The Definitive Guide to Acid For Etching Knives: Cost, Materials & Top Vendors
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for acid for etching knives
In the competitive landscape of knife manufacturing and customization, sourcing high-quality acid for etching knives presents a critical challenge for B2B buyers. With the growing demand for personalized and unique designs, understanding the nuances of acid etching is essential for businesses aiming to enhance their product offerings. This guide delves into the diverse types of etching acids available, their applications across various metal types, and the intricacies of supplier vetting to ensure safety and quality.
By addressing key considerations such as cost, regulatory compliance, and environmental impact, this comprehensive resource empowers international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets like Vietnam and Germany. It equips decision-makers with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions, ultimately leading to improved product quality and customer satisfaction.
As the knife market evolves, leveraging the right etching solutions can differentiate your business and meet the rising expectations of consumers seeking both functionality and artistry in their tools. Whether you are a manufacturer looking to expand your capabilities or a retailer aiming to provide custom options, this guide serves as your roadmap to navigating the global market for acid used in knife etching.
Understanding acid for etching knives Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ferric Chloride | Commonly used, effective on various metals | Custom knife manufacturing, hobbyists | Pros: Readily available, effective, and affordable. Cons: Requires careful handling and disposal. |
| Nitric Acid | Strong etching ability, faster reaction time | Industrial applications, metal art | Pros: Quick results, versatile on different materials. Cons: Highly corrosive, requires safety measures. |
| Hydrochloric Acid | Aggressive etching, primarily for stainless steel | Heavy-duty industrial etching | Pros: Effective for deep etches. Cons: Strong fumes, requires specialized safety equipment. |
| Phosphoric Acid | Milder, often used for surface preparation | Surface finishing, rust removal | Pros: Less hazardous, good for pre-treatment. Cons: Slower etching process, less effective on hard metals. |
| Sulfuric Acid | Very strong, used for precision etching | Electronics, custom engraving | Pros: High precision, effective on a range of substrates. Cons: Extremely hazardous, requires careful handling. |
What Are the Characteristics of Ferric Chloride for Etching Knives?
Ferric Chloride is a widely used acid for etching knives due to its effectiveness and availability. It operates well on various metals, making it suitable for both custom knife manufacturers and hobbyists. When considering B2B purchases, buyers should note its affordability and ease of use. However, it requires careful handling and proper disposal due to its corrosive nature, which can pose environmental risks if not managed correctly.
How Does Nitric Acid Differ in Etching Applications?
Nitric Acid is known for its strong etching ability and faster reaction time compared to other acids. It is predominantly used in industrial applications and metal art, where quick results are essential. Buyers should consider the need for safety measures when handling Nitric Acid, as it is highly corrosive. While its versatility on different materials is a significant advantage, the potential hazards associated with its use necessitate thorough training and protective equipment for workers.
Why Choose Hydrochloric Acid for Heavy-Duty Etching?
Hydrochloric Acid is recognized for its aggressive etching capabilities, making it particularly effective for stainless steel. This makes it a preferred choice for heavy-duty industrial etching applications. While its ability to create deep etches is beneficial, buyers must be aware of the strong fumes it emits, which require specialized safety equipment. Businesses should evaluate their safety protocols and training before incorporating Hydrochloric Acid into their processes.
What Are the Benefits of Using Phosphoric Acid in Surface Preparation?
Phosphoric Acid is a milder option often used for surface preparation and rust removal. It is less hazardous compared to stronger acids, making it suitable for businesses that prioritize worker safety. Although it is slower in its etching process, its effectiveness in pre-treatment applications is notable. Buyers should weigh the slower etching speed against the safety benefits when deciding on its use in their operations.
When to Consider Sulfuric Acid for Precision Etching?
Sulfuric Acid is a very strong acid ideal for precision etching applications, particularly in electronics and custom engraving. Its high precision is a key advantage for businesses requiring detailed work. However, it is extremely hazardous and requires careful handling, including specialized equipment and training for employees. Organizations must ensure compliance with safety regulations to mitigate risks associated with Sulfuric Acid use in their etching processes.

Illustrative image related to acid for etching knives
Key Industrial Applications of acid for etching knives
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of acid for etching knives | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Custom knife production for industrial use | Enhances product differentiation and branding through unique designs | Reliable acid quality and safe handling procedures |
| Culinary | Etching high-end kitchen knives with logos or designs | Adds aesthetic appeal and personalization, increasing customer loyalty | Compliance with food safety regulations |
| Artisanal Crafts | Personalization of handmade knives | Creates unique, bespoke products that can command higher prices | Availability of various acid types suitable for different metals |
| Outdoor Equipment | Branding on survival and tactical knives | Builds brand recognition and trust among outdoor enthusiasts | Consistency in acid concentration for uniform results |
| Restoration Services | Restoration of vintage knives | Restores original markings and aesthetics, increasing value | Knowledge of historical knife materials and appropriate etching methods |
How is Acid for Etching Knives Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, acid for etching knives is primarily employed to create custom designs and markings on industrial knives. This allows manufacturers to differentiate their products in a competitive market. The etching process can resolve issues related to brand recognition and product identity, making it essential for businesses aiming for a unique market position. Buyers should ensure they source high-quality acids and have robust safety protocols in place, especially when dealing with large-scale production.
What Role Does Acid Etching Play in the Culinary Industry?
In the culinary industry, acid etching is utilized to personalize high-end kitchen knives with logos or unique designs. This not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the knives but also fosters customer loyalty by providing a personalized touch. For international buyers, especially from regions with strict food safety regulations, it is crucial to ensure that the acids used are compliant with health standards to avoid contamination and maintain product integrity.
How Do Artisanal Crafts Benefit from Acid Etching?
Artisanal crafts leverage acid for etching knives to create bespoke, personalized products that stand out in the market. This technique allows artisans to add intricate designs and markings that reflect their craftsmanship, thus commanding higher prices. Buyers in this sector should consider the variety of acids available and their compatibility with different metals, ensuring that the etching process enhances rather than diminishes the quality of the final product.

Illustrative image related to acid for etching knives
Why is Acid Etching Important for Outdoor Equipment?
For outdoor equipment manufacturers, acid etching serves as a method to brand survival and tactical knives effectively. This process not only enhances product aesthetics but also builds trust among outdoor enthusiasts who value quality and branding. Buyers should focus on sourcing acids that provide consistent results, as variations in etching can affect brand perception and product reliability.
How Can Restoration Services Utilize Acid Etching?
Restoration services utilize acid for etching knives to restore original markings and aesthetics on vintage knives. This not only revitalizes the item but also increases its market value. Buyers in this field should possess a deep understanding of historical knife materials and the appropriate etching methods, ensuring that restoration does not compromise the knife’s integrity or authenticity.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘acid for etching knives’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Etching Results Leading to Product Quality Issues
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter inconsistencies in the etching results when using acid, leading to quality issues that can affect the end product’s aesthetics and marketability. Variations in etching depth, uneven application, or unintentional damage to the blade can diminish the overall quality of the knives. This inconsistency not only impacts customer satisfaction but can also lead to increased return rates, wasted materials, and potential reputational damage in competitive markets.
The Solution: To achieve consistent etching results, buyers should invest in comprehensive training for their staff on the acid etching process. This includes understanding the specific types of acid suitable for different metal compositions and the effects of various concentrations. Additionally, implementing a standardized procedure for surface preparation, including thorough cleaning and proper masking, can significantly improve outcomes. Regularly calibrating and maintaining etching equipment is also crucial. For example, utilizing a controlled environment with consistent temperature and humidity can lead to more predictable results. Finally, consider employing a quality assurance step where test etches are performed on scrap material before full production runs to ensure the desired quality is achieved.

Illustrative image related to acid for etching knives
Scenario 2: Safety and Regulatory Compliance Challenges with Acid Handling
The Problem: Handling acids for etching poses significant safety risks, including skin burns and inhalation of harmful vapors. B2B buyers must comply with local and international safety regulations, which can be complex and vary significantly by region. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in severe penalties, accidents, or even business shutdowns. Buyers often find it challenging to ensure that their teams are properly trained in safe handling practices while also meeting compliance requirements.
The Solution: Buyers should establish a robust safety program that includes comprehensive training for all employees involved in the etching process. This training should cover the proper handling, storage, and disposal of acids, as well as the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and masks. Implementing a clear labeling system for all chemicals and maintaining a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for each substance used is essential for compliance. Additionally, buyers can work with local regulatory bodies to ensure that all practices align with current safety standards. Investing in specialized storage solutions, like acid-resistant cabinets, can also enhance safety and compliance. Regular safety audits can help identify potential risks and improve training programs.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Sourcing High-Quality Acid for Etching
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle to find reliable suppliers for high-quality acids needed for etching processes. Inconsistent quality of the acid can lead to unsatisfactory etching results, affecting the overall quality of the knives produced. Additionally, suppliers may not provide adequate information regarding the acid’s composition, concentration, or suitability for specific metals, leading to further complications in the etching process.
The Solution: To mitigate sourcing issues, buyers should establish partnerships with reputable suppliers who specialize in chemicals for industrial applications. Conducting thorough supplier evaluations based on quality certifications, customer reviews, and product consistency is essential. It may also be beneficial to attend industry trade shows or chemical expos to connect with potential suppliers and gain insights into new products and technologies. Buyers can request samples from suppliers to test for compatibility with their specific etching processes before making bulk orders. Additionally, consider forming cooperative purchasing groups with other businesses to negotiate better terms and ensure access to high-quality materials. Regular communication with suppliers about their quality assurance processes can further ensure consistent delivery of the required acids for etching.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for acid for etching knives
What Are the Key Materials for Acid Etching Knives?
When considering acid for etching knives, selecting the right material is crucial for achieving optimal results. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the acid etching process, focusing on their properties, advantages and disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.

Illustrative image related to acid for etching knives
1. Ferric Chloride
Key Properties: Ferric Chloride is widely used for etching due to its effectiveness in removing metal from surfaces. It operates effectively at room temperature and has a relatively low viscosity, making it easy to work with in various applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of Ferric Chloride is its strong etching capability on ferrous metals, which makes it suitable for knife blades. It is cost-effective and readily available in many regions. However, it can be corrosive to other materials and requires careful handling and storage to avoid environmental hazards.
Impact on Application: Ferric Chloride is compatible with a variety of steel types commonly used in knife manufacturing. Its effectiveness can vary based on the concentration and temperature, necessitating careful preparation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local regulations regarding the handling and disposal of hazardous materials. Compliance with international safety standards such as ASTM and local regulations is essential.
2. Hydrochloric Acid
Key Properties: Hydrochloric Acid is a strong acid that can etch a wide range of metals. It is effective at higher temperatures, which can enhance its etching speed.
Pros & Cons: Its primary advantage is the speed of etching, which can significantly reduce production time. However, it is highly corrosive and poses safety risks, requiring stringent safety measures during use. Additionally, it can damage non-target areas if not applied carefully.
Impact on Application: Hydrochloric Acid is particularly effective on stainless steels, making it a good choice for high-end knife manufacturers. However, its aggressive nature can lead to unwanted pitting if not monitored closely.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with safety standards is critical, especially in regions with strict environmental regulations. Buyers should ensure they have the necessary safety equipment and training for handling this material.
3. Sulfuric Acid
Key Properties: Sulfuric Acid is a strong dehydrating agent and can be used for etching metals. It is effective at room temperature but can be enhanced with heat.
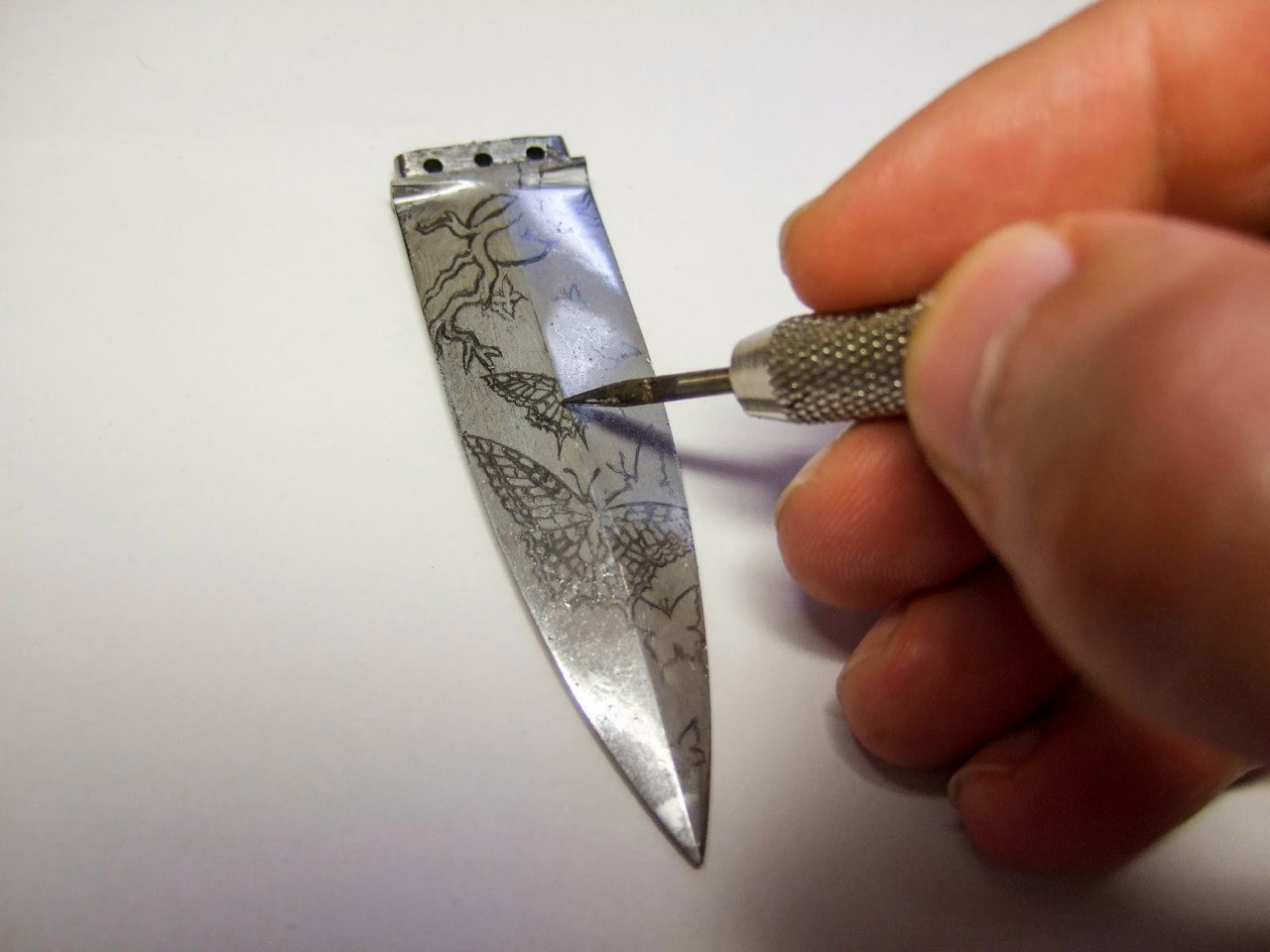

Illustrative image related to acid for etching knives
Pros & Cons: The advantage of Sulfuric Acid lies in its ability to create deep etches, which can enhance the aesthetic appeal of knives. However, it is highly corrosive and can be dangerous if mishandled. The disposal of sulfuric waste also poses environmental challenges.
Impact on Application: This acid is particularly effective on carbon steels and can produce a distinct finish. However, its aggressive nature may require additional protective measures to prevent damage to the knife’s structure.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should be aware of the stringent regulations regarding the use of sulfuric acid. Compliance with EU REACH regulations is essential for safe handling and disposal.
4. Phosphoric Acid
Key Properties: Phosphoric Acid is less aggressive than the aforementioned acids and is often used for etching and passivation. It is effective at room temperature and can be used safely with proper precautions.
Pros & Cons: Its primary advantage is that it is less corrosive, making it safer for operators and the environment. However, it may require longer etching times compared to stronger acids, which could extend production cycles.
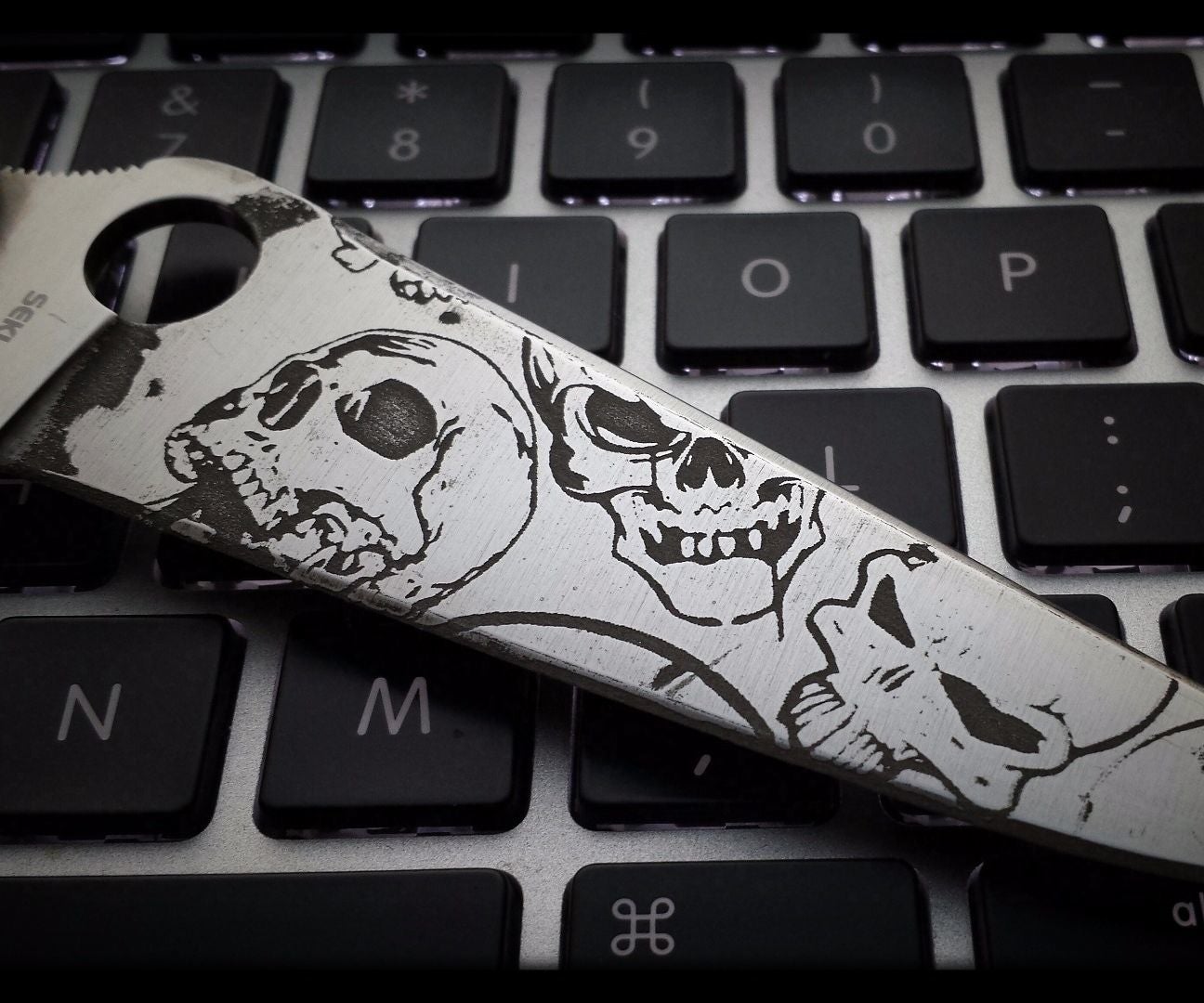

Illustrative image related to acid for etching knives
Impact on Application: Phosphoric Acid is suitable for stainless steels and can improve corrosion resistance, making it ideal for knife applications where durability is essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: For buyers in regions like Vietnam and Germany, understanding local safety standards and environmental regulations is crucial. Phosphoric Acid may be subject to fewer restrictions compared to stronger acids, but safety protocols should still be followed.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for acid for etching knives | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferric Chloride | Etching ferrous metals for knife blades | Effective and cost-efficient | Corrosive and requires careful handling | Low |
| Hydrochloric Acid | Fast etching of stainless steels | Speed of etching | Highly corrosive and safety risks | Med |
| Sulfuric Acid | Deep etching for aesthetic finishes | Creates distinct finishes | Dangerous and environmental concerns | High |
| Phosphoric Acid | Etching and passivation of stainless steels | Less corrosive and safer to handle | Longer etching times | Med |
This guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials used for acid etching knives, enabling informed decisions that align with operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for acid for etching knives
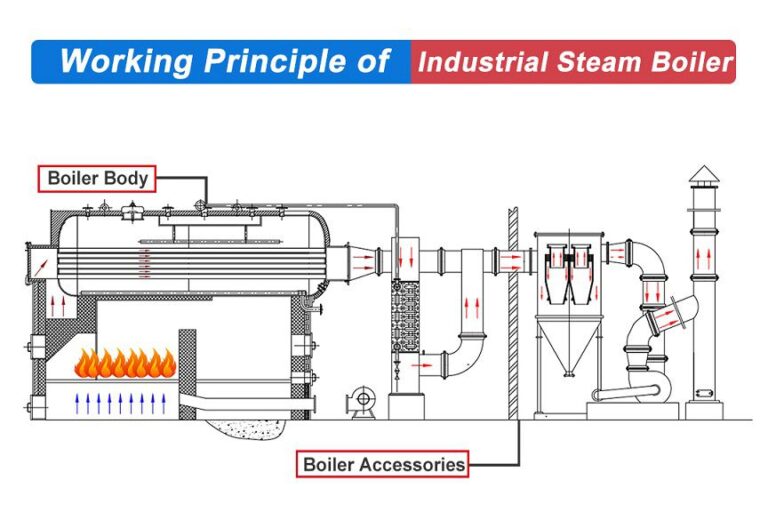
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Acid Used in Knife Etching?
The manufacturing process for acid used in etching knives involves several critical stages that ensure both the quality of the acid and its suitability for various applications. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: This initial phase involves sourcing high-quality raw materials, such as Ferric Chloride, which is commonly used for etching. Suppliers must ensure that the chemicals meet industry standards and regulations. This may include testing for purity and concentration levels. Proper storage conditions are also essential to maintain the integrity of the chemicals.
-
Forming: In this stage, the prepared materials are mixed to create the etching solution. For instance, Ferric Chloride may be diluted with distilled water to achieve the desired concentration. The mixing process requires precise measurements and adherence to safety protocols, as improper handling can lead to hazardous reactions.
-
Assembly: While the term “assembly” may not directly apply to the manufacturing of acids, it is crucial to ensure that all components, such as containers and packaging materials, are compatible with the acid. This stage also includes labeling and safety information to comply with international regulations.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves quality checks and packaging. The acid solution is transferred into suitable containers, which are then sealed to prevent contamination. Proper labeling is vital to communicate safety information and usage instructions. This stage ensures that the product is ready for distribution while maintaining quality.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Acid for Etching Knives?
Quality control (QC) is paramount in the production of acid for etching knives, ensuring that the final product meets international standards and customer expectations. Key aspects of QC include adherence to relevant international standards, implementation of QC checkpoints, and employing common testing methods.
-
International Standards Compliance: Manufacturers should comply with ISO 9001, which outlines the requirements for a quality management system. This standard emphasizes customer satisfaction and continuous improvement. Additionally, certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) indicate compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards, while API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may be relevant depending on the application of the acid.
-
QC Checkpoints:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step verifies the quality of raw materials before production. Testing methods may include chemical analysis to confirm purity levels and concentration.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, various checkpoints are established to monitor the quality of the acid. This includes checking the mixing process and ensuring proper handling and storage conditions.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Before packaging, a final inspection is performed to verify that the acid meets all specifications. This may involve additional chemical testing to confirm concentration and purity. -
Common Testing Methods:
– pH Testing: Ensures the acidity level is within the desired range.
– Concentration Analysis: Utilizes titration methods to verify that the acid is at the correct dilution.
– Contaminant Testing: Checks for any impurities that could affect the acid’s performance.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of suppliers, ensuring that the acid they purchase meets their specific requirements.
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers provides insights into their quality management systems and manufacturing practices. This may include reviewing their compliance with ISO standards and other certifications.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality control procedures, including test results for batches of acid. These reports should outline the methods used and the results obtained, allowing buyers to assess the reliability of the supplier’s QC measures.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can further validate the quality of the acid. These independent organizations can conduct tests and provide unbiased assessments of the supplier’s products.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider in Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several nuances in quality control must be considered to ensure compliance and product reliability.
-
Regulatory Variations: Different regions have varying regulations concerning chemical manufacturing and safety. Buyers must be aware of local laws regarding the importation and use of acids, including necessary documentation and certifications.
-
Cultural and Communication Differences: Engaging with suppliers from diverse cultural backgrounds may present challenges in communication. Clear specifications and expectations should be established upfront to avoid misunderstandings regarding quality standards.
-
Logistics and Transportation: The transportation of acids can be subject to strict regulations. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust logistics in place to handle hazardous materials safely, including appropriate packaging and labeling.
-
Sustainability Practices: Increasingly, buyers are looking for suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. Understanding a supplier’s approach to environmental responsibility, including waste management and disposal of hazardous materials, is becoming a critical factor in supplier selection.
Conclusion
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for acid used in etching knives are multifaceted and require careful consideration by B2B buyers. By understanding the key manufacturing stages, quality control measures, and how to verify supplier practices, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements. This knowledge not only enhances product quality but also fosters long-term relationships with reliable suppliers in the international market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘acid for etching knives’
In the competitive world of knife production and customization, sourcing the right acid for etching knives is crucial for quality and efficiency. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the procurement process, ensuring they select the best materials and suppliers for their needs.
Step 1: Identify Your Etching Requirements
Before sourcing acid, clearly define your etching needs. Consider the type of knives you will be etching and the desired finish. Different acids may yield various effects on steel, so understanding your specific requirements will help you select the appropriate product.
- Types of Steel: Different steels react uniquely to acids; ensure compatibility.
- Etching Depth: Determine how deep you want the etch to be, as this will influence the acid concentration.
Step 2: Research Available Acid Types
There are several types of acids used for etching knives, with Ferric Chloride being a popular choice. Familiarize yourself with the properties of different acids to make an informed decision.
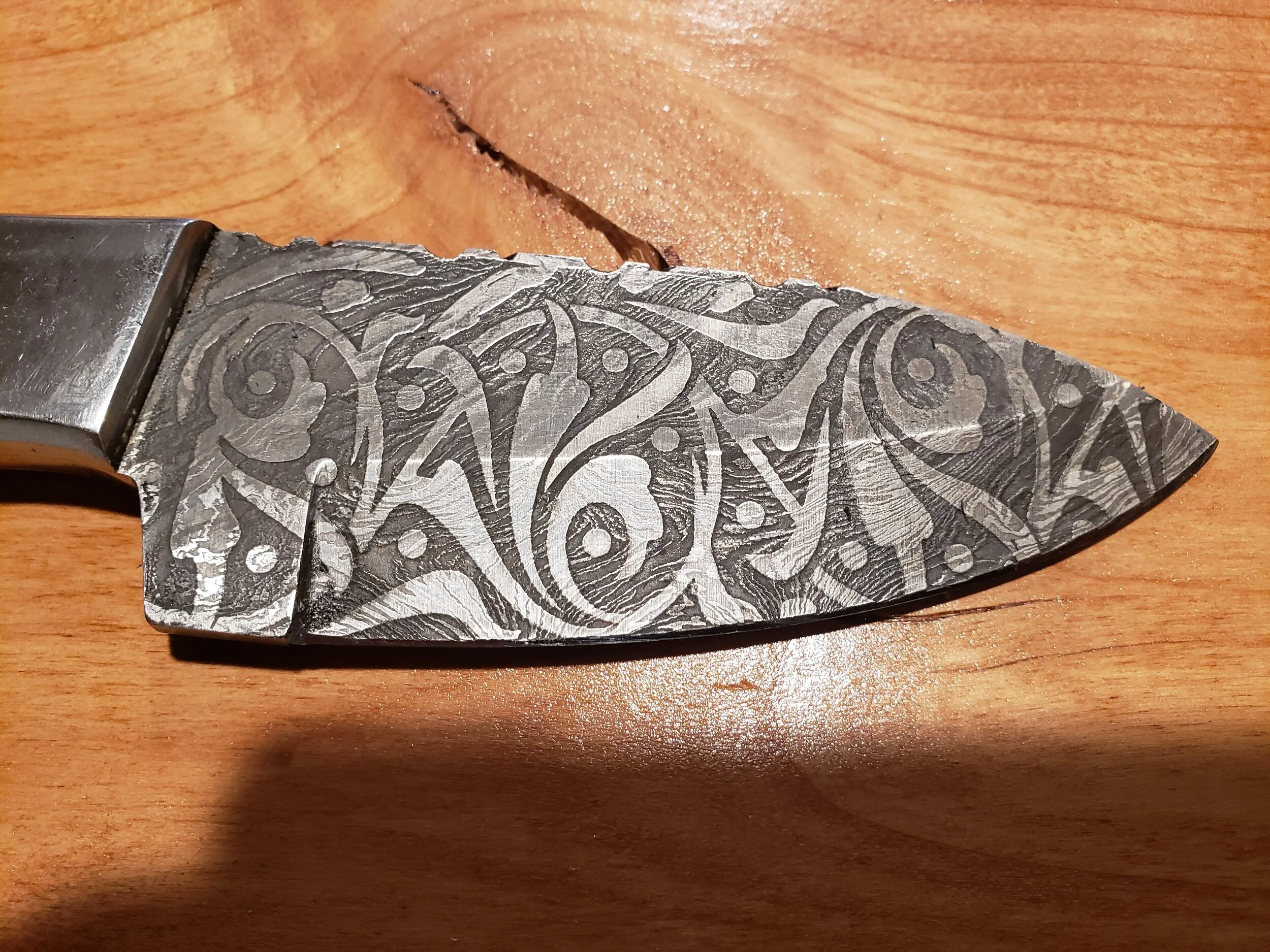

Illustrative image related to acid for etching knives
- Ferric Chloride: Effective for iron and steel, offering a good balance between ease of use and etching quality.
- Other Acids: Explore options like hydrochloric or sulfuric acid, but understand their safety and handling requirements.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
When sourcing acid, ensure that your suppliers have the necessary certifications and adhere to safety standards. This step is vital for maintaining compliance and ensuring product quality.
- ISO Certification: Check if the supplier meets international quality management standards.
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS): Request SDS to understand the handling, storage, and disposal guidelines of the acids.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the acid from potential suppliers. Testing the product on your knives will help you assess its performance and compatibility.
- Conduct Trials: Use the samples on various knife materials to see how the acid reacts.
- Evaluate Results: Analyze the etching quality and depth to determine if it meets your standards.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, compare their pricing, delivery terms, and payment options. Pricing can vary significantly, so ensure you are getting value for your investment.
- Bulk Discounts: Inquire about discounts for large orders to optimize your procurement costs.
- Lead Times: Understand the delivery timelines to ensure they align with your production schedule.
Step 6: Assess Supplier Reputation and Experience
Research the reputation and experience of your potential suppliers in the industry. A supplier with a solid track record is likely to provide better service and quality.
- Client Testimonials: Seek feedback from other businesses that have sourced acid from them.
- Industry Experience: Suppliers with extensive experience in etching materials can offer valuable insights and support.
Step 7: Finalize Your Order and Ensure Compliance
Once you’ve selected a supplier, finalize your order while ensuring that all compliance and regulatory requirements are met. This step helps prevent future legal and safety issues.
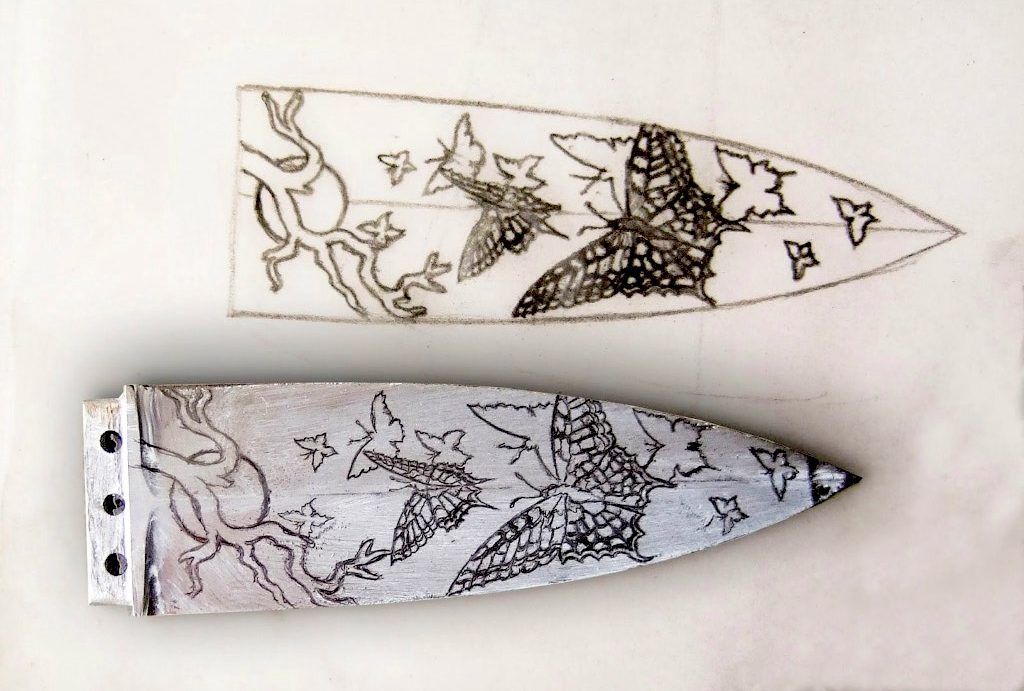

Illustrative image related to acid for etching knives
- Documentation: Ensure all necessary paperwork is in order, including purchase orders and safety compliance documents.
- Delivery Inspection: Upon receipt, inspect the acid to confirm it matches the specifications agreed upon.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for acid used in etching knives, ensuring they select the right products and suppliers to enhance their manufacturing capabilities.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for acid for etching knives Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Acid for Etching Knives?
When sourcing acid for etching knives, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary components that contribute to the overall cost include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The primary acid used for etching knives, such as Ferric Chloride, has varying prices based on purity and supplier. Costs can differ significantly between bulk purchases and smaller quantities.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages for personnel involved in manufacturing, quality testing, and packaging. Skilled labor may be required for precise quality control, which can drive up costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these costs.
-
Tooling: If specialized equipment is necessary for etching processes, tooling costs may add to the total expenditure. This includes both initial capital investments and ongoing maintenance costs.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that the acid meets specific standards requires rigorous quality checks, which can increase costs. Certifications and compliance with safety regulations are also critical.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely depending on the supplier’s location, the buyer’s location, and the chosen shipping method. International buyers must consider additional customs duties and tariffs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their operational costs and profit. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand, competition, and supplier relationships.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Acid for Etching Knives Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of acid for etching knives, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often results in lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for minimum order quantities (MOQ), making it essential for buyers to evaluate their needs accurately.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized formulations or specific concentrations of acid can lead to higher prices. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality acids, which may include certifications for purity and safety, typically come at a premium. Buyers must assess the trade-off between cost and quality based on their application needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer suppliers might offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can affect the overall cost. Different terms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in logistics, impacting shipping costs and risk.
What Are Some Tips for Buyers to Optimize Costs?
B2B buyers should adopt strategic approaches to optimize their sourcing of acid for etching knives:
-
Negotiation: Always engage in negotiations with suppliers. Highlight your purchasing potential and inquire about bulk discounts or favorable payment terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes initial costs, operational costs, and disposal fees. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher long-term expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: International buyers must be aware of currency fluctuations, local taxes, and shipping costs. Establishing relationships with local suppliers can mitigate some of these complexities.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Regularly monitor market conditions and price fluctuations for acid products. Being informed can provide leverage during negotiations and help in making timely purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer
Prices and cost structures provided in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always conduct thorough research and consult with multiple suppliers to get the best value for your needs.

Illustrative image related to acid for etching knives
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing acid for etching knives With Other Solutions
The choice of etching methods for knives is critical for manufacturers and artisans aiming for precision, aesthetics, and cost-effectiveness. While acid etching remains a popular technique, several alternative solutions offer distinct advantages and drawbacks. This analysis provides insights into these alternatives, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Acid For Etching Knives | Laser Etching | Electrochemical Etching |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision; can create intricate designs; dependent on acid concentration and metal type | Exceptional detail and uniformity; can etch complex patterns quickly | Effective for various metals; requires careful control of current and voltage |
| Cost | Low initial cost for materials; recurring costs for acid replenishment | Higher upfront investment for laser equipment; lower operational costs over time | Moderate cost for equipment; potential ongoing costs for electricity and maintenance |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively simple process; requires minimal training | Requires skilled operator; setup and calibration can be complex | Moderately complex; requires knowledge of electrochemistry |
| Maintenance | Regular disposal of hazardous waste; need for careful storage | Minimal; mainly equipment upkeep | Requires regular maintenance of the electrochemical setup |
| Best Use Case | Customization and personalization of knives | High-volume production with consistent quality | Industrial applications needing precision etching on various substrates |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Laser Etching as an Alternative?
Laser etching is renowned for its precision and speed, making it ideal for high-volume production environments. It can etch complex designs with exceptional detail and uniformity, which is invaluable for branding and personalization. However, the initial investment in laser equipment can be significant, making it less accessible for smaller operations. Additionally, it requires skilled operators to manage the machinery effectively, adding to labor costs.
How Does Electrochemical Etching Compare to Acid Etching?
Electrochemical etching offers a unique advantage in terms of safety and environmental impact, as it typically produces less hazardous waste compared to acid methods. This technique can be effective on a variety of metals and can achieve high precision with the right control of current and voltage. However, it requires a solid understanding of electrochemistry, making it somewhat complex for operators without technical training. The equipment also incurs moderate costs and necessitates regular maintenance, which can impact overall profitability.
Conclusion: Which Etching Solution Should B2B Buyers Choose?
When selecting an etching method, B2B buyers must consider factors such as production volume, budget constraints, and the desired quality of the finished product. Acid etching is a cost-effective solution for smaller-scale operations or custom work but may not be suitable for high-volume production due to its variability and waste disposal concerns. In contrast, laser etching is preferable for businesses seeking speed and uniformity but requires a higher initial investment. Electrochemical etching serves as a middle ground, balancing precision and environmental considerations. Ultimately, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each method will enable buyers to align their choice with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for acid for etching knives
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Acid for Etching Knives?
When sourcing acid for etching knives, understanding its technical properties is crucial for ensuring quality and efficiency in the etching process. Here are some essential specifications to consider:

Illustrative image related to acid for etching knives
-
Concentration of Acid
The concentration of the acid solution, typically measured in percentage, directly impacts the etching speed and depth. For example, a 50% Ferric Chloride solution is commonly used for knife etching. Higher concentrations can result in faster etching but may also increase the risk of over-etching, which can damage the blade. Knowing the right concentration allows buyers to achieve the desired etching results without compromising the integrity of the knife. -
Material Compatibility
Different acids react differently with various metals. Ferric Chloride, for instance, is suitable for carbon steels and stainless steels but may not be effective for certain alloys. Understanding material compatibility ensures that the chosen acid will perform effectively without causing unwanted reactions, such as pitting or excessive corrosion. -
pH Level
The pH level of the acid solution can affect the etching process. A lower pH (more acidic) generally increases the etching rate. Buyers should be aware of the pH level to tailor the etching process to the specific requirements of the knife material being used, ensuring optimal results. -
Temperature Stability
Acid solutions can vary in performance based on temperature. Higher temperatures may accelerate the etching process, while cooler temperatures can slow it down. Buyers should consider temperature stability and how it might affect the etching time and quality, particularly in varying environmental conditions. -
Safety and Handling Properties
Acids can be hazardous materials, and safety handling properties are paramount. Buyers should look for suppliers that provide comprehensive safety data sheets (SDS) detailing the handling, storage, and disposal guidelines for acid products. Ensuring safe usage protects workers and complies with local regulations.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Acid Etching Industry?
Understanding industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some key terms to be familiar with:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of acid for etching knives, it can denote suppliers who provide acid solutions specifically formulated for knife manufacturers. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers as it affects inventory costs and production schedules. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs while maintaining cost efficiency. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price bids from suppliers for specific products or services. In the acid etching industry, submitting an RFQ can help buyers compare prices, terms, and delivery options from multiple suppliers to make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized terms used in international trade to clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. Understanding Incoterms helps buyers manage shipping costs, risk, and logistics, ensuring smooth transactions across borders. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. Knowing the lead time is critical for B2B buyers to plan their production schedules effectively, particularly when dealing with chemicals that may have strict storage requirements. -
Safety Data Sheet (SDS)
An SDS is a document that provides information on the properties of a chemical substance, including its hazards, handling, and emergency measures. Buyers should always request an SDS for acids to ensure safe handling and compliance with health regulations.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms will enable B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing acid for etching knives, ensuring both safety and quality in their production processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the acid for etching knives Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing the Acid for Etching Knives Sector?
The acid for etching knives market is witnessing a transformative phase driven by a blend of technological advancements, evolving consumer preferences, and increased global competition. Key trends include the rise of personalized products, as knife enthusiasts seek unique designs and makers’ marks, leading to a surge in demand for acid etching materials like Ferric Chloride. Additionally, advancements in precision etching technology are enabling manufacturers to achieve finer details and more intricate patterns, enhancing product value.
B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly seeking reliable suppliers that can offer consistent quality and competitive pricing. The globalization of supply chains has made it easier for businesses to source these materials internationally, yet it also requires vigilance regarding quality control and compliance with local regulations. Emerging technologies such as automation in the etching process are further reshaping sourcing strategies, allowing for faster turnaround times and reduced labor costs.
Moreover, as industries evolve, there is a growing emphasis on digital platforms for B2B transactions, with online marketplaces and e-commerce solutions facilitating easier access to suppliers across borders. Buyers are encouraged to leverage these platforms to compare prices, quality, and supplier reputations effectively.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Acid for Etching Knives Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the acid for etching knives sector, driven by increasing regulatory pressures and consumer demand for environmentally friendly practices. The production and disposal of acid etching materials can pose significant environmental risks, necessitating responsible sourcing strategies that prioritize eco-friendly alternatives.
B2B buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through certifications such as ISO 14001 or other green credentials. These certifications not only indicate adherence to environmental management standards but also reflect a company’s dedication to minimizing its ecological footprint.
Furthermore, the demand for ‘green’ materials, such as biodegradable etching solutions, is on the rise. This shift not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also enhances brand reputation among environmentally conscious consumers. Suppliers that prioritize ethical sourcing and sustainable practices can offer a competitive advantage, appealing to a growing segment of the market that values corporate responsibility.
What Is the Historical Context of Acid for Etching Knives in B2B Markets?
The practice of acid etching dates back centuries, initially utilized in decorative arts and printmaking before its adaptation for metalworking. The modern application of acid for etching knives emerged in the late 20th century as manufacturers began to explore innovative ways to personalize and enhance knife designs. This evolution was largely influenced by the rise of the custom knife market, where artisans sought unique methods to distinguish their products.
As technology advanced, the introduction of safer and more effective acids, such as Ferric Chloride, further popularized the technique among both hobbyists and professional manufacturers. Today, acid etching is not only a means of personalization but also a critical component of branding in the knife industry, allowing companies to embed logos and intricate designs directly into their products.

Illustrative image related to acid for etching knives
In conclusion, understanding the market dynamics, sustainability practices, and historical context of acid for etching knives can significantly empower B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions, aligning with both market demands and ethical considerations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of acid for etching knives
-
How do I select the right acid for etching knives?
Choosing the right acid for etching knives primarily depends on the metal type and desired finish. Ferric Chloride is widely used due to its effectiveness on various steels and ease of use. For intricate designs, consider using specialized etching acids that provide better control. Always inquire about the acid’s composition and concentration from suppliers to ensure compatibility with your specific etching needs. Additionally, consider the safety data sheets (SDS) to understand handling and disposal requirements. -
What is the best practice for using acid in knife etching?
The best practice for using acid in knife etching involves meticulous preparation and safety precautions. Begin by cleaning the knife thoroughly to remove any oils, as this ensures better adherence of the etch resist. Use rubber gloves and work in a well-ventilated area to minimize inhalation of fumes. Mixing the acid properly—always adding acid to water—is crucial to prevent violent reactions. Short dipping times, with frequent rinses, tend to yield the best results, allowing for greater control over the etching process. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for acid purchases?
Minimum order quantities for acids can vary significantly by supplier and region. Generally, MOQs can range from 1 liter to several kilograms, depending on the supplier’s policies and the acid’s intended use. When sourcing from international suppliers, it’s essential to clarify MOQs upfront to avoid unexpected costs. Additionally, consider your production needs; ordering larger quantities may reduce costs per unit but ensure you have adequate storage and handling facilities. -
How do I vet suppliers for acid used in etching knives?
Vetting suppliers for acid involves several key steps. Start by reviewing their certifications and compliance with local and international safety standards. Check for customer reviews and testimonials to gauge reliability and product quality. Request samples to test the acid’s performance on your specific materials before committing to a larger order. Furthermore, inquire about their supply chain practices, including sourcing, handling, and shipping, to ensure consistency and quality in their products. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing acid internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of acid can vary widely based on the supplier and the transaction’s scale. Common terms include advance payment, letter of credit, or open account terms. It’s essential to negotiate terms that balance security and cash flow. Consider using escrow services for larger transactions to mitigate risks. Always review the payment terms in the context of your overall budget and project timeline to ensure that they align with your financial strategy. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing acid for etching?
Logistics for importing acid involve several critical factors. First, verify the import regulations and safety standards in your country, as acids can be classified as hazardous materials. Work with logistics providers experienced in handling chemicals to ensure compliance with transportation regulations. Consider the shipping method—air freight may be faster but more expensive than sea freight. Additionally, factor in lead times for customs clearance and potential delays when planning your inventory. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for acid products?
To ensure quality assurance for acid products, establish a clear QA protocol with your supplier. Request certificates of analysis (COAs) for each batch to verify the acid’s concentration and purity. Conduct regular quality checks upon receipt, including testing small samples to assess performance. Consider establishing a feedback loop with your supplier, where you can report any issues and receive timely support. Collaborating on QA measures can help build a stronger partnership and maintain product consistency. -
Can I customize acid formulations for specific etching needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for acid formulations tailored to specific etching requirements. When discussing customization, provide detailed information about the types of metals you will be etching and the desired outcomes. This could include factors like the depth of etch, speed of reaction, and finish quality. Be prepared for potential minimum order requirements for custom formulations, and ensure you establish clear communication regarding your needs to achieve the best results.
Top 6 Acid For Etching Knives Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Instructables – Acid Etching Supplies
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Supplies needed for acid etching: Ferric Chloride (PCB etch), plastic container, distilled water, etch resist/stencil (nail polish, stickers, vinyl, electrical tape, Sharpie marker), acetone, cotton swabs/Q-tips, paperclip/dental floss, rubber gloves, high grit wet/dry sandpaper or steel wool.
2. Bladesmiths Forum – Recommended Etching Acids
Domain: bladesmithsforum.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Recommended acids for etching: nitric acid or ferric chloride for copper; ferric chloride for steel. Ferric chloride is available in liquid or dry powder form at electronics supply stores. Dilute ferric chloride 1:4 with distilled water for use on steel. Muriatic acid can be used but may be watered down; a concentration of at least 27% is suggested for etching copper. Ferric chloride lasts a long …
3. Ferric Chloride – Etching Solution
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Ferric chloride is recommended for etching blades, providing improved results compared to muriatic acid. Muriatic acid can be used but may not yield the best outcome. Users have shared methods for creating ferric chloride from steel wool and hydrogen peroxide, emphasizing safety precautions due to fumes. The discussion highlights the effectiveness of ferric chloride for revealing patterns in Damas…
4. BladeForums – Acid Etching Techniques
Domain: bladeforums.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: The thread discusses acid etching techniques for knife blades, specifically using ferric chloride and vinegar as etching solutions. It mentions the use of nail polish as a resist for creating designs on the blade. Key points include: ferric chloride does not need to be heated and can be reused, while vinegar should be heated for better results. The discussion also touches on the effects of etching…
5. iForge Iron – Etching Solutions and Techniques
Domain: iforgeiron.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Etching solutions used: white vinegar, hydrogen peroxide, muriatic acid (hydrochloric acid). Techniques mentioned: boiling in vinegar, adding salt and soap, neutralizing with baking soda, and oiling after etching. Steel types mentioned: 1080, 1084. Equipment used: toothbrush, 1500 grit sandpaper, flat sharpening rods, sharpening stones. Key issues: loss of damascus design, pitting, fine oxide remo…
6. KnifeDogs – Ferric Chloride Etching Solution
Domain: knifedogs.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Ferric Chloride is mixed with distilled water in a ratio of 4:1 (4 parts water to 1 part Ferric Chloride) for etching blades. Some users also add about 35% distilled white vinegar to the mix. It is recommended to store the solution in a plastic container and to always add the acid to the water, not the other way around. The dilution affects the etching speed and quality: a more diluted solution (6…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for acid for etching knives
As the demand for personalized and high-quality knives continues to rise, the strategic sourcing of acid for etching knives becomes increasingly vital for businesses in the knife manufacturing and customization sectors. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer not only high-grade acids, such as Ferric Chloride, but also comprehensive support in sourcing, safety, and application techniques. Understanding the nuances of acid concentration, metal compatibility, and proper handling can lead to superior etching results, enhancing product appeal and customer satisfaction.
International buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are encouraged to explore partnerships that prioritize sustainability and compliance with regional regulations. Engaging with reputable suppliers ensures access to reliable materials while fostering innovation in knife design.
Looking ahead, the market for acid etching presents significant opportunities for growth. By leveraging strategic sourcing practices, businesses can stay ahead of industry trends and consumer demands. Invest in quality today, and position your company for success in the competitive landscape of knife manufacturing and customization.

Illustrative image related to acid for etching knives
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to acid for etching knives