Top 7 Marking Instrument Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for marking instrument
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality marking instruments poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The diverse applications of marking tools—from precision engraving for product identification to intricate designs in manufacturing—demand a thorough understanding of the various types available, including laser marking systems, electrochemical etching machines, and traditional hand tools. This guide delves into the complexities of the global market for marking instruments, offering insights into the latest technologies, their applications across industries, and the critical factors to consider when selecting suppliers.
Buyers will gain a comprehensive overview of the different types of marking instruments, their specific uses, and how to assess quality and reliability. Additionally, the guide will cover essential aspects of supplier vetting, cost considerations, and the importance of after-sales support. By empowering buyers with actionable knowledge and practical tools, this resource is designed to facilitate informed purchasing decisions that align with both operational needs and budgetary constraints. Whether you are a procurement officer in a manufacturing plant in Vietnam or a logistics manager in Saudi Arabia, this guide aims to streamline your sourcing process and enhance your competitive edge in the marketplace.
Understanding marking instrument Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Gauge | Utilizes a base and spindle for precise markings | Metalworking, woodworking, engineering | Pros: High accuracy; versatile. Cons: Can be cumbersome for small tasks. |
| Laser Marking Machine | Employs laser technology for permanent engravings | Packaging, electronics, automotive, medical devices | Pros: Long-lasting marks; high speed. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Electrolyte Marking Machine | Uses electrochemical etching for clean, precise marks | Metal identification, product labeling | Pros: Cost-effective; easy to maintain. Cons: Limited to conductive materials. |
| Scriber | Sharp tool for tracing outlines on various surfaces | Metal fabrication, woodworking, mechanical workshops | Pros: Simple to use; precise. Cons: Requires skill for effective use. |
| Divider | Marks geometrical shapes and transfers measurements | Drafting, engineering design, woodworking | Pros: Great for precision layout; easy to use. Cons: Limited to 2D shapes. |
What Are Surface Gauges and Their B2B Applications?
Surface gauges are essential tools in precision marking, primarily used in metalworking and woodworking. They consist of a sturdy base and a spindle that allows users to draw straight lines or mark points on surfaces. Their accuracy makes them ideal for layout work in engineering and manufacturing settings. When purchasing surface gauges, buyers should consider the material quality and the gauge’s stability to ensure consistent performance in their operations.
How Do Laser Marking Machines Benefit Businesses?
Laser marking machines utilize advanced laser technology to create permanent markings on various materials, including metals, plastics, and glass. These machines are widely used in industries such as packaging, electronics, and medical devices due to their ability to produce high-speed, precise markings that are resistant to wear. While the upfront cost may be higher than traditional marking tools, the long-term benefits, such as reduced maintenance and increased efficiency, make them a worthwhile investment for B2B buyers.
What Advantages Do Electrolyte Marking Machines Offer?
Electrolyte marking machines are designed for clean and accurate marking through electrochemical etching. They are particularly useful for marking metals without altering their properties. This technology is favored in applications like product labeling and metal identification. Buyers should note the ease of maintenance and operation, making these machines suitable for businesses with varying levels of technical expertise. However, they are limited to conductive materials, which could restrict their application in certain industries.
Why Choose Scribers for Precision Marking?
Scribers are sharp, pointed instruments commonly used in mechanical workshops to trace outlines on materials. Their simplicity and effectiveness make them a preferred choice for tasks requiring precision. While they are easy to use, effective operation demands a certain level of skill and experience. B2B buyers should assess the scriber’s material and design to ensure it meets their specific marking needs, especially in demanding environments.
How Do Dividers Enhance Precision in Marking?
Dividers are versatile marking tools used to create geometrical shapes and transfer measurements accurately. They are commonly employed in drafting, engineering design, and woodworking. Their ability to mark precise distances and angles makes them invaluable in various technical applications. When selecting dividers, buyers should consider the quality of the tips and the ease of adjustment, ensuring they can meet the precision requirements of their projects effectively.
Key Industrial Applications of marking instrument
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Marking Instrument | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Precision marking for component alignment | Increases production accuracy and reduces waste | Supplier reliability and technology compatibility |
| Automotive | Marking of parts for identification and traceability | Enhances quality control and compliance with regulations | Certification standards and delivery timelines |
| Construction | Layout marking for building projects | Improves project efficiency and reduces rework | Durability and weather resistance of marking tools |
| Electronics | Marking circuit boards and components | Facilitates assembly and quality assurance | Compatibility with various materials and precision needs |
| Medical Devices | Marking for product identification and compliance | Ensures traceability and regulatory compliance | Regulatory certifications and precision engraving options |
How is Marking Instrument Used in Manufacturing, and What Problems Does It Solve?
In the manufacturing sector, marking instruments are vital for precision marking during component alignment. This application ensures that parts are positioned accurately, reducing the risk of errors that could lead to costly rework or scrap. International buyers need to consider the reliability of suppliers, as well as the technology compatibility of marking tools with existing machinery. Tools that offer advanced features such as digital displays or automated adjustments can significantly enhance productivity.
What Role Does Marking Instrument Play in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive industry, marking instruments are used for labeling parts to ensure traceability and compliance with safety regulations. Each component must be clearly marked to facilitate quality control checks throughout the production process. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should prioritize suppliers that adhere to international certification standards, as this will influence the quality of the marking tools and their compliance with local regulations.
How Are Marking Instruments Essential for Construction Projects?
Construction projects utilize marking instruments for layout marking, which is critical for accurate building execution. These tools help in delineating areas for foundations, walls, and other structural elements, ultimately improving project efficiency and minimizing rework. Buyers in Africa and South America should seek marking tools that are durable and weather-resistant, as construction environments can be harsh and demanding.
Illustrative image related to marking instrument
Why Are Marking Instruments Important in the Electronics Sector?
In the electronics industry, marking instruments are used for marking circuit boards and components. This application aids in assembly processes and ensures quality assurance throughout production. International buyers must consider the compatibility of marking tools with various materials, including plastics and metals, as well as the precision requirements necessary for intricate electronic components.
How Do Marking Instruments Support Medical Device Manufacturing?
Marking instruments play a crucial role in the medical device sector by providing necessary product identification and compliance markings. This ensures traceability, which is essential for regulatory compliance and safety. Buyers must prioritize suppliers that offer precision engraving options and hold relevant regulatory certifications, as these factors significantly impact the quality and compliance of medical products in international markets.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘marking instrument’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inaccurate Markings Leading to Costly Errors
The Problem: In many manufacturing and construction environments, precision is critical. A B2B buyer may face the challenge of inaccurate markings due to the limitations of their current marking instruments. This can lead to misaligned components, wasted materials, and, ultimately, financial losses. For instance, if a company is using low-quality marking tools or outdated methods, the markings may not be precise enough for complex projects, resulting in costly rework and delays.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, it’s essential to invest in high-quality precision marking tools that are specifically designed for the materials and applications being used. Buyers should evaluate their current processes and determine the specific requirements for accuracy and precision. For example, utilizing laser marking machines can provide highly accurate and permanent markings, reducing the chance of errors. Additionally, implementing a systematic training program for employees on how to properly use these instruments will ensure that the tools are used effectively, further enhancing accuracy. Regular maintenance and calibration of marking tools should also be scheduled to ensure they remain in optimal working condition, thereby preventing inaccuracies over time.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Marking Complex Shapes
The Problem: Many industries, such as automotive and aerospace, require the marking of complex shapes and designs on various materials. A B2B buyer may encounter challenges when existing marking instruments are inadequate for this task. Traditional tools may not offer the flexibility needed to replicate intricate designs or contours, leading to frustration and potential project delays. This limitation can hinder productivity, especially when clients demand high levels of customization.
The Solution: To address this pain point, buyers should consider investing in advanced marking systems, such as contour gauges or specialized marking templates that can easily adapt to complex shapes. For instance, angle-izer template tools can be utilized to create accurate patterns for various applications, from mold making to tiling. Additionally, integrating digital measuring tools can enhance precision and efficiency when marking complex designs. Buyers should also explore partnerships with suppliers who offer customizable marking solutions tailored to their specific needs. By leveraging technology and innovative tools, companies can streamline their marking processes and improve overall productivity.
Scenario 3: Limited Tool Versatility for Diverse Applications
The Problem: In many manufacturing settings, the need for versatility in marking tools is paramount. A B2B buyer might struggle with a limited range of marking instruments that are only suitable for specific applications, resulting in inefficiencies and increased costs. For example, if a company primarily uses a single type of marking tool, they may find themselves unable to effectively mark different materials or surfaces, leading to delays in production and potential loss of contracts.
The Solution: To enhance operational flexibility, buyers should invest in a diverse range of marking tools that can cater to various materials and applications. This includes not only traditional tools like scribers and center punches but also modern options such as laser marking machines and electrolytic marking systems, which can be used across multiple substrates including metal, plastic, and wood. It’s also beneficial to conduct a thorough assessment of the specific materials and marking needs of the business to ensure the right tools are selected. Suppliers should be evaluated based on their ability to provide comprehensive solutions that meet diverse marking requirements. By adopting a versatile toolset, companies can improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and respond more swiftly to client demands, ultimately driving business growth.

Illustrative image related to marking instrument
Strategic Material Selection Guide for marking instrument
What Are the Key Materials Used in Marking Instruments?
When selecting marking instruments for various applications, the choice of material is critical. Different materials offer unique properties that can significantly affect performance, durability, and suitability for specific tasks. Below, we analyze four common materials used in marking instruments, focusing on their key properties, advantages and disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Steel Perform as a Material for Marking Instruments?
Steel is a prevalent choice for marking tools, particularly due to its strength and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Steel’s resistance to wear and deformation under stress is a significant advantage, ensuring long-lasting performance.
Pros: Steel marking tools are highly durable and can maintain sharp edges, which is essential for precision marking. They are also relatively cost-effective compared to other materials.
Cons: However, steel can be prone to corrosion if not properly treated or maintained, which may limit its use in humid or corrosive environments. Additionally, manufacturing complexity can increase with specialized coatings to enhance corrosion resistance.
Impact on Application: Steel marking tools are compatible with a wide range of media, including metal and wood, making them versatile for various industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM for steel quality is crucial. Buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should also consider local climatic conditions that may affect the choice of steel versus other materials.
What Are the Advantages of Aluminum in Marking Instruments?
Aluminum is another popular material for marking instruments, particularly for tools that require lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. Its low density makes it easy to handle, while its natural resistance to oxidation enhances its durability.
Pros: Aluminum marking tools are lightweight, making them ideal for applications where portability is essential. They also resist corrosion, which is advantageous in humid environments.
Cons: On the downside, aluminum may not offer the same level of hardness as steel, which can affect its longevity in heavy-duty applications. Additionally, it can be more expensive than steel.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for marking on softer materials, such as plastics and composites, but may not perform as well on harder substrates.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local and international standards, such as DIN for aluminum quality. In markets like South America, where humidity is high, aluminum’s corrosion resistance can be a significant selling point.
How Does Plastic Compare as a Material for Marking Instruments?
Plastic marking instruments are often utilized for specific applications, particularly in environments where weight and cost are critical factors. They are available in various formulations, allowing for customization based on specific needs.
Pros: Plastic tools are lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to many chemicals, making them suitable for a variety of applications.
Cons: However, plastic may not withstand high temperatures and can wear out faster than metal options. Its durability is often less than that of steel or aluminum.
Impact on Application: Plastic marking instruments are ideal for marking on paper, cardboard, and some plastics but may not be suitable for metal or wood.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with safety standards relevant to plastics, such as those set by JIS in Japan. In regions like Europe, where environmental regulations are stringent, the recyclability of plastic materials may also be a consideration.
Why Is Stainless Steel a Preferred Material for Marking Instruments?
Stainless steel combines the best properties of steel and corrosion resistance, making it an excellent choice for marking tools used in various environments. Its strength and durability are complemented by its aesthetic appeal and resistance to rust.
Pros: Stainless steel marking instruments are highly durable and maintain their appearance over time, which is important for branding and professional use.
Cons: The primary drawback is the higher cost compared to standard steel and aluminum. Manufacturing processes can also be more complex due to the need for specialized equipment.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for marking on a wide range of materials, including metals and plastics, and is often used in food and medical applications due to its hygienic properties.

Illustrative image related to marking instrument
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO is essential, especially in industries with strict hygiene requirements, such as food processing in Europe and the Middle East.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Marking Instruments
| Material | Typical Use Case for marking instrument | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty marking tools | High durability and wear resistance | Prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight marking tools | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less hardness than steel | Medium |
| Plastic | Marking on softer materials | Cost-effective and lightweight | Limited durability | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Professional marking in various industries | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
This guide should assist B2B buyers in making informed decisions regarding material selection for marking instruments, considering both performance requirements and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for marking instrument
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Marking Instruments?
The manufacturing process of marking instruments is intricate, involving several key stages that ensure the final product meets quality and precision standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
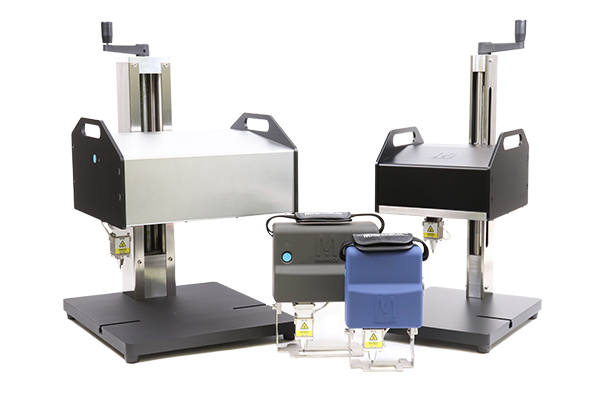

Illustrative image related to marking instrument
How Is Material Prepared for Marking Instruments?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. It typically involves sourcing high-grade materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, or high-density plastics, depending on the specific requirements of the marking tool. Suppliers must ensure that the materials conform to industry standards, which may involve checking for properties such as hardness, durability, and resistance to corrosion. A thorough inspection of raw materials is vital to prevent defects in the final product.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Marking Instruments?
Once materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This involves various techniques such as machining, stamping, and molding. For instance, precision machining is commonly used for components like blades in marking knives, while injection molding may be employed for plastic parts. Techniques like laser cutting are increasingly popular for their accuracy and efficiency in producing complex shapes. Each technique has its advantages and is selected based on the specific design and performance requirements of the marking instrument.
How Are Marking Instruments Assembled?
After forming, the components undergo assembly. This stage involves fitting together the various parts, which may include handles, blades, and measurement scales. Automated assembly systems are often used to enhance precision and reduce human error. Quality control checks are integrated into this stage to ensure that components fit together correctly and function as intended. This attention to detail is critical, as improper assembly can affect the instrument’s accuracy and reliability.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Marking Instruments?
Finishing is the final stage of manufacturing, which enhances the appearance and performance of marking tools. Processes such as anodizing, coating, or polishing may be applied to protect the instruments from wear and corrosion. Additionally, marking tools may undergo laser engraving to provide branding or specifications directly onto the product. This not only adds aesthetic value but also improves traceability for B2B transactions.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Production of Marking Instruments?
Quality assurance (QA) in the manufacturing of marking instruments is critical to ensure they meet international standards and customer expectations. Various international and industry-specific standards guide the QA process.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized international standards for quality management systems. It emphasizes a process approach to enhance customer satisfaction through effective system implementation. B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers are certified to ISO 9001, as this indicates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for products sold in Europe or API standards for tools used in the oil and gas industry may also be relevant. These certifications ensure compliance with safety and performance standards specific to the marking instruments’ intended application.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. These checkpoints typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting the raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, inspections are conducted to monitor processes and detect any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the marking instruments are assembled, a final inspection is performed to verify that the product meets all specifications and quality standards before shipping.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Testing methods vary based on the type of marking instrument, but common practices include dimensional checks, functionality tests, and durability assessments. For example, measuring tools may undergo calibration checks to ensure accuracy, while laser marking systems might be tested for engraving precision and speed. These tests help to validate that the instruments perform effectively under expected conditions.

Illustrative image related to marking instrument
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers have several avenues to verify the quality control measures of their suppliers. Conducting audits is one of the most effective methods. An audit allows buyers to assess the supplier’s manufacturing processes and QA systems firsthand. This can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality and their ability to meet international standards.
Additionally, requesting quality control reports can be beneficial. These documents should detail the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC processes, giving buyers a clear picture of the quality assurance measures in place.
Engaging third-party inspection services can also add an extra layer of assurance. These independent entities can conduct thorough assessments of the manufacturing facility and the products being produced, providing unbiased feedback on compliance with quality standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding quality control nuances is essential. Different regions may have varying compliance requirements and standards, which can affect the quality and certification of marking instruments.
Buyers should be aware of local regulations and ensure that suppliers are compliant with both international standards and regional laws. This may involve understanding tariffs, import regulations, and certification processes specific to their markets.
Furthermore, language barriers and cultural differences can impact communication about quality expectations. Establishing clear lines of communication and setting explicit quality benchmarks can help mitigate misunderstandings and ensure that products meet the required standards.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for marking instruments are multi-faceted and critical to delivering high-quality products. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they partner with suppliers who prioritize quality and compliance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘marking instrument’
In the competitive landscape of B2B procurement, sourcing marking instruments requires a systematic approach to ensure quality and reliability. This guide provides a comprehensive checklist for international buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, helping you make informed decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, it’s essential to establish clear technical specifications for your marking instruments. Consider the materials you will be working with (e.g., metal, plastic, wood) and the types of markings required (e.g., precision, depth, permanence). Specificity in your requirements helps suppliers understand your needs and recommend suitable products.
- Types of Markings: Identify whether you need laser engravings, electrochemical etchings, or traditional marking tools.
- Precision Requirements: Determine the level of accuracy needed for your applications.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers that specialize in marking instruments. Utilize online directories, industry forums, and trade shows to compile a list of potential candidates.
- Industry Experience: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your specific industry.
- Customer Reviews: Read testimonials and case studies to gauge the reliability of their products and services.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify the certifications and quality standards of potential suppliers. This step is crucial to ensure that the marking instruments meet international quality and safety standards.

Illustrative image related to marking instrument
- ISO Certifications: Confirm that the supplier adheres to ISO quality management standards, which reflect their commitment to quality.
- Compliance with Local Regulations: Ensure that the products comply with regional regulations where you intend to use them.
Step 4: Request Samples
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the marking instruments to evaluate their performance. Testing samples allows you to assess the quality and suitability of the instruments for your specific applications.
- Test for Durability: Check the longevity of the markings on various materials.
- Evaluate Ease of Use: Ensure that the instruments are user-friendly for your team.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, compare their pricing and terms. While cost is important, consider the value offered, including warranty, after-sales support, and delivery timelines.
- Bulk Discounts: Inquire about discounts for larger orders, which can significantly reduce costs.
- Payment Terms: Understand payment options and any financing available to ease cash flow.
Step 6: Finalize Contractual Terms
After selecting a supplier, ensure that all contractual terms are clearly defined before proceeding with the order. This includes delivery schedules, payment terms, and return policies.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Establish SLAs to ensure the supplier meets your quality and delivery expectations.
- Dispute Resolution: Include clauses for resolving any potential disputes to protect your interests.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship
Post-purchase, focus on building a long-term relationship with your chosen supplier. Regular communication and feedback can lead to better service, improved product offerings, and collaborative problem-solving in future projects.
- Feedback Loop: Share your experiences to help the supplier improve their offerings.
- Future Needs: Discuss potential future projects to align your needs with their capabilities.
By following this checklist, you can navigate the procurement process of marking instruments more effectively, ensuring that you choose the right suppliers for your business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for marking instrument Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Marking Instrument Manufacturing?
Understanding the cost structure of marking instruments is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize their purchasing strategies. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of materials used significantly affects the overall cost. High-quality steel, aluminum, or specialized plastics may increase prices, while lower-grade materials can reduce costs but may compromise durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region, with countries like Vietnam and those in South America often offering lower wage rates compared to Europe or the Middle East. This can influence the pricing of both standard and custom marking instruments.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient production processes and technology can help keep these costs down.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for specialized marking instruments can be significant, particularly for custom designs. However, these costs are often amortized over large production runs, making them less impactful per unit as volume increases.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that marking instruments meet quality standards involves costs related to inspections and testing. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with robust QC processes to avoid future liabilities.
-
Logistics: Transportation and storage costs can vary widely depending on the distance from the supplier and the chosen shipping method. Incoterms play a critical role in determining who bears these costs.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins can range from 10% to 40% depending on market conditions, competition, and the uniqueness of the product.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Marking Instrument Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of marking instruments:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders generally lead to better pricing due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate for bulk discounts to maximize savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom tools or specific features will typically incur additional costs. Buyers should evaluate whether the additional features justify the price increase.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Instruments made from premium materials or those that comply with international quality standards (e.g., ISO certifications) may command higher prices. These certifications can also enhance product reliability, which is critical in B2B transactions.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge a premium, but they often provide better service and support.
-
Incoterms: Different shipping agreements can significantly impact the total cost. For instance, choosing DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) can simplify logistics but might be pricier compared to EXW (Ex Works), where the buyer assumes more responsibility.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices?
-
Negotiate Effectively: Open discussions with suppliers regarding pricing can yield discounts, especially for long-term partnerships or larger orders. Presenting data on competitor pricing can also strengthen your negotiating position.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. This includes maintenance costs, durability, and potential downtime, which can significantly impact overall expenses.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Purchases: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East should be aware of potential tariffs, taxes, and logistical challenges that can affect pricing. Familiarizing yourself with local regulations and import duties can help avoid unexpected costs.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure that suppliers provide comprehensive quotes that break down costs into materials, labor, and other components. This transparency allows for better comparisons and informed decisions.
-
Evaluate Supplier Stability: Choose suppliers who demonstrate financial stability and consistent quality. This minimizes the risk of supply chain disruptions, which can lead to increased costs over time.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for marking instruments can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. The figures presented are indicative and should be confirmed through direct consultation with suppliers to ensure accuracy and relevance to specific purchasing scenarios.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing marking instrument With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Marking Instruments in B2B Applications
In the realm of marking and engraving, various tools and technologies are available to suit different operational needs. While traditional marking instruments are widely used for their reliability and precision, alternative solutions like laser marking systems and electrolytic marking machines have gained traction due to their advanced capabilities and efficiencies. This section provides an analysis of these alternatives, allowing B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific requirements.
Comparison Table of Marking Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Marking Instrument | Laser Marking System | Electrolytic Marking Machine |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for manual tasks | High speed and accuracy with complex designs | Good accuracy, slower than laser systems |
| Cost | Generally low initial cost | Higher initial investment but low operational cost | Moderate investment, cost-effective for large batches |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple and straightforward setup | Requires trained personnel for setup and operation | User-friendly, minimal training needed |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Requires regular servicing and calibration | Minimal maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | Crafting, woodwork, and metal layout | Industrial applications, branding, and intricate designs | Marking on metals and plastics, ideal for production lines |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Laser Marking System
Laser marking systems utilize focused laser beams to etch or engrave markings onto various materials. This technology offers high speed and precision, making it suitable for complex designs and high-volume production. One of the main advantages is the minimal wear and tear on the equipment, as there are no physical contacts involved in the marking process. However, the initial investment can be significant, and it requires skilled personnel for setup and operation, which may not be feasible for smaller businesses or workshops.
2. Electrolytic Marking Machine
Electrolytic marking machines use electrochemical processes to mark surfaces, making them ideal for metal components. These machines provide a good balance of cost and performance, especially in applications where durability and corrosion resistance are crucial. They are relatively easy to operate, often requiring less technical knowledge than laser systems. However, they typically operate at a slower pace compared to laser marking, which can be a disadvantage in high-output environments.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Marking Solution for Your Business
Selecting the appropriate marking solution hinges on understanding your specific needs and operational context. If precision and speed are paramount, especially in high-volume production settings, a laser marking system may be the best choice despite its higher cost and complexity. Conversely, for businesses focused on cost-effectiveness and simplicity, traditional marking instruments or electrolytic marking machines might be more suitable. Consider factors such as material types, production volumes, and available technical expertise to make a well-informed decision that aligns with your business objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for marking instrument
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Marking Instruments?
When selecting marking instruments, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for ensuring precision and efficiency in your operations. Here are some essential properties that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
Marking tools are often made from various materials, such as high-carbon steel, stainless steel, or specialty alloys. The material grade influences durability, resistance to wear, and the ability to maintain sharp edges. For industries like automotive or aerospace, where precision is paramount, selecting tools made from higher-grade materials can significantly impact the quality of work and reduce long-term costs.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In marking instruments, tighter tolerances ensure that marks are consistently accurate, which is vital for subsequent machining or assembly processes. Understanding tolerance levels helps buyers choose tools suitable for their specific applications, ensuring that the final product meets industry standards.
3. Marking Depth
The depth of the mark made by the instrument affects visibility and durability. For example, deeper marks may be necessary for materials subjected to harsh environments, while shallower marks suffice for less demanding applications. Knowing the required marking depth helps buyers select the appropriate tool for their specific marking needs.
4. Ergonomics
Ergonomic design focuses on user comfort and efficiency. Tools that are comfortable to hold and operate can improve productivity and reduce the risk of repetitive strain injuries. B2B buyers should consider ergonomic factors when selecting marking tools, especially for industries with high-volume marking tasks.
5. Precision and Accuracy
Precision refers to the tool’s ability to produce consistent results, while accuracy indicates how close a mark is to the intended target. High-precision marking tools are essential in sectors like electronics and medical device manufacturing, where even the slightest deviation can lead to product failure. Buyers should prioritize tools with demonstrated precision and accuracy to ensure operational success.
What Trade Terms Should You Know When Purchasing Marking Instruments?
Navigating the B2B landscape requires familiarity with industry jargon. Here are some essential trade terms that buyers should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For marking tools, an OEM may supply components that are integrated into larger machinery. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and assess the quality of the tools they are purchasing.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should consider their operational needs to ensure they can meet the MOQ without overstocking or running short on essential tools.
3. RFQ (Request for Quote)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing for specific products or services. This process is essential for B2B buyers looking to compare costs and terms across different suppliers. Crafting a comprehensive RFQ can lead to better pricing and more favorable terms.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify who pays for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers engaged in international trade, as they help mitigate risks and clarify obligations.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration between placing an order and receiving the goods. In the context of marking instruments, understanding lead times can help buyers plan their production schedules and manage inventory effectively.
By familiarizing yourself with these technical properties and trade terms, you can make informed decisions when sourcing marking instruments, ensuring that your operations run smoothly and efficiently.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the marking instrument Sector
What Are the Key Trends Influencing the Marking Instrument Market?
The marking instrument sector is currently experiencing significant evolution, driven by technological advancements and changing market demands. Global drivers such as the increasing need for precision in manufacturing and the rising trend of automation are shaping the landscape. B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking high-quality, efficient marking solutions that can integrate seamlessly into their production processes.
Emerging technologies, such as laser marking systems and automated engraving machines, are gaining traction due to their ability to deliver high precision and speed, which are essential in industries ranging from automotive to electronics. Furthermore, the adoption of Industry 4.0 principles is encouraging manufacturers to invest in smart, connected marking solutions that enhance productivity and reduce downtime.
Another notable trend is the shift towards customized marking solutions tailored to specific industry needs. For international buyers, understanding local market dynamics, such as regulatory requirements and cultural preferences, is crucial in sourcing the right marking instruments. This growing emphasis on localization is prompting suppliers to diversify their offerings and adapt to regional market nuances.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Marking Instrument Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the marking instrument industry as B2B buyers increasingly prioritize environmentally friendly practices. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, such as waste generation and carbon emissions, has led companies to seek suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices.
Illustrative image related to marking instrument
Ethical sourcing is also gaining importance, with buyers looking for suppliers who ensure fair labor practices and responsible sourcing of raw materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other ‘green’ certifications can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
In the marking instrument sector, materials used in production—such as eco-friendly inks and sustainable packaging—are also under scrutiny. Suppliers that offer innovative, sustainable materials not only enhance their appeal to conscious buyers but also contribute to reducing the overall environmental footprint of the marking process. As buyers from regions like Africa and South America increasingly emphasize sustainability, suppliers must align their practices with these expectations to remain competitive.
What Is the Historical Context of Marking Instruments in B2B Transactions?
The evolution of marking instruments can be traced back to ancient times when basic tools were used for marking materials for various applications. Over the centuries, these tools have transformed significantly, driven by advancements in material science and manufacturing techniques. The introduction of precision tools during the Industrial Revolution marked a turning point, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of marking processes.
In the modern context, the shift towards digital technologies has further revolutionized the sector. Innovations such as laser engraving and automated marking systems have dramatically increased the capabilities of marking instruments, allowing for intricate designs and high-speed production. This historical context is vital for B2B buyers to understand the trajectory of the market and anticipate future trends, ensuring they invest in solutions that meet both current and future demands.
In summary, the marking instrument sector is poised for continued growth and innovation, driven by technological advancements, sustainability imperatives, and the evolving needs of international B2B buyers. Understanding these dynamics is essential for making informed sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of marking instrument
-
How do I choose the right marking instrument for my business needs?
Choosing the right marking instrument depends on the materials you work with and the complexity of your projects. For instance, laser marking machines are ideal for high precision on materials like metal and plastic, while traditional tools like scribers and marking knives work well for wood and softer surfaces. Assess your specific applications, such as whether you need permanent markings or temporary ones, and consider factors like ease of use, maintenance, and the volume of production. Consulting with suppliers and reviewing product specifications can help you make an informed choice. -
What are the advantages of using laser marking machines?
Laser marking machines offer numerous advantages, including precision, speed, and versatility. They can produce high-quality, permanent marks on a wide range of materials, including metal, plastic, and glass, making them suitable for various industries. Additionally, they are often programmable, allowing for complex designs without the need for physical templates. Moreover, laser marking is a non-contact process, reducing wear on the tools and minimizing material wastage. This technology is particularly beneficial for high-volume production environments. -
What factors should I consider when vetting a marking instrument supplier?
When vetting a marking instrument supplier, consider their industry experience, product quality, and customer service. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your specific industry, as they will better understand your needs. Request references and check reviews from other clients. Additionally, assess their ability to provide customization options, support services, and timely delivery. It’s also wise to evaluate their compliance with international quality standards and certifications, ensuring they meet your quality assurance requirements. -
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQ) for marking instruments?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for marking instruments can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of product. Some manufacturers may have MOQs as low as 10 units for basic tools, while specialized equipment like laser marking machines may require orders of 50 or more. Always inquire about MOQs when requesting quotes and consider the implications for your inventory management. If you’re a smaller business, look for suppliers that offer flexible ordering options or the ability to mix and match products to meet MOQ requirements. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing marking instruments internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of marking instruments can vary widely depending on the supplier and the country of origin. Common terms include payment in full upfront, a 30% deposit with the balance due before shipment, or net 30/60 days after delivery. Be sure to clarify these terms before finalizing your order. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to protect your transaction. Always review the currency exchange rates and any potential transaction fees involved in international payments. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing marking instruments?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing marking instruments, request detailed product specifications and certifications from the supplier. Look for compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Additionally, ask about their quality control processes, including inspections and testing procedures for each product batch. If possible, request samples before placing a larger order to evaluate the quality firsthand. Establishing a clear communication channel for addressing quality concerns is also crucial. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing marking instruments?
When importing marking instruments, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Air freight is faster but typically more expensive than sea freight, so choose based on your urgency and budget. Ensure that you understand the customs clearance process in your country, including any tariffs or duties applicable to your products. Collaborate with your supplier to provide accurate documentation and comply with all regulations to avoid delays. Additionally, consider insurance for your shipment to protect against loss or damage during transit. -
Can marking instruments be customized to meet specific business requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for marking instruments to cater to specific business needs. Customizations can include modifications in size, material, design, and even branding options like logos. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications to the supplier to ensure they understand your requirements. Keep in mind that custom orders may come with higher costs and longer lead times, so plan accordingly. Evaluating several suppliers can help you find one that offers the right balance of customization and affordability.
Top 7 Marking Instrument Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. General Tools – Precision Marking Tools
Domain: generaltools.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Precision Marking Tools include large and small contour gauges for duplicating shapes, suitable for pattern and mold making, fitting carpet, tiles, or linoleum around door casings and pipes. Notable products include the #836 Angle-izer Template Tool for making bulls eyes, arches, and plumb cuts on roof joists, as well as for DIY projects like laying out brick patios or tile floors. Other products …
2. Rockler – Marking Tools
Domain: rockler.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Marking Tools category includes various tools for woodworking and hardware projects. It features digital measuring tools, setup and specialty gauges, tape measures, rulers, calipers, moisture meters, metal detectors, center finders, angle finders, and protractors.
3. KCTool – Pica MASTER-SET Contractor
Domain: kctool.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: This company, KCTool – Pica MASTER-SET Contractor, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Marking Machinery – Key Products
Domain: markingmachinery.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Marking tools include a variety of products used in marking systems to create images, designs, and impressions on materials such as metal, glass, plastic, stone, wood, leather, and textiles. Key products include:
1. **Dot Peen Machine** – High-performance machines for identification systems.
2. **Embossing Machine** – Used for creating raised designs on surfaces.
3. **Engraving Machine** – For eng…
5. Blue Spruce Tool Works – Marking Tool System
Domain: bluesprucetoolworks.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Marking Tool System includes Classic Marking Knife, Marking System – Collets, Marking System – Handles, and Marking System – Wallet.
6. Fine Science – Instrument Marking Tape
Domain: finescience.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Instrument Marking Tape – 8 Assorted Colors
7. Lee Valley – Marking Multi-Tool
Domain: leevalley.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Marking Multi-Tool; Versatile tool modeled after an antique; Functions: bevel gauge, ruler, depth gauge, diameter gauge, try square, T-square, extension ruler, marking gauge, protractor, compass, angle-transfer tool, divider; Twin stainless-steel arms; Sliding thumbscrew for locking arms at any point on 6″ length and any angle; Laser-etched markings graduated in 16ths; Angle guides at 30°, 45°, 60…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for marking instrument
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Marking Instrument Procurement?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing is pivotal for international B2B buyers seeking high-quality marking instruments. By understanding the diverse applications of these tools—from precision marking to industrial engraving—businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs. The market offers a variety of solutions, including laser marking systems and traditional hand tools, each catering to specific requirements across industries such as automotive, medical, and construction.
Investing time in evaluating suppliers, understanding the technological advancements in marking tools, and assessing cost-effectiveness will ultimately lead to better procurement outcomes. Moreover, establishing strong supplier relationships can facilitate smoother transactions and enhance support for maintenance and training.
As you navigate the global landscape of marking instruments, consider the unique demands of your region—whether in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe. Embrace this opportunity to leverage strategic sourcing to not only improve your operational efficiency but also drive innovation in your production processes. Reach out to potential suppliers today to explore how the right marking solutions can elevate your business.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.