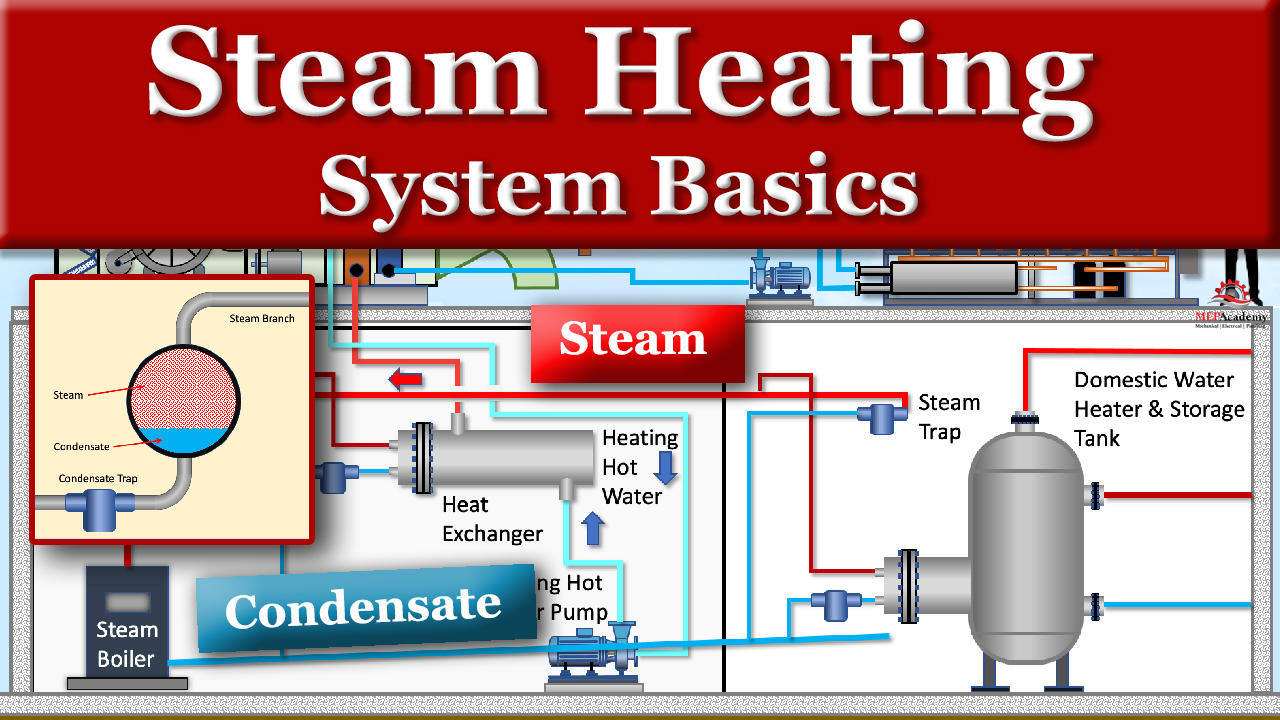
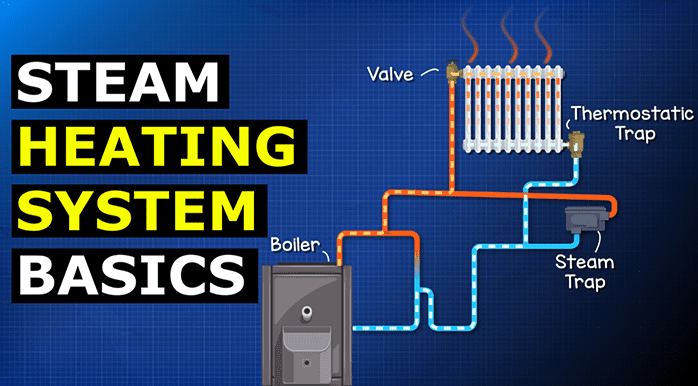
Unlocking Value: A Strategic Analysis of the Steam Heat System Diagram Market
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for steam heat system diagram
Navigating the complexities of sourcing an effective steam heat system diagram can be daunting for B2B buyers, particularly in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the intricacies of steam heating systems—including their types, applications, and operational efficiencies—is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, detailing various steam heating system designs, their applications in industrial and commercial settings, and essential considerations for supplier vetting and cost assessment.
As global markets continue to evolve, the demand for efficient and reliable steam heating solutions is paramount. This guide empowers B2B buyers by providing actionable insights into the key components of steam heat systems, from single-pipe configurations to advanced steam trap systems. It addresses common challenges faced by decision-makers, such as ensuring optimal heat modulation and selecting the right equipment for specific applications, whether in healthcare facilities or educational institutions.
With a focus on actionable strategies and practical advice, this guide will help you navigate the global market effectively, enabling you to select the right steam heating solutions that meet your operational needs and budget constraints. By leveraging the insights presented, international buyers can enhance their procurement processes, optimize energy efficiency, and ultimately drive business growth.
Understanding steam heat system diagram Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Pipe Steam System (Pitched Towards Boiler) | Uses the same pipes for steam and condensate; air valves required. | Warehouses, garages | Pros: Low installation costs. Cons: Poor heat control. |
| Single Pipe Steam System (Pitched Away from Boiler) | Improved separation of steam and condensate in different pipes. | Industrial facilities | Pros: Better efficiency. Cons: Still limited heat modulation. |
| Single Pipe Steam System (Overhead Distribution) | Complete separation of steam and condensate lines. | Large commercial buildings | Pros: Enhanced control over heating. Cons: Higher installation costs. |
| Steam Trap System | Utilizes traps to hold steam, allowing for better heat modulation. | Healthcare facilities, processing plants | Pros: Better individual radiator control. Cons: Increased complexity. |
| Two-Pipe Steam System | Separate pipes for steam supply and condensate return. | Academic institutions, large offices | Pros: Excellent heat control. Cons: Higher installation and maintenance costs. |
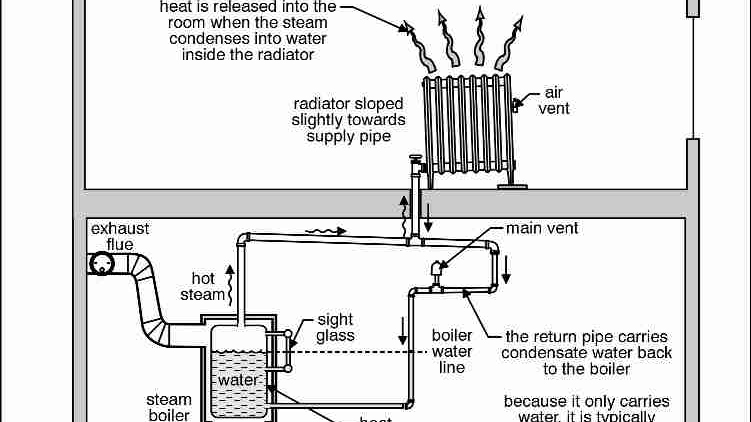
What are the Characteristics of the Single Pipe Steam System (Pitched Towards Boiler)?
The Single Pipe Steam System pitched towards the boiler is the most basic design, where both steam and condensate travel in the same pipe. This system is best suited for applications where individual radiator control is not critical, such as warehouses and garages. Buyers should consider that while installation costs are low, the system struggles with heat modulation, leading to inefficiencies in heating control.
How Does the Single Pipe Steam System (Pitched Away from Boiler) Improve Efficiency?
The Single Pipe Steam System pitched away from the boiler enhances steam and condensate separation by utilizing distinct paths for each. This design is preferable for industrial facilities where moderate efficiency is required. While it offers improved performance over the simpler design, it still lacks the ability to finely control heat output, which may be a consideration for buyers needing precise temperature regulation.
What Advantages Does the Overhead Distribution System Offer?
The Single Pipe Steam System with overhead distribution features complete separation of steam and condensate lines, allowing for optimal heat management. This system is ideal for large commercial buildings where diverse heating needs are present. Although it provides enhanced control over heating elements, the increased complexity and higher installation costs may deter some budget-conscious buyers.
Why is the Steam Trap System Important for B2B Buyers?
The Steam Trap System is crucial for businesses requiring precise heat control, such as healthcare facilities. By preventing steam loss and allowing for better modulation of heating elements, this system enhances overall energy efficiency. However, the added complexity and equipment requirements may lead to higher initial costs, making it essential for buyers to weigh these factors against the potential for long-term savings.
What Makes the Two-Pipe Steam System a Preferred Choice?
The Two-Pipe Steam System stands out for its ability to maintain separate supply and return lines for steam and condensate, enabling superior control over heating performance. This system is commonly used in academic institutions and large office buildings, where consistent temperature regulation is necessary. While it delivers excellent heat management, the higher installation and maintenance costs should be carefully evaluated by prospective buyers to ensure alignment with their operational budgets.
Key Industrial Applications of steam heat system diagram
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of steam heat system diagram | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Steam for sterilization and humidification | Ensures sterile environments and optimal humidity levels | Compliance with health regulations, reliability, efficiency |
| Food and Beverage | Steam heating for cooking and pasteurization | Enhances food safety and product quality | Equipment durability, energy efficiency, maintenance support |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Steam heat exchangers for process heating | Increases efficiency and control over chemical reactions | High-pressure systems, material compatibility, safety certifications |
| Textile Industry | Steam for dyeing and finishing processes | Improves fabric quality and process efficiency | Temperature control, steam quality, sourcing of parts |
| Power Generation | Steam in turbine operations | Maximizes energy output and operational efficiency | Boiler specifications, regulatory compliance, sourcing of spare parts |
How is the ‘steam heat system diagram’ used in Healthcare Facilities?
In healthcare settings, steam heat systems are crucial for sterilization and humidification processes. These systems help maintain sterile environments necessary for surgeries and other medical procedures, while also ensuring that humidity levels are optimal for patient comfort and equipment functionality. Buyers in this sector should prioritize systems that comply with health regulations and offer reliability to avoid any disruptions in critical operations. Additionally, energy efficiency is a key consideration, as hospitals often operate continuously and seek to minimize operational costs.
What role does steam heating play in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage industry, steam heating is extensively used for cooking, pasteurization, and sterilization of products. This application enhances food safety by effectively eliminating pathogens while preserving the quality and flavor of the food. For B2B buyers, it is essential to source equipment that guarantees durability and energy efficiency, as these factors directly impact production costs. Furthermore, maintenance support is crucial to ensure minimal downtime and uninterrupted production.
How is steam utilized in Chemical Manufacturing?
Steam heat exchangers are integral to chemical manufacturing processes, where they provide precise temperature control necessary for various reactions. By efficiently transferring heat, these systems help improve reaction rates and overall production efficiency. When sourcing steam systems for this sector, buyers must consider the specifications for high-pressure systems, material compatibility with chemicals, and necessary safety certifications to mitigate risks associated with chemical processing.
Why is steam heating important in the Textile Industry?
In the textile industry, steam is vital for dyeing and finishing processes, where it helps improve fabric quality by ensuring even dye application and proper finishing. The use of steam heat systems can significantly enhance process efficiency, reducing production times and waste. Buyers should focus on systems that offer precise temperature control and high-quality steam, as these features are essential for achieving optimal results in textile processing. Additionally, sourcing reliable parts is critical for maintaining operational efficiency.
How does steam contribute to Power Generation?
In power generation, steam plays a pivotal role in turbine operations, where it is used to convert thermal energy into mechanical energy. This process maximizes energy output and operational efficiency, making steam systems a cornerstone of modern power plants. For international buyers, key considerations include boiler specifications that meet regulatory standards, ensuring the sourcing of high-quality components, and having access to spare parts for maintenance. These factors are crucial for maintaining efficient and reliable power generation operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘steam heat system diagram’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Understanding Complex Steam Heat System Diagrams
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially those new to steam heating systems, face challenges in interpreting complex steam heat system diagrams. These diagrams often contain intricate details that can be overwhelming, leading to misunderstandings about how components interact. This confusion can result in poor decision-making regarding system design, installation, and maintenance, which ultimately impacts operational efficiency and safety.
The Solution: To navigate this complexity, buyers should invest time in training sessions or workshops focused on steam heating systems. Engaging with experienced engineers or consultants who can break down the diagrams into simpler, digestible parts is beneficial. Additionally, sourcing high-quality, annotated diagrams that highlight critical components and their functions can aid comprehension. For instance, diagrams that differentiate between steam and condensate lines, show the locations of steam traps, and indicate control valves can provide clarity. Utilizing software tools designed for creating and analyzing steam heat system diagrams can also simplify the process by allowing users to visualize changes and their impacts before actual implementation.
Illustrative image related to steam heat system diagram
Scenario 2: Inadequate Modulation and Control of Heat Output
The Problem: In many installations, B2B buyers encounter steam heating systems that lack effective modulation capabilities. Simple systems, like single-pipe setups, often result in uneven heating and inefficiencies because they can’t adequately control the heat output in different areas. This issue can lead to excessive energy consumption and increased operational costs, especially in large facilities where varying heat demands exist.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should consider upgrading to more sophisticated steam heat systems, such as those incorporating separate steam and condensate lines with steam traps. These systems allow for better heat modulation by enabling individual control of each heating element, ensuring that heat is distributed evenly across the facility. When specifying a new system or renovating an existing one, it is crucial to collaborate with HVAC professionals who can recommend the right components, such as thermostatic radiator valves, that enhance control capabilities. Furthermore, investing in advanced control systems that can monitor and adjust steam pressure and flow based on real-time demand can significantly improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Maintenance and Troubleshooting Existing Systems
The Problem: Many organizations grapple with outdated steam heating systems that are often neglected due to a lack of expertise in maintenance and troubleshooting. As experienced personnel retire, the knowledge transfer regarding the nuances of steam systems diminishes. This gap can lead to prolonged downtimes, costly repairs, and safety hazards, as issues like steam leaks or condensate buildup are not promptly addressed.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, organizations should prioritize creating a comprehensive maintenance program that includes regular training for current staff on steam heat system operation and troubleshooting techniques. Implementing a system of routine inspections, coupled with detailed documentation of previous issues and solutions, can empower teams to identify and rectify problems swiftly. Leveraging technology, such as IoT sensors for real-time monitoring of steam pressure and temperature, can also help detect anomalies early, facilitating proactive maintenance. Additionally, establishing partnerships with specialized service providers can ensure that expert support is available when needed, enhancing overall system reliability and safety.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for steam heat system diagram
What Are the Key Materials Used in Steam Heat Systems?
When selecting materials for steam heat systems, it is crucial to consider their properties, benefits, and limitations. Here, we analyze four common materials: carbon steel, stainless steel, copper, and cast iron. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly impact system performance and longevity.
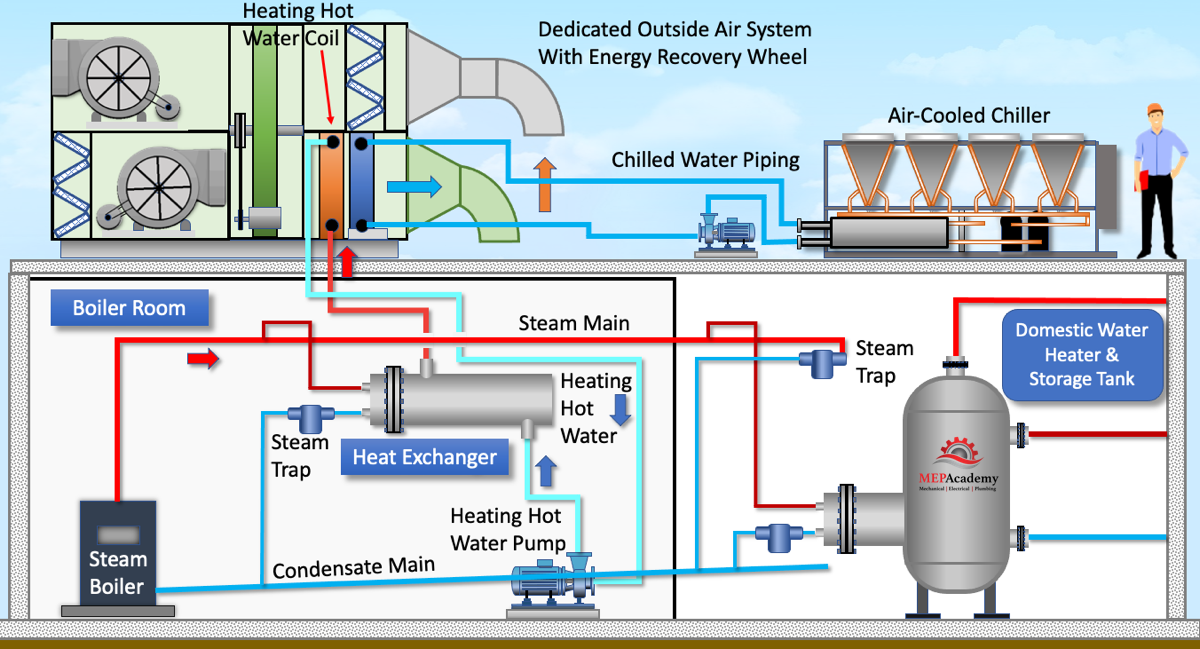
Illustrative image related to steam heat system diagram
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Steam Heat Systems?
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its strength and ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures, making it suitable for steam applications. It typically has a temperature rating up to 400°F (204°C) and can handle pressures exceeding 150 psi.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its cost-effectiveness and durability. However, it is susceptible to corrosion, especially in humid environments or when exposed to certain chemicals. This can lead to increased maintenance costs over time.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is compatible with steam and condensate but requires proper treatment to prevent corrosion, especially in regions with high humidity or aggressive water chemistry.
International Considerations: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM A106 for seamless carbon steel pipes. In Europe, adherence to DIN standards is crucial, while JIS specifications are relevant in Asia.
What Are the Advantages of Stainless Steel in Steam Heat Applications?
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures (up to 1,200°F or 649°C) and pressures. It is often used in applications requiring hygiene, such as food processing and healthcare.
Pros & Cons: The corrosion resistance of stainless steel is its greatest advantage, making it suitable for a wide range of environments. However, it is significantly more expensive than carbon steel and can be more challenging to fabricate.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for systems that require frequent cleaning or are exposed to corrosive substances. Its compatibility with steam makes it a preferred choice for heat exchangers and sterilization processes.
International Considerations: Compliance with ASTM A312 or EN 10216-5 is essential for international buyers. Regions with stringent hygiene standards, such as Europe, will favor stainless steel for its cleanliness and durability.
Why Is Copper a Preferred Material for Smaller Steam Heat Systems?
Key Properties: Copper has excellent thermal conductivity and can handle moderate pressures and temperatures, typically up to 300°F (149°C) and 100 psi. Its antimicrobial properties make it suitable for certain applications.
Pros & Cons: Copper’s high thermal conductivity allows for efficient heat transfer, making it ideal for smaller systems. However, it is more expensive than carbon steel and can be prone to corrosion in certain conditions.
Impact on Application: Copper is commonly used in residential steam heating systems and smaller commercial applications. Its compatibility with steam allows for efficient operation, but care must be taken to avoid corrosion from acidic environments.
International Considerations: Buyers should ensure compliance with ASTM B88 for copper tubing. In regions like the Middle East, where higher temperatures are common, proper insulation is necessary to maintain efficiency.
What Role Does Cast Iron Play in Steam Heat Systems?
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its durability and ability to retain heat. It can handle high temperatures (up to 1,000°F or 538°C) and pressures, making it suitable for steam applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of cast iron is its longevity and heat retention capabilities. However, it is heavy and can be brittle, making it less suitable for applications requiring frequent movement or modifications.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is often used in radiators and large steam heating systems where heat retention is critical. Its compatibility with steam makes it a reliable choice, but it requires careful handling to avoid cracking.
International Considerations: Compliance with ASTM A48 is essential for cast iron products. Buyers in Europe may look for adherence to EN standards, while those in South America should consider local regulations regarding material specifications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Steam Heat Systems
| Material | Typical Use Case for steam heat system diagram | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Main piping in industrial steam systems | Cost-effective and durable | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Heat exchangers in healthcare and food sectors | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and fabrication complexity | High |
| Copper | Residential steam heating systems | High thermal conductivity | Prone to corrosion in acidic conditions | Medium |
| Cast Iron | Radiators and large steam heating systems | Longevity and heat retention | Heavy and brittle | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions tailored to their specific regional requirements and applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for steam heat system diagram
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Steam Heat Systems?
The manufacturing process for steam heat systems involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a vital role in ensuring that the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Selected and Processed?
The manufacturing journey begins with selecting high-quality raw materials, which typically include carbon steel, stainless steel, and copper for pipes and fittings. Each material is chosen based on its thermal conductivity, resistance to corrosion, and suitability for high-pressure applications.
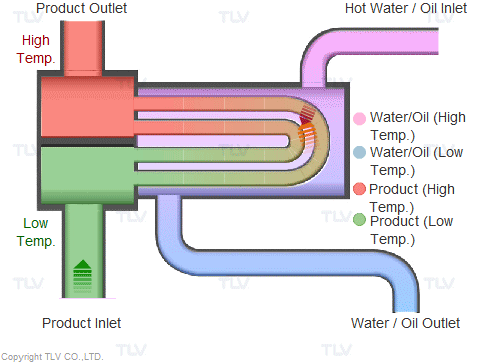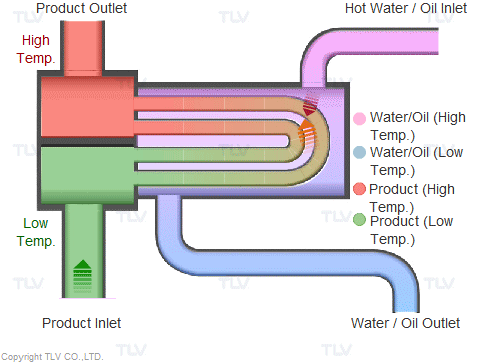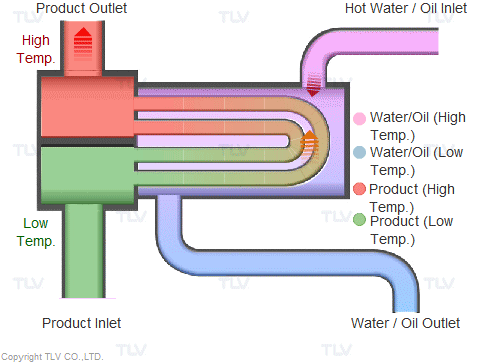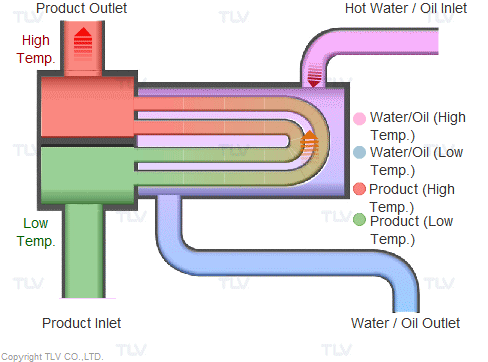
Illustrative image related to steam heat system diagram
Once selected, materials undergo preparation processes such as cutting, bending, and surface treatment. Cutting involves precision tools to ensure that each piece meets the specific dimensions required for the steam heat system. Surface treatments, such as galvanizing or coating, are applied to enhance durability and resistance to environmental factors.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Components?
The forming stage uses techniques like welding, machining, and forging to shape the components of the steam heat system. Welding is particularly significant as it creates strong joints between pipes and fittings, ensuring the system can withstand high pressure and temperature.
Machining further refines components to precise specifications, often employing CNC machines for accuracy. Forging may be used for critical parts, such as valves and flanges, to enhance strength through controlled deformation. Each technique contributes to the overall integrity and functionality of the system.
Assembly: How Are Different Components Integrated into a Complete System?
Once the components are formed, they are assembled into the complete steam heat system. This phase involves integrating various parts, including boilers, heat exchangers, and piping systems.
Assembly requires skilled labor to ensure that all connections are secure and leak-free. During this stage, attention is also given to the layout of the system, ensuring that steam flows efficiently and that condensate is properly managed.
Finishing: What Processes Ensure the System Meets Quality Standards?
The finishing stage includes cleaning, painting, and applying protective coatings to the assembled system. Cleaning removes any contaminants from manufacturing, while painting and coatings provide additional protection against corrosion and wear.
This stage often includes rigorous inspections to ensure that the product meets the necessary quality and safety standards before it is dispatched.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Steam Heat Systems?
Quality assurance (QA) is crucial in the manufacturing of steam heat systems to ensure reliability, safety, and performance.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should be familiar with several international standards that govern the quality of steam heat systems. ISO 9001 is a fundamental quality management standard applicable across various industries, ensuring that manufacturers implement effective quality management systems.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking in Europe and API standards for the petroleum industry provide assurance of compliance with safety and performance requirements. These certifications are critical for buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where regulatory compliance is a priority.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established at various stages of the manufacturing process to maintain high standards. These include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Ensures raw materials meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Involves monitoring and inspecting products during manufacturing to identify defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducted after assembly to verify that the complete system meets all specifications and standards.
Each of these checkpoints helps to minimize defects and ensure that only high-quality products reach the market.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance for Steam Heat Systems?
Testing is a critical component of the quality assurance process. Common methods include:
- Pressure Testing: Verifies that the system can withstand specified pressure levels without leaking.
- Leak Testing: Identifies any potential leaks in the system that could compromise performance.
- Functional Testing: Assesses the operation of all components under simulated conditions to ensure proper functionality.
These testing methods provide confidence in the performance and safety of steam heat systems.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers:
- Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of the manufacturing facilities can provide insight into the supplier’s QA processes and adherence to standards.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC.
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Hiring independent inspection agencies can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality assurance practices.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local regulations and standards is essential.
Buyers should be aware of variations in certification requirements and quality expectations across different markets. Engaging with suppliers who understand these nuances can facilitate smoother transactions and ensure compliance with local laws. Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences may affect communication, making it essential to establish clear channels of dialogue.
By focusing on robust manufacturing processes and stringent quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can confidently invest in steam heat systems that meet their operational needs while adhering to international standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘steam heat system diagram’
In this guide, we will outline a practical, step-by-step checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure steam heat system diagrams. This checklist will help ensure that you make informed decisions, select the right suppliers, and ultimately acquire the appropriate steam heating solutions for your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline your technical requirements for the steam heat system. This includes understanding the type of steam system you need (e.g., single pipe or two-pipe systems), the expected capacity, and the integration with existing infrastructure. Having detailed specifications will facilitate better communication with suppliers and ensure that the solutions proposed meet your operational needs.
Step 2: Research Industry Standards and Regulations
Familiarize yourself with relevant industry standards and regulations that apply to steam heating systems in your region. Compliance with these standards is crucial for safety, efficiency, and legal operation. Look for guidelines from organizations such as ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) or local regulatory bodies to ensure that your procurement aligns with best practices.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers of steam heat system diagrams. Review their company profiles, case studies, and testimonials from previous clients, particularly those in similar industries or regions. This evaluation helps you gauge their expertise and reliability, ensuring that you partner with a supplier capable of meeting your specific requirements.
- Key Considerations:
- Check for industry certifications and affiliations.
- Assess their experience with steam heating systems.
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed proposals that include technical specifications, pricing, and delivery timelines. A comprehensive proposal will allow you to compare offerings effectively and understand the value each supplier brings to the table. Pay attention to the clarity of the diagrams and whether they align with your predefined specifications.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Support and After-Sales Service
Evaluate the level of support and after-sales service offered by each supplier. Reliable support can significantly impact the long-term performance of your steam heating system. Check if they provide training, maintenance, and troubleshooting assistance, as well as warranties for their products.
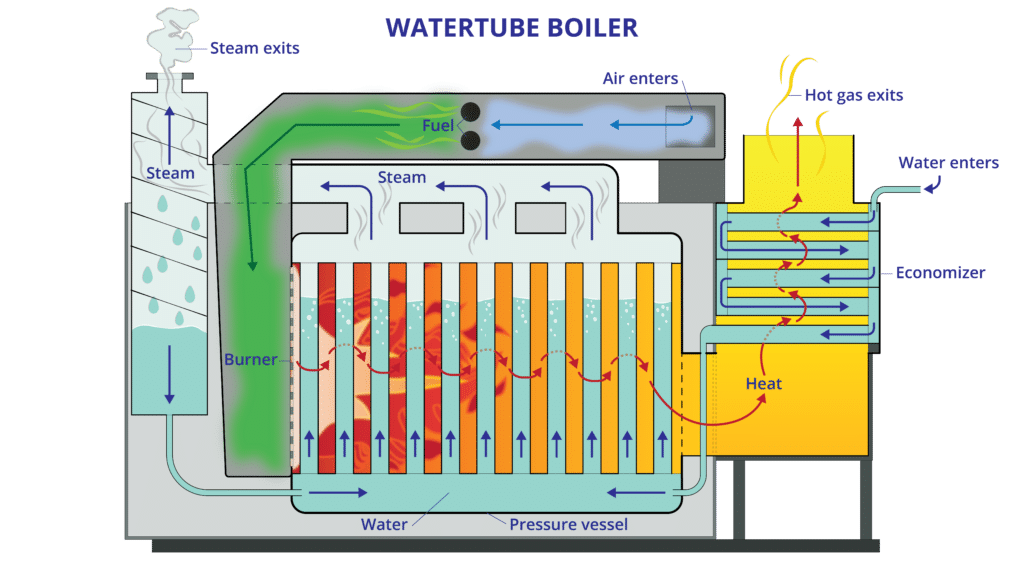
Illustrative image related to steam heat system diagram
- Important Questions to Ask:
- What is the typical response time for support inquiries?
- Are there training programs available for your staff?
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Finalize Contracts
Once you have selected a supplier based on the proposals and evaluations, engage in negotiations to finalize the terms of the contract. This includes pricing, payment terms, delivery schedules, and any warranties or service agreements. Clear contractual terms help prevent misunderstandings and ensure that both parties are aligned on expectations.
Step 7: Implement and Monitor the System
After procurement, ensure a smooth implementation of the steam heat system according to the provided diagrams. Monitor the system’s performance and efficiency to identify any issues early on. Regular assessments can help you maintain optimal operation and inform future procurement decisions.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement process for steam heat system diagrams, ensuring they select the right systems for their operational needs while also fostering strong supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for steam heat system diagram Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Steam Heat System Diagrams?
When sourcing steam heat system diagrams, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margin.
Materials account for a significant portion of the total cost, primarily due to the types of pipes, valves, and heat exchangers required. For instance, the choice between standard and high-grade materials can substantially affect pricing. Labor costs depend on the complexity of the system and the skill level required for installation and maintenance.
Illustrative image related to steam heat system diagram
Manufacturing overhead encompasses expenses related to production facilities, equipment, and utilities, which can vary widely by region. Tooling costs are linked to the specific machinery required to create customized components, influencing both lead times and pricing. Quality control ensures that the components meet industry standards, which is crucial for reliability but can add to the overall cost.
Logistics expenses, including transportation and customs duties, can significantly affect pricing, especially for international buyers. Lastly, the supplier margin reflects the profit margin that manufacturers or distributors apply to their products, influenced by market demand and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Steam Heat System Diagram Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of steam heat system diagrams. Volume and minimum order quantities (MOQ) play a critical role; larger orders typically result in lower unit costs due to economies of scale. Additionally, specifications and customization can drive up costs. A more complex design or unique materials will require more resources and time, thus increasing the overall price.
The quality and certifications of materials also influence pricing. Components that comply with international standards or carry quality certifications may command a premium, but they often provide enhanced reliability and efficiency, leading to lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) over time.
Illustrative image related to steam heat system diagram
Supplier factors such as reputation, experience, and customer service can also affect pricing. Established suppliers may offer higher prices due to their expertise and reliability, while newer entrants might provide lower costs to gain market share.
Lastly, Incoterms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, impacting the overall price. Understanding these terms can help buyers anticipate additional costs related to shipping, insurance, and duties.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs in Steam Heat System Diagram Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, negotiating effectively can yield significant savings. Begin by gathering comprehensive quotes from multiple suppliers to establish a baseline for negotiation. Leverage your purchasing power by discussing volume discounts or long-term contracts that can lead to reduced pricing.
When assessing Total Cost of Ownership, consider not just the initial purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and operational costs. Investing in higher-quality components may lead to lower maintenance costs and enhanced energy efficiency over time, resulting in savings that far outweigh the initial expenditure.
Familiarize yourself with pricing nuances specific to your region. For instance, tariffs and import duties can vary significantly, impacting the final cost. Additionally, understanding local market conditions and supplier capabilities can help you negotiate better terms.
Lastly, always request a detailed breakdown of pricing from suppliers. This transparency can facilitate more informed discussions about potential cost reductions and help identify areas where you can cut costs without compromising quality.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Please note that the prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can fluctuate based on market conditions, material availability, and specific project requirements. Always conduct thorough due diligence and obtain updated quotes from suppliers before making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing steam heat system diagram With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Heating Solutions
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial heating solutions, understanding the alternatives to traditional steam heating systems is crucial for B2B buyers. Steam heat systems have long been favored for their efficiency and reliability, but emerging technologies and methods present viable options that may better suit specific operational needs. This analysis will compare steam heat system diagrams against two alternative heating solutions: hot water heating systems and electric heating systems.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Steam Heat System Diagram | Hot Water Heating System | Electric Heating System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High thermal efficiency, suitable for large spaces | Moderate thermal efficiency, slower heating times | Quick heat-up time, less efficient for large areas |
| Cost | Moderate initial costs, but higher long-term maintenance | Lower installation costs, moderate operational costs | Higher initial costs, lower maintenance |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor for installation and maintenance | Relatively easier installation, often more straightforward | Simple installation, minimal technical expertise required |
| Maintenance | Regular checks needed, potential for leaks and pressure issues | Lower maintenance needs, but requires regular checks for water quality | Minimal maintenance, but reliance on electrical systems |
| Best Use Case | Large industrial settings, healthcare facilities | Residential buildings, commercial spaces | Small offices, temporary setups, or areas without gas supply |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Hot Water Heating Systems
Hot water heating systems use water as a heat transfer medium, which can be heated by a boiler or a heat exchanger. The advantages include lower installation costs and a simpler setup process compared to steam systems. Additionally, these systems are often more efficient in smaller spaces. However, they may not provide the same level of thermal efficiency for larger areas and can take longer to heat up. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure water quality and system integrity, making them suitable for residential buildings and smaller commercial applications.
Electric Heating Systems
Electric heating systems convert electrical energy directly into heat, offering quick heat-up times and minimal maintenance requirements. They are ideal for small offices or temporary setups, particularly in regions without access to gas or steam. The simplicity of installation is a significant advantage, as it requires less technical expertise compared to steam systems. However, the higher initial costs and lower efficiency in larger spaces can be a drawback, making them less suitable for extensive industrial applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Heating Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a heating solution, B2B buyers must consider various factors, including the scale of their operations, budget constraints, and specific heating requirements. Steam heat systems remain a robust choice for large-scale industrial applications, particularly in sectors like healthcare and manufacturing. However, for smaller setups or regions with limited gas access, hot water and electric heating systems offer viable alternatives that may be more cost-effective and easier to implement. By carefully assessing the pros and cons of each option, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and financial goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for steam heat system diagram
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of a Steam Heat System Diagram?
When evaluating steam heat systems, certain technical properties are critical for ensuring efficiency, reliability, and safety. Here are some of the most important specifications to consider:
Illustrative image related to steam heat system diagram
-
Material Grade
The materials used in steam heat systems, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, or copper, must be suited to withstand high temperatures and pressures. Material selection affects not only the system’s durability but also its thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion. B2B buyers should prioritize materials that align with local environmental conditions and regulatory standards to prevent costly failures. -
Operating Pressure
The operating pressure of a steam system is crucial for performance and safety. Systems are typically designed for low, medium, or high pressure, which influences the design of pipes, fittings, and heat exchangers. Understanding the required operating pressure helps in selecting the appropriate components, ensuring operational efficiency and compliance with safety regulations. -
Thermal Efficiency
This property measures how effectively a steam system converts energy into heat. High thermal efficiency reduces fuel consumption and operational costs, making it a key consideration for B2B buyers looking to enhance their energy management. Evaluating thermal efficiency involves analyzing the heat exchangers and insulation used in the system. -
Heat Transfer Rate
The heat transfer rate quantifies the amount of heat exchanged per unit time, which is vital for determining system capacity. This specification is critical in applications such as industrial processes and building heating, where precise temperature control is necessary. A higher heat transfer rate can lead to improved performance and reduced energy waste. -
Condensate Return Ratio
This ratio indicates the efficiency of condensate recovery in a steam system. A higher condensate return ratio signifies that more steam is converted back to water and reused, enhancing overall system efficiency. For B2B buyers, understanding this metric can lead to better investment decisions regarding system upgrades or replacements.
Which Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Understand in Steam Heat Systems?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the steam heat sector. Here are some key terms that buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces parts and equipment that are used in another company’s end products. In the context of steam heat systems, working with an OEM ensures that the components meet specific standards and are compatible with existing systems, ultimately leading to better performance and reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects purchasing decisions and inventory management, especially when dealing with specialized components for steam systems. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. Crafting a detailed RFQ can help B2B buyers obtain competitive pricing and better understand the market landscape for steam heat systems. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers navigate shipping, insurance, and delivery responsibilities, ensuring smoother transactions and reducing the risk of misunderstandings. -
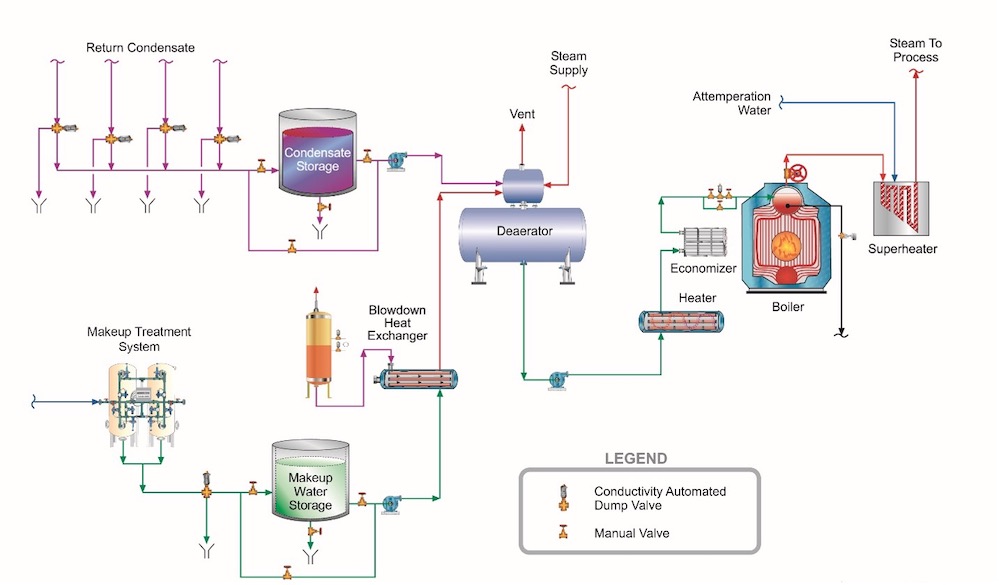
Heat Exchanger
A heat exchanger is a critical component in steam heating systems, facilitating the transfer of heat between two or more fluids. Understanding the types and specifications of heat exchangers can aid B2B buyers in selecting the right equipment for their specific applications. -
Steam Trap
A steam trap is a device that allows condensate and air to escape while preventing steam from leaving the system. Knowledge of steam traps is essential for B2B buyers as they play a significant role in system efficiency and performance.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize their steam heating systems, and achieve better operational outcomes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the steam heat system diagram Sector
What Are the Global Drivers and Key Trends Influencing the Steam Heat System Diagram Market?
The steam heat system diagram sector is experiencing notable shifts driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and evolving energy needs. Globally, the push for energy efficiency and carbon reduction is reshaping steam heating solutions. This is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where there is a growing emphasis on sustainable practices. The integration of smart technologies, including IoT-enabled steam systems, is emerging as a significant trend, allowing for real-time monitoring and optimization of energy consumption.
Moreover, the increasing focus on operational efficiency is leading to a demand for systems that can handle varying load requirements without compromising performance. In regions like Vietnam and Germany, where industrialization is rapidly advancing, buyers are looking for systems that can adapt to high-demand environments while maintaining cost-effectiveness. The market is also witnessing a rise in hybrid systems that combine steam with other heating methods, enhancing flexibility and efficiency.
International buyers should also consider the evolving landscape of regulatory standards that govern emissions and energy usage. Compliance with these regulations is becoming a critical factor in purchasing decisions, making it essential for suppliers to provide systems that not only meet current standards but are also future-proof.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Steam Heat System Diagram Market?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of purchasing strategies in the steam heat system diagram sector. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing solutions that minimize environmental impact, which includes selecting materials and technologies that are energy-efficient and have a lower carbon footprint. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions where environmental regulations are stringent and consumer awareness is high.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers that demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices throughout their supply chains. This includes the use of ‘green’ certifications and materials, which can signal to stakeholders a dedication to responsible sourcing and production methods. For instance, companies that utilize recycled materials or have effective waste management systems in place are becoming more attractive to discerning buyers.
Furthermore, the integration of renewable energy sources into steam heating systems is gaining traction. Systems that can incorporate biofuels or solar energy not only align with sustainability goals but also provide a competitive edge in terms of operational costs. By emphasizing these aspects, B2B buyers can ensure that their procurement strategies not only meet immediate operational needs but also contribute to broader environmental goals.
What Is the Historical Context of Steam Heat Systems in the B2B Sector?
The evolution of steam heat systems dates back to the industrial revolution when steam became a primary energy source for heating and power generation. Initially, these systems were simple and cost-effective, utilizing single-pipe designs that were easy to implement in industrial settings. Over time, as industries expanded and energy needs became more complex, the technology evolved to include multi-pipe systems and advanced heat exchangers.
In recent decades, the focus has shifted towards improving efficiency and reducing emissions, spurred by technological advancements and regulatory pressures. As a result, modern steam systems are designed with greater sophistication, enabling better control over heating processes and energy consumption. This historical context is crucial for B2B buyers, as it highlights the importance of selecting systems that not only meet current demands but also reflect the ongoing evolution towards sustainability and efficiency in the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of steam heat system diagram
-
How do I select the right steam heat system for my facility?
Choosing the appropriate steam heat system depends on several factors, including your facility’s heating requirements, the size of the space, and the intended application. For large industrial setups or healthcare facilities, consider a two-pipe or steam trap system for better control and efficiency. For smaller spaces, a single-pipe system may suffice. Evaluate your budget, energy efficiency goals, and maintenance capabilities. Consulting with an experienced engineer can provide tailored recommendations based on your specific needs. -
What are the advantages of a steam heat system compared to other heating systems?
Steam heat systems offer several advantages, including high heat transfer efficiency and the ability to maintain consistent temperatures in large spaces. They are particularly effective for industrial applications and can be used for both heating and process needs. Additionally, steam heating can be integrated with existing systems, making it a flexible option. However, it’s essential to consider the initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs when comparing it to alternatives like electric or hot water heating systems. -
What customization options are available for steam heat systems?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for steam heat systems to meet specific operational needs. These can include varying pipe sizes, different types of heat exchangers, and tailored control systems for temperature modulation. When discussing options with suppliers, be clear about your requirements, such as energy efficiency goals or unique facility constraints. Customization can enhance system performance and longevity, making it a worthwhile investment. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for steam heat systems?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for steam heat systems can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the specific products. Typically, MOQs may range from a single unit for smaller systems to larger quantities for industrial-grade installations. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements directly with potential suppliers to understand their policies and negotiate terms that suit your project needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing steam heat systems internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, especially in international transactions. Common terms include upfront deposits, progress payments, and final payments upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or letters of credit for larger orders. Always clarify payment terms early in negotiations and ensure they align with your budget and cash flow requirements. It’s also crucial to consider currency fluctuations and payment processing fees in international transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for steam heat systems?
To ensure quality assurance, source steam heat systems from reputable manufacturers with established certifications, such as ISO or ASME. Request detailed product specifications, testing results, and warranties. Additionally, consider conducting factory visits or audits, if feasible, to assess manufacturing practices. Engaging third-party inspection services can provide further assurance of product quality before shipment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing steam heat systems?
Logistics are crucial when importing steam heat systems. Consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that may apply to your order. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can provide support with documentation. Additionally, factor in lead times for production and shipping to ensure your project timelines are met. Collaborating with a reliable freight forwarder can simplify the process and mitigate risks. -
How do I troubleshoot common issues with steam heat systems?
Troubleshooting steam heat systems involves identifying common issues such as inconsistent heating, pressure drops, or leaks. Start by inspecting the system for blockages or malfunctioning steam traps. Checking the pressure gauges and ensuring proper insulation can also help identify problems. Regular maintenance, including cleaning and monitoring, is essential for preventing issues. If problems persist, consulting with a qualified engineer or technician can provide expert diagnosis and solutions tailored to your system.
Top 4 Steam Heat System Diagram Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. New England Steamworks – Premium Steam Piping Solutions
Domain: newenglandsteamworks.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Steam Header Piping & Steam Piping Illustrations, Premium Quality, Serving Eastern Massachusetts, Eastern Connecticut, Southern NH, and all of Rhode Island.
2. Engineering Toolbox – Steam Heating Systems
Domain: engineeringtoolbox.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Steam Heating Systems are designed for efficient heating applications, with various configurations available. The simplest system is the Single Pipe Steam System with Main Pipes Pitched Towards the Boiler, where steam and condensate share the same pipes, leading to challenges in heat control. This system is suitable for applications like warehouses and garages but not for individual radiator modul…
3. HeatingHelp – Steam Boiler Piping Guide
Domain: heatinghelp.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Steam Boiler Piping Diagram: The right way to pipe takeoffs from a header. Published on February 20, 2018. Related content includes a seminar on old steam heating systems and troubleshooting issues.
4. Pinterest – Hot Water Piping System Diagram
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: This company, Pinterest – Hot Water Piping System Diagram, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for steam heat system diagram
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in Steam Heat Systems?
As we conclude this guide on steam heat systems, it’s essential to recognize the strategic advantages that come with effective sourcing and implementation of these systems. Understanding the various configurations—such as single-pipe versus two-pipe systems—allows businesses to select the most suitable options for their operational needs. Moreover, investing in advanced systems like steam trap mechanisms can lead to improved efficiency and better modulation of heat, directly impacting energy costs and operational reliability.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Operations?
Strategic sourcing not only optimizes your supply chain but also enhances your capability to respond to market demands. For international buyers, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, and the Middle East, tapping into innovative steam heat solutions can significantly elevate your competitive edge. By aligning with reputable suppliers and manufacturers, you can ensure that your systems are not only cost-effective but also technologically advanced, providing long-term value.
Illustrative image related to steam heat system diagram
What’s Next for Your Business in Steam Heating?
Looking ahead, the future of steam heating systems is poised for innovation. As industries evolve, there will be an increasing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability. We encourage you to take the next step in exploring advanced steam heating solutions that align with your business goals. Engage with trusted suppliers, attend industry seminars, and invest in training for your team to stay at the forefront of this essential technology. Your proactive approach will not only enhance operational performance but also contribute to a more sustainable future.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.