A Deep Dive into Entry Level Head Resurfacing Machine Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for entry level head resurfacing machine
In the competitive landscape of automotive repair and maintenance, sourcing an entry-level head resurfacing machine is a critical challenge for B2B buyers. These machines are essential for restoring engine components to optimal condition, ensuring the precision and reliability that modern engines demand. However, navigating the myriad options available can be daunting, especially for international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Vietnam and Nigeria.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of entry-level head resurfacing machines, their applications across various automotive sectors, and the key factors to consider when selecting a supplier. From understanding the technological advancements that enhance performance, such as CNC capabilities, to evaluating cost-effective solutions that meet budget constraints, this resource aims to equip buyers with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions.
Moreover, we will explore essential criteria for vetting suppliers, ensuring that your investment not only fulfills immediate operational needs but also aligns with long-term business goals. By empowering B2B buyers with actionable insights, this guide serves as a vital tool for those looking to enhance their workshop capabilities and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market. Whether you are a seasoned professional or venturing into engine resurfacing for the first time, you will find valuable information to navigate your purchasing journey effectively.
Understanding entry level head resurfacing machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Belt Resurfacer | Simple design, manual operation, suitable for light-duty tasks. | Small automotive shops, DIY mechanics. | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to use. Cons: Limited precision and automation. |
| CNC Cylinder Head Resurfacer | Automated operation, high precision, capable of multiple functions. | Large automotive repair shops, performance tuning. | Pros: High accuracy, reduced labor costs. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Multi-Purpose Machining Center | Combines surfacing with other machining capabilities (boring, drilling). | Versatile operations in automotive and non-automotive sectors. | Pros: Space-saving, multi-functional. Cons: Expensive, potential bottleneck in high-volume settings. |
| Manual Cylinder Head Resurfacer | Operated by skilled technicians, offers flexibility in operation. | Custom engine builders, specialized repair shops. | Pros: Adaptable to various tasks. Cons: Requires skilled labor, slower output. |
| Portable Resurfacing Machine | Lightweight, easy to transport, ideal for on-site repairs. | Mobile service providers, field repairs. | Pros: Flexibility, convenience. Cons: Limited capabilities compared to stationary machines. |
What are the Characteristics of Basic Belt Resurfacers?
Basic belt resurfacers are entry-level machines designed for straightforward tasks, primarily used in small automotive shops and by DIY enthusiasts. They feature a simple design and manual operation, making them user-friendly. However, their precision is limited compared to more advanced models, which may affect the quality of the finish. When considering this type, buyers should evaluate their workload and whether they require higher precision for professional applications.
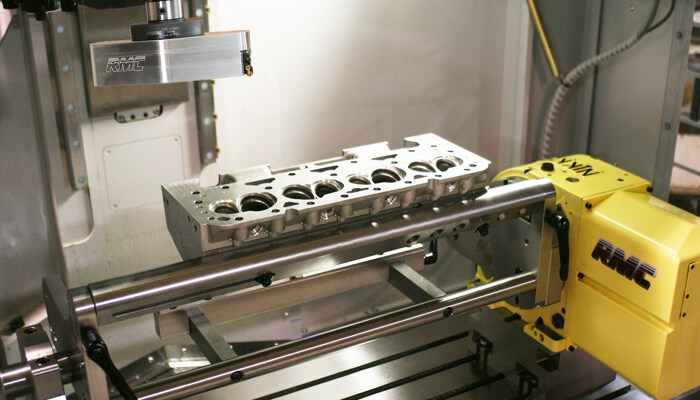
How Do CNC Cylinder Head Resurfacers Stand Out?
CNC cylinder head resurfacers are ideal for businesses focusing on high-precision work. These machines automate the resurfacing process, providing consistent results and reducing labor costs. They are particularly suitable for large automotive repair shops and performance tuning facilities that need to meet strict tolerances. While the initial investment is higher, the long-term benefits in efficiency and quality often justify the cost for B2B buyers looking to enhance their service offerings.
Why Choose a Multi-Purpose Machining Center?
Multi-purpose machining centers are versatile machines that combine surfacing capabilities with other functions such as boring and drilling. This makes them a valuable asset for businesses involved in both automotive and non-automotive machining. They can save space and improve efficiency by allowing multiple operations to be performed on a single setup. However, their high cost and potential for bottlenecks in busy environments should be carefully considered by buyers with high production demands.
What Advantages Do Manual Cylinder Head Resurfacers Offer?
Manual cylinder head resurfacers provide flexibility and adaptability, allowing skilled technicians to perform a variety of tasks. These machines are particularly beneficial for custom engine builders and specialized repair shops that require tailored solutions. While they may not match the speed and precision of automated machines, their lower cost and reliance on skilled labor can be advantageous for smaller operations. Buyers should assess their workforce capabilities and the types of projects they typically handle.
When Should You Consider a Portable Resurfacing Machine?
Portable resurfacing machines are designed for convenience, allowing for on-site repairs and mobility in service operations. They are especially useful for mobile service providers and field repairs, where transporting larger equipment may be impractical. While they offer flexibility, buyers should be aware that portable machines may have limited capabilities compared to stationary models. Evaluating the types of jobs they plan to undertake is essential for determining if this option meets their needs.
Key Industrial Applications of entry level head resurfacing machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of entry level head resurfacing machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Repair | Resurfacing cylinder heads and engine blocks for vehicles | Ensures flatness and precision, improving engine performance and longevity | Availability of spare parts, machine versatility, and technical support |
| Heavy Machinery | Maintenance of large diesel engines in construction equipment | Reduces downtime by restoring surface integrity, enhancing reliability | Capacity for larger components, durability, and cost-effectiveness |
| Marine Engineering | Refurbishing marine engine components | Increases operational efficiency and reduces fuel consumption | Resistance to corrosion, precision in machining, and compliance with marine standards |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Machining flat surfaces on various industrial components | Improves product quality and reduces scrap rates | Customization options, compatibility with existing systems, and serviceability |
| Custom Fabrication | Producing specialized engine parts for niche markets | Expands service offerings and attracts diverse clientele | Flexibility in operations, support for diverse materials, and ease of use |
How is an entry level head resurfacing machine utilized in automotive repair?
In automotive repair shops, entry level head resurfacing machines are crucial for resurfacing cylinder heads and engine blocks. These machines restore the flatness and surface finish necessary for optimal engine performance, particularly after incidents like blown head gaskets. Buyers in this sector should consider the machine’s versatility to handle various engine types, as well as the availability of spare parts and technical support to minimize downtime.
What role does an entry level head resurfacing machine play in heavy machinery maintenance?
In the heavy machinery sector, these machines are employed to maintain large diesel engines found in construction equipment. By resurfacing engine components, businesses can significantly reduce downtime and enhance the reliability of their machinery. Buyers should prioritize machines with the capacity to accommodate larger components and evaluate the durability of the equipment, given the demanding operating conditions of heavy machinery.
How does an entry level head resurfacing machine benefit marine engineering?
Marine engineering applications involve refurbishing engine components to ensure optimal performance in marine vessels. An entry level head resurfacing machine is essential in this context as it enhances operational efficiency and can lead to reduced fuel consumption. Buyers must look for machines that resist corrosion and provide precision machining to meet the stringent standards of the marine industry.
In what ways does an entry level head resurfacing machine contribute to industrial manufacturing?
In industrial manufacturing, these machines are used to machine flat surfaces on various components, ensuring high-quality production and reduced scrap rates. The ability to achieve precise surface finishes is critical for maintaining product quality. Buyers should consider customization options and compatibility with existing manufacturing systems to ensure seamless integration into their production processes.
How can an entry level head resurfacing machine support custom fabrication needs?
In custom fabrication, entry level head resurfacing machines are utilized to produce specialized engine parts tailored to niche markets. This capability allows businesses to expand their service offerings and attract a diverse clientele. Key considerations for buyers include the flexibility of operations, support for various materials, and ease of use to accommodate different fabrication demands.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘entry level head resurfacing machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Achieving Precision in Surface Finishing
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers, particularly those operating in regions with limited access to high-quality machinery, often find that entry-level head resurfacing machines struggle to achieve the precision necessary for modern engine applications. This challenge is compounded by the fact that many older engines, particularly those common in Africa and South America, may have significant wear and tear, resulting in warped or uneven surfaces. These buyers may experience frustration when their resurfacing machines produce inconsistent results, leading to further complications in engine assembly and performance issues down the line.
The Solution:
To address precision challenges, buyers should prioritize sourcing machines that feature advanced control systems, such as CNC capabilities. For instance, models like the Comec RP1000 CNC include laser sensors that automatically scan and adjust to ensure optimal surface flatness. Buyers should also invest in proper training for their operators, emphasizing the importance of setup and calibration before each use. Implementing a routine maintenance schedule for the machines is crucial, as regular upkeep can significantly improve their longevity and precision. Additionally, sourcing high-quality cutting tools and abrasives designed for the specific materials being resurfaced—whether cast iron or aluminum—can enhance the overall finish quality and reduce the risk of damage to the workpiece.
Scenario 2: Limited Budget Constraints for Entry-Level Machinery
The Problem:
Budget constraints are a common hurdle for B2B buyers, especially in developing markets. Many potential customers are seeking reliable entry-level head resurfacing machines that deliver adequate performance without breaking the bank. However, the lower price point often correlates with compromised features, leading to concerns about long-term viability and the potential for hidden costs associated with repairs and replacements.
The Solution:
Buyers should take a strategic approach by comparing not only the initial purchase price but also the total cost of ownership over the machine’s lifecycle. This includes considering factors such as energy efficiency, maintenance requirements, and the availability of spare parts. Opting for a machine that offers a good balance between cost and functionality, like the Comec SPN800, can provide the necessary features without overspending. Additionally, exploring options for financing or leasing can alleviate upfront costs while allowing businesses to invest in higher-quality machinery. Engaging with suppliers who offer warranties and robust after-sales support can also provide peace of mind, ensuring that any potential issues can be addressed without incurring significant additional costs.
Scenario 3: Training and Skill Gaps Among Operators
The Problem:
A significant pain point for many B2B buyers is the lack of skilled operators capable of efficiently using entry-level head resurfacing machines. This gap can lead to operational inefficiencies, wasted materials, and poor-quality finishes, which ultimately affect customer satisfaction and profitability. In regions with less access to vocational training programs, such as certain parts of Africa and South America, this issue can be particularly pronounced.
The Solution:
Investing in comprehensive training programs is essential for maximizing the return on investment in resurfacing machines. Buyers should seek out suppliers that provide training resources, including manuals, online tutorials, and hands-on workshops. Creating an in-house training program that includes experienced machinists as mentors can also foster skill development among less experienced staff. Furthermore, implementing a continuous improvement strategy, where operators are encouraged to share insights and techniques, can cultivate a culture of learning and skill enhancement. Ultimately, well-trained operators will not only enhance the performance of the machines but also contribute to higher quality outcomes and increased operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for entry level head resurfacing machine
What Are the Key Materials for Entry-Level Head Resurfacing Machines?
When selecting materials for entry-level head resurfacing machines, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The choice of material directly impacts the machine’s performance, durability, and suitability for various applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these machines: cast iron, aluminum, stainless steel, and composite materials.
How Does Cast Iron Contribute to the Performance of Head Resurfacing Machines?
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its excellent wear resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures. It has a high compressive strength, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros & Cons: The durability of cast iron is one of its significant advantages, as it can endure the rigors of resurfacing operations. However, it is relatively heavy, which can complicate transportation and installation. Additionally, cast iron can be prone to rust if not properly maintained, necessitating protective coatings.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is compatible with various media used in resurfacing, including coolant and lubricants. Its ability to maintain flatness over time makes it ideal for achieving the precision required in resurfacing operations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards for material quality and performance. Cast iron products often conform to ASTM A48 or similar standards, which can influence purchasing decisions.
Why Choose Aluminum for Entry-Level Head Resurfacing Machines?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good thermal conductivity, which is beneficial in dissipating heat during operations.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, making machines easier to handle and transport. However, aluminum is less durable than cast iron and may not withstand high-pressure applications as effectively. It is also more susceptible to scratching and denting.
Impact on Application: Aluminum surfaces are often used in machines designed for lighter applications or where precision is crucial, such as in automotive engine work.
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions with high humidity, such as parts of the Middle East, aluminum components may require protective coatings to prevent corrosion. Compliance with JIS standards can also be a factor in material selection.
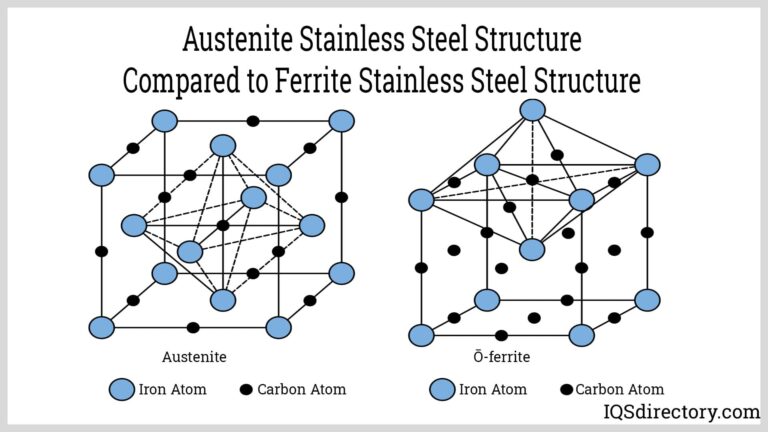
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Head Resurfacing Machines?
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and strength, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons: The corrosion resistance of stainless steel is a significant advantage, especially in humid or chemically aggressive environments. However, it is generally more expensive than cast iron or aluminum, which can be a drawback for budget-conscious buyers.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is particularly effective in applications where cleanliness and resistance to contamination are critical. It is often used in components that come into contact with coolants and lubricants.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe may prefer stainless steel due to stringent environmental regulations and standards. Compliance with DIN standards is crucial for ensuring quality and performance.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Head Resurfacing Machines?
Key Properties: Composite materials are engineered to provide high strength-to-weight ratios and can be tailored for specific applications.
Pros & Cons: The flexibility in design and weight savings are significant advantages of composite materials. However, they can be expensive to manufacture and may not provide the same level of durability as metals.
Impact on Application: Composites are often used in non-structural components or where weight savings are essential, such as in portable resurfacing machines.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying standards for composites in different regions. Ensuring that materials meet local compliance requirements is essential for market entry.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Entry-Level Head Resurfacing Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for entry level head resurfacing machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Heavy-duty resurfacing machines for automotive engines | Excellent wear resistance and durability | Heavy and prone to rust without maintenance | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight machines for precision automotive work | Lightweight and good thermal conductivity | Less durable and more prone to damage | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Machines in humid or chemically aggressive environments | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost compared to other metals | High |
| Composite Materials | Portable resurfacing machines | High strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive and potentially less durable | High |
This analysis provides valuable insights for B2B buyers in various regions, helping them make informed decisions when selecting materials for entry-level head resurfacing machines.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for entry level head resurfacing machine
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Entry-Level Head Resurfacing Machines?
The manufacturing of entry-level head resurfacing machines involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications and performance standards. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, each utilizing specific techniques to achieve high precision and quality.
How Is Material Prepared for Head Resurfacing Machines?
The first stage of manufacturing involves the careful selection and preparation of materials. Typically, manufacturers use high-grade steel or cast iron for the machine frame and components, ensuring durability and rigidity. The material is subjected to processes such as cutting and machining to achieve the desired dimensions.
After cutting, the materials undergo surface treatment processes, including sandblasting or polishing, to remove any impurities. This step is crucial for ensuring that subsequent processes, such as coating or painting, adhere properly.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Head Resurfacing Machine Manufacturing?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage involves forming, which primarily includes machining operations. Advanced techniques such as Computer Numerical Control (CNC) milling are commonly employed to achieve precision shaping of components like the table, spindle, and base.
CNC technology allows for intricate designs and high repeatability, which is essential for maintaining accuracy across multiple units. Additionally, forming may include welding processes to assemble different parts of the machine structure, ensuring that they are securely fastened and aligned.
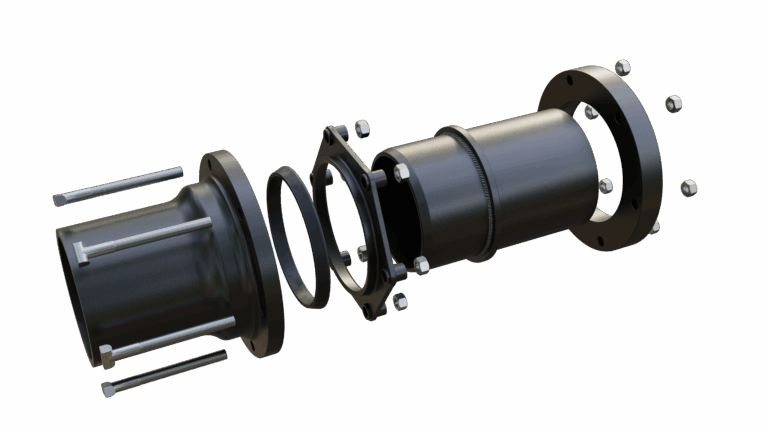
How Are Entry-Level Head Resurfacing Machines Assembled?
The assembly stage is where all the machined components come together. This process typically involves several steps:
- Component Installation: Key components such as the motor, drive system, and control panels are installed into the machine frame.
- Alignment and Calibration: Precise alignment is critical to ensure that the machine operates smoothly. Calibration of moving parts is performed to ensure that they meet specified tolerances.
- Wiring and Electronics: Electrical components are wired and tested to ensure that all controls and sensors function correctly.
Each assembly process is meticulously monitored to maintain quality, and manufacturers often utilize jigs and fixtures to ensure consistent assembly across all units.
What Finishing Techniques Enhance the Quality of Head Resurfacing Machines?
Finishing is the final stage of manufacturing, where the machine is prepared for delivery. This includes processes such as:
- Painting and Coating: The machine surfaces are often coated with protective paint to prevent rust and wear. Powder coating is a popular choice due to its durability and resistance to chipping.
- Final Assembly Checks: A thorough inspection is performed to ensure that all parts are correctly assembled and that the machine operates as intended.
What Are the Quality Assurance Standards for Head Resurfacing Machines?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, particularly for equipment used in automotive applications. Manufacturers of entry-level head resurfacing machines typically adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system.
How Do Manufacturers Implement Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout the manufacturing process with specific checkpoints, including:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Upon receiving materials, manufacturers conduct inspections to verify that they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, random samples are tested for dimensional accuracy and performance to catch any deviations early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, the completed machines undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet all operational and safety standards.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used?
Manufacturers employ various testing methods to validate the performance and safety of head resurfacing machines:
- Functional Testing: Machines are operated under simulated conditions to ensure they perform as expected.
- Load Testing: The machines are subjected to maximum operational loads to assess structural integrity.
- Surface Finish Testing: The quality of the resurfaced surfaces is evaluated using tools like profilometers to ensure they meet the required specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is vital. Here are some strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality control systems in place.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask suppliers for detailed QC reports, including inspection records and testing results.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s manufacturing practices and product quality.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
When sourcing head resurfacing machines internationally, buyers should be aware of specific certification requirements that may vary by region. For instance:
- CE Marking: In Europe, machines may need to meet specific safety, health, and environmental protection standards to obtain CE marking.
- API Certification: For buyers in the oil and gas sectors, equipment may need to comply with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards.
Understanding these nuances helps buyers ensure compliance with local regulations and standards, ultimately leading to safer and more reliable equipment.
Conclusion
Manufacturing entry-level head resurfacing machines involves a comprehensive process that encompasses material preparation, precise forming techniques, meticulous assembly, and thorough finishing. Coupled with rigorous quality assurance practices, these processes ensure that the machines meet the high standards required in the automotive industry. For B2B buyers, understanding these manufacturing and QC processes is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions and ensuring the reliability of their investments.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘entry level head resurfacing machine’
Introduction
This sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in procuring an entry-level head resurfacing machine. By following this checklist, you will ensure that your investment meets your operational needs, adheres to quality standards, and is sourced from reliable suppliers.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, outline the technical requirements for the resurfacing machine. Consider factors such as:
– Material Compatibility: Ensure the machine can handle both cast iron and aluminum.
– Precision Needs: Determine the level of precision required for your specific applications.
Clearly defined specifications help streamline the selection process and ensure that the machine will meet your operational demands.
Step 2: Assess Your Budget and Financing Options
Establish a budget that encompasses not only the purchase price but also installation, training, and maintenance costs.
– Total Cost of Ownership: Consider ongoing expenses such as tooling, spare parts, and energy consumption.
– Financing Alternatives: Explore leasing options or financing plans that may provide flexibility and reduce upfront costs.
A comprehensive budget will prevent unexpected financial strains and ensure you can sustain the machine’s operation.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers to ensure reliability and quality.
– Reputation and Experience: Look for suppliers with a solid track record in the industry and positive reviews from previous clients.
– Certifications and Compliance: Verify that the supplier adheres to relevant quality standards and certifications.
A reputable supplier will not only provide a quality machine but also support you with after-sales service.
Step 4: Compare Machine Features and Capabilities
Analyze various models and their features to find the best fit for your needs.
– CNC vs. Manual Operation: Decide if a CNC machine with automation features is necessary or if a manual option suffices for your production volume.
– Flexibility and Accessories: Check for adaptability in tooling and optional accessories that can enhance the machine’s functionality.
Understanding the capabilities of different machines ensures that you invest in a model that will grow with your business.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations and Trial Runs
Once you narrow down your options, request demonstrations or trial runs from suppliers.
– Hands-On Experience: Operating the machine allows you to assess its ease of use, noise levels, and overall performance.
– Evaluate Results: Review the quality of the surfaces produced during the demonstration to confirm they meet your specifications.
This step is vital in validating the machine’s performance before making a financial commitment.
Step 6: Review Warranty and Support Services
Examine the warranty terms and the level of support offered by the supplier.
– Warranty Coverage: Ensure the warranty covers essential components and includes a reasonable duration.
– Technical Support: Inquire about the availability of technical support and training for your staff post-purchase.
A robust warranty and support system can significantly impact your machine’s longevity and operational efficiency.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase and Logistics
After selecting the machine and supplier, finalize the purchase agreement, ensuring all terms are clearly outlined.
– Delivery and Installation: Discuss the logistics of delivery and installation, including who will handle setup and training.
– Payment Terms: Confirm payment methods and schedules to avoid any misunderstandings.
Finalizing these details will ensure a smooth transaction and set the stage for successful machine integration into your operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for entry level head resurfacing machine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Entry-Level Head Resurfacing Machines?
When sourcing entry-level head resurfacing machines, several cost components significantly influence the overall expenditure. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the supplier’s profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials used in the construction of the machines—such as cast iron or aluminum—affects both durability and cost. Higher-quality materials typically lead to increased machine longevity and performance, justifying a higher initial investment.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct manufacturing labor and indirect labor, such as engineering and assembly. Skilled labor may command higher wages, which can impact the final pricing of the machine.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and equipment used in the production process. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead, positively affecting the final price.
-
Tooling: The cost of tooling is crucial, as it determines the precision and quality of the resurfacing machines. Custom tooling can add to costs, while standardized tools may offer savings.
-
Quality Control: Investing in rigorous QC processes ensures the machines meet industry standards, which can be a selling point for international buyers. However, this also contributes to the overall cost structure.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, especially for international shipments, can be significant. Factors such as shipping distance, mode of transport, and customs duties can influence final pricing.
-
Margin: Finally, the manufacturer’s profit margin varies and can reflect the brand’s reputation and market positioning. Established brands may charge more due to perceived reliability and service support.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Entry-Level Head Resurfacing Machine Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of entry-level head resurfacing machines, which potential buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can affect pricing; larger orders often lead to bulk discounts. Buyers should evaluate whether they can commit to larger orders for cost savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Machines with advanced features or customization options typically come at a premium. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to avoid overpaying for unnecessary features.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Machines built with higher-grade materials and certified for quality assurance (such as ISO certifications) may command higher prices but offer better performance and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may offer better support and warranty services, which can justify higher costs.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms and conditions can significantly impact costs. Terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) will dictate who bears the shipping costs and risks, which can influence overall expenditure.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Engage in thorough negotiations with suppliers. Building a relationship can lead to better pricing, especially for repeat orders.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the TCO rather than just the upfront cost. Evaluate maintenance, operating costs, and potential downtime when assessing machine value.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of fluctuating currency rates and regional market conditions that may impact pricing. Establishing contracts in stable currencies can mitigate risks.
-
Research and Comparisons: Conduct thorough market research to compare machine specifications and prices across different suppliers. This due diligence can uncover hidden costs and better deals.
-
Utilize Local Representatives: If possible, engage local representatives or agents who understand the regional market and can facilitate better communication with suppliers.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for entry-level head resurfacing machines vary widely based on specifications, supplier, and market conditions. The figures mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may not reflect actual costs at the time of purchase. Buyers should conduct their own research and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing entry level head resurfacing machine With Other Solutions
In the realm of engine repair and maintenance, selecting the right resurfacing solution is critical for ensuring optimal engine performance and longevity. While entry-level head resurfacing machines provide a viable option for many workshops, it’s essential to consider alternative methods and technologies that may better suit specific operational needs or budget constraints.
| Comparison Aspect | Entry Level Head Resurfacing Machine | CNC Machining Center | Belt Sander/Grinder |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Adequate for basic resurfacing tasks | High precision and versatility | Variable results, dependent on operator skill |
| Cost | $30,000 – $45,000 | $80,000 – $280,000+ | $1,000 – $5,000 |
| Ease of Implementation | User-friendly, minimal setup | Complex, requires training | Simple, familiar to many users |
| Maintenance | Moderate maintenance needs | High maintenance, skilled technicians required | Low maintenance, easy to replace parts |
| Best Use Case | Small to medium shops, basic tasks | High-volume operations, multi-functional machining | Quick jobs, low-budget workshops |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using a CNC Machining Center?
CNC machining centers represent a significant upgrade from entry-level resurfacing machines. These multi-functional machines can perform various operations, including surfacing, boring, and drilling. The primary advantage is their high precision and capability to handle complex tasks, making them suitable for high-volume workshops needing diverse machining capabilities. However, they come with a higher price tag and require skilled operators for effective use, which may not be feasible for smaller shops or those with limited budgets.
How Does a Belt Sander or Grinder Compare to an Entry Level Resurfacing Machine?
Belt sanders and grinders have traditionally been used for resurfacing tasks, especially in budget-conscious environments. They are relatively inexpensive and easy to operate, making them accessible to many workshops. However, the quality of the finish is highly dependent on the operator’s skill, and they often fail to achieve the precision required for modern engine components, especially with multi-layer steel head gaskets. While suitable for quick jobs, they may not meet the standards demanded by more advanced engine repair work.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Resurfacing Solution?
For B2B buyers, the decision on which resurfacing solution to invest in should be based on several factors, including the volume of work, the range of services offered, and budget constraints. Entry-level head resurfacing machines provide a solid foundation for workshops focusing on basic resurfacing needs. However, for those looking to expand their service offerings or improve precision, a CNC machining center may be a worthy investment despite the higher costs. Conversely, shops with limited budgets or those performing only occasional resurfacing might find that belt sanders or grinders meet their needs adequately. Ultimately, assessing the specific operational requirements and future growth plans will guide buyers in making the most informed decision.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for entry level head resurfacing machine
What Are the Key Technical Properties of an Entry-Level Head Resurfacing Machine?
When considering an entry-level head resurfacing machine, several technical properties are crucial for ensuring quality and efficiency in operations. Here are some of the most critical specifications:
-
Material Grade
The material used in the construction of the machine, such as cast iron or aluminum, significantly affects durability and performance. Cast iron is preferred for its rigidity and ability to withstand high cutting forces, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Understanding the material grade helps buyers assess the machine’s longevity and maintenance needs, which is particularly important in markets with challenging working conditions. -
Surface Finish Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension, particularly concerning the flatness of the resurfaced surface. For modern engines that use MLS (Multi-Layer Steel) head gaskets, achieving a tolerance of 0.001 inches or better is essential for sealing and performance. Buyers should prioritize machines that can consistently maintain these tolerances, as this will directly impact the reliability of their engine repairs. -
Motor Power and Type
The motor power, typically measured in horsepower (HP), is a critical factor influencing the machine’s cutting speed and efficiency. Machines with higher HP can handle tougher materials and thicker sections, which is especially important in regions with a diverse range of engine types. Additionally, the type of motor—whether it’s a brushless or standard motor—can affect energy consumption and maintenance requirements. -
Milling Head Configuration
The configuration of the milling head, which may include features such as adjustable height and angle, determines the versatility of the machine. This is particularly valuable for shops that handle various engine types. A machine with a flexible milling head can accommodate both small and large jobs without needing constant reconfiguration, saving time and increasing productivity. -
Feed Rate Control
The feed rate, often adjustable via an inverter, influences how quickly the machine moves across the surface being milled. A controlled feed rate allows for optimal cutting conditions, enhancing surface finish quality and tool life. For B2B buyers, understanding this feature can guide their decision-making in selecting a machine that matches their operational needs. -
Size and Capacity
The physical dimensions of the machine and the maximum size of the head or block it can handle are crucial for operational efficiency. Machines with larger capacities can service a broader range of vehicles, making them more valuable in diverse markets. Buyers should evaluate their typical workload to ensure the selected machine can accommodate their needs.
What Are Common Trade Terminologies Related to Head Resurfacing Machines?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother communication during the purchasing process. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications can help buyers ensure compatibility with existing equipment and assess quality standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Recognizing MOQ is vital for B2B buyers to manage inventory costs effectively, especially in regions where storage space may be limited. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by buyers to solicit price offers from suppliers. This is a standard practice in B2B transactions, allowing for comparison across different manufacturers and ensuring competitive pricing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). They clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which is crucial for international transactions, especially for buyers in regions like Africa and South America. -
CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
CNC refers to machines that are controlled by computers to perform precise machining operations. This technology enhances accuracy and consistency in resurfacing, making it a vital consideration for modern workshops aiming for high-quality outputs. -
Flatness
Flatness is a measure of how level a surface is across its entirety. In head resurfacing, maintaining flatness is critical for engine performance, particularly with modern engines that require precise sealing surfaces. Understanding this term can help buyers evaluate machine capabilities effectively.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting entry-level head resurfacing machines that meet their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the entry level head resurfacing machine Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends for Entry-Level Head Resurfacing Machines?
The global market for entry-level head resurfacing machines is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for precision-engineered automotive components. As vehicle technology evolves, particularly with the rise of high-performance and electric vehicles, the need for accurate resurfacing has become paramount. B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly focused on sourcing machines that offer a balance of affordability and advanced features. Emerging technologies, including CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems, are becoming standard even in entry-level machines, enabling enhanced accuracy and ease of operation.
Additionally, there is a growing trend towards multi-functional machinery. Buyers are seeking machines that not only resurface but also perform additional machining operations, allowing them to maximize productivity and minimize floor space. This shift is particularly relevant for shops with limited budgets and space, as multi-purpose machines can eliminate the need for multiple separate units. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce platforms is transforming the sourcing landscape, allowing international buyers to easily compare options and make informed decisions.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Becoming Important in the Entry-Level Head Resurfacing Machine Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming increasingly critical factors for B2B buyers in the entry-level head resurfacing machine sector. Environmental concerns are driving manufacturers to adopt more sustainable practices, such as using energy-efficient machines and recyclable materials. The demand for “green” certifications is on the rise, with buyers looking for suppliers who can demonstrate their commitment to minimizing environmental impact.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing their suppliers to ensure they adhere to ethical labor practices and responsible sourcing of materials. This trend is particularly pronounced in emerging markets where regulatory frameworks may be less stringent. Suppliers who can provide transparency in their sourcing and production processes will likely gain a competitive advantage. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, businesses can not only meet regulatory requirements but also enhance their brand reputation and appeal to a growing segment of environmentally-conscious consumers.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Head Resurfacing Machines?
The evolution of head resurfacing machines can be traced back to the early 20th century when manual tools dominated the market. Initially, these machines were rudimentary, primarily designed for basic resurfacing tasks. However, as automotive technology advanced, so too did the need for more precise and efficient machinery. The introduction of CNC technology in the late 20th century marked a significant turning point, allowing for greater precision and automation in the resurfacing process.
Today, entry-level head resurfacing machines are equipped with sophisticated features such as programmable settings and automated tooling, catering to the demands of modern engine designs. The focus has shifted towards not just performance but also user-friendliness and versatility. With the ongoing development of new materials and engine technologies, the market is poised for further innovations that will continue to shape the future of head resurfacing machinery.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of entry level head resurfacing machine
-
How do I select the right entry-level head resurfacing machine for my workshop?
Choosing the right entry-level head resurfacing machine depends on several factors, including your specific needs, budget, and the types of engines you work on. Consider machines with a reliable milling mechanism that can handle both cast iron and aluminum surfaces. Look for features like adjustable speed controls and precision settings to ensure high-quality finishes. Additionally, check the machine’s capacity to accommodate the sizes of the components you typically work with and ensure that it has the necessary accessories and tooling available for your operations. -
What is the best entry-level head resurfacing machine for small to medium-sized workshops?
For small to medium-sized workshops, machines like the Comec SPN800 or the RP330 offer a balance between performance and affordability. These models are designed for ease of use and provide reliable resurfacing for both cylinder heads and engine blocks. They are equipped with essential features that allow for precision milling, making them ideal for shops that may not require the extensive capabilities of higher-end CNC machines. Always assess the specific needs of your workshop to ensure the selected machine aligns with your operational demands. -
What should I consider regarding the warranty and after-sales support when purchasing a resurfacing machine?
When investing in a resurfacing machine, it’s crucial to consider the warranty offered by the manufacturer, as it reflects the quality and reliability of the product. Look for warranties that cover parts and labor for a substantial period. Additionally, assess the availability of after-sales support, including access to spare parts and technical assistance. A robust support network can significantly reduce downtime and maintenance costs, ensuring your machine operates efficiently for years to come. -
How do I verify the credibility of suppliers for head resurfacing machines?
To verify the credibility of suppliers, conduct thorough research by checking their online presence, customer reviews, and industry reputation. Request references from previous clients and inquire about their experiences with the supplier. Additionally, confirm if the supplier is compliant with international quality standards and certifications. Engaging in direct communication to discuss your needs and their offerings can also provide insights into their responsiveness and customer service approach. -
What are the common payment terms offered by suppliers for head resurfacing machines?
Payment terms can vary significantly among suppliers, but common arrangements include upfront payments, partial deposits with the balance due upon delivery, or payment upon installation. Some suppliers may offer financing options, which can be beneficial for buyers looking to manage cash flow. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing the purchase to avoid misunderstandings and ensure that you are comfortable with the financial commitment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing a resurfacing machine?
When importing a resurfacing machine, consider the shipping method, customs duties, and local regulations. Choose a reliable logistics partner experienced in handling machinery imports to ensure safe and timely delivery. Additionally, factor in the machine’s dimensions and weight, as these will influence shipping costs and methods. It is also advisable to prepare all necessary documentation, such as invoices and import licenses, to facilitate a smooth customs clearance process. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for head resurfacing machines?
Minimum order quantities for head resurfacing machines can vary based on the supplier and the type of machine. Many suppliers allow for single unit purchases, especially for entry-level machines. However, bulk orders may attract discounts or better payment terms. If you are considering purchasing multiple machines for a larger operation, it’s worth discussing MOQs directly with the supplier to explore potential savings and ensure your needs are met. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when purchasing a resurfacing machine?
To ensure quality assurance when purchasing a resurfacing machine, request detailed specifications and quality certifications from the manufacturer. Look for machines that have undergone rigorous testing and come with guarantees of performance. Conducting a pre-purchase inspection, if possible, can also help assess the machine’s condition. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s return policy and warranty terms, as these can provide further assurance of the machine’s quality and reliability.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Entry Level Head Resurfacing Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Comec – Cylinder Head Resurfacing Machines
Domain: comecpn.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Comec cylinder head resurfacing machines are designed for both car and truck cylinder heads and blocks. They utilize high-speed milling technology for cast iron and aluminum, following a CNC production cycle for high-quality standards. Key models include SPN800, RP330, RP850, RP1000, RP1000 CNC, RP1300, and RP1400. The RP1000 CNC model features automatic operation with a laser sensor for surface s…
2. Jamisonequipment – Peterson RG-1203 Belt Resurfacer
Domain: jamisonequipment.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: [{‘name’: ‘Peterson RG-1203 Belt Resurfacer’, ‘price’: ‘$3,200.00’, ‘capacity’: ’28 inch length’, ‘motor’: ‘3hp’, ‘voltage’: ‘230 volt 3 phase’, ‘extras’: ‘includes extra belts’}, {‘name’: ‘Winona Van Norman VM2000 cylinder head and block milling machine’, ‘price’: ‘$9,685.00’, ‘description’: ‘Ready to go to work, includes block tooling’}, {‘name’: ‘Comec 300/900 CBN Head & Block Resurfacer’, ‘pri…
3. Engine Builder Mag – Head and Block Resurfacing Equipment
Domain: enginebuildermag.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Head and Block Resurfacing Equipment is essential for engine work, including stock, performance, diesel, and marine engines. Surfacing is necessary to restore surface finish and flatness, especially for high mileage heads and blocks that may be corroded, pitted, scratched, or out-of-flat. Dry milling is the preferred method for surfacing, providing consistent, high-quality finishes compared to old…
4. Reddit – Engine Machining Services
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 1. Milling Cylinder Heads: Low barrier to entry, can buy old mills cheaply, practice on scrap heads.
2. Crankshaft Turning: Difficult work with zero room for error, requires significant equipment.
3. Boring and Sleeving Engines: Time-consuming, dependent on machine shop workload; consideration for a 4-axis CNC for efficiency.
4. Line Honing: Requires knowledge and experience, potential for auction…
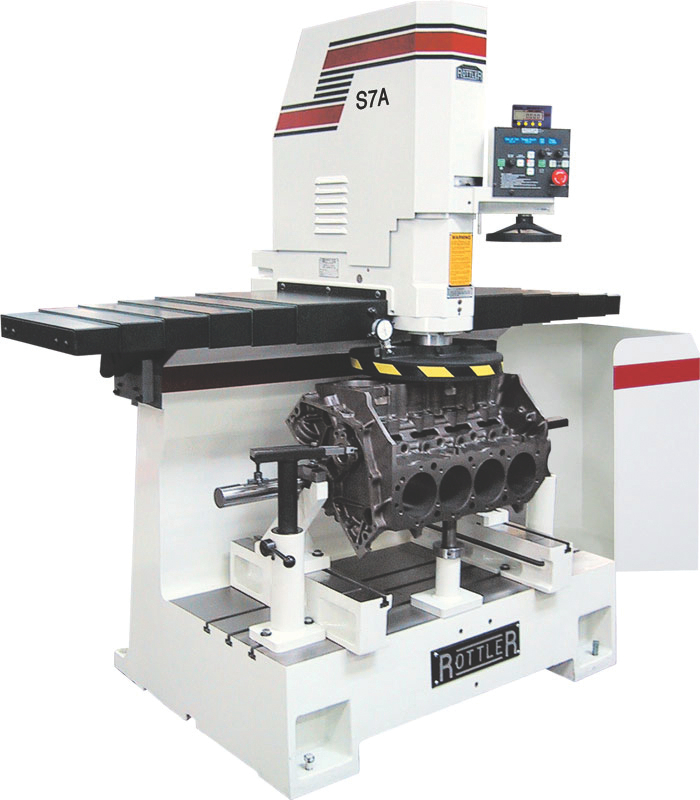
5. Rottler – Cylinder Head Resurfacing Equipment
Domain: rottlermfg.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Rottler Cylinder Head Resurfacing Equipment includes Multi Purpose Automatic CNC & Manual Surfacers. Key product series include EM100, EM60, EM70, F Series, F60 Series, H80 Series, S Series, SG Series, and VR Series. Features include 5 Axis CNC Digitizing, Automatic Tool Changer, Block Surfacing, Blue Print Boring, Boring & Sleeving, Circular Interpolation, CNC Head Porting, Connecting Rod Boring,…
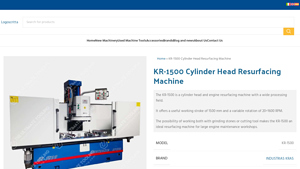
6. INDUSTRIAS KRAS – KR-1500 Cylinder Head Resurfacing Machine
Domain: theultimatetooling.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: {“model”:”KR-1500″,”type”:”Cylinder Head Resurfacing Machine”,”brand”:”INDUSTRIAS KRAS”,”weight”:”1800 kg”,”dimensions”:”277 × 110 × 200 cm”,”table_surface”:”1290 × 220 mm”,”useful_table_surface”:”1500 mm”,”max_traversal_table_travel”:”1650 mm”,”table_variable_feed_speed”:”0 ÷ 2000 mm/min”,”max_distance_table_grinding_wheel”:”800 mm”,”grinding_wheel_diameter”:”Ø 410 mm”,”distance_column_guides_tab…
7. Comec – RP1000 Resurfacer
Domain: comecmachines.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Comec RP1000 resurfacer for cylinder heads and blocks of cars and trucks. Key specifications include: Table travel 1070 mm, Max workpiece length 895 mm, Max workpiece width 355 mm, Min – Max workpiece height 125÷545 mm, Useful table surface 920×210 mm, Segmented grinding wheel diameter 355 mm (14″), Variable head speed rotation 300÷1500 rpm, Variable table travel speed 0÷1500 mm/min, Head motor 4….
8. Homemodel Engine Machinist – Cylinder Head Machining
Domain: homemodelenginemachinist.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Machining a cylinder head for Jeep I6 4.0 inline and Dodge 5.9 V8 steel heads. Recommended tooling includes a fly cutter and face mill. Typical facing depth is 40-60 thousandths of an inch, affecting compression ratio (130 lbs to 155-165 lbs per cylinder). Mill specifications: older Enco using R8 shank, heavy-duty. Suggested practices include ensuring the mill is flat and properly indicated, using…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for entry level head resurfacing machine
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Business with Entry-Level Head Resurfacing Machines?
In today’s competitive landscape, the strategic sourcing of entry-level head resurfacing machines is paramount for businesses looking to enhance operational efficiency and service quality. By selecting the right equipment, organizations can ensure precision in resurfacing tasks, which is critical for maintaining engine performance and longevity. The versatility of machines like the Comec SPN800 and RP1000 CNC allows businesses to cater to diverse customer needs, ranging from standard car repairs to high-performance modifications.
Furthermore, leveraging global suppliers can offer cost-effective solutions without compromising quality. This is especially relevant for international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where accessing high-quality machinery at competitive prices can significantly impact profitability. Investing in advanced technology not only streamlines operations but also positions businesses to explore new market opportunities, such as CNC machining for non-automotive applications.
As you consider your sourcing strategies, envision the future growth of your business and the role that modern resurfacing technology can play. Take action today to invest in the right equipment that aligns with your operational goals, ultimately driving your business forward in a rapidly evolving market.