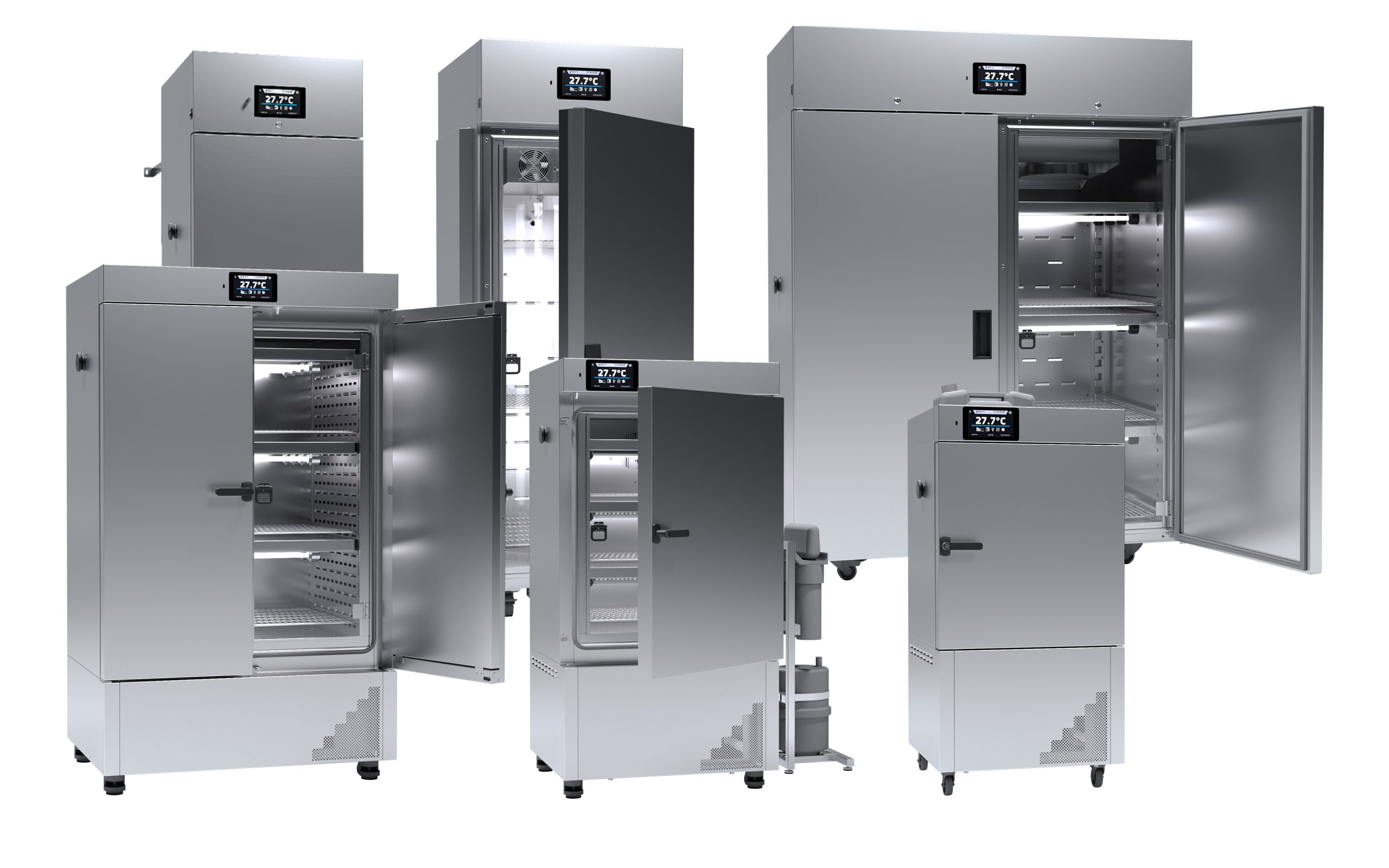
A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Climate Chamber: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for climate chamber
In today’s rapidly evolving global market, sourcing reliable climate chambers poses significant challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse environments like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As businesses strive to ensure product quality and compliance with stringent testing standards, the need for precise control over environmental conditions becomes paramount. This guide is designed to empower decision-makers by providing a comprehensive overview of climate chambers, detailing various types—including humidity chambers, temperature test chambers, and walk-in chambers—along with their specific applications, such as drug stability studies and shelf-life testing.
Furthermore, this guide delves into essential factors that influence purchasing decisions, such as supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and technological advancements in chamber design. By equipping buyers with in-depth insights and actionable strategies, we aim to facilitate informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements. Whether you are based in Saudi Arabia, Nigeria, or elsewhere, understanding the nuances of climate chamber selection is crucial for optimizing product testing and ensuring compliance with local and international standards. Join us as we navigate the intricate landscape of climate chambers to help you make confident, data-driven choices for your business.
Understanding climate chamber Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Test Chamber | Controlled temperature range; often programmable | Product testing, quality control | Pros: Precision testing; Cons: High initial cost |
| Humidity Chamber | Regulates humidity levels along with temperature | Stability testing, shelf-life studies | Pros: Essential for moisture-sensitive products; Cons: Maintenance can be complex |
| Walk-in Chamber | Large capacity for bulk testing; customizable environment | Industrial applications, large-scale testing | Pros: Space-efficient for large samples; Cons: Requires significant floor space |
| Growth Chamber | Includes light control for biological studies | Plant growth studies, biological research | Pros: Supports various growth conditions; Cons: Limited to specific applications |
| Battery Test Chamber | Designed for testing batteries under various conditions | Battery performance testing, safety assessments | Pros: Tailored for specific battery needs; Cons: Niche application limits wider use |
What Are the Characteristics of a Temperature Test Chamber?
Temperature test chambers are designed to create and maintain precise temperature conditions, often ranging from -40°C to +100°C. They are commonly used in product testing and quality control processes, ensuring that products can withstand extreme temperatures. B2B buyers should consider the chamber’s temperature uniformity, programmability, and energy efficiency, as these factors can significantly affect testing outcomes and operational costs.
How Does a Humidity Chamber Differ from Other Types?
Humidity chambers not only control temperature but also maintain specific humidity levels, making them vital for stability testing and shelf-life studies. They are particularly important for industries dealing with pharmaceuticals, food, and cosmetics, where moisture sensitivity is crucial. Buyers should evaluate the chamber’s humidity range, ease of calibration, and maintenance requirements to ensure it meets their testing needs.
Why Choose a Walk-in Chamber for Industrial Applications?
Walk-in chambers offer a large testing environment that can accommodate bulk samples or equipment, making them ideal for industrial applications. Their customizable settings allow for precise control over temperature and humidity, which is essential for stability testing. However, buyers need to consider the substantial floor space required and the higher installation costs associated with these chambers.
What Makes a Growth Chamber Ideal for Biological Research?
Growth chambers are specifically designed for biological studies, featuring controlled light, temperature, and humidity conditions. They are essential for research involving plant growth or cellular studies. When purchasing, B2B buyers should assess the flexibility of light conditions and the ability to replicate various environmental scenarios, which are critical for successful research outcomes.

Illustrative image related to climate chamber
How Does a Battery Test Chamber Enhance Performance Testing?
Battery test chambers are engineered to simulate various environmental conditions for battery performance testing, including temperature extremes and humidity levels. They are crucial for safety assessments and performance evaluations of battery technologies. Buyers should focus on the chamber’s adaptability to different battery sizes and types, as well as its compliance with industry testing standards, ensuring that it meets their specific testing requirements.
Key Industrial Applications of climate chamber
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of climate chamber | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals | Drug Stability Testing | Ensures product efficacy and safety over shelf life | Compliance with ICH guidelines, temperature/humidity ranges |
| Food and Beverage | Shelf-life Testing | Validates product longevity and quality | Regulatory compliance, varied temperature/humidity settings |
| Electronics | Battery Testing | Assesses performance under extreme conditions | Capacity for temperature variations, safety certifications |
| Agriculture | Seed Germination Studies | Optimizes crop yield and viability | Control over humidity and temperature, size of chamber |
| Automotive | Component Testing | Evaluates resilience of parts under diverse conditions | Customization for specific tests, energy efficiency requirements |
How is a Climate Chamber Used in Pharmaceuticals for Drug Stability Testing?
In the pharmaceutical sector, climate chambers are essential for conducting drug stability tests. These chambers simulate various environmental conditions, allowing companies to assess how their products will perform over time under different temperatures and humidity levels. This is crucial for ensuring compliance with International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines and for maintaining the efficacy and safety of medications. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should prioritize chambers with precise temperature control and data logging capabilities to meet stringent regulatory requirements.
What Role Do Climate Chambers Play in Food and Beverage Shelf-life Testing?
In the food and beverage industry, climate chambers are utilized for shelf-life testing to determine how long products maintain their quality and safety. By replicating various environmental conditions, manufacturers can identify the optimal storage conditions and predict product degradation. This testing is vital for compliance with food safety regulations and for optimizing inventory management. International buyers should consider sourcing chambers that can accommodate diverse humidity and temperature ranges to cater to different product types.
Why Are Climate Chambers Important for Battery Testing in Electronics?
In the electronics industry, climate chambers are pivotal for battery testing, particularly in assessing performance under extreme conditions. These chambers can simulate high and low temperatures, as well as humidity levels, to evaluate how batteries will operate in real-world scenarios. This testing is crucial for ensuring product reliability and safety. B2B buyers, particularly from the Middle East and Europe, should look for chambers that offer customizable settings and robust safety features to meet industry standards.
How Do Climate Chambers Aid in Seed Germination Studies for Agriculture?
Agricultural companies leverage climate chambers for seed germination studies, where controlled environmental conditions are crucial for optimizing crop yield. These chambers allow researchers to manipulate temperature and humidity levels to find the ideal conditions for seed viability. This data is essential for improving agricultural practices and ensuring food security. Buyers in regions with varying climates, such as Africa, should focus on sourcing chambers that provide precise control over environmental factors and have a capacity suitable for large-scale testing.

Illustrative image related to climate chamber
What Benefits Do Climate Chambers Provide for Automotive Component Testing?
In the automotive sector, climate chambers are used to test components for resilience against varying environmental conditions. These tests help manufacturers ensure that parts can withstand extreme temperatures and humidity, which is vital for vehicle safety and performance. For B2B buyers, especially in regions with harsh climates, it is important to select chambers that can be customized for specific testing protocols and that offer energy-efficient operation to reduce operational costs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘climate chamber’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Temperature and Humidity Control Affecting Test Results
The Problem: A leading pharmaceutical company based in Nigeria faces significant challenges in ensuring consistent temperature and humidity levels within their climate chambers. During critical stability testing for new drug formulations, fluctuations in these parameters have led to unreliable test results, causing delays in product approvals. This inconsistency not only hampers research timelines but also raises concerns about product efficacy and compliance with international regulatory standards.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, the company should invest in climate chambers equipped with advanced microprocessor controls and precision sensors that guarantee temperature and humidity stability. Selecting models that offer real-time monitoring and logging capabilities is essential. Furthermore, implementing a routine calibration schedule for the sensors will ensure ongoing accuracy. Regular maintenance checks, including verification of sealing and insulation, can prevent external environmental influences from affecting chamber conditions. Establishing a standardized operating procedure (SOP) for chamber usage, including protocols for loading samples and conducting tests, can further enhance reliability.

Illustrative image related to climate chamber
Scenario 2: High Operational Costs Due to Inefficient Equipment
The Problem: A research facility in Brazil has been struggling with high operational costs linked to their older model climate chambers. These units consume excessive energy and frequently require repairs, leading to unplanned downtime that disrupts ongoing research projects. As a result, the facility is facing budget constraints, impacting their ability to secure funding for new research initiatives.
The Solution: Transitioning to energy-efficient climate chambers designed with modern insulation materials and energy-saving technologies can significantly reduce operational costs. B2B buyers should prioritize chambers that have received energy efficiency certifications, such as ENERGY STAR. Additionally, considering models with programmable features that allow users to optimize operational schedules can lead to further energy savings. Exploring financing options or leasing arrangements for new equipment can also help alleviate immediate budget pressures while ensuring access to the latest technology. Collaborating with suppliers who offer comprehensive maintenance packages can prevent unexpected repair costs and ensure chambers operate at peak efficiency.
Scenario 3: Difficulty Sourcing the Right Climate Chamber for Specific Applications
The Problem: An agricultural research institution in South Africa is facing challenges in sourcing a climate chamber that meets specific research needs for plant growth studies under varying humidity and temperature conditions. The institution has encountered vendors that offer generic solutions, failing to provide the precise configurations required for their unique research protocols. This mismatch can lead to suboptimal growth conditions, skewing experimental results.
The Solution: To address this sourcing challenge, the institution should first conduct a thorough analysis of their specific testing requirements, including temperature and humidity ranges, chamber size, and any additional features such as light exposure. Engaging in discussions with multiple suppliers to communicate these requirements will help identify vendors that specialize in custom solutions. Requesting detailed product specifications and past performance data from potential suppliers can aid in making informed decisions. Additionally, considering suppliers that offer customization options or modular designs can provide the flexibility needed to adapt the chamber for various research applications over time. Forming partnerships with manufacturers that support post-purchase technical assistance will ensure that the institution can maximize the utility of their climate chambers throughout their research lifecycle.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for climate chamber
What are the Key Materials Used in Climate Chambers?
When selecting a climate chamber, the choice of material is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, durability, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in climate chambers: stainless steel, powder-coated cold-rolled steel, aluminum, and glass. Each material has distinct properties that can significantly impact the functionality and suitability of climate chambers for various applications.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Climate Chambers?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand a wide range of temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating of -40°C to +110°C, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel is a significant advantage, as it can endure harsh environments without degrading. However, its higher cost compared to other materials can be a drawback for budget-conscious buyers. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as it requires specialized equipment for shaping and welding.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including chemicals and biological samples, making it ideal for laboratories and pharmaceutical applications. Its non-reactive nature ensures that it does not contaminate sensitive samples.
Illustrative image related to climate chamber
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East must consider local corrosion factors, such as humidity and salinity, which can affect the longevity of stainless steel. Compliance with standards like ASTM and DIN is essential for ensuring quality and reliability.
What Advantages Does Powder-Coated Cold-Rolled Steel Offer?
Key Properties: Powder-coated cold-rolled steel is characterized by its robust surface finish, which enhances corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. It can withstand temperatures ranging from -10°C to +100°C.
Pros & Cons: This material is generally more cost-effective than stainless steel, making it attractive for buyers with budget constraints. However, it may not be as durable under extreme conditions and can be prone to chipping or scratching, which compromises its protective coating.
Impact on Application: Powder-coated steel is suitable for applications where aesthetics are important, such as in commercial settings. However, it may not be ideal for environments with high humidity or corrosive substances.

Illustrative image related to climate chamber
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local regulations regarding coatings and materials is crucial. Buyers should verify that the powder coating meets relevant standards to ensure durability in their specific climate conditions.
Why Choose Aluminum for Climate Chambers?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and offers good thermal conductivity, with a temperature range typically between -20°C and +70°C. Its natural resistance to corrosion makes it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which facilitates easier installation and mobility of climate chambers. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and can be more expensive than powder-coated options.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly effective for applications requiring rapid temperature changes due to its excellent thermal properties. However, it may not be suitable for all chemical environments, as certain substances can corrode aluminum.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum climate chambers comply with international standards, especially in regions with specific environmental regulations. The material’s performance can vary significantly based on local conditions.
How Does Glass Contribute to Climate Chamber Design?
Key Properties: Glass is often used for viewing panels in climate chambers, providing visibility into the chamber’s interior. It can withstand moderate temperature ranges but is primarily valued for its optical clarity.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of glass is its ability to allow visual monitoring without compromising the chamber’s integrity. However, it is fragile and can break easily, making it less suitable for high-impact environments.

Illustrative image related to climate chamber
Impact on Application: Glass is ideal for applications where monitoring is crucial, such as in research and development settings. However, it should be used in conjunction with more durable materials to ensure overall chamber integrity.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding glass safety standards, especially in regions prone to seismic activity or high traffic.
Summary Table of Material Properties for Climate Chambers
| Material | Typical Use Case for climate chamber | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Pharmaceutical and laboratory use | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost compared to alternatives | High |
| Powder-Coated Cold-Rolled Steel | Commercial applications | Cost-effective | Less durable under extreme conditions | Medium |
| Aluminum | Rapid temperature change applications | Lightweight and good thermal conductivity | Less durable than stainless steel | Medium |
| Glass | Monitoring and visibility | Allows visual monitoring | Fragile and prone to breakage | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide aims to equip B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed decisions when selecting climate chambers, ensuring compatibility with their specific applications and compliance with international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for climate chamber
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Climate Chambers?
The manufacturing process of climate chambers involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets the required specifications for performance and reliability. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing climate chambers is the selection and preparation of materials. Common materials include stainless steel and powder-coated cold-rolled steel, chosen for their durability and resistance to corrosion. Suppliers often source materials from certified vendors to ensure quality. Pre-processing techniques such as cutting, welding, and surface treatment (e.g., powder coating) are employed to prepare these materials for the next stage.

Illustrative image related to climate chamber
Forming Techniques
During the forming stage, various techniques such as bending, stamping, and machining are utilized to shape the components of the climate chamber. Advanced technologies like CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining provide precision in creating parts such as doors, panels, and internal shelving. The use of laser cutting technology is also prevalent, allowing for intricate designs and reducing material wastage.
Assembly Process
Once components are formed, the assembly process begins. This stage typically involves assembling the framework, insulation, and internal systems (like heating, cooling, and humidity control mechanisms). Skilled technicians use standardized procedures to ensure that all parts fit together correctly and function as intended. Quality checks are performed at this stage to catch any discrepancies early in the process.
Finishing Touches
The final stage of manufacturing involves finishing processes such as painting, polishing, and installing electronic components (e.g., controllers and displays). This is also the stage where safety features are added, such as alarms and emergency shut-off systems. A thorough inspection is conducted to confirm that the climate chamber meets all specifications before it is packaged for shipment.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Climate Chamber Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of climate chambers, particularly given the critical applications they serve in industries like pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and materials testing. A robust QA process includes adherence to international standards, systematic QC checkpoints, and a variety of testing methods.
What International Standards Guide Climate Chamber Quality?
Manufacturers typically adhere to international quality management standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with CE marking regulations is also essential for products sold in Europe, indicating that the product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards. For specific applications, such as pharmaceuticals, compliance with API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient) guidelines may also be necessary.

Illustrative image related to climate chamber
What QC Checkpoints Are Critical in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control in climate chamber manufacturing involves several key checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, regular checks are performed to ensure that assembly and production techniques adhere to established guidelines. This includes verifying the dimensional accuracy of components and the functionality of integrated systems.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before packaging, each climate chamber undergoes a comprehensive final inspection. This may include testing the functionality of temperature and humidity controls, ensuring that the chamber maintains specified conditions, and verifying safety features.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Climate Chambers?
Testing methods for climate chambers are critical to ensure performance under various environmental conditions. Common tests include:
-
Stability Testing: This evaluates how well the climate chamber maintains specific temperature and humidity levels over time. This is crucial for applications requiring consistent environmental conditions.
-
Performance Testing: This involves subjecting the chamber to extreme conditions to ensure it operates effectively under stress. For example, it may include temperature cycling tests that simulate rapid changes in environmental conditions.
-
Safety Testing: This ensures that all safety features, such as alarms and emergency shut-off mechanisms, function correctly.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control measures of suppliers is crucial. Here are some effective strategies:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. This includes evaluating their adherence to international standards and internal quality protocols.
-
Request Quality Assurance Documentation: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality control processes, including test results and certifications. This transparency helps buyers assess the reliability of the products.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. These inspectors can evaluate compliance with international standards and the effectiveness of QC checkpoints.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Certification for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various nuances regarding quality certifications, especially when sourcing from different regions.
-
Understanding Local Regulations: Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and standards in their own countries, as these can differ significantly from international standards.
-
Recognizing Certification Validity: Certificates such as ISO 9001 or CE marking should be verified for authenticity. Buyers should confirm that the certifications are current and issued by recognized bodies.
-
Cultural and Communication Barriers: Language and cultural differences may affect communication with suppliers. Establishing clear channels for discussing quality expectations and requirements can mitigate misunderstandings.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in climate chamber production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ensuring that they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘climate chamber’
Introduction:
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure climate chambers. Climate chambers are essential for various applications, including drug stability testing, controlled storage, and biological research. By following these steps, you can ensure that you make an informed decision that meets your operational needs and compliance standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Identifying your specific requirements is the foundation of a successful procurement process. Consider factors such as temperature and humidity ranges, chamber size, and material specifications.
– Temperature Range: Ensure the chamber can operate within the required limits (e.g., -40°C to +100°C) for your applications.
– Capacity Needs: Evaluate the volume of products that need testing or storage to determine the chamber size, whether it’s a small unit or a walk-in chamber.

Illustrative image related to climate chamber
Step 2: Research Industry Standards and Compliance
Familiarize yourself with relevant industry standards and compliance regulations that apply to your sector. Adhering to these standards ensures that your climate chamber meets quality and safety benchmarks.
– ISO and ICH Guidelines: For pharmaceutical applications, verify compliance with International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines.
– Local Regulations: Be aware of any regional requirements that may impact chamber specifications or operations, especially in countries like Nigeria or Saudi Arabia.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your technical requirements and deliver reliable products. Request detailed company profiles and references from existing clients.
– Supplier Reputation: Look for suppliers with a strong track record in your industry, as this can indicate reliability and product quality.
– Customer Support: Assess the level of customer service and technical support offered, as this can be crucial during installation and maintenance.
Step 4: Request Product Demonstrations or Samples
Before finalizing your purchase, request product demonstrations or samples to evaluate the chamber’s performance in real-world conditions. This step is vital for assessing usability and reliability.
– Performance Testing: Confirm that the chamber maintains consistent temperature and humidity levels under various operational conditions.
– User Interface: Evaluate the ease of use of the control system, ensuring it meets your operational needs.
Step 5: Review Warranty and Maintenance Options
Understanding the warranty and maintenance services provided by the supplier is crucial for long-term operational success. This helps protect your investment and ensures ongoing performance.
– Warranty Terms: Look for comprehensive warranty coverage, including parts and labor, to safeguard against potential defects.
– Maintenance Services: Inquire about routine maintenance options and availability of spare parts to minimize downtime.
Step 6: Compare Pricing and Financing Options
Evaluate pricing structures from various suppliers, considering both the initial cost and long-term value. Look for financing options that may alleviate upfront financial burdens.
– Total Cost of Ownership: Consider operational costs, including energy consumption and maintenance, to assess the chamber’s overall value.
– Flexible Payment Terms: Seek suppliers who offer flexible financing or leasing arrangements to suit your budgetary constraints.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
Once you have selected a supplier, ensure that all terms and conditions are clearly defined in the purchase agreement. This protects both parties and sets expectations for delivery and performance.
– Delivery Timeline: Confirm delivery schedules and installation support to ensure timely setup.
– Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Establish SLAs that outline performance metrics and response times for service requests.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for climate chambers, ensuring they select a solution that meets their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for climate chamber Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Climate Chamber Sourcing?
When evaluating the cost structure for climate chambers, several components come into play. The primary cost drivers include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects the cost. Stainless steel, which is commonly used for its durability and resistance to corrosion, typically commands a higher price than powder-coated cold-rolled steel. The selection of insulation materials and electronic components also impacts overall costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on the region of manufacturing. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this can sometimes compromise quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operation, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient production processes can help keep overhead low.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specialized chambers can lead to increased initial costs. However, these costs may be amortized over large production runs, making it essential to consider volume when evaluating tooling expenses.
-
Quality Control: QC processes are vital for ensuring product reliability and compliance with international standards, adding to the overall expense. Certifications such as ISO and CE can further enhance costs but are crucial for market acceptance.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can be substantial, especially for large and heavy equipment like climate chambers. Consideration of Incoterms is essential, as they dictate who is responsible for freight, insurance, and other transport-related expenses.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Climate Chamber Costs?
Several factors influence pricing beyond the raw costs associated with manufacturing.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ): Suppliers often provide discounts for bulk purchases. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized chambers tailored to specific applications or regulatory requirements can significantly increase the price. Buyers should assess their precise needs to avoid unnecessary expenditures.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality chambers that meet stringent standards will typically cost more. Buyers in regulated industries must weigh the benefits of compliance against the initial investment.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better warranties and customer support, which can reduce long-term costs.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs for Climate Chambers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider several strategies to optimize their purchasing decisions.
-
Negotiation: Always approach negotiations armed with data about market prices and competitor offerings. Leverage volume purchases to negotiate favorable terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also maintenance, energy consumption, and operational costs over the chamber’s lifecycle.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local regulations that can affect pricing. Understanding local market conditions can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and flexibility in payment terms.
Conclusion
While the initial price of climate chambers can vary widely based on multiple factors, understanding the underlying cost components and price influencers allows international B2B buyers to make informed decisions. By applying strategic negotiation tactics and considering the Total Cost of Ownership, buyers can ensure they achieve the best value for their investment in climate chambers.

Illustrative image related to climate chamber
Disclaimer: Prices for climate chambers can fluctuate based on market conditions and specific configurations. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and up-to-date pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing climate chamber With Other Solutions
When evaluating solutions for environmental testing and stability studies, businesses often consider various alternatives to climate chambers. While climate chambers provide controlled environments for temperature and humidity testing, other technologies can also serve similar purposes. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their specific operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Climate Chamber | Alternative 1: Walk-in Environmental Room | Alternative 2: Refrigerated Incubator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision in temperature and humidity control | Excellent for large-scale testing; flexible space | Good for temperature-sensitive samples; limited humidity control |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; ongoing maintenance costs | Significant upfront costs; operational costs may vary | Moderate cost; less expensive than climate chambers |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional setup and calibration | Complex installation; requires dedicated space | Generally easier to install and relocate |
| Maintenance | Regular calibration and servicing needed | Maintenance can be costly and labor-intensive | Lower maintenance; simpler technology |
| Best Use Case | Pharmaceutical stability testing, biological research | Large-scale testing for multiple products | Storing and testing biological samples |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Walk-in Environmental Room
Walk-in environmental rooms are designed for high-capacity testing and can maintain various environmental conditions. They are ideal for companies needing to test multiple products simultaneously in a controlled setting. However, the initial investment is significant, and they require a dedicated space, making them less flexible for smaller operations. Additionally, ongoing maintenance can be labor-intensive and costly.
Refrigerated Incubator
Refrigerated incubators are often used for temperature-sensitive biological samples and can maintain a stable environment. They are generally easier to implement and relocate compared to climate chambers and walk-in rooms, making them a practical choice for laboratories with limited space. However, their ability to control humidity is often limited, which can be a drawback for specific applications, such as long-term stability testing of pharmaceuticals.
Conclusion
Choosing the right solution for environmental testing depends on various factors, including the specific requirements of your operations, budget constraints, and space availability. Climate chambers offer high precision and are ideal for critical stability studies but come with higher costs and maintenance needs. Walk-in environmental rooms provide flexibility for large-scale testing but require significant investment and space. Refrigerated incubators are a cost-effective alternative for temperature-sensitive samples but may lack the humidity control needed for comprehensive testing. By assessing these factors, B2B buyers can select the most suitable option that aligns with their operational goals and regulatory requirements.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for climate chamber
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Climate Chambers for B2B Buyers?
When selecting a climate chamber, several technical specifications significantly impact performance and suitability for various applications. Understanding these properties can help decision-makers make informed purchasing choices.
1. Temperature Range
The temperature range of a climate chamber indicates the minimum and maximum temperatures it can maintain. Common ranges include -20°C to 100°C or 0°C to 70°C. This specification is crucial for buyers in industries like pharmaceuticals or agriculture, where specific temperature conditions are essential for product stability and testing.
2. Humidity Control
Humidity levels within a chamber are typically specified as a percentage (e.g., 10% to 90% RH). Precise humidity control is vital for applications such as shelf-life testing and material performance evaluation. For B2B buyers, understanding the chamber’s humidity range and its uniformity is essential for ensuring accurate and reliable test results.
3. Chamber Material
The materials used in constructing climate chambers, such as stainless steel or powder-coated cold-rolled steel, affect durability, ease of cleaning, and resistance to corrosion. Selecting the appropriate material is crucial for long-term use, particularly in harsh environments, making this specification a key consideration for procurement teams.
4. Capacity
The capacity of a climate chamber, often measured in liters (e.g., 102 L to 750 L), dictates how much product can be accommodated. Buyers must assess their testing needs to choose a chamber with adequate capacity, ensuring that it meets their specific application requirements without compromising performance.
5. Power Supply and Voltage Requirements
Understanding the voltage and power supply specifications (e.g., 230V, 400V) is critical for ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure. This specification is particularly important for international buyers, as power supply standards vary by region, and selecting the wrong voltage can lead to operational issues.
What Common Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know When Purchasing Climate Chambers?
Navigating the procurement process for climate chambers requires familiarity with certain industry jargon. Here are key terms that can aid in effective communication and negotiation.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that manufactures products that may be marketed by another company. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking for specific features or customizations in climate chambers, as it can influence pricing and availability.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for buyers, especially in markets like Africa or South America, where budget constraints may limit purchasing capabilities. Knowing the MOQ helps in planning inventory and aligning with budgetary restrictions.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services. Understanding how to prepare and issue RFQs can streamline the procurement process, enabling buyers to compare offers from different manufacturers effectively.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms is vital for B2B buyers, particularly when importing climate chambers, as they dictate shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks.
5. Calibration
Calibration involves adjusting the climate chamber’s instruments to ensure accurate readings of temperature and humidity. For buyers, understanding calibration protocols is essential for maintaining compliance with industry standards and ensuring reliable testing results.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can navigate the procurement of climate chambers more effectively, ensuring that they select the right equipment for their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the climate chamber Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing the Climate Chamber Sector?
The climate chamber market is experiencing significant growth driven by increased demand across various sectors, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and food industries. Global drivers such as stringent regulatory requirements regarding product stability and safety, particularly in regions like Europe and North America, are pushing companies to invest in advanced testing and storage solutions. For international B2B buyers, especially in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, the availability of diverse climate chambers that offer customizable features—such as temperature ranges, humidity control, and capacity—are becoming essential for meeting local compliance standards and market demands.
Emerging trends such as the integration of IoT technology into climate chambers are reshaping sourcing strategies. Smart climate chambers equipped with real-time monitoring and data analytics capabilities allow businesses to optimize their operations, enhance product quality, and reduce operational costs. Furthermore, the growing emphasis on sustainability is prompting manufacturers to develop eco-friendly chambers, which not only align with environmental regulations but also appeal to increasingly conscious consumers.

Illustrative image related to climate chamber
International buyers must also consider the implications of supply chain dynamics. Geopolitical factors and trade policies can affect sourcing timelines and costs. Thus, fostering relationships with local suppliers and understanding regional market nuances can provide a competitive edge.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Climate Chamber Market?
Sustainability has become a pivotal factor in the climate chamber sector, with businesses increasingly recognizing the importance of reducing their environmental footprint. The production and operation of climate chambers can have significant environmental impacts, including energy consumption and waste generation. As a result, manufacturers are focusing on creating energy-efficient models that utilize renewable energy sources and incorporate advanced insulation technologies.
Ethical sourcing is gaining traction, as businesses are held accountable for their supply chains. Buyers are encouraged to prioritize suppliers who demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and obtaining certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management. Such certifications not only bolster a company’s reputation but also ensure compliance with international standards.
Moreover, the demand for “green” materials in the construction of climate chambers is on the rise. Products that utilize low-impact materials or have been produced through sustainable processes are becoming more desirable. Buyers who prioritize these aspects can enhance their brand’s appeal in a marketplace increasingly driven by ethical consumerism.

Illustrative image related to climate chamber
What is the Evolution of Climate Chambers and Their Importance in B2B Context?
The evolution of climate chambers dates back to the early 20th century, when basic environmental testing equipment was developed primarily for research and agricultural purposes. Over the decades, advancements in technology have transformed climate chambers into sophisticated systems capable of simulating a wide range of environmental conditions, including temperature fluctuations, humidity levels, and light exposure.
This evolution is particularly significant for B2B buyers today, as modern climate chambers are designed to meet rigorous testing and compliance standards across various industries. The integration of automation and smart technology has not only improved their functionality but has also made them more accessible and user-friendly. As businesses increasingly rely on data-driven decisions, the role of climate chambers in ensuring product quality and safety has never been more critical. Understanding this historical context helps buyers appreciate the advancements and capabilities that modern climate chambers offer, ultimately enabling them to make informed purchasing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of climate chamber
-
How do I choose the right climate chamber for my specific testing needs?
Selecting the appropriate climate chamber involves assessing your specific application requirements, such as temperature and humidity ranges, capacity, and intended use (e.g., stability testing, shelf-life studies). Consider the environmental conditions your products will face and ensure the chamber can replicate these scenarios accurately. Additionally, evaluate the features like programmable settings, data logging capabilities, and construction materials for durability and compliance with international standards. -
What is the best climate chamber for testing pharmaceuticals?
For pharmaceutical testing, a humidity test chamber with a precise temperature range and the ability to maintain stable humidity levels is essential. Look for chambers that comply with ICH guidelines and offer programmable features to simulate various environmental conditions. Models with stainless steel construction are preferred for cleanliness and durability. Ensure the chamber has adequate capacity for your samples and includes data logging features for compliance documentation. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for climate chambers?
MOQs for climate chambers can vary significantly based on the supplier, model, and customization options. Generally, standard models may have lower MOQs, while customized units could require larger orders. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies, especially if you are considering bulk purchases for multiple facilities across different regions. -
How can I ensure the quality of climate chambers from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, conduct thorough research on suppliers, including checking certifications (like ISO or CE), reading customer reviews, and requesting product samples if possible. Establish clear communication regarding your quality expectations and ask for detailed specifications and performance data. Additionally, consider suppliers that offer warranties and post-sale support to address any potential issues with the chambers. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing climate chambers internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among international suppliers. Common practices include a deposit upfront (typically 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or installation. Some suppliers may offer financing options or letters of credit for larger orders. It’s essential to clarify payment terms in your contract and ensure they align with your financial capabilities and risk management strategies. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing climate chambers?
When importing climate chambers, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Ensure that your supplier provides the necessary documentation for customs clearance, including invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. It’s also wise to partner with a logistics provider experienced in handling specialized equipment to mitigate risks associated with shipping delays and damages. -
Can climate chambers be customized to meet specific testing requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for climate chambers. You can request specific temperature and humidity ranges, chamber sizes, and additional features like lighting or gas control systems. Discuss your requirements with the supplier during the selection process to ensure that they can meet your needs without compromising on performance or compliance with industry standards. -
What are the common maintenance requirements for climate chambers?
Regular maintenance of climate chambers is vital for optimal performance and longevity. This typically includes routine calibration of temperature and humidity sensors, cleaning of internal components, and inspection of seals and insulation. Establish a maintenance schedule based on the manufacturer’s recommendations and ensure your staff is trained in basic troubleshooting to address minor issues promptly. Consider a service contract with the supplier for comprehensive support.
Top 7 Climate Chamber Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Fisher Scientific – Environmental Chambers
Domain: fishersci.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: {“Product Type”: “Environmental Chambers”, “Features”: “Control of light, humidity, air pressure, and gas”, “Applications”: [“Drug stability studies”, “Shelf-life testing”, “Controlled temperature storage”, “Biological research applications”], “Capacity (Metric)”: [102, 1020, 1070, 127, 1388, 1473, 1610, 2265, 2269, 228, 247, 262, 311, 311.5, 400, 472, 5.3, 651, 679.6, 684, 698, 7.5, 700, 727, 734…
2. Weiss Technik – Environmental Test Chambers
Domain: weiss-na.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Weiss Technik offers a broad portfolio of environmental test chambers, including: Temperature Test Chambers, Humidity Test Chambers, Walk-In & Drive-In Environmental Test Chambers, Thermal Shock Chambers, Battery Test Chambers, HALT/HASS/AGREE & Vibration Test Chambers, Altitude & Space Simulation Test Chambers, Life Science, Stability Test Chambers & Containment Systems, Heat Technology & Product…
3. SCS – Custom Environmental Test Chambers
Domain: scs-usa.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Custom Environmental Test Chambers designed for precise temperature and humidity control for environmental testing and manufacturing across various industries. Capable of replicating extreme temperatures, moisture, and humidity conditions for testing industrial products, machinery, components, biological products, and more. Types of chambers include Stability Chambers, Temperature Chambers, Humidi…
4. Memmert – Constant Climate Chamber HPPeco
Domain: memmert.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Memmert offers a range of climate chambers and humidity chambers designed for various applications including stability testing, environmental testing, and conditioning. Key products include:
1. **Constant Climate Chamber HPPeco**:
– Maximum energy efficiency for stability studies according to ICH guidelines, cosmetics, and food testing.
2. **Humidity Chamber HCP**:
– Active humidity co…
5. IQS Directory – Climate Chambers
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Climate chambers are advanced enclosed spaces designed to mimic and regulate various environmental conditions for testing industrial products, electronics, materials, and biological samples. They can operate in two modes: constant (steady conditions) and dynamic (varying conditions). Key types of climate chambers include: 1. Benchtop Climate Chambers: Compact, versatile, suitable for laboratories;…
6. CSZ – Environmental Test Chambers
Domain: cszindustrial.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: CSZ Environmental Test Chambers include a variety of products such as Temperature Humidity Chambers, Stability Chambers, Thermal Shock Chambers, Vibration Test Chambers, Industrial Freezers, and Custom Designed Chambers. Specific models include Z Plus MicroClimate, Benchtop MicroClimate 3, VTS Compact, VTS Large, TSB Liquid Horizontal Thermal Shock, HALT-HASS Chambers, AV Series, and CV Series. Th…
7. ACS – Environmental Test Chambers
Domain: acstestchambers.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: ACS environmental test chambers offer a wide range of climatic chambers capable of simulating various environmental conditions. Key product details include:
– Types of tests: Altitude Test, Climatic Test, ESS Test, Air/Air Thermal Shock Test, Solar Light Test, Stress Screening, Corrosion Test, Vibration Test, Vacuum Test, and more.
– Applications across multiple sectors: Electronics, Automotive,…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for climate chamber
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Climate Chamber Procurement?
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of climate chambers offers international B2B buyers a pathway to enhanced operational efficiency and product reliability. By understanding the diverse range of environmental chambers available—ranging from humidity test chambers to large-scale walk-in units—buyers can select solutions tailored to their specific testing and storage needs. Leveraging suppliers with robust capabilities ensures compliance with international standards and maximizes the return on investment.
The value of strategic sourcing lies not only in cost-effectiveness but also in fostering long-term partnerships with manufacturers who prioritize quality and innovation. This approach is crucial for industries spanning pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and materials science, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
As markets evolve and technological advancements emerge, staying ahead through informed sourcing decisions will be essential. We encourage you to engage with leading suppliers, evaluate the latest offerings, and invest in climate chambers that will sustain your competitive edge in an increasingly dynamic landscape. Your next step could redefine your testing capabilities—seize this opportunity to elevate your business today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.