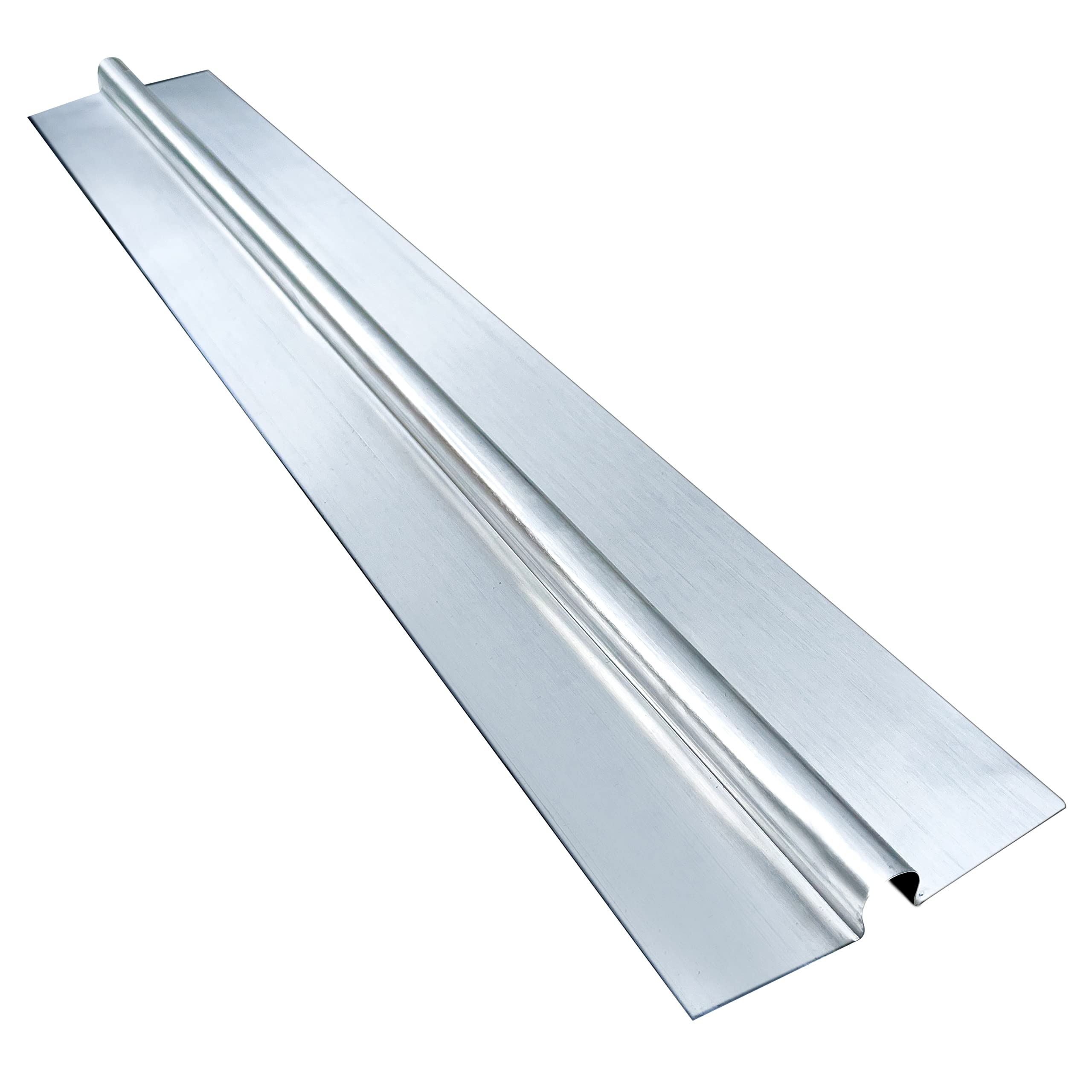
Heat Transfer Plates For Radiant Heating Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for heat transfer plates for radiant heating
In the ever-evolving landscape of radiant heating systems, sourcing high-quality heat transfer plates is crucial for optimizing energy efficiency and enhancing comfort in commercial and residential spaces. B2B buyers face the challenge of navigating diverse materials, designs, and applications, all while ensuring cost-effectiveness and compliance with local regulations. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of heat transfer plates, covering essential topics such as types of materials (aluminum vs. alternatives), installation methods, and performance metrics that impact overall system efficiency.
We aim to equip international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Germany and Nigeria—with the insights needed to make informed purchasing decisions. The guide will explore supplier vetting processes, enabling buyers to identify reputable manufacturers who can deliver products that meet stringent quality standards. Additionally, we will analyze pricing structures and cost-saving strategies to help businesses maximize their investment.
By consolidating vital information and expert recommendations, this guide empowers B2B buyers to confidently navigate the global market for heat transfer plates. Whether you’re looking to enhance your existing systems or invest in new radiant heating solutions, our insights will ensure you select the best options tailored to your operational needs and regional considerations.
Understanding heat transfer plates for radiant heating Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Gauge Aluminum | Thicker material for superior heat transfer efficiency | High-performance radiant heating systems | Pros: Excellent heat transfer, durable. Cons: Higher cost, requires more installation effort. |
| Light Gauge Aluminum | Lighter, more economical option | Residential and commercial heating projects | Pros: Cost-effective, easier installation. Cons: Slightly less efficient than heavier options. |
| Pre-stamped Plates | Pre-shaped for easy installation | DIY projects and standard installations | Pros: Quick to install, versatile. Cons: Limited customization options. |
| Custom Fabricated Plates | Tailored designs for specific applications | Specialized heating needs, unique building layouts | Pros: Optimized for specific environments. Cons: Higher lead times and costs. |
| Sandwich Installation Plates | Designed for PEX tubing between layers | Efficient space utilization in tight areas | Pros: Effective heat distribution, space-saving. Cons: More complex installation process. |
What are the characteristics of Heavy Gauge Aluminum Heat Transfer Plates?
Heavy gauge aluminum heat transfer plates are designed for high-performance radiant heating systems. Their thickness allows for superior heat transfer efficiency, making them ideal for applications where maximum heat output is critical. Businesses that prioritize energy efficiency and long-term performance will find these plates beneficial, despite their higher initial cost. When considering this option, buyers should evaluate the total lifecycle costs and potential energy savings against the upfront investment.
How do Light Gauge Aluminum Plates compare in terms of suitability?
Light gauge aluminum plates offer a more economical solution for radiant heating systems, particularly in residential and less demanding commercial applications. While they are not as efficient as their heavier counterparts, they provide adequate heat distribution and are easier to install. B2B buyers looking for cost-effective solutions without compromising performance too much may find this option appealing. It’s essential to balance budget constraints with the desired efficiency levels when selecting this type.
What advantages do Pre-stamped Plates offer for B2B buyers?
Pre-stamped heat transfer plates are designed for quick and easy installation, making them ideal for DIY projects and standard heating installations. Their pre-shaped design allows for a straightforward application process, reducing labor costs. However, buyers should be aware that while these plates offer versatility, they may lack customization options for unique heating needs. Evaluating the specific requirements of a project will help determine if pre-stamped plates are the right choice.
Why consider Custom Fabricated Plates for specialized needs?
Custom fabricated heat transfer plates are tailored to meet specific heating applications and building layouts. This option is particularly advantageous for businesses with unique requirements that standard plates cannot address. While they provide optimized performance, the downside includes longer lead times and potentially higher costs. B2B buyers should assess the trade-off between customization benefits and budget constraints when considering this option.
What is the purpose of Sandwich Installation Plates in radiant heating?
Sandwich installation plates are designed for scenarios where PEX tubing is placed between layers, allowing for effective heat distribution in tight spaces. This design is particularly useful in multi-story buildings or areas with limited installation depth. The primary advantage of this approach is its ability to maximize heat transfer while conserving space. However, the installation process can be more complex, requiring skilled labor. Buyers should consider the specific spatial constraints of their projects when evaluating this option.
Key Industrial Applications of heat transfer plates for radiant heating
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of heat transfer plates for radiant heating | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Installation in residential and commercial buildings | Enhances energy efficiency and comfort, reducing heating costs | Material quality (aluminum type), thickness, and coverage options |
| Agriculture | Heating in greenhouses and livestock facilities | Improves crop yield and animal welfare through controlled temperatures | Durability in humid environments, ease of installation |
| Hospitality | Radiant heating in hotels and resorts | Increases guest comfort and satisfaction, leading to higher occupancy rates | Aesthetic design compatibility, energy efficiency ratings |
| Manufacturing | Process heating in industrial facilities | Optimizes production processes and reduces energy consumption | Compliance with safety standards, thermal efficiency requirements |
| Renewable Energy | Integration in solar heating systems | Supports sustainable energy practices and reduces reliance on fossil fuels | Compatibility with existing systems, efficiency ratings |
How Are Heat Transfer Plates Used in Construction Projects?
In the construction sector, heat transfer plates are integral to radiant heating systems, installed beneath floors in both residential and commercial buildings. They facilitate efficient heat transfer from PEX tubing to the floor surface, ensuring consistent warmth throughout spaces. This not only enhances occupant comfort but also leads to significant cost savings on heating bills. International buyers should consider the material quality and thickness of the plates, as these factors directly impact performance and durability in varying climates, particularly in regions like Europe and Africa where temperature fluctuations can be extreme.
What Role Do Heat Transfer Plates Play in Agriculture?
In agricultural settings, heat transfer plates are utilized in greenhouses and livestock facilities to maintain optimal temperatures. By effectively distributing heat from radiant heating systems, these plates help in creating a controlled environment that can enhance crop growth and improve animal welfare. For businesses in South America and Africa, sourcing plates that can withstand humid conditions and provide long-term durability is essential. Additionally, the ability to efficiently operate at lower temperatures can significantly reduce energy costs in these energy-sensitive applications.
How Do Heat Transfer Plates Enhance Hospitality Experiences?
The hospitality industry benefits from heat transfer plates by providing radiant heating solutions in hotels and resorts. By ensuring even heat distribution, these plates contribute to a more comfortable guest experience, which can lead to higher occupancy rates and repeat business. When sourcing for this application, businesses should consider the aesthetic compatibility of the plates with interior designs and energy efficiency ratings to align with sustainability goals, particularly in Europe where eco-friendly practices are increasingly prioritized.

Illustrative image related to heat transfer plates for radiant heating
In What Ways Are Heat Transfer Plates Critical for Manufacturing?
In manufacturing facilities, heat transfer plates are essential for process heating, enabling efficient temperature control across various production processes. By optimizing heat transfer, these plates help reduce energy consumption and improve overall operational efficiency. Companies should ensure that the plates comply with safety and thermal efficiency standards, especially when operating in high-temperature environments. This is particularly crucial for international buyers in the Middle East, where extreme heat can impact equipment performance.
How Are Heat Transfer Plates Utilized in Renewable Energy Systems?
Heat transfer plates play a significant role in renewable energy applications, especially in solar heating systems. They enhance the efficiency of these systems by effectively transferring heat to the desired medium, thereby supporting sustainable energy practices. Buyers looking to integrate these plates into existing systems should focus on compatibility and efficiency ratings, ensuring that the plates can operate effectively within their specific renewable energy setups. This is particularly relevant for businesses in regions like Africa and South America, where the push for renewable energy solutions is rapidly growing.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘heat transfer plates for radiant heating’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Optimal Heat Distribution in Radiant Heating Systems
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with uneven heat distribution across spaces when installing radiant heating systems. This can lead to cold spots on the floor, resulting in discomfort for occupants and decreased system efficiency. Factors contributing to this issue include improper installation of heat transfer plates or inadequate coverage of the tubing. Buyers may find themselves unsure of how to balance the cost of materials with the need for effective heat transfer.
The Solution: To address this challenge, it is crucial for buyers to invest in high-quality heat transfer plates that ensure optimal heat distribution. Buyers should consider using aluminum plates that fully cover the tubing, as research indicates that full coverage can increase heat output by up to 60%. When selecting plates, opt for medium to heavy gauge aluminum, as these materials provide better thermal conductivity and support for the tubing. Additionally, buyers should follow a calculated installation approach by ensuring that plates are securely fastened to the subfloor. This can be achieved by using screws or staples at regular intervals, which prevents sagging of the tubing and ensures consistent contact between the plates and the floor above.
Scenario 2: Managing Costs While Maximizing Efficiency
The Problem: Cost management is a significant concern for B2B buyers, particularly in regions where budgets for heating systems are tight. Many buyers are tempted to opt for lower-cost options, such as lighter gauge aluminum or even alternatives to aluminum, which can ultimately lead to inefficiencies and higher operational costs over time. This poses a dilemma: how to stay within budget while ensuring an effective heating solution.
The Solution: Buyers should take a strategic approach to balancing costs and performance by conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis of different heat transfer plate options. It is recommended to invest in medium gauge aluminum plates that strike a balance between price and efficiency. While heavier gauges offer better performance, the medium gauge provides sufficient heat transfer capabilities at a lower cost. Furthermore, proper insulation beneath the plates can reduce heat loss, leading to lower operating temperatures and costs in the long run. Buyers should also consider bulk purchasing options or establishing long-term supplier relationships to negotiate better pricing on quality materials.
Scenario 3: Addressing Installation Challenges in Various Environments
The Problem: Installation environments can vary widely, especially in international markets. Buyers might face unique challenges such as irregular subfloor surfaces or extreme temperature fluctuations, which can complicate the installation of heat transfer plates. Inadequate preparation for these conditions can lead to installation failures and increased maintenance costs.
The Solution: To overcome installation challenges, buyers should conduct a comprehensive site assessment prior to installation. This includes measuring the subfloor’s evenness and ensuring that any irregularities are addressed before laying down heat transfer plates. In cases where the subfloor is uneven, using a leveling compound can create a suitable base for the plates. Additionally, buyers should be aware of the thermal properties of their installation environment—considering factors like humidity and temperature fluctuations. Opting for heat transfer plates with lower emissivity can help mitigate heat loss in such environments. Finally, engaging experienced installers who understand the nuances of radiant heating systems can further ensure a successful installation that meets performance expectations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for heat transfer plates for radiant heating
When selecting materials for heat transfer plates in radiant heating systems, it is crucial to consider various factors that influence performance, cost, and application suitability. This analysis focuses on four common materials: aluminum, copper, stainless steel, and plastic composites. Each material’s properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international buyers will be discussed.
What are the Key Properties of Aluminum for Heat Transfer Plates?
Aluminum is the most commonly used material for heat transfer plates due to its exceptional thermal conductivity, which allows for efficient heat transfer from the tubing to the flooring above. It typically has a temperature rating up to 300°F (149°C) and is resistant to corrosion when properly treated. The low emissivity of aluminum also minimizes heat loss, making it a preferred choice for radiant heating applications.

Illustrative image related to heat transfer plates for radiant heating
Pros: Aluminum plates are lightweight, easy to install, and provide excellent heat distribution, reducing cold spots in flooring. They are also cost-effective compared to other metals.
Cons: The primary drawback of aluminum is its susceptibility to deformation under high temperatures if not adequately supported. Additionally, while aluminum is generally affordable, the cost can increase significantly for thicker or specialized plates.
Impact on Application: Aluminum plates are compatible with various heating media, including water and glycol mixtures, making them versatile for different radiant heating systems.

Illustrative image related to heat transfer plates for radiant heating
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM in the U.S. and DIN in Germany. In regions like Africa and South America, where environmental factors may vary, selecting aluminum with appropriate coatings can enhance durability.
How Does Copper Compare as a Material for Heat Transfer Plates?
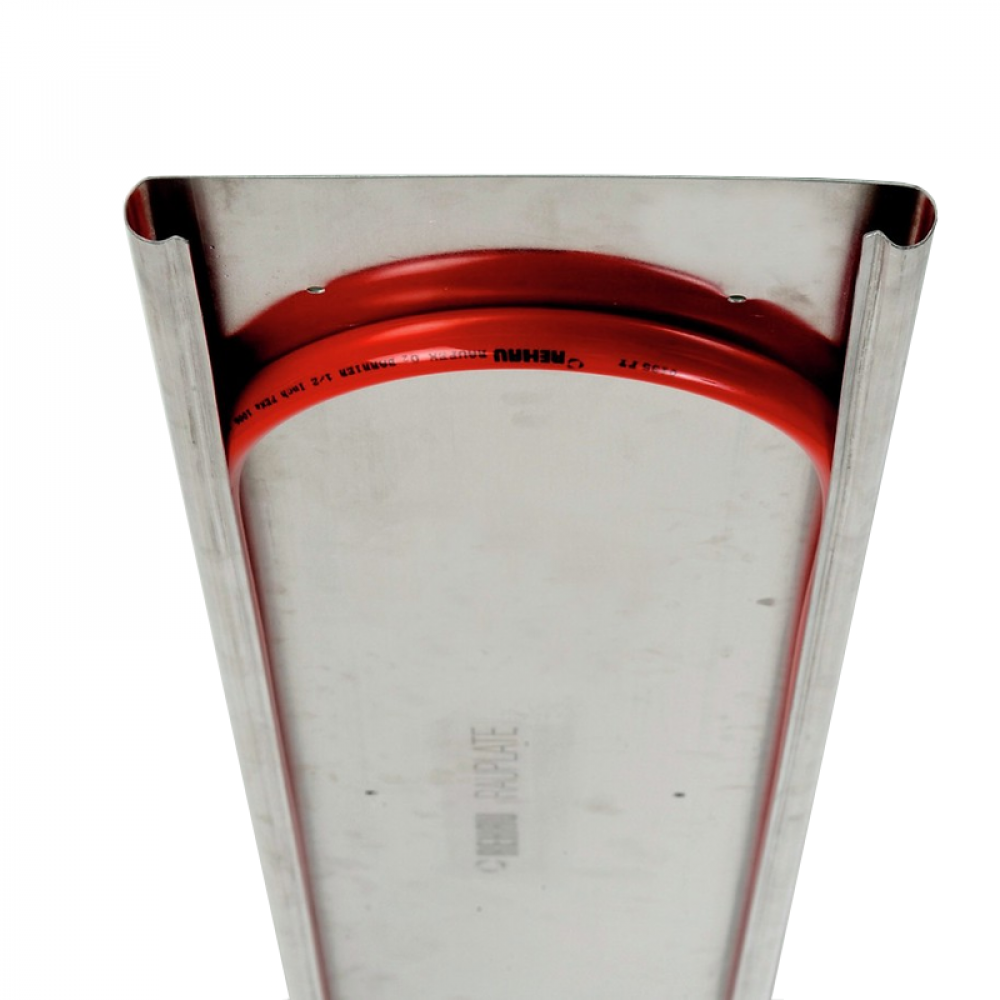
Copper is renowned for its superior thermal conductivity, even better than aluminum, making it an excellent choice for heat transfer applications. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, typically rated up to 400°F (204°C).
Pros: The primary advantage of copper is its efficiency in heat transfer, which can lead to lower operating costs and improved system performance. Copper is also highly durable and resistant to corrosion.
Cons: However, copper is significantly more expensive than aluminum, which can be a limiting factor for large-scale projects. Additionally, the weight of copper plates can complicate installation.

Illustrative image related to heat transfer plates for radiant heating
Impact on Application: Copper plates are particularly effective in high-temperature systems, making them suitable for applications where rapid heat transfer is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the fluctuating copper prices and ensure compliance with international standards, particularly in regions where copper theft is prevalent.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Heat Transfer Plates?
Stainless steel is another option for heat transfer plates, known for its strength and corrosion resistance. It can perform well in environments with high humidity or exposure to corrosive elements.
Pros: The durability of stainless steel makes it an ideal choice for long-term applications, especially in harsh environments. It also has a good temperature rating, typically up to 500°F (260°C).
Cons: The main disadvantage is the cost, as stainless steel is generally more expensive than both aluminum and copper. Its thermal conductivity is lower than that of aluminum and copper, which may affect heat transfer efficiency.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for systems that require high durability and corrosion resistance, such as those in coastal areas or industrial settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards is critical, particularly for buyers in Europe where stringent regulations may apply.
Are Plastic Composites a Viable Option for Heat Transfer Plates?
Plastic composites are emerging as an alternative for heat transfer plates, combining lightweight properties with reasonable thermal performance. They are often used in low-temperature applications.

Illustrative image related to heat transfer plates for radiant heating
Pros: These materials are resistant to corrosion and can be manufactured at a lower cost compared to metals. They are also lightweight and easy to handle.
Cons: However, plastic composites generally have lower thermal conductivity than metals, which may limit their effectiveness in high-performance systems. They also have lower temperature ratings, typically around 180°F (82°C).
Impact on Application: Plastic composites are best suited for residential applications or systems where budget constraints are a priority.

Illustrative image related to heat transfer plates for radiant heating
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the composites meet local building codes and standards, especially in regions where high temperatures may be a concern.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Heat Transfer Plates
| Material | Typical Use Case for heat transfer plates for radiant heating | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Residential and commercial radiant heating systems | Excellent thermal conductivity | Susceptible to deformation | Medium |
| Copper | High-performance heating applications | Superior heat transfer efficiency | High cost and weight | High |
| Stainless Steel | Harsh environments and industrial applications | High durability and corrosion resistance | Lower thermal conductivity | High |
| Plastic Composites | Low-temperature residential applications | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower thermal performance | Low |
This guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers in diverse regions, enabling informed decisions regarding material selection for heat transfer plates in radiant heating systems.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for heat transfer plates for radiant heating
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Heat Transfer Plates?
The manufacturing process for heat transfer plates involves several critical stages, each contributing to the final product’s efficiency and performance. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
How is Material Prepared for Manufacturing Heat Transfer Plates?
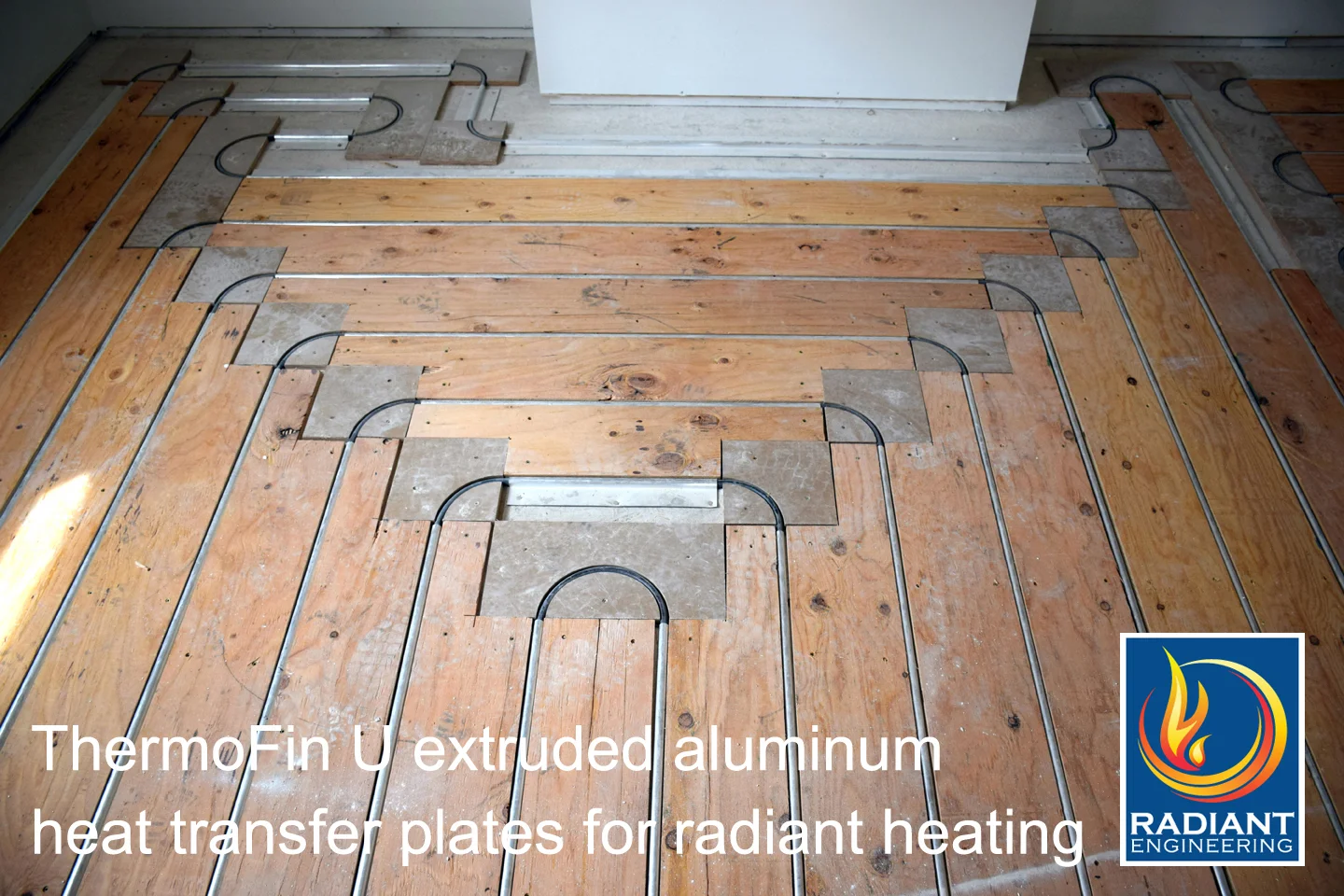
The first stage in the manufacturing of heat transfer plates is material preparation. High-quality aluminum is typically chosen for its excellent thermal conductivity. The aluminum sheets are sourced from reputable suppliers who adhere to international standards to ensure the material’s integrity. The sheets are then cut to the required dimensions, which can vary based on the intended application, such as staple-up systems or sandwich installations.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Heat Transfer Plate Production?
Once the material is prepared, the next step is forming. This can be achieved through various techniques such as stamping, extrusion, or die-casting.
-
Stamping: In this method, the aluminum sheets are placed in a stamping machine that shapes them into the desired form, including the grooves necessary for PEX tubing. Stamping is efficient for high-volume production and ensures consistent dimensions.
-
Extrusion: This technique involves forcing heated aluminum through a die to create long shapes with specific profiles. This is particularly useful for custom designs that require specific channel configurations.
Each technique has its benefits, and the choice often depends on the volume of production and specific design requirements.
What Are the Assembly and Finishing Processes for Heat Transfer Plates?
After forming, the plates undergo an assembly process where additional features, such as mounting holes or insulation backing, may be added. This step may include:
-
Attachment of Insulation: For applications requiring reduced heat loss, insulation can be attached to the back of the plates.
-
Surface Treatment: Plates may be anodized or coated to enhance corrosion resistance and improve thermal efficiency.
Finishing is critical as it ensures that the plates meet aesthetic and functional requirements. This stage might also include cutting plates to size and reaming out tubing channels to prevent damage to PEX pipes during installation.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Heat Transfer Plates?
Quality control (QC) is paramount in the manufacturing of heat transfer plates. Implementing rigorous QC measures ensures that the final products meet industry standards and customer specifications.
Which International Standards Should Heat Transfer Plate Manufacturers Comply With?
Manufacturers should adhere to several international standards to ensure product quality and reliability. Common standards include:
-
ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is vital for ensuring consistent quality in manufacturing processes.
-
CE Marking: In Europe, products must conform to health, safety, and environmental protection standards to be sold in the European market.
-
API Certification: For applications in the oil and gas sector, API certifications may be necessary to ensure that products meet specific performance and safety criteria.
These certifications signal to B2B buyers that the supplier is committed to quality and compliance with relevant regulations.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing Heat Transfer Plates?
Quality control checkpoints should be established throughout the manufacturing process to catch any defects early. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected for conformity to specifications before they enter the production line. This step ensures that only high-quality aluminum is used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, processes are monitored to identify deviations from established standards. This may include measuring dimensions, checking for defects, and ensuring that forming techniques are consistently applied.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, final inspections are conducted to ensure that each batch of heat transfer plates meets the required specifications. This could involve thermal efficiency testing and visual inspections for surface defects.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used to Ensure Heat Transfer Plate Quality?
Testing methods are essential for validating the performance of heat transfer plates. Common testing techniques include:
-
Thermal Conductivity Tests: These tests measure how effectively the plates transfer heat, ensuring they meet performance standards.
-
Mechanical Strength Tests: Assessing the structural integrity of the plates under various conditions ensures they can withstand installation and operational stresses.
-
Corrosion Resistance Tests: Given that heat transfer plates are often exposed to moisture and varying temperatures, testing for corrosion resistance is crucial for long-term durability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers. These include:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess manufacturing processes, quality control checkpoints, and adherence to international standards firsthand.
-
Requesting Quality Assurance Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation that details their quality control processes, testing methods, and results from recent batches.
-
Third-party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s manufacturing and quality assurance processes.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers in Diverse Markets?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges in quality assurance. Here are some considerations:
-
Understanding Local Regulations: Different regions may have specific regulations regarding product safety and performance. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are compliant with local laws and standards.
-
Logistical Challenges: Transportation and storage conditions can affect the quality of heat transfer plates. Buyers should discuss handling and logistics with suppliers to mitigate risks associated with international shipping.
-
Cultural and Communication Barriers: Effective communication is vital to ensure that quality expectations are understood and met. Buyers should establish clear lines of communication with suppliers to address any concerns promptly.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for heat transfer plates, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their radiant heating systems’ efficiency and reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘heat transfer plates for radiant heating’
To assist B2B buyers in procuring heat transfer plates for radiant heating systems effectively, this guide outlines essential steps to ensure a successful sourcing process. By following this checklist, you will be equipped to make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and budget constraints.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the heat transfer plates based on your project needs. Consider factors such as material type (aluminum gauge), dimensions, and compatibility with existing systems. Knowing your specifications helps streamline the selection process and ensures compatibility with your radiant heating setup.
Step 2: Research Material Options and Performance Metrics
Understand the different material types available for heat transfer plates, primarily focusing on aluminum gauges. Evaluate the performance metrics, such as heat transfer efficiency and emissivity rates. For instance, heavier gauge aluminum may offer better heat transfer but at a higher cost. Prioritize materials that balance performance and budgetary constraints.

Illustrative image related to heat transfer plates for radiant heating
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers to ensure reliability and quality. Request documentation such as company profiles, product certifications, and references from existing clients in similar sectors. Pay attention to suppliers’ ability to meet international standards, especially if sourcing from different regions.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing a supplier, request samples of the heat transfer plates for testing. This step allows you to assess the quality and performance firsthand, ensuring that the plates meet your specifications. Testing can also reveal how well the plates interact with your specific installation conditions, which is critical for optimal performance.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers hold relevant certifications that comply with international quality and safety standards. Certifications may include ISO, CE, or specific local regulations pertinent to your region. Verified certifications indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality, which can significantly reduce the risk of product failure.
Step 6: Assess Pricing and Shipping Options
Analyze the pricing structures offered by different suppliers, keeping an eye out for any hidden costs associated with shipping or handling. Additionally, check the shipping options available, including delivery timelines and costs, especially if you require expedited services. Understanding the total cost will help you stay within budget.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Maintain open lines of communication with your suppliers throughout the sourcing process. Establishing clear communication can help address any questions or concerns promptly, ensuring a smoother procurement experience. Ensure that the supplier is responsive and provides timely updates on order status, shipping, and any potential issues.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the procurement of heat transfer plates for radiant heating systems with confidence, ensuring they select the best options that meet their technical and budgetary requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for heat transfer plates for radiant heating Sourcing
The cost structure for heat transfer plates used in radiant heating systems involves multiple components that contribute to the overall pricing. Understanding these elements can help international B2B buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Heat Transfer Plates?
-
Materials: The primary material used in heat transfer plates is aluminum, which can vary in gauge and quality. Lighter gauge aluminum is more cost-effective but may not provide the same heat transfer efficiency as heavier gauge options. Buyers should weigh the cost against performance needs, as well as the environmental impact of sourcing materials.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages for manufacturing workers, which can differ significantly based on the region. For instance, labor costs in Europe may be higher than those in Africa or South America. This factor can affect the final pricing of the plates.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to the facility, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Manufacturers often pass these costs onto buyers, so understanding the operational efficiency of a supplier can provide insight into potential price variances.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specialized plate designs can represent a significant cost. If a buyer requires unique dimensions or shapes, this may lead to increased expenses in both initial setup and production.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that heat transfer plates meet specific standards requires investment in quality control processes. Certifications and testing can add to the cost but are essential for ensuring product reliability and safety.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the distance and delivery method. For international buyers, understanding the logistics costs associated with different Incoterms is crucial, as they dictate who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
-
Margin: Manufacturers and suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This can vary widely based on the competitive landscape and the perceived value of the product.
What Influences the Pricing of Heat Transfer Plates?
Several factors can influence the pricing of heat transfer plates, making it essential for buyers to consider them during negotiations:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often lead to discounts. Buyers should assess their project needs and determine if they can meet MOQ requirements to take advantage of cost savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products usually carry higher costs. Buyers need to evaluate whether the added expense is justified by the performance benefits.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may increase costs but can also enhance the product’s reliability and longevity, affecting the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier play a significant role in pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record of delivering quality products and customer service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms can affect total costs. For example, CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) terms might lead to higher prices than FOB (Free on Board) terms, where the buyer assumes more responsibility for shipping costs.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following strategies:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Understand market prices by researching various suppliers and comparing offerings. This knowledge empowers buyers during negotiations.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus on the long-term value rather than just the upfront cost. Analyzing energy efficiency, durability, and maintenance can lead to better decisions.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better terms and pricing. Long-term partnerships often result in loyalty discounts.
-
Flexibility in Orders: If possible, consider staggered orders to meet MOQ while maintaining flexibility in cash flow and inventory management.
Conclusion
While indicative prices can vary widely based on the factors outlined, understanding the cost structure and pricing influencers associated with heat transfer plates for radiant heating can help international B2B buyers make more informed decisions. By leveraging this knowledge, buyers can negotiate effectively and optimize their sourcing strategies for better overall value.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing heat transfer plates for radiant heating With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions for Radiant Heating
When considering solutions for radiant heating, it’s crucial to explore various alternatives to heat transfer plates. Each option can offer unique advantages and drawbacks depending on the specific requirements of your project, including performance, cost, and installation complexity. Below, we compare heat transfer plates for radiant heating with two viable alternatives: Hydronic Radiant Heating Systems and Electric Radiant Heating Mats.
| Comparison Aspect | Heat Transfer Plates For Radiant Heating | Hydronic Radiant Heating Systems | Electric Radiant Heating Mats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent heat distribution; reduces cold spots; effective at lower temperatures. | High efficiency; can be tailored for large spaces; excellent heat retention. | Quick heat response; easy to control temperature. |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; installation can vary. | Higher upfront investment; operational costs can be lower in the long run. | Lower initial cost; higher energy costs if used extensively. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires careful installation; can be DIY-friendly with proper tools. | More complex installation; often requires professional setup and plumbing work. | Simple installation; often comes pre-assembled and ready to install. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; occasional checks for leaks or insulation integrity. | Moderate maintenance; requires monitoring of the boiler and piping systems. | Low maintenance; minimal oversight needed post-installation. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for residential and commercial applications with existing subfloors. | Best for larger buildings or areas needing consistent heating over time. | Suitable for smaller spaces or areas needing quick heat, like bathrooms. |
Hydronic Radiant Heating Systems: Pros and Cons
Hydronic radiant heating systems circulate hot water through pipes installed beneath the floor. This method is highly efficient and can provide a consistent heat source for larger areas. One of the main advantages is its ability to maintain a stable temperature with lower energy consumption compared to traditional heating methods. However, the initial investment can be significant due to the plumbing and boiler requirements. Additionally, it may require ongoing maintenance to ensure the integrity of the system.
Electric Radiant Heating Mats: Pros and Cons
Electric radiant heating mats offer a convenient solution, especially for small spaces or areas requiring rapid heating, such as bathrooms. These mats are relatively easy to install and can often be integrated into existing flooring with minimal disruption. The upfront costs are generally lower than hydronic systems; however, they can lead to higher energy bills if used extensively, particularly in larger areas. Additionally, while they provide quick heating, their energy efficiency may not match that of hydronic systems over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Radiant Heating Needs
Choosing the right solution for radiant heating depends on various factors, including the size of the space, budget constraints, and heating requirements. Heat transfer plates for radiant heating excel in performance and cost-effectiveness for medium to large installations, while hydronic systems may be preferable for larger projects needing sustained heat. Conversely, electric mats can be an ideal choice for smaller areas requiring quick heat. By carefully assessing the unique needs of your project, you can select a heating solution that maximizes efficiency and comfort while fitting within your budget.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for heat transfer plates for radiant heating
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Heat Transfer Plates for Radiant Heating Systems?
Understanding the technical specifications of heat transfer plates is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to enhance the efficiency and performance of radiant heating systems. Here are some essential properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
Heat transfer plates are primarily made from aluminum due to its excellent thermal conductivity. The grade of aluminum, whether heavy gauge or lighter gauge, influences both heat transfer efficiency and cost. For instance, heavy gauge aluminum provides superior heat transfer but at a higher price, while lighter gauge options are more economical but may not perform as efficiently. Buyers should weigh the material grade against project budgets and performance requirements.
2. Thickness
The thickness of the aluminum plate significantly impacts its ability to conduct heat. Thicker plates typically transfer heat more efficiently than thinner ones. However, they also increase installation complexity and costs. A balance must be struck between thickness for effective heat distribution and the economic feasibility of installation, especially for larger projects.
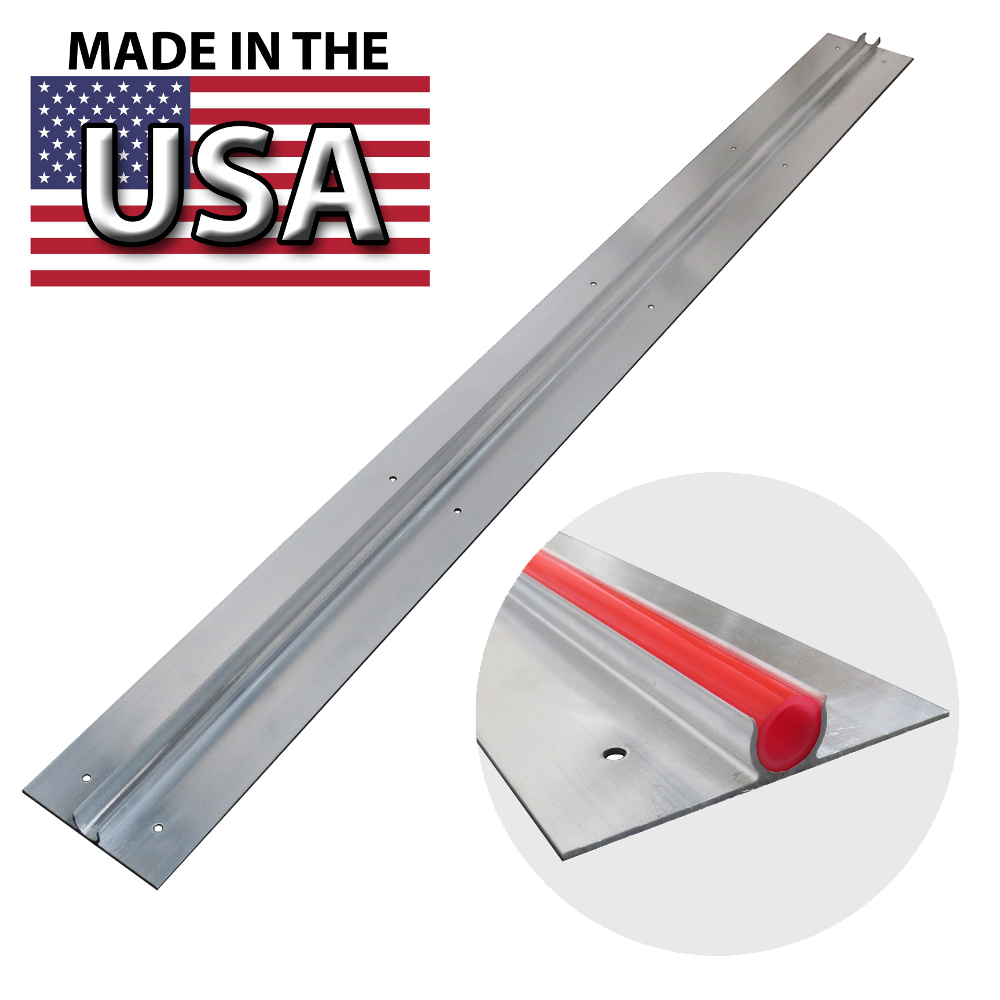

Illustrative image related to heat transfer plates for radiant heating
3. Surface Finish
The surface finish of heat transfer plates can affect their emissivity and thermal performance. Aluminum plates often have a low emissivity rating, meaning they emit less heat compared to other materials. A smooth surface can enhance contact with the tubing, leading to improved heat transfer. Buyers should inquire about the surface treatment of plates to ensure they meet performance expectations.
4. Dimensions and Shape
Heat transfer plates come in various shapes and sizes, tailored to specific installation requirements. Standard dimensions are often designed to fit common joist spacings, making them easy to install. Custom shapes may be necessary for unique applications. Understanding the dimensional specifications can help buyers optimize their designs and reduce waste during installation.
5. Heat Transfer Efficiency
This is a critical performance metric that indicates how effectively the plate can transfer heat from the tubing to the flooring above. Heat transfer efficiency can be affected by factors like material grade, thickness, and installation method. Buyers should evaluate product specifications that highlight performance metrics to ensure their systems operate at optimal levels.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Heat Transfer Plates for Radiant Heating?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of heat transfer plates, OEMs may provide custom solutions tailored to specific heating systems, ensuring compatibility and performance.

Illustrative image related to heat transfer plates for radiant heating
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for buyers to manage inventory and cash flow effectively, especially when sourcing heat transfer plates for larger projects.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products. In the realm of heat transfer plates, submitting an RFQ can help buyers obtain competitive pricing and detailed specifications, facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping and delivery obligations. Familiarity with these terms is essential for B2B buyers, particularly when sourcing products from international manufacturers.
5. Backloss
Backloss refers to the loss of heat that travels downward instead of upwards, which can significantly diminish the efficiency of a radiant heating system. Understanding this term is crucial for buyers to ensure that their systems minimize heat loss and maximize performance.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of radiant heating systems, ultimately leading to better performance and cost savings.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the heat transfer plates for radiant heating Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Affecting Heat Transfer Plates for Radiant Heating?
The global market for heat transfer plates in radiant heating systems is witnessing significant growth driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient heating solutions. Key drivers include rising energy costs, a growing emphasis on sustainable construction practices, and advancements in technology that enhance heating system performance. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking efficient radiant heating solutions to meet their diverse climate needs.
Emerging trends indicate a shift towards lightweight and cost-effective materials, such as thinner aluminum plates, which still provide adequate heat transfer capabilities. Buyers are gravitating towards suppliers that offer customizable solutions tailored to specific installation requirements. Moreover, the integration of smart technologies in heating systems is gaining traction, allowing for better control over energy consumption and enhanced user experience. This trend is particularly relevant in developed markets like Germany, where energy efficiency regulations are stringent.
In addition, the sourcing landscape is evolving with an increasing emphasis on local suppliers to reduce lead times and transportation costs. International buyers are encouraged to assess the reliability of suppliers based on their production capabilities, technological advancements, and adherence to quality standards. As the market continues to mature, buyers must stay informed about innovations in heat transfer plate designs and materials to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational goals.
How Does Sustainability Influence Sourcing Decisions for Heat Transfer Plates?
Sustainability is becoming a paramount consideration in the sourcing of heat transfer plates for radiant heating systems. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and materials used in these products is under scrutiny, pushing buyers towards suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices. Ethical sourcing is not only about selecting sustainable materials but also about ensuring that the entire supply chain adheres to responsible practices, including fair labor conditions and minimal environmental degradation.
Buyers are increasingly seeking heat transfer plates made from recycled aluminum or other sustainable materials. Certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and ISO 14001 for environmental management systems are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability. Additionally, the emphasis on reducing carbon footprints is prompting buyers to explore options for locally sourced products, which can lower transportation emissions and support local economies.
The importance of sustainability extends beyond compliance; it can also influence market competitiveness. Companies that adopt green practices often enjoy enhanced brand loyalty and can differentiate themselves in a crowded marketplace. As international regulations surrounding environmental impact tighten, B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers who not only deliver quality products but also align with their sustainability objectives.
How Have Heat Transfer Plates Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of heat transfer plates for radiant heating systems has been marked by significant technological advancements and material innovations. Initially, these plates were primarily made from heavier gauge aluminum, which, while effective in heat transfer, presented challenges in terms of installation and cost. Over the years, manufacturers have focused on optimizing aluminum usage, leading to the development of lighter gauge options that maintain high thermal efficiency while reducing overall material costs.
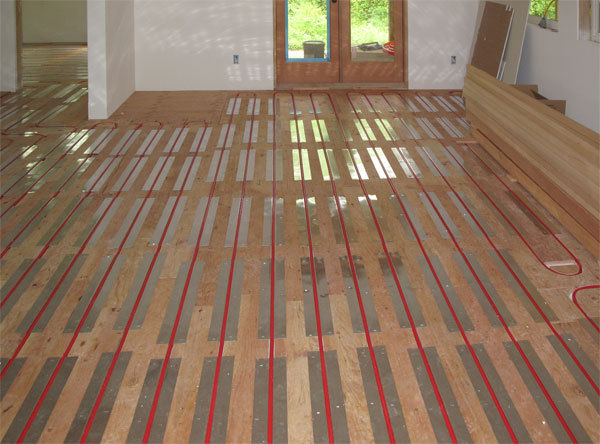

Illustrative image related to heat transfer plates for radiant heating
The introduction of pre-stamped aluminum plates revolutionized installation processes, enabling quicker setups with fewer tools required. This shift has made radiant heating systems more accessible to both professional installers and DIY enthusiasts. Additionally, advancements in manufacturing techniques have resulted in plates that are not only more efficient but also customizable to fit various joist configurations and flooring types.
As a result, the modern heat transfer plate market is characterized by a diverse range of products that cater to different installation scenarios and energy efficiency needs. This evolution underscores the importance of staying informed about the latest trends and technologies, enabling buyers to select the most effective solutions for their specific heating applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of heat transfer plates for radiant heating
1. How do I choose the right heat transfer plates for my radiant heating system?
Selecting the appropriate heat transfer plates involves considering factors such as the gauge of aluminum, coverage area, and your specific heating needs. For maximum efficiency, medium to heavy gauge aluminum is recommended, as it enhances heat transfer while minimizing backloss. Assess your installation type—staple-up or sandwich systems—and the floor material above. Additionally, consult with suppliers about their performance data and seek samples if possible to evaluate quality before making a bulk purchase.
2. What is the best material for heat transfer plates in radiant heating applications?
Aluminum is the most effective material for heat transfer plates due to its excellent thermal conductivity and low emissivity, which reduces heat loss. The choice between lighter and heavier gauge aluminum should depend on your budget and installation requirements. Lighter plates are easier to install and more cost-effective, while heavier plates may offer superior performance in terms of heat distribution. Always ensure the plates are compatible with your specific PEX tubing for optimal results.
3. How do I determine the quantity of heat transfer plates needed for my project?
A general guideline for estimating the number of heat transfer plates is to calculate based on the spacing of your joists. For joists spaced 16 inches on center, you will typically need around 60 two-foot plates for every 100 square feet of heated area. However, this can vary based on the layout of your heating system and the specific requirements of your project. It’s advisable to consult with your supplier for tailored recommendations based on your floor plan.

Illustrative image related to heat transfer plates for radiant heating
4. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for heat transfer plates?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers and regions. Typically, MOQs for heat transfer plates range from 100 to 500 units, depending on the manufacturer and the specific product line. It’s essential to discuss your needs with potential suppliers to determine if they can accommodate smaller orders or if they provide discounts for larger quantities. Additionally, consider the logistics and storage capacity when planning your order.
5. How can I vet suppliers of heat transfer plates for international trade?
When sourcing suppliers for heat transfer plates, conduct thorough due diligence. Start by checking their certifications, such as ISO quality management, and request references or case studies from previous clients. Utilize platforms like Alibaba or Global Sources to find verified suppliers and read reviews. Additionally, consider visiting their manufacturing facilities or engaging third-party inspection services to ensure they meet your quality standards and production capabilities.
6. What payment terms should I expect when ordering heat transfer plates internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers and are often influenced by factors such as order size and buyer-supplier relationships. Common terms include a 30% deposit upon order confirmation and the remaining balance before shipping. Some suppliers may offer letter of credit (LC) options for larger transactions, providing added security. Always clarify payment methods accepted, including bank transfers, credit cards, or escrow services, and ensure all terms are documented in your contract.
7. What quality assurance measures should I look for in heat transfer plates?
Quality assurance is critical when sourcing heat transfer plates. Look for suppliers that implement rigorous testing protocols, including thermal performance evaluations and material inspections. Request documentation of compliance with international standards, such as ASTM or EN certifications. Additionally, inquire about their warranty policy and return procedures, ensuring you have recourse if the products do not meet specified performance criteria.
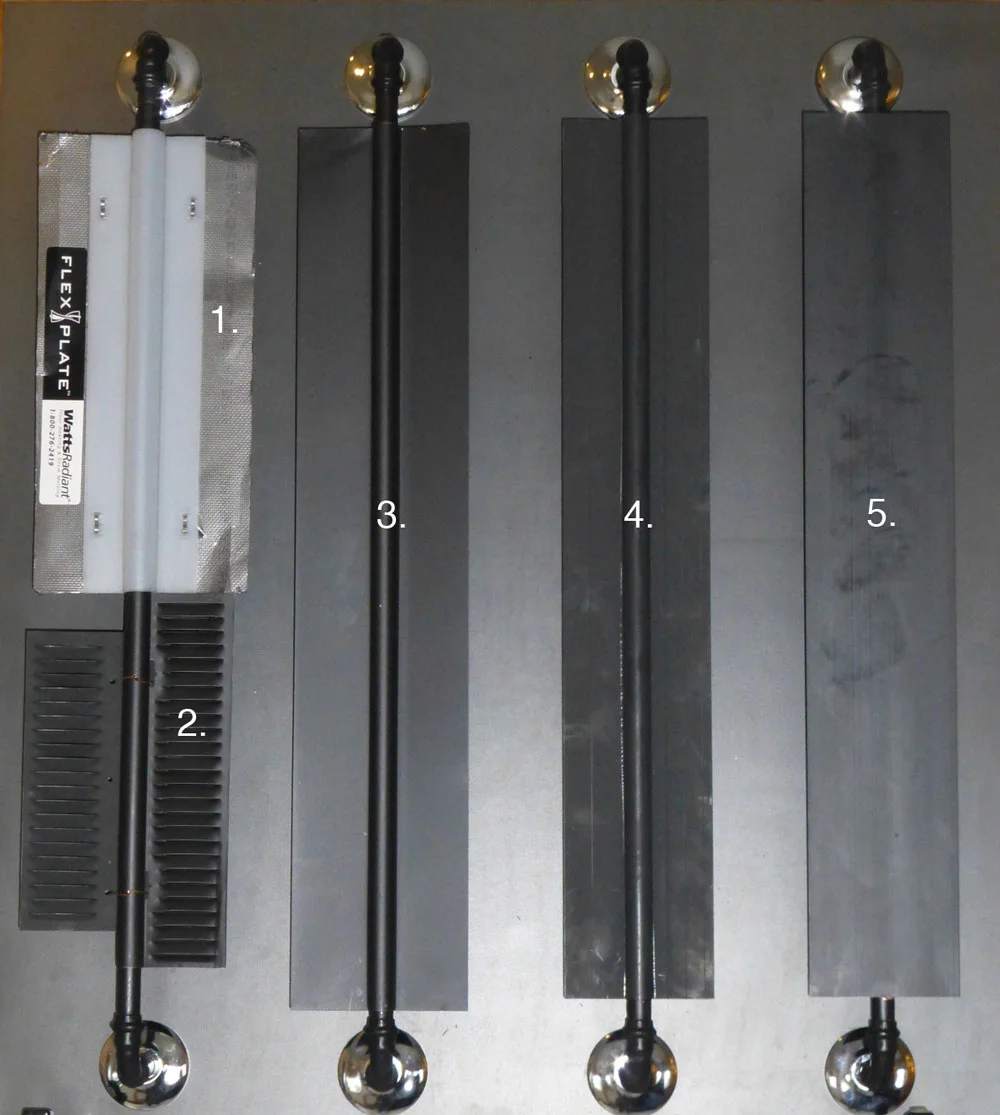
Illustrative image related to heat transfer plates for radiant heating
8. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing heat transfer plates?
Logistics play a crucial role in the successful importation of heat transfer plates. Confirm the shipping methods offered by your supplier, whether by air or sea, and evaluate the associated costs and transit times. Understand the customs regulations in your country, including tariffs and import duties, to avoid unexpected expenses. It’s also wise to partner with a reliable freight forwarder who can handle documentation and ensure compliance with local laws.
Top 6 Heat Transfer Plates For Radiant Heating Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Radiantec – Heat Transfer Plates
Domain: radiantec.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Heat Transfer Plates are used in staple up systems to warm floors by placing heating tubes underneath. They are made of lighter gauge and heavy gauge aluminum, with options for half coverage. The plates perform three key functions: carrying heat away from the tubing, distributing it through the joist space and along the floor, and supporting the plastic heat exchanger tubing while reducing downwar…
2. Blue Ridge Company – RHT OMEGA Heat Transfer Plates
Domain: blueridgecompany.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: RHT OMEGA Heat Transfer Plates are designed to efficiently distribute radiant heat from PEX tubing. They are made in America from mill finish aluminum and feature a wrap-around omega shape (Ω) channel that securely holds the tubing in place. The plates are available for 3/8″ or 1/2″ PEX tubing and are suitable for use in above floor systems such as the RHT Floor Panel System.
3. Reddit – Heat Transfer Plates for Mini-Split Heating
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Heat Transfer Plates for 2nd floor; used to supplement mini-split heating in winter; preferred for aesthetic reasons over radiators; insulation recommended below; potential flooring options include engineered laminate or bamboo; feedback suggests better for retrofitting than new builds; alternative product mentioned: Warmboard, which is more efficient but expensive; Eccowarm is a more affordable o…
4. Radiant Design and Supply – ThermoFin Radiant Heat Transfer Plates
Domain: radiantdesignandsupply.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: ThermoFin Radiant Heat Transfer Plates are available in three types: ThermoFin C (4″ wide x .0625″ thick), ThinFin C (3.5″ wide x .050″ thick), and ThermoFin U (4″ wide x .050″ thick). ThermoFin C and ThinFin C are designed for installation under the sub-floor, while ThermoFin U can be installed on top of the sub-floor, as well as in walls and ceilings. Plates come in lengths of 8 ft and 4 ft, sol…
5. VEVOR – PEX Heat Transfer Plates
Domain: vevor.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “VEVOR PEX Heat Transfer Plates”, “Quantity”: “100 pcs”, “Material”: “Aluminum”, “Length”: “4 ft”, “Width”: “4.25 in”, “Thickness”: “0.016 in”, “Compatibility”: “1/2 inch PEX tubing (5/8 inch OD)”, “Design”: “U-shaped to reduce thermal voids”, “Installation”: “Can be stapled by hand or stapler, cuttable design”, “Application”: “Suitable for radiant heating systems in homes, apartm…
6. Fine Homebuilding – Heat Transfer Plates
Domain: finehomebuilding.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Heat transfer plates are recommended for maximum support and heating efficiency when installing radiant tubing. Aluminum transfer plates with a slight air gap and insulation below are noted to be the most efficient for transferring heat to the floor. Plates are necessary in most full heat situations unless using very high water temperatures or low heating loads. Heavy gauge plates can increase out…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for heat transfer plates for radiant heating
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of heat transfer plates for radiant heating systems presents a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers to enhance energy efficiency and reduce operating costs. By selecting high-quality aluminum plates that effectively manage heat transfer, buyers can ensure optimal performance in their heating systems. Key considerations include the gauge of aluminum, the extent of coverage over heating tubes, and the long-term benefits of reduced heat loss.
Investing in quality heat transfer plates not only improves comfort levels in residential and commercial spaces but also aligns with sustainable practices by lowering energy consumption. As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe evolve, the demand for efficient heating solutions is likely to increase, making it imperative for buyers to evaluate their sourcing strategies carefully.
Looking ahead, international buyers should leverage supplier partnerships to access innovative products and optimize their radiant heating systems. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, you can position your business to meet the growing demand for energy-efficient solutions while capitalizing on cost-effective technologies. Engage with reputable suppliers today to explore tailored solutions that meet your specific needs and contribute to a sustainable future.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.