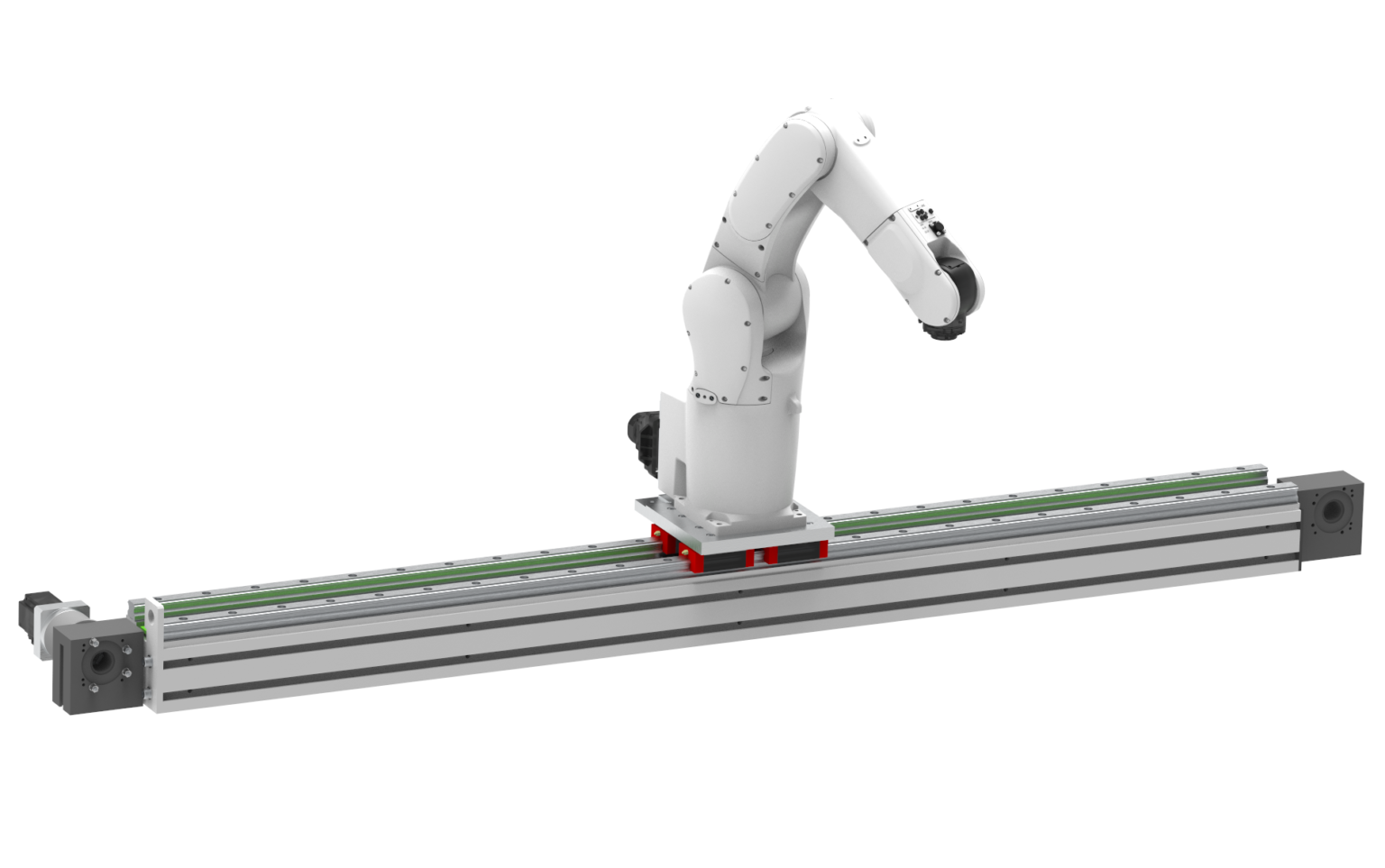
Linear Track Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for linear track
Navigating the complex landscape of sourcing linear track systems can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those operating across diverse markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The need for reliable, efficient linear track solutions is paramount, as these systems play a crucial role in various applications, from automated manufacturing lines to customizable living spaces. This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of linear track options, detailing the various types available, their specific applications, and key considerations for supplier vetting and cost evaluation.
In an era of rapid technological advancement and globalization, making informed purchasing decisions is essential for businesses aiming to optimize their operations. This guide equips international buyers with the insights needed to navigate the global market effectively, ensuring they can identify quality suppliers and products that meet their specific requirements. From understanding the nuances of light-duty versus heavy-duty systems to assessing the long-term value of customizable solutions, this resource provides actionable information designed to empower decision-makers.
Whether you are in Germany seeking precision components for industrial applications or in Saudi Arabia looking for versatile solutions for architectural projects, this guide serves as your roadmap to successfully sourcing linear track systems that align with your business goals.
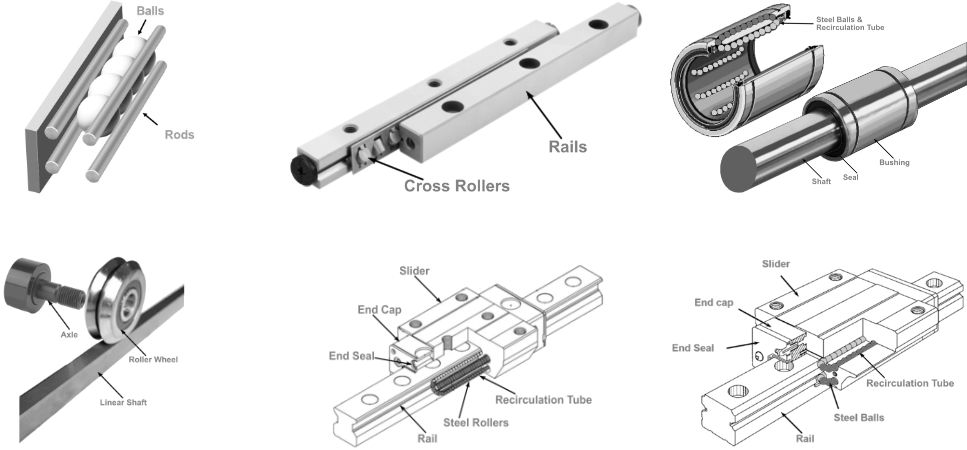
Understanding linear track Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light-Duty Linear Track | Slim profile, lightweight, ideal for low-load applications | Residential sliding doors, display panels | Pros: Cost-effective, easy installation. Cons: Limited load capacity. |
| Medium-Duty Linear Track | Versatile design, suitable for moderate loads | Retail fixtures, industrial partitions | Pros: Balanced strength and flexibility. Cons: May require more maintenance than heavy-duty options. |
| Heavy-Duty Linear Track | Robust construction, designed for high-load environments | Warehousing, automotive assembly lines | Pros: High load capacity, durable. Cons: Heavier and more expensive. |
| Modular Linear Rail Systems | Customizable components, adaptable for various setups | Robotics, automated assembly lines | Pros: Flexibility in design, scalable. Cons: Complex setup may require specialized knowledge. |
| Precision Linear Rails | High accuracy, designed for precision applications | CNC machines, medical equipment | Pros: Exceptional performance, long lifespan. Cons: Higher cost, requires precise alignment. |
What are the Characteristics of Light-Duty Linear Tracks?
Light-duty linear tracks are characterized by their slim profiles and lightweight materials, making them suitable for applications with lower load requirements. Commonly used in residential settings for sliding doors and display panels, these tracks offer a cost-effective solution for businesses looking to enhance functionality without significant investment. Buyers should consider the limited load capacity and potential need for replacement in high-traffic environments.
How Do Medium-Duty Linear Tracks Stand Out?
Medium-duty linear tracks provide a balance between strength and versatility, making them ideal for retail fixtures and industrial partitions. Their design allows for moderate load handling, which suits a variety of applications across different sectors. Buyers should appreciate the flexibility these tracks offer, but they may need to factor in potential maintenance requirements, especially in high-use scenarios.
Why Choose Heavy-Duty Linear Tracks for Your Business?
Heavy-duty linear tracks are built for robustness and high-load applications, often found in warehousing and automotive assembly lines. Their construction ensures durability and reliability, accommodating significant weight without compromising performance. While these tracks are ideal for demanding environments, buyers should be prepared for a higher initial investment and the additional weight they impose on structures.
What Advantages Do Modular Linear Rail Systems Provide?
Modular linear rail systems are designed for customization, allowing businesses to adapt their setups based on specific operational needs. These systems are particularly useful in robotics and automated assembly lines, where flexibility and scalability are essential. While they offer significant advantages in terms of adaptability, buyers may need specialized knowledge for setup and integration, which could impact overall project timelines.
How Do Precision Linear Rails Enhance Operational Efficiency?
Precision linear rails are engineered for high accuracy, making them indispensable in applications like CNC machines and medical equipment. Their design ensures smooth and precise movement, contributing to enhanced operational efficiency and product quality. However, the cost associated with these high-performance rails can be a consideration for businesses, as well as the necessity for precise installation to achieve optimal results.
Key Industrial Applications of linear track
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of linear track | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Robotic assembly lines using linear tracks for precision | Enhanced efficiency and reduced cycle times in production | Compatibility with existing robotics and load capacity |
| Healthcare | Sliding doors and partitions in hospitals | Improved patient access and space optimization | Corrosion resistance and ease of maintenance |
| Retail | Customizable sliding displays and partitions | Increased flexibility in store layouts and improved customer flow | Aesthetic design and ease of installation |
| Aerospace | Linear tracks for cargo handling systems | Streamlined logistics and enhanced safety | Load ratings and material specifications for durability |
| Construction | Linear guide systems for movable walls and structures | Maximized space usage and adaptability in design | Custom lengths and modularity to fit specific project needs |
How is Linear Track Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive sector, linear tracks are integral to robotic assembly lines. They facilitate precise movements of robots that handle tasks such as welding and part assembly. This application significantly boosts production efficiency by minimizing cycle times and ensuring high accuracy in operations. For international buyers, especially in regions like Germany and Saudi Arabia, sourcing linear tracks that are compatible with existing robotic systems and can handle specific load capacities is crucial for seamless integration into their manufacturing processes.
What Role Does Linear Track Play in Healthcare Facilities?
In healthcare environments, linear tracks are widely used for sliding doors and movable partitions in hospitals. This application not only enhances patient access but also optimizes the use of space, allowing for flexible room configurations. Buyers from regions such as Africa and the Middle East must prioritize sourcing linear track systems that are corrosion-resistant and easy to maintain, ensuring longevity and hygiene in sensitive healthcare settings.
How Do Retailers Benefit from Linear Track Applications?
Retailers leverage linear track systems for customizable sliding displays and partitions, allowing them to create dynamic store layouts that can adapt to changing marketing strategies. This flexibility improves customer flow and enhances the shopping experience. When sourcing these systems, businesses in Europe and South America should consider aesthetic designs that align with their branding, as well as ease of installation to minimize disruptions during store renovations.
What Are the Advantages of Linear Tracks in Aerospace?
In the aerospace industry, linear tracks are essential for cargo handling systems, where they streamline logistics and enhance safety during the transport of heavy components. The reliability of these systems is critical in maintaining operational efficiency. Buyers must focus on load ratings and material specifications that ensure durability under demanding conditions, particularly in regions with high humidity or temperature variations.
How Do Construction Projects Utilize Linear Guide Systems?
Construction projects often incorporate linear guide systems for movable walls and structures, maximizing space usage and allowing for adaptable designs. This versatility is particularly beneficial in urban environments where space is at a premium. When sourcing linear tracks for such applications, international buyers should seek out options that offer custom lengths and modular designs to fit the specific needs of their projects, ensuring compatibility with various construction techniques.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘linear track’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Smooth Operation in High-Demand Environments
The Problem: B2B buyers in industries such as manufacturing and warehousing often face the challenge of ensuring that their linear track systems can handle heavy loads and constant use without failure. For instance, in a busy assembly line, any hitch in the sliding mechanism can lead to significant downtime, resulting in lost productivity and increased operational costs. Buyers need a reliable solution that guarantees smooth operation under demanding conditions.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should prioritize sourcing linear track systems specifically designed for heavy-duty applications. Look for options that feature robust materials, such as corrosion-resistant aluminum or high-strength steel, which can withstand the rigors of frequent use. Additionally, consider modular systems that allow for customization based on specific operational needs. Engaging with suppliers who offer comprehensive testing and performance data can also help ensure that the chosen system meets necessary load and movement requirements. Implementing regular maintenance schedules, including lubrication and inspection of moving parts, will further enhance the longevity and reliability of the linear track system.
Scenario 2: Navigating Customization Challenges for Unique Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter difficulties when trying to adapt linear track systems for unique applications, such as automated robotic movements or custom sliding doors. They may struggle with finding compatible components or may not know how to specify the right dimensions and load capacities. This can lead to costly mistakes, delays, and even the need for complete system overhauls.
The Solution: To overcome customization challenges, buyers should collaborate closely with suppliers who offer tailored solutions. Start by conducting a thorough needs assessment to determine the specific requirements of the application, including load capacity, travel distance, and environmental conditions. Utilize modular linear track systems, which allow for easy integration of various components, such as cassettes and brackets, to meet unique needs. Additionally, engaging with a supplier’s engineering team can provide valuable insights into system configuration and design, ensuring that all components work harmoniously together. Investing in a prototype or pilot program can also mitigate risks and validate the effectiveness of the chosen linear track solution before full-scale implementation.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Noise and Vibration Issues in Sensitive Environments
The Problem: In sectors such as healthcare or high-tech manufacturing, noise and vibration from linear track systems can disrupt operations and impact sensitive equipment or patient comfort. Buyers in these environments often find themselves challenged to select linear tracks that minimize operational noise while still maintaining functional efficiency.
The Solution: To address noise and vibration concerns, buyers should explore linear track systems that incorporate specialized dampening features or materials designed to absorb sound. Opting for systems with sealed bearings can also help reduce noise levels, as they are less exposed to contaminants and require less maintenance. It is essential to evaluate the operational environment and select systems that are specifically engineered for low-noise applications, such as those used in hospitals or laboratories. Additionally, conducting an acoustic analysis during the design phase can help identify potential noise issues early on. Finally, consider investing in regular maintenance and alignment checks to ensure optimal performance and minimize noise over time.
Illustrative image related to linear track
Strategic Material Selection Guide for linear track
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Linear Track Systems?
When selecting materials for linear track systems, several factors such as load capacity, environmental conditions, and specific application requirements must be considered. Here, we analyze four common materials: aluminum, stainless steel, carbon steel, and plastic composites.
Aluminum: A Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant Option
Aluminum is a popular choice for linear track systems due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. It typically performs well in environments where humidity and exposure to chemicals are concerns. The temperature rating for aluminum tracks generally ranges from -40°C to 80°C, making them suitable for various applications.
Pros: Aluminum is durable and easy to machine, which allows for custom lengths and configurations. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to other metals.
Cons: While strong, aluminum may not be suitable for high-load applications compared to steel. Additionally, it can be more susceptible to deformation under extreme stress.
Impact on Application: Aluminum tracks are ideal for applications in retail, healthcare, and residential settings where aesthetics and lightweight design are essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial, especially in Europe and the Middle East. Buyers should also consider local manufacturing capabilities and availability.
Stainless Steel: Strength and Durability in Harsh Environments
Stainless steel is known for its exceptional strength and resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for demanding environments, including food processing and pharmaceuticals. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 300°C, depending on the grade.
Illustrative image related to linear track
Pros: Stainless steel tracks offer high durability and can withstand heavy loads, making them suitable for industrial applications. They are also easy to clean and maintain.
Cons: The primary drawback is cost; stainless steel is generally more expensive than aluminum and plastic options. Additionally, it is heavier, which may affect installation.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel tracks are ideal for environments requiring hygiene and resistance to corrosion, such as in the food and beverage industry.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure compliance with local regulations and standards, particularly in the food sector. Additionally, sourcing stainless steel from reputable suppliers is critical to guarantee quality.
Carbon Steel: Cost-Effective and Strong
Carbon steel is another option for linear track systems, particularly in heavy-duty applications. It offers excellent strength and load-bearing capabilities, with a temperature rating that can vary widely based on treatment.
Pros: Carbon steel is typically less expensive than aluminum and stainless steel, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects. It is also highly durable and can be treated for additional corrosion resistance.
Cons: Carbon steel is prone to rusting if not properly coated or maintained, which can limit its lifespan in humid or corrosive environments.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel tracks are suitable for industrial applications where high load capacity is required, such as in manufacturing and warehousing.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local standards and regulations regarding carbon steel, especially in regions with high humidity. Proper treatment and coating options should also be evaluated.
Plastic Composites: Versatile and Lightweight
Plastic composites are increasingly being used in linear track systems due to their lightweight, corrosion-resistant properties. They can handle moderate loads and have temperature ratings typically around -20°C to 60°C.
Pros: Plastic composites are resistant to chemicals and moisture, making them suitable for various environments. They are also lightweight and easy to install.

Illustrative image related to linear track
Cons: While suitable for lighter applications, plastic composites may not withstand heavy loads as effectively as metal options. Their lifespan can also be shorter under extreme conditions.
Impact on Application: Plastic tracks are ideal for applications in clean rooms, laboratories, and environments where corrosion resistance is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with environmental regulations and standards is essential, especially in Europe. Buyers should also consider the availability of specific composite materials in their region.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Linear Track Systems
| Material | Typical Use Case for linear track | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Retail, healthcare, residential | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited load capacity under stress | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | High durability and hygiene | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Carbon Steel | Manufacturing, warehousing | Cost-effective and strong | Prone to rust without treatment | Low |
| Plastic Composites | Clean rooms, laboratories | Corrosion-resistant and lightweight | Limited load capacity | Medium |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for linear track
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for linear track systems are pivotal in ensuring that these products meet industry standards and customer expectations. This section explores the key stages of manufacturing and the critical quality control (QC) measures that B2B buyers should consider when sourcing linear track solutions.
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Linear Track Systems?
The manufacturing of linear track systems typically involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a crucial role in determining the performance and reliability of the final product.
1. Material Preparation: Which Materials Are Used in Linear Tracks?
The primary materials for linear tracks include aluminum, stainless steel, and carbon steel. Each material is selected based on the application requirements, such as load capacity, environmental conditions, and corrosion resistance. For instance, aluminum is favored for its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, making it ideal for applications in humid environments or where aesthetics are a priority.
Before fabrication, raw materials undergo thorough inspections to ensure they meet specified standards. This may include checking for material composition and mechanical properties, which are essential for the subsequent manufacturing processes.
2. Forming: What Techniques Are Employed in Shaping Linear Tracks?
The forming process involves shaping the raw materials into the desired configurations. Techniques such as extrusion, machining, and bending are commonly used.
- Extrusion: This method is particularly effective for aluminum, allowing manufacturers to create complex shapes and profiles with consistent quality.
- Machining: Precision machining is used to achieve tight tolerances, essential for ensuring smooth operation and compatibility with moving components.
- Bending: For certain designs, bending techniques are employed to create curves or angles in the tracks, enhancing their functionality in various applications.
The choice of forming technique directly impacts the structural integrity and performance characteristics of the linear tracks.
3. Assembly: How Are Linear Tracks Assembled for Optimal Performance?
Once the individual components are formed, the assembly process begins. This stage may involve integrating various elements such as bearings, rollers, and track systems into a cohesive unit.
Modular assembly techniques are increasingly used, allowing for flexibility in design and ease of maintenance. This modular approach enables manufacturers to customize linear track systems according to specific customer requirements, making them suitable for diverse applications ranging from industrial automation to architectural solutions.
4. Finishing: What Role Does Finishing Play in the Longevity of Linear Tracks?
The finishing stage is critical for enhancing both the aesthetic appeal and functional performance of linear tracks. Common finishing processes include anodizing, powder coating, and painting, which provide protective layers against environmental factors and wear.
Anodizing, for example, not only improves corrosion resistance but also allows for color customization, which can be essential for architectural applications. The finishing process also includes quality checks to ensure that coatings are uniform and free from defects.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Linear Track Systems?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of linear tracks, ensuring that products meet industry standards and customer specifications.
1. What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are crucial for assessing the quality management systems of manufacturers. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer has established processes for continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.

Illustrative image related to linear track
Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking in Europe and API standards in the oil and gas sector ensure that linear track systems meet essential safety and performance criteria. These certifications are particularly important for B2B buyers in regulated industries, as they provide assurance of product reliability and safety.
2. What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control processes typically involve several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing cycle:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials before they enter the production process.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC measures are implemented to monitor critical parameters, ensuring that the processes remain within specified limits.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly and finishing, the final inspection verifies that the completed linear track systems meet all design specifications and performance criteria.
These checkpoints help identify and rectify potential issues early in the manufacturing process, minimizing defects and ensuring consistent quality.
3. How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. This includes reviewing their adherence to international standards and internal QA protocols.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand the inspection and testing methods employed by suppliers. This documentation should outline the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. This is particularly important for international buyers who may not have direct access to the manufacturing facilities.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
For B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the local regulations and standards is essential. This knowledge ensures compliance with both international and regional requirements, which can vary significantly.
Buyers should also consider the logistical challenges of sourcing linear track systems globally. Factors such as shipping, customs regulations, and local market conditions can impact the overall quality and delivery timelines. Thus, establishing clear communication with suppliers and understanding their operational capabilities is vital for a successful partnership.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for linear track systems are intricate and multifaceted. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that ensure they source high-quality, reliable products tailored to their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘linear track’
In this guide, we provide a practical checklist to assist B2B buyers in sourcing linear track systems effectively. This checklist will help you navigate the complexities of procurement, ensuring that you make informed decisions based on your specific operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for your linear track systems. Consider factors such as load capacity, dimensions, and material types (e.g., aluminum, steel) based on your application—whether it’s for robotics, sliding doors, or industrial machinery. This step is crucial to ensure that the linear track will perform optimally under your operational conditions.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers that specialize in linear track systems. Look for manufacturers with a strong reputation in your industry and check their product offerings for customization options. Utilize industry forums, trade shows, and online platforms to gather insights and reviews from other buyers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify the certifications and quality standards of your shortlisted suppliers. Look for ISO certifications or compliance with international standards, which indicate a commitment to quality and safety. Suppliers that conduct rigorous testing and have quality assurance processes in place are more likely to deliver reliable products.
Step 4: Request Samples and Specifications
Before finalizing a purchase, request samples of the linear track systems along with detailed specifications. Evaluate the samples for quality, durability, and ease of installation. This hands-on assessment allows you to identify any potential issues and ensures that the product meets your requirements before bulk procurement.
Step 5: Assess Customization Capabilities
Inquire about the supplier’s ability to customize linear track systems to meet specific needs. This includes adjustments in length, material finishes, and load capacities. A supplier that offers customization can help you optimize your operations and achieve better integration with existing systems.
Step 6: Review Pricing and Payment Terms
Analyze the pricing structure of each supplier, including any additional costs for shipping, handling, or customization. Ensure that the payment terms are favorable and align with your budget. It’s essential to balance cost with quality; the cheapest option may not always provide the best value in the long run.
Step 7: Establish After-Sales Support and Warranty Terms
Confirm the warranty terms and after-sales support offered by the supplier. A solid warranty demonstrates the supplier’s confidence in their product, while reliable after-sales support can be critical for addressing any issues that arise post-purchase. Look for suppliers that provide technical assistance and have a responsive customer service team.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for linear track systems, ensuring that they choose suppliers who meet their operational requirements and contribute to their overall success.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for linear track Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Linear Track Manufacturing?
When sourcing linear tracks, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences pricing. Common materials like aluminum and stainless steel are favored for their durability and corrosion resistance, but they can vary in cost based on quality and sourcing location.
-
Labor: Labor costs can fluctuate based on geographic location and the complexity of manufacturing processes. In regions with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, expect increased pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient manufacturers typically have lower overheads, which can translate into better pricing for buyers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific linear track designs can add substantial upfront costs. For larger orders, these costs can be amortized over the production run, lowering the per-unit price.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that products meet international standards, particularly important for buyers from regions with strict regulatory requirements. Enhanced QC measures can add to the cost but are essential for maintaining quality.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on distance, mode of transport, and weight. Buyers should consider logistics in their total cost calculations, especially when importing from international suppliers.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build in a profit margin that can vary based on their market position, brand reputation, and the competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Linear Track Sourcing?
Several factors can influence pricing and should be considered when sourcing linear tracks:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ): Larger orders often attract bulk pricing discounts. Understanding the supplier’s MOQ can help buyers negotiate better rates.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can significantly increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and compliance with certifications (e.g., ISO) can elevate costs but may be necessary for specific applications, particularly in industries like automotive or aerospace.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a strong reputation may charge more but offer better reliability and service. Evaluating supplier credentials can help mitigate risks associated with quality and delivery.
-
Incoterms: Understanding international shipping terms is crucial. Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping logistics, impacting the total landed cost.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for International B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation can lead to significant cost savings:
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a rapport with suppliers can foster trust and lead to better pricing and terms.
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): When negotiating, consider not just the purchase price but the total cost over the product’s lifecycle, including maintenance and potential downtime costs.
-
Be Informed: Research market trends and competitor pricing. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations, enabling them to argue for more favorable terms.
-
Consider Payment Terms: Flexible payment terms can ease cash flow concerns and may lead to better pricing arrangements.
-
Request Samples: Before committing to large orders, requesting samples can help ensure the quality meets expectations without incurring the full costs upfront.
What Should International Buyers Know About Pricing Nuances?
Buyers from diverse regions should be aware of specific pricing nuances:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rate volatility can impact pricing for international transactions. It’s wise to consider locking in rates or using hedging strategies.
-
Import Duties and Taxes: Be aware of local tariffs that could affect the total cost of imported linear tracks. Understanding these can prevent budget overruns.
-
Cultural Differences: Negotiation styles and business practices can vary widely across cultures. Adapting to local customs can facilitate smoother transactions and better relationships.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices mentioned in product listings can serve as a guideline but may vary based on supplier negotiations, quantity, and specific buyer requirements. It’s advisable to request formal quotes for accurate and current pricing tailored to your needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing linear track With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Linear Track Systems in B2B Applications
In the realm of industrial solutions, particularly for motion and material handling, linear track systems are widely recognized for their versatility and efficiency. However, there are several alternative technologies that can also fulfill similar needs in various applications. This analysis aims to compare linear track systems with two viable alternatives: Precision Linear Rails and Robotic Linear Axes. Understanding the nuances between these options can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Linear Track | Precision Linear Rails | Robotic Linear Axes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High load capacity, smooth movement | High precision for applications needing tight tolerances | Dynamic movement, adaptable to various robotic applications |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment, long-term durability | Competitive pricing with varied configurations | Higher upfront costs due to advanced technology |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate complexity, requires careful installation | Generally straightforward, often pre-assembled | Complex integration depending on the robotic system |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; durable materials | Minimal maintenance needed; sealed bearings | Requires regular checks to ensure precision and functionality |
| Best Use Case | Sliding doors, partitions, and heavy machinery | Precision applications like machine guarding and conveyor systems | Automated processes in manufacturing, especially for robotics |
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Precision Linear Rails?
Precision Linear Rails are engineered for applications requiring high accuracy and load-bearing capabilities. They are often used in environments where precision is critical, such as in the aerospace or automotive industries. The primary advantage of these systems is their ability to maintain tight tolerances over extended periods, thanks to sealed bearing units that protect against contaminants. However, they can be more expensive than standard linear tracks, and their performance can be affected by environmental factors if not properly shielded.

Illustrative image related to linear track
How Do Robotic Linear Axes Enhance Automation?
Robotic Linear Axes represent a sophisticated alternative designed specifically for robotic applications. They provide seamless motion for automated processes, allowing for dynamic movement and flexibility in configuration. The modular design allows for easy scaling and customization, making them suitable for complex manufacturing environments. The downside is that they typically come with a higher initial investment and require careful integration into existing systems, which may involve additional engineering resources.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Motion Solution for Your Business?
When selecting between linear track systems, precision linear rails, and robotic linear axes, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including the specific application, budget constraints, and long-term maintenance requirements. For businesses focused on simple, robust solutions for sliding mechanisms, linear tracks may be ideal. Conversely, for applications demanding high precision and adaptability, precision rails or robotic axes could provide better long-term value despite higher initial costs. Evaluating these alternatives in the context of operational needs and future scalability will lead to a more strategic investment in motion technologies.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for linear track
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Linear Track Systems?
When selecting linear track systems for industrial applications, understanding critical technical specifications is essential for ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Here are some key properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Linear tracks are typically made from materials like aluminum, steel, or stainless steel. Aluminum offers a lightweight, corrosion-resistant option ideal for environments with moisture, while steel provides enhanced strength and load-bearing capacity. The choice of material affects durability, maintenance needs, and overall cost, making it vital for B2B buyers to select the right material for their specific applications. -
Load Capacity
– This specification indicates the maximum weight that a linear track can support without compromising performance. Load capacity varies between light-duty, medium-duty, and heavy-duty systems. For businesses, understanding load capacity is crucial to prevent system failures and ensure safety in operations, especially in sectors like manufacturing and logistics where heavy materials are moved frequently. -
Precision and Tolerance
– Precision refers to how accurately the linear track can guide the movement of its carriers or components. Tolerance is the allowable deviation from specified dimensions. Higher precision and tighter tolerances result in smoother operation and reduced wear over time. For B2B buyers, investing in high-precision systems can lead to lower maintenance costs and longer service life, which translates to better ROI. -
Profile Design
– The design of the rail profile affects the system’s compatibility with various carriers and its overall performance. Common profiles include V-shaped, square, and round rails, each suited for different applications. Understanding profile design helps buyers select the right system that aligns with their operational requirements and can facilitate easier integration into existing machinery. -
Environmental Resistance
– Many linear track systems are designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures, humidity, or exposure to chemicals. Buyers should consider environmental resistance to ensure longevity and reliability, especially in industries like food processing, pharmaceuticals, and outdoor applications. -
Mounting Options
– The flexibility in mounting configurations (e.g., floor-mounted, ceiling-mounted, or wall-mounted) allows for versatile installation in various settings. This adaptability is crucial for optimizing space and ensuring operational efficiency. B2B buyers should evaluate the available mounting options to ensure compatibility with their specific installation requirements.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Linear Track Systems?
Understanding trade terminology is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are several common terms that buyers should be familiar with:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of linear tracks, it refers to suppliers that provide original components for machinery or systems. Establishing relationships with OEMs can lead to better pricing and quality assurance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for buyers to manage inventory costs and ensure they meet their operational needs without overcommitting financially. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a standard business process where a buyer requests pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products. Issuing an RFQ allows businesses to compare offers and negotiate better deals, enhancing procurement efficiency. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities involved in cross-border purchases of linear track systems. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order until it is delivered. Understanding lead times is crucial for buyers to plan their inventory and production schedules effectively, reducing the risk of operational delays. -
Warranty
– A warranty is a guarantee from the manufacturer regarding the performance and longevity of the product. Knowing the warranty terms can protect buyers from unexpected costs and provide assurance of product quality, which is particularly important for high-investment items like linear track systems.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the linear track Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Linear Track Sector?
The global linear track market is experiencing robust growth, driven by the increasing demand for automation and efficiency in various sectors, including manufacturing, logistics, and construction. Key trends shaping the market include the integration of advanced technologies such as robotics and artificial intelligence, which enhance the functionality and adaptability of linear track systems. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the emphasis is shifting towards modular and customizable solutions that meet specific operational needs.
Moreover, the rise of e-commerce is fueling demand for linear track systems in warehouse automation, where fast and precise movement is critical. Buyers are increasingly looking for systems that offer not only high performance but also flexibility in design and application. The emergence of smart linear motion systems, which incorporate IoT capabilities for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, is a significant trend that enhances operational efficiency.
In regions such as Saudi Arabia and Germany, investments in infrastructure and industrial automation are driving the adoption of advanced linear rail systems. The focus on reducing operational downtime and maximizing throughput is leading companies to seek partnerships with suppliers who can deliver high-quality, durable products backed by strong after-sales support.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Linear Track Market?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of business strategy in the linear track sector. Buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of their sourcing decisions, leading to a growing demand for products made from sustainable materials and processes. The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated; B2B buyers are scrutinizing their suppliers’ practices, ensuring that they adhere to environmental regulations and labor standards.
A notable trend is the adoption of ‘green’ certifications for linear track products, which assure buyers that the materials used are sourced responsibly and that the manufacturing processes minimize ecological footprints. For example, aluminum linear rails, known for their recyclability and lightweight properties, are gaining popularity among environmentally conscious buyers. Companies are also investing in innovative technologies that reduce energy consumption during production and operation, further enhancing their sustainability credentials.
By prioritizing sustainable sourcing, businesses not only contribute to environmental conservation but also improve their marketability. As consumers increasingly favor brands with strong sustainability commitments, B2B buyers can leverage this trend to enhance their competitive edge.
What is the Brief Evolution and History of Linear Track Systems?
The evolution of linear track systems can be traced back to the early industrial era when simple rail systems were utilized for transporting goods within factories. Over the decades, advancements in materials and engineering led to the development of more sophisticated linear motion systems. The introduction of high-precision components and automation technologies in the late 20th century revolutionized the sector, enabling faster and more efficient movement of goods and machinery.
Today, linear track systems are integral to various industries, from robotics to construction, reflecting a significant shift towards automation and enhanced operational efficiency. The continuous innovation in design and technology, coupled with the growing emphasis on sustainability, shapes the future of linear track solutions, making them a vital component for businesses looking to thrive in an increasingly competitive global market.

Illustrative image related to linear track
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of linear track
-
How do I solve compatibility issues when sourcing linear track systems?
To address compatibility issues with linear track systems, first ensure that you thoroughly understand your application requirements, including load capacity, dimensions, and environmental conditions. Consult with suppliers about their product specifications and compatibility with existing systems. It’s also advisable to request samples or detailed technical documentation before finalizing your order. Engaging in a dialogue with the supplier can help clarify any concerns about integration with other components or machinery. -
What is the best linear track system for automated processes?
For automated processes, a robust linear track system that supports high load capacities and dynamic movements is crucial. Look for systems that offer modular designs for flexibility and scalability, such as those from manufacturers specializing in robotics or industrial automation. Consider features like low noise levels and precision movement to enhance efficiency. Systems designed for specific applications, such as those used in automotive assembly or packaging, may provide the best performance for your needs. -
How can I customize linear track systems to fit my specific needs?
Customization options for linear track systems often include length adjustments, material choices, and specialized mounting configurations. When sourcing, inquire about the supplier’s capabilities for tailoring products to your specifications. Many manufacturers offer modular systems that can be easily modified. Provide detailed requirements to the supplier, including load specifications and environmental considerations, to ensure the final product meets your operational demands. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for linear track systems?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly between suppliers and may depend on the specific products and customization options you require. Some manufacturers may have no MOQ for standard products, while customized solutions might require larger orders to justify production costs. Always clarify MOQs during the negotiation phase to avoid unexpected costs and ensure that your order aligns with your budget and project timelines. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing linear track systems internationally?
International payment terms can vary based on the supplier’s policies and your relationship with them. Common options include advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s essential to discuss and agree upon terms that protect both parties, such as partial payments based on production milestones. Additionally, consider the implications of currency exchange rates and transaction fees, particularly when sourcing from different regions. -
How do I ensure the quality assurance of linear track systems?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing linear track systems, request detailed information about the supplier’s quality control processes, including certifications (e.g., ISO). Ask for test reports or product samples to evaluate performance before committing to a large order. Establish clear quality expectations and specifications in your contracts, and consider including provisions for third-party inspections if necessary, especially for critical applications. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing linear track systems?
When importing linear track systems, logistics considerations include shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Ensure you understand the supplier’s shipping terms and the expected delivery timeline, as delays can impact your operations. Familiarize yourself with import duties and taxes applicable in your country to budget appropriately. Collaborating with a logistics provider experienced in international shipping can help streamline the process and mitigate potential challenges. -
How can I vet suppliers for linear track systems effectively?
To effectively vet suppliers for linear track systems, start by researching their reputation within the industry. Check for customer reviews, case studies, and any certifications they hold. Request references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and quality of service. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s facilities if possible, or engage in virtual meetings to assess their capabilities and commitment to customer support. Establishing a solid relationship based on transparency will be beneficial for long-term collaboration.
A Look at Linear Track Manufacturers & Suppliers
Could not verify enough suppliers for linear track to create a list at this time.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for linear track
In the evolving landscape of linear track systems, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal factor for international B2B buyers. Key considerations include understanding the diverse applications and benefits of linear tracks, from enhancing operational efficiency in industrial settings to providing seamless movement in architectural designs. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer customization options, rigorous performance testing, and robust warranties, ensuring that their investments align with specific project requirements and long-term goals.
Moreover, the versatility of linear track systems—from light-duty solutions for residential applications to heavy-duty systems suitable for industrial automation—highlights the importance of selecting the right product based on load capacities and environmental conditions. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to innovate, embracing advanced linear track technologies will be crucial for maintaining competitive advantages.
Looking ahead, international buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who not only provide high-quality products but also offer strategic insights and support. By fostering strong partnerships and staying informed about market trends, businesses can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing linear tracks, positioning themselves for growth in an increasingly interconnected global market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.