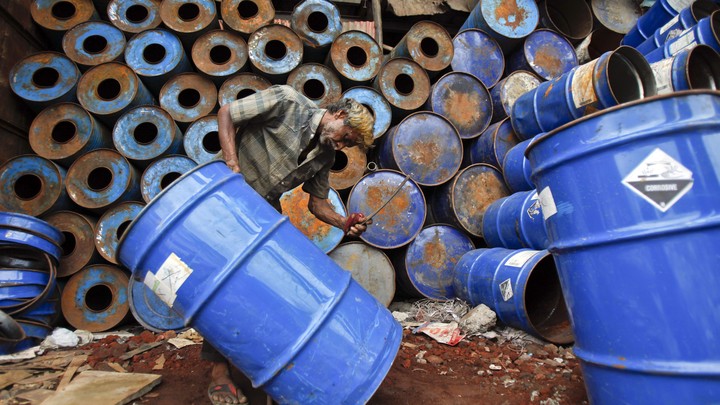
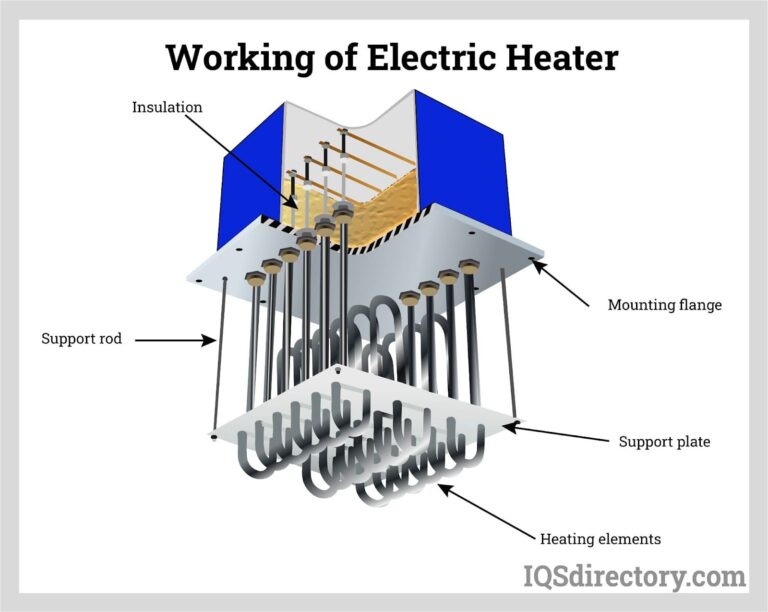
Top 5 Waste Drum Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for waste drum
In today’s complex global market, sourcing waste drums that meet stringent safety and regulatory standards can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe grapple with increasing environmental regulations and the need for safe waste management solutions, understanding the diverse options available is crucial. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of waste drums, including plastic lab pack drums and their applications in safely transporting hazardous materials.
By exploring essential factors such as supplier vetting, cost considerations, and compliance with international standards, this guide empowers international B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are located in dynamic markets like Vietnam or established economies like Germany, knowing how to identify reliable suppliers and the specific requirements for waste drum usage can streamline your procurement process.
Additionally, this guide provides insights into the latest innovations in waste drum technology and best practices for waste disposal, ensuring that your operations not only comply with local regulations but also contribute to sustainable practices. Equip yourself with the knowledge needed to navigate the global market for waste drums effectively, ensuring safety and compliance in your operations while minimizing environmental impact.
Understanding waste drum Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lab Pack Drums | Constructed from high-density polyethylene, various closure types, suitable for non-leaking hazardous materials. | Chemical storage, transportation, spill containment. | Pros: Durable, lightweight, compliant with regulations. Cons: Not suitable for free liquids. |
| Steel Drums | Made from carbon steel, often with a protective lining, available in various sizes. | Industrial waste, oil and chemical storage. | Pros: Robust, high capacity, suitable for various materials. Cons: Heavier, may corrode without proper lining. |
| Plastic Drums | Made from HDPE or polypropylene, lightweight, resistant to chemicals and UV rays. | Food waste, pharmaceuticals, hazardous materials. | Pros: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, recyclable. Cons: Limited temperature resistance compared to steel. |
| Open-Head Drums | Features a removable lid secured with a ring or lever, easy access for filling and emptying. | Bulk waste collection, industrial applications. | Pros: Easy access, versatile for different waste types. Cons: Less secure for hazardous materials. |
| Closed-Head Drums | Designed with a sealed lid, often used for transporting liquids. | Liquid waste disposal, chemical transport. | Pros: Secure, prevents leaks during transport. Cons: Limited access for filling and emptying. |
What Are Lab Pack Drums and Their Applications?
Lab pack drums are specialized containers designed for the safe transport and disposal of hazardous materials. Constructed from high-density polyethylene (HDPE), they feature various closure types, such as lever-lock or screw-on lids, catering to the specific needs of chemical storage. These drums are ideal for educational institutions, research laboratories, and industrial facilities where hazardous waste is generated. When purchasing lab pack drums, buyers should consider the regulatory requirements for hazardous waste in their region to ensure compliance.
Why Choose Steel Drums for Industrial Waste?
Steel drums are commonly used in industrial applications due to their robustness and high capacity. Made from carbon steel and often lined for added protection against corrosion, these drums can safely store a variety of materials, including oils and chemicals. They are particularly suitable for companies needing durable solutions for bulk waste collection. Buyers should evaluate the weight and corrosion resistance of steel drums to ensure they meet their operational needs, especially in harsh environments.
How Do Plastic Drums Compare for Waste Management?
Plastic drums, typically made from HDPE or polypropylene, are favored for their lightweight and chemical-resistant properties. They are widely used in industries dealing with food waste, pharmaceuticals, and hazardous materials. Their recyclability also makes them an environmentally friendly choice. When selecting plastic drums, buyers should assess their temperature resistance and compatibility with the materials they plan to store to avoid any adverse reactions.
What Are the Benefits of Open-Head Drums?
Open-head drums are designed with a removable lid, making them ideal for applications requiring frequent access to the contents. They are commonly used for bulk waste collection in various industrial settings. The versatility of open-head drums allows for easy filling and emptying, but buyers should be cautious about their security when storing hazardous materials. Evaluating the need for secure storage versus accessibility is critical when considering these drums.
When Should You Use Closed-Head Drums?
Closed-head drums are specifically designed for securely transporting liquids, preventing leaks and spills during transit. They are essential for companies involved in the disposal of liquid waste or chemical transport. While their sealed design offers a high level of security, it limits access for filling and emptying, which may not suit all applications. Buyers should weigh the benefits of secure transport against the potential need for frequent access when deciding on closed-head drums.
Key Industrial Applications of waste drum
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Waste Drum | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Manufacturing | Storage and transport of hazardous waste materials | Ensures compliance with safety regulations and minimizes risk of spills | Verify UN certification and compatibility with waste types |
| Healthcare | Disposal of medical waste and biohazardous materials | Enhances safety and sanitation in healthcare settings | Ensure compliance with local regulations for medical waste disposal |
| Oil and Gas | Containment of drilling mud and hazardous substances | Reduces environmental impact and maintains regulatory compliance | Assess durability and resistance to chemicals used in drilling |
| Construction | Temporary storage of construction debris and hazardous materials | Streamlines waste management on job sites | Look for stackable options and easy transport features |
| Food and Beverage | Disposal of food waste and by-products | Supports sustainability initiatives and waste reduction | Consider materials that are food-safe and comply with health regulations |
How is Waste Drum Utilized in Chemical Manufacturing?
In the chemical manufacturing sector, waste drums are essential for the secure storage and transport of hazardous waste materials. These drums, often made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE), are designed to meet stringent regulatory requirements, thereby ensuring compliance with safety standards. By using waste drums, businesses minimize the risk of spills and leaks, which can lead to costly environmental damage and regulatory fines. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing drums that are UN certified and compatible with the specific types of chemicals they handle.
What Role Do Waste Drums Play in Healthcare Waste Management?
In healthcare settings, waste drums are critical for the safe disposal of medical waste and biohazardous materials. These drums help maintain high sanitation standards and protect healthcare workers from exposure to hazardous substances. They are often required to meet specific regulations, which vary by country, making it crucial for international buyers to understand local disposal laws. When sourcing waste drums for medical applications, it’s important to ensure they are clearly labeled and designed to prevent leaks, thus enhancing safety and compliance.
Why Are Waste Drums Important in the Oil and Gas Industry?
The oil and gas industry frequently utilizes waste drums for the containment of drilling mud and other hazardous substances. These drums are designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions and resist chemical degradation, which is vital for maintaining operational safety and environmental integrity. Businesses benefit from using waste drums by reducing the risk of spills that could harm ecosystems and lead to substantial fines. Buyers should consider the durability and chemical resistance of the drums, as well as their capacity to handle specific substances used in drilling operations.
How Do Waste Drums Enhance Waste Management in Construction?
In the construction industry, waste drums serve as temporary storage solutions for construction debris and hazardous materials. Their use streamlines waste management processes on job sites, allowing for efficient collection and disposal of materials. This not only improves site safety but also supports compliance with local waste disposal regulations. When sourcing waste drums for construction applications, businesses should look for models that are stackable and easy to transport, facilitating better management of waste materials during projects.
What Benefits Do Waste Drums Provide in Food and Beverage Waste Disposal?
The food and beverage industry employs waste drums for the disposal of food waste and by-products, contributing to sustainability efforts by reducing landfill contributions. These drums must be made from food-safe materials that comply with health regulations to prevent contamination. By utilizing waste drums for organic waste, businesses can enhance their waste management strategies and support recycling and composting initiatives. Buyers should seek drums that are designed for easy cleaning and have features that facilitate compliance with local health and safety standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘waste drum’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Struggling with Compliance in Hazardous Waste Management
The Problem:
B2B buyers in industries such as manufacturing and healthcare often face stringent regulations when it comes to the storage and transportation of hazardous waste. The consequences of non-compliance can be severe, including hefty fines, legal repercussions, and reputational damage. Many buyers find it challenging to understand the specific requirements related to labeling, closure types, and segregation of incompatible materials. This confusion can lead to improper handling of waste, which not only endangers employee safety but also violates environmental regulations.
The Solution:
To navigate compliance effectively, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing waste drums that meet both local and international regulatory standards. It is essential to consult with manufacturers or suppliers who specialize in hazardous materials packaging to ensure that the drums are certified for specific waste types. Buyers should also invest in training for employees on the importance of proper labeling and segregation of hazardous materials. Utilizing technology, such as compliance management software, can streamline the tracking of materials and ensure adherence to safety protocols. Regular audits and inspections of waste management practices will further bolster compliance efforts and safeguard against potential violations.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Storage Solutions Leading to Spills
The Problem:
One common pain point for businesses handling hazardous materials is inadequate storage solutions, which can lead to spills and accidents. Many buyers underestimate the importance of selecting the right type of waste drum based on their specific needs, such as the chemical compatibility of the materials being stored. Inadequate or improper storage not only poses safety risks but can also result in costly cleanup efforts and disruptions to operations.
The Solution:
To mitigate the risk of spills, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their waste materials and choose waste drums specifically designed for those substances. This includes selecting drums made of compatible materials, such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE) for corrosive substances. Additionally, implementing secondary containment systems, like spill pallets or containment trays, can provide an extra layer of protection. Regular maintenance checks on the drums and immediate reporting of any signs of wear or damage are crucial. Suppliers can also offer recommendations on best practices for storage conditions, including temperature control and ventilation, to further minimize risks.
Scenario 3: Cost Management Challenges in Waste Disposal
The Problem:
Managing costs associated with waste disposal can be a significant concern for B2B buyers, especially in industries generating large volumes of hazardous waste. Many organizations struggle with budgeting for waste disposal due to fluctuating disposal fees and the costs associated with compliance and transportation. This uncertainty can hinder strategic planning and resource allocation, leading to financial strain.
The Solution:
B2B buyers should consider establishing long-term contracts with licensed hazardous waste disposal companies to lock in rates and reduce variability in disposal costs. Additionally, adopting a waste reduction strategy can help minimize the volume of waste produced, ultimately lowering disposal fees. Implementing a recycling program for certain materials can also offset costs and contribute to sustainability efforts. Buyers should work closely with their suppliers to evaluate the most cost-effective waste drums and disposal methods, ensuring that they balance quality and compliance with budgetary constraints. Regularly reviewing waste management processes and expenses can also identify areas for improvement and cost savings.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for waste drum
What Are the Key Materials Used for Waste Drums?
When selecting a waste drum for hazardous materials, the choice of material is crucial, as it directly influences performance, safety, and compliance with regulations. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the production of waste drums: steel, high-density polyethylene (HDPE), fiberglass, and aluminum. Each material has unique properties, advantages, and limitations that international B2B buyers should consider.
How Does Steel Perform as a Material for Waste Drums?
Steel waste drums are known for their strength and durability. They typically have a high-temperature rating and excellent resistance to physical impacts. Steel drums are often used for storing and transporting hazardous materials, including chemicals and oils, due to their robust nature.
Pros: Steel drums are highly durable, can withstand high pressures, and are resistant to punctures and dents. They are also recyclable, which can reduce disposal costs.
Cons: The primary drawback is their susceptibility to corrosion, especially when exposed to moisture or certain chemicals. Additionally, steel drums can be heavier than other materials, increasing transportation costs.
Impact on Application: Steel waste drums are ideal for storing flammable liquids or materials that require a high level of containment. However, they may not be suitable for corrosive substances without proper lining.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential when selecting steel drums. Buyers should also consider the availability of corrosion-resistant coatings for specific applications, particularly in humid climates.
What Are the Advantages of High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Waste Drums?
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is a popular choice for waste drums due to its lightweight nature and chemical resistance. HDPE drums are often used for storing non-leaking hazardous materials and are designed to meet specific regulatory requirements.
Pros: HDPE drums are resistant to a wide range of chemicals and are less likely to corrode. They are also lighter than steel, making them easier to handle and transport.

Illustrative image related to waste drum
Cons: While HDPE is durable, it may not withstand high temperatures as effectively as steel. Additionally, it can be more susceptible to physical damage from impacts.
Impact on Application: HDPE is suitable for storing various chemicals, including acids and bases. However, it is not recommended for high-temperature applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that HDPE drums comply with local regulations and standards, such as JIS or EN. The availability of UV inhibitors is also important for outdoor storage in regions with high sun exposure.
How Does Fiberglass Compare as a Material for Waste Drums?
Fiberglass waste drums offer excellent chemical resistance and are lightweight, making them suitable for various hazardous materials. They are often used in industries where corrosion is a significant concern.
Pros: Fiberglass drums are highly resistant to corrosion and can handle a wide range of chemicals. They are also lightweight, which reduces shipping costs.
Cons: The manufacturing process for fiberglass can be more complex and costly than for other materials. Additionally, they may not be as durable under physical stress compared to steel.
Impact on Application: Fiberglass drums are ideal for storing corrosive chemicals, making them suitable for the chemical industry. However, they may not be suitable for applications involving high impact or pressure.

Illustrative image related to waste drum
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international shipping regulations is crucial, especially for hazardous materials. Buyers should also consider the thermal stability of fiberglass in extreme temperatures.
What Are the Key Features of Aluminum Waste Drums?
Aluminum waste drums are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making them a viable option for transporting hazardous materials. They are often used in industries that require frequent handling and transportation.
Pros: Aluminum drums are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can be manufactured in various sizes. They are also recyclable, making them an environmentally friendly option.
Cons: Although aluminum is durable, it may not withstand as much pressure as steel. Additionally, it can be more expensive than other materials.
Impact on Application: Aluminum drums are suitable for storing a variety of chemicals, including those that may corrode other materials. However, they may not be ideal for high-pressure applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant international standards and consider the cost implications of aluminum compared to other materials.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Waste Drums
| Material | Typical Use Case for Waste Drum | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Storing and transporting flammable liquids | High durability and pressure resistance | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| High-Density Polyethylene | Storing non-leaking hazardous materials | Lightweight and chemical resistant | Less effective in high temperatures | Low |
| Fiberglass | Storing corrosive chemicals | Excellent chemical resistance | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Transporting various hazardous materials | Lightweight and recyclable | Less pressure resistance | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of common materials used for waste drums, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regulatory requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for waste drum
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Waste Drums?
The manufacturing process of waste drums typically involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is crucial to ensure the final product meets the required safety and quality standards.
-
Material Preparation: The first step involves selecting appropriate materials, often high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or metal, depending on the type of waste to be stored. These materials must be resistant to chemical degradation and capable of withstanding environmental conditions. Suppliers often source materials that meet international standards for hazardous waste containment.
-
Forming: During this stage, the prepared materials are shaped into the form of drums. For plastic drums, processes like blow molding or injection molding are commonly used. Metal drums may undergo processes such as rolling and welding. The choice of technique affects the drum’s durability and leak-proof capabilities.
-
Assembly: After forming, the drums are assembled with closures, which can vary based on regulatory requirements and the nature of the materials being contained. Closure types can include screw-on lids, lever-locks, or bolt rings, each designed to ensure a secure seal that prevents leakage.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves surface treatment and labeling. Drums may undergo UV treatment to enhance resistance against sunlight, and they are labeled with hazard warnings and identification numbers. This stage is critical for compliance with transport and storage regulations.
Which Key Techniques Are Used in Waste Drum Manufacturing?
The manufacturing of waste drums employs various techniques to ensure they meet specific performance criteria.
-
Blow Molding: Used predominantly for plastic drums, this method allows for the creation of hollow objects with uniform wall thickness. It’s efficient for high-volume production, ensuring consistency in quality.
-
Welding: In metal drum production, welding techniques are employed to join various components securely. Techniques like TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) or MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding are common, ensuring strong and durable seams.
-
Surface Treatment: This includes processes like galvanization for metal drums to enhance corrosion resistance. For plastic drums, UV inhibitors may be added to prevent degradation from sunlight exposure.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Waste Drums?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of waste drums, especially when dealing with hazardous materials. International standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems are essential. Compliance with these standards helps ensure that manufacturers consistently produce high-quality products.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking in Europe or API standards for oil and gas sectors may apply. These certifications demonstrate that products meet stringent safety and performance criteria, providing peace of mind to B2B buyers.

Illustrative image related to waste drum
What Are the Critical Quality Control Checkpoints in Waste Drum Production?
Quality control (QC) is integral throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Before production begins, incoming materials are inspected for compliance with specifications. This includes checking for the correct material type, dimensions, and chemical resistance.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, processes are monitored to ensure adherence to quality standards. This may involve regular checks of the molding process, weld integrity, and dimensional accuracy.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once drums are completed, a thorough inspection is conducted. This includes testing for leaks, structural integrity, and proper labeling. Random sampling of finished products may also be performed to validate compliance with quality standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Quality Assurance of Waste Drums?
Several testing methods are employed to verify the quality and safety of waste drums:
-
Hydrostatic Testing: This method checks for leaks by filling the drum with water and pressurizing it to ensure it can withstand internal pressures without failure.
-
Drop Testing: Drums are subjected to drop tests to evaluate their durability during transport. This simulates real-world conditions and helps assess the likelihood of failure.
-
Chemical Resistance Testing: Samples of the drum material are exposed to various chemicals to determine their resistance and ensure they can safely contain hazardous materials.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to ensure their suppliers maintain high-quality standards:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. This includes reviewing their certifications and quality management systems.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to provide detailed quality reports that outline their QC processes, test results, and compliance with international standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality management practices and the integrity of their products.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers face unique challenges related to quality assurance and certification. Understanding regional regulations and standards is essential. For example, buyers from Africa may need to be aware of local environmental regulations, while those in Europe must comply with EU directives.
Furthermore, varying levels of certification acceptance can complicate procurement. Buyers should ensure that suppliers provide documentation that meets the regulatory requirements of their specific markets. This can include ISO certifications, local regulatory compliance documents, and specific certifications for hazardous material handling.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in waste drum production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and ensure they source reliable products that meet their safety and operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘waste drum’
This guide provides a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure waste drums, particularly for handling hazardous materials. Understanding the essential steps in the procurement process can ensure compliance with regulations and optimize operational efficiency.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline the technical requirements for the waste drums. This includes specifying the material (plastic, metal, etc.), capacity (e.g., 20-gallon, 55-gallon), and closure type (screw-on, lever-lock). Understanding these specifications helps in narrowing down suppliers and ensuring that the drums meet safety and regulatory standards.

Illustrative image related to waste drum
Step 2: Research Regulatory Compliance
Ensure that the waste drums you intend to purchase comply with local and international regulations concerning hazardous materials. Regulatory bodies in different regions, such as the EPA in the U.S. or REACH in Europe, have specific guidelines that must be adhered to. This step is crucial for avoiding legal issues and ensuring safe disposal practices.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, certifications, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in handling hazardous materials and those who comply with international shipping and safety regulations.
- Check Certifications: Ensure suppliers hold relevant certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates quality management standards.
- Review Customer Feedback: Investigate online reviews and testimonials to gauge supplier reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Assess Product Quality and Durability
Quality is paramount when it comes to waste drums, especially those intended for hazardous materials. Assess the durability of the drums by reviewing the materials used (e.g., high-density polyethylene for plastic drums) and their resistance to chemicals and environmental conditions.
- Request Samples: If possible, request samples to evaluate the physical properties and closure mechanisms of the drums.
- Inquire About Testing: Confirm whether the drums undergo rigorous testing for leaks and structural integrity.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, compare pricing structures and payment terms. Ensure that the pricing reflects the quality of the drums and includes all necessary fees, such as shipping and handling.
- Negotiate Bulk Discounts: If purchasing in large quantities, inquire about bulk pricing options or long-term contracts that may offer better rates.
- Review Return Policies: Understand the supplier’s return and exchange policies in case the drums do not meet your expectations or regulatory requirements.
Step 6: Confirm Logistics and Delivery Times
Logistics play a crucial role in the procurement process, particularly for international shipments. Confirm the logistics capabilities of the supplier, including their ability to handle customs clearance and timely deliveries.
- Discuss Shipping Options: Evaluate different shipping methods (air, sea, land) and their associated costs.
- Establish a Timeline: Set clear expectations for delivery timelines to ensure that the drums arrive when needed for operational continuity.
Step 7: Finalize Your Order and Documentation
Before placing your final order, ensure all documentation is in order. This includes purchase orders, compliance certifications, and any necessary shipping documents.
- Keep Records: Maintain detailed records of all transactions and communications with suppliers for future reference.
- Verify Order Details: Double-check quantities, specifications, and delivery addresses to prevent any errors that could delay the procurement process.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement of waste drums, ensuring compliance, quality, and efficiency in handling hazardous materials.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for waste drum Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Waste Drum Sourcing?
In the B2B landscape of waste drum sourcing, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of material significantly influences the cost. For instance, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) is commonly used for plastic waste drums due to its durability and resistance to chemicals, which can result in higher initial costs but lower long-term maintenance expenses.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. In countries with higher labor costs, such as Germany, the overall expense might be significantly greater compared to regions in Africa or South America, where labor is typically cheaper.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, equipment depreciation, and facility maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: Customization of waste drums often requires specific tooling, which can add to the upfront costs. This is particularly relevant for specialized drums that need to meet particular regulatory standards.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring compliance with safety and environmental regulations is vital. Investing in stringent QC processes can enhance product reliability but may also increase costs.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary significantly based on location, shipping method, and Incoterms. International shipping may involve additional fees, such as customs duties, which can affect the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to their costs. Understanding the markup can provide insights into potential negotiation strategies.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Waste Drum Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of waste drums in the B2B market. Understanding these can aid buyers in securing better deals.
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases often lead to discounts. Suppliers are generally willing to negotiate better rates for larger orders, reducing the per-unit cost significantly.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom drums tailored for specific applications or regulatory compliance may command higher prices. Buyers should weigh the necessity of custom features against their budgets.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Drums made from superior materials or those that meet specific quality certifications can be more expensive. However, investing in high-quality products often results in reduced risk of leaks and failures.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and customer service can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge premium prices.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects shipping costs and responsibilities, impacting the overall cost structure. For instance, DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) may offer more predictable costs compared to FOB (Free on Board), where buyers assume more risk.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Waste Drums Internationally?
International B2B buyers should adopt strategic approaches to enhance cost-efficiency when sourcing waste drums.
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders. Leverage market research to support your negotiation stance.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, compliance, and disposal. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher TCO if the drums do not meet quality standards.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations and how local economic conditions can affect costs. For example, sourcing from suppliers in regions with lower manufacturing costs, like parts of South America, may yield significant savings.
-
Assess Supplier Capabilities: Evaluate suppliers on their ability to meet regulatory requirements and their experience with international logistics, which can affect lead times and costs.
-
Request Samples: Before committing to large orders, request samples to ensure the quality meets your expectations. This can prevent costly mistakes down the line.
By understanding these cost components, price influencers, and effective sourcing strategies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.

Illustrative image related to waste drum
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing waste drum With Other Solutions
When considering waste management solutions, businesses often evaluate the effectiveness, cost, and convenience of various options. Waste drums are a common choice for storing and transporting hazardous materials; however, other alternatives may offer distinct advantages depending on specific operational needs. This analysis compares waste drums with two viable alternatives: Lab Pack Drums and Bulk Containers.
| Comparison Aspect | Waste Drum | Lab Pack Drum | Bulk Container |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Suitable for various waste types; durable and leak-resistant. | Designed for smaller containers; excellent for hazardous materials transport. | High capacity; ideal for large volumes of waste. |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; long-term durability reduces replacement costs. | Generally lower cost for smaller quantities; may require more units. | Higher upfront cost but cost-effective for large-scale operations. |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple to use; minimal setup required. | Requires sorting and packing of smaller containers. | Requires more space and equipment for loading/unloading. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; periodic inspections recommended. | Low maintenance; must ensure proper sealing and labeling. | Moderate maintenance; checks needed for structural integrity. |
| Best Use Case | General waste storage and transport; versatile across industries. | Ideal for laboratories and institutions handling small hazardous waste. | Best for industrial applications requiring bulk waste management. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Lab Pack Drums?
Lab Pack Drums are specialized containers designed for the safe transport of smaller hazardous materials like bottles and cans. Their primary advantage lies in their compliance with strict regulatory requirements, making them ideal for educational and research settings. They are lightweight and easy to handle, ensuring safe transport. However, their capacity limits may necessitate the use of multiple units, potentially increasing costs for larger waste volumes. Additionally, they require careful sorting and packing of materials to avoid chemical reactions, which can complicate the disposal process.
How Do Bulk Containers Compare as an Alternative?
Bulk Containers are designed to hold large quantities of waste, making them suitable for industrial applications where waste generation is high. Their primary advantage is efficiency; they reduce the number of trips needed for waste transport and can lower overall disposal costs when dealing with large volumes. However, they require a larger initial investment and may necessitate specialized equipment for loading and unloading. The maintenance demands are also higher, as they need regular inspections to ensure structural integrity and compliance with safety regulations.

Illustrative image related to waste drum
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Waste Management Solution?
When selecting a waste management solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational requirements, including the type and volume of waste generated, regulatory compliance, and budget constraints. Waste drums may provide the versatility needed for various industries, while Lab Pack Drums excel in environments with stringent safety regulations. Conversely, Bulk Containers are ideal for businesses that produce large quantities of waste and seek to optimize their disposal processes. Evaluating these factors will help businesses select the most effective and cost-efficient waste management solution tailored to their needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for waste drum
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Waste Drums?
When it comes to waste drums, understanding the technical specifications is crucial for ensuring safety, compliance, and efficiency in handling hazardous materials. Here are the essential properties that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
Waste drums are typically made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or steel, each offering distinct advantages. HDPE drums are lightweight, resistant to chemicals, and suitable for various waste types. Steel drums, on the other hand, provide superior strength and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Selecting the appropriate material grade is vital for ensuring the drum’s compatibility with the waste it will contain and for meeting regulatory requirements.
2. Capacity
The capacity of waste drums varies widely, typically ranging from 10 gallons to 55 gallons. Understanding the capacity needed is essential for logistics and compliance. Larger drums reduce the frequency of disposal but may pose handling challenges, while smaller drums allow for easier maneuverability but might require more frequent changes. B2B buyers should assess their waste generation rates to determine the most efficient drum size.
3. Closure Type
The closure mechanism of a waste drum is a critical safety feature. Common closure types include screw-on lids, lever-locks, and bolt rings. Each type offers different levels of security and accessibility. For instance, screw-on lids provide a tight seal to prevent leaks, while lever-locks facilitate quicker access. Choosing the right closure type is essential to ensure containment and compliance with hazardous materials regulations.
4. UN Rating
Waste drums must often comply with United Nations (UN) standards, which classify containers based on their ability to safely transport hazardous materials. The UN rating indicates the drum’s suitability for specific types of waste, such as flammable liquids or corrosive substances. Buyers should verify the UN rating to ensure regulatory compliance and safe transportation of hazardous materials.
5. Weight Capacity
The weight capacity of a waste drum is another important specification. Drums must be able to support the weight of their contents without risk of failure. This is particularly crucial when transporting hazardous materials, as overloading can lead to spills and environmental hazards. B2B buyers should consider both the weight of the drum itself and the maximum weight of the waste it will hold.

Illustrative image related to waste drum
6. Chemical Resistance
Different waste materials react differently with various drum materials. It is essential to evaluate the chemical resistance of the drum to ensure it can safely contain the specific waste type without degradation or leakage. This is particularly important in industries such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and waste management, where compliance with environmental regulations is mandatory.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Waste Drums?
Navigating the purchasing process for waste drums involves understanding several key trade terms that streamline communication and transactions. Here are some commonly used terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
In the context of waste drums, OEM refers to manufacturers who produce drums based on specific designs or specifications provided by a buyer. This allows for customized solutions tailored to unique waste management needs, ensuring that the drums meet specific regulatory and operational requirements.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. Understanding the MOQ is crucial for buyers as it can affect inventory management and cost efficiency. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs to avoid overstocking or underutilizing resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products, such as waste drums. This document typically outlines the quantities, specifications, and delivery timelines required. Issuing an RFQ helps buyers compare offers and select the best supplier based on price, quality, and service.

Illustrative image related to waste drum
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods, including waste drums. They clarify aspects such as delivery points, risk transfer, and cost responsibilities. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for international buyers to ensure smooth transactions and mitigate potential disputes.
5. Compliance Standards
This term refers to the regulations and guidelines that waste drums must meet for safe storage, transportation, and disposal of hazardous materials. Compliance standards can vary by region, making it imperative for buyers to understand local regulations and ensure that their selected drums adhere to these requirements.
6. Hazardous Waste Classification
Understanding the classification of hazardous waste is essential for proper drum selection and compliance. Different types of waste (e.g., flammable, corrosive, reactive) require specific containment solutions. Buyers should ensure that the waste drums they procure are suitable for the classifications of the materials they will store or transport.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance safety, compliance, and operational efficiency in their waste management processes.

Illustrative image related to waste drum
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the waste drum Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Waste Drum Market?
The global waste drum market is increasingly shaped by stringent regulatory frameworks aimed at managing hazardous materials. Countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are enhancing their waste management protocols, driving demand for compliant waste drums. Additionally, the rise of industrialization in emerging markets like Vietnam is contributing to increased waste generation, necessitating robust waste containment solutions. Technological advancements in materials science, such as the development of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and other durable composites, have resulted in lighter, more resilient products that are easier to transport and handle.
Emerging trends in B2B sourcing include a shift towards digital platforms for procurement, enabling international buyers to access a wider range of suppliers and products. E-commerce platforms are facilitating faster transactions and enhanced visibility into product specifications and compliance certifications. Furthermore, the integration of IoT technology in waste management is gaining traction, with smart waste drums equipped with sensors that provide real-time data on fill levels and environmental conditions, thereby optimizing logistics and reducing operational costs.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Waste Drum Supply Chain?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of the waste drum sector, with increasing pressure on manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly practices. The environmental impact of waste management is prompting buyers to prioritize suppliers with sustainable sourcing and production methods. Ethical supply chains are not just a trend but a necessity, as businesses face scrutiny from stakeholders regarding their environmental footprint.
The use of recycled materials in the production of waste drums is gaining popularity, as it reduces reliance on virgin resources and minimizes waste. Buyers should seek out products certified with ‘green’ labels or environmental certifications that indicate compliance with sustainability standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and certifications for recycled content can serve as benchmarks for responsible sourcing. By opting for sustainable options, B2B buyers can enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles and contribute positively to the environment while fulfilling their operational needs.
What Is the Historical Context of Waste Drums in B2B Supply?
The evolution of waste drums can be traced back to the early 20th century when the need for safe storage and transportation of hazardous materials became apparent. Initially, metal drums were the standard, but advances in materials science led to the introduction of plastic alternatives that offer benefits such as corrosion resistance and lighter weight. The increasing regulatory landscape around hazardous waste management has further propelled innovations in drum design, focusing on safety features and compliance with international standards.

Illustrative image related to waste drum
Today, waste drums are integral to diverse industries, including pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and energy, and their design continues to evolve to meet the challenges posed by modern waste management practices. As international regulations become more stringent, the demand for high-quality, compliant waste drums is expected to grow, highlighting the importance of understanding historical trends to navigate current and future market dynamics effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of waste drum
-
How do I choose the right waste drum for hazardous materials?
Selecting the appropriate waste drum involves understanding the type of hazardous materials you will be storing or transporting. Consider factors such as the chemical compatibility of the drum material, capacity requirements, and local regulatory compliance. For instance, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) drums are commonly used for chemical waste due to their resistance to various substances. Additionally, evaluate closure types—metal lever-locks or screw-on lids may provide different levels of security and ease of access. Consulting with suppliers can also offer insights into the best options for your specific needs. -
What are the different types of waste drums available for purchase?
Waste drums come in various materials and configurations, each suited for specific applications. Common types include plastic lab pack drums, metal drums, and fiber drums. Plastic drums are lightweight and resistant to chemicals, making them ideal for hazardous waste. Metal drums, while heavier, offer durability and are often used for bulk storage. Fiber drums are typically used for dry materials. When sourcing, assess the intended use, regulatory requirements, and whether the drum design facilitates easy handling and transport. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for waste drums?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of waste drum. Many manufacturers may set a MOQ ranging from 50 to 500 units, especially for specialized or customized drums. It’s important to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your operational requirements. Additionally, consider the impact of bulk ordering on pricing, shipping costs, and inventory management. -
How can I ensure compliance with international shipping regulations for waste drums?
To comply with international shipping regulations, familiarize yourself with the specific guidelines set forth by organizations such as the International Air Transport Association (IATA) and the International Maritime Organization (IMO). Ensure that your waste drums are properly labeled according to hazardous materials regulations, including UN identification numbers and hazard symbols. Partnering with a logistics provider experienced in hazardous materials can streamline compliance, as they will understand the necessary documentation and packaging requirements for safe transport. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for waste drums?
When vetting suppliers, assess their reputation, experience, and certifications in handling hazardous materials. Request references and check customer reviews to gauge reliability and service quality. Ensure that the supplier complies with relevant regulations and quality standards, such as ISO certifications. Additionally, inquire about their production capabilities, lead times, and after-sales support, as these factors can impact your procurement and ongoing relationship. -
Are customization options available for waste drums?
Many suppliers offer customization options for waste drums, including variations in size, color, and labeling. Customization can be particularly beneficial for branding purposes or to meet specific regulatory requirements. When discussing customization, clarify your needs regarding material specifications, closure types, and any required safety features. Be mindful that customized orders may have longer lead times and different pricing structures compared to standard products. -
What payment terms are typically offered for waste drum purchases?
Payment terms can vary widely between suppliers, often influenced by factors such as order size and buyer-supplier relationships. Common terms include upfront payment, net 30 or net 60 days, and letter of credit arrangements for larger orders. It is advisable to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and operational timelines. Always ensure that payment methods are secure and that you have a clear understanding of any penalties for late payments or changes in order quantities. -
How do I handle quality assurance for waste drums?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical when sourcing waste drums to ensure they meet safety and regulatory standards. Request documentation of quality control processes from suppliers, including testing procedures and material certifications. Conduct periodic inspections of received products to verify compliance with specifications. Additionally, establish a clear return policy for defective products and maintain open communication with suppliers to address any QA concerns promptly. Regularly reviewing supplier performance can help ensure ongoing compliance and quality standards are upheld.
Top 5 Waste Drum Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Justrite – Lab Pack Drums
Domain: eagle.justrite.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Lab Pack Drums, Plastic, designed for transporting bottles, cans, carboys, and non-leaking hazardous materials. Constructed from blow-molded, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) with UV inhibitors, these drums are durable, lightweight, weather and chemical resistant. They feature a screw-on lid and are ideal for safe storage, handling, and transportation of hazardous materials. Lab packs are not to b…
2. Alex’s Caves – Waste Drum
Domain: alexscaves.wiki.gg
Introduction: {“name”:”Waste Drum”,”renewable”:”Yes”,”stackable”:”Yes (64)”,”tool”:”N/A”,”blast_resistance”:”N/A”,”hardness”:”N/A”,”luminous”:”No”,”transparent”:”No”,”flammable”:”No”,”catches_fire_from_lava”:”No”,”description”:”Waste Drums are a naturally occurring block found in the Toxic Caves.”,”obtaining”:{“natural_generation”:”Found in various Toxic Ruins and scattered around the Toxic Caves.”,”mob_loot”:”…
3. Hazmat Resource – 55 Gallon Plastic Drum with Lid
Domain: hazmatresource.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: {“name”: “55 Gallon Plastic Drum with Lid – Decontamination Collection”, “price”: “$207.89”, “sku”: “1656MBBG”, “weight_capacity”: “551 lbs (250 kg)”, “weight”: “25 lbs”, “dimensions”: “22 × 24 × 38 in”, “material”: “High-density polyethylene (HDPE) with UV inhibitors”, “closure_type”: “Metal lever-lock band closure”, “inside_dimensions”: {“top_diameter”: “20 1/16 in (31 cm)”, “bottom_diameter”: “…
4. Gaiaca – Hazardous Waste Drums
Domain: gaiaca.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Hazardous waste drums are 55-gallon barrels used for storing and transporting hazardous wastes. They come in various sizes and materials, with different closure types. Key considerations for choosing hazardous waste drums include: suitability for contents (liquid vs. solid), material compatibility, proper labeling, compliance with federal regulations for transport, and proper emptying before reuse…
5. The Cary Company – 55 Gallon Open Head Reconditioned Steel Drums
Domain: thecarycompany.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Open Head Reconditioned Steel Drums, 55 Gallon, Unlined Cover, Lever Lock Fittings
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for waste drum
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Waste Drum Procurement?
In today’s global marketplace, strategic sourcing for waste drums is vital for businesses engaged in hazardous material management. By prioritizing quality, compliance, and sustainability, B2B buyers can significantly enhance operational efficiency and mitigate risks associated with hazardous waste. The importance of selecting the right type of waste drum—whether plastic lab packs or metal containers—cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts safety, regulatory compliance, and cost-effectiveness.
Moreover, understanding regional regulations and supplier capabilities across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe is crucial. Buyers must leverage strong supplier relationships and prioritize vendors who demonstrate a commitment to quality and environmental responsibility. This approach not only ensures compliance with local and international standards but also fosters innovation in waste management solutions.
As we look to the future, the demand for sustainable and efficient waste disposal solutions will only grow. International B2B buyers are encouraged to actively engage in strategic sourcing practices, ensuring their procurement processes are aligned with best practices in environmental stewardship and regulatory compliance. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your waste management strategies by investing in reliable waste drum solutions today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to waste drum
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.