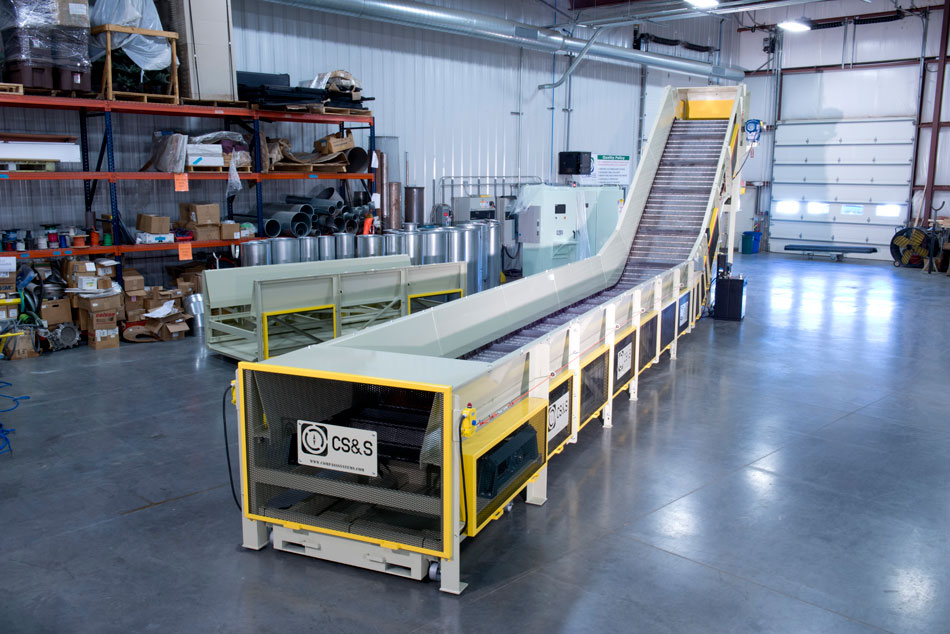
Is Your Mechanical Conveyor Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read This 2025 Report
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for mechanical conveyor
In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, sourcing reliable mechanical conveyors is a critical challenge faced by businesses worldwide. Whether you’re in Nigeria’s burgeoning manufacturing sector or Saudi Arabia’s dynamic logistics industry, the right conveyor system can significantly enhance efficiency and productivity. This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of mechanical conveyors available, including belt, screw, and vibratory conveyors, each tailored for specific applications across various industries.
Additionally, we will explore the nuances of supplier vetting, essential cost considerations, and the latest technological advancements in conveyor systems. By providing actionable insights and practical advice, this guide empowers international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to make informed purchasing decisions. You’ll learn how to assess your operational needs, choose the right conveyor type, and optimize your supply chain for enhanced performance.
Understanding the global market for mechanical conveyors is not just about selecting equipment; it’s about investing in solutions that drive long-term success. With the right knowledge and resources, businesses can streamline their operations, reduce costs, and stay ahead of the competition. Let’s navigate this critical market together, ensuring your investment in mechanical conveyors yields significant returns.
Understanding mechanical conveyor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Belt Conveyors | Continuous belt over pulleys, versatile for various materials | Manufacturing, warehousing | Pros: High efficiency, low maintenance; Cons: Limited incline capability. |
| Drag Chain Conveyors | Flexible transport on inclines, self-loading capabilities | Wood processing, chemical, food industry | Pros: Versatile loading; Cons: More complex installation. |
| Screw Conveyors | Spiral screw design for bulk materials, compact footprint | Food, dairy, pharmaceutical industries | Pros: Cost-effective, handles large volumes; Cons: Limited distance coverage. |
| Bucket Elevators | Vertical transport with buckets on chains | Agriculture, mining, food processing | Pros: High speed, space-saving; Cons: Buckets wear out quickly. |
| Vibratory Conveyors | Single trough design that vibrates to move materials | Chemical, food processing | Pros: Handles various materials; Cons: Requires precise installation for effective operation. |
What Are Belt Conveyors and Their Key Characteristics?
Belt conveyors are among the most common mechanical conveyors, featuring a continuous belt that moves over pulleys. Their versatility allows them to transport a wide range of materials, making them suitable for various industries, including manufacturing and warehousing. When considering a belt conveyor, B2B buyers should evaluate factors such as the load capacity, belt material, and maintenance requirements, as these elements significantly influence operational efficiency and longevity.
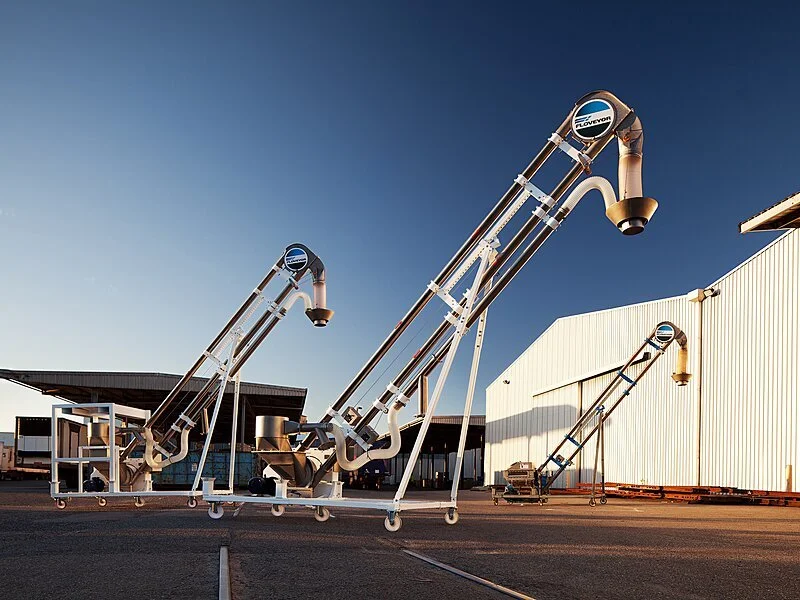

Illustrative image related to mechanical conveyor
Why Choose Drag Chain Conveyors for Your Operations?
Drag chain conveyors are distinguished by their ability to transport materials both vertically and horizontally, making them an excellent choice for industries like wood processing and food manufacturing. These conveyors often utilize hoppers for loading, enhancing their flexibility. B2B buyers should consider the complexity of installation and maintenance when selecting drag chain systems, as these factors can impact operational costs and efficiency.
What Makes Screw Conveyors an Economical Option?
Screw conveyors utilize a rotating spiral screw within a tube to move bulk materials, making them a cost-effective solution for transporting grains, powders, and chemicals. Their compact design allows for installation in tight spaces, which is advantageous for many facilities. Buyers should assess the required throughput and distance when choosing screw conveyors, as these systems are most effective for shorter runs and specific material types.
How Do Bucket Elevators Maximize Space and Efficiency?
Bucket elevators are designed for vertical transport, utilizing buckets attached to chains to move materials swiftly. They are ideal for applications in agriculture and mining, where space constraints are common. While bucket elevators operate at high speeds, buyers should be aware of their wear and tear, as well as the need for regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance over time.
Why Consider Vibratory Conveyors for Diverse Material Handling?
Vibratory conveyors feature a single trough design that vibrates to transport materials upward and forward, making them suitable for various applications, including the chemical and food industries. Their flexibility in handling different materials is a significant advantage. Buyers should focus on the installation precision and the specific materials to be transported, as these factors can greatly influence the conveyor’s effectiveness and reliability.
Key Industrial Applications of mechanical conveyor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Mechanical Conveyor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Transporting bulk ingredients and finished products | Increases efficiency, reduces handling errors | Compliance with food safety standards, material durability |
| Manufacturing | Moving components and assemblies along the production line | Enhances workflow efficiency, minimizes labor costs | Customization for specific production needs, maintenance support |
| Mining | Transporting mined materials from extraction sites | Reduces manual labor, improves safety and speed | Robust design for harsh environments, high load capacity |
| Agriculture | Handling grains and fertilizers | Streamlines operations, increases throughput | Resistance to corrosion, adaptability to various materials |
| Pharmaceuticals | Conveying raw materials and finished products | Ensures accuracy in dosage and compliance | Precision engineering, adherence to industry regulations |
How is Mechanical Conveyor Used in Food Processing?
In the food processing industry, mechanical conveyors are essential for transporting bulk ingredients, such as grains, fruits, and vegetables, as well as finished products like packaged goods. They streamline operations by automating the movement of materials, which reduces manual handling and the risk of contamination. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing conveyors that comply with local food safety standards is critical. Additionally, selecting materials that can withstand cleaning processes and resist wear over time will enhance operational longevity.
What Role Does Mechanical Conveyor Play in Manufacturing?
Mechanical conveyors in manufacturing facilitate the efficient movement of components and assemblies along production lines. This automation minimizes labor costs and enhances overall workflow efficiency. Buyers from regions such as the Middle East and Europe should prioritize conveyors that can be customized to specific production line requirements, including load capacity and speed. Furthermore, maintenance support and the availability of spare parts are key considerations to ensure continuous operation and minimize downtime.
How are Mechanical Conveyors Utilized in Mining?
In the mining sector, mechanical conveyors are vital for transporting mined materials from extraction points to processing facilities. This equipment significantly reduces manual labor, improving safety and increasing operational speed. For buyers in harsh environments, such as those found in Africa and South America, sourcing robust conveyor systems that can handle high loads and resist wear from abrasive materials is crucial. Additionally, evaluating the conveyor’s adaptability to various terrains and operational conditions will ensure optimal performance.
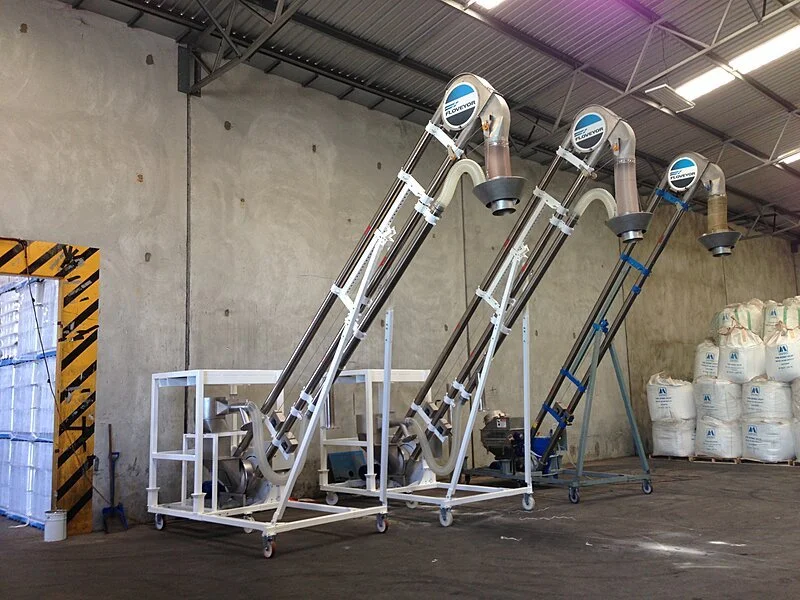

Illustrative image related to mechanical conveyor
In What Ways Do Mechanical Conveyors Benefit Agriculture?
Agricultural operations utilize mechanical conveyors to handle grains, fertilizers, and other bulk materials efficiently. This equipment streamlines processes such as loading, unloading, and transporting products, which increases throughput and reduces labor costs. Buyers in agricultural sectors, especially in regions like Africa, should consider conveyors that are resistant to corrosion and can adapt to different types of materials. Ensuring that the selected conveyors can handle varying load capacities is also essential for meeting seasonal demand fluctuations.
How Does Mechanical Conveyor Impact the Pharmaceutical Industry?
In the pharmaceutical industry, mechanical conveyors are used to transport raw materials and finished products with precision. This ensures accurate dosage and compliance with strict regulatory standards. For international buyers, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, sourcing conveyors that meet industry regulations and are engineered for precision is paramount. Additionally, the ability to integrate these systems with existing automation technologies can enhance operational efficiency and product tracking throughout the supply chain.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘mechanical conveyor’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Conveyor System Downtime Due to Maintenance Challenges
The Problem: One of the most pressing challenges faced by B2B buyers is unplanned downtime caused by conveyor system maintenance. Many companies rely heavily on mechanical conveyors for efficient production and material handling. However, issues such as wear and tear, misalignment, or unexpected breakdowns can lead to significant operational interruptions. This not only affects productivity but also results in increased labor costs and delayed delivery timelines, which can harm client relationships and bottom-line profitability.
The Solution: To mitigate maintenance-related downtime, companies should invest in predictive maintenance technologies. These technologies utilize sensors and IoT devices to monitor the health of conveyor systems in real-time. By analyzing data on vibration, temperature, and operational performance, businesses can identify potential issues before they escalate into significant problems. Additionally, establishing a routine maintenance schedule based on manufacturer guidelines can help ensure that conveyor systems are regularly inspected and serviced, thereby extending their lifespan and reliability. When sourcing conveyors, buyers should prioritize those that come equipped with diagnostic capabilities, as these features can provide valuable insights into the system’s performance and maintenance needs.
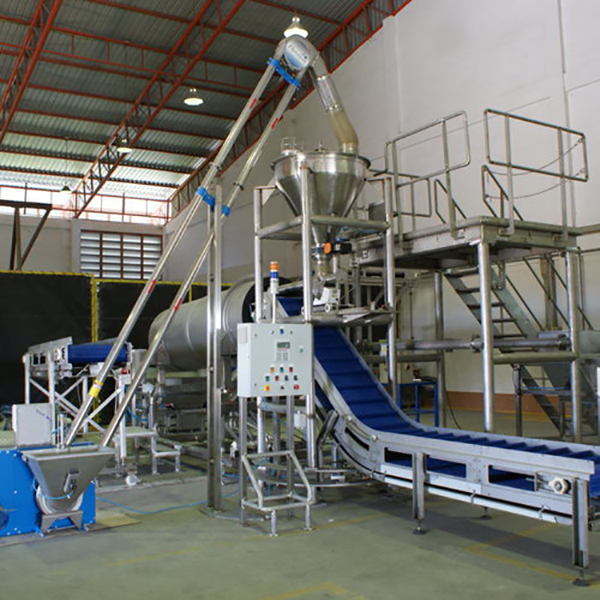

Illustrative image related to mechanical conveyor
Scenario 2: Inadequate Conveyor System Flexibility for Diverse Operations
The Problem: Many organizations struggle with the inflexibility of their conveyor systems, which can limit their ability to adapt to changing operational needs. For example, a manufacturing facility may experience fluctuations in product types and sizes, necessitating different handling requirements. Rigid conveyor systems can lead to inefficiencies, increased labor costs for manual handling, and ultimately, a reduced ability to respond to market demands.
The Solution: To address this issue, businesses should consider investing in modular conveyor systems that offer customizable configurations. Modular conveyors can be easily reconfigured or expanded as operational requirements evolve, allowing for greater versatility in handling different products. When specifying a new conveyor system, buyers should focus on those with adjustable components, such as width and height, as well as compatibility with various types of attachments. Collaborating with a supplier that offers tailored solutions based on specific operational needs can also ensure that the chosen system enhances overall workflow efficiency and adaptability.
Scenario 3: Safety Concerns Leading to Increased Liability Risks
The Problem: Safety is a significant concern in environments where mechanical conveyors are used. Injuries can occur due to improper guarding, lack of safety training, or inadequate signage. Such incidents not only pose risks to employees but can also result in costly liability claims and damage to a company’s reputation. For international buyers, the challenge may be compounded by varying safety regulations across regions, making compliance a complex issue.
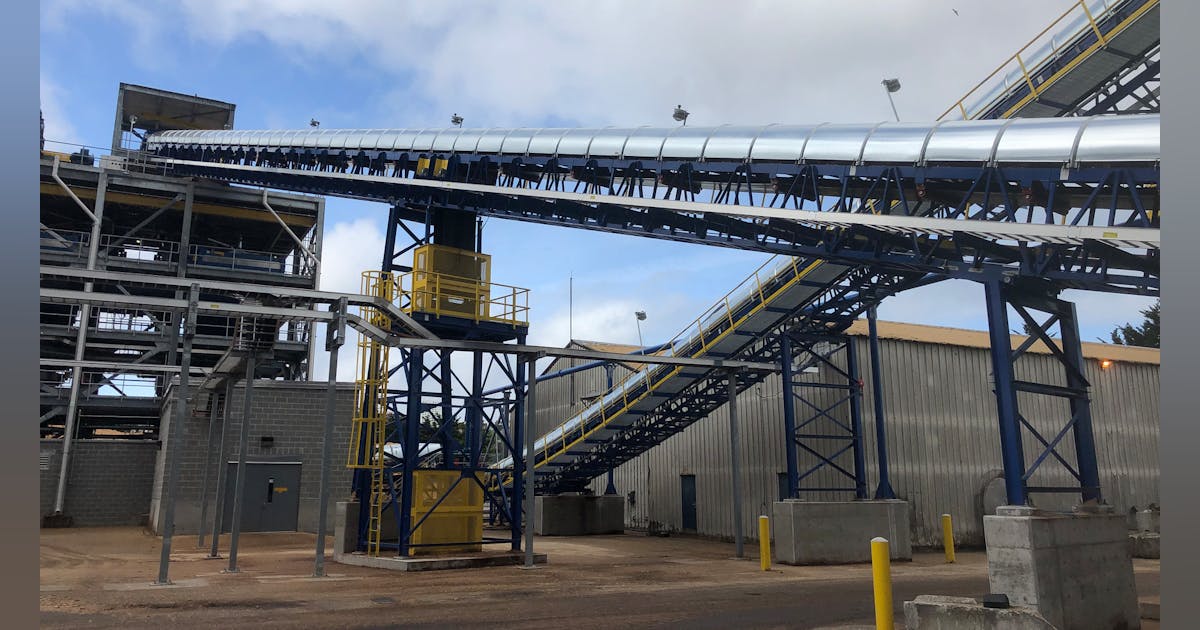

Illustrative image related to mechanical conveyor
The Solution: To enhance safety and reduce liability risks, companies should prioritize the integration of comprehensive safety features into their conveyor systems. This includes installing emergency stop buttons, safety guards, and sensors that detect obstructions. Providing thorough training for employees on safe operating procedures is equally crucial. Additionally, organizations should conduct regular safety audits to ensure compliance with local regulations and standards. When selecting a conveyor system, buyers should request detailed safety documentation from manufacturers and verify that the systems meet or exceed relevant safety certifications. Investing in safety not only protects employees but also fosters a culture of accountability and care within the organization.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for mechanical conveyor
What Are the Key Materials Used in Mechanical Conveyors?
When selecting materials for mechanical conveyors, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in mechanical conveyors: steel, plastic, rubber, and stainless steel.
How Does Steel Perform in Mechanical Conveyors?
Steel is a widely used material in mechanical conveyors due to its strength and durability. It typically has a high-temperature rating and excellent resistance to wear and tear. Steel conveyors can handle heavy loads and are often used in industries like mining and manufacturing.
Pros: Steel offers exceptional durability and load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to other materials.
Cons: The primary drawback is its susceptibility to corrosion, particularly in humid or chemical-laden environments. Additionally, steel conveyors can be heavier, which may complicate installation and maintenance.
Impact on Application: Steel conveyors are suitable for transporting heavy and abrasive materials, but they may require protective coatings or treatments to mitigate corrosion.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN for quality assurance. In markets like Saudi Arabia, where humidity is high, selecting corrosion-resistant coatings is crucial.
What Are the Benefits of Using Plastic in Mechanical Conveyors?
Plastic is another popular material for mechanical conveyors, particularly in food processing and packaging industries. It offers good resistance to chemicals and moisture, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros: Plastic conveyors are lightweight, which simplifies installation and reduces energy consumption. They also exhibit excellent corrosion resistance and can be easily molded into different shapes.
Cons: However, plastic may not withstand high temperatures or heavy loads as effectively as steel. It can also be more expensive to manufacture, depending on the type of plastic used.
Impact on Application: Plastic conveyors are ideal for transporting lightweight and non-abrasive materials, especially in environments where hygiene is a priority.
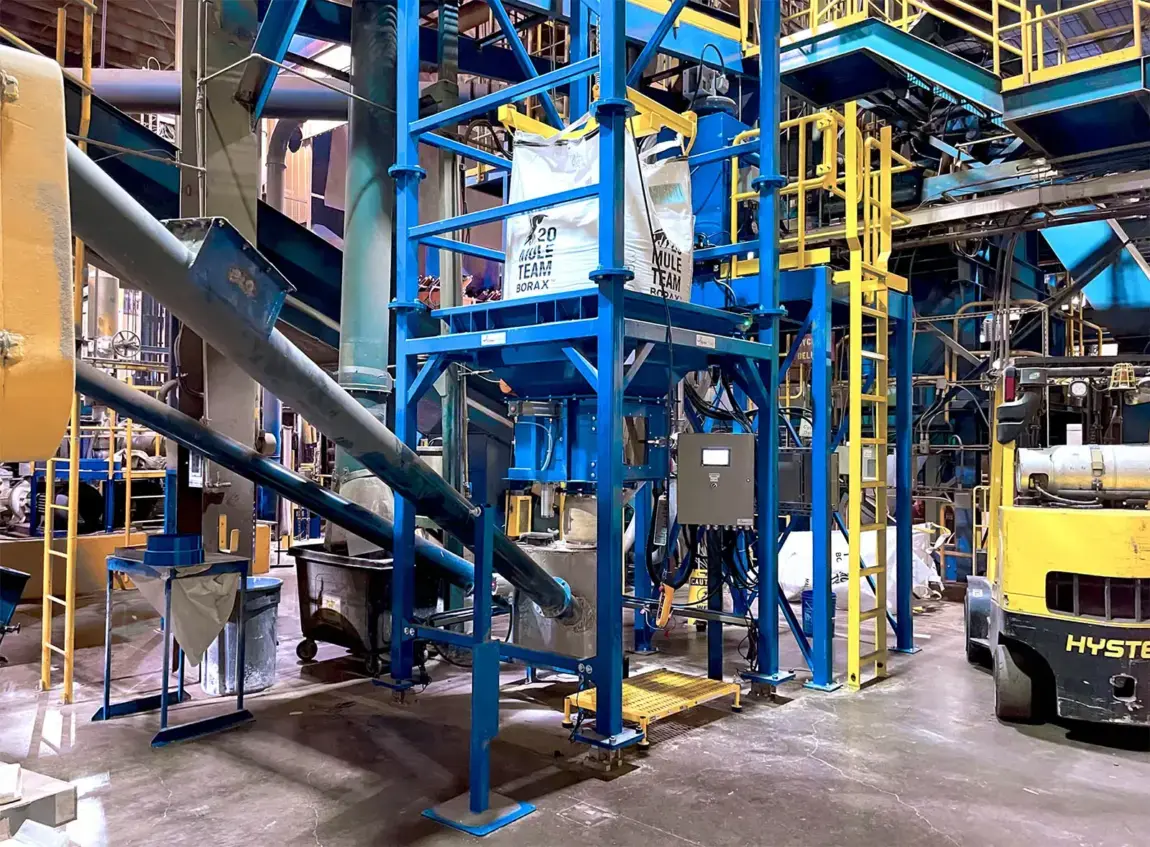

Illustrative image related to mechanical conveyor
Considerations for International Buyers: Ensure that the selected plastic materials meet food safety standards, such as those set by the FDA or EU regulations. Buyers should also consider the environmental impact of plastic materials and potential recycling options.
Why Choose Rubber for Mechanical Conveyors?
Rubber is frequently used in conveyor belts due to its flexibility and grip. It is particularly effective in applications requiring a high degree of traction.
Pros: Rubber provides excellent shock absorption and is resistant to wear, making it suitable for transporting various materials. It is also relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture.
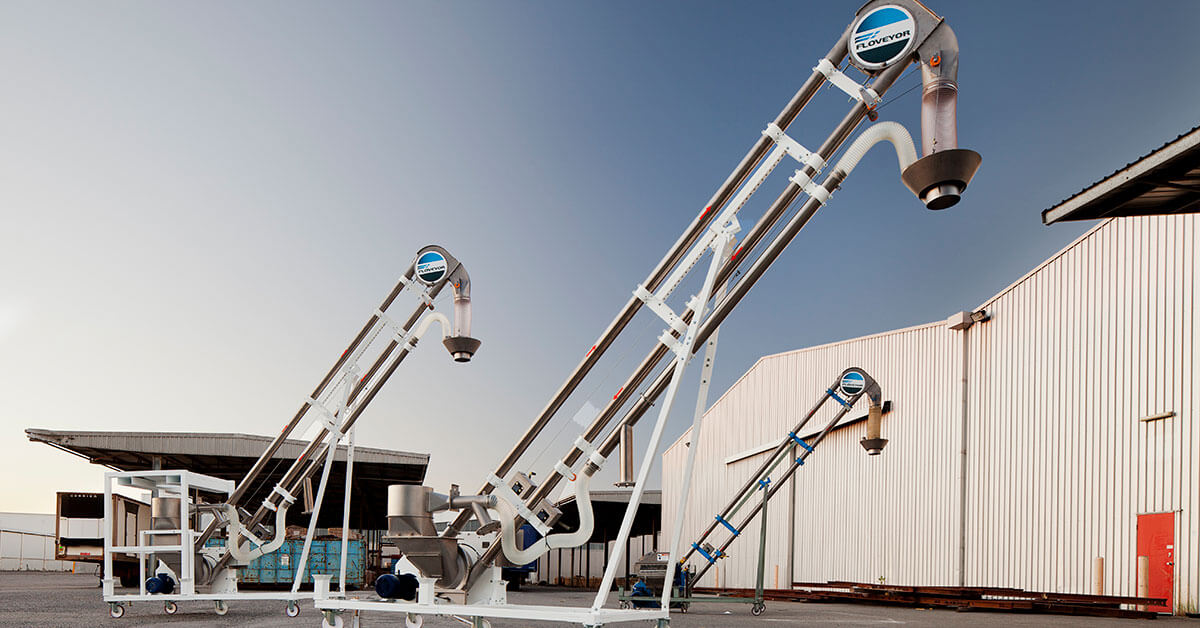

Illustrative image related to mechanical conveyor
Cons: The primary limitation is its susceptibility to degradation from UV exposure and certain chemicals, which can affect its longevity.
Impact on Application: Rubber conveyors excel in applications requiring high friction, such as in the automotive and agricultural sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with international standards regarding rubber quality and chemical resistance, particularly in regions with extreme weather conditions.
What Advantages Does Stainless Steel Offer for Mechanical Conveyors?
Stainless steel is often used in environments where hygiene and corrosion resistance are paramount, such as in food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Pros: This material is highly resistant to corrosion and staining, making it ideal for sanitary applications. It also has a high-temperature rating and can withstand harsh cleaning processes.
Cons: The main disadvantage is its higher cost compared to other materials. Additionally, stainless steel can be more challenging to fabricate, requiring specialized skills and equipment.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel conveyors are perfect for applications where cleanliness and durability are critical, such as in food and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that stainless steel meets relevant international standards, such as ASTM or ISO, especially in regions with strict food safety regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Mechanical Conveyors
| Material | Typical Use Case for mechanical conveyor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty applications in mining | Exceptional durability and strength | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Plastic | Food processing and packaging | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited load capacity | Medium to High |
| Rubber | Automotive and agricultural sectors | High traction and shock absorption | Degrades from UV exposure | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food and pharmaceutical industries | High corrosion resistance and hygiene | Higher cost and complex fabrication | High |
This comprehensive analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into the strategic selection of materials for mechanical conveyors, ensuring that they make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs and regional considerations.

Illustrative image related to mechanical conveyor
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for mechanical conveyor
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Mechanical Conveyors?
The manufacturing process of mechanical conveyors involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: What Raw Materials Are Used?
The first step in the manufacturing process is the preparation of raw materials. Mechanical conveyors are typically made from materials such as steel, aluminum, and various plastics, chosen for their durability and resistance to wear and tear. The selection of material depends on the application—heavy-duty conveyors for industrial settings may utilize steel for strength, while lighter applications may employ aluminum or plastic for cost-effectiveness and weight reduction.
During material preparation, raw materials undergo cutting, shaping, and machining to create components like belts, chains, and frames. This stage is crucial as it sets the foundation for the subsequent manufacturing processes. The use of precision tools and technology ensures that components are produced to exact specifications, reducing the risk of defects later in the assembly process.
How Are Components Formed and Assembled?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. Techniques such as welding, bending, and molding are employed to create the various parts of the conveyor system. For example, steel frames may be welded together for structural integrity, while plastic components may be molded into specific shapes.
After forming, the assembly process begins. This involves fitting together the various components, such as belts, pulleys, and motors, to create a functioning conveyor system. Precision during assembly is critical, as misalignments can lead to operational inefficiencies or even failures. Automated assembly lines are increasingly common, enhancing speed and accuracy while reducing labor costs.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Mechanical Conveyors?
The finishing stage involves applying protective coatings, painting, and ensuring that all surfaces are smooth and free from defects. This step not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the conveyor but also provides protection against corrosion and wear, which is essential for longevity, especially in demanding environments.
Finishing processes may also include the installation of safety features, such as guards and emergency stops, which are vital for compliance with safety regulations. Additionally, this stage often incorporates testing to ensure that the conveyor meets operational standards before it is shipped to customers.
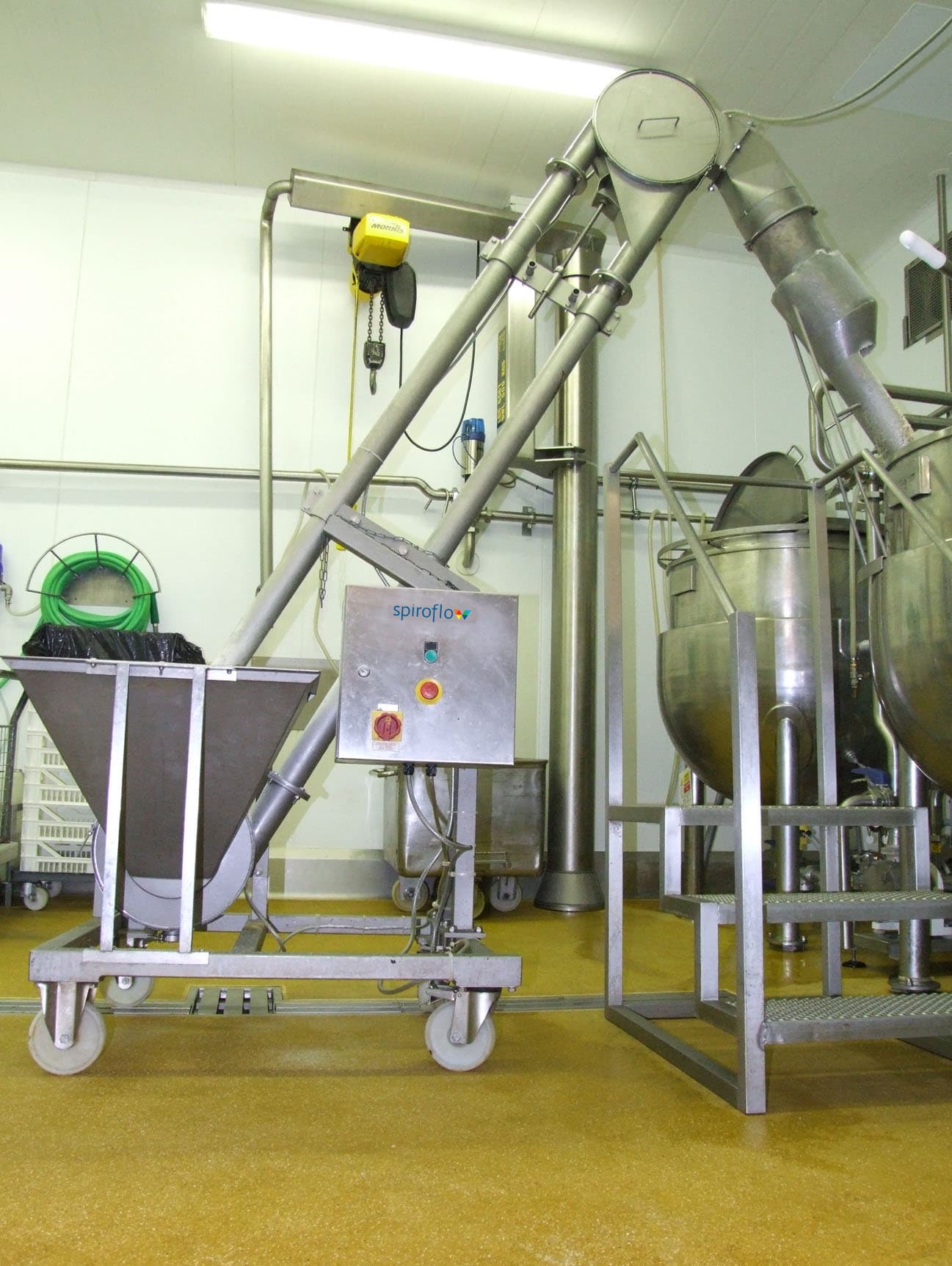

Illustrative image related to mechanical conveyor
What Quality Control Standards Are Relevant for Mechanical Conveyors?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of mechanical conveyors, as these systems are integral to the efficiency of various operations. International standards like ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems, ensuring that products consistently meet customer requirements and regulatory standards.
Industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for products sold in Europe, and API standards for the oil and gas sector, may also apply. These certifications indicate that the products comply with safety and performance regulations pertinent to their intended use.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Integrated into the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that each stage meets the necessary standards. The primary checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. This may involve checking for material specifications, dimensional accuracy, and surface quality.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, components are regularly inspected to identify and rectify issues before they escalate. This may include monitoring the welding quality and ensuring proper assembly techniques are employed.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the complete conveyor system undergoes rigorous testing to verify its performance and compliance with specifications. This testing may include load tests, speed tests, and safety checks.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to stringent quality control practices. Here are several methods to verify supplier quality assurance:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality control processes. This can be done in person or through third-party auditing firms, focusing on adherence to international standards and internal protocols.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand how suppliers manage their quality assurance processes. These reports should outline test results, compliance with industry standards, and any corrective actions taken in response to quality issues.
-
Third-party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality management practices. These inspections can be performed at various stages of the manufacturing process, ensuring adherence to quality standards.
-
Certifications: Buyers should verify that their suppliers possess relevant certifications such as ISO 9001, CE, or industry-specific qualifications. This can be a strong indicator of a supplier’s commitment to quality.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is crucial. Different regions may have varying compliance requirements, which can affect the quality of products.

Illustrative image related to mechanical conveyor
-
Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must familiarize themselves with local regulations and standards that may apply to their industry. For instance, products imported into the EU must meet CE marking requirements, while those in the U.S. may need to comply with OSHA standards.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality assurance can impact supplier relationships. In some regions, there may be a stronger emphasis on compliance, while in others, relationships may play a more significant role in ensuring quality.
-
Supply Chain Transparency: Buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer transparency in their supply chains. This includes providing information on sourcing materials, manufacturing processes, and quality control measures, which can help mitigate risks associated with quality issues.
By thoroughly understanding these aspects of manufacturing processes and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting mechanical conveyor suppliers, ultimately ensuring that their operations remain efficient and reliable.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘mechanical conveyor’
To effectively procure a mechanical conveyor, it’s essential to follow a structured approach that ensures you select the right system for your operational needs. This checklist will guide you through the necessary steps to make an informed decision, catering specifically to the unique requirements of your business.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial as it dictates the type of mechanical conveyor that will suit your operational needs. Consider factors such as the materials being transported (e.g., bulk solids, powders, or heavy items), required capacity, and the layout of your facility. Additionally, think about environmental conditions like temperature and humidity, which may affect the conveyor’s performance.

Illustrative image related to mechanical conveyor
Step 2: Evaluate Different Conveyor Types
Understanding the various types of mechanical conveyors available is vital for making an informed choice. Common options include belt conveyors, screw conveyors, and bucket elevators, each with unique advantages depending on the application. For instance, belt conveyors are ideal for general material transport, while screw conveyors are well-suited for bulk materials in tight spaces.
Step 3: Assess Your Budget and Total Cost of Ownership
Budget considerations should encompass not only the initial purchase price but also the total cost of ownership over the conveyor’s lifespan. This includes maintenance costs, energy consumption, and potential downtime. Analyzing these factors can help you make a more economically sound decision that aligns with your long-term operational goals.
Step 4: Research and Verify Supplier Credentials
Before finalizing a supplier, conduct thorough research to verify their credentials and reputation in the industry. Look for certifications that demonstrate compliance with international standards, such as ISO certifications. Additionally, request references or case studies from similar industries to gauge their reliability and quality of service.
Step 5: Evaluate Customization Options
Many suppliers offer customizable conveyor systems tailored to specific operational needs. Assess whether the potential supplier can accommodate your unique requirements, such as size, material, and functionality. Custom solutions can enhance efficiency and ensure that the conveyor integrates seamlessly with existing operations.

Illustrative image related to mechanical conveyor
Step 6: Request Quotes and Compare Offers
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that outline the specifications, pricing, delivery timelines, and warranty information. Comparing offers allows you to evaluate not just the price but also the value each supplier brings, including after-sales support and service agreements.
Step 7: Plan for Installation and Training
A successful implementation goes beyond purchasing the conveyor; it includes proper installation and training for your team. Discuss installation timelines with the supplier and ensure they provide adequate training for your staff on operation and maintenance. This proactive approach minimizes disruptions and enhances operational efficiency from day one.
By following this checklist, you will be better equipped to navigate the complexities of sourcing a mechanical conveyor that meets your business needs, ensuring a smooth procurement process and long-term operational success.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for mechanical conveyor Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Mechanical Conveyor Manufacturing?
When sourcing mechanical conveyors, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the overall cost. For instance, conveyors made from stainless steel are more expensive than those made from carbon steel due to their resistance to corrosion and durability. The selection of materials should align with the intended application, particularly in industries like food processing or pharmaceuticals where hygiene is paramount.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly based on geographical location and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Regions with higher labor costs may affect the overall pricing, making it essential for buyers to consider sourcing from areas with competitive labor rates while ensuring quality standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses expenses related to factory operations, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Understanding the overhead can provide insights into a supplier’s pricing strategy and help buyers gauge if the costs are justified.
-
Tooling: Depending on the conveyor design, tooling costs can vary. Custom conveyors typically require specialized tooling, which can increase initial costs. Buyers should assess whether the investment in custom tooling will yield long-term benefits.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that products meet required standards and specifications. While these processes may add to the cost, they are vital for minimizing defects and ensuring operational efficiency in the long run.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can significantly impact the total cost, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and Incoterms should be considered when calculating logistics costs.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins also play a role in the final price. Understanding typical margins in the industry can help buyers identify reasonable pricing and negotiate effectively.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Mechanical Conveyor Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of mechanical conveyors, including:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Ordering in larger volumes often leads to discounts. Buyers should evaluate their operational needs to determine the optimal order quantity that balances cost savings and inventory management.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs due to additional design and manufacturing requirements. Buyers should weigh the necessity of custom features against potential savings from standard models.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials or those with specific certifications (such as ISO or CE) often come at a premium. Buyers should assess the importance of these certifications in relation to their operational requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and reliability can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer suppliers might offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping and delivery can greatly affect total costs. Understanding Incoterms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is essential for buyers to calculate their total landed costs accurately.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Conveyor Pricing?
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation strategies are crucial:
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): When negotiating, consider not just the upfront costs but the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. A lower initial price may lead to higher long-term costs if the equipment is not durable or efficient.
-
Negotiate Based on Volume: Utilize the volume of your order as a bargaining chip. Suppliers are often willing to offer better rates for larger orders or long-term contracts.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Gathering quotes from various suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations. It helps to have a clear understanding of the market price range.
-
Understand Local Market Dynamics: Knowledge of local market conditions can aid in negotiations, especially regarding labor costs and material availability. This understanding can help justify pricing discussions with suppliers.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be mindful of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and trade regulations that can impact pricing. Being informed will enhance negotiation effectiveness.
Conclusion
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the cost components, pricing influencers, and effective negotiation strategies is essential for international B2B buyers sourcing mechanical conveyors. While prices can vary widely, a strategic approach can lead to more favorable terms and ensure that investments align with operational goals. Always remember that the prices discussed are indicative and can fluctuate based on market conditions and specific requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing mechanical conveyor With Other Solutions
In the realm of material handling, selecting the right transportation solution is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and reducing costs. While mechanical conveyors are widely recognized for their reliability and versatility, several alternative solutions exist that may better suit specific applications or organizational needs. This analysis will compare mechanical conveyors with two viable alternatives: pneumatic conveyors and automated guided vehicles (AGVs).
| Comparison Aspect | Mechanical Conveyor | Pneumatic Conveyor | Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High throughput; effective for bulk materials | Excellent for fine powders; limited to specific materials | High flexibility; suitable for dynamic environments |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; ongoing maintenance costs | Higher initial costs; lower operational costs | High upfront costs; potential for significant labor savings |
| Ease of Implementation | Generally straightforward; requires space for installation | Requires careful design for air flow and pressure | Complex setup; needs integration with existing systems |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed; parts may wear over time | Low maintenance; fewer moving parts | Maintenance required; battery and software management |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for continuous, high-volume material transport | Best for transporting fine powders or granules over distances | Effective in environments requiring flexibility and automation |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Pneumatic Conveyors?
Pneumatic conveyors utilize air pressure to transport materials, particularly fine powders like cement or flour. The primary advantage of this system is its ability to move materials through a closed system, reducing contamination and dust emissions. Moreover, pneumatic conveyors are highly adaptable and can navigate around obstacles in a facility. However, they tend to have higher initial costs due to the need for compressors and specialized piping. Additionally, they may not be suitable for heavier or bulk materials, limiting their application scope.

Illustrative image related to mechanical conveyor
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)?
Automated Guided Vehicles are mobile robots that transport materials autonomously throughout a facility. They offer significant flexibility, allowing for dynamic routing and reconfiguration as operational needs change. AGVs can handle various materials and integrate seamlessly with warehouse management systems, enhancing overall productivity. However, they come with a high upfront investment and require sophisticated software for navigation and coordination. Maintenance can also be more involved due to battery management and software updates.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When choosing between mechanical conveyors and alternative solutions like pneumatic conveyors or AGVs, B2B buyers should consider several factors. First, evaluate the types of materials being transported and the specific operational requirements, such as volume, distance, and environmental conditions. Next, assess the initial investment against long-term operational costs and maintenance requirements. Finally, consider the flexibility and scalability of the solution, especially if future growth or changes in product lines are anticipated. By aligning these factors with organizational goals, buyers can select the most effective material handling solution for their unique circumstances.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for mechanical conveyor
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Mechanical Conveyors?
Understanding the essential technical specifications of mechanical conveyors is crucial for B2B buyers seeking to optimize material handling processes. Here are several critical properties to consider:

Illustrative image related to mechanical conveyor
1. Material Grade
The material grade of the conveyor components, such as the belt and frame, directly impacts durability and performance. Common materials include stainless steel, plastic, and rubber. Each material offers different levels of corrosion resistance, strength, and flexibility, which can affect the conveyor’s lifespan and maintenance needs. Selecting the appropriate material grade helps ensure that the conveyor system meets operational demands while minimizing replacement costs.
2. Load Capacity
Load capacity refers to the maximum weight a conveyor can handle at any given time. This specification is vital for determining whether a conveyor can support the weight of the materials being transported. Exceeding the load capacity can lead to mechanical failures, increased wear, and potential safety hazards. B2B buyers should assess their specific material handling requirements to choose a conveyor with an adequate load capacity that aligns with operational needs.
3. Speed and Throughput
Speed is a measure of how quickly materials move along the conveyor, often expressed in meters per second (m/s) or feet per minute (FPM). Throughput, on the other hand, indicates the volume of materials processed over a specific time period. Both factors are critical for optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring that production schedules are met. Buyers should evaluate the speed and throughput capabilities of conveyor systems to match their operational pace and volume requirements.
4. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions during manufacturing. High tolerance levels ensure that components fit together precisely, which is essential for smooth operation and longevity of the conveyor system. Inaccurate tolerances can lead to misalignment, excessive wear, and costly downtime. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that maintain rigorous quality control to ensure that the conveyor meets necessary tolerances.
5. Power Requirements
Power requirements indicate the energy needed to operate the conveyor system. This specification includes the type of motor (e.g., electric or hydraulic) and its wattage. Understanding power requirements is crucial for integrating the conveyor into existing systems and ensuring that energy consumption aligns with budgetary constraints. Buyers should evaluate the energy efficiency of conveyor systems to optimize operational costs.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Conveyor Industry?
Familiarizing oneself with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the mechanical conveyor market. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the conveyor industry, OEMs often supply specific components to system integrators or end-users, ensuring compatibility and quality. Understanding OEM relationships can enhance procurement strategies and product reliability.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In the context of mechanical conveyors, knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchases effectively, particularly when dealing with custom solutions or specialized components. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their operational needs without incurring excess inventory costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. When seeking mechanical conveyors, issuing an RFQ helps buyers gather competitive bids, compare options, and make informed decisions based on price, lead time, and specifications.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. These terms clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, thus reducing misunderstandings. B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with Incoterms to navigate international procurement effectively.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the product. In the conveyor industry, understanding lead times is essential for planning production schedules and managing supply chain logistics. Buyers should communicate clearly with suppliers to establish realistic lead times that align with operational timelines.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring their conveyor systems meet both current and future operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the mechanical conveyor Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Mechanical Conveyor Market?
The mechanical conveyor market is currently experiencing significant transformation driven by global economic trends and technological advancements. One of the primary drivers is the increasing demand for automation across industries, particularly in manufacturing, logistics, and food processing. As businesses aim to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs, the integration of conveyor systems into production lines has become essential. This trend is particularly pronounced in emerging markets in Africa and South America, where rapid industrialization is taking place.

Illustrative image related to mechanical conveyor
Moreover, the rise of e-commerce has created a surge in demand for efficient logistics solutions, prompting companies to invest in advanced conveyor systems that can handle varying product types and volumes. The adoption of smart technologies, such as IoT and AI, is also gaining traction, enabling predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and improved supply chain management. International buyers should focus on suppliers that are innovating in these areas, as they will likely offer enhanced operational capabilities and competitive pricing.
Another emerging trend is the growing emphasis on customization and modular systems that can be tailored to specific operational needs. This flexibility allows businesses in diverse regions, including the Middle East and Europe, to optimize their conveyor solutions according to their unique workflows and space constraints. As market dynamics evolve, understanding these trends will be crucial for B2B buyers seeking to make informed sourcing decisions.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Decisions in the Conveyor Sector?
Sustainability has become a central concern for businesses across the globe, and the mechanical conveyor sector is no exception. The environmental impact of conveyor systems, particularly in terms of energy consumption and material waste, necessitates a shift towards more sustainable practices. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who employ eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient technologies, as these choices can significantly reduce operational carbon footprints.
The importance of ethical supply chains is also paramount. As consumers and stakeholders increasingly demand transparency, companies that adopt sustainable sourcing practices are likely to enhance their reputations and customer loyalty. This includes sourcing from suppliers that adhere to strict environmental regulations and demonstrate a commitment to reducing waste throughout the supply chain.
Buyers should also look for ‘green’ certifications for mechanical conveyor systems, such as ISO 14001, which focuses on effective environmental management systems. By prioritizing suppliers with these credentials, businesses can ensure that their operations align with global sustainability goals while also meeting regulatory requirements. This approach not only benefits the environment but can also lead to cost savings through reduced energy consumption and waste management.

Illustrative image related to mechanical conveyor
What Is the Historical Context of Mechanical Conveyors and Their Evolution?
The mechanical conveyor has a rich history that dates back to the late 18th century, when early versions were used in agriculture for moving grain. Over the years, these systems have evolved significantly, paralleling advancements in technology and manufacturing processes. The introduction of electric motors in the early 20th century revolutionized conveyor systems, allowing for faster and more efficient material handling.
As industrialization progressed, conveyor systems became integral to assembly lines, notably in the automotive sector during the 1920s. The latter half of the 20th century saw the emergence of various types of conveyors, including belt, screw, and pneumatic systems, each designed to cater to specific industry needs. Today, with the advent of automation and smart technologies, mechanical conveyors continue to play a crucial role in enhancing operational efficiency and productivity across diverse sectors.
Understanding this evolution is essential for B2B buyers, as it highlights the potential for innovation and customization in current conveyor solutions, enabling businesses to optimize their operations effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of mechanical conveyor
-
How do I choose the right mechanical conveyor for my operation?
Selecting the right mechanical conveyor involves assessing your specific operational needs, including the type of materials you handle, the required load capacity, and the layout of your facility. Consider factors such as the conveyor’s speed, ease of maintenance, and whether it needs to integrate with existing systems. Consulting with suppliers about your requirements can help you understand the best options available, including customized solutions tailored to your business. -
What is the best type of conveyor for bulk materials handling?
For bulk materials handling, screw conveyors and bucket elevators are often the best choices. Screw conveyors efficiently transport powders, grains, and other bulk materials through a rotating spiral, making them ideal for applications in agriculture and food processing. Bucket elevators, on the other hand, are designed to lift materials vertically and are well-suited for high-capacity needs, particularly in mining and agriculture. Evaluate your specific application to determine the best fit. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for mechanical conveyors?
Minimum order quantities for mechanical conveyors can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the complexity of the conveyor system. Generally, MOQs may range from a single unit for standard conveyors to larger quantities for customized solutions. It’s essential to communicate your specific needs to suppliers and inquire about their MOQ policies, especially if you are considering bulk purchases for large projects. -
How can I vet suppliers of mechanical conveyors for international trade?
When vetting suppliers, consider their reputation, experience, and certifications. Look for reviews from other clients, request case studies, and check their compliance with international quality standards. It’s also advisable to conduct virtual or in-person visits to their facilities if possible, and ask about their after-sales support and warranty policies. Establishing clear communication channels can help build trust and ensure a smooth procurement process. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing mechanical conveyors?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common arrangements include a deposit upon order confirmation, followed by the balance before shipping. Some suppliers may offer credit terms, allowing payment after delivery. Always clarify payment terms upfront, including any conditions related to international transactions, such as currency exchange rates and potential tariffs, to avoid unexpected costs. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for mechanical conveyors?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation of the manufacturer’s quality control processes, including certifications and inspection reports. Consider conducting factory audits to observe their manufacturing practices firsthand. Additionally, inquire about warranty terms and after-sales service, as reputable suppliers will often provide support and replacement parts for a specified period post-purchase. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing mechanical conveyors?
Logistics for importing mechanical conveyors include understanding shipping methods, customs clearance processes, and potential tariffs or duties. It’s crucial to collaborate with a logistics provider experienced in handling industrial equipment to navigate these challenges effectively. Ensure that you also verify the lead times for production and shipping to align with your operational timelines, especially when coordinating installation schedules. -
Can mechanical conveyors be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options to tailor mechanical conveyors to specific applications. Customizations may include modifications in size, material, and configuration to accommodate unique handling requirements. When discussing customization with suppliers, provide detailed specifications about your operational needs, such as load capacity, material type, and environmental conditions, to receive the most effective solution.
Top 4 Mechanical Conveyor Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. May Conveyor – Specialty Engineered Belting
Domain: mayconveyor.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Belt Types: Chip Conveyor Belts, Combination Conveyor Belts, “Z” Apron Pan Belts, Steel Hinge Belts, Beaded Apron Belts, Specialty Engineered Belting. Types of Mechanical Conveyors: 1. Belt: Commonly used for transporting materials in various sizes. 2. Drag Chain: Transports solids on inclines, vertically or horizontally; used in wood processing and food industries. 3. Screw: Economical solution f…
2. AMG – Mechanical Conveying Systems
Domain: blog.amg-eng.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Mechanical conveying systems are efficient for transferring large amounts of product over long distances, ideal for quickly offloading vehicles like trucks and rail cars. They can handle various product shapes, sizes, and weights, offering design flexibility for horizontal, inclined, or vertical conveying. Key types include: 1. Screw Conveyors – good for small spaces and wet products, ideal for mi…
3. Compass Systems – Steel Hinged Belt Conveyors
Domain: compasssystems.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Compass Systems offers custom-engineered mechanical conveyor solutions designed for various materials and operating environments. Key product details include: 1. Steel Hinged Belt Conveyors: Durable for heavy-duty scrap handling, custom-designed for specific materials, features include automatic lubrication, easy maintenance access, and scalability. 2. Oscillating Conveyors: Tray-type design for s…
4. Ocado Intelligent Automation – Conveyor Systems
Domain: ocadointelligentautomation.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: A conveyor system is a mechanical handling apparatus designed for automatically transporting loads and materials within an area. It minimizes human error, lowers workplace risks, and reduces labor costs. Conveyor systems can use belts, wheels, rollers, or chains to transport objects. They consist of a belt stretched across two or more pulleys, with a drive pulley that moves the belt. Common types …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for mechanical conveyor
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Mechanical Conveyor Procurement?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing is vital for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their mechanical conveyor systems. By understanding the diverse types of conveyors—such as belt, screw, and drag chain—and their specific applications, businesses can tailor solutions that enhance operational efficiency and productivity. Investing in the right conveyor system not only streamlines material handling processes but also reduces costs and minimizes risks associated with manual labor.
Moreover, companies across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must consider the long-term benefits of automated systems. These systems can drastically improve accuracy, safety, and space utilization in various industries, from manufacturing to food processing.
As you prepare to source your mechanical conveyors, engage with reputable suppliers who offer customization and integration capabilities. This proactive approach will ensure that your operations are equipped with the most effective solutions tailored to your unique needs.
The future of material handling is evolving, and now is the time to invest in advanced conveyor technologies. Start your journey towards enhanced operational excellence today, and position your business for sustainable growth in the global marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.