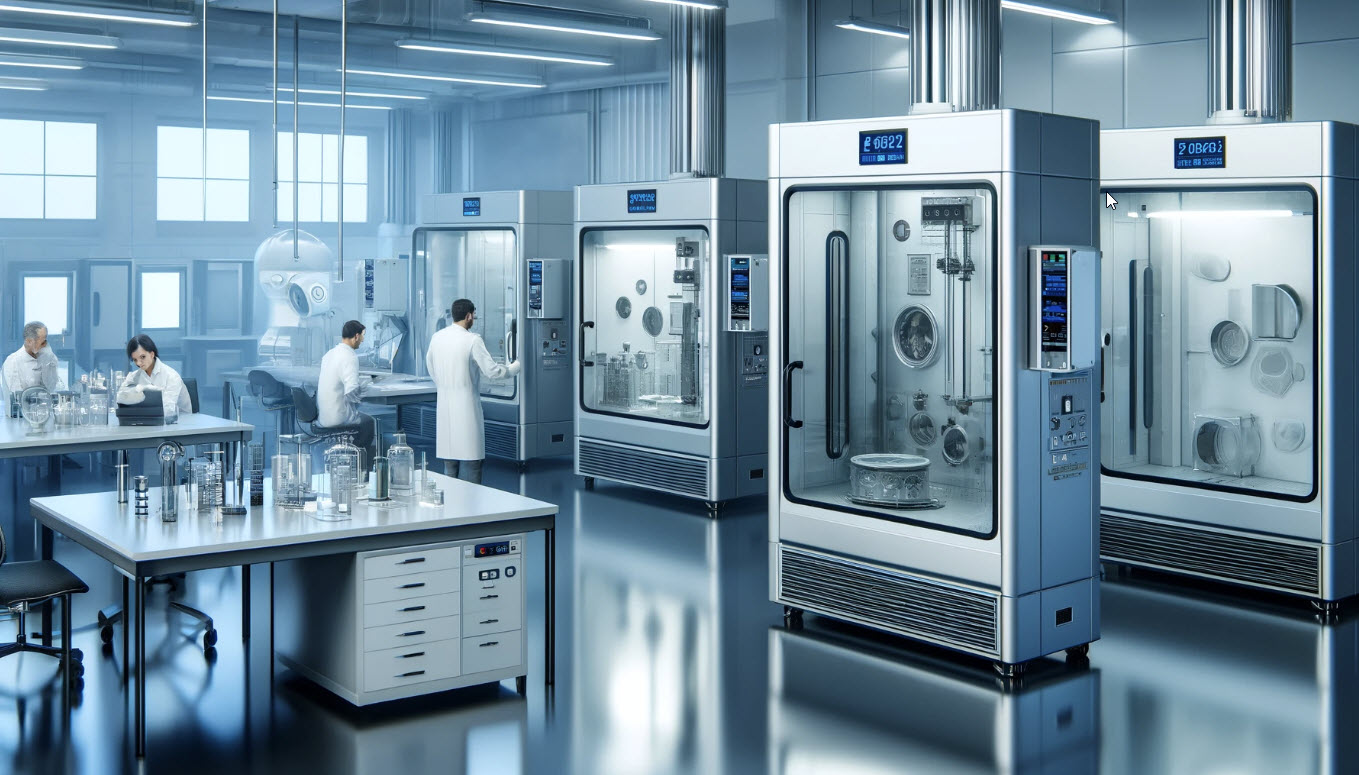
The Definitive Guide to Laboratory Chambers: Cost, Materials & Top Vendors
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for laboratory chambers
In today’s competitive landscape, navigating the global market for laboratory chambers can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. The need for precision and reliability in environments for drug stability studies, biological research, and quality control testing is paramount. With various types of environmental chambers available—ranging from humidity and temperature test chambers to walk-in solutions—sourcing the right equipment requires a strategic approach. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, addressing crucial aspects such as the types of chambers, their applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
For B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, such as Germany and Brazil, making informed purchasing decisions is essential to ensure compliance with international standards and operational efficiency. The guide not only highlights the technical specifications and performance metrics of various laboratory chambers but also offers insights into supplier reliability and market trends. By leveraging this information, buyers can confidently select the right equipment tailored to their specific needs, optimizing both productivity and investment. As the demand for high-quality laboratory environments continues to grow, this guide empowers decision-makers to navigate the complexities of the market and secure solutions that drive scientific advancement.
Understanding laboratory chambers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Chambers | Controlled light, humidity, temperature, and gas levels | Drug stability studies, biological research, shelf-life testing | Pros: Versatile applications, customizable; Cons: Initial investment can be high. |
| Humidity Chambers | High humidity control, often with temperature regulation | Material testing, pharmaceutical stability tests | Pros: Accurate humidity control; Cons: May require regular maintenance. |
| Temperature Test Chambers | Precise temperature regulation, often programmable | Electronics testing, materials testing | Pros: High accuracy; Cons: Limited humidity control. |
| Growth Chambers | Specialized lighting and temperature for biological growth | Plant growth studies, microbiological research | Pros: Optimized for growth; Cons: Higher energy consumption. |
| Walk-in Chambers | Large capacity, customizable environment settings | Bulk storage, extensive stability testing | Pros: Ample space for large samples; Cons: Requires significant floor space. |
What Are Environmental Chambers and Their B2B Relevance?
Environmental chambers are versatile enclosures that allow for precise control of various environmental factors such as light, humidity, air pressure, and gas composition. They are particularly useful for businesses involved in drug stability studies, shelf-life testing, and biological research. When selecting an environmental chamber, B2B buyers should consider the specific capacity requirements, temperature range, and the ability to customize settings based on their research needs. The initial investment can be substantial, but the long-term benefits often outweigh the costs, especially in industries where compliance and accuracy are critical.
How Do Humidity Chambers Function and What Are Their Applications?
Humidity chambers are designed to maintain specific humidity levels alongside temperature control, making them ideal for material testing and pharmaceutical stability assessments. These chambers are crucial for industries that need to understand how materials react under varying humidity conditions. B2B buyers should look for features such as humidity range, chamber size, and ease of calibration. While humidity chambers provide accurate control, they may require regular maintenance to ensure consistent performance.
What Makes Temperature Test Chambers Essential for B2B Buyers?
Temperature test chambers focus on providing precise temperature regulation, often equipped with programmable features for automated testing. These chambers are essential for industries involved in electronics testing and materials analysis, where temperature fluctuations can significantly impact results. Buyers should consider the temperature range, uniformity, and energy efficiency when selecting a temperature test chamber. While they excel in temperature control, their limited humidity capabilities may necessitate additional equipment for comprehensive testing.
How Are Growth Chambers Tailored for Biological Research?
Growth chambers are specially designed to support biological processes by regulating light and temperature, making them indispensable for plant growth studies and microbiological research. These chambers typically feature advanced lighting systems and can accommodate various plant species under controlled conditions. B2B buyers should evaluate the lighting options, temperature stability, and energy consumption when purchasing growth chambers. Although they are optimized for biological growth, the higher energy demands can lead to increased operational costs.
What Are the Advantages and Considerations for Walk-in Chambers?
Walk-in chambers offer expansive space for bulk storage and extensive stability testing, accommodating large samples or multiple products simultaneously. These chambers can be customized to maintain specific environmental conditions, making them suitable for various applications, including pharmaceuticals and food storage. Buyers should assess the available space, customization options, and energy efficiency when considering walk-in chambers. While they provide significant capacity, the requirement for considerable floor space and investment can be a drawback for smaller operations.
Key Industrial Applications of laboratory chambers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of laboratory chambers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical | Drug stability testing in controlled environments | Ensures product efficacy and safety, meeting regulatory standards | Compliance with ICH guidelines, temperature and humidity control |
| Food and Beverage | Shelf-life testing for packaged products | Helps in optimizing product formulations and reducing waste | Capacity and versatility to handle various product types |
| Agriculture | Research on seed germination and plant growth under controlled conditions | Enhances agricultural research and development | Specific temperature and humidity ranges tailored for plant needs |
| Electronics | Environmental testing for electronic components | Validates product reliability and performance in various climates | Ability to simulate extreme conditions like humidity and temperature |
| Biotechnology | Cultivation of microorganisms and cell lines | Supports innovations in health and medicine | Sterilization features and precise control over environmental factors |
How Are Laboratory Chambers Used in the Pharmaceutical Industry?
In the pharmaceutical sector, laboratory chambers are essential for conducting drug stability tests. These chambers simulate various environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, to assess how drugs maintain their efficacy over time. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing chambers that comply with International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines is crucial. This ensures that products meet regulatory standards, ultimately safeguarding public health.
What Role Do Laboratory Chambers Play in the Food and Beverage Sector?
In the food and beverage industry, laboratory chambers are utilized for shelf-life testing of products. By controlling environmental factors, businesses can accurately predict how long products will remain safe and effective for consumption. This capability helps companies in Europe, such as Germany, optimize their formulations and reduce waste. Buyers should consider chambers that offer versatility in capacity and functionality to accommodate a wide range of food products.
How Are Laboratory Chambers Beneficial for Agricultural Research?
Laboratory chambers are increasingly important in agriculture for research on seed germination and plant growth. By providing controlled conditions, these chambers enable scientists to study the effects of various environmental factors on plant development. For buyers in the Middle East, where environmental conditions can be extreme, selecting chambers with specific temperature and humidity ranges tailored for plant needs is vital. This can significantly enhance agricultural research and development efforts.
Why Are Laboratory Chambers Important for the Electronics Industry?
In the electronics sector, laboratory chambers are used for environmental testing of electronic components to ensure reliability and performance under various climatic conditions. This testing is crucial for manufacturers looking to market their products globally, as it validates their durability in different environments. Buyers should prioritize sourcing chambers capable of simulating extreme conditions, such as high humidity and temperature fluctuations, to ensure comprehensive testing.
How Do Laboratory Chambers Support Innovations in Biotechnology?
In biotechnology, laboratory chambers facilitate the cultivation of microorganisms and cell lines under controlled conditions. This is essential for research and development in health and medicine, where precise environmental control can lead to breakthroughs in treatments and therapies. For international buyers, especially in emerging markets, sourcing chambers with sterilization features and the ability to maintain specific environmental factors is critical for successful research outcomes.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘laboratory chambers’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Environmental Conditions Affecting Research Outcomes
The Problem:
B2B buyers, particularly those in pharmaceutical and biological research, often face significant challenges with environmental chambers that do not maintain consistent temperature and humidity levels. This inconsistency can lead to unreliable data, skewed test results, and ultimately, compromised product quality. For example, if a drug stability study is conducted in an environmental chamber that fluctuates in temperature, it may fail to meet regulatory standards, resulting in costly delays and potential recalls.
The Solution:
To mitigate this issue, buyers should prioritize environmental chambers with advanced temperature and humidity control systems, ensuring precise calibration and stability. Look for models equipped with microprocessor-based controls that offer programmable settings for various testing conditions. Additionally, consider chambers that include features such as real-time monitoring and alarms for any deviations in conditions. Regular maintenance and calibration checks are essential; establish a routine schedule with a qualified service provider to keep the equipment in optimal condition. This proactive approach not only safeguards the integrity of your research but also enhances compliance with regulatory requirements.
Scenario 2: Limited Space for Large Laboratory Chambers
The Problem:
Laboratories in urban areas or those with constrained physical spaces often struggle to find suitable environmental chambers that fit their limited footprints. Large walk-in chambers may be impractical due to space restrictions, leading to the frustration of having to compromise on the quality of experiments or even abandon critical research projects due to lack of proper equipment.
The Solution:
B2B buyers should explore compact laboratory chambers that provide the same functionality as larger models without the extensive spatial requirements. Vertical environmental chambers or modular designs can effectively utilize vertical space while maintaining all necessary environmental controls. When sourcing, consider manufacturers that offer custom solutions tailored to specific spatial constraints, ensuring you receive a chamber that fits perfectly within your laboratory. Additionally, investing in multi-purpose chambers that can handle various testing conditions (e.g., temperature, humidity, and light) can maximize efficiency and minimize the need for multiple units, effectively optimizing the available space.
Scenario 3: High Operational Costs Due to Inefficient Equipment
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers are unaware of the operational costs associated with running laboratory chambers, particularly in terms of energy consumption and maintenance. Inefficient chambers can lead to exorbitant electricity bills and unexpected repair costs, which can strain budgets and reduce overall profitability, especially for smaller companies operating in competitive markets.
The Solution:
To address this pain point, buyers should prioritize energy-efficient models when selecting laboratory chambers. Look for equipment that incorporates environmentally friendly technologies, such as thermoelectric cooling systems or advanced insulation materials that minimize energy loss. Additionally, consider chambers with programmable energy-saving modes that allow for optimized usage based on testing schedules. Perform a total cost of ownership analysis before purchasing to understand not just the initial investment but also the long-term operational costs. Engaging in a dialogue with suppliers about energy efficiency certifications and warranties can also provide additional assurance that the equipment will remain cost-effective over time. By taking these steps, businesses can not only reduce their operational costs but also align with sustainability initiatives, which can enhance their reputation in the market.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for laboratory chambers
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Laboratory Chambers?
When selecting materials for laboratory chambers, understanding their properties is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in various applications. The most commonly used materials include stainless steel, powder-coated cold-rolled steel, aluminum, and glass. Each material has unique characteristics that can impact the chamber’s functionality, durability, and suitability for specific applications.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Laboratory Chambers?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and durability, making it a popular choice for laboratory chambers. It typically withstands a wide range of temperatures and pressures, which is essential for maintaining stability during experiments. The material is easy to clean and sterilize, making it suitable for applications involving biological samples or pharmaceuticals.
Pros: Stainless steel is highly durable and resistant to corrosion, ensuring longevity. It also has good thermal conductivity, which aids in maintaining uniform temperature distribution.
Cons: The primary drawback is its higher cost compared to other materials. Additionally, manufacturing stainless steel chambers can be complex due to the need for specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including corrosive substances, which makes it ideal for pharmaceutical and chemical testing.

Illustrative image related to laboratory chambers
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions such as Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM and DIN, which often dictate specific stainless steel grades for laboratory use.
What Are the Benefits of Powder-Coated Cold-Rolled Steel?
Powder-coated cold-rolled steel offers a cost-effective alternative to stainless steel. The powder coating provides a protective layer that enhances corrosion resistance and aesthetics. This material is often used in less demanding environments where high chemical resistance is not a primary concern.
Pros: It is generally less expensive than stainless steel and can be produced in various colors, allowing for customization.
Cons: The powder coating can chip or wear off over time, exposing the underlying steel to corrosion. Additionally, it may not withstand extreme temperatures as effectively as stainless steel.
Impact on Application: This material is suitable for applications that do not involve highly corrosive substances, such as general environmental testing.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify the quality of the powder coating and ensure it meets local standards for durability and safety.

Illustrative image related to laboratory chambers
How Does Aluminum Compare for Use in Laboratory Chambers?
Aluminum is lightweight and has good thermal conductivity, making it an attractive option for laboratory chambers that require quick temperature changes. Its resistance to corrosion is moderate, often enhanced by anodizing processes.
Pros: Aluminum is lightweight and easy to manipulate, which can reduce shipping costs. Its thermal properties allow for efficient temperature control.
Cons: While aluminum is resistant to corrosion, it is not as robust as stainless steel. It may also react with certain chemicals, limiting its application range.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in chambers designed for temperature cycling or environmental testing where weight is a consideration.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the chemical compatibility of aluminum with specific substances, particularly in regions with diverse industrial applications.
What Role Does Glass Play in Laboratory Chambers?
Glass is often used for viewing windows in laboratory chambers, allowing users to monitor experiments without opening the chamber. It provides excellent visibility and is chemically inert, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Pros: Glass is non-reactive and provides clear visibility, which is essential for monitoring experiments.
Cons: Glass is fragile and can break easily, which poses a risk in high-traffic laboratory environments. It also has poor insulation properties compared to metals.
Impact on Application: Glass is ideal for applications requiring visual monitoring, such as biological or environmental studies.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that glass components meet safety standards to prevent breakage and potential hazards.
Summary Table of Material Properties for Laboratory Chambers
| Material | Typical Use Case for laboratory chambers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Pharmaceutical and chemical testing | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Powder-Coated Cold-Rolled Steel | General environmental testing | Cost-effective and customizable | Susceptible to chipping and corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Temperature cycling applications | Lightweight and good thermal conductivity | Limited chemical resistance | Medium |
| Glass | Monitoring experiments | Excellent visibility and inertness | Fragile and poor insulation | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions when sourcing laboratory chambers tailored to their specific needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for laboratory chambers
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Laboratory Chambers?
The manufacturing process of laboratory chambers encompasses several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the stringent requirements of various applications, including drug stability studies, controlled temperature storage, and biological research. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Laboratory Chambers?
Material preparation begins with the selection of high-quality materials, typically stainless steel or powder-coated cold-rolled steel, known for their durability and resistance to corrosion. Suppliers often source materials that comply with international standards, ensuring they meet the performance requirements for laboratory environments. The materials undergo rigorous inspections for quality and consistency before being moved to the next phase.

Illustrative image related to laboratory chambers
What Forming Techniques Are Utilized in Laboratory Chamber Manufacturing?
The forming stage involves shaping the materials into the desired configurations. Common techniques include laser cutting, CNC machining, and bending. These methods allow for precise dimensions and shapes, which are crucial for ensuring that the chambers can maintain the required environmental conditions. Advanced forming techniques also help in reducing waste and enhancing the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process.
How Are Laboratory Chambers Assembled?
Once the individual components are formed, the assembly process begins. This stage typically involves welding, riveting, or using adhesive bonding techniques to join parts together. The assembly is conducted in a controlled environment to prevent contamination and ensure that all components fit together seamlessly. Quality control checks are integrated throughout this stage to verify that the assembly meets design specifications.
What Finishing Processes Are Involved in Laboratory Chamber Production?
The finishing stage is vital for enhancing the aesthetic and functional properties of the chambers. This may include surface treatments like polishing, coating, and applying insulation materials to improve thermal efficiency. Finishing processes not only contribute to the visual appeal but also play a critical role in ensuring that the chambers meet regulatory compliance and durability standards.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Laboratory Chamber Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process for laboratory chambers. It ensures that products meet both international and industry-specific standards, providing B2B buyers with confidence in their purchases.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Laboratory Chambers?
Manufacturers often adhere to various international standards, such as ISO 9001, which outlines the requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO standards helps ensure consistent quality and continuous improvement in manufacturing processes. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) are critical for laboratory chambers used in specific applications, such as pharmaceuticals and energy.
What Are the Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to monitor compliance with quality standards. These checkpoints typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified quality standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to identify any deviations from the established parameters.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of the finished product to ensure it meets all design and performance specifications before shipping.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Quality?
Testing methods for laboratory chambers often include environmental testing, temperature uniformity assessments, and humidity stability tests. Manufacturers may also utilize non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques to check for structural integrity without compromising the product. These tests are crucial for validating that the chambers will perform as expected under operational conditions.

Illustrative image related to laboratory chambers
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers need to ensure that their suppliers maintain robust quality control processes. There are several ways to verify these practices:
- Conducting Supplier Audits: Buyers can perform on-site audits to assess the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality assurance practices, and compliance with international standards.
- Requesting Quality Assurance Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed reports outlining their quality control measures, testing results, and compliance certifications.
- Engaging Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices and the products being manufactured.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific quality control and certification nuances. For example, different regions may have varying regulatory requirements and standards. It is essential for buyers to understand these differences to ensure compliance and facilitate smoother transactions.
Furthermore, language barriers and cultural differences can impact communication regarding quality expectations. Therefore, establishing clear lines of communication and understanding each party’s quality standards is critical to successful international procurement.

Illustrative image related to laboratory chambers
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for laboratory chambers are complex and multifaceted. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ensuring that they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs. This knowledge not only enhances the buyer’s procurement strategy but also fosters stronger partnerships with suppliers in a global marketplace.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘laboratory chambers’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of laboratory chambers can be challenging, especially when considering the diverse needs across various industries. This guide serves as a practical checklist to help B2B buyers streamline their sourcing process, ensuring they select the right laboratory chambers tailored to their specific applications and requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of an effective procurement process. Determine the specific requirements such as temperature range, humidity control, and chamber capacity based on your intended applications, whether it’s for drug stability studies or biological research.
- Key Parameters to Consider:
- Temperature range (e.g., -20°C to 100°C)
- Humidity control levels (e.g., 10% to 90% RH)
- Chamber size and capacity (liters or cubic meters)
Step 2: Identify Your Budget Constraints
Understanding your budget is critical to narrow down options and prevent overspending. Conduct a cost-benefit analysis to weigh the features you need against the available budget.
- Considerations:
- Initial purchase cost vs. long-term operational costs
- Potential savings from energy-efficient models
- Maintenance and servicing costs
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it’s essential to vet potential suppliers comprehensively. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from similar industries to assess their reliability and product quality.
- Important Aspects to Verify:
- Supplier experience and expertise in laboratory equipment
- Reviews or testimonials from other B2B buyers
- Availability of technical support and customer service
Step 4: Check Compliance and Certification Standards
Ensuring that the laboratory chambers comply with relevant industry standards is crucial for regulatory adherence and product integrity. This step can mitigate risks associated with non-compliance, which can lead to operational setbacks.
- Certifications to Look For:
- ISO certifications (e.g., ISO 9001)
- CE marking for European markets
- UL listing for safety standards
Step 5: Assess Customization Options
Laboratory needs can vary significantly; thus, exploring customization options is essential. Discuss with suppliers the potential for tailoring features such as chamber size, shelving configurations, and control systems to suit your specific research or testing requirements.
- Customization Considerations:
- Ability to integrate additional sensors or monitoring systems
- Flexibility in design to accommodate unique workflows
- Options for upgrades or expansions in the future
Step 6: Request Demonstrations and Trials
Before finalizing your purchase, request demonstrations or trial periods for the laboratory chambers. This hands-on approach allows you to evaluate performance, usability, and compatibility with existing systems.
- Trial Insights:
- Evaluate ease of use and control interface
- Assess temperature and humidity consistency
- Observe the chamber’s response to different environmental settings
Step 7: Finalize Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve selected a supplier and product, it’s crucial to negotiate terms and conditions clearly. This includes pricing, warranty coverage, service agreements, and delivery timelines to ensure a smooth procurement process.
- Key Elements to Discuss:
- Warranty duration and terms
- Service and maintenance agreements
- Penalties or recourse for delayed delivery or defects
By following this comprehensive checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing laboratory chambers, ensuring they meet their operational needs while maintaining budgetary constraints.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for laboratory chambers Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Laboratory Chambers?
When sourcing laboratory chambers, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the supplier’s profit margin.
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost. Stainless steel is commonly used for its durability and resistance to corrosion, but it is more expensive than alternatives like powder-coated cold rolled steel.
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and supplier. In countries with higher labor costs, such as Germany, the overall price may be elevated compared to suppliers in Africa or South America.
Manufacturing Overhead and Tooling: Overhead costs, which cover utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation, play a vital role in pricing. Tooling costs, particularly for custom designs or specialized configurations, can also contribute significantly to the final price.
Quality Control: Rigorous QC processes ensure that the chambers meet specified standards and certifications. This can add to the cost but is crucial for compliance, especially in regulated industries like pharmaceuticals.
Logistics: Shipping costs are influenced by distance, weight, and the choice of transportation. International buyers should consider import duties and taxes, which can add to the total expenditure.
Margin: Finally, the supplier’s margin, which reflects their business model and market positioning, will affect the final price. Premium suppliers may charge more due to brand reputation or superior service.
What Factors Influence the Pricing of Laboratory Chambers?
Several factors can affect the pricing of laboratory chambers, particularly for international B2B buyers:
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes typically lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate for better pricing based on their purchasing potential.
Specifications and Customization: Chambers with specialized features, such as advanced temperature controls or enhanced humidity capabilities, will generally cost more. Custom designs may incur additional tooling and engineering costs.
Material Quality and Certifications: Premium materials and certifications (e.g., ISO compliance) often come with higher costs. Buyers should assess the necessity of these features based on their operational requirements.
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence price. Established suppliers may offer better warranties and support, justifying a higher price point.
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery is crucial. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can significantly impact the total cost, as they define who is responsible for shipping costs and risks.
What Are the Best Negotiation Strategies for B2B Buyers of Laboratory Chambers?
Effective negotiation is key to achieving cost efficiency in sourcing laboratory chambers. Here are some strategies tailored for international buyers:
Conduct Market Research: Understand the market rates for various types of laboratory chambers and the cost structure of suppliers in different regions. This knowledge empowers buyers during negotiations.
Leverage Volume Discounts: If possible, commit to larger orders to negotiate lower prices. Suppliers are often willing to offer significant discounts for bulk purchases.
Discuss Payment Terms: Consider negotiating favorable payment terms that align with cash flow needs. Extended payment periods or milestone payments can ease financial pressure.
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Buyers should assess not only the initial purchase price but also ongoing operational costs, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. This holistic view can guide purchasing decisions.
Be Culturally Aware: When negotiating with suppliers from different regions, understanding cultural nuances can facilitate smoother interactions and lead to better deals.
Why is it Important to Understand Pricing Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers should be aware of pricing nuances that can affect their purchasing decisions. Currency fluctuations can influence costs, as can changes in international trade policies. Additionally, varying standards of quality and certification across regions necessitate careful evaluation to ensure compliance with local regulations.

Illustrative image related to laboratory chambers
Disclaimer: The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on supplier negotiations, regional market conditions, and specific product specifications. Always consult multiple sources and suppliers to obtain the most accurate pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing laboratory chambers With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Laboratory Chambers for Controlled Environments
In the realm of scientific research and industrial applications, maintaining specific environmental conditions is crucial. While laboratory chambers are widely used for this purpose, several alternative solutions exist that can also achieve similar outcomes. Understanding these alternatives helps B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and specific application needs.
Comparison Table of Laboratory Chambers and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Laboratory Chambers | Walk-in Environmental Rooms | Portable Climate Control Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision in temperature and humidity control | Excellent for large-scale testing; versatile | Adequate for small-scale, short-term use; less precision |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; varies with specifications | High upfront cost; cost-effective for large volumes | Lower initial cost; economical for temporary setups |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional installation; complex setup | Requires significant space; installation can be complex | User-friendly; can be easily set up and relocated |
| Maintenance | Regular calibration needed; technical support may be necessary | Requires ongoing maintenance and monitoring | Minimal maintenance; easy to service |
| Best Use Case | Long-term stability studies, pharmaceutical testing | Large batch testing, environmental studies | Field studies, temporary testing scenarios |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Walk-in Environmental Rooms
Walk-in environmental rooms are large, controlled spaces designed for extensive testing. They offer flexibility in terms of scale and can accommodate multiple experiments simultaneously. The main advantages of walk-in rooms are their capacity and versatility; however, they require a considerable investment and a significant amount of space, making them less practical for smaller laboratories. Additionally, installation can be complex, necessitating expert input.
2. Portable Climate Control Units
Portable climate control units are compact devices that provide a controlled environment for short-term applications. They are particularly advantageous for fieldwork or temporary installations, as they are easy to set up and transport. Their lower initial cost makes them attractive for small businesses or research teams with limited budgets. However, they typically offer less precision in temperature and humidity control compared to laboratory chambers, making them less suitable for critical applications that require stringent environmental conditions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate solution for environmental control hinges on your specific requirements. Laboratory chambers excel in precision and reliability, making them ideal for critical applications such as pharmaceutical stability testing. In contrast, walk-in environmental rooms are best suited for extensive testing scenarios where space and volume are priorities. For flexibility and cost-effectiveness, portable climate control units are a viable option for short-term or less demanding applications. Ultimately, a thorough assessment of your operational needs, budget constraints, and long-term goals will guide you in making the most informed decision.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for laboratory chambers
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Laboratory Chambers?
When evaluating laboratory chambers, understanding the essential technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The materials used in laboratory chambers, such as stainless steel or powder-coated cold-rolled steel, significantly affect durability, corrosion resistance, and ease of cleaning. Stainless steel, particularly grades 304 and 316, is preferred for its resistance to rust and chemical reactions, making it suitable for various laboratory environments. Choosing the right material can enhance the lifespan of the equipment and reduce maintenance costs, which is essential for budget-conscious organizations.

Illustrative image related to laboratory chambers
2. Temperature Range
Laboratory chambers are designed to operate within specific temperature ranges, often between -40°C to +100°C. This specification is critical for applications like drug stability testing and biological research, where precise temperature control is necessary. Understanding the temperature range helps buyers ensure that the chamber can accommodate the specific testing requirements of their products, thus preventing costly errors.
3. Humidity Control
The ability to control humidity levels is vital for many laboratory applications. Chambers may offer humidity ranges from 10% to 98% RH (Relative Humidity). This feature is crucial for industries such as pharmaceuticals and food sciences, where moisture levels can affect product quality. Buyers should assess the humidity control specifications to ensure they align with their testing protocols.
4. Capacity
Laboratory chambers come in various sizes, typically measured in liters (e.g., 102 L to 2265 L). The capacity determines how much material can be tested simultaneously, impacting operational efficiency. Organizations should consider their current and future needs to select a chamber that optimizes their testing capabilities without incurring unnecessary costs.
5. Power Supply and Voltage Requirements
Understanding the voltage and power supply requirements (e.g., 115V, 230V) is essential for ensuring compatibility with existing electrical systems. This consideration is particularly important for international buyers who may encounter differing electrical standards. Proper voltage alignment not only ensures efficient operation but also prevents potential equipment damage.

Illustrative image related to laboratory chambers
What Common Trade Terms Should Buyers Understand?
Navigating the procurement of laboratory chambers involves familiarizing oneself with industry jargon. Here are some common terms that buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure they are purchasing quality products.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for budget management, as it helps buyers understand the minimum financial commitment required for a bulk purchase, which can often lead to cost savings.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. This process is crucial for ensuring competitive pricing and helps buyers compare offers from different manufacturers effectively.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping costs, risks, and delivery points. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers avoid misunderstandings and financial liabilities during the procurement process.
5. Calibration
Calibration refers to the process of adjusting and verifying the accuracy of measurement instruments. In laboratory settings, ensuring that equipment is properly calibrated is essential for maintaining compliance with industry standards and regulations.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing laboratory chambers, ultimately leading to better outcomes for their organizations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the laboratory chambers Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing Laboratory Chambers?
The laboratory chambers market is experiencing significant growth, driven by an increasing demand for controlled environments in various sectors, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and food safety. Globalization is fostering international collaboration in research and development, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As a result, B2B buyers are seeking advanced laboratory chambers that can accommodate diverse testing requirements, such as drug stability studies and environmental testing.
Emerging technologies are reshaping the sourcing landscape. The integration of IoT (Internet of Things) in laboratory chambers enables real-time monitoring and data collection, enhancing operational efficiency and compliance with regulatory standards. Additionally, advancements in materials science are leading to the development of more durable and energy-efficient chambers, appealing to budget-conscious buyers.
Another significant trend is the customization of laboratory chambers. Suppliers are increasingly offering tailored solutions to meet specific client needs, such as varying temperature ranges and humidity controls. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers who require chambers that can withstand diverse climatic conditions. As competition intensifies, B2B buyers must evaluate suppliers based on their ability to provide flexible, scalable, and technologically advanced solutions.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Laboratory Chambers?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical factor in the sourcing of laboratory chambers. The environmental impact of manufacturing and operating these chambers is under scrutiny, leading to a rising demand for eco-friendly products. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recyclable materials and minimizing energy consumption.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, with buyers seeking suppliers that adhere to responsible manufacturing practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 and Energy Star are becoming essential in the decision-making process, as they signify a commitment to environmental management and energy efficiency. Buyers should evaluate potential suppliers not only on the performance of their laboratory chambers but also on their sustainability credentials.
Moreover, the adoption of ‘green’ technologies, such as thermoelectric cooling, is revolutionizing the industry. These technologies reduce energy usage and lower operational costs, appealing to environmentally conscious buyers. Ultimately, aligning purchasing decisions with sustainability goals can enhance brand reputation and drive long-term success in the marketplace.
How Have Laboratory Chambers Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of laboratory chambers has been marked by significant advancements in technology and design. Initially, these chambers were simple enclosures with limited capabilities, primarily used for basic temperature control. Over the years, the introduction of sophisticated temperature and humidity control systems has transformed laboratory chambers into versatile tools for various applications.
The integration of digital technology has further enhanced their functionality. Modern chambers now feature programmable settings, real-time data logging, and remote monitoring capabilities, enabling users to ensure compliance with stringent regulatory requirements. This evolution reflects the growing complexity of laboratory needs and the increasing emphasis on precision and reliability in scientific research.
In summary, understanding market dynamics and sourcing trends in the laboratory chambers sector is essential for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. By prioritizing sustainability and recognizing the evolution of laboratory technology, buyers can effectively navigate this dynamic landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of laboratory chambers
-
1. How do I choose the right laboratory chamber for my specific applications?
Choosing the right laboratory chamber involves assessing your specific application needs, such as temperature range, humidity control, and chamber size. Consider the intended use, whether it’s for drug stability studies, biological research, or shelf-life testing. Evaluate features such as programmability, energy efficiency, and compliance with international standards. Consulting with suppliers for expert advice and utilizing detailed product specifications can help in making an informed decision that aligns with your operational requirements. -
2. What is the best environmental chamber for stability testing in pharmaceuticals?
For stability testing in pharmaceuticals, a chamber that offers precise temperature and humidity control is crucial. Look for chambers with a wide temperature range (e.g., -20°C to +100°C) and humidity control capabilities (10% to 90% RH). Models that comply with ICH guidelines and have features like programmable settings and data logging are ideal. Suppliers often provide specialized pharmaceutical chambers designed to meet strict regulatory requirements, ensuring your tests are reliable and repeatable. -
3. What are the key factors to consider when sourcing laboratory chambers internationally?
When sourcing laboratory chambers internationally, consider factors such as supplier reputation, product quality certifications, compliance with local regulations, and after-sales support. Assess the supplier’s ability to customize products to meet specific needs and their experience in international shipping logistics. Additionally, review payment terms, warranty conditions, and any potential tariffs or duties that may apply when importing equipment into your region. -
4. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for laboratory chambers?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for laboratory chambers can vary significantly between suppliers and product types. Some manufacturers may offer single units for specialized models, while others may require larger orders for standard products. It’s essential to discuss your needs directly with suppliers to find options that fit your budget and inventory requirements. In some cases, consolidating orders with other equipment can help meet MOQs while maximizing shipping efficiency. -
5. How can I ensure the quality and reliability of laboratory chambers from suppliers?
To ensure quality and reliability, request certifications such as ISO and CE for the laboratory chambers you are considering. Conduct thorough supplier vetting by checking references and reviews from other customers. It’s also beneficial to request product samples or demonstrations, if possible. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s quality assurance processes, warranty terms, and service agreements to understand the level of support you can expect after purchase. -
6. What payment terms should I negotiate with suppliers when buying laboratory chambers?
Negotiating payment terms is crucial for managing cash flow and ensuring a successful transaction. Common terms include advance payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and balance upon delivery. It’s advisable to seek flexibility, such as extended payment periods for larger orders or installment payments for high-value items. Always clarify any additional fees related to shipping, customs, or handling to avoid unexpected costs. -
7. How long does it typically take for laboratory chambers to be delivered internationally?
Delivery times for laboratory chambers can vary based on the supplier’s location, shipping method, and customs clearance processes. Generally, expect delivery within 4 to 12 weeks for international orders. Factors such as the complexity of the order, customization requests, and the shipping route can influence timelines. Communicating with your supplier about expected lead times and tracking shipments can help ensure timely delivery. -
8. What types of customization options are available for laboratory chambers?
Customization options for laboratory chambers can include adjustments to size, temperature and humidity ranges, interior configurations, and specific material choices. Some suppliers offer features like enhanced insulation, additional ports for monitoring, or specialized shelving. Discussing your specific requirements with the supplier can lead to tailored solutions that fit your unique operational needs, ensuring optimal performance for your applications.
Top 8 Laboratory Chambers Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Fisher Sci – Environmental Chambers
Domain: fishersci.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Environmental chambers are enclosures that allow control of light, humidity, air pressure, and gas. They are available in multiple capacities, ranging from cold chamber kits and onstage incubators to industrial-quality chambers. Ideal for drug stability studies, shelf-life testing, controlled temperature storage, and biological research applications. Key specifications include:
– **Capacity (Metr…
2. Lab Repco – Stability Chambers & Automated Storage Solutions
Domain: labrepco.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Stability Chambers/Rooms, Pre-Fabricated Rooms, Controlled Room Temp Cabinets, Automated Cold Storage, Ambient down to -20C, Automated Storage System -80C, Bulk Automated Storage System -190C, Automated Storage System, Automated Thawing Systems, Temperature & Humidity Monitoring Systems, Freezer Inventory & Tracking Management Systems.
3. Lab Depot Inc – Temperature Stability Test Chambers
Domain: labdepotinc.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Temperature stability test chambers are designed for laboratories to assess the effects of temperature and humidity on various products or samples. They are utilized for testing the shelf life of drugs, container stability, electrical components, or industrial materials. The chambers are available with glass or metal doors, and different door configurations, including side-by-side or single doors….
4. Cryostar Industries – Environmental Test Chambers
Domain: cryostarindustries.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Environmental test chambers, also known as climatic or climate chambers, are critical tools used in laboratories to test the effects of environmental conditions on biological specimens, electronics, and industrial products. They expose products to changes in humidity, temperature, stability, vibration, radiation, and pressure to determine how they will perform under these conditions. Industries th…
5. Weiss – Benchtop Environmental Chambers
Domain: weiss-na.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Benchtop Environmental Chambers – Economical and effective design for small spaces such as factories or test laboratories. Ideal for testing various temperature or humidity tests on small products or components. Includes categories like Benchtop Stability Chambers, Laboratory Test Chambers, and Benchtop Temperature Test Chamber.
6. Associated Environmental Systems – Environmental Test Chambers
Domain: associatedenvironmentalsystems.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Environmental Test Chambers include: 1. Temperature Chambers – precise temperature control and uniformity. 2. Battery Test Chambers – optimized for safe and reliable battery testing. 3. Temperature/Humidity Chambers – accurate and repeatable humidity control. 4. Thermal Shock Chambers – fast and reliable thermal cycling. 5. Laboratory Ovens – for drying, baking, curing, and fast-cooling with liqui…
7. LabsUp – Environmental Chambers
Domain: labsup.net
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Environmental Chambers, also known as climate chambers or temperature and humidity chambers, are designed to run programs of varying temperature and humidity levels for testing materials, devices, pharmaceuticals, and other items. They ensure stability and continuity of function under different environmental conditions. Laboratory Supply Network offers a range of environmental chambers with the fo…
8. CSZ – MicroClimate® Benchtop Test Chambers
Domain: cszindustrial.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: CSZ MicroClimate® Benchtop Test Chambers
– Size: 1.2 cubic feet (35 liters)
– Temperature Range: Single Stage: -30°C to +190°C (-22°F to +375°F); Cascade: -68°C to +190°C (-90°F to +375°F)
– Optional Humidity Range: 10% to 95% RH
– Interior Dimensions: 16″W x 11″D x 12″H (40.64cm x 28cm x 30cm)
– Exterior Dimensions: 37″W x 32″D x 28″H (94cm x 81cm x 71cm)
– Features: EZT-430S Touch Screen Control…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for laboratory chambers
In the competitive landscape of laboratory chambers, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical factor for international B2B buyers. By understanding the diverse types and specifications of environmental chambers—from humidity and temperature test chambers to walk-in units—buyers can tailor their procurement strategies to meet specific research and quality assurance needs. The ability to evaluate suppliers based on factors such as chamber capacity, material composition, and energy efficiency allows organizations to not only enhance their operational efficiencies but also achieve cost savings over time.
As the demand for laboratory chambers grows across regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is essential for buyers to prioritize sustainability and technological advancements in their sourcing decisions. Investing in high-quality chambers that meet international standards can significantly improve product reliability and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Looking ahead, the future of laboratory chambers is promising, with innovations in smart technology and energy efficiency on the horizon. International buyers are encouraged to embrace these advancements and collaborate with reputable suppliers to ensure their laboratory environments are equipped for the challenges of tomorrow. Engage with suppliers today to explore how strategic sourcing can transform your laboratory operations and drive success in your industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.