A Deep Dive into Automatic Assembly Line Manufacturers Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for automatic assembly line manufacturers
In the ever-evolving landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing automatic assembly line manufacturers has emerged as a critical challenge for businesses looking to enhance productivity and efficiency. With diverse applications spanning industries—from automotive and electronics to food processing and medical supplies—companies face the daunting task of identifying suppliers that not only meet their technical requirements but also align with their operational goals. This comprehensive guide serves as a vital resource for international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Brazil and Nigeria.
Within this guide, you will find an in-depth exploration of various types of assembly lines, ranging from traditional conveyor systems to advanced robotic automation. We delve into the nuances of supplier vetting, providing actionable insights on evaluating potential partners based on their expertise, product offerings, and customer support capabilities. Additionally, we analyze cost considerations, enabling you to make informed financial decisions that align with your budget and project timelines.
By navigating this complex market with our structured approach, you will be empowered to make strategic purchasing decisions that not only enhance your production capabilities but also position your business for long-term success in a competitive global arena. Whether you are looking to optimize existing operations or invest in new technologies, this guide will be your trusted companion in the quest for excellence in automatic assembly line solutions.
Understanding automatic assembly line manufacturers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Robotic Assembly Lines | High integration of robotics for precision and speed | Automotive, Electronics, Heavy Machinery | Pros: High efficiency, reduced labor costs. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Conveyor Belt Systems | Use of conveyor belts to transport products between stations | Food Processing, Packaging, Assembly | Pros: Streamlined workflow, scalability. Cons: Limited flexibility for product changes. |
| Automated Screwdriver Systems | Automated insertion of screws with various configurations | Electronics, Automotive, Furniture | Pros: Increased accuracy, reduced manual labor. Cons: Maintenance complexity. |
| Collaborative Robots (Cobots) | Designed to work alongside human operators safely | Small Assembly, Electronics, Medical Devices | Pros: Enhanced safety, flexibility. Cons: Slower than fully automated systems. |
| Custom Automation Solutions | Tailored systems for specific production needs | Specialized Manufacturing, Aerospace | Pros: Optimized for unique requirements. Cons: Longer lead times and higher costs. |
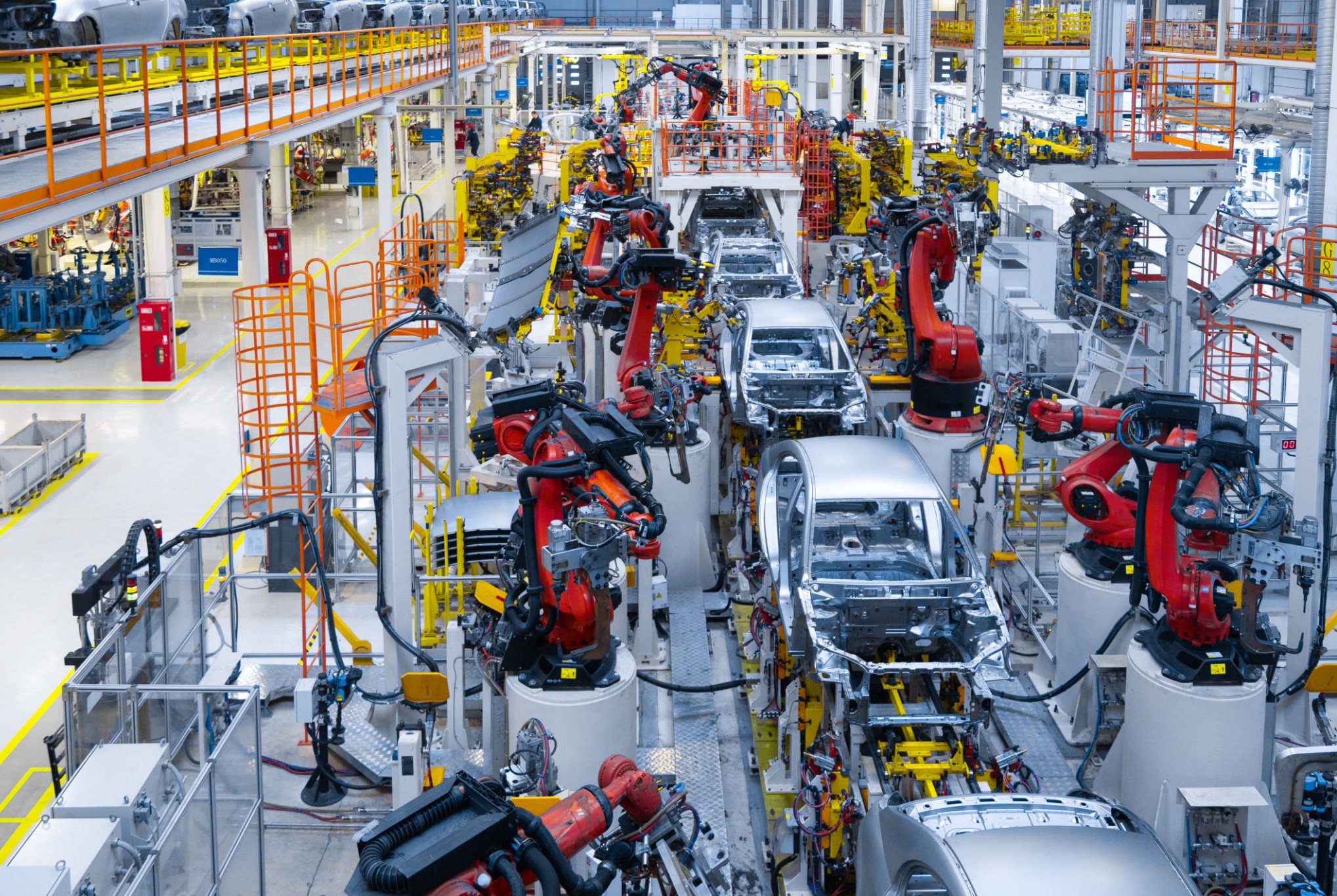
What Are the Key Characteristics of Robotic Assembly Lines?
Robotic assembly lines are characterized by their integration of advanced robotics, which enhances precision and speed in the manufacturing process. These systems are particularly suitable for industries such as automotive and electronics, where high-volume production is critical. When considering a robotic assembly line, buyers should evaluate the complexity of the products being manufactured and the level of automation required, as well as the potential return on investment through reduced labor costs and increased output.
How Do Conveyor Belt Systems Improve Manufacturing Efficiency?
Conveyor belt systems are designed to facilitate the movement of products between different assembly stations, ensuring a smooth and continuous workflow. They are widely used in food processing, packaging, and general assembly operations. Buyers should consider the layout of their production facility and the types of products being handled, as these factors will influence the design and configuration of the conveyor system. While these systems are scalable and efficient, they may lack the flexibility needed for rapid product changes.
What Are the Advantages of Automated Screwdriver Systems?
Automated screwdriver systems are specialized tools that insert screws automatically during assembly, enhancing accuracy and efficiency. These systems are commonly used in the electronics and automotive industries. When purchasing, B2B buyers should assess the specific requirements of their production line, including screw types and insertion speeds. While these systems reduce manual labor and improve precision, they also require careful maintenance and programming expertise.
How Do Collaborative Robots (Cobots) Enhance Workplace Safety?
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are designed to work alongside human operators, providing flexibility and enhancing safety in various assembly tasks. They are particularly suitable for small-scale assembly operations, electronics, and medical devices. Buyers should evaluate the tasks cobots will perform and the necessary safety measures, as these robots can significantly improve operational efficiency without compromising worker safety. However, they may not match the speed of fully automated systems.
Why Consider Custom Automation Solutions for Unique Production Needs?
Custom automation solutions are tailored to meet the specific needs of a business, making them ideal for specialized manufacturing sectors such as aerospace. These systems can optimize production processes for unique products but often involve higher costs and longer lead times. B2B buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their production requirements and consider the potential for increased efficiency and reduced waste that custom solutions can provide, despite the initial investment.
Key Industrial Applications of automatic assembly line manufacturers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of automatic assembly line manufacturers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Automated assembly of vehicle components | Increases production speed and consistency, reduces labor costs. | Look for manufacturers with experience in automotive standards and certifications. |
| Electronics Production | Assembly of circuit boards and electronic devices | Enhances precision and reduces errors in production. | Ensure compatibility with various electronic components and flexibility for changes in design. |
| Food and Beverage Processing | Packaging and bottling lines | Streamlines operations, increases shelf-life, and reduces waste. | Consider hygiene standards and the ability to handle diverse product types. |
| Medical Device Manufacturing | Assembly of surgical instruments and devices | Ensures high precision and compliance with health regulations. | Verify adherence to international medical standards and quality assurance processes. |
| Heavy Machinery Production | Assembly of construction and agricultural equipment | Improves efficiency and reduces time-to-market for large products. | Assess the robustness of machinery to handle heavy components and the need for customization. |
What Are the Key Applications of Automatic Assembly Lines in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive sector, automatic assembly lines are employed to streamline the production of vehicle components, such as engines, transmissions, and chassis. By automating repetitive tasks, manufacturers can achieve higher production speeds and maintain consistent quality, thereby lowering labor costs. International buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, should prioritize suppliers that comply with automotive standards and certifications to ensure product reliability and safety.
How Are Automatic Assembly Lines Transforming Electronics Production?
For electronics production, automatic assembly lines facilitate the precise assembly of circuit boards and electronic devices. These lines utilize advanced robotics and automation technologies to minimize errors and enhance efficiency. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East must consider the flexibility of the assembly lines to adapt to evolving electronic designs and ensure compatibility with a wide range of components, which is crucial for maintaining competitive advantage in fast-paced markets.
What Benefits Do Automatic Assembly Lines Offer in Food and Beverage Processing?
In the food and beverage industry, automatic assembly lines are vital for packaging and bottling processes. They help streamline operations, extend product shelf-life, and minimize waste, which is critical for maintaining profitability. B2B buyers from regions like Nigeria and Brazil should focus on sourcing lines that meet strict hygiene standards and can accommodate various product types, ensuring compliance with local regulations and consumer preferences.
How Do Automatic Assembly Lines Support Medical Device Manufacturing?
Medical device manufacturers leverage automatic assembly lines to produce surgical instruments and devices with high precision. This automation ensures compliance with stringent health regulations and maintains the quality needed for critical applications. Buyers in the healthcare sector must verify that potential suppliers adhere to international medical standards and have robust quality assurance processes in place to safeguard patient safety.

Illustrative image related to automatic assembly line manufacturers
What Role Do Automatic Assembly Lines Play in Heavy Machinery Production?
In heavy machinery production, automatic assembly lines are used to assemble large components for construction and agricultural equipment. These lines enhance efficiency and significantly reduce time-to-market for complex products. International buyers should evaluate the robustness of the machinery and the potential need for customization to meet specific production requirements, ensuring that the assembly line can handle the scale and weight of heavy components effectively.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘automatic assembly line manufacturers’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Production Quality
The Problem: Many manufacturers investing in automatic assembly lines face challenges related to the consistency and quality of the products being produced. Variability in the assembly process can lead to defects, which not only affects the product’s marketability but can also result in costly recalls or repairs. For B2B buyers, this inconsistency can stem from various factors, including poorly calibrated machines, inadequate training for operators, or substandard components being fed into the system.
The Solution: To tackle quality issues, it’s essential for buyers to conduct thorough due diligence when selecting automatic assembly line manufacturers. Start by ensuring that potential manufacturers adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001. Request detailed specifications and performance metrics of the machines, along with case studies that demonstrate their reliability in real-world applications. Additionally, implementing a robust training program for operators is crucial. This can include on-site training by the manufacturer’s technical team to ensure that staff are proficient in machine operation and maintenance. Regular calibration and preventive maintenance schedules should also be established, minimizing the risk of defects and ensuring consistent output quality.
Scenario 2: High Initial Investment Costs
The Problem: One of the most significant barriers for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Africa and South America, is the high initial investment required for automatic assembly line systems. Many manufacturers hesitate to commit large sums to automation due to concerns about the return on investment (ROI), especially when compared to manual labor costs. This fear can lead to missed opportunities for efficiency gains and productivity improvements.

Illustrative image related to automatic assembly line manufacturers
The Solution: To mitigate financial concerns, buyers should focus on a phased approach to automation. Rather than implementing a full assembly line at once, consider starting with specific modules or components that can be integrated gradually. This allows for spreading out the costs while assessing the effectiveness of automation in your production process. Additionally, seek out manufacturers that offer flexible financing options or leasing programs. These arrangements can make it easier to manage cash flow while still investing in automation technology. Finally, conduct a thorough ROI analysis that includes not only cost savings but also potential increases in production capacity and product quality, reinforcing the long-term value of automation.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Integrating with Existing Systems
The Problem: As companies look to upgrade their production capabilities, a common pain point is the difficulty in integrating new automatic assembly lines with existing manufacturing systems. This can create bottlenecks in production, inefficiencies, and frustration among staff. Buyers often find themselves grappling with compatibility issues between new technologies and legacy systems, leading to delays and increased costs.
The Solution: To address integration challenges, start by conducting a comprehensive assessment of your current manufacturing processes and systems before engaging with an assembly line manufacturer. This will help identify specific areas where integration might pose issues. When selecting an automatic assembly line manufacturer, prioritize those with a proven track record in system integration and customization. Request detailed implementation plans that include integration strategies tailored to your existing infrastructure. Furthermore, consider enlisting third-party integration specialists who can facilitate a smoother transition. They can help ensure that both software and hardware components work seamlessly together, minimizing disruption during the implementation phase and optimizing overall production efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for automatic assembly line manufacturers
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Automatic Assembly Lines?
When selecting materials for automatic assembly lines, manufacturers must consider various factors including durability, cost, and specific application requirements. Here, we analyze four common materials utilized in this sector: steel, aluminum, plastics, and composites.
How Does Steel Perform in Automatic Assembly Line Applications?
Steel is a widely used material in the construction of assembly line machinery due to its exceptional strength and durability. Key properties include high tensile strength, excellent wear resistance, and the ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. However, steel is susceptible to corrosion unless treated, which can be a significant drawback in humid or corrosive environments.

Illustrative image related to automatic assembly line manufacturers
Pros: Steel is durable and can handle heavy loads, making it suitable for high-stress applications. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to other materials.
Cons: The weight of steel can complicate manufacturing and transportation. Additionally, its susceptibility to rust means that protective coatings or stainless steel variants may be necessary, increasing costs.
For international buyers, compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 or DIN 17100 is crucial. In regions like Africa or South America, where humidity can be high, selecting corrosion-resistant steel options is advisable.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Offer for Assembly Line Equipment?
Aluminum is another popular choice, particularly for components that require a balance between weight and strength. It is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has good thermal conductivity. Aluminum can be easily machined and fabricated, which simplifies the manufacturing process.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum reduces energy costs in automated systems and allows for faster assembly line speeds. Its resistance to corrosion makes it ideal for various environments.
Cons: While aluminum is strong, it is not as strong as steel, which can limit its use in heavy-duty applications. Additionally, aluminum can be more expensive than steel, which may impact budget-conscious projects.
International buyers should be aware of standards such as ASTM B221 and JIS H4000 when sourcing aluminum components. In markets like Europe, where environmental regulations are stringent, aluminum’s recyclability is a significant advantage.
How Do Plastics Contribute to Automatic Assembly Line Efficiency?
Plastics are increasingly used in assembly lines due to their versatility and lightweight characteristics. They can be engineered to possess specific properties such as high impact resistance, chemical resistance, and low friction.
Pros: Plastics can be produced in various shapes and sizes, making them ideal for custom applications. They are generally less expensive than metals and can reduce overall production costs.
Cons: Plastics may not withstand high temperatures or heavy loads as well as metals, which can limit their application. Additionally, some plastics may degrade over time when exposed to UV light or certain chemicals.
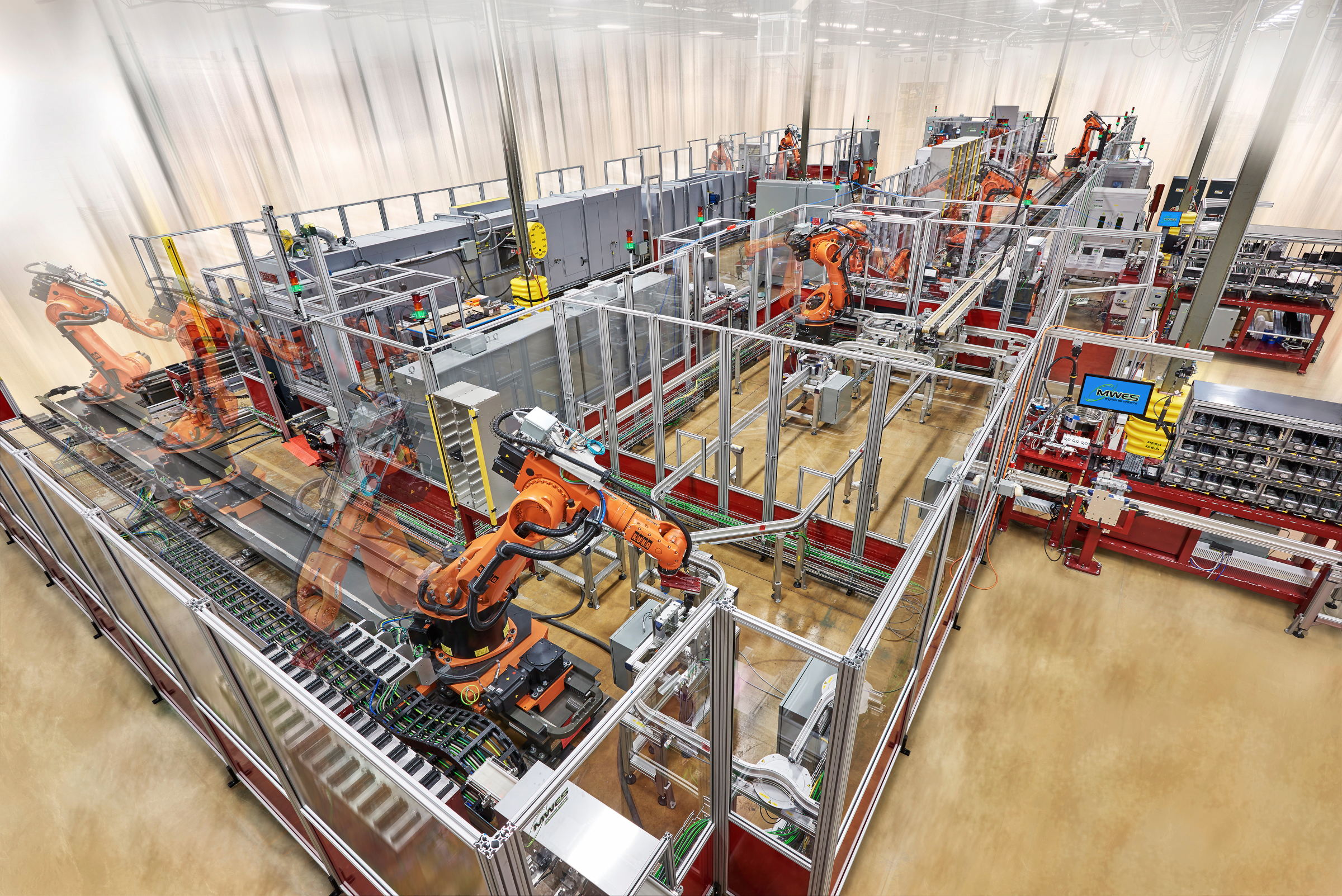

Illustrative image related to automatic assembly line manufacturers
For B2B buyers, understanding the specific type of plastic (e.g., ABS, PVC, or polycarbonate) and its compliance with standards such as ASTM D638 is essential. In regions like Brazil, where temperature fluctuations can be significant, selecting heat-resistant plastics is crucial.
What Role Do Composites Play in Modern Assembly Line Design?
Composite materials, which combine two or more constituent materials, offer unique advantages in assembly line applications. They can be engineered to provide high strength-to-weight ratios, excellent corrosion resistance, and tailored thermal properties.
Pros: Composites are lightweight yet strong, making them ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical. They also offer superior resistance to environmental degradation.
Illustrative image related to automatic assembly line manufacturers
Cons: The manufacturing process for composites can be complex and costly, which may deter some manufacturers. Additionally, the repair and recycling of composite materials can pose challenges.
International buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ASTM D3039 for composites. In regions like the Middle East, where extreme temperatures can affect material performance, selecting composites designed for thermal stability is vital.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Automatic Assembly Lines
| Material | Typical Use Case for automatic assembly line manufacturers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural components, frames, and heavy machinery | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight frames, conveyor systems, and parts | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength compared to steel | High |
| Plastics | Custom parts, housings, and non-load-bearing components | Versatile and cost-effective | Limited heat and load resistance | Low |
| Composites | Specialized components requiring high strength-to-weight ratio | Superior environmental resistance | Complex manufacturing and repair | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of materials commonly used in automatic assembly lines, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for automatic assembly line manufacturers
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes for Automatic Assembly Line Manufacturers?
Automatic assembly line manufacturers typically follow a structured manufacturing process that encompasses several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is critical to ensuring that the final product meets both quality and performance standards.
Illustrative image related to automatic assembly line manufacturers
-
Material Preparation: This initial stage involves sourcing and preparing raw materials, which may include metals, plastics, or electronic components. Suppliers are often vetted based on their ability to provide materials that meet international standards. Material inspection is crucial here, with checks for quality and compliance with specifications. B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers employ rigorous material preparation protocols to mitigate issues down the line.
-
Forming: In this stage, raw materials are shaped into parts through various techniques such as stamping, molding, or machining. Advanced technologies such as Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining or additive manufacturing (3D printing) are frequently employed to enhance precision. The choice of technique will depend on the complexity of the part and the material being used. Buyers should inquire about the specific forming technologies utilized by their suppliers, as this can impact both quality and cost.
-
Assembly: The assembly stage is where the magic happens, as individual components are brought together to create the final product. This process can be highly automated, leveraging robotic systems and conveyor belts to ensure efficiency. Techniques such as automated screw driving and part placement are commonplace. For B2B buyers, understanding the level of automation and the types of assembly techniques used can help in assessing the supplier’s capacity to meet large-scale production demands.
-
Finishing: Once the assembly is complete, the product undergoes finishing processes that may include painting, coating, or surface treatment. This stage not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the product but also improves durability and resistance to wear and corrosion. Buyers should verify that their suppliers utilize finishing processes that comply with relevant industry standards, as this can affect the product’s longevity and performance.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Automatic Assembly Line Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral part of the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet specified standards and regulations. Automatic assembly line manufacturers typically adhere to both international and industry-specific quality standards.
-
What International Standards Are Relevant for Quality Assurance?
The ISO 9001 standard is one of the most recognized international quality management systems. It emphasizes a process-oriented approach to quality assurance and is applicable across various industries. Suppliers may also comply with additional certifications such as CE marking for products sold in the European market or API standards for oil and gas equipment. Buyers should request documentation of these certifications to ensure compliance. -
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is often structured around several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials before they enter production. It includes inspections and testing to confirm that materials meet predefined specifications.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during the manufacturing process, IPQC ensures that each stage adheres to quality standards. This may involve real-time monitoring and adjustments to maintain quality.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): This is the last line of defense before products are shipped. FQC typically includes comprehensive testing and inspections to verify that the final product meets all quality and safety standards. -
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Control?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure product quality, including:
– Dimensional Inspection: Verifying that parts meet specified dimensions using calipers, gauges, or coordinate measuring machines (CMM).
– Functional Testing: Assessing the performance of the product under operational conditions.
– Material Testing: Evaluating the properties of materials to ensure they meet specified standards, including tensile strength and hardness tests.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits can help verify that suppliers adhere to their stated quality processes and standards. Buyers should consider establishing a schedule for audits and ensuring they cover all critical aspects of the manufacturing process.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality control processes and results. This may include reports from IQC, IPQC, and FQC phases, as well as any corrective actions taken in response to quality issues.
-
Utilize Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. This is particularly valuable for buyers in regions where they may not have direct oversight capabilities.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are specific nuances to consider:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and ensure that suppliers comply with both international standards and local laws.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices and communication can facilitate smoother interactions with suppliers. Buyers should be aware of these nuances to avoid misunderstandings that could affect quality assurance.
-
Risk Management: Political, economic, and logistical factors can influence supply chains, especially in developing regions. Buyers should assess these risks and consider diversifying their supplier base to mitigate potential disruptions.
In conclusion, B2B buyers seeking automatic assembly line manufacturers should be well-versed in the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols to ensure they partner with reliable suppliers. By understanding the intricacies of each stage of production and the relevant quality standards, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘automatic assembly line manufacturers’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist international B2B buyers in procuring automatic assembly line manufacturers. Given the complexity and technical specifications involved in sourcing assembly lines, this checklist will help streamline your decision-making process and ensure you select the right manufacturer for your operational needs.

Illustrative image related to automatic assembly line manufacturers
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with potential suppliers, it’s essential to clearly outline your requirements. Consider the types of products you will be assembling, the scale of production, and specific functionalities such as automation levels and integration capabilities. This clarity will help you identify manufacturers that specialize in your specific needs and avoid misalignment down the line.
Step 2: Research Potential Manufacturers
Take the time to compile a list of manufacturers that meet your defined specifications. Utilize online resources, industry directories, and trade shows to find reputable companies. Pay attention to their experience in your industry and their geographical reach, as this can impact delivery times and support services.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers hold relevant industry certifications and comply with international standards. Look for ISO certifications, CE marks, or other industry-specific qualifications that demonstrate quality and reliability. This step is crucial as it reflects the manufacturer’s commitment to quality assurance and adherence to safety regulations.
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you have shortlisted potential manufacturers, request detailed proposals that include technical specifications, pricing, and lead times. A comprehensive proposal will provide insights into their capabilities and help you compare offerings effectively. Ensure that proposals also outline warranty terms and post-installation support.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Maintenance
Evaluate the after-sales support that manufacturers offer. A reliable supplier should provide maintenance services, training for your staff, and readily available spare parts. This support can significantly reduce downtime and ensure smooth operation of your assembly lines in the long term.
Step 6: Check References and Case Studies
Before making a final decision, request references and case studies from the manufacturer. Speaking with previous clients can provide valuable insights into their reliability and customer service. Look for testimonials from businesses in similar industries or geographical areas to gauge how well the manufacturer meets specific challenges.

Illustrative image related to automatic assembly line manufacturers
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a manufacturer, it’s time to negotiate terms. Discuss pricing, payment terms, delivery schedules, and any customization options available. Be clear about your expectations and ensure that both parties agree on the terms to avoid misunderstandings later in the project.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing automatic assembly line manufacturers, ensuring a successful partnership that meets their operational goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for automatic assembly line manufacturers Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Automatic Assembly Line Manufacturers?
When sourcing automatic assembly lines, it’s essential to understand the various cost components that contribute to the overall price. The primary elements include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials varies significantly based on quality and type. Components such as conveyor belts, robotic arms, and specialized tools like automatic screwdrivers must be sourced from reputable suppliers to ensure reliability and longevity.
-
Labor: Although automation reduces the need for a large workforce, skilled technicians are still necessary for installation, maintenance, and operation. Labor costs can fluctuate based on geographic location and the level of expertise required.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and general administrative expenses. A manufacturer’s location can significantly impact these costs, with regions offering tax incentives potentially lowering the overall overhead.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a substantial investment, especially for unique assembly line requirements. The complexity and specificity of the tooling directly influence the cost, which can be amortized over a larger production volume to reduce the per-unit cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that assembly lines meet industry standards requires investment in quality control systems. These costs may include testing equipment and personnel trained in quality assurance practices.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely, particularly for international buyers. Costs will depend on the distance, weight, and dimensions of the equipment, as well as the chosen logistics provider.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on competition, market demand, and brand reputation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors influence the pricing of automatic assembly lines, which international buyers should consider:
Illustrative image related to automatic assembly line manufacturers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Ordering in larger quantities often results in lower per-unit prices. Understanding the manufacturer’s MOQ can help buyers negotiate better deals.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-designed systems or specialized features can lead to increased costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their needs to balance customization with budget constraints.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can significantly impact the cost. Higher-grade materials may offer better durability but come with a higher price tag. Buyers should weigh the benefits against their budget.
-
Quality and Certifications: Equipment that meets international quality standards or has specific certifications may be priced higher. However, investing in higher-quality equipment can lead to lower maintenance costs and longer service life.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established manufacturers may charge a premium due to their track record, while newer entrants might offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery (Incoterms) is critical for cost calculations. Different terms can result in varying responsibilities and costs for the buyer.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Negotiating Prices?
Navigating the pricing landscape for automatic assembly lines requires strategic approaches:
-
Negotiate: Always enter negotiations with a clear understanding of your budget and the market rates. Leverage quotes from multiple suppliers to strengthen your negotiating position.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs over the equipment’s lifecycle. A higher initial investment may result in lower long-term costs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of potential tariffs, import duties, and other costs that can impact the final price.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and more favorable terms over time. Trust and reliability are crucial in B2B sourcing.
-
Stay Informed: Keep abreast of market trends and technological advancements in assembly line manufacturing. This knowledge can empower you to make informed decisions and negotiate effectively.
Disclaimer
Prices and costs mentioned are indicative and may vary based on specific project requirements and market conditions. Always consult with suppliers for accurate and tailored pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing automatic assembly line manufacturers With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Automatic Assembly Line Manufacturers
In the quest for efficient production processes, businesses often evaluate various manufacturing solutions. Automatic assembly line manufacturers have long been the standard for mass production, but alternative technologies and methods are emerging as viable options. This analysis will compare automatic assembly lines with two alternatives: modular manufacturing systems and manual assembly processes.
| Comparison Aspect | Automatic Assembly Line Manufacturers | Modular Manufacturing Systems | Manual Assembly Processes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High throughput and efficiency | Flexible, scalable solutions | Variable, dependent on labor |
| Cost | High initial investment, low long-term costs | Moderate investment, operational flexibility | Low initial investment, higher long-term labor costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex setup requiring skilled labor | Easier to implement with modular components | Simple, no specialized equipment needed |
| Maintenance | Requires specialized technicians | Generally lower, but modular parts need regular checks | Minimal maintenance, reliant on workforce skill |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production of uniform products | Customizable production runs, varied products | Low-volume, artisanal, or complex products |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Modular Manufacturing Systems?
Modular manufacturing systems provide an adaptable alternative to traditional assembly lines. They consist of independent units that can be reconfigured based on production needs, allowing for quick adjustments in product design or production volume.
Pros:
– Flexibility in product design and production volume.
– Easier to scale operations up or down based on demand.
– Lower initial costs compared to fully automated lines.
Cons:
– May not achieve the same high throughput as dedicated assembly lines.
– Requires careful planning to ensure efficiency in the modular setup.
Illustrative image related to automatic assembly line manufacturers
How Do Manual Assembly Processes Compare?
Manual assembly processes rely on human labor to assemble products, offering a contrasting approach to automated solutions. This method is often used for specialized or small-batch production where precision and craftsmanship are vital.
Pros:
– Low initial setup costs and minimal capital investment in machinery.
– High adaptability for custom or complex products.
– Greater craftsmanship and attention to detail.
Cons:
– Labor-intensive and subject to human error, which can affect consistency.
– Slower production rates compared to automated systems.
– Potential for higher long-term labor costs due to wage increases.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
When evaluating which manufacturing solution is best for your business, consider your production volume, product complexity, and budget. Automatic assembly lines excel in high-volume environments where efficiency and consistency are critical. However, if your production requires flexibility and customization, modular manufacturing systems or manual assembly may be more suitable.
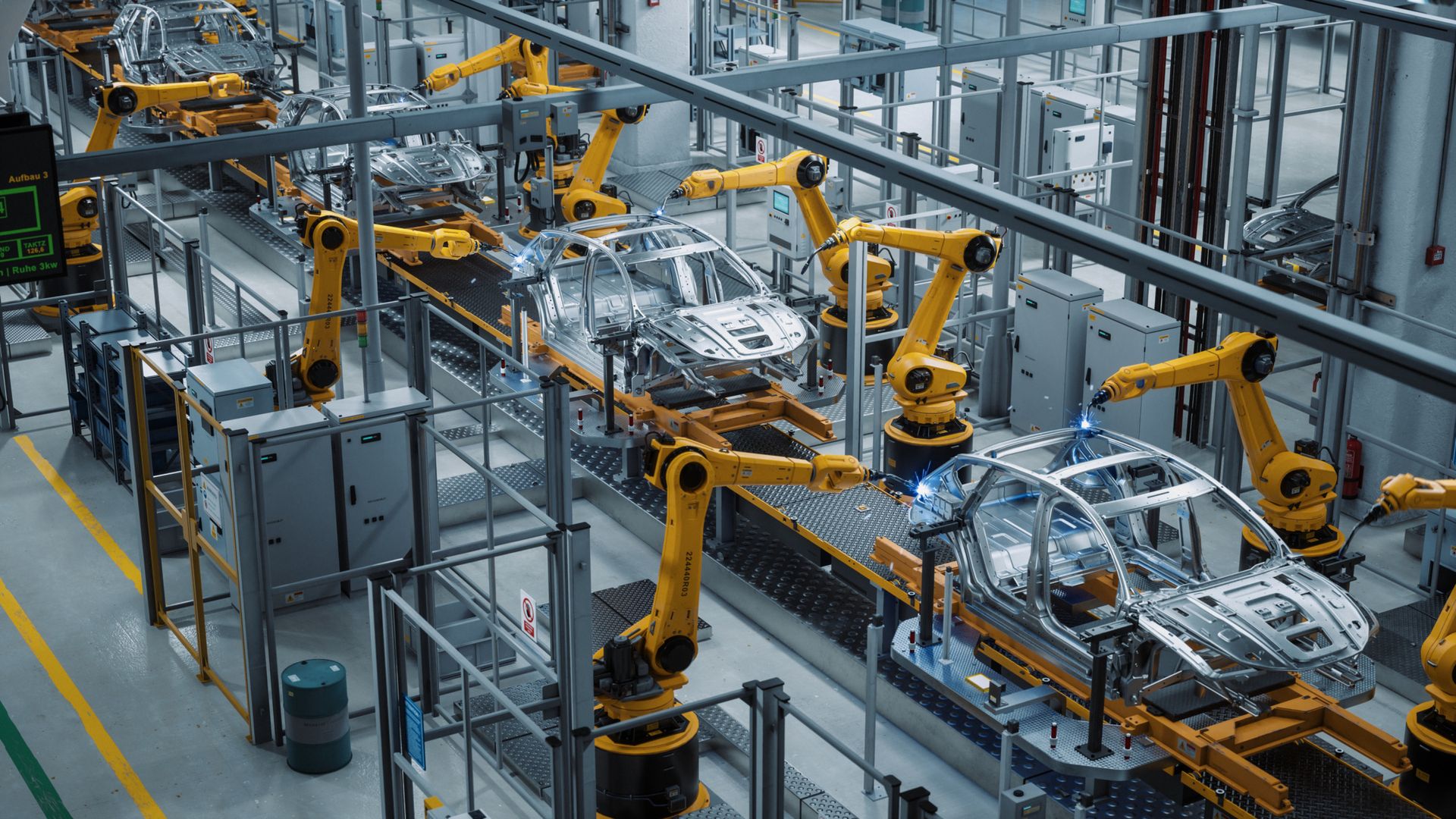

Illustrative image related to automatic assembly line manufacturers
Ultimately, the decision should align with your operational goals, available resources, and the specific demands of your market. Understanding the trade-offs between these options will empower you to make informed choices that enhance productivity and competitiveness in your industry.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for automatic assembly line manufacturers
What Are the Key Technical Properties for Automatic Assembly Line Manufacturers?
When sourcing components and systems for automatic assembly lines, several technical properties are essential to ensure optimal performance and compatibility. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material grade indicates the quality and type of materials used in manufacturing components. Common materials include stainless steel for durability, aluminum for lightweight applications, and plastics for specific non-structural elements. Selecting the right material grade is vital for ensuring that components can withstand operational stress, environmental factors, and wear over time, leading to reduced downtime and maintenance costs. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the acceptable limits of variation in a physical dimension. In assembly line manufacturing, tight tolerances are crucial for ensuring that parts fit together correctly, which is essential for maintaining quality and reducing assembly errors. Understanding tolerance specifications helps buyers ensure that suppliers can meet their precise manufacturing needs, leading to enhanced operational efficiency. -
Cycle Time
Cycle time is the total time required to complete one cycle of the manufacturing process, from the start of production to the finished product. This metric is critical for assessing the efficiency of an assembly line. Buyers must evaluate cycle times to understand production capacity and throughput, impacting overall operational costs and delivery timelines. -
Load Capacity
Load capacity defines the maximum weight or force a component or system can handle during operation. This property is particularly important for automated systems like conveyor belts and robotic arms, which must support the weight of products being assembled. Understanding load capacity helps buyers avoid equipment failures and ensure safety in the workplace. -
Automation Level
The automation level indicates the extent to which manual labor is replaced by automated processes. Higher automation levels can lead to increased efficiency and reduced labor costs, but require a skilled workforce for maintenance and oversight. Assessing the automation level is crucial for buyers aiming to balance productivity with operational costs.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Automatic Assembly Line Manufacturing?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communications and negotiations. Here are some essential trade terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of assembly lines, OEMs provide specialized components that are critical for system integration. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure they are sourcing high-quality parts that meet specific requirements. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers looking to manage inventory costs and ensure that their procurement strategies align with production needs. Knowing MOQs helps companies avoid overstocking or stockouts. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price proposals from suppliers for specific products or services. This term is essential for initiating the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare offers and select the best supplier based on price, quality, and delivery terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is vital for buyers engaged in cross-border procurement, as they clarify shipping, insurance, and risk management responsibilities. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the total time from the initiation of an order to its delivery. This metric is crucial for planning and inventory management, as longer lead times can impact production schedules. Buyers must evaluate lead times to ensure they align with their operational timelines.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing automatic assembly line solutions, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and competitiveness in the market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the automatic assembly line manufacturers Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Impacting Automatic Assembly Line Manufacturers?
The automatic assembly line manufacturing sector is experiencing a significant transformation driven by various global factors. Increased demand for efficiency and productivity is pushing companies to adopt advanced automation technologies. Key trends include the integration of robotics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning into assembly processes. These technologies facilitate rapid production cycles and enhance precision, crucial for meeting the rising expectations of global supply chains.
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is vital. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can provide flexible, scalable solutions that can be adapted to diverse production needs. The trend toward customization and modular assembly systems is also notable, allowing businesses to adjust their operations swiftly in response to market changes. Furthermore, the rise of Industry 4.0 is fostering a connected ecosystem where data analytics plays a crucial role in optimizing production efficiency and reducing downtime.
Emerging sourcing trends reflect a growing emphasis on local suppliers and nearshoring practices to mitigate risks associated with global supply chains. Buyers are also focusing on suppliers that can demonstrate a commitment to innovation and sustainability, aligning with their corporate social responsibility goals.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Automatic Assembly Line Manufacturing Sector?
Sustainability is no longer a choice but a necessity for automatic assembly line manufacturers. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes has become a critical concern, prompting companies to adopt greener practices. This includes minimizing waste, reducing energy consumption, and utilizing eco-friendly materials. For international buyers, sourcing from manufacturers with robust sustainability practices can enhance their brand reputation and meet regulatory requirements in various markets.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing their suppliers’ practices, seeking partners who prioritize fair labor practices and transparency. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety are gaining traction. These certifications not only reflect a manufacturer’s commitment to sustainability but also provide buyers with assurance that they are engaging with responsible suppliers.
Moreover, the demand for ‘green’ materials and processes is influencing product design and manufacturing strategies. Buyers should consider manufacturers that invest in developing sustainable technologies, such as energy-efficient machinery and recyclable components, to align with their sustainability goals.
How Has the Automatic Assembly Line Manufacturing Sector Evolved Over Time?
The concept of the assembly line has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century, primarily attributed to Henry Ford’s innovations in the automotive industry. Initially characterized by manual labor and simple mechanization, the assembly line has transitioned into a sophisticated network of automated systems. The introduction of robotics in the 1980s marked a pivotal moment, enabling higher precision and speed in production processes.
Today, the evolution continues with the integration of smart technologies that enable real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This shift not only enhances productivity but also allows manufacturers to respond proactively to potential issues, ensuring uninterrupted operations. As the industry progresses, the focus on automation, sustainability, and ethical sourcing remains paramount, offering a compelling narrative for B2B buyers looking to navigate the complexities of the modern manufacturing landscape.
In summary, the automatic assembly line manufacturing sector is at the forefront of technological advancement, sustainability, and ethical practices. Buyers who remain informed and adaptable will be well-positioned to leverage these trends for competitive advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of automatic assembly line manufacturers
1. How do I choose the right automatic assembly line manufacturer for my business?
Selecting the right manufacturer involves several key considerations. First, assess their experience and reputation in your industry. Look for case studies or references that demonstrate successful implementations similar to your needs. Evaluate their technological capabilities, such as the use of robotics and automation systems, which can enhance efficiency. Additionally, consider their ability to offer customization options to meet specific requirements and their support services, including installation and maintenance. Finally, ensure they have a robust quality assurance process to guarantee product reliability.
2. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for assembly lines?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the complexity of the assembly line. Generally, MOQs can range from a single unit for highly customized systems to larger quantities for standardized models. When sourcing from international manufacturers, it’s crucial to discuss MOQs upfront, as lower quantities may incur higher costs per unit. Understanding the cost implications and lead times associated with different order sizes can help you make informed decisions that align with your production needs.
3. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing from international assembly line manufacturers?
Payment terms vary widely among manufacturers and may depend on your business relationship, the order size, and the manufacturer’s policies. Common arrangements include a deposit upfront (typically 30-50%), with the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. Some manufacturers may offer financing options or extended payment plans for larger orders. Always ensure that the payment terms are clearly outlined in the contract to avoid misunderstandings. It’s advisable to utilize secure payment methods that provide buyer protection, especially in international transactions.
4. How do I ensure quality assurance in assembly line production?
Quality assurance is critical in manufacturing to ensure that the assembly line meets your specifications and industry standards. Start by requesting detailed quality control processes from the manufacturer, including certifications such as ISO 9001. Regular inspections during production and final quality checks before shipment are essential. Establish clear communication channels for reporting issues and ensuring timely resolutions. Additionally, consider visiting the manufacturer’s facility if possible, or request third-party inspections to verify compliance with your quality standards.
5. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing assembly lines?
Logistics play a crucial role in the successful importation of assembly lines. Key factors to consider include shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your country. Work closely with freight forwarders who have experience in handling heavy machinery and can navigate international shipping complexities. Ensure that all documentation, such as bills of lading and import permits, is in order to avoid delays. Additionally, factor in potential tariffs and taxes that may apply to your order, which can impact overall costs.
6. Can I customize the assembly line to fit my specific production needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options to tailor assembly lines according to specific production requirements. This can include modifications in layout, machinery types, and integration with existing systems. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications of your production process, including product dimensions, throughput rates, and required automation levels. Collaborating closely with the manufacturer during the design phase can ensure that the final product aligns with your operational goals and enhances efficiency.
7. How can I vet potential assembly line suppliers effectively?
Vetting suppliers is essential for mitigating risks in your supply chain. Start by researching their background, including years in business, industry experience, and client testimonials. Request references and case studies to evaluate their past performance. Conduct site visits if possible to assess their manufacturing capabilities and quality control practices. Additionally, verify certifications and compliance with international standards. Engaging third-party organizations for audits can also provide an objective assessment of a supplier’s reliability and operational practices.
8. What industries benefit the most from automatic assembly lines?
Automatic assembly lines are beneficial across various industries, including automotive, electronics, food processing, and medical supplies. In the automotive sector, they enable mass production of vehicles, reducing assembly time and costs. Electronics manufacturers utilize assembly lines for the efficient production of components like circuit boards. The food industry benefits from automation in packaging and processing, while medical supply manufacturers rely on precise assembly for devices and pharmaceuticals. Understanding the applications of assembly lines in your industry can help you leverage their full potential for improved productivity.
Top 5 Automatic Assembly Line Manufacturers Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Assembly Machinery – Automated Assembly Solutions
Domain: assemblymachinery.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Assembly line manufacturers and suppliers provide a variety of automated assembly products, including robotic screwdrivers, auto-fed screw & nut drivers, auto-fed part placers, parts feeding systems, and assembly cells. Companies like Dixon Automatic Tool, Inc. and Invio Automation specialize in robotic automation and AGV (Automated Guided Vehicles) solutions. Advent Design Corporation offers cust…
2. IQS Directory – Assembly Line Manufacturers
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: IQS Directory provides a detailed list of assembly line manufacturers and suppliers. Key companies include: 1. Applied Manufacturing Technologies – Specializes in auto-guided vehicles and systems. 2. Fusion, Inc. – Offers automated brazing and soldering machines. 3. Rodix, Inc. – Manufactures vibratory feeder controls and part feeding systems. 4. Actionpac Scales & Automation – Scale manufacturer …
3. Edgewater Automation – Automated Assembly Solutions
Domain: edgewaterautomation.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Edgewater Automation specializes in automated assembly systems, focusing on design for manufacturing. The process begins with product specifications and tolerances, followed by a site review to assess environmental conditions. They offer a tailored automated assembly solution leveraging extensive expertise and a network of suppliers. Key services include:
– Engineering, design, development, testi…
4. Osai – Custom Automated Assembly Lines
Domain: osai-as.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Osai manufactures automatic assembly lines tailored to specific customer needs, utilizing a modular approach with dedicated stations for each production step. Key features include:
– Smart solutions for lean manufacturing
– Modular design optimizing construction times, design, and investments
– Integration of advanced robotic systems, IoT, and machine learning for intelligent and autonomous produc…
5. TEAL – Fully Automatic Assembly Line
Domain: titanteal.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Fully Automatic Assembly Line developed and manufactured by TEAL for manless automated manufacturing using linear and rotary transfer systems. Designed for fast, stable, and accurate production flow across various industries including Transportation, Energy, Electronics, Life Sciences, Engineering, and Consumer Products. Key features include tailor-made automation systems, incorporation of cutting…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for automatic assembly line manufacturers
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing for automatic assembly line manufacturers is not merely a procurement function; it is a critical driver of operational efficiency and innovation. By leveraging advanced technologies such as robotics and automation systems, businesses can significantly enhance production capabilities, reduce labor costs, and improve product quality. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of sourcing these sophisticated systems is essential for staying ahead in the market.
What should buyers consider when sourcing automatic assembly lines? First, prioritize manufacturers that offer customizable solutions tailored to specific production needs. Second, evaluate the integration capabilities of automation systems with existing processes to ensure seamless operation. Lastly, consider the long-term support and maintenance services provided by manufacturers, as these can be crucial for maximizing uptime and minimizing disruptions.
Looking ahead, the future of assembly line manufacturing is poised for further transformation with the integration of smart technologies and IoT capabilities. Now is the time for international buyers to engage with leading manufacturers to explore innovative solutions that will not only meet current demands but also position their businesses for sustainable growth. Embrace this opportunity to elevate your operations through strategic sourcing.

Illustrative image related to automatic assembly line manufacturers
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.