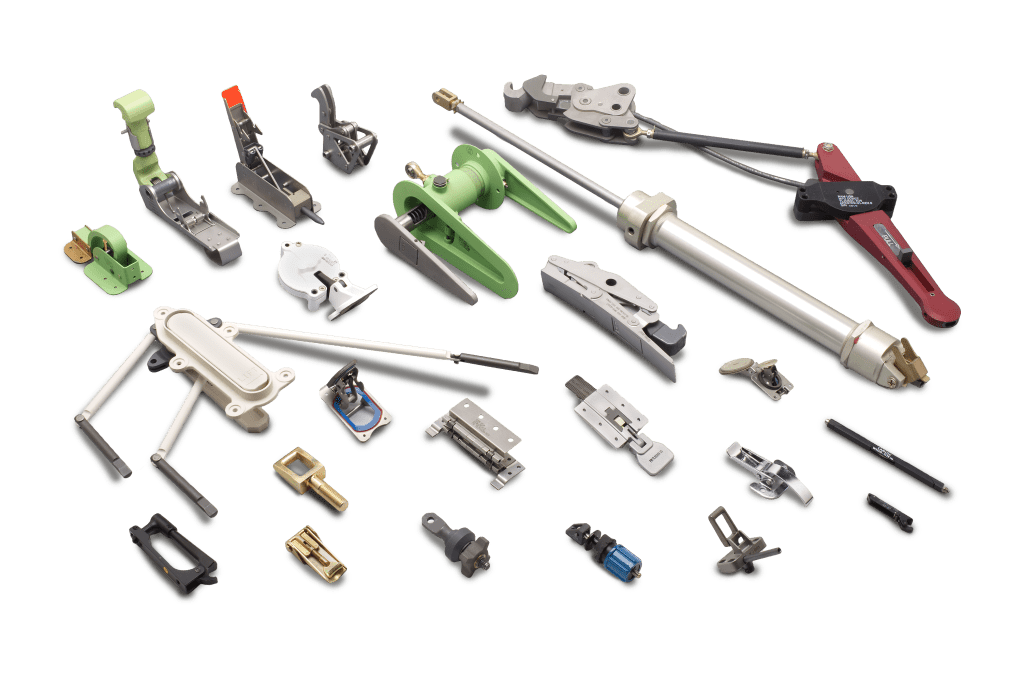
Latching Device Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for latching device
In the rapidly evolving landscape of global commerce, sourcing reliable latching devices poses a unique challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As businesses strive to meet stringent safety regulations and operational demands, the right latching device becomes critical not only for security but also for compliance and efficiency. This guide aims to illuminate the multifaceted world of latching devices, offering insights into various types—including panic exit devices, snap locks, and slam latches—along with their specific applications across different sectors.
Navigating supplier vetting processes, understanding cost structures, and recognizing the importance of certifications can be daunting tasks for international buyers. This comprehensive resource empowers decision-makers by providing actionable strategies for evaluating suppliers, comparing product specifications, and assessing market trends. By equipping B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions, this guide enhances your ability to secure high-quality latching devices that meet both functional and regulatory requirements.
Ultimately, whether you are sourcing for high-traffic commercial spaces or specialized industrial applications, this guide serves as a crucial tool in your procurement arsenal, enabling you to confidently navigate the complexities of the global latching device market.
Understanding latching device Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Three-Point Latching Device | Secures doors at three points; UL listed for panic exit; heavy-duty; suitable for high traffic. | Commercial buildings, schools, hospitals | Pros: Enhanced security; durable; ideal for high-use areas. Cons: Higher cost; may require professional installation. |
| Mortise Latch | Integrated into the door; available in various sizes; offers aesthetic appeal. | Retail stores, office buildings | Pros: Sleek design; customizable; reliable. Cons: Complex installation; can be more expensive than surface mounts. |
| Surface-Mounted Latch | Mounted on the surface of the door; easy installation; versatile. | Warehouses, factories, residential properties | Pros: Simple installation; cost-effective; suitable for various door types. Cons: Less secure than mortise latches. |
| Electromagnetic Latch | Operates with an electric current; holds doors securely; often used with access control systems. | Security-sensitive facilities | Pros: High security; integrates with access control systems. Cons: Requires electrical setup; potential for failure during power outages. |
| Sliding Door Latch | Designed specifically for sliding doors; often includes locking mechanisms. | Warehouses, retail spaces, residential homes | Pros: Space-saving design; easy to operate; effective for large openings. Cons: Limited to sliding door applications; may require regular maintenance. |
What are the Characteristics of a Three-Point Latching Device?
Three-point latching devices secure doors at three distinct points: the top, middle, and bottom. This design enhances security and stability, making it ideal for high-traffic commercial environments such as schools and hospitals. When purchasing, consider the UL listing for panic exit hardware, as this ensures compliance with safety standards. Buyers should also assess the durability and installation requirements, as these devices can be more complex than standard latches.
How Does a Mortise Latch Differ from Other Latches?
Mortise latches are installed within the door itself, providing a clean, aesthetically pleasing finish. They come in various sizes and styles, making them suitable for diverse applications, particularly in retail and office settings. Key purchasing considerations include the latch’s durability, ease of use, and customization options. While they may be more expensive and require professional installation, their reliable performance and design often justify the investment.
What Makes Surface-Mounted Latches a Popular Choice?
Surface-mounted latches are affixed directly to the door’s surface, making them easy to install and versatile for various door types. They are particularly popular in warehouses and factories where quick installation and cost-effectiveness are priorities. However, buyers should note that while they are generally less expensive, they may not provide the same level of security as mortise latches, making them more suitable for lower-risk environments.
Why Choose an Electromagnetic Latch for Security?
Electromagnetic latches offer high security, operating with an electric current to hold doors securely closed. They are often integrated with access control systems, making them ideal for security-sensitive facilities. When considering an electromagnetic latch, buyers must evaluate the electrical setup requirements and potential vulnerabilities, such as reliance on power supply. These latches are excellent for high-security applications, but their complexity may deter some buyers.
What are the Benefits of Sliding Door Latches?
Sliding door latches are specifically designed for sliding doors, providing effective locking mechanisms while saving space. They are commonly used in warehouses, retail spaces, and residential properties. When purchasing, consider the ease of operation and the latch’s effectiveness for larger openings. While they are practical, buyers should be aware of their maintenance needs and limitations, as sliding door latches cannot be used for traditional hinged doors.

Illustrative image related to latching device
Key Industrial Applications of latching device
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of latching device | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial Construction | Panic exit hardware for emergency exits | Ensures safety compliance and quick evacuation | UL listing for safety, durability under high usage, and ease of installation |
| Transportation | Secure latching systems for cargo doors | Enhances security and operational efficiency | Weather resistance, compatibility with various door types, and weight capacity |
| Manufacturing | Latching devices for machinery enclosures | Protects personnel and machinery from accidents | Compliance with safety standards, reliability under heavy use, and ease of maintenance |
| Automotive | Latching mechanisms for vehicle doors | Improves safety and user experience | Lightweight materials, corrosion resistance, and ease of integration |
| Marine | Latching systems for boat hatches | Enhances safety and prevents water ingress | Saltwater resistance, durability, and ability to withstand harsh environments |
How Are Latching Devices Used in Commercial Construction?
In the commercial construction sector, latching devices, particularly panic exit hardware, are crucial for emergency exits in buildings. These devices ensure compliance with safety regulations, allowing for quick evacuation during emergencies. Buyers in this sector should prioritize UL-listed products that guarantee reliability under high-traffic conditions. The latching devices must be compatible with various door types and heights, ensuring they can accommodate different architectural designs.
What Role Do Latching Devices Play in Transportation?
In transportation, latching devices are essential for securing cargo doors in vehicles, such as trucks and shipping containers. These systems enhance security and operational efficiency by preventing unauthorized access and ensuring that cargo remains secure during transit. Buyers should look for devices that are weather-resistant and compatible with various door types, as well as those that can handle significant weight loads. This is particularly important for international logistics, where different regulations may apply.
How Are Latching Devices Essential in Manufacturing?
Manufacturing facilities utilize latching devices in machinery enclosures to protect both personnel and equipment from accidents. These devices ensure that access to potentially dangerous machinery is controlled and secure. Buyers should focus on latching solutions that comply with industry safety standards and can withstand the rigors of heavy use. Reliability and ease of maintenance are key considerations, especially in environments with high operational demands.
How Do Latching Devices Improve Automotive Safety?
In the automotive industry, latching mechanisms are vital for vehicle doors, providing safety and enhancing user experience. Effective latching systems ensure that doors remain securely closed while allowing for easy access. Buyers should consider lightweight materials that offer corrosion resistance and ease of integration with existing vehicle designs. This is essential for manufacturers aiming to improve safety features and overall vehicle performance.
Why Are Latching Devices Important for Marine Applications?
In marine applications, latching systems are critical for securing boat hatches, preventing water ingress, and enhancing safety on board. These devices must be designed to withstand harsh marine environments, including exposure to saltwater and extreme weather conditions. Buyers should seek out latching solutions that offer durability, ease of operation, and reliable performance under challenging conditions, ensuring safety for all aboard.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘latching device’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Latching Device for High-Traffic Areas
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges when it comes to selecting latching devices that can withstand the rigors of high-traffic environments, such as schools, hospitals, and commercial facilities. Many devices may fail under constant use, leading to costly repairs and replacements. Buyers might also struggle with understanding which grades of devices are suitable for their specific applications, risking non-compliance with safety standards. This confusion can result in potential safety hazards, increased liability, and customer dissatisfaction.
The Solution: To effectively select the right latching device, buyers should start by assessing their specific needs based on traffic patterns and usage frequency. Opt for devices that are ANSI certified, such as Grade 1 latching devices, which are designed for heavy-duty applications. For high-traffic areas, consider three-point latching systems, like the Von Duprin 9957EO, which provide enhanced security and durability. Additionally, consulting with manufacturers or suppliers to obtain detailed specifications and recommendations based on your unique environment can help ensure compliance with local regulations and standards. It’s also advisable to request samples or conduct field tests to evaluate performance before making a bulk purchase.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Compatibility with Existing Door Systems
The Problem: A common frustration for B2B buyers is ensuring that new latching devices are compatible with existing door systems. This is particularly relevant in facilities with mixed door types (metal and wood) or different door sizes. Incompatibility can lead to additional costs for modifications, installation delays, or even the need to replace entire door systems, which can be disruptive to business operations.
The Solution: To mitigate compatibility issues, buyers should thoroughly document the specifications of their existing doors, including dimensions, materials, and existing hardware types. When sourcing latching devices, look for products that offer adjustable features or are labeled as “non-handed,” allowing for easier installation on various door types. Collaborating with suppliers who provide comprehensive installation guides and support can also streamline the process. Consider engaging with a knowledgeable contractor who can assess the door systems and recommend latching devices that fit seamlessly without requiring extensive modifications.
Scenario 3: Navigating Compliance and Safety Standards
The Problem: Compliance with local and international safety standards is critical in industries such as healthcare, education, and government. B2B buyers frequently encounter confusion regarding which latching devices meet these requirements, especially when dealing with multiple jurisdictions. Failure to comply can lead to fines, legal repercussions, and increased liability for the organization.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize sourcing latching devices that are UL-listed and meet ANSI standards, as these certifications provide assurance of compliance with safety regulations. It is essential to stay informed about the specific regulations applicable to your region or industry; this might involve consulting legal experts or industry associations. Additionally, establishing a relationship with manufacturers who provide documentation on compliance can facilitate the procurement process. Consider implementing a compliance checklist to evaluate potential latching devices against local codes, ensuring that all purchased products meet necessary safety standards before installation. Regular training for staff on compliance issues can also help reinforce the importance of adhering to safety protocols.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for latching device
What Are the Common Materials Used in Latching Devices?
When selecting materials for latching devices, it is essential to consider the specific properties and performance requirements that align with the intended application. Here, we analyze four common materials: stainless steel, zinc alloy, aluminum, and plastic, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Latching Devices?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, making it a popular choice for latching devices in various environments. Its ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures further enhances its suitability for heavy-duty applications. The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability, which translates to a longer lifespan and reduced maintenance costs. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, and its manufacturing complexity may lead to higher production costs.
For international buyers, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East, compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Stainless steel latching devices often meet these standards, ensuring quality and reliability.
What Benefits Do Zinc Alloys Offer for Latching Devices?
Zinc alloys are frequently used in latching devices due to their excellent corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties. They are lighter than stainless steel, which can be advantageous in applications where weight is a concern. Zinc alloy latches are typically less expensive to manufacture, making them a cost-effective option for many applications.
However, zinc alloys may not perform well under extreme temperatures, which can limit their use in high-heat environments. Additionally, they may be less durable than stainless steel, leading to a shorter lifespan. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider the specific environmental conditions when selecting zinc alloy latching devices.
Why Choose Aluminum for Latching Devices?
Aluminum is another material commonly used in latching devices, known for its lightweight properties and resistance to corrosion. It is particularly suitable for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in transportation and aerospace industries. The manufacturing process for aluminum is generally simpler and less costly than for stainless steel, which can result in lower prices for end products.
On the downside, aluminum may not offer the same strength as stainless steel or zinc alloys, making it less suitable for heavy-duty applications. International buyers should be aware of the specific strength requirements for their applications and ensure that aluminum latching devices meet relevant standards.

Illustrative image related to latching device
What Role Does Plastic Play in Latching Devices?
Plastic materials, such as polycarbonate and nylon, are increasingly used in latching devices due to their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. They offer excellent flexibility and can be molded into complex shapes, making them ideal for innovative designs. Plastic latches are generally the most cost-effective option, appealing to budget-conscious buyers.
However, plastic materials may not withstand high temperatures or heavy loads as effectively as metals. This limitation can restrict their use in industrial applications where durability and strength are paramount. Buyers from regions with varying climates, such as the Middle East and Europe, should consider the environmental impacts on plastic performance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Latching Devices
| Material | Typical Use Case for latching device | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Heavy-duty commercial applications | Exceptional strength and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Zinc Alloy | General-purpose latching devices | Cost-effective and good corrosion resistance | Limited high-temperature performance | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight applications | Lightweight and easy to manufacture | Lower strength compared to metals | Medium |
| Plastic | Budget-friendly latching solutions | Cost-effective and flexible design | Limited durability under high loads | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in latching devices, equipping international B2B buyers with the insights needed for informed decision-making. Understanding the properties and implications of each material will help ensure that the selected latching device meets both performance and compliance standards in their respective markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for latching device
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Latching Devices?
The manufacturing of latching devices is a complex process that involves several key stages, each contributing to the final product’s functionality and reliability.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Selected and Processed?
The first stage of manufacturing latching devices begins with the careful selection of raw materials. High-quality metals, such as stainless steel and zinc alloys, are commonly used due to their durability and resistance to corrosion. These materials undergo rigorous inspection to ensure they meet industry standards.
Once selected, the materials are cut to size using precision cutting techniques such as laser cutting or CNC machining. This ensures accuracy in dimensions, which is critical for the proper functioning of latching devices. After cutting, the materials are cleaned and treated to remove any impurities that could affect the final product.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Latching Components?
In the forming stage, various techniques are employed to shape the components of latching devices. Stamping and forging are common methods used to create parts such as latch bolts and rods. Stamping utilizes high-pressure dies to cut and form metal sheets, while forging involves shaping the metal by applying compressive forces.
For more intricate designs, processes like injection molding may be used to create plastic components that are often part of the latching mechanism. The choice of forming technique is crucial as it impacts the strength and durability of the final product.
Assembly: How Are Latching Devices Assembled for Optimal Performance?
The assembly process combines the individual components into a functional latching device. This is typically done in a controlled environment to minimize contamination and ensure precision. Workers or automated systems assemble the parts, which may include attaching springs, bolts, and the latching mechanism itself.
Quality checks during assembly are vital. Each assembly line may incorporate specific checkpoints where components are tested for fit and functionality. This proactive approach helps to identify any potential issues early in the production process.
Finishing: What Final Treatments Are Applied to Enhance Durability?
After assembly, latching devices undergo finishing treatments. These processes can include coating, painting, or plating to enhance corrosion resistance and improve aesthetics. Common finishes include powder coating or anodizing, which provide a protective layer that extends the lifespan of the product.
Each finishing treatment is tailored to the intended environment of use. For instance, devices intended for outdoor use may require more robust finishes to withstand environmental stressors.
What Are the Quality Assurance Protocols for Latching Devices?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of latching devices, especially given their critical role in safety and security applications.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards play a significant role in ensuring the quality and reliability of latching devices. Standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers adhere to consistent quality practices. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking in Europe and API standards for oil and gas applications are crucial for compliance.
B2B buyers should look for suppliers who are certified to these standards, as this indicates a commitment to quality and reliability in manufacturing processes.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. Any subpar materials are rejected before they enter the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to monitor the quality of components as they are formed and assembled. This may include dimensional checks and functional testing of individual parts.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the latching devices are fully assembled, they undergo comprehensive testing to ensure they meet performance specifications. This can involve functional tests, durability tests, and safety checks.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is critical. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of the supplier’s facilities can provide insights into their manufacturing and quality control processes. This helps ensure compliance with international standards and industry best practices.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to provide documentation of their quality assurance processes, including test reports and certifications. This transparency is vital for building trust.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. This is particularly important when sourcing from regions where quality standards may vary.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing latching devices from international suppliers, B2B buyers should be aware of specific quality control nuances:
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Different regions may have varying quality expectations and regulations. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should familiarize themselves with local standards and practices.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Risks: International shipping can introduce risks such as damage during transit or delays that affect product quality. Buyers should consider suppliers with robust logistics capabilities and quality assurance throughout the supply chain.
-
Language Barriers: Effective communication is essential for quality assurance. Buyers should ensure that they can communicate clearly with suppliers regarding specifications, standards, and expectations.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for latching devices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source products that meet their needs and maintain high standards of quality and reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘latching device’
To assist B2B buyers in procuring latching devices effectively, this guide outlines a practical, step-by-step checklist that ensures a thorough evaluation and selection process. By following these steps, buyers can make informed decisions that meet their specific needs while adhering to industry standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the latching device you need. Consider factors such as door types, sizes, and the specific applications (e.g., panic exit, heavy-duty use). A precise specification helps narrow down potential products and ensures compatibility with existing infrastructure.
- Door Type: Identify whether you need a device for single or double doors.
- Dimensions: Specify door heights and widths to ensure the latching device fits properly.
Step 2: Research Regulatory Compliance
Ensure that the latching devices you consider meet local and international safety standards. Compliance with regulations such as ANSI, UL, or specific regional standards is essential for ensuring safety and reliability.
- Certification: Look for devices that are certified for panic exit hardware or fire safety if applicable.
- Documentation: Request certificates and compliance documents from suppliers to verify adherence to necessary standards.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website; seek firsthand accounts of their products and services.
- Reputation: Investigate the supplier’s history and customer feedback.
- Experience: Prefer suppliers with extensive experience in providing latching devices for your specific application.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Whenever possible, request samples of the latching devices you are considering. Testing samples allows you to evaluate the quality, durability, and functionality of the products firsthand before making a bulk purchase.
- Functionality: Test the latching mechanism to ensure it operates smoothly and meets your specifications.
- Durability: Assess the materials used and overall construction quality to ensure they can withstand the intended use.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers and compare not only the prices but also the terms of sale, including warranty, delivery times, and payment options. Understanding the total cost of ownership is critical for budgeting.
Illustrative image related to latching device
- Hidden Costs: Be aware of additional costs such as shipping, installation, and maintenance.
- Warranty and Support: Evaluate the warranty period and after-sales support offered by the supplier.
Step 6: Confirm After-Sales Service and Support
Before finalizing your purchase, inquire about the after-sales service and support provided by the supplier. Good support can mitigate issues that arise post-installation and ensures ongoing satisfaction with the product.
- Technical Assistance: Check if they provide installation support or technical guidance.
- Maintenance Services: Understand what maintenance services are available and how they can assist in prolonging the device’s lifespan.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
Once you are satisfied with the supplier and the product, finalize the purchase agreement. Ensure that all terms discussed are documented, including delivery schedules, payment terms, and any specific conditions related to the latching devices.
- Documentation: Keep records of all communications and agreements for future reference.
- Clear Terms: Ensure that the terms are clear to avoid any potential disputes later on.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the sourcing process for latching devices, ensuring they select the right products and suppliers for their needs while adhering to industry standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for latching device Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Latching Devices?
When sourcing latching devices, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and financial planning. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects the cost. High-quality metals or specialty alloys used for durability and security can elevate prices. Additionally, the sourcing of materials may vary by region, impacting overall costs based on local market conditions.
-
Labor: Labor costs can fluctuate based on the manufacturing location. For instance, labor-intensive processes may be cheaper in developing regions compared to developed countries. Understanding the labor market dynamics in the supplier’s region can provide insights into potential cost savings.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to production facilities, utilities, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing practices can lower overhead, allowing suppliers to offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for custom designs can be substantial. For standard products, costs are typically amortized over larger production runs, leading to lower unit prices as volume increases.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC processes ensures product reliability but adds to manufacturing costs. Buyers should consider whether the added cost of enhanced QC measures is justified by the quality assurance they provide.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely based on distance, mode of transport, and regional logistics infrastructure. Buyers should evaluate logistics costs when considering suppliers from different geographical areas.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins will depend on market competition, product demand, and the perceived value of the latching devices. Understanding the market landscape can help buyers gauge whether proposed margins are reasonable.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Latching Devices?
Several factors can influence the pricing of latching devices, which buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can affect pricing. Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their inventory needs while maximizing cost-efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized latching devices will often incur higher costs due to unique tooling and design requirements. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against budget constraints.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and certifications (e.g., UL listing for safety) can significantly influence price. Higher quality and certification standards may come at a premium but can enhance product reliability and marketability.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, experience, and location can impact pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge more, but they often provide better reliability and customer service.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can affect overall costs, including insurance, duties, and shipping responsibilities. Understanding these terms is essential for accurate budgeting.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing of Latching Devices?
To optimize sourcing strategies, buyers can implement several best practices:
-
Negotiation: Leverage volume commitments to negotiate better pricing. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to favorable terms and discounts.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also the TCO, which includes installation, maintenance, and potential downtime. Investing in higher-quality latching devices may yield long-term savings.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must be aware of currency fluctuations and import tariffs that could affect total costs. Engaging with local experts or consultants can provide valuable insights.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough research on suppliers to compare prices and quality. Utilizing platforms that aggregate supplier information can aid in making informed decisions.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Buyers are encouraged to conduct their own research to obtain accurate pricing tailored to their needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing latching device With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Latching Devices in Industrial Applications
When considering security and accessibility in commercial and institutional environments, latching devices are often a go-to solution. However, buyers should also explore alternative locking mechanisms that may better suit their specific needs. This analysis compares latching devices with two viable alternatives: electronic locking systems and traditional padlocks, providing insight into their respective advantages and disadvantages.
| Comparison Aspect | Latching Device | Electronic Locking System | Traditional Padlock |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High durability; designed for heavy use | Versatile; can integrate with access control systems | Basic security; suitable for temporary use |
| Cost | Moderate; initial investment can be high | Higher upfront cost; potential long-term savings on management | Low-cost; minimal initial investment |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional installation; often complex | May require specialized installation; user-friendly interfaces | Very easy to implement; no installation required |
| Maintenance | Low; occasional inspections recommended | Moderate; software updates may be needed | Low; regular checks necessary to ensure functionality |
| Best Use Case | High-traffic commercial settings | Facilities requiring controlled access and monitoring | Temporary or low-security applications |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Electronic Locking Systems?
Electronic locking systems offer advanced security features, such as remote access and audit trails, making them ideal for facilities that need to monitor entry and exit points closely. They can integrate with existing security systems, providing a centralized management solution. However, the initial investment can be significant, and ongoing maintenance, including software updates and battery replacements, can add to the total cost. Additionally, reliance on technology can lead to vulnerabilities if not properly managed.
Why Consider Traditional Padlocks as an Alternative?
Traditional padlocks are a simple and cost-effective solution for securing doors, gates, and storage areas. They are particularly useful for temporary setups or in low-security environments where high-tech solutions may be unnecessary. Their ease of use makes them accessible to everyone without the need for technical training. On the downside, padlocks typically offer lower security than latching devices or electronic locks and can be easily bypassed if not used with high-quality locks. They are also less suited for high-traffic areas where quick access is necessary.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Selecting the appropriate locking mechanism requires a thorough understanding of your specific operational needs and security requirements. Buyers should assess factors such as the traffic volume, potential security threats, and budget constraints. For high-use environments that demand reliable security, latching devices or electronic locking systems may be the best choices. Conversely, for low-security needs or temporary applications, traditional padlocks might suffice. Ultimately, the decision should align with the overall safety strategy and operational efficiency of the facility.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for latching device
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Latching Devices?
Understanding the technical specifications of latching devices is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties to consider:

Illustrative image related to latching device
-
Material Grade
Latching devices are commonly made from various materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, and zinc-coated metals. The material grade impacts durability, corrosion resistance, and overall performance. For instance, stainless steel is ideal for environments exposed to moisture, while zinc-coated options may suffice for less demanding applications. Selecting the right material ensures longevity and reduces maintenance costs. -
Throw Length
This refers to the distance the latch bolt extends into the strike when engaged. Typical throw lengths range from 5/8” to 3/4”. A longer throw length often provides better security and resistance against forced entry. Understanding throw lengths is vital for aligning the latching device with the door frame and ensuring optimal performance. -
Fire Rating
Fire ratings indicate the device’s ability to withstand high temperatures during a fire. Non-fire-rated devices may not offer sufficient protection in emergency situations. For applications requiring compliance with fire safety codes, selecting a fire-rated latching device is essential to ensure safety and legal adherence. -
Load Capacity
Load capacity defines the maximum weight that the latching device can support while maintaining functionality. Devices designed for heavy-duty applications are typically rated for higher loads. Assessing load capacity is critical for ensuring that the device will perform effectively in its intended application, especially in commercial and industrial settings. -
ANSI Grade
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) grades latching devices based on performance and durability. Devices graded Grade 1 are the most robust and are designed for high-traffic environments. Understanding ANSI grading helps buyers ensure they are investing in quality products that meet industry standards. -
Dogging Feature
This feature allows the latch to be held in an open position, making it easier for high-traffic areas. Devices can have different types of dogging, such as hex key or key-operated. The choice of dogging feature can significantly affect usability in commercial settings where frequent access is required.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Latching Device Industry?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are several common terms you should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This refers to companies that manufacture products or components that are used in another company’s end product. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers looking to source latching devices, as it can affect pricing and quality assurance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ specifies the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, as it can impact your purchasing strategy and overall costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request sent to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for specific products. This process helps buyers compare options and negotiate favorable terms, making it a key step in procurement. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are internationally recognized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms can help buyers understand shipping costs and responsibilities, ensuring smooth logistics. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of goods. Understanding lead times is important for planning and inventory management, especially in industries where timely delivery is critical. -
Warranty
A warranty is a guarantee provided by the manufacturer regarding the product’s quality and performance. Knowing the warranty terms can protect buyers against defects and provide assurance of product reliability.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms equips B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right latching devices for their specific applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the latching device Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Affecting the Latching Device Sector?
The latching device sector is witnessing significant evolution, driven by global market demands and technological advancements. In recent years, the surge in construction activities across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe has amplified the need for robust and reliable latching devices. Factors such as urbanization, increased safety regulations, and a focus on high-quality materials are reshaping market dynamics. Buyers are particularly interested in devices that meet stringent safety standards, such as ANSI A156.3, which are critical in commercial and institutional applications.
Emerging technologies, including smart latching devices that integrate with IoT systems, are becoming prevalent. These devices not only enhance security but also provide remote access and monitoring capabilities, appealing to modern buyers looking for efficiency and advanced features. Furthermore, digital sourcing platforms are gaining traction, allowing international buyers to compare products, assess suppliers, and streamline purchasing processes.
In addition, the rise of e-commerce has transformed the way latching devices are marketed and sold. Buyers from diverse regions can now access a global marketplace, providing them with a broader selection of products and competitive pricing. As suppliers adapt to these changes, the importance of localization and understanding regional market needs becomes paramount.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Latching Device Market?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of modern procurement strategies in the latching device sector. As environmental concerns grow, buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices. This includes the use of eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes that minimize waste and reduce carbon footprints.
Illustrative image related to latching device
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, as businesses recognize the importance of maintaining transparent supply chains. Buyers are more inclined to partner with manufacturers who can provide certifications for environmentally friendly practices and materials, such as recycled metals or sustainably sourced wood. Certifications like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and ISO 14001, which focus on environmental management, are becoming critical factors in supplier selection.
Furthermore, the demand for “green” latching devices—those made with sustainable materials—aligns with the broader industry trend toward corporate social responsibility. This shift not only helps in reducing environmental impact but also enhances brand reputation, making it a vital consideration for international buyers looking to strengthen their market position.
What Has Been the Historical Evolution of Latching Devices in the B2B Context?
The evolution of latching devices can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where basic locking mechanisms were first developed to secure properties. Over the centuries, advancements in metallurgy and engineering led to more sophisticated designs, culminating in the modern latching devices we see today. The industrial revolution marked a significant turning point, as mass production techniques allowed for greater consistency and affordability.
Illustrative image related to latching device
In the B2B context, the introduction of standards such as ANSI and UL certifications has standardized safety and quality across the industry. This has enabled buyers to make informed decisions based on reliability and compliance. Today, the focus is not only on functionality but also on integrating technology, paving the way for smart latching systems that cater to the needs of modern commercial environments. This historical perspective underscores the continuous innovation and adaptation within the sector, essential for meeting the evolving demands of international buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of latching device
1. How do I choose the right latching device for my application?
Choosing the right latching device depends on several factors, including the type of door, the frequency of use, and the security requirements of your facility. Consider the door material (metal or wood), height, and whether it is a single or double door. Additionally, evaluate the environment—devices rated for heavy-duty use are ideal for high-traffic areas. It’s also essential to check compliance with local regulations, such as ANSI standards for safety and durability.
2. What are the advantages of a three-point latching device?
A three-point latching device offers enhanced security by securing the door at three points: top, middle, and bottom. This feature provides superior resistance against forced entry and is particularly beneficial for high-traffic commercial and institutional applications. Additionally, it helps maintain the door’s alignment, reducing wear and tear over time. For businesses in regions with strict security needs, this type of latching device is often recommended.
3. What customization options are available for latching devices?
Many manufacturers offer customization options, including size, finish, and specific functionalities such as signal switches or dogging features. Custom solutions can enhance the latching device’s compatibility with your existing systems and aesthetic requirements. When sourcing, communicate your specific needs to suppliers and inquire about their capabilities to ensure you receive a tailored solution that meets your operational demands.
4. What should I consider regarding minimum order quantities (MOQs) for latching devices?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers and may depend on the type of device and customization options. For international buyers, it’s crucial to discuss MOQs upfront to ensure that they align with your purchasing capabilities. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time orders or bulk purchases, so it’s advisable to negotiate terms that suit your operational scale while considering potential cost savings.
5. How can I vet suppliers of latching devices effectively?
To vet suppliers, start by checking their industry reputation and reviews from previous clients. Request references and case studies that demonstrate their experience with similar projects. Assess their production capabilities, certifications (e.g., ISO), and compliance with international standards. It’s also beneficial to communicate directly to gauge their responsiveness and willingness to address your specific needs, which can indicate their commitment to quality service.
6. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing latching devices internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely based on supplier policies and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include upfront deposits, payment upon shipment, or net 30/60 days after delivery. It’s essential to clarify terms before finalizing orders, considering factors like currency fluctuations and international banking fees. Using secure payment methods and establishing a clear invoice process can help mitigate risks associated with international transactions.
7. How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) for latching devices?
Implementing a robust quality assurance process involves several steps. Start by defining quality standards based on industry benchmarks and regulatory requirements. Request samples for testing prior to bulk orders and consider third-party inspections to verify compliance with specifications. Establishing a clear communication channel with your supplier for ongoing quality checks can also help maintain product consistency and performance.

Illustrative image related to latching device
8. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing latching devices?
Logistics play a crucial role in the timely delivery of latching devices. Consider factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your country. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping to ensure compliance with import duties and tariffs. Additionally, plan for storage and handling upon arrival to prevent damage during transit, and establish a reliable distribution strategy to manage inventory effectively.
Top 4 Latching Device Manufacturers & Suppliers List
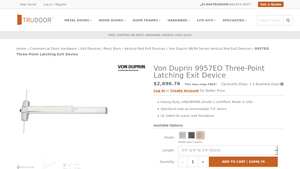
1. Von Duprin – 9957EO Three-Point Latching Exit Device
Domain: trudoor.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Von Duprin 9957EO Three-Point Latching Exit Device\nShipping: Usually Ships in 1-2 Business Days\nCertification: Heavy Duty, ANSI/BHMA Grade-1 certified, Made in USA\nUL Listed: Yes, for panic exit hardware\nAvailable Options: Finish (Anodized Aluminum, Dark Bronze, Satin Chrome)\nLength: 3’0″ (for 2’4″ to 3’0″ doors), 4’0″ (for 3’1″ to 4’0″ doors)\nDevice Type: Three-Point Latching …
2. Kipp – Zinc Latches with Concealed Fastening
Domain: kippusa.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: {“ec_name”:”Latches, zinc with sheet metal bracket, fastening holes concealed”,”ec_description”:”Latches, zinc with sheet metal bracket, fastening holes concealed”,”ec_variant_codes”:[“agid.35345″,”k2359.10064″,”k2359.20064″,”k2359.30064″,”k2359.10076″,”k2359.20076″,”k2359.30076″,”agid.35346″,”k2359.11064″,”k2359.21064″,”k2359.31064″,”k2359.11076″,”k2359.21076″,”k2359.31076″],”price_dict”:10.83,”e…
3. Herga – Latching Switches
Domain: herga.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Latching switches from Herga can be wired normally open or normally closed. When pressed once, they close the electrical circuit and remain on until pressed again to open the circuit. Common applications include light switches, computers, central heating devices, and televisions. Specific Herga products include the 6871 air switch, used in spa baths and waste disposals, and footswitches such as th…
4. Law Insider – Latching Device
Domain: lawinsider.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Latching device means an instrument used to secure a seclusion room door that does not require the use of a key or combination.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for latching device
In the competitive landscape of the latching device market, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal strategy for B2B buyers across diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By investing in high-quality, reliable latching devices such as the three-point exit mechanisms and advanced locking solutions, businesses can enhance security, comply with safety standards, and improve operational efficiency.
The importance of choosing the right supplier cannot be overstated; partnering with reputable manufacturers ensures access to innovative products that meet stringent industry standards, such as UL listings and ANSI certifications. Additionally, understanding the unique needs of your market—whether it’s adapting to regional regulations or accommodating specific design preferences—can lead to significant cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.

Illustrative image related to latching device
Looking ahead, international buyers are encouraged to actively engage with suppliers to explore the latest advancements in latching technology. By prioritizing strategic sourcing now, businesses can position themselves for future growth and success in an evolving marketplace. Seize the opportunity to enhance your operations with premium latching solutions that meet your specific requirements and drive your business forward.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.