Spur Gear Dimensions: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for spur gear dimensions
In today’s competitive landscape, international B2B buyers face the daunting challenge of sourcing spur gear dimensions that meet specific operational requirements while ensuring compatibility with diverse machinery and applications. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including countries like Saudi Arabia and Germany) continue to expand, the need for precision-engineered spur gears has never been more critical. This guide serves as an essential resource, offering a comprehensive overview of spur gear dimensions, including standard sizes, profile shift coefficients, and key calculations necessary for effective gear design.
Throughout this guide, we will explore various types of spur gears and their applications across multiple sectors, from automotive to manufacturing. Additionally, we will delve into supplier vetting processes, helping buyers identify reliable manufacturers that adhere to international quality standards. Cost considerations will also be examined, enabling informed budget planning and strategic sourcing decisions.
By providing actionable insights and practical information, this guide empowers B2B buyers to make knowledgeable purchasing decisions in a complex global market. Whether you are a purchasing manager or an engineer, understanding the intricacies of spur gear dimensions will not only enhance your procurement process but also support the long-term success of your projects.
Understanding spur gear dimensions Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Spur Gears | Simple design, no profile shift, easy to manufacture | General machinery, conveyor systems | Pros: Cost-effective, readily available. Cons: Limited customization options. |
| Profile Shifted Spur Gears | Allows for customization of tooth profile and center distance | Precision machinery, automotive | Pros: Enhanced performance, reduced undercut risk. Cons: More complex calculations required. |
| Rack and Pinion Gears | Translates rotational motion into linear motion | Robotics, automotive steering systems | Pros: Efficient linear motion transfer. Cons: Requires precise alignment for optimal performance. |
| Internal Spur Gears | Teeth are cut on the inside of a cylindrical shape | Gearboxes, differential systems | Pros: Compact design, high torque capacity. Cons: More challenging to manufacture and install. |
| Helical Spur Gears | Angled teeth for smoother operation and higher load capacity | Heavy machinery, industrial equipment | Pros: Quieter operation, higher load-bearing capacity. Cons: Higher cost due to complex design. |
What Are Standard Spur Gears and Their Applications?
Standard spur gears are characterized by their straightforward design, featuring teeth that are parallel to the axis of rotation. They are predominantly used in applications requiring basic gear transmission, such as conveyor systems and general machinery. Buyers appreciate their cost-effectiveness and availability; however, the lack of customization options can be a drawback for specialized applications.
How Do Profile Shifted Spur Gears Enhance Performance?
Profile shifted spur gears differ from standard gears by incorporating a profile shift, allowing for adjustments in tooth shape and center distance. This feature makes them suitable for precision applications like automotive and industrial machinery, where performance is critical. While they offer improved performance and reduced risk of undercutting, the complexity of their calculations can pose challenges for buyers needing quick solutions.
What Are Rack and Pinion Gears and Their Benefits?
Rack and pinion gears convert rotational motion into linear motion, making them essential in applications such as robotics and automotive steering systems. Their efficiency in transferring motion makes them a popular choice among manufacturers. However, precise alignment is crucial for optimal performance, which can complicate installation and maintenance.
Why Choose Internal Spur Gears for Compact Applications?
Internal spur gears feature teeth on the inside of a cylindrical shape, allowing them to mesh with external gears. This design is particularly beneficial in applications like gearboxes and differential systems where space is limited. Their ability to handle high torque makes them attractive, but the manufacturing complexity can lead to increased costs and installation challenges.
What Advantages Do Helical Spur Gears Offer?
Helical spur gears have angled teeth that provide smoother operation and higher load capacities compared to standard spur gears. They are commonly used in heavy machinery and industrial equipment due to their quieter operation and ability to handle greater loads. However, the increased complexity of their design results in higher costs, making them a consideration for buyers with specific performance needs.
Key Industrial Applications of spur gear dimensions
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of spur gear dimensions | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Transmission systems in vehicles | Enhanced power transmission and efficiency | Precision in dimensions, material quality, and compliance with industry standards |
| Manufacturing | Conveyor systems for material handling | Improved operational efficiency and reduced downtime | Customization options, load capacity, and durability under harsh conditions |
| Renewable Energy | Wind turbine gearboxes | Increased energy output and operational reliability | Resistance to environmental factors and high load tolerances |
| Construction | Heavy machinery and equipment | Enhanced performance and longevity in demanding environments | Size specifications, weight considerations, and compatibility with existing systems |
| Mining | Equipment for ore extraction and processing | Improved productivity and reduced maintenance costs | High strength materials, precise gear ratios, and adaptability to different machinery |
How Are Spur Gear Dimensions Utilized in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, spur gear dimensions are crucial for the design and functionality of transmission systems. These gears facilitate the effective transfer of power from the engine to the wheels, ensuring smooth operation and efficiency. Buyers in this sector require precise dimensions to meet stringent performance standards and regulatory compliance. Additionally, they must consider factors like material strength and heat resistance to withstand the demanding conditions of vehicle operation.
What Role Do Spur Gear Dimensions Play in Manufacturing Applications?
In manufacturing, spur gears are integral to conveyor systems that transport materials across various processes. The dimensions of these gears dictate their ability to handle specific loads and speeds, directly impacting operational efficiency. Buyers must prioritize gears with accurate dimensions that can be customized to fit existing machinery while ensuring durability against wear and tear. This attention to detail can significantly minimize downtime and enhance productivity.
How Are Spur Gear Dimensions Applied in Renewable Energy?
In the renewable energy sector, particularly in wind turbines, spur gear dimensions are vital for gearboxes that convert wind energy into usable power. The precise calculations of gear dimensions ensure optimal energy transfer and operational reliability. International buyers should focus on sourcing gears that can withstand environmental stresses and provide high load tolerances. This helps maximize energy output and minimizes maintenance needs, essential for maintaining competitive advantage.
What Importance Do Spur Gear Dimensions Hold in Construction Equipment?
For construction machinery, spur gear dimensions are essential for enhancing the performance of heavy equipment. These gears are designed to handle high loads and provide reliable operation in challenging environments. Buyers should consider specific size requirements and weight specifications to ensure compatibility with existing systems. Furthermore, selecting gears made from robust materials can lead to increased longevity and reduced operational costs, critical factors in the construction industry.
Why Are Spur Gear Dimensions Critical in Mining Operations?
In mining, spur gears are used in equipment designed for ore extraction and processing. The precise dimensions of these gears are vital for ensuring efficient power transmission and minimizing wear and tear under extreme conditions. Buyers in this sector must focus on sourcing gears made from high-strength materials that can accommodate the unique demands of mining operations. This focus on quality can lead to improved productivity and lower maintenance expenses, which are crucial for profitability.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘spur gear dimensions’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inaccurate Gear Sizing Leading to Operational Failures
The Problem: A common challenge faced by B2B buyers when selecting spur gears is the difficulty in accurately sizing gears for specific applications. For instance, a manufacturing company in Germany may order spur gears based on estimated dimensions, only to find that the gears do not mesh properly, resulting in operational inefficiencies and costly downtime. This issue can arise from miscalculations in module size, number of teeth, or pressure angle, which are crucial for achieving the correct center distance and load capacity.
Illustrative image related to spur gear dimensions
The Solution: To mitigate sizing inaccuracies, B2B buyers should adopt a systematic approach to gear dimensioning. Begin by utilizing reliable gear calculation tools that allow for precise input of parameters such as module, number of teeth, and pressure angle. It’s beneficial to consult technical resources or gear manufacturers who provide detailed specifications and calculators. Additionally, implementing a verification process—where dimensions are cross-checked against application requirements—can prevent errors. Engaging with a knowledgeable supplier who can assist with custom gear solutions may also ensure that the dimensions are accurately tailored to specific machinery needs.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Understanding Gear Standards and Specifications
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter confusion surrounding the myriad of gear standards and specifications, such as ISO, DIN, or AGMA, particularly when sourcing spur gears internationally. A buyer from Saudi Arabia might struggle to interpret these standards, leading to the selection of gears that do not meet their operational or regulatory needs. This can result in compatibility issues with existing machinery or even compliance failures.
The Solution: To navigate the complexities of gear standards, buyers should invest in training or workshops focused on gear specifications and international standards. Establishing a solid relationship with suppliers who have expertise in global standards can also provide clarity. Suppliers should be able to explain how their products meet specific standards and how those relate to the buyer’s operational context. Furthermore, utilizing standardized gear catalogs can simplify the selection process, ensuring that buyers can easily identify and compare gear specifications that align with their requirements.
Scenario 3: Misalignment of Supplier Capabilities with Project Needs
The Problem: Another frequent pain point arises when a B2B buyer’s project demands exceed the capabilities of their selected gear supplier. For example, a company in South America might require custom spur gears with precise dimensions for a specialized application but finds that their supplier can only provide off-the-shelf options. This misalignment can lead to project delays, increased costs, and a compromised final product.
Illustrative image related to spur gear dimensions
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers before initiating a partnership. This includes evaluating their manufacturing capabilities, expertise in custom gear production, and past project success stories. Engaging in upfront discussions about specific project requirements and potential customizations can help clarify whether a supplier can meet those needs. Additionally, it’s advisable to request samples or prototypes to validate that the supplier can deliver the necessary precision and quality. Establishing clear communication channels and project timelines will also facilitate a smoother collaboration, allowing for adjustments as needed throughout the project lifecycle.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for spur gear dimensions
What Are the Key Materials for Spur Gear Dimensions in B2B Applications?
Selecting the right material for spur gears is critical for ensuring optimal performance and longevity in various applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in spur gear manufacturing, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Steel Perform as a Material for Spur Gears?
Steel is the most commonly used material for spur gears due to its excellent mechanical properties. It typically offers high strength, good wear resistance, and the ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. Carbon steel is particularly favored for its balance of toughness and machinability, while alloy steels can provide enhanced properties through heat treatment.
Pros: Steel gears are durable and can handle heavy loads, making them suitable for high-stress applications. They are also relatively cost-effective and widely available.
Cons: However, steel gears can be prone to corrosion if not properly treated or coated. They may also require more complex manufacturing processes, such as heat treatment, which can increase production time and costs.
Impact on Application: Steel gears are compatible with a wide range of media, but their susceptibility to rust necessitates careful selection in corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial, especially in regions like Germany and Saudi Arabia, where quality assurance is paramount. Buyers should also consider the availability of steel grades that meet local regulations.
What Role Does Plastic Play in Spur Gear Manufacturing?
Plastic gears, often made from materials such as nylon or acetal, are gaining popularity due to their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. They are particularly effective in applications where noise reduction is essential, such as in consumer electronics.
Pros: Plastic gears are less expensive to produce and can be manufactured with complex geometries. They also exhibit good chemical resistance and are less prone to rust.
Illustrative image related to spur gear dimensions
Cons: The main limitations include lower strength and durability compared to metal gears. They may not perform well under high loads or extreme temperatures.
Impact on Application: Plastic gears are ideal for low-load applications and environments where moisture or chemicals are present. However, they may not be suitable for heavy-duty machinery.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastic materials comply with relevant standards, such as ISO or JIS, particularly in regions like South America where specific certifications may be required.
Illustrative image related to spur gear dimensions
How Do Bronze and Brass Compare for Spur Gear Applications?
Bronze and brass are often used for spur gears in applications requiring excellent wear resistance and low friction. These materials are particularly effective in marine environments due to their corrosion resistance.
Pros: Both materials provide good machinability and are less likely to seize under load. They also have self-lubricating properties, which can reduce the need for additional lubrication.
Cons: The primary drawback is the cost; bronze and brass are generally more expensive than steel or plastic. Additionally, they may not support as high a load as steel gears.
Impact on Application: Bronze and brass gears are well-suited for applications involving water or other corrosive media, making them ideal for marine and chemical processing industries.
Illustrative image related to spur gear dimensions
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM and DIN standards is essential for ensuring quality and performance in international markets, particularly in Europe and the Middle East.
What Are the Advantages of Using Composite Materials for Spur Gears?
Composite materials, such as reinforced plastics or carbon fiber, are emerging as alternatives for spur gears, offering unique advantages in specific applications.
Pros: Composites can be engineered to provide high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance. They also offer design flexibility and can reduce noise and vibration.
Cons: However, composites can be more expensive and may require specialized manufacturing techniques. Their performance under high temperatures and loads can vary significantly based on the formulation.
Impact on Application: Composites are suitable for specialized applications, such as aerospace and automotive, where weight savings and performance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that composite materials meet industry-specific standards and performance criteria, particularly in regions with strict regulations like Germany.
Summary of Material Selection for Spur Gear Dimensions
| Material | Typical Use Case for spur gear dimensions | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy machinery, automotive | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Plastic | Consumer electronics, low-load applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength | Low |
| Bronze/Brass | Marine and chemical processing | Excellent wear resistance | Higher cost | High |
| Composite | Aerospace, automotive | High strength-to-weight ratio | Specialized manufacturing required | High |
This comprehensive guide provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for spur gears, ensuring informed decisions that align with specific application needs and regional compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for spur gear dimensions
What Are the Typical Manufacturing Processes for Spur Gear Dimensions?
The manufacturing of spur gears involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the precision and functionality of the final product. Understanding these processes can help international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, make informed decisions when sourcing gears for their applications.
Which Materials Are Commonly Used for Spur Gears?
The choice of material is foundational in spur gear manufacturing. Common materials include carbon steel, alloy steel, and sometimes non-ferrous metals like aluminum or plastic, depending on the application requirements. Carbon steel is often selected for its strength and wear resistance, while alloy steels are used for high-load applications due to their enhanced mechanical properties. Plastic gears are suitable for lightweight applications or where noise reduction is critical.
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process?
-
Material Preparation: The process begins with the selection and preparation of raw materials. This can involve cutting the metal into manageable sizes and ensuring that it meets specific mechanical properties through heat treatment or alloying.
-
Forming Techniques: This stage typically involves several methods:
– Machining: This includes processes like milling, turning, and grinding, which help achieve the precise tooth dimensions required for spur gears. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is often employed for its accuracy and efficiency.
– Hobbing: A specialized process for cutting the gear teeth. Hobbing machines use a rotating cutter to create the gear profile, allowing for high production rates.
– Shaping: An alternative method to hobbing, shaping can be more suitable for gears with larger diameters or specific tooth profiles. -
Assembly: If the spur gear is part of a larger assembly, this stage involves integrating it with other components. Careful alignment is crucial to ensure smooth operation and minimize wear.
-
Finishing Processes: After the basic shape is achieved, gears often undergo finishing processes like:
– Heat Treatment: To enhance hardness and wear resistance.
– Surface Finishing: Techniques such as grinding or polishing to achieve the desired surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
– Coating: Applying protective coatings can improve corrosion resistance and reduce friction.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Spur Gear Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in ensuring that spur gears meet international standards and customer specifications. For B2B buyers, understanding QA practices can aid in evaluating suppliers effectively.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Many international standards govern gear manufacturing, with ISO 9001 being the most recognized for quality management systems. Compliance with this standard indicates that a manufacturer follows best practices in quality control and continuous improvement. Other industry-specific certifications may include:
– CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, ensuring they meet safety and environmental protection standards.
– API Standards: Relevant for gears used in oil and gas applications, focusing on safety and reliability.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Ensuring that materials meet specified standards can prevent defects later in the production process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, continuous monitoring is crucial. This may involve checking dimensions and tolerances at various stages of machining and forming to ensure consistency and adherence to specifications.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once manufacturing is complete, a final inspection ensures that the gears meet all design specifications and quality standards. This may include dimensional checks, tooth profile inspections, and surface quality assessments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential to ensure that they receive reliable products. Here are several actionable steps:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insight into the manufacturer’s quality processes, including equipment, staff training, and adherence to standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed reports on previous quality control inspections can reveal a manufacturer’s track record. This includes information on defect rates, corrective actions taken, and compliance with standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality management practices and product quality.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Control?
Testing methods for spur gears can vary based on the application, but some common approaches include:
-
Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing calipers, micrometers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to verify that the gear dimensions meet specified tolerances.
-
Load Testing: Simulating operational conditions to ensure that the gear can withstand expected loads without failure.
-
Surface Roughness Measurement: Assessing the surface finish to ensure it meets application requirements, which can affect performance and longevity.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Methods like ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection can detect internal flaws without damaging the gear.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Control?
International buyers must be aware of regional differences in quality standards and certifications. In Europe, for instance, the CE marking is mandatory for many products, while in the Middle East and Africa, different compliance requirements may exist. Buyers should also consider language barriers and cultural differences that may affect communication regarding quality expectations.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for spur gears is essential for B2B buyers to ensure they are sourcing high-quality components that meet their operational needs. By focusing on material selection, manufacturing techniques, and thorough quality control measures, buyers can mitigate risks and enhance the reliability of their applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘spur gear dimensions’
Introduction
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure spur gear dimensions. Understanding the precise specifications and requirements for spur gears is essential for ensuring compatibility and performance in your machinery. By following this step-by-step guide, you can streamline your sourcing process and make informed purchasing decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your sourcing process. This includes determining the module, number of teeth, pressure angle, and profile shift coefficient. Accurate specifications help ensure the gears will perform optimally in their intended application and reduce the likelihood of costly errors later on.
- Module (m): This is a measure of the gear tooth size and should be consistent with your machinery requirements.
- Number of Teeth (z): Ensure you calculate the appropriate number of teeth to achieve the desired gear ratio and performance.
Step 2: Identify Application Requirements
Understanding the specific application for which the spur gears will be used is critical. Different applications may require different gear characteristics, such as load capacity, speed, and environment.
Illustrative image related to spur gear dimensions
- Load Capacity: Consider the maximum load the gears will bear and choose materials that can withstand these forces.
- Operating Environment: Factors like temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals can influence material selection.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Before committing to a supplier, assess their manufacturing capabilities and experience with spur gears. A reliable supplier should have a robust production process and quality control measures in place.
- Certifications: Look for suppliers with ISO certifications or other industry-related credentials to ensure compliance with international standards.
- Experience: Consider suppliers with a proven track record in producing spur gears for your specific industry.
Step 4: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you have identified potential suppliers, request detailed quotations. This should include pricing, lead times, and any additional costs for tooling or customization.
- Breakdown of Costs: Ensure the quotation provides a clear breakdown of costs, including material, manufacturing, and shipping fees.
- Lead Times: Confirm the expected lead times to avoid disruptions in your production schedule.
Step 5: Verify Quality Assurance Processes
Quality assurance is a vital aspect of gear manufacturing. Ensure that your supplier employs rigorous testing and quality control procedures throughout their manufacturing process.
- Testing Methods: Inquire about the specific testing methods used to verify gear dimensions and performance, such as dimensional inspections and material testing.
- Quality Control Documentation: Request documentation that outlines the quality control measures in place, including any inspection reports from previous orders.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support
Strong after-sales support can significantly impact your overall experience with a supplier. Evaluate the level of support offered, including warranty terms and technical assistance.
- Warranty: Understand the warranty terms for the gears, including what is covered and the duration.
- Technical Support: Confirm whether the supplier provides ongoing technical support to assist with installation or troubleshooting.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication with your supplier is crucial for a successful procurement process. Establish a clear communication plan to address any questions or concerns throughout the sourcing journey.
- Regular Updates: Agree on a schedule for regular updates regarding production status and delivery timelines.
- Point of Contact: Designate a specific contact person on both sides to streamline communication and facilitate quick resolution of any issues.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing spur gear dimensions, ensuring that they procure the right products for their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for spur gear dimensions Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing for sourcing spur gear dimensions is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The cost components and price influencers can significantly affect procurement strategies and overall project budgets.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Spur Gear Sourcing?
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in spur gear manufacturing is the raw materials used, typically high-strength alloys or specialized plastics. The choice of material affects both performance and durability, influencing the final price.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages for skilled workers involved in the machining and assembly of gears. Regions with lower labor costs can offer competitive pricing, but the trade-off may be in the quality of craftsmanship.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, facility costs, and administrative expenses that contribute to the production process. Efficient production facilities can lower overhead costs, thus reducing the overall price.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling and machinery for producing gears can be substantial. Custom tooling for unique specifications can further increase costs. Buyers should inquire about tooling amortization in pricing to assess long-term value.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are essential to ensure the gears meet specified tolerances and standards. This adds to the cost but is critical for reliability, especially in high-stakes applications.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary widely based on the shipping method, distance, and import/export regulations. For international buyers, understanding Incoterms is vital to clarify who bears these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and risks. This margin can vary based on market demand, competition, and the supplier’s positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Spur Gear Costs?
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to optimize pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom gears tailored to specific applications may incur additional design and manufacturing costs. Standardized gears are generally more cost-effective.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (like ISO or API) can increase costs but also enhance reliability. Buyers must balance cost and quality based on their operational needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, production capabilities, and experience in the industry can influence pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to perceived reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping can help buyers manage costs effectively. Different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) dictate who is responsible for various shipping expenses.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help Optimize Costs?
-
Clarify Requirements: Be explicit about specifications and performance requirements to prevent misunderstandings that could lead to increased costs.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but the long-term costs associated with maintenance, replacement, and potential downtime.
-
Leverage Competition: Obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to foster competition, which can lead to better pricing and terms.
-
Build Relationships: Long-term partnerships with suppliers can result in better pricing, improved service, and priority during peak times.
What Pricing Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and local regulations that can impact pricing. Additionally, cultural differences in negotiation styles can affect discussions. Being well-informed about regional market conditions will empower buyers to make strategic decisions that align with their procurement goals.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for spur gears can vary significantly based on the factors outlined above. The information provided serves as a general guide and is subject to change based on market conditions and specific buyer requirements. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and up-to-date pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing spur gear dimensions With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Spur Gear Dimensions
In the realm of mechanical design and engineering, spur gears are widely recognized for their simplicity and effectiveness. However, various alternative solutions exist that can achieve similar goals in power transmission and motion control. Understanding these alternatives can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their specific applications.
Comparison Table of Spur Gear Dimensions and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Spur Gear Dimensions | Helical Gears | Worm Gears |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency; low backlash | Better load distribution; smoother operation | High torque transmission; compact design |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to complexity | Moderate cost; depends on material |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward design and manufacturing | More complex; requires precise alignment | Requires specific mounting and alignment |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance needs | Moderate; depends on load conditions | Regular lubrication needed |
| Best Use Case | General applications, moderate loads | Applications requiring high speed and load | High torque applications, space-constrained environments |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Helical Gears
Helical gears offer a significant advantage in performance due to their design, which allows for smoother engagement between teeth. This results in less noise and vibration compared to spur gears. However, the complexity of their manufacturing and the need for precise alignment can lead to higher costs. Helical gears are ideal for applications requiring high speed and load, such as automotive transmissions and industrial machinery.
Worm Gears
Worm gears are particularly advantageous in applications where high torque transmission is required in a compact space. They excel in scenarios that demand a significant reduction in speed while increasing torque. However, the design necessitates specific mounting and alignment, which can complicate installation. Additionally, worm gears typically require regular lubrication to maintain optimal performance. They are best suited for applications like conveyor systems and lifts, where space constraints are a critical consideration.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Gear Solution
When selecting the appropriate gear solution, B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their specific needs, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and ease of implementation. Spur gears may be the most straightforward choice for general applications, while helical and worm gears offer specialized advantages that could justify their higher costs in specific contexts. By considering factors such as load requirements, operating environment, and maintenance capabilities, buyers can make strategic decisions that align with their operational goals.
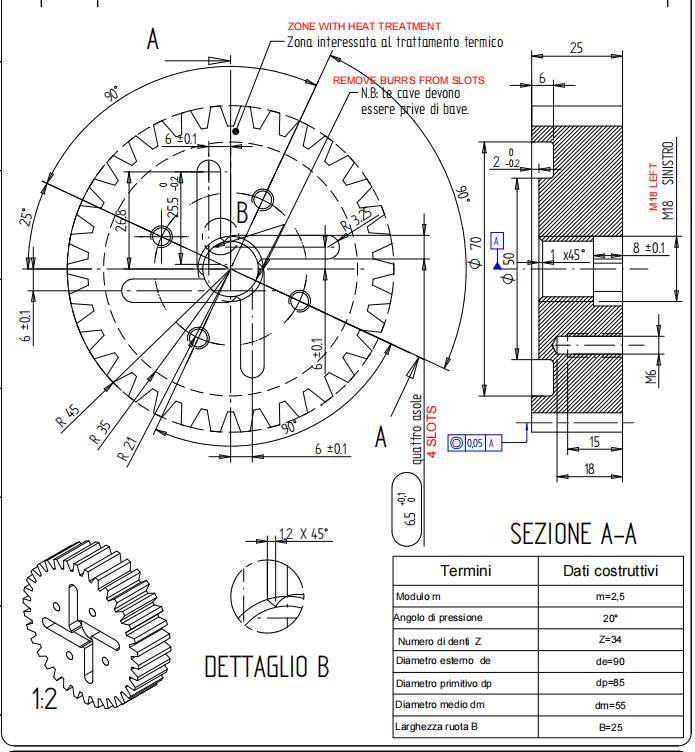
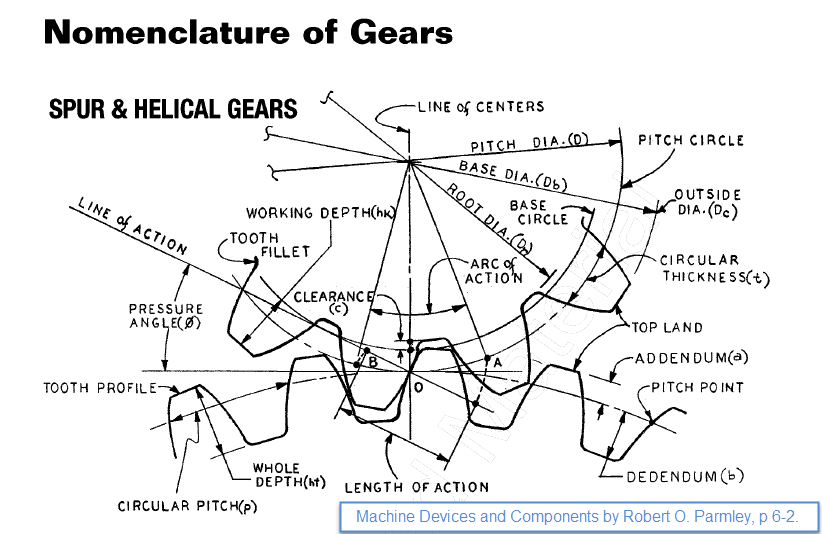
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for spur gear dimensions
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Spur Gear Dimensions?
Understanding the essential specifications of spur gears is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when optimizing performance and ensuring compatibility in mechanical systems. Here are some critical properties to consider:
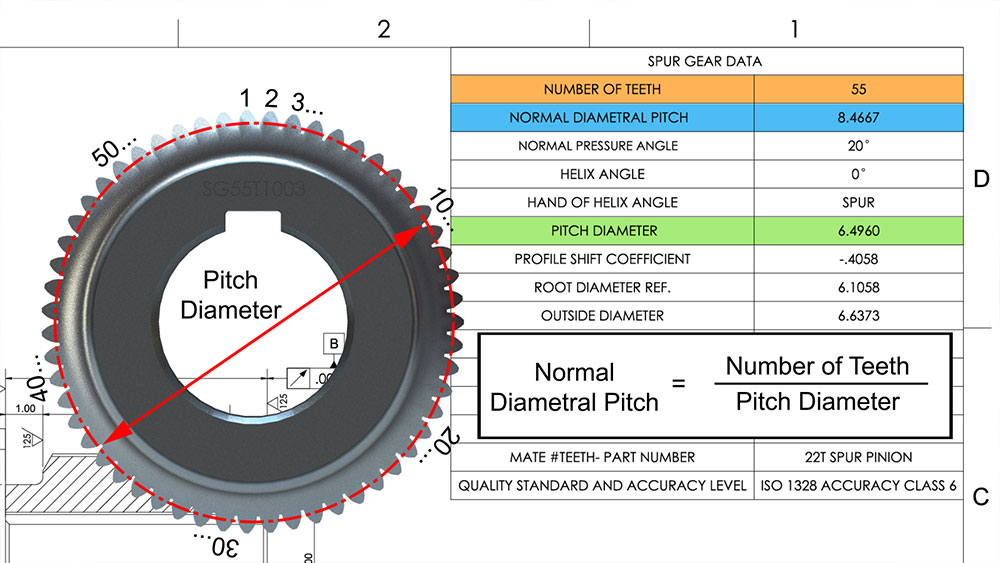
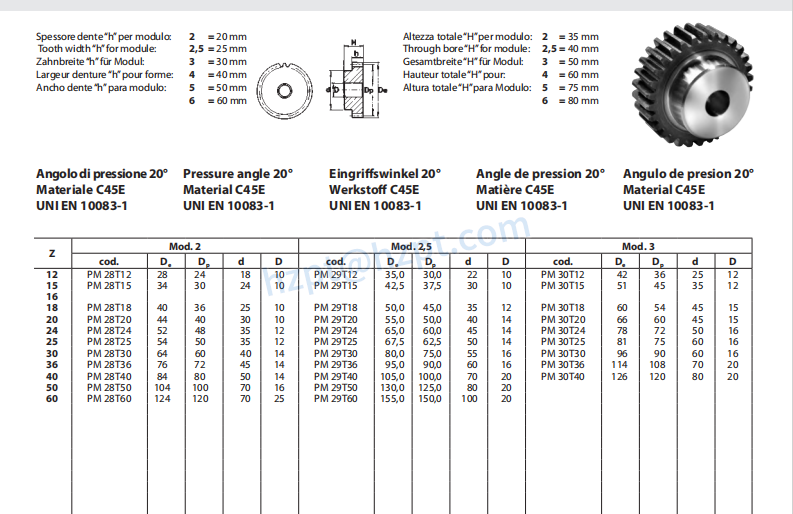
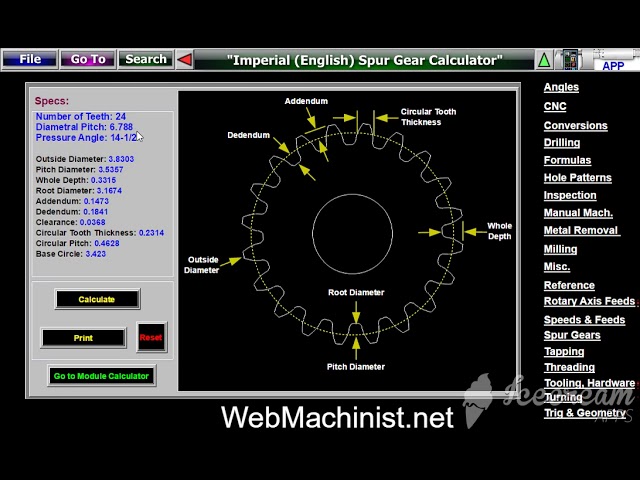
1. Module (m)
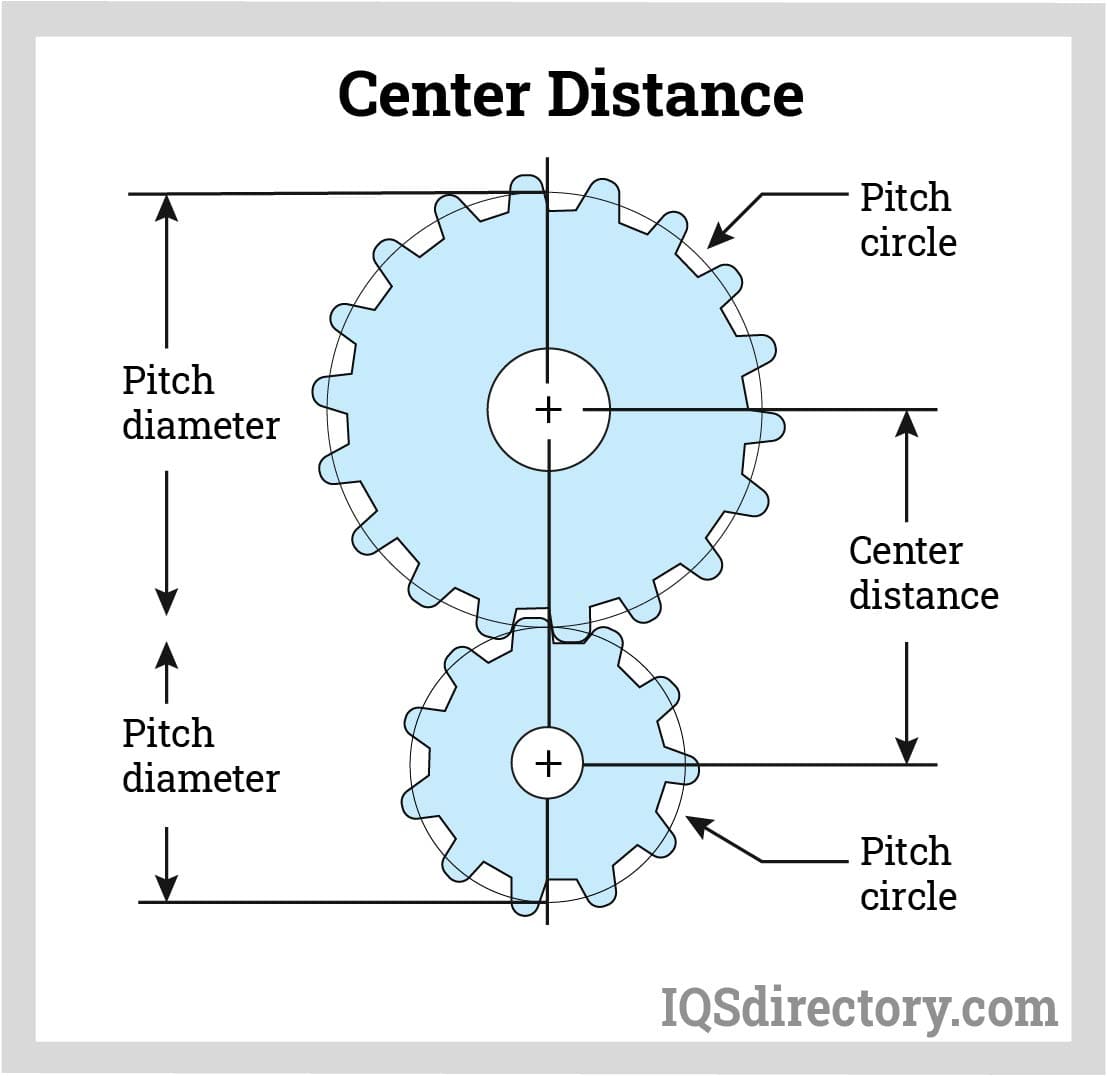
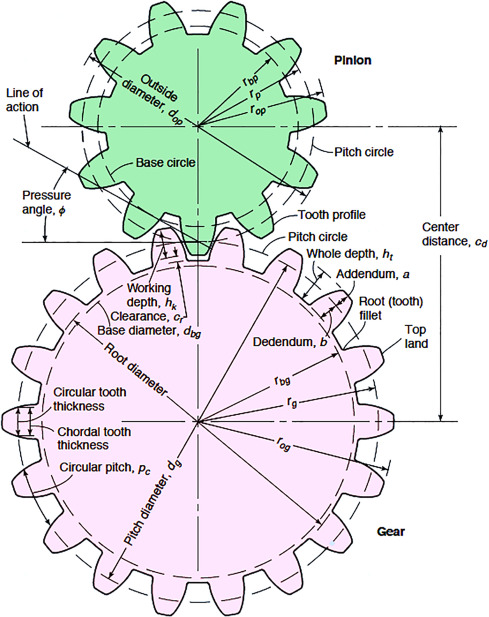
The module is a fundamental parameter that defines the size of the gear teeth. It is calculated as the ratio of the pitch diameter to the number of teeth. A larger module indicates larger teeth, which can affect strength and load capacity. For B2B buyers, selecting the correct module ensures compatibility with existing gear systems, which is vital for reducing operational downtime and maintenance costs.
Illustrative image related to spur gear dimensions
2. Number of Teeth (z)
This specification directly influences the gear’s torque and speed characteristics. A gear with more teeth will typically result in a slower speed but higher torque output, while fewer teeth can provide faster speeds but lower torque. Buyers must carefully assess the required torque and speed of their machinery to select gears that meet operational demands, ensuring efficiency and performance.
3. Pressure Angle (α)
The pressure angle affects the shape of the gear teeth and their ability to transmit force. Common angles are 20° and 14.5°. A higher pressure angle can lead to greater load-carrying capacity, making it essential for heavy-duty applications. Understanding the pressure angle helps buyers determine the gear’s suitability for specific applications, impacting the overall efficiency of mechanical systems.
4. Tolerance and Fit
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in gear manufacturing. Proper tolerances ensure that gears mesh correctly, minimizing wear and maximizing efficiency. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can guarantee the required tolerances, as this affects the longevity and reliability of the gear systems.
5. Material Grade
The material from which the spur gear is made influences its strength, durability, and suitability for various applications. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and plastic composites. Selecting the right material grade is critical for achieving the desired balance between performance and cost, particularly in environments exposed to high stress or corrosive conditions.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Spur Gears?
In the B2B landscape, understanding industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms associated with spur gears:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For buyers, working with OEMs ensures that they receive high-quality products that meet industry standards, which is crucial for maintaining equipment reliability.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for buyers, as it impacts inventory management and capital investment. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs while also considering cost-efficiency.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing information for specific products or services. It is an essential step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare costs and terms across different suppliers, thus enabling informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms helps buyers navigate shipping logistics, risk management, and cost allocation effectively.
5. Profile Shift Coefficient (x)
This term relates to the modification of gear tooth profiles to optimize performance. Adjusting the profile shift can help in achieving desired tooth contact patterns and reducing undercutting. Buyers should be aware of this specification when selecting gears to ensure optimal performance in their applications.
Conclusion
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, grasping the technical properties and trade terminology associated with spur gear dimensions is crucial. These insights will facilitate informed decisions, ensuring that the selected gears meet both operational requirements and budget constraints.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the spur gear dimensions Sector
What Are the Current Market Trends for Spur Gear Dimensions in B2B?
The global spur gear dimensions market is experiencing a transformative phase driven by technological advancements and increasing demand across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. Key trends include the integration of automation and Industry 4.0 technologies, which necessitate precise gear dimensions for efficient machinery operation. In regions like Europe and the Middle East, investments in infrastructure and renewable energy projects are further propelling the demand for high-quality spur gears. Additionally, suppliers are increasingly offering custom solutions to meet specific application needs, enhancing the competitive landscape for international buyers.
Emerging technologies such as 3D printing and advanced materials are revolutionizing the manufacturing processes of spur gears, allowing for lighter, stronger, and more efficient designs. This is particularly relevant for B2B buyers from Africa and South America, where local industries are looking to modernize their equipment to improve productivity. Furthermore, the rising importance of digital tools for sourcing, including AI-driven platforms, is helping businesses streamline procurement processes and access a broader range of suppliers, thereby increasing market competitiveness.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing Spur Gear Procurement?
Sustainability has become a pivotal focus for B2B buyers in the spur gear dimensions sector. Companies are increasingly aware of their environmental impact, driving a shift towards ethical sourcing practices. Suppliers are now expected to adhere to stringent environmental regulations and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability through certifications such as ISO 14001. For international buyers, particularly those in Europe and the Middle East, opting for suppliers with green certifications can enhance brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
The use of sustainable materials in spur gear production is also gaining traction. Manufacturers are exploring alternatives like recycled metals and bio-based composites, which not only reduce environmental footprints but can also lower production costs in the long run. As the demand for eco-friendly products rises, buyers are encouraged to prioritize suppliers that implement sustainable practices, thus contributing to a circular economy within the manufacturing sector. This approach not only mitigates risks associated with regulatory compliance but also aligns with global sustainability goals, making it a vital consideration for modern B2B procurement strategies.
What Historical Developments Have Shaped the Spur Gear Dimensions Market?
The evolution of spur gears can be traced back to ancient mechanical devices, where they were utilized for simple machines. Over centuries, the designs and manufacturing techniques have significantly advanced, particularly during the Industrial Revolution, which saw a surge in demand for more precise and durable gears. The introduction of standardized gear dimensions allowed for greater interchangeability, which is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
In the 20th century, advancements in materials science and computer-aided design (CAD) facilitated the development of complex gear systems, leading to improved efficiency and performance. As industries expanded globally, the need for reliable and consistent spur gear dimensions became critical in ensuring operational efficiency across various applications. Today, the sector continues to evolve, driven by technological innovation and the increasing importance of sustainability, setting the stage for future advancements in gear design and manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of spur gear dimensions
-
How do I solve sizing issues when selecting spur gears for my application?
To address sizing issues, start by determining the required specifications: module, number of teeth, and pressure angle. Use these parameters to calculate the reference diameter, center distance, and other critical dimensions. If standard options do not fit, consider customizing the gears to meet specific operational needs. Collaborating with a reliable supplier who understands your application can also help ensure optimal gear performance. -
What is the best material for spur gears used in high-load applications?
For high-load applications, steel is often the preferred material due to its strength and durability. Alloy steels, such as 4140 or 4340, can offer enhanced toughness and fatigue resistance. Additionally, surface treatments like carburizing or nitriding can further improve wear resistance. For applications requiring lower weight, consider aluminum or high-strength plastics, but ensure they meet the load and durability requirements of your application. -
What are the common dimensions I should consider when sourcing spur gears?
Key dimensions to consider include the module, number of teeth, pressure angle, and center distance. The module is crucial for determining gear size, while the number of teeth affects the gear ratio. Additionally, understanding the tip and root diameters is essential for ensuring proper meshing with other gears. Always verify these dimensions against your specifications to avoid compatibility issues. -
How can I ensure the quality of spur gears when sourcing from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, request certifications such as ISO 9001 from suppliers, which demonstrate adherence to quality management standards. Additionally, inquire about their manufacturing processes, material sourcing, and quality control measures. Consider requesting samples for testing before placing large orders. Establishing a clear communication channel for quality expectations can also enhance the relationship with the supplier. -
What customization options are available for spur gears?
Customization options for spur gears include variations in size, material, tooth profile, and surface treatments. Suppliers may offer services like profile shifting or modifications to the pressure angle to improve performance in specific applications. Discuss your requirements in detail with the supplier to explore tailored solutions that can enhance efficiency and longevity in your operational context. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for spur gears?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on factors such as production methods and material types. Typically, MOQs range from 50 to 500 units for standard spur gears. For custom designs, the MOQ may be higher due to setup costs. Always clarify MOQs during negotiations to align with your project requirements and budget constraints. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing spur gears internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases often include options like advance payment, letters of credit, or net payment terms ranging from 30 to 90 days. The specific terms may depend on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. Discuss and negotiate payment methods that ensure both parties are comfortable, and consider the impact of currency fluctuations on pricing. -
How should I handle logistics and shipping for spur gear orders?
When managing logistics, consider the supplier’s location and shipping methods available. Discuss shipping costs, delivery times, and responsibilities for customs clearance upfront. It’s advisable to work with a freight forwarder who can navigate international shipping complexities. Ensure that your order is properly packaged to prevent damage during transit and confirm insurance options to mitigate risks.
Top 5 Spur Gear Dimensions Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. KHK – Gear Dimension Calculation
Domain: khkgears.net
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Calculation of Gear Dimensions | KHK
– Product Categories: Spur Gears, Worm Gears, Bevel Gears, Gear Rack, Helical Gears, Miter Gears, Plastic Gears, Screw Gears, Internal Gears, Bevel Gearbox, Other Products.
– Key Specifications for Gear Dimensions:
– Module (m)
– Number of Teeth (z)
– Pressure Angle (α)
– Profile Shift Coefficient (x)
– Types of Gears Discussed:
– Spur Gears: Simpl…
2. Evolvent Design – Gear Dimensions Calculator
Domain: evolventdesign.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Gear Dimensions Calculator allows users to calculate key dimensions for external spur gears including pitch diameter, root diameter, and outer diameter. Users input gear parameters such as tooth count, pitch (module), and pressure angle. The calculator generates tooth dimensions: addendum, dedendum, working depth, and whole depth. Units available are mm (Module) and 1/inch (Diametral Pitch). Commo…
3. WM Berg – Spur Gear Measurement Guide
Domain: wmberg.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Spur Gear Measurement Guide includes definitions and equations for key measurements: Pitch, Pitch Diameter, Pitch Circle, Number of Teeth, Gear Module, Diametral Pitch, Outside Diameter, Center Distance, Addendum, Dedendum, Whole Depth, Pressure Angle, Face Width, and Backlash. Each measurement has specific uses in gear design and calculations, such as determining gear ratios, assessing gear stren…
4. Reddit – Gear Module and Specifications
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Module: 2, Pitch Circle Diameter: 50mm (first gear), Pitch Circle Diameter: 20mm (second gear), Gear Ratio: 2.5:1, Pressure Angle: 20 degrees.
5. Maedler – Plastic Gear 48 Teeth
Domain: maedlernorthamerica.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: {‘part_number’: ‘29811048’, ‘material’: ‘Plastic (POM black)’, ‘tooth_quality’: 8, ‘surface’: ‘Blank’, ‘module’: 3, ‘hub’: ‘One sided’, ‘number_of_teeth’: 48, ‘tooth_width_mm’: 30, ‘outer_diameter_mm’: 150, ‘pitch_circle_diameter_mm’: 144, ‘hub_length_mm’: 20, ‘hub_diameter_mm’: 95, ‘bore_mm’: 20, ‘max_torque_Nm’: 63.8, ‘weight_g’: 880, ‘price_usd’: 130.05}
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for spur gear dimensions
In summary, understanding spur gear dimensions is critical for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their machinery and production processes. The strategic sourcing of these components can lead to improved operational efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced product reliability. By focusing on essential specifications such as module, number of teeth, and pressure angle, buyers can ensure they select the most suitable gears for their applications.
As the global market continues to expand, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for high-quality spur gears will only increase. Companies that prioritize strategic sourcing will not only gain a competitive edge but also foster long-term partnerships with suppliers who can meet their unique needs.
Illustrative image related to spur gear dimensions
Looking ahead, international buyers are encouraged to leverage data-driven insights and market trends to make informed decisions. By embracing innovation and adopting best practices in gear selection, organizations can position themselves for success in the evolving landscape of industrial machinery. Take the next step in your sourcing journey today and explore the vast opportunities available in the spur gear market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
Illustrative image related to spur gear dimensions
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.