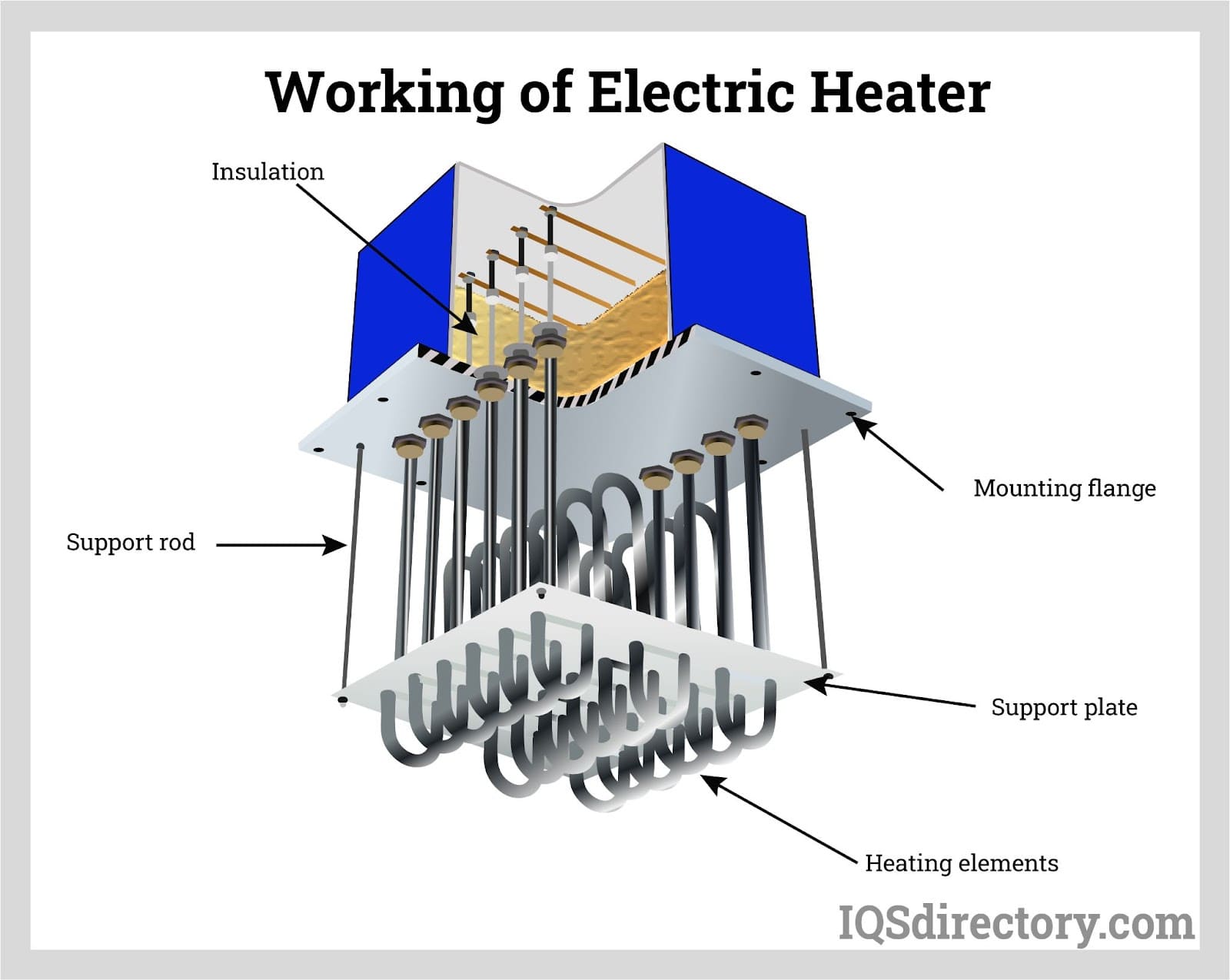
Top 4 Working Of Heater Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for working of heater
In an increasingly interconnected world, sourcing reliable heating solutions is a critical challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly those seeking the optimal working of heaters for diverse applications. Whether you’re in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe—navigating the complexities of heater technology, supplier reliability, and cost-effectiveness can be daunting. This guide aims to demystify the various types of heaters, from electric to industrial models, providing insights into their operational mechanisms and applications across different sectors.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, you’ll find detailed analyses of heater types, including their unique functionalities and suitability for specific environments. The guide also covers essential aspects such as supplier vetting processes, ensuring that you make informed choices when selecting partners for your heating needs. Furthermore, we delve into cost considerations, enabling you to budget effectively while maximizing efficiency and sustainability in your operations.
By empowering international B2B buyers with actionable insights and practical knowledge, this guide serves as a valuable tool in your decision-making process. Whether you’re based in Germany or Nigeria, understanding the intricacies of heaters will enhance your ability to choose the right solutions that meet your business requirements and contribute to long-term success.
Understanding working of heater Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Heaters | Converts electrical energy into heat; standalone units | Residential heating, offices | Pros: High energy efficiency, programmable; Cons: Higher initial cost compared to traditional systems. |
| Band Heaters | Clamps onto objects; provides external heat | Manufacturing, plastics processing | Pros: Precise heat application; Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Cartridge Heaters | Cylindrical design; inserted into materials for heating | Machinery, equipment heating | Pros: Focused heat delivery; Cons: Requires precise installation. |
| Oil-Filled Radiators | Uses thermal fluid; retains heat longer | Large spaces, warehouses | Pros: Energy-efficient, retains heat; Cons: Slower to heat up. |
| Infrared Heaters | Uses infrared radiation for direct heating | Warehouses, outdoor spaces | Pros: Immediate heat; Cons: Limited range, not suitable for enclosed spaces. |
What Are Electric Heaters and Their Key Features?
Electric heaters operate by converting electrical energy into heat, making them versatile for various applications, from residential spaces to offices. They typically function as standalone units, allowing for independent temperature control in different rooms. This feature enhances energy efficiency and reliability, particularly as they do not rely on a boiler or extensive piping systems. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment versus long-term savings on energy costs and maintenance.
How Do Band Heaters Work and Where Are They Used?
Band heaters are designed to provide external heat to cylindrical objects, making them ideal for applications in manufacturing and plastics processing. Their ability to clamp securely onto surfaces allows for precise heat delivery, which is crucial for processes like extrusion. When purchasing band heaters, businesses should evaluate the compatibility with their equipment and the specific temperature requirements of their operations.
Illustrative image related to working of heater
What Makes Cartridge Heaters Suitable for Industrial Applications?
Cartridge heaters are cylindrical heating elements that deliver focused heat by being inserted into the materials they are designed to heat. Commonly used in machinery and equipment, their design allows for efficient thermal transfer. B2B buyers should consider the dimensions of the holes in which these heaters will be installed and the wattage needed for optimal performance, ensuring they meet the heating demands of their applications.
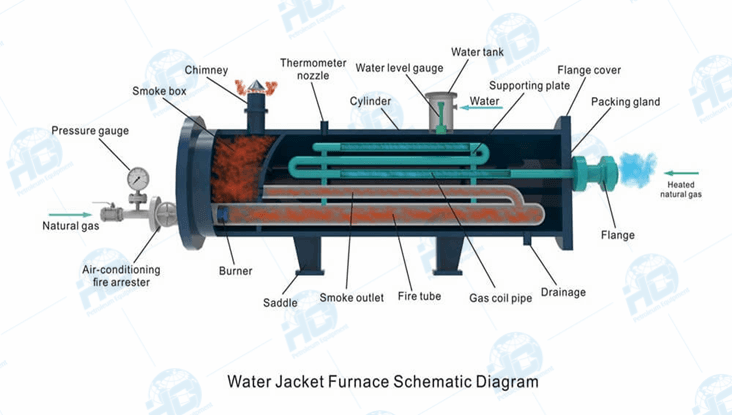
Why Choose Oil-Filled Radiators for Larger Spaces?
Oil-filled radiators are known for their ability to retain heat longer, making them particularly effective in large spaces such as warehouses. They operate by heating thermal fluid, which then radiates warmth, providing a consistent and comfortable environment. Buyers should weigh the benefits of energy efficiency against the slower heating time, especially in settings where immediate warmth is necessary.
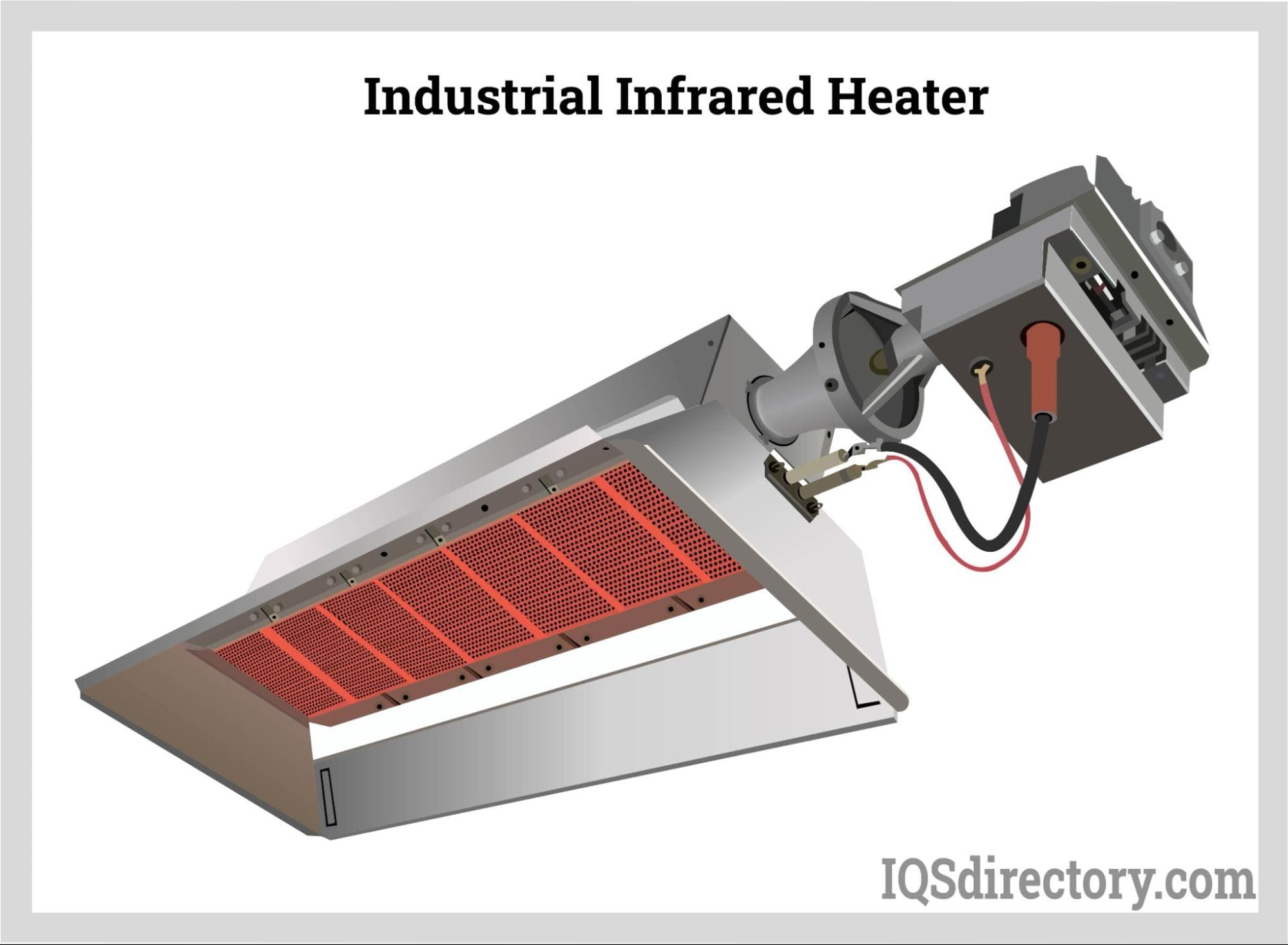
What Are the Advantages and Limitations of Infrared Heaters?
Infrared heaters utilize radiation to provide direct heating, making them effective for large, open spaces such as warehouses and outdoor areas. They offer the advantage of immediate heat, which can be beneficial in environments requiring quick temperature adjustments. However, their effectiveness diminishes in enclosed spaces, and buyers should assess the layout of their facilities to determine if infrared heating is a suitable option.
Key Industrial Applications of working of heater
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of working of heater | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastics Manufacturing | Band Heaters for Injection Molding | Enhanced temperature control leads to improved product quality and reduced waste. | Ensure compatibility with machinery and precise temperature specifications. |
| Food Processing | Electric Heaters for Cooking and Pasteurization | Efficient heating ensures food safety and quality, reducing energy costs. | Look for energy-efficient models that meet health and safety standards. |
| Chemical Processing | Cartridge Heaters for Material Heating | Provides consistent heat for reactions, improving process efficiency and safety. | Assess material compatibility and temperature range requirements. |
| HVAC Systems | Electric Radiators for Climate Control | Offers precise temperature control, enhancing comfort and reducing energy consumption. | Evaluate smart technology integration and maintenance requirements. |
| Textile Industry | Drying Heaters for Fabric Treatment | Speeds up drying processes, increasing production rates and reducing energy use. | Consider the size and capacity needed to match production volumes. |
How Are Band Heaters Used in Plastics Manufacturing?
In the plastics manufacturing industry, band heaters are crucial for injection molding processes. They provide external heat to the molds, ensuring optimal material flow and reducing cycle times. This precise temperature control helps to enhance product quality while minimizing waste caused by defects. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing band heaters that meet specific machinery compatibility and temperature requirements is essential for maintaining production efficiency.
What Role Do Electric Heaters Play in Food Processing?
Electric heaters are pivotal in food processing, particularly for cooking and pasteurization. They ensure that food products reach the necessary temperatures for safety and quality, significantly reducing the risk of contamination. Efficient heating also leads to lower energy costs, which is a critical consideration for businesses in the Middle East and Europe facing rising energy prices. Buyers should prioritize energy-efficient models that comply with local health and safety regulations to ensure product integrity.
Why Are Cartridge Heaters Important in Chemical Processing?
In chemical processing, cartridge heaters are utilized to deliver precise internal heating to various materials and equipment. This is vital for maintaining consistent temperatures during reactions, which directly impacts efficiency and safety. For businesses in Europe and Africa, selecting cartridge heaters that are compatible with specific chemical substances and can handle required temperature ranges is crucial. This ensures optimal performance while minimizing risks associated with thermal fluctuations.
How Do Electric Radiators Benefit HVAC Systems?
Electric radiators are increasingly being integrated into HVAC systems for climate control. They offer precise temperature management, which enhances comfort for occupants and reduces overall energy consumption. This technology is particularly advantageous for businesses in colder regions of Europe and the Middle East. When sourcing electric radiators, buyers should consider the integration of smart technology, which allows for programmable heating schedules, contributing to further energy savings.
What Advantages Do Drying Heaters Provide in the Textile Industry?
In the textile industry, drying heaters are essential for efficiently treating fabrics post-manufacturing. They expedite the drying process, thereby increasing production rates and decreasing energy consumption. For international buyers, especially in regions with high humidity, selecting drying heaters that match production capacities and provide consistent temperature control is critical for maintaining quality and efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘working of heater’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges with Inconsistent Heating Across Facilities
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly those in industries like manufacturing and warehousing, face the challenge of inconsistent heating across large facilities. This inconsistency can lead to uncomfortable working conditions, decreased productivity, and even damage to temperature-sensitive products. Buyers often struggle to identify the right heating solutions that can provide uniform heat distribution, especially in spaces with varying sizes and layouts.
The Solution: To address this problem, businesses should consider implementing a centralized electric heating system with zoning capabilities. By using smart heaters that can be controlled individually in different zones, companies can effectively tailor heating to specific areas based on their needs. When sourcing heaters, look for models equipped with programmable thermostats and IoT connectivity, which allows for remote monitoring and control. This enables facilities managers to adjust heating settings in real time, ensuring that every area of the facility maintains a consistent temperature, thus improving overall comfort and productivity.
Scenario 2: High Energy Costs Due to Inefficient Heating Systems
The Problem: B2B buyers are often confronted with rising energy costs linked to inefficient heating systems. Traditional heating methods, such as gas or oil-fired units, can lead to significant operational expenses, especially in colder climates or during peak usage times. This is particularly problematic for companies that operate on thin margins and need to keep overhead costs down.
The Solution: Transitioning to electric heaters can significantly enhance energy efficiency and reduce costs. Buyers should focus on sourcing high-efficiency electric heating units that utilize advanced technologies like thermal-fluid or ceramic cores, which are known for their superior heat retention and distribution capabilities. Furthermore, integrating these heaters with smart home technology allows for programmable heating schedules, ensuring that energy is only consumed when necessary. Companies can also explore bulk purchasing options or energy-efficient models eligible for government rebates, maximizing savings while investing in sustainable practices.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Maintenance and Reliability of Heating Systems
The Problem: Reliability and maintenance challenges are common pain points for businesses that rely on heating systems for operations. Frequent breakdowns or complicated maintenance procedures can lead to costly downtime, impacting production schedules and customer satisfaction. Buyers often find themselves overwhelmed when trying to assess the long-term viability and upkeep of their heating solutions.
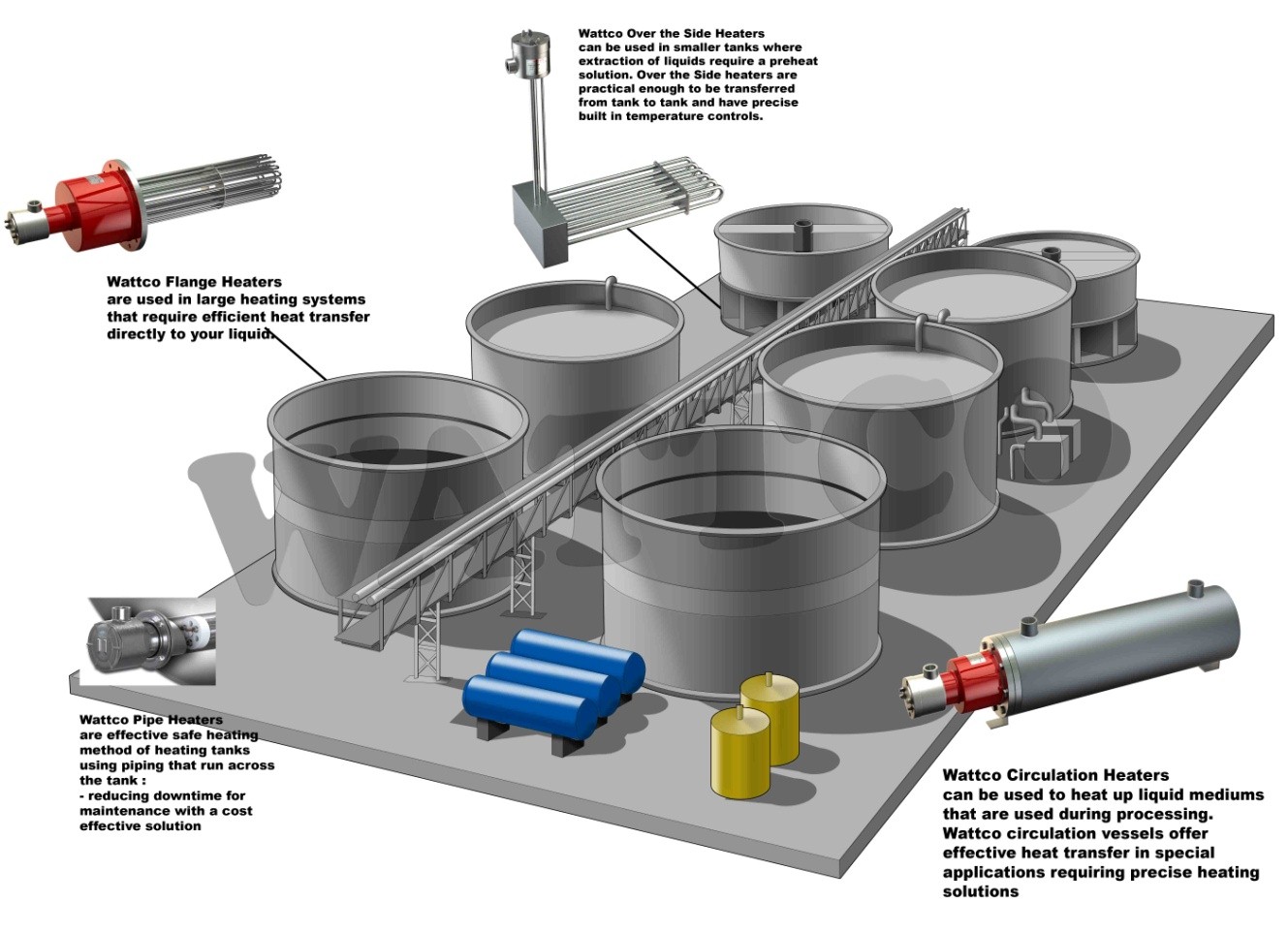
Illustrative image related to working of heater
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, businesses should prioritize sourcing electric heaters known for their durability and low maintenance requirements. Products with features such as self-diagnostic capabilities can alert users to potential issues before they escalate, allowing for proactive maintenance. Additionally, investing in high-quality heaters from reputable manufacturers, preferably with warranties and robust customer support, can provide peace of mind. Regular training for staff on maintenance best practices can also empower teams to handle minor issues, minimizing disruption and ensuring consistent heating performance.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for working of heater
What Are the Key Materials Used in Heaters?
When selecting materials for the construction of heaters, several factors come into play, including thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, cost, and manufacturing complexity. Here, we analyze four common materials used in heater applications: stainless steel, aluminum, ceramic, and copper. Each material has its unique properties and implications for performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Heater Applications?
Stainless steel is widely recognized for its excellent corrosion resistance and high-temperature performance. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 800°C (1472°F) and can withstand moderate pressure. The durability of stainless steel makes it suitable for various heating applications, including industrial heaters and residential heating systems.
Pros: Stainless steel is highly durable, resistant to rust and corrosion, and can endure high temperatures without deforming. It is also relatively easy to fabricate, which simplifies manufacturing processes.

Illustrative image related to working of heater
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost; stainless steel is more expensive than other materials like aluminum. Additionally, while it performs well under high temperatures, it may not be as efficient in heat transfer compared to copper.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with various heating media, including water and oil. Its corrosion resistance is particularly advantageous in humid or chemically aggressive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that the material meets local regulations for safety and environmental impact.
What Are the Benefits of Using Aluminum in Heaters?
Aluminum is another popular choice for heater construction due to its lightweight nature and excellent thermal conductivity. It typically has a temperature rating of around 600°C (1112°F), making it suitable for a variety of heating applications.

Illustrative image related to working of heater
Pros: Aluminum is cost-effective, lightweight, and offers good thermal conductivity, which enhances heating efficiency. Its ease of manufacturing allows for intricate designs and shapes.
Cons: While aluminum is resistant to corrosion, it can oxidize under certain conditions, which may affect its longevity. Additionally, its lower melting point compared to stainless steel makes it less suitable for extremely high-temperature applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various heating media but is particularly effective in applications requiring rapid heating and cooling cycles.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum components meet standards such as JIS for Japan and similar regulations in Europe. The material’s lightweight nature can also reduce shipping costs, which is an advantage for international procurement.
How Do Ceramic Materials Enhance Heater Performance?
Ceramic materials are often used in electric heaters due to their excellent thermal insulation properties and high-temperature resistance, typically rated up to 1000°C (1832°F). They are commonly found in applications like space heaters and industrial heating elements.
Pros: Ceramics are highly durable and can withstand extreme temperatures without degrading. They also provide excellent insulation, which helps in maintaining energy efficiency.
Cons: The brittleness of ceramic materials can be a concern, as they may crack or shatter under mechanical stress. Additionally, manufacturing complex shapes can be challenging and may increase costs.
Impact on Application: Ceramics are particularly well-suited for applications involving direct heat transfer to air or other gases, making them ideal for space heating.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards is essential, especially for safety in high-temperature applications. Buyers should also consider the availability of ceramic materials in their region, as sourcing can vary.
Why Is Copper a Preferred Material for Heaters?
Copper is renowned for its superior thermal conductivity, making it an excellent choice for heating elements. It typically operates effectively at temperatures up to 250°C (482°F) and is often used in applications like heat exchangers and electric heating elements.

Illustrative image related to working of heater
Pros: Copper’s high thermal conductivity ensures efficient heat transfer, which can lead to lower energy consumption. It is also highly malleable, allowing for versatile manufacturing options.
Cons: The main disadvantages of copper are its susceptibility to corrosion and higher cost compared to aluminum. It may require additional coatings or treatments to enhance its corrosion resistance.
Impact on Application: Copper is ideal for applications where rapid heat transfer is critical. However, it may not be suitable for corrosive environments without protective measures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that copper components comply with relevant standards such as ASTM for quality assurance. Given its cost, buyers in regions with budget constraints may need to weigh the benefits against the investment.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Heaters
| Material | Typical Use Case for working of heater | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Industrial heaters, residential heating | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost than aluminum | High |
| Aluminum | Rapid heating applications | Lightweight and cost-effective | Oxidizes under certain conditions | Medium |
| Ceramic | Space heaters, industrial heating | High-temperature resistance | Brittle and complex to manufacture | Medium |
| Copper | Heat exchangers, electric heating | Superior thermal conductivity | Susceptible to corrosion | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the properties and implications of various materials used in heater applications, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
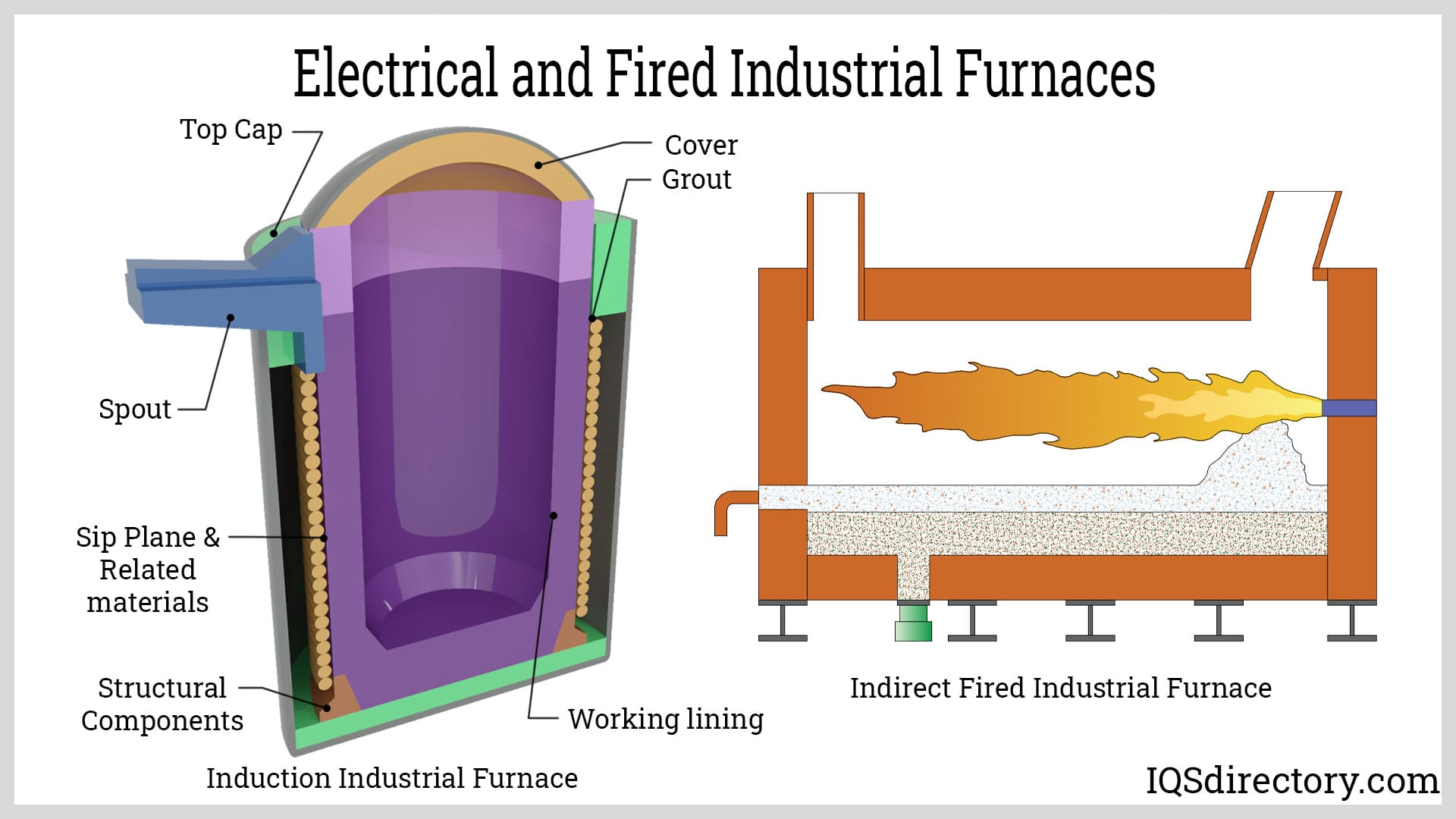
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for working of heater
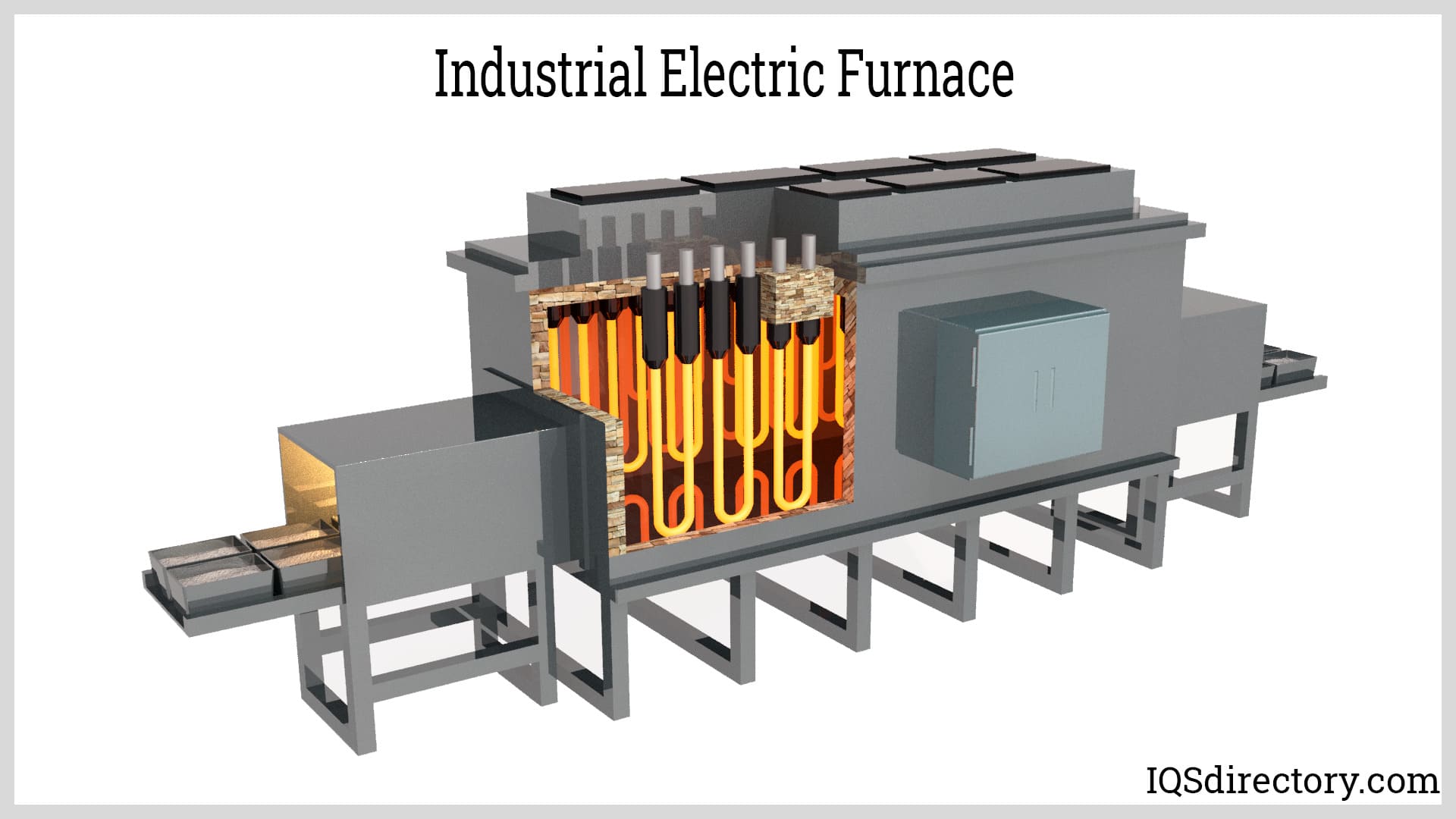
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Electric Heaters?
The manufacturing process of electric heaters involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets stringent quality and performance standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Electric Heater Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the first step in manufacturing electric heaters. This stage involves selecting high-quality raw materials that can withstand high temperatures and provide efficient heat conduction. Common materials include metals like aluminum, stainless steel, and copper, as well as ceramic and plastic components for insulation and casing.
Once materials are selected, they undergo a thorough inspection to ensure they meet specific standards. This may involve checking for impurities, verifying dimensions, and assessing material properties. Suppliers often need to provide certification documents that demonstrate compliance with international standards, such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems.
What Techniques Are Used for Forming Electric Heaters?
After preparation, the forming stage utilizes various techniques to shape the materials into components suitable for electric heaters. Common forming techniques include:
- Casting: Used for creating complex shapes, often for metal parts.
- Machining: Involves cutting, drilling, and shaping materials to achieve precise dimensions.
- Stamping: Commonly used for producing flat components, such as brackets and plates.
- Welding: Essential for assembling metal parts, ensuring strong and durable connections.
Each technique is selected based on the design specifications and the material’s properties, ensuring that the components can handle operational stresses.
How Are Electric Heaters Assembled?
The assembly stage is where all the prepared and formed components come together. This process typically involves:
- Component Integration: Parts such as heating elements, insulators, and casings are assembled into a complete unit.
- Electrical Connections: This includes wiring the heating elements to ensure proper functionality and safety.
- Quality Checks: Each unit undergoes initial quality checks to ensure all components are correctly installed and operational.
Automated assembly lines are often employed to enhance efficiency and consistency. However, skilled technicians oversee critical assembly tasks to ensure quality and safety standards are met.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Electric Heaters?
The finishing stage enhances both the aesthetic appeal and functional performance of electric heaters. Key processes include:
- Coating: Applying protective coatings to prevent corrosion and enhance durability.
- Painting: This provides a visually appealing finish and can be tailored to customer specifications.
- Final Inspection: Comprehensive checks are conducted to ensure the heater meets all design and safety standards.
Finishing touches often involve branding or labeling, which is vital for B2B buyers who may require specific identification for their products.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented During Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process of electric heaters. It encompasses various international and industry-specific standards to ensure that products are safe, reliable, and effective.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Electric Heaters?
Electric heater manufacturers typically adhere to several international standards, including:
- ISO 9001: Focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- API Standards: Relevant for electric heaters used in specific industrial applications, particularly in oil and gas sectors.
These certifications enhance product credibility and are crucial for B2B buyers who prioritize compliance and safety.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is conducted at various stages of the manufacturing process, typically categorized into three checkpoints:
Illustrative image related to working of heater
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring the manufacturing process to detect any deviations from quality standards in real time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting comprehensive tests on the finished product to ensure it meets all performance and safety standards before shipment.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Electric Heaters?
Testing methods are critical to ensuring that electric heaters operate safely and efficiently. Common testing methods include:
- Electrical Testing: Verifying insulation resistance, continuity, and functionality of heating elements.
- Thermal Testing: Measuring the heater’s performance in terms of heat output and efficiency.
- Safety Testing: Ensuring compliance with electrical safety standards to prevent hazards such as overheating or short circuits.
These tests are often documented in detailed reports, which can be crucial for B2B buyers who require evidence of compliance and performance.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is vital for ensuring product reliability. Here are actionable steps:
Illustrative image related to working of heater
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of manufacturing facilities can help assess compliance with quality standards and production capabilities.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality assurance reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC checks, to validate their processes.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can offer unbiased assessments of product quality and adherence to international standards.
-
Understand Regional Compliance Nuances: Buyers should familiarize themselves with specific compliance requirements in their regions. For instance, European buyers may prioritize CE marking, while those in Nigeria may need to verify compliance with local standards.
By implementing these practices, B2B buyers can ensure that they partner with reliable suppliers who prioritize quality in the manufacturing of electric heaters. This not only mitigates risks but also enhances the overall supply chain integrity, leading to better customer satisfaction and business success.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘working of heater’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to equip B2B buyers with a comprehensive checklist for procuring effective heating solutions. Understanding the working of heaters is essential for making informed purchasing decisions, ensuring efficiency, sustainability, and compatibility with your specific needs. This checklist will help you navigate the complexities of selecting the right heating technology for your business.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the heating solution you need. Consider factors such as heating capacity, energy efficiency, and the specific environment in which the heater will operate.
– Heating Capacity: Determine the required BTU (British Thermal Units) or wattage based on the space and application.
– Energy Efficiency: Look for heaters with high efficiency ratings to minimize operational costs.
Illustrative image related to working of heater
Step 2: Research Different Types of Heaters
Familiarize yourself with the various types of electric heaters available in the market, such as electric radiators, band heaters, and cartridge heaters. Each type has unique applications and benefits.
– Electric Radiators: Ideal for central heating systems without the need for boilers.
– Cartridge Heaters: Best suited for precise heating applications, especially in industrial settings.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a purchase, conduct thorough research on potential suppliers. Assess their experience, customer reviews, and product offerings.
– Company Profiles: Request detailed profiles that highlight their expertise in manufacturing and supplying heaters.
– Case Studies and References: Look for testimonials or examples of previous projects, especially those relevant to your industry.
Step 4: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that the heaters comply with local and international safety standards. This step is crucial for mitigating risks associated with electrical appliances.
– Certifications: Check for compliance with standards such as CE (European Conformity), UL (Underwriters Laboratories), or ISO certifications.
– Safety Features: Investigate built-in safety features like overheat protection and automatic shut-off mechanisms.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
Inquire about the after-sales support offered by suppliers, including warranty terms and maintenance services. Reliable support can significantly reduce downtime in case of equipment failure.
– Warranty Duration: Look for warranties that cover parts and labor for an extended period.
– Maintenance Services: Ensure that the supplier provides accessible support for repairs and maintenance.
Illustrative image related to working of heater
Step 6: Request Samples or Demonstrations
If possible, request samples or demonstrations of the heaters you are considering. This hands-on experience can be invaluable in assessing performance and suitability.
– Performance Testing: Evaluate the heater’s efficiency and heating capabilities in real-world conditions.
– User Experience: Assess ease of use, installation, and integration into existing systems.
Step 7: Compare Pricing and Payment Terms
Finally, compare pricing among various suppliers while considering the total cost of ownership, not just the initial purchase price.
– Total Cost of Ownership: Factor in energy consumption, maintenance, and potential savings from energy-efficient models.
– Payment Flexibility: Discuss payment terms that suit your cash flow requirements and negotiate bulk purchase discounts if applicable.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing heaters, ensuring optimal performance and reliability for their operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for working of heater Sourcing
When sourcing electric heaters, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for B2B buyers. The costs associated with the ‘working of heater’ can be categorized into several key components, each influencing the overall price.
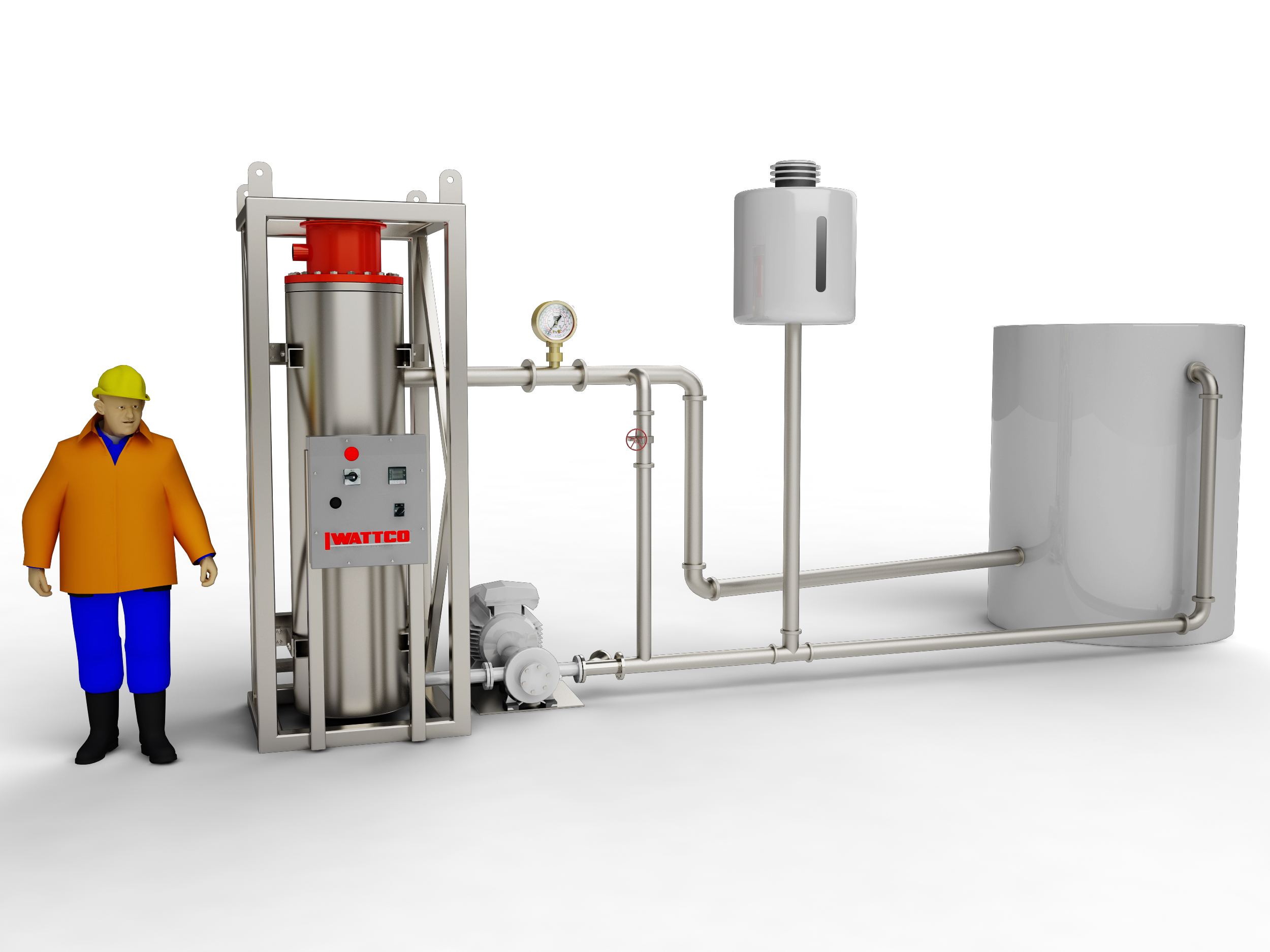
Illustrative image related to working of heater
What Are the Key Cost Components in Electric Heater Manufacturing?
-
Materials: The primary materials used in electric heaters include metals for the casing, electrical resistors, and insulation materials. High-quality materials often lead to better energy efficiency and longer lifespan, impacting the purchase price. For instance, heaters with ceramic cores may have a higher upfront cost but provide better performance and durability.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages paid to skilled workers involved in manufacturing, assembly, and quality assurance. The labor cost can vary significantly based on the region of production; countries with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, maintenance, and administrative costs. Efficient production processes can help minimize overhead costs, contributing to a more favorable pricing structure.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs refer to the investment in machinery and tools required for production. Custom tooling for specialized heater designs can increase initial costs but may yield better quality and efficiency in the long run.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that each heater meets safety and performance standards is essential. QC processes can add to costs but are crucial for maintaining product reliability, especially in markets with stringent regulations.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling expenses are significant, especially for international buyers. Factors such as shipping distance, mode of transport, and customs duties can influence the final cost of the heaters.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on market demand, competition, and the perceived value of the heater’s features.
What Factors Influence Pricing for Electric Heaters?
Several key factors can influence the pricing of electric heaters:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher order volumes can lead to discounts, reducing the per-unit cost. Buyers should consider their demand forecasts when negotiating with suppliers.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications can significantly increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected price increases.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Heaters with higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., energy efficiency ratings) typically command higher prices but offer better performance and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products, but they often provide better service and assurance of quality.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed-upon Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential as they dictate who bears the responsibility and costs of shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
How Can Buyers Optimize Costs When Sourcing Electric Heaters?
B2B buyers can adopt several strategies to optimize their sourcing costs:
-
Negotiation: Engaging in negotiations with suppliers can yield better pricing, especially if buyers demonstrate their commitment to larger orders or long-term partnerships.
-
Cost-Efficiency Analysis: Conducting a Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis can help buyers understand not just the upfront costs but also operational costs, maintenance, and energy consumption over the product’s lifecycle.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East should be aware of local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and import regulations that may affect pricing.
-
Research and Comparison: Conducting thorough market research and comparing multiple suppliers can uncover competitive pricing and better product options.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It’s important to note that the prices for electric heaters can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. Buyers should always seek quotes from multiple suppliers and take the time to understand the specific conditions that may affect pricing in their region.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing working of heater With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Heating Solutions
In the quest for efficient heating solutions, businesses often explore various technologies to meet their unique operational requirements. While traditional heaters are widely used, alternatives such as infrared heaters and heat pumps present distinct advantages. Understanding the differences in performance, cost, and implementation can guide B2B buyers in making informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Working of Heater | Infrared Heaters | Heat Pumps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Effective for localized heating; quick to warm up spaces. | Provides direct, radiant heat; highly efficient in enclosed spaces. | Transfers heat from the environment; can heat or cool spaces. |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; operational costs vary based on electricity rates. | Lower upfront costs; energy-efficient with lower operational costs. | Higher initial investment; long-term savings on energy bills. |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy installation; requires electrical supply. | Simple setup; can be portable or fixed. | More complex installation; may require professional setup. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; occasional checks needed. | Minimal maintenance; clean surfaces regularly. | Regular maintenance needed for optimal performance. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for individual rooms or small areas needing quick heat. | Best for workshops, garages, or outdoor areas; effective in heating people and objects directly. | Suitable for larger buildings; efficient for both heating and cooling needs. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Infrared Heaters: What Are Their Advantages and Disadvantages?
Infrared heaters utilize radiant heat to warm objects and people directly, rather than heating the air. This method offers high energy efficiency and is particularly effective in enclosed spaces, making it suitable for workshops or outdoor settings. The initial investment is generally lower compared to traditional heaters, and they often have lower operational costs. However, infrared heaters may not be as effective in larger, open areas, as their heat dissipates quickly without surfaces to absorb it.
Heat Pumps: How Do They Compare?
Heat pumps work by transferring heat from the external environment into a building, making them versatile for both heating and cooling applications. Although the initial setup cost can be significant, heat pumps provide long-term savings on energy bills due to their high efficiency. They are particularly advantageous in regions with moderate climates. On the downside, their installation can be complex and may require professional assistance, which could deter some businesses from adopting this solution.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Heating Solution for Your Business Needs
When selecting a heating solution, B2B buyers must consider various factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and the specific operational environment. For quick, localized heating, traditional heaters may suffice. However, for businesses looking for energy-efficient options with lower operational costs, infrared heaters or heat pumps could present more sustainable choices. Ultimately, the best solution will depend on the unique demands of the business and its long-term heating strategy.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for working of heater
What are the Key Technical Properties of Heaters Important for B2B Buyers?
When selecting heaters for industrial applications, understanding the critical technical properties can significantly impact operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of a heater refers to the type of materials used in its construction, such as stainless steel, aluminum, or ceramic. High-grade materials enhance durability and resistance to corrosion, which is crucial in harsh environments. For B2B buyers, selecting heaters with appropriate material grades can minimize maintenance costs and extend service life, ensuring reliable operation over time.
2. Wattage and Power Rating
Wattage indicates the power consumption of the heater and its ability to generate heat. A higher wattage typically results in faster heating times, which can be essential for processes requiring rapid temperature adjustments. Buyers should consider the specific heating needs of their applications to avoid underperformance or excessive energy consumption, leading to unnecessary operational costs.
3. Temperature Range
The temperature range specifies the minimum and maximum temperatures the heater can safely achieve. This property is vital for ensuring the heater meets the operational requirements of specific processes. Understanding the temperature range helps buyers select heaters that provide optimal performance without risking damage to equipment or materials being heated.
4. Heating Element Type
Different heating elements, such as resistive wire, ceramic, or induction coils, affect the efficiency and suitability of the heater for particular applications. For example, ceramic heaters may provide rapid heating but have lower efficiency compared to induction heating systems. Buyers should evaluate the heating element type in relation to their operational needs, balancing efficiency, speed, and cost.
5. Control Systems
Modern heaters often come equipped with advanced control systems, including programmable thermostats and digital interfaces. These systems allow for precise temperature management and can improve energy efficiency. For B2B buyers, investing in heaters with sophisticated control options can lead to significant savings and enhanced operational flexibility.
What are Common Trade Terms Relevant to the Heater Industry?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B heater market. Here are several key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces components or products that are then marketed by another company under its own brand. In the heater industry, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify quality manufacturers and ensure compatibility with existing systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for buyers to understand as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses plan purchases more effectively, especially when dealing with large-scale operations.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request price quotes from suppliers for specific products. This is essential for B2B transactions as it allows businesses to compare prices and terms from multiple vendors, ensuring they receive the best value for their investment.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers to clarify shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, thereby avoiding misunderstandings in international transactions.
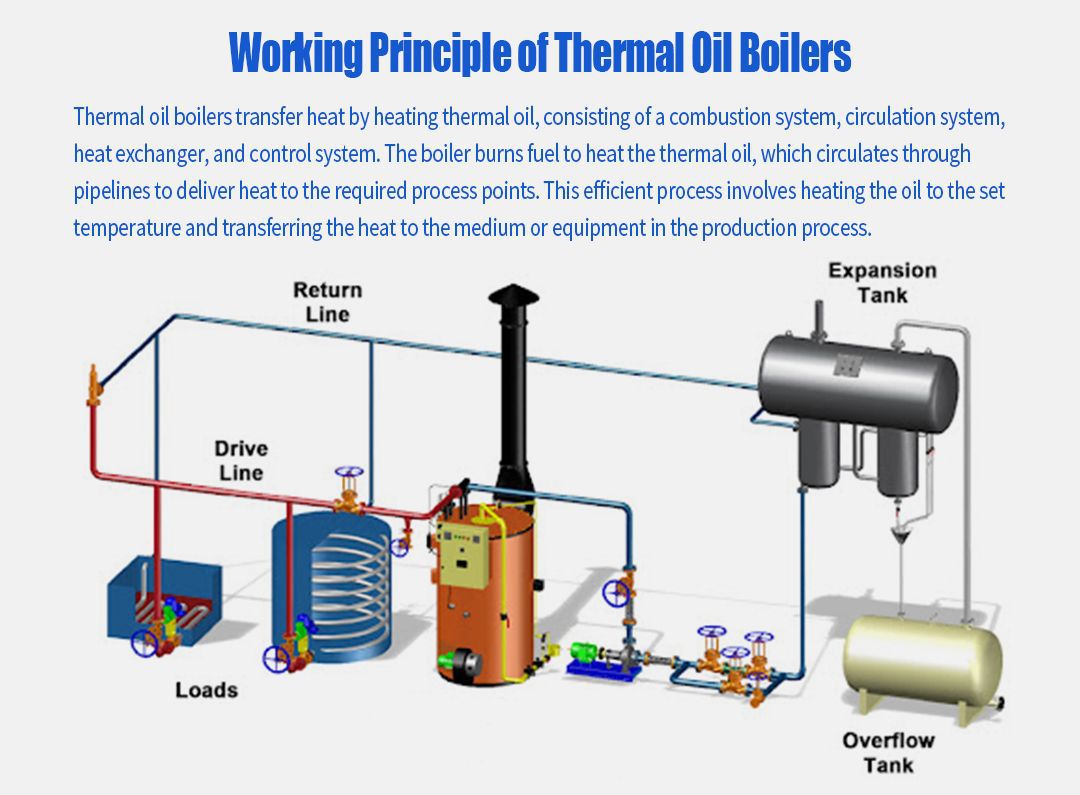
Illustrative image related to working of heater
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. In the heater industry, lead times can impact project timelines and operational planning. Buyers should consider lead times when negotiating contracts to ensure timely delivery of heating solutions.
By comprehensively understanding these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize their purchasing strategies, and enhance operational efficiency in their heating applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the working of heater Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Heater Sector?
The heater sector is witnessing transformative changes driven by various global trends. The increasing demand for energy-efficient heating solutions is paramount, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With a growing emphasis on sustainability, many countries are implementing regulations that promote electric and renewable energy sources over fossil fuels. This shift not only reduces carbon footprints but also aligns with international commitments to combat climate change.
Illustrative image related to working of heater
Emerging technologies are reshaping how heaters operate, with smart heating systems gaining traction. These systems allow users to control their heating remotely via smartphone applications, offering enhanced convenience and energy management. As businesses increasingly adopt smart home technologies, B2B buyers should consider sourcing heaters that integrate with Internet of Things (IoT) devices, providing more efficient energy consumption and user-friendly interfaces.
Moreover, the rising trend of customization in heating solutions is notable. Businesses are seeking heaters tailored to specific applications, such as industrial band heaters and cartridge heaters, which offer targeted heat for various materials. This customization not only enhances operational efficiency but also meets the diverse needs of different industries, from manufacturing to residential heating.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Heater Sector?
In the modern B2B landscape, sustainability and ethical sourcing are no longer optional; they are essential components of corporate responsibility. The environmental impact of heating solutions, particularly those that rely on fossil fuels, has led to an urgent need for eco-friendly alternatives. Electric heaters, which can be powered by renewable energy sources, are increasingly favored for their lower emissions and reduced environmental footprint.
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to ethical supply chains. This includes sourcing materials that are sustainably produced and ensuring that manufacturing processes adhere to environmental regulations. Certifications such as ENERGY STAR or eco-labels can serve as indicators of a product’s energy efficiency and environmental responsibility.
Moreover, businesses that adopt green practices not only contribute positively to the environment but also enhance their brand reputation. With consumers increasingly preferring to engage with eco-conscious brands, ethical sourcing can be a significant differentiator in competitive markets. By investing in sustainable heating solutions, companies can align their operations with broader environmental goals while potentially reducing costs associated with energy consumption.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Heating Technology Relevant to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of heating technology has been marked by significant advancements, transitioning from traditional fossil fuel reliance to innovative electric solutions. Initially, heating systems primarily depended on combustion methods, which posed both efficiency and environmental challenges. The introduction of electric heaters revolutionized the sector, offering more efficient and cleaner heating options.
Over the past few decades, technological innovations have further advanced heating systems, leading to the development of smart heaters that utilize AI and IoT capabilities. These modern systems not only provide efficient heating but also enable businesses to monitor and manage their energy usage effectively. This evolution has opened new avenues for B2B buyers to invest in advanced heating solutions that enhance operational efficiency while contributing to sustainability goals.
As the heater sector continues to evolve, international B2B buyers must stay informed about market dynamics and sourcing trends to make strategic decisions that align with their operational needs and corporate values.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of working of heater
-
1. How do I choose the right type of electric heater for my business needs?
Choosing the right electric heater for your business involves evaluating several factors such as the size of the space to be heated, the required temperature, and energy efficiency. For larger industrial applications, consider options like band heaters or cartridge heaters, which provide targeted heating. Additionally, assess the heater’s compatibility with existing systems and whether you require smart technology features for enhanced control. Consulting with suppliers for product specifications and recommendations based on your specific needs can significantly streamline your selection process. -
2. What are the key benefits of electric heaters compared to traditional heating systems?
Electric heaters offer numerous advantages over traditional heating systems, including higher energy efficiency, reduced operational costs, and lower emissions. They do not rely on combustion, making them more environmentally friendly. Additionally, many electric heaters are designed for easy installation and maintenance, requiring less infrastructure than conventional systems. Furthermore, the ability to customize heating schedules and zones enhances comfort and energy savings, making them an appealing option for diverse business environments. -
3. What customization options should I consider when sourcing electric heaters?
When sourcing electric heaters, consider customization options such as size, heating capacity, and control features. Some suppliers offer units that can be tailored to meet specific energy efficiency standards or to fit unique installation spaces. Additionally, inquire about smart technology integration, which allows for programmable settings and remote control. Custom branding and color options may also be available, allowing you to align the heaters with your business’s aesthetic and branding requirements. -
4. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for electric heaters?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for electric heaters can vary widely among manufacturers and suppliers. Typically, MOQs are influenced by factors such as the type of heater, customization requirements, and production capacity. For bulk purchases, some suppliers may offer reduced pricing or flexible terms. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms that align with your purchasing strategy. -
5. How do I verify the quality of electric heaters from international suppliers?
To verify the quality of electric heaters from international suppliers, request certifications and compliance documentation that meet international standards, such as CE, UL, or ISO certifications. Conduct thorough research on the supplier’s reputation, including reviews and testimonials from previous clients. If possible, request samples or conduct factory visits to assess the manufacturing processes. Establishing a quality assurance protocol and maintaining open communication throughout the procurement process can further ensure that you receive high-quality products. -
6. What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of electric heaters?
Payment terms for electric heaters can vary significantly based on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. Common options include upfront payments, net 30 or net 60 terms, and letter of credit arrangements for larger orders. Some suppliers may offer financing options or payment plans to accommodate your cash flow needs. It’s essential to discuss and negotiate payment terms upfront to ensure clarity and mutual agreement before finalizing contracts. -
7. What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing electric heaters?
When importing electric heaters, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs duties, and delivery timelines. Evaluate whether the supplier offers assistance with shipping and customs clearance to streamline the process. Additionally, factor in potential delays related to international shipping and ensure that you have contingency plans in place. Proper documentation, including invoices and certificates of origin, is also critical to facilitate smooth customs processing and avoid unexpected costs. -
8. How can I optimize energy efficiency with electric heaters in my facility?
Optimizing energy efficiency with electric heaters involves several strategies, including regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance, using programmable thermostats to manage heating schedules, and investing in heaters with high energy efficiency ratings. Additionally, insulating the space effectively can reduce heat loss and improve overall efficiency. Training staff on proper usage and monitoring energy consumption can further enhance savings, allowing your business to benefit from lower operational costs while maintaining a comfortable environment.
Top 4 Working Of Heater Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Industrial Electric Heaters
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Industrial electric heaters operate through a resistor within a circuit, generating heat as electricity meets resistance. They are known for efficiency, safety, and flexibility, with designs including oil-filled heaters and dry core electric radiators. Key components include heating elements made from durable materials like nichrome wire, and types of resistance heating wires include open wire, op…
2. Physics Stack Exchange – Heater Element Dynamics
Domain: physics.stackexchange.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: This company, Physics Stack Exchange – Heater Element Dynamics, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Scott Precision Wire – Heating Coils
Domain: scottprecisionwire.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: A heating coil consists of a coil of resistance wire, typically made from nickel chromium (nichrome) or iron chrome aluminum alloy, which has high resistivity and melting point. It is connected to an electrical power supply, generating heat through joule heating when an electric current flows through it. Heating coils can be used for air heating or in appliances like toasters and coffee machines. …
4. Moody Heating and Air – Heating Services
Domain: moodyheatingandair.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Moody Heating and Air Conditioning offers a range of heating services including heating maintenance, heating installation, heating repair, and ductless system services. Their heating systems include furnaces, boilers, and heat pumps, with key components such as thermostats, heat sources, and distribution systems. They emphasize the importance of energy efficiency and provide expert support with ce…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for working of heater
The evolving landscape of electric heating solutions presents significant opportunities for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By understanding the operational efficiencies of electric heaters—ranging from standalone units to advanced smart technology—businesses can make informed decisions that enhance both performance and sustainability.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Heating Solutions?
Strategic sourcing plays a crucial role in optimizing procurement processes, ensuring access to high-quality heating technologies while minimizing costs. By partnering with reliable suppliers, companies can leverage cutting-edge innovations, such as programmable and energy-efficient electric heaters, that not only reduce operational expenses but also support environmental sustainability goals.

Illustrative image related to working of heater
What Should International Buyers Consider Moving Forward?
As you navigate the complexities of sourcing heaters, consider the diverse applications and benefits of various types, such as oil-filled versus ceramic core units, to meet specific operational needs. The future of heating lies in adaptability and efficiency; therefore, investing in smart heating solutions will position your business for success in a competitive market.
In conclusion, seize the opportunity to enhance your heating solutions through strategic sourcing. Engage with trusted suppliers today to secure the best technology for your business’s heating requirements, paving the way for a more sustainable and efficient future.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.