for producing parts with multiple cavities or intricate designs. The process involves compressing rubber into a pot, which is then forced through sprues to fill the mold cavities. This method is particularly suitable for applications requiring high dimensional tolerance, such as automotive components and seals. Buyers should consider the cost implications of material waste and the need for precise molds when opting for this method.
How Does Rubber Compression Molding Work?
Rubber compression molding is one of the oldest molding processes, where pre-formed rubber is placed in open molds and cured under heat and pressure. This method is best suited for low to medium production volumes, making it a cost-effective choice for producing seals and O-rings. However, it requires longer curing times and specific molds, which can impact lead times. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of strong material performance against the potential delays in production.

Illustrative image related to rubber plastic molding
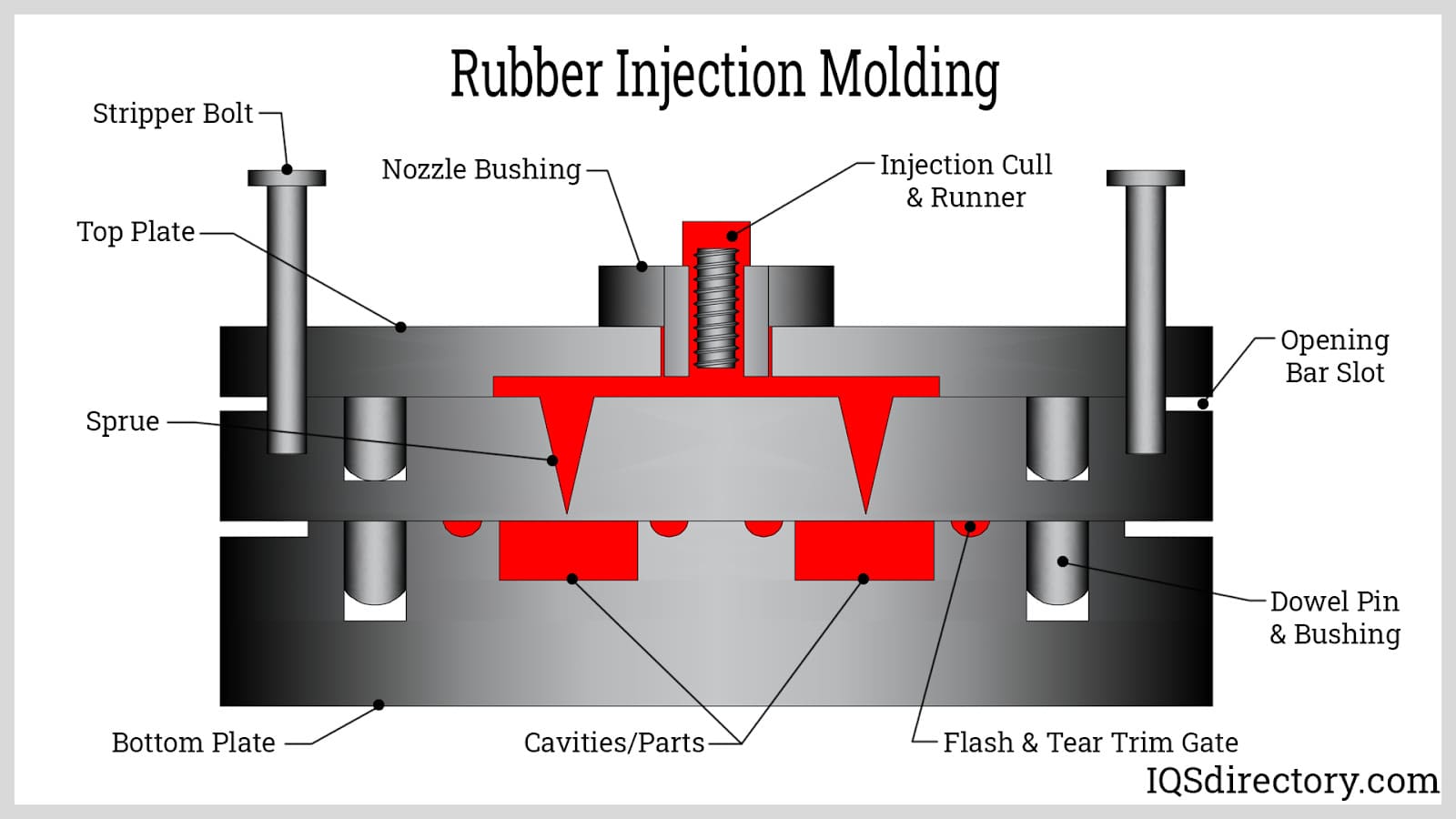
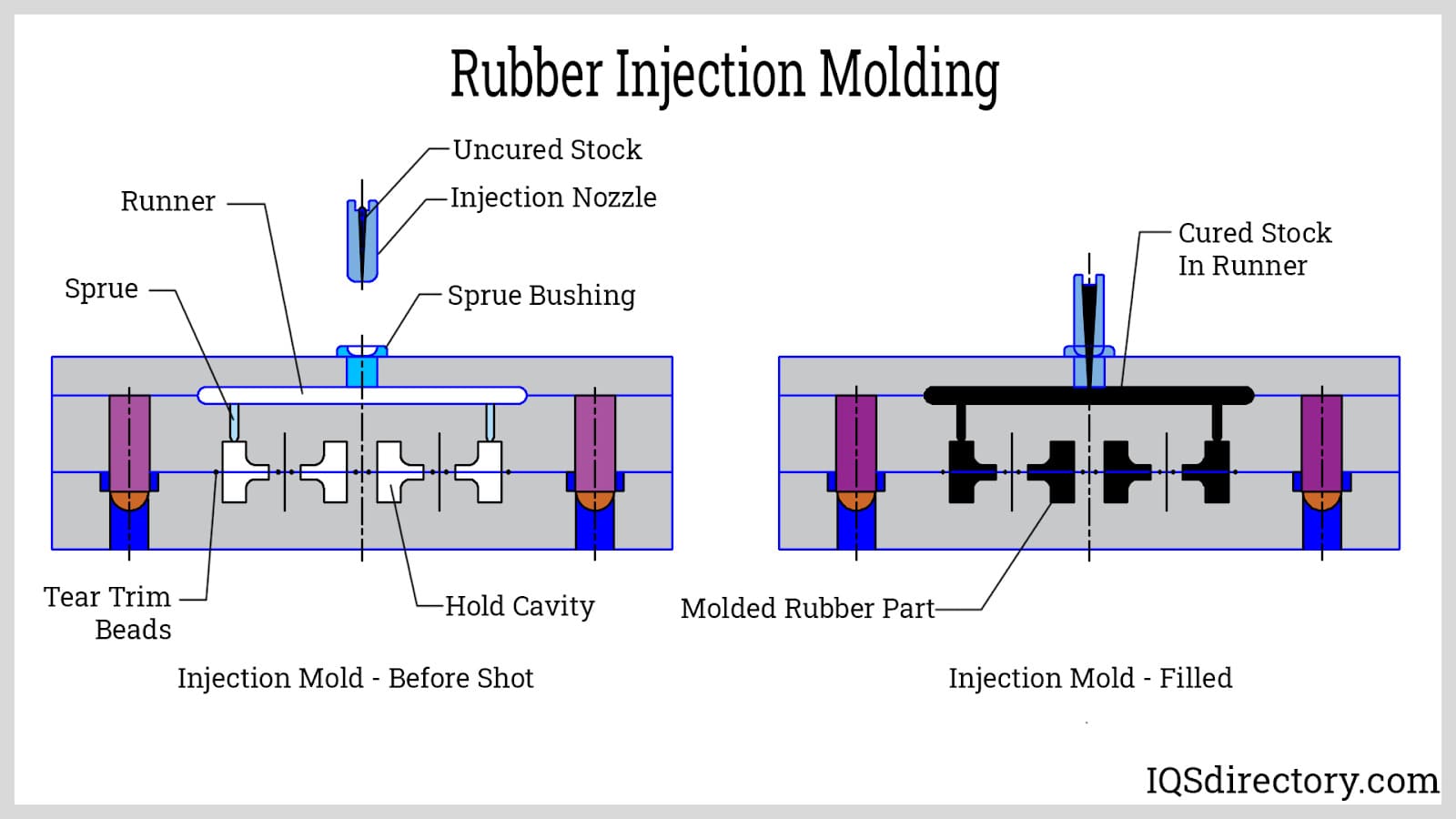
Why Choose Rubber Injection Molding?
Rubber injection molding is distinguished by its ability to operate under high pressure, which allows for rapid production of medium to high precision components. This method eliminates the need for pre-forms, streamlining the manufacturing process. It is widely used in the production of consumer goods and medical devices, where speed and precision are critical. Buyers should consider the initial setup costs but can benefit from reduced cycle times and minimal material waste over high-volume runs.
What Are the Advantages of Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR)?
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) molding utilizes a two-part silicone mixture, which is injected into molds through a closed system. This process is particularly advantageous for producing complex shapes with reduced contamination risks, making it popular in medical and automotive applications. B2B buyers should note the necessity for specialized molds and the potential for higher initial costs, but the benefits of faster cycle times and high-quality finishes often justify the investment.
How Does Thermoplastic Rubber Injection Differ?
Thermoplastic rubber injection processes elastomers similarly to plastics, allowing for efficient production and the ability to recycle materials. This method is particularly effective for creating colorful and versatile products such as toys and automotive components. However, it is limited to applications that can withstand higher temperatures. B2B buyers must assess the suitability of thermoplastic elastomers for their specific applications, balancing efficiency with performance requirements.
Key Industrial Applications of rubber plastic molding
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of rubber plastic molding | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Seals and Gaskets | Enhanced durability and performance of vehicle components | Material compatibility, compliance with automotive standards |
| Electronics | Insulation and Housing Parts | Improved safety and performance of electronic devices | Precision in design, temperature resistance, and certifications |
| Medical Devices | Custom Molds for Medical Components | High precision and reliability in critical applications | Biocompatibility, regulatory compliance, and rapid prototyping |
| Construction | Vibration Dampening Components | Increased longevity and safety of construction machinery | Customization options, environmental resistance, and bulk pricing |
| Consumer Goods | Custom Rubber Grips and Handles | Enhanced user experience and product differentiation | Design flexibility, color options, and production volume requirements |
How is Rubber Plastic Molding Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, rubber plastic molding is primarily utilized for the production of seals and gaskets. These components are essential for preventing leaks and maintaining optimal performance in vehicles. International buyers need to consider material compatibility with various fluids and environmental conditions, as well as compliance with industry standards. The ability to customize these parts ensures they can withstand the rigors of different climates, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where temperature variations can be significant.
What Are the Applications in Electronics?
Rubber plastic molding is crucial in the electronics industry for creating insulation and housing parts that protect sensitive components. These molded parts provide safety against electrical hazards and environmental factors. Buyers must focus on precision manufacturing to ensure proper fit and function, along with temperature resistance to prevent failures. Compliance with international safety standards is also paramount, especially for markets in Europe and the Middle East, where regulatory scrutiny is high.
How is Rubber Molding Used in Medical Devices?
In the medical device sector, rubber plastic molding is employed to create custom molds for various components, including seals and housings. The high precision required in medical applications ensures that devices operate reliably and safely. International buyers should prioritize biocompatibility and adherence to strict regulatory standards, such as those outlined by the FDA or ISO certifications. Rapid prototyping capabilities can also be a significant advantage, enabling quicker time-to-market for innovative medical solutions.
What is the Role in Construction?
Rubber plastic molding finds significant application in construction through the production of vibration dampening components. These parts help to minimize wear and tear on machinery, enhancing safety and durability. Buyers should consider customization options that cater to specific machinery types, as well as environmental resistance to ensure longevity in diverse settings. Cost-effective bulk pricing can also be a vital factor for construction companies operating in emerging markets.
How is it Applied in Consumer Goods?
In the consumer goods industry, rubber plastic molding is often used to produce custom rubber grips and handles that enhance the user experience. These components can differentiate products in a competitive market. Buyers should focus on design flexibility and the ability to incorporate various colors and textures. Additionally, understanding production volume requirements is essential to ensure cost-effectiveness, particularly for businesses targeting mass markets across regions such as Africa and South America.

Illustrative image related to rubber plastic molding
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘rubber plastic molding’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Struggling with Inconsistent Quality in Rubber Molding Parts
The Problem: A manufacturing company in Nigeria is facing challenges with the quality of rubber molded components. They often receive parts that vary significantly in dimensions and properties, leading to increased rework, production delays, and dissatisfied customers. The inconsistency not only impacts their bottom line but also strains relationships with clients who depend on precise specifications for their operations.
The Solution: To tackle this issue, it is essential to partner with a reliable rubber molding supplier that emphasizes quality control. Start by conducting thorough due diligence on potential suppliers, looking for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicate a commitment to quality management. Engage in discussions about their molding processes, focusing on their capabilities in maintaining dimensional tolerances and material properties. Request samples to evaluate consistency before placing larger orders. Implement a systematic quality assurance process on your end, including regular inspections and testing of received parts. By ensuring that your supplier adheres to strict quality protocols and that you have your quality checks in place, you can significantly reduce variability and enhance the reliability of your rubber molded products.
Scenario 2: High Production Costs Due to Inefficient Molding Processes
The Problem: A company in South America is struggling with high production costs associated with rubber plastic molding. They are using compression molding for their parts, which is labor-intensive and time-consuming. As demand increases, the slow production rate and high labor costs are eroding their profit margins, making it difficult to compete in the market.

Illustrative image related to rubber plastic molding
The Solution: Transitioning to injection molding could be a game-changer for this company. Injection molding allows for higher production rates, reduced labor costs, and minimal material waste. Begin by evaluating the feasibility of switching to injection molding by assessing your part designs and volumes. Collaborate with an experienced rubber molding supplier who can assist in redesigning parts for optimal injection molding performance. Ensure that the supplier can accommodate your production volume and has the necessary machinery and expertise. By making this shift, you can streamline your production process, decrease cycle times, and ultimately reduce costs, enhancing your competitiveness in the market.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Customizing Rubber Parts for Specific Applications
The Problem: A business in the Middle East requires specialized rubber components for its machinery but faces challenges in finding a supplier capable of delivering custom solutions. Off-the-shelf parts do not meet the unique specifications needed for their equipment, leading to performance issues and frequent malfunctions.
The Solution: To address this pain point, it’s crucial to seek out suppliers that specialize in custom rubber injection molding. Start by clearly defining your specific requirements, including dimensions, material properties, and performance standards. Engage with potential suppliers who have a proven track record in custom solutions and can demonstrate their capabilities through case studies or references. Request prototyping services to test the fit and function of the custom parts before finalizing orders. Establishing a strong collaborative relationship with your supplier will enable you to iterate on designs efficiently. By investing in custom rubber parts tailored to your needs, you can enhance the performance and reliability of your machinery, reducing downtime and improving overall operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rubber plastic molding
What Are the Key Materials Used in Rubber Plastic Molding?
When selecting materials for rubber plastic molding, international B2B buyers must consider various factors, including performance properties, cost-effectiveness, and compliance with regional standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in rubber plastic molding, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.

Illustrative image related to rubber plastic molding
1. Natural Rubber
Key Properties: Natural rubber exhibits excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and resilience. It has a temperature rating of approximately -40°C to 80°C and offers good abrasion resistance.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of natural rubber is its superior flexibility and durability, making it ideal for applications requiring high resilience. However, it has limited resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals, which can restrict its use in certain environments. Additionally, natural rubber can be more expensive than synthetic alternatives due to its sourcing and processing.
Impact on Application: Natural rubber is particularly suitable for dynamic applications such as seals, gaskets, and vibration dampers. Its compatibility with various media, including water and air, enhances its versatility.
Illustrative image related to rubber plastic molding
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM D2000 standards is essential for ensuring product quality. Buyers in regions with high humidity, such as parts of Africa and South America, should consider the potential for degradation over time.
2. Silicone Rubber
Key Properties: Silicone rubber is known for its high-temperature resistance, ranging from -60°C to 230°C, and excellent chemical stability. It is also UV resistant and maintains flexibility in extreme temperatures.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of silicone rubber is its ability to withstand harsh environments, making it suitable for medical and food-grade applications. However, it tends to be more expensive than other rubber materials and may have lower tensile strength, which can limit its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Silicone rubber is ideal for applications involving exposure to extreme temperatures or corrosive substances, such as seals in automotive and aerospace industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure compliance with FDA and other relevant standards, particularly for food and medical applications. In regions like Europe, adherence to REACH regulations is critical.
3. EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer)
Key Properties: EPDM rubber is characterized by its excellent weather resistance, ozone resistance, and temperature range of -50°C to 150°C. It is also resistant to steam and water.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of EPDM is its durability and resistance to environmental factors, making it suitable for outdoor applications. However, it has limited oil and solvent resistance, which may restrict its use in certain industrial settings.
Impact on Application: EPDM is commonly used in roofing membranes, automotive weather seals, and hoses. Its compatibility with water and steam makes it ideal for plumbing applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of ASTM D1418 and other relevant standards to ensure product quality. In regions with extreme weather conditions, such as the Middle East, EPDM’s resistance to UV and ozone is particularly beneficial.
Illustrative image related to rubber plastic molding
4. Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Key Properties: Nitrile rubber offers excellent oil and fuel resistance, with a temperature range of -40°C to 120°C. It also has good abrasion resistance and tensile strength.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of NBR is its superior resistance to oils and fuels, making it a preferred choice for automotive and industrial applications. However, it has limited resistance to heat and ozone, which can lead to degradation in certain environments.
Impact on Application: NBR is widely used in the production of gaskets, seals, and hoses that come into contact with petroleum-based products.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM D2000 and other industry standards is crucial for ensuring product reliability. Buyers in oil-rich regions, such as parts of South America and the Middle East, will find NBR particularly advantageous.
Summary Table of Materials for Rubber Plastic Molding
| Material | Typical Use Case for rubber plastic molding | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber | Seals, gaskets, vibration dampers | Superior flexibility and durability | Limited resistance to heat and chemicals | Medium |
| Silicone Rubber | Medical devices, food-grade applications | High-temperature and chemical resistance | Higher cost and lower tensile strength | High |
| EPDM | Roofing membranes, automotive seals | Excellent weather and ozone resistance | Limited oil and solvent resistance | Medium |
| Nitrile Rubber | Gaskets, seals, hoses | Superior oil and fuel resistance | Limited heat and ozone resistance | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide aims to empower B2B buyers with the insights necessary to make informed decisions regarding rubber plastic molding materials, ensuring that they meet both performance and compliance requirements in their respective markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rubber plastic molding
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Rubber Plastic Molding?
Rubber plastic molding is a sophisticated process that requires careful planning and execution to ensure that the final products meet the specific needs of various industries. The manufacturing process can be broken down into four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.

Illustrative image related to rubber plastic molding
How Is Material Prepared for Rubber Plastic Molding?
Material preparation is the foundational step in the rubber plastic molding process. The quality of the raw materials directly impacts the performance and durability of the final product. Typically, this stage involves sourcing high-quality rubber compounds, which can include natural rubber, synthetic rubber, or thermoplastic elastomers (TPE).
The preparation process includes several critical steps:
-
Mixing: Raw rubber materials are blended with additives such as curing agents, fillers, and pigments to achieve the desired properties. This is usually done in a large mixer, where the temperature and timing are controlled to ensure a homogenous mixture.
-
Stripping: The mixed rubber is then stripped into consistent strips or pre-forms. This uniformity is essential for the subsequent molding process, as irregular sizes can lead to defects.
-
Quality Checks: Before moving to the next stage, the prepared material undergoes initial quality checks to ensure it meets specifications. This can include viscosity measurements and visual inspections.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Rubber Plastic Molding?
Forming is where the prepared rubber is shaped into the desired components. There are several techniques commonly employed, each suited to specific applications.
-
Compression Molding: This traditional technique involves placing a pre-measured amount of rubber into an open mold. Heat and pressure are applied to cure the rubber into the desired shape. It is cost-effective for low-volume production but may have longer cycle times.
-
Transfer Molding: Ideal for parts with complex geometries, this method involves transferring rubber from a pot into a closed mold. It allows for better control over dimensions but can lead to material waste.
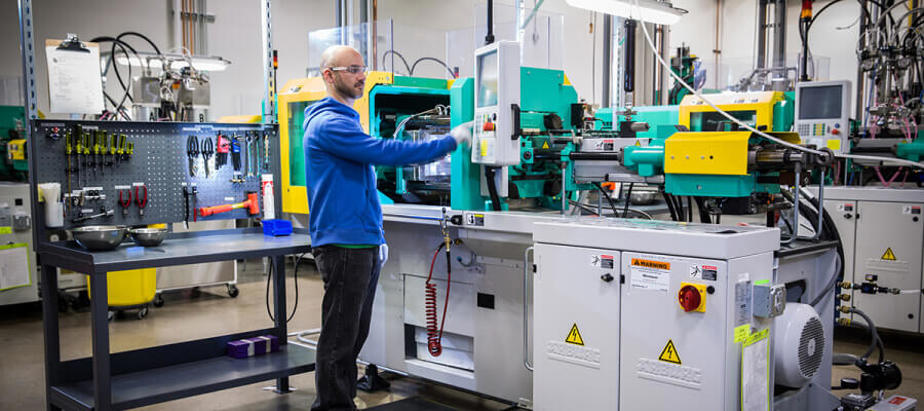
-
Injection Molding: The most widely used method, injection molding, involves heating the rubber and injecting it into a mold under high pressure. This technique allows for high precision and is suitable for mass production. Variants like Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) injection offer benefits such as reduced contamination and shorter cycle times.
How Is Assembly Handled in Rubber Plastic Molding?
Once the rubber parts are formed, the next step is assembly, particularly for components that require multiple parts to function correctly. This can include:
-
Bonding: Rubber parts may need to be bonded to other materials, such as metals or plastics, using adhesives or mechanical fastening techniques. This is critical in industries like automotive and aerospace where component integrity is paramount.
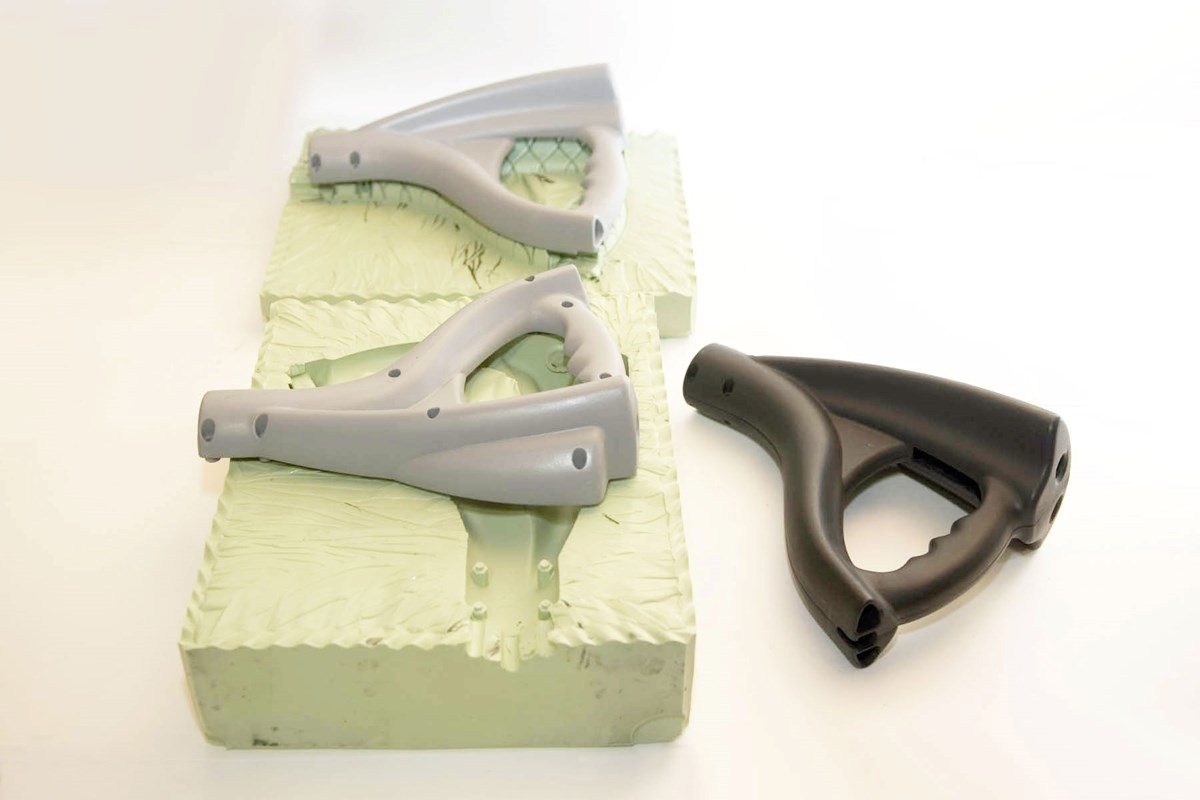
-
Overmolding: This technique involves molding rubber over existing parts, creating a seamless integration of materials. It’s commonly used for ergonomic grips and seals.
What Are the Finishing Processes in Rubber Plastic Molding?
Finishing processes enhance the aesthetic and functional qualities of the molded rubber products. Common finishing techniques include:
-
Trimming: Excess rubber or flash is removed to achieve the final dimensions and improve appearance.
-
Surface Treatments: Processes such as texturing, painting, or coating can be applied to enhance grip, appearance, and resistance to environmental factors.
-
Quality Assurance: Final products undergo rigorous inspections to ensure they meet specified standards before shipment.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Important in Rubber Plastic Molding?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the rubber plastic molding process. Implementing a robust QA system helps ensure that products meet international standards and customer expectations.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For B2B buyers, it’s crucial to understand the relevant international quality standards that govern the rubber plastic molding industry. Key standards include:

Illustrative image related to rubber plastic molding
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system, ensuring consistent quality in products and services.
-
CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: Particularly relevant in the oil and gas industry, API standards ensure that rubber components used in these sectors meet stringent performance requirements.
What Are Common Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process help identify defects early. Common checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the production line. Suppliers should provide documentation to verify material specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, regular checks are made to monitor the quality of the molding process. Parameters such as temperature, pressure, and cycle times are recorded.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products are shipped, final inspections are conducted to ensure they meet the required specifications and standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to ensure reliable product delivery. Here are actionable steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their quality management systems and adherence to industry standards.
-
Request Reports: Suppliers should be willing to share their quality control reports, including testing results and compliance with international standards.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality assurance processes.
What Nuances Exist in QC for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control:
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality can help in effectively communicating expectations with suppliers.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulations regarding rubber products. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are compliant with local laws and international standards.
-
Logistical Considerations: Transporting rubber products across borders can introduce quality risks. It’s essential to work with suppliers who have robust packaging and shipping protocols to prevent damage during transit.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in rubber plastic molding, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product quality.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘rubber plastic molding’
In the competitive landscape of rubber plastic molding, making informed sourcing decisions is crucial for optimizing production and ensuring quality. This step-by-step checklist serves as a practical guide for B2B buyers aiming to procure rubber plastic molding services effectively. By following these steps, you can streamline your sourcing process and select the right partners for your manufacturing needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly articulating your technical specifications is the foundation of a successful sourcing process. These specifications should include details such as size, geometry, material type, and production volume. Providing comprehensive specifications helps suppliers understand your requirements and enables them to offer tailored solutions that meet your production needs.
Step 2: Research Different Molding Processes
Understanding the various rubber molding processes—such as compression molding, transfer molding, and injection molding—will aid in choosing the right method for your application. Each process has unique advantages and limitations based on factors like production volume and part complexity. Evaluate your project needs against these processes to make an informed decision.
Step 3: Identify and Vet Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s essential to conduct thorough due diligence. Request company profiles, certifications, and case studies relevant to your industry. Look for testimonials or references from other buyers who have worked with the supplier, particularly in your region, to gauge their reliability and quality of service.
Step 4: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities and Technology
Assess the technological capabilities of potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your specifications. This includes evaluating their machinery, production techniques, and quality control measures. A supplier with advanced technology can offer greater precision, efficiency, and adaptability in the molding process, which is critical for producing high-quality parts.
Step 5: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before finalizing your order, request samples or prototypes of the rubber parts you need. This step allows you to evaluate the quality and performance of the products firsthand. Pay attention to dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and material properties, as these factors directly impact the functionality of the final product.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Engage in negotiations to establish favorable terms and pricing with your selected supplier. Ensure clarity on lead times, payment terms, and any potential additional costs associated with customization or expedited services. A transparent negotiation process lays the groundwork for a productive partnership.
Step 7: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Finally, ensure that your chosen supplier complies with relevant industry standards and certifications. This may include ISO certifications or specific regulatory requirements based on your industry. Verifying compliance not only protects your business but also ensures that the products meet safety and quality standards.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing process for rubber plastic molding, ensuring they find reliable partners who can meet their specific needs effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rubber plastic molding Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of rubber plastic molding is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their sourcing strategies. This analysis delves into the primary cost components, the factors influencing pricing, and essential tips for negotiating favorable terms.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Rubber Plastic Molding?
The cost structure for rubber plastic molding encompasses several critical components:
-
Materials: The choice of rubber compounds significantly affects the overall cost. For instance, specialty materials such as silicone or thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) can command higher prices due to their unique properties and applications. Additionally, the fluctuation in raw material prices driven by global supply chain dynamics can impact procurement costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the complexity of the molding process. Processes like injection molding may require skilled technicians, leading to higher labor costs compared to simpler methods like compression molding. In regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa and South America, buyers may find more cost-effective sourcing options.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the costs associated with running the manufacturing facility, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility depreciation. These expenses are often factored into the unit cost of production.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can be substantial, particularly for custom molds. Initial investments in tooling are critical but can be amortized over larger production runs, making them more economical per unit in high-volume scenarios.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality can add to costs, particularly for industries with strict regulatory requirements. Certifications like ISO or specific industry standards can increase the cost but may be essential for market entry, especially in Europe and North America.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs are vital, particularly for international shipments. Factors such as shipping distance, mode of transport, and customs duties play a significant role in determining the total logistics cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically incorporate a profit margin into their pricing, which can vary widely based on market competition and the uniqueness of the product.
What Factors Influence Pricing in Rubber Plastic Molding?
Pricing for rubber plastic molding is influenced by several key factors:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher order volumes typically result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their demand forecasts to negotiate better terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts that require unique designs or materials will generally incur higher costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected charges later.
-
Materials Used: The type of rubber or plastic chosen affects the overall cost. For example, custom compounds or those with enhanced properties will increase material costs.
-
Quality Standards and Certifications: Suppliers that meet higher quality standards may charge a premium. Buyers should weigh the importance of certifications against the cost implications.
-
Supplier Factors: Relationship dynamics with suppliers can influence pricing. Long-term partnerships or bulk purchasing agreements may lead to favorable pricing structures.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) affects the final price by determining who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms is crucial for accurate cost estimation.
How Can Buyers Optimize Costs and Negotiate Effectively?
To achieve cost-efficiency in rubber plastic molding sourcing, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Volume Discounts: Leveraging order size can lead to significant savings. Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing tiers based on volume commitments.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on unit price, consider the TCO, which includes all expenses over the product lifecycle, including maintenance and logistics.
-
Assess Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of currency fluctuations and potential tariffs that could affect pricing. Engaging a local expert can provide insights into regional market conditions.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure that suppliers provide comprehensive quotes that break down all cost components. This transparency allows for better comparisons and informed negotiations.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of rubber plastic molding sourcing requires a strategic approach to understanding cost structures and pricing influences. By leveraging insights into cost components, negotiating effectively, and considering the total cost of ownership, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business objectives.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing rubber plastic molding With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Rubber Plastic Molding
In the realm of manufacturing, selecting the appropriate molding process is crucial for achieving efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness. While rubber plastic molding is a popular choice for producing durable and flexible parts, other viable alternatives exist. This section explores these alternatives, comparing them based on key aspects relevant to B2B buyers.

Illustrative image related to rubber plastic molding
| Comparison Aspect | Rubber Plastic Molding | Thermoforming | Blow Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and flexibility for complex designs | Suitable for large parts with moderate detail | Best for hollow structures with uniform walls |
| Cost | Moderate to high, particularly for custom molds | Generally lower, especially for large production runs | Cost-effective for high-volume production |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment and skilled labor | Easier setup with less technical skill needed | Requires specific machinery, more complex than thermoforming |
| Maintenance | Moderate; molds need regular upkeep | Low; less wear and tear on equipment | Moderate; equipment maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | Precision parts, seals, gaskets, and custom applications | Large sheets, packaging, and automotive components | Bottles, containers, and other hollow items |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Thermoforming?
Thermoforming is a molding process where plastic sheets are heated to a pliable state and then formed into specific shapes using a mold. The primary advantage of thermoforming lies in its cost-effectiveness, especially for large production runs. It is relatively easy to implement, requiring less specialized skills compared to rubber plastic molding. However, the performance may not match the precision of rubber molding, making it less suitable for intricate designs or applications requiring high durability.
How Does Blow Molding Compare to Rubber Plastic Molding?
Blow molding is another alternative primarily used for producing hollow plastic products. This method excels in cost-effectiveness for high-volume production, making it ideal for items like bottles and containers. While it offers efficiency and speed, the limitations include reduced design flexibility and precision compared to rubber plastic molding. Blow molded items typically have uniform wall thickness, which may not meet the requirements for applications needing complex geometries or specific material properties.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Molding Solution for Your Business Needs
Selecting the right molding solution depends on various factors, including the specific application, production volume, material requirements, and budget constraints. Rubber plastic molding stands out for applications demanding high precision and durability, while alternatives like thermoforming and blow molding may offer cost advantages for certain projects. B2B buyers should assess their unique needs, consider the trade-offs associated with each method, and consult with suppliers to ensure they choose a solution that aligns with their operational goals and product specifications.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rubber plastic molding
What Are the Key Technical Properties in Rubber Plastic Molding?
Understanding the technical specifications in rubber plastic molding is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing components for machinery and automotive applications. Here are some of the most critical properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of rubber materials based on their performance characteristics, including elasticity, temperature resistance, and chemical stability. Different grades are suitable for various applications, from automotive seals to medical devices. Selecting the right material grade ensures that the final product meets performance standards and regulatory requirements.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In rubber molding, tight tolerances are essential for ensuring that parts fit correctly and function as intended, especially in assemblies where multiple components interact. High precision in tolerances reduces the risk of product failures and improves operational efficiency, making it a vital specification for B2B buyers.
3. Hardness
Measured on the Shore durometer scale, hardness indicates the resistance of rubber to indentation. This property directly affects the material’s durability and flexibility, impacting how it performs under stress. For applications requiring shock absorption or vibration dampening, the correct hardness level is crucial for ensuring longevity and reliability.
4. Compression Set
Compression set is the measure of a material’s ability to return to its original thickness after being compressed. A low compression set indicates that the rubber will maintain its shape and functionality over time. For B2B buyers, understanding this property helps assess the longevity of rubber parts in applications where they undergo repeated stress.
5. Volume and Production Capacity
Volume refers to the quantity of parts that can be produced during a specific timeframe. Understanding the production capacity of a supplier is essential for managing inventory and meeting demand. Buyers must evaluate whether a manufacturer can scale production to meet their needs without sacrificing quality or increasing lead times.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Rubber Plastic Molding?
Familiarity with industry terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the rubber molding sector. Here are several key terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that manufactures products or components that are purchased by another company and sold under the latter’s brand name. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers who can deliver high-quality parts that meet their specifications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to produce or sell. This term is crucial for buyers to understand as it impacts pricing and inventory management. A high MOQ may require buyers to stock more parts than needed, potentially increasing costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing for specific goods or services. It typically includes detailed specifications and quantities. For buyers, issuing RFQs is a vital step in obtaining competitive quotes and ensuring they get the best value for their procurement needs.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms helps buyers mitigate risks and avoid misunderstandings during cross-border transactions.

Illustrative image related to rubber plastic molding
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the finished product. This metric is essential for supply chain management, as it affects production schedules and inventory levels. Buyers should always inquire about lead times to ensure timely delivery of critical components.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product quality in the rubber plastic molding industry.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the rubber plastic molding Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Rubber Plastic Molding?
The rubber plastic molding sector is experiencing significant growth driven by global economic recovery and technological advancements. Key markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing an increase in demand for molded rubber products due to their extensive applications in automotive, medical, and industrial machinery sectors. Emerging trends include the integration of automation and Industry 4.0 technologies in manufacturing processes, which enhance efficiency and reduce production costs. For instance, advanced robotics and AI-driven analytics are streamlining operations, enabling quicker turnaround times for custom orders and reducing material waste.

Illustrative image related to rubber plastic molding
Additionally, there is a noticeable shift towards customization, where buyers seek tailored solutions to meet specific operational requirements. This trend is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers who are looking for innovative solutions that can adapt to various geographic and industry-specific needs. The rise of e-commerce platforms is also transforming sourcing practices, allowing buyers from regions like Vietnam and Nigeria to access a wider pool of suppliers and products, thus facilitating competitive pricing and improved supply chain flexibility.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Rubber Plastic Molding Sector?
Sustainability has become a paramount concern in the rubber plastic molding industry, influencing sourcing decisions across the globe. The environmental impact of rubber production, including deforestation and greenhouse gas emissions, has prompted buyers to prioritize suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. This includes sourcing from manufacturers that utilize eco-friendly materials, such as natural rubber derived from responsibly managed plantations, and implementing recycling initiatives for waste reduction.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains is increasingly recognized, as consumers and businesses alike demand transparency in sourcing practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) mark for sustainable forestry are becoming critical in supplier evaluations. By choosing suppliers with these certifications, B2B buyers can mitigate risks associated with reputational damage and align their operations with global sustainability goals, thereby enhancing their brand image and market competitiveness.

Illustrative image related to rubber plastic molding
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Rubber Plastic Molding Relevant to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of rubber plastic molding has been marked by significant technological advancements since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially, rubber molding processes were limited to compression and transfer molding techniques, primarily used for low-volume production. However, the introduction of injection molding in the 1960s revolutionized the industry by enabling high-volume production with enhanced precision and efficiency.
Over the decades, innovations such as liquid silicone rubber (LSR) injection and thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) injection have expanded the capabilities of rubber molding, allowing for more complex designs and applications. This historical context is crucial for B2B buyers as it underscores the continuous improvement in manufacturing techniques that can lead to cost savings and better product performance. Understanding these developments not only helps in sourcing decisions but also equips buyers with knowledge about the potential for customization and innovation in their supply chain.
By staying informed about these market dynamics, sustainability trends, and the historical context of rubber plastic molding, international B2B buyers can make strategic decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and align with global best practices.

Illustrative image related to rubber plastic molding
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rubber plastic molding
-
How do I choose the right rubber molding process for my product?
Selecting the appropriate rubber molding process depends on several factors, including the complexity of the part, production volume, and material properties. For intricate designs or multi-cavity molds, transfer molding may be ideal. If you’re producing medium to high volumes with precision, injection molding offers efficiency and minimal waste. Compression molding is suited for lower volume production and larger parts. Assess your specific needs and consult with potential suppliers to determine the best fit for your application. -
What are the advantages of using injection molding for rubber components?
Injection molding offers significant benefits, including reduced cycle times, high precision, and minimal waste. The process eliminates the need for labor-intensive pre-forms, allowing for efficient material flow and lower viscosity, which enhances cavity filling. Additionally, it enables the production of complex shapes and overmolded components, making it a versatile choice for a variety of applications. For high-volume production, injection molding is often the most economical option. -
What should I consider when sourcing rubber molding suppliers internationally?
When sourcing suppliers, evaluate their experience, production capabilities, and quality assurance processes. Look for certifications such as ISO to ensure compliance with international standards. It’s also crucial to understand their communication practices and responsiveness. Check references and seek testimonials from other clients, particularly those in your region. Additionally, consider their logistics capabilities, including shipping times and costs, to avoid delays in your supply chain. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for custom rubber molding?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the complexity of the mold. Generally, MOQs for custom rubber parts range from a few hundred to several thousand units. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers to determine their specific MOQs and explore options for prototyping if you are uncertain about committing to large orders initially. -
What payment terms are common in international rubber molding transactions?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common arrangements include advance payments, letters of credit, or net terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days). It’s essential to clarify payment terms upfront and ensure they are documented in the contract. Consider negotiating favorable terms that balance risk and cash flow, especially if you are placing large orders. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in my rubber molding products?
To ensure quality, work with suppliers who have established quality assurance protocols, such as regular inspections and testing of materials and finished products. Request documentation of their quality control processes, including certifications and standards they adhere to. You may also consider third-party inspection services to verify quality before shipment, particularly for large orders or critical components. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing rubber molded products?
When importing, consider shipping methods, costs, and lead times. Understand the customs regulations in your country, including duties and taxes that may apply. Collaborating with suppliers who have experience in international shipping can streamline the process. Also, evaluate the packaging methods to ensure products arrive undamaged and ready for use. Timely communication with logistics partners is essential to avoid delays. -
How can I customize rubber molded products to meet specific requirements?
Customizing rubber molded products typically involves collaborating closely with your supplier from the design phase. Provide detailed specifications regarding dimensions, materials, and any unique performance characteristics required. Many suppliers offer prototyping services to create samples before full production, allowing you to assess the design and functionality. Ensure that the supplier has the capability to adapt their processes to meet your specific needs, including adjustments to the molding technique or materials used.
Top 5 Rubber Plastic Molding Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Timco Rubber – Rubber Injection Molding Process
Domain: timcorubber.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Rubber Injection Molding Process: Developed in the mid 1960s, this process involves heating rubber and applying high pressure for molding, differing from plastic injection molding. Key advantages include elimination of pre-forms, reduced cycle times, flashless tooling, and minimal material waste. Transfer Molding: Involves placing pre-forms in a pot and using a plunger to transfer material into ca…
2. Lake Erie Rubber – Rubber Molding Solutions
Domain: lakeerierubber.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Rubber molding is a manufacturing process that transforms uncured rubber into usable products using heating and reshaping in a metal cavity. The three main types of rubber molding are: 1. Injection Molding: Involves injecting uncured rubber into a mold where it vulcanizes into its final shape. 2. Compression Molding: Preformed shapes of uncured rubber are placed in heated molds and closed with hyd…
3. Dynatect – Custom Rubber Molding Solutions
Domain: dynatect.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Custom Rubber Molding by Dynatect offers a range of capabilities for producing rubber parts tailored to specific applications. Key features include:
– Press capacity for both small, high-volume production and large-scale parts.
– Over 75 presses with capacities ranging from 40 to 2500 tons and platen sizes up to 20 feet long and 50 feet wide.
– In-house Branbury mixing for custom compound producti…
4. Da/Pro Rubber – Custom Molded Rubber Parts
Domain: daprorubber.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Da/Pro Rubber offers a variety of rubber molding techniques and plastic molding processes for custom molded rubber parts. Key products include custom o-rings, seals, gaskets, diaphragms, and one-way sealing valves. The company specializes in several molding methods: 1. Rubber Compression Molding: Involves a top and bottom plate mold, suitable for both complex and straightforward needs, with advant…
5. Protolabs – Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding
Domain: protolabs.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) Injection Molding produces custom prototypes and end-use production parts in 15 days or less. The service offers small, simple molded parts in as fast as 1 day. Protolabs uses aluminum molds for cost-efficient tooling and accelerated manufacturing cycles, and stocks various grades and durometers of LSR materials. Common applications include low-volume production, bridg…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rubber plastic molding
As the global demand for rubber and plastic molded products continues to grow, strategic sourcing becomes essential for businesses looking to enhance their operational efficiency and competitiveness. Understanding the intricacies of various molding processes—such as injection, transfer, and compression molding—empowers buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs. Each method offers unique benefits, including reduced cycle times, minimal material waste, and the ability to produce complex geometries, which are crucial for industries ranging from automotive to medical.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging strategic sourcing can lead to significant cost savings and improved product quality. Engaging with reliable suppliers who can provide customized solutions ensures that businesses remain agile and innovative in a fast-paced market.
Looking ahead, the rubber plastic molding industry is poised for transformation through advancements in technology and materials. Now is the time for businesses to evaluate their sourcing strategies and explore partnerships that can drive growth. Embrace the future of molding solutions by connecting with expert manufacturers who can help turn your vision into reality.

Illustrative image related to rubber plastic molding
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.