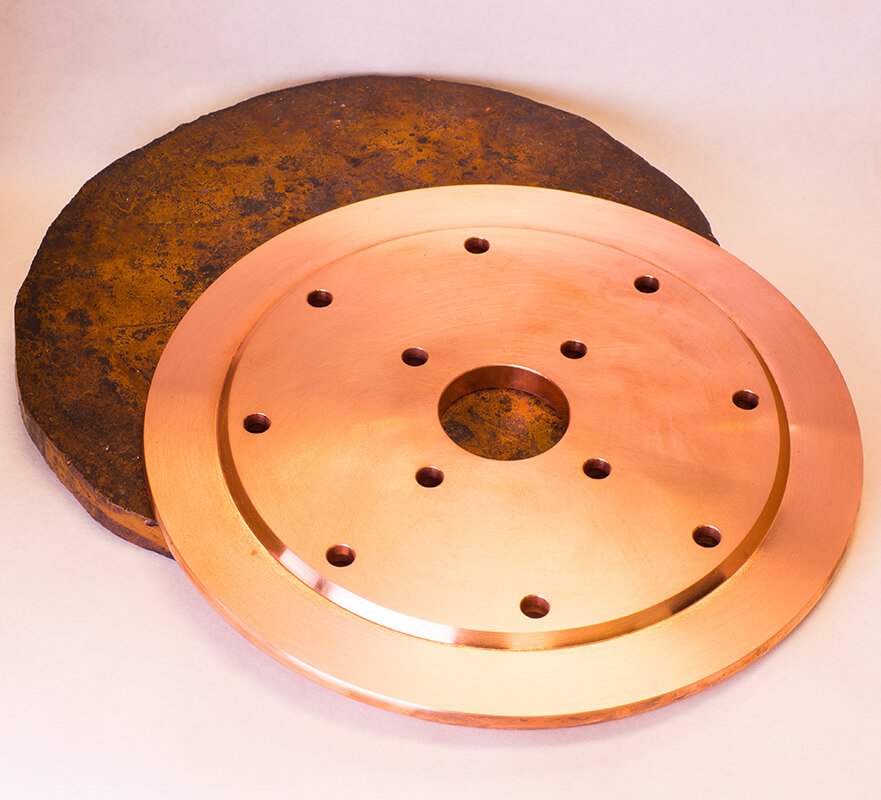
Copper Forging: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for copper forging
Navigating the global market for copper forging presents unique challenges for international B2B buyers seeking high-quality, reliable suppliers. With the increasing demand for precision-engineered components across various sectors—such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics—sourcing the right copper forgings can be daunting. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of copper forging by covering essential topics, including the different types of copper alloys, their applications, and effective strategies for supplier vetting and cost optimization.
As businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including key markets like Germany and Nigeria) explore the benefits of copper forgings, they must understand the intricacies involved in selecting materials that meet stringent quality standards. This guide empowers decision-makers by providing actionable insights into the forging process, the properties of various copper alloys, and their suitability for specific applications. By equipping B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions, we aim to streamline their sourcing efforts and enhance their competitive edge in the global marketplace.
From understanding the advantages of different copper alloys to identifying potential suppliers and evaluating costs, this comprehensive resource is designed to facilitate your journey in the copper forging landscape. Embrace the opportunities within this vital industry and ensure your business remains at the forefront of innovation and efficiency.
Understanding copper forging Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brass Forging | Copper-zinc alloy; excellent corrosion resistance | Plumbing fixtures, electrical components | Pros: High malleability, good aesthetic appeal. Cons: May tarnish over time. |
| Bronze Forging | Copper-tin alloy; exceptional wear resistance | Marine applications, industrial components | Pros: Superior durability, good corrosion resistance. Cons: Heavier than other alloys. |
| Leaded Copper Forging | Copper-lead alloy; superior machinability | Electrical connectors, precision parts | Pros: Easy to machine, excellent electrical conductivity. Cons: Toxicity concerns limit applications. |
| Copper-Nickel Forging | Copper-nickel alloy; outstanding marine resistance | Shipbuilding, offshore applications | Pros: High strength and corrosion resistance in saltwater. Cons: Higher cost compared to standard copper. |
| Nickel-Silver Forging | Copper-nickel-zinc alloy; anti-tarnish properties | Jewelry, decorative items, plumbing | Pros: Aesthetic appeal, good resistance to tarnish. Cons: Not suitable for high-temperature applications. |
What Are the Characteristics of Brass Forging?
Brass forging utilizes a copper-zinc alloy that is highly malleable and resistant to corrosion. This makes it ideal for applications in plumbing fixtures and electrical components. When considering brass for forging, buyers should evaluate the alloy’s aesthetic qualities and its performance in various environments. While brass can tarnish over time, its ability to be shaped into intricate designs offers significant value in decorative applications.
Why Choose Bronze Forging for Marine Applications?
Bronze forging, primarily composed of copper and tin, is renowned for its exceptional wear resistance and durability. This makes it particularly suitable for marine applications, such as ship components and industrial machinery. B2B buyers should consider bronze’s weight, as it can be heavier than other alloys, which may impact shipping costs. However, its longevity and resistance to seawater corrosion make it a preferred choice for many industries.
What Are the Advantages of Leaded Copper Forging?
Leaded copper forging combines copper and lead to create an alloy known for its excellent machinability and electrical conductivity. This makes it a popular choice for electrical connectors and precision engineering components. However, buyers must be aware of the toxicity associated with lead, which can limit its use in food-related applications. The ease of machining and rapid production capabilities are significant advantages for manufacturers looking to optimize their processes.
How Does Copper-Nickel Forging Stand Out?
Copper-nickel forging is characterized by its remarkable strength and resistance to corrosion, especially in marine environments. This alloy is frequently used in shipbuilding and offshore applications where exposure to saltwater is common. B2B buyers should consider the higher costs associated with copper-nickel compared to standard copper alloys. However, the long-term durability and performance in harsh environments justify the investment for many businesses.
What Makes Nickel-Silver Forging Unique?
Nickel-silver forging, a copper-nickel-zinc alloy, is favored for its aesthetic properties and anti-tarnish characteristics. Commonly used in jewelry and decorative items, it offers a silvery appearance without containing actual silver. Buyers should note that while nickel-silver is suitable for many applications, it is not ideal for high-temperature environments. The combination of visual appeal and resistance to tarnish makes it an attractive option for industries focused on design and functionality.
Key Industrial Applications of copper forging
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Copper Forging | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical Engineering | Electrical connectors and terminals | High electrical conductivity ensures efficient power transfer, reducing energy loss. | Look for suppliers with certifications in electrical standards and reliable quality control processes. |
| Plumbing and HVAC | Valves and fittings for plumbing systems | Corrosion resistance and durability enhance lifespan, reducing maintenance costs. | Consider suppliers with experience in local regulations and standards for plumbing materials. |
| Aerospace | Aircraft engine components | Lightweight yet strong materials improve fuel efficiency and safety. | Ensure compliance with aerospace manufacturing standards and traceability of materials used. |
| Oil & Gas | Components for extraction and transportation | Enhanced resistance to harsh environments increases reliability and performance. | Source from manufacturers with expertise in oil and gas specifications and certifications. |
| Renewable Energy | Wind turbine components | High strength-to-weight ratio contributes to efficient energy generation. | Evaluate suppliers on their ability to meet stringent quality and environmental standards. |
How is Copper Forging Utilized in Electrical Engineering Applications?
In the electrical engineering sector, copper forging is critical for producing connectors and terminals that facilitate electrical connections. The high electrical conductivity of forged copper ensures minimal energy loss, which is vital for efficiency in power distribution systems. International buyers must prioritize suppliers that adhere to strict electrical standards and offer robust quality control processes to ensure the reliability of their products.
What Role Does Copper Forging Play in Plumbing and HVAC Systems?
Copper forging is extensively used to manufacture valves and fittings in plumbing and HVAC systems. The inherent corrosion resistance and durability of copper make it an ideal choice for components that must withstand exposure to water and varying temperatures. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing from manufacturers familiar with local plumbing regulations and standards to ensure compliance and performance.
Why is Copper Forging Essential in Aerospace Applications?
In aerospace, copper forging is employed to create critical engine components that require a combination of lightweight and high strength. The use of forged copper enhances fuel efficiency and safety in aircraft operations. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can meet rigorous aerospace manufacturing standards and provide traceability for the materials used, as this is essential for maintaining safety and compliance.
How Does Copper Forging Benefit the Oil & Gas Industry?
The oil and gas industry relies on copper forging for components used in extraction and transportation processes. Forged copper parts exhibit enhanced resistance to harsh environmental conditions, which is crucial for maintaining performance and reliability in challenging settings. Buyers should seek manufacturers experienced in the specific certifications and specifications required for oil and gas applications to ensure product integrity.
What Advantages Does Copper Forging Offer in Renewable Energy?
In renewable energy, particularly in wind turbine construction, copper forging is used to produce components that require a high strength-to-weight ratio. This characteristic is vital for optimizing energy generation efficiency. Buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their ability to meet stringent quality and environmental standards, as these factors are increasingly important in the renewable energy sector.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘copper forging’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Quality Consistency in Copper Forging Products
The Problem: A B2B buyer sourcing copper forgings for critical applications, such as electrical connectors or aerospace components, often faces challenges with quality consistency. Variations in the material properties or dimensions can lead to product failures, increased costs, and project delays. Buyers may find themselves navigating multiple suppliers, each with different manufacturing processes, which can further complicate quality assurance. This inconsistency can be especially concerning when dealing with tight tolerances or compliance with international standards, which are crucial for industries like aviation and automotive.
The Solution: To ensure quality consistency, buyers should prioritize suppliers with rigorous quality management systems and certifications such as ISO 9001. Conduct thorough supplier audits to evaluate their forging processes, including material sourcing, forging methods, and post-forging treatments like heat treatment and surface hardening. Establish clear specifications for the desired properties of the copper forgings and require suppliers to provide detailed documentation, including material test reports and dimensional inspections. Additionally, consider implementing a sampling inspection process where a certain percentage of products are tested for quality before full-scale acceptance. This proactive approach helps mitigate risks and ensures that the supplied components meet the required standards.
Scenario 2: Cost Management in Copper Forging Projects
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter difficulties managing costs associated with copper forging projects, particularly when there are fluctuations in raw material prices or unexpected production delays. These challenges can significantly impact budgets, especially for large-scale projects where precise cost forecasting is essential. Buyers may feel pressure to find the most cost-effective solutions without compromising quality, leading to a complex balancing act that can strain supplier relationships and project timelines.
The Solution: To effectively manage costs, buyers should engage in strategic sourcing by building long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers who can offer competitive pricing based on bulk orders or long-term contracts. Additionally, consider utilizing advanced planning and inventory management systems to forecast material needs more accurately and avoid last-minute purchases at inflated prices. Implementing value engineering practices can also help identify areas where costs can be reduced without sacrificing quality. For instance, explore alternative copper alloys that maintain the required properties but come at a lower cost, or negotiate for flexible payment terms that align better with project cash flows. Regular communication with suppliers can provide insights into market trends, allowing for timely adjustments to sourcing strategies.

Illustrative image related to copper forging
Scenario 3: Complexity in Custom Copper Forging Designs
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges when it comes to custom copper forging designs, especially when specific shapes or properties are required for unique applications. The complexity of these designs can lead to miscommunication with suppliers, resulting in prototypes that do not meet expectations or require extensive rework. This not only delays project timelines but can also inflate costs and reduce overall project viability.
The Solution: To overcome design complexities, buyers should invest in collaborative design processes that involve both their engineering teams and the forging suppliers from the outset. Utilizing 3D modeling and simulation tools can facilitate clearer communication of design specifications and help identify potential manufacturing challenges before production begins. Additionally, consider requesting prototypes or small batch runs to validate designs and materials before scaling up. Establishing a clear feedback loop during the design phase allows for iterative improvements and fosters a more collaborative relationship with suppliers. Finally, ensure that all design parameters, including tolerances and material specifications, are documented and agreed upon to minimize misunderstandings. This proactive approach can significantly streamline the custom forging process and enhance the likelihood of successful outcomes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for copper forging
What Are the Key Properties of Common Copper Alloys Used in Forging?
Copper forging is a crucial process in various industries, and the selection of the right copper alloy can significantly impact product performance. Below, we analyze four common copper alloys used in forging, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Brass Perform in Copper Forging Applications?
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, is widely utilized in forging due to its excellent corrosion resistance and malleability. It typically exhibits good thermal and electrical conductivity, making it suitable for electrical connectors and plumbing fixtures. Brass can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, which is beneficial for applications in plumbing and electrical systems.
Pros: Brass is durable and easy to machine, allowing for intricate designs. It is also cost-effective, making it a popular choice for mass production.
Cons: While brass has good corrosion resistance, it may not perform well in highly acidic or alkaline environments. Additionally, its mechanical properties can degrade at elevated temperatures.
Impact on Application: Brass is ideal for applications involving water and gas, but care should be taken in environments with extreme pH levels.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B36/B36M (for brass) is essential. Buyers in regions like Europe and Africa should be aware of local regulations regarding lead content in brass, as leaded brass may be restricted in certain applications.

Illustrative image related to copper forging
What Advantages Does Bronze Offer for Forging?
Bronze, primarily composed of copper and tin, is known for its excellent wear resistance and strength. It performs well under high temperatures and is resistant to corrosion, particularly in marine environments. This makes bronze an excellent choice for components like ship fittings and industrial machinery.
Pros: Bronze’s durability and resistance to fatigue make it suitable for high-stress applications. It also has good machinability and can be easily forged into complex shapes.
Cons: Bronze can be more expensive than brass due to the cost of tin. Additionally, it may not be as readily available in some regions, impacting lead times.
Impact on Application: Bronze is particularly well-suited for applications exposed to seawater and high wear conditions, such as marine hardware and bearings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that bronze alloys meet international standards like ASTM B505. In regions like South America, where marine applications are prevalent, the corrosion resistance of bronze is a significant selling point.
How Do Copper-Nickel Alloys Enhance Forging Capabilities?
Copper-nickel alloys, which combine copper with nickel, are particularly valued in marine applications due to their exceptional resistance to saltwater corrosion. These alloys maintain structural integrity at high temperatures, making them suitable for components in shipbuilding and offshore structures.
Pros: Copper-nickel alloys are lightweight yet strong, offering excellent durability. Their resistance to biofouling makes them ideal for marine environments.
Cons: The cost of nickel can make these alloys more expensive than other copper options. Additionally, they may require specialized machining techniques due to their hardness.
Illustrative image related to copper forging
Impact on Application: These alloys are perfect for components that require high resistance to corrosion and thermal stability, such as heat exchangers and marine fittings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with marine standards such as ASTM B171. In the Middle East, where marine applications are significant, the use of copper-nickel alloys is often preferred.
What Makes Leaded Copper a Viable Option for Forging?
Leaded copper, primarily composed of copper with added lead, is known for its excellent machinability and thermal conductivity. It is commonly used in electrical applications where precision is critical.
Pros: The addition of lead enhances workability, allowing for faster and more efficient machining. Leaded copper is also cost-effective for high-volume production.

Illustrative image related to copper forging
Cons: The presence of lead raises health concerns, particularly in food-related applications. This limits its use in certain sectors.
Impact on Application: Leaded copper is suitable for electrical connectors and components that require precise dimensions and excellent conductivity.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with regulations regarding lead content is crucial. In Europe, for instance, the RoHS directive restricts lead in electrical components, impacting the use of leaded copper.
Summary Table of Common Copper Alloys for Forging
| Material | Typical Use Case for copper forging | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | Plumbing fixtures, electrical connectors | Excellent corrosion resistance, cost-effective | Degrades in extreme pH environments | Low |
| Bronze | Marine components, industrial machinery | High wear resistance, durable | More expensive, limited availability | Med |
| Copper-Nickel | Marine fittings, heat exchangers | Exceptional corrosion resistance, lightweight | Higher cost, requires specialized machining | High |
| Leaded Copper | Electrical connectors, precision parts | Excellent machinability | Health concerns due to lead content | Med |
This guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into selecting the right copper alloy for forging, considering both performance characteristics and compliance with international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for copper forging
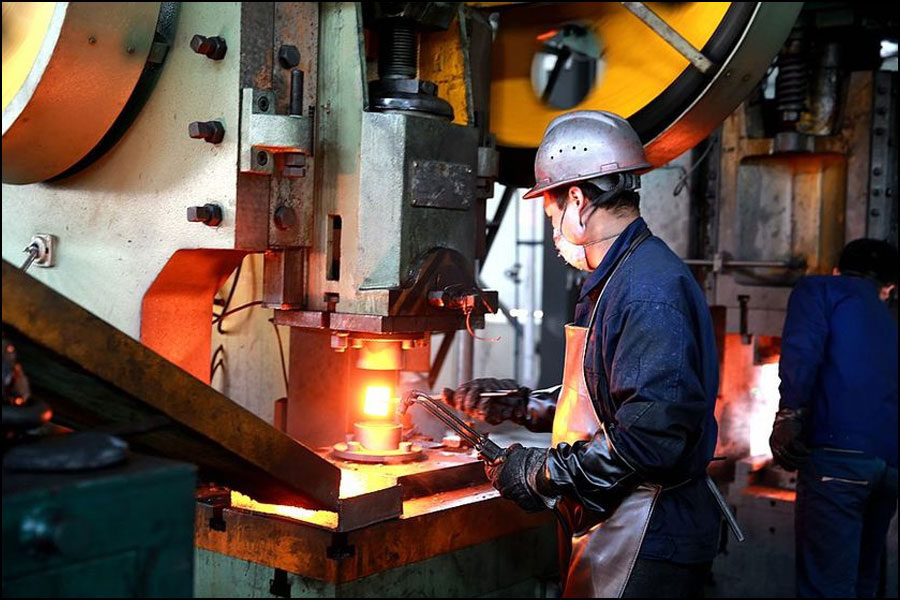
What Are the Main Stages of the Copper Forging Manufacturing Process?
The manufacturing process of copper forging is typically divided into several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a crucial role in ensuring that the final product meets the desired specifications and quality standards.
How is Material Prepared for Copper Forging?
Material preparation begins with the selection of high-quality copper or copper alloy ingots. The choice of alloy can significantly influence the properties of the final product, with common choices including brass, bronze, and high copper alloys. After selecting the appropriate material, the ingots are heated to a specific temperature range (typically between 1350-1700 °F or 732-927 °C), which enhances their malleability and makes them easier to forge.
Following heating, the ingots may undergo surface treatment to remove any oxides or impurities that could affect the forging process. This step ensures a clean surface, which is vital for achieving a strong bond during the forging process.
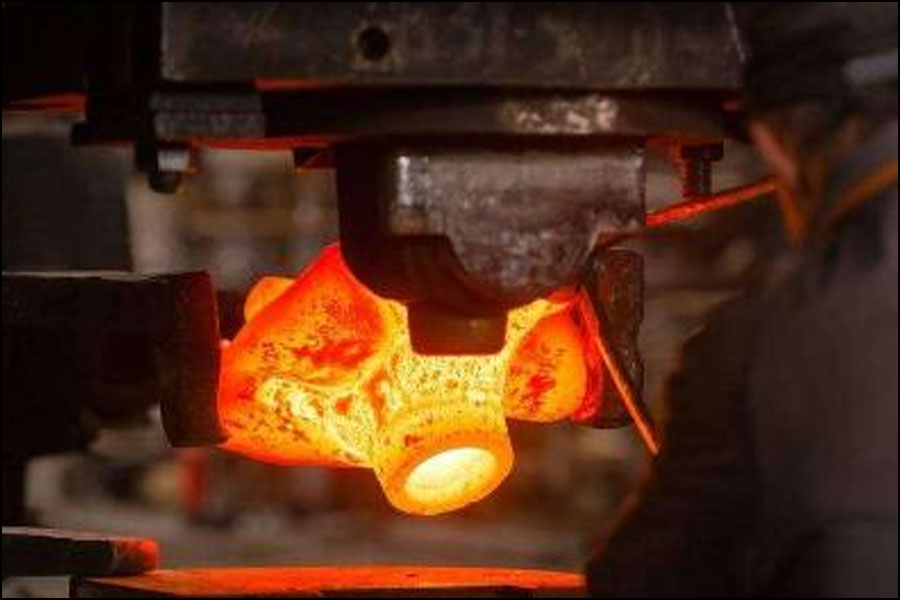
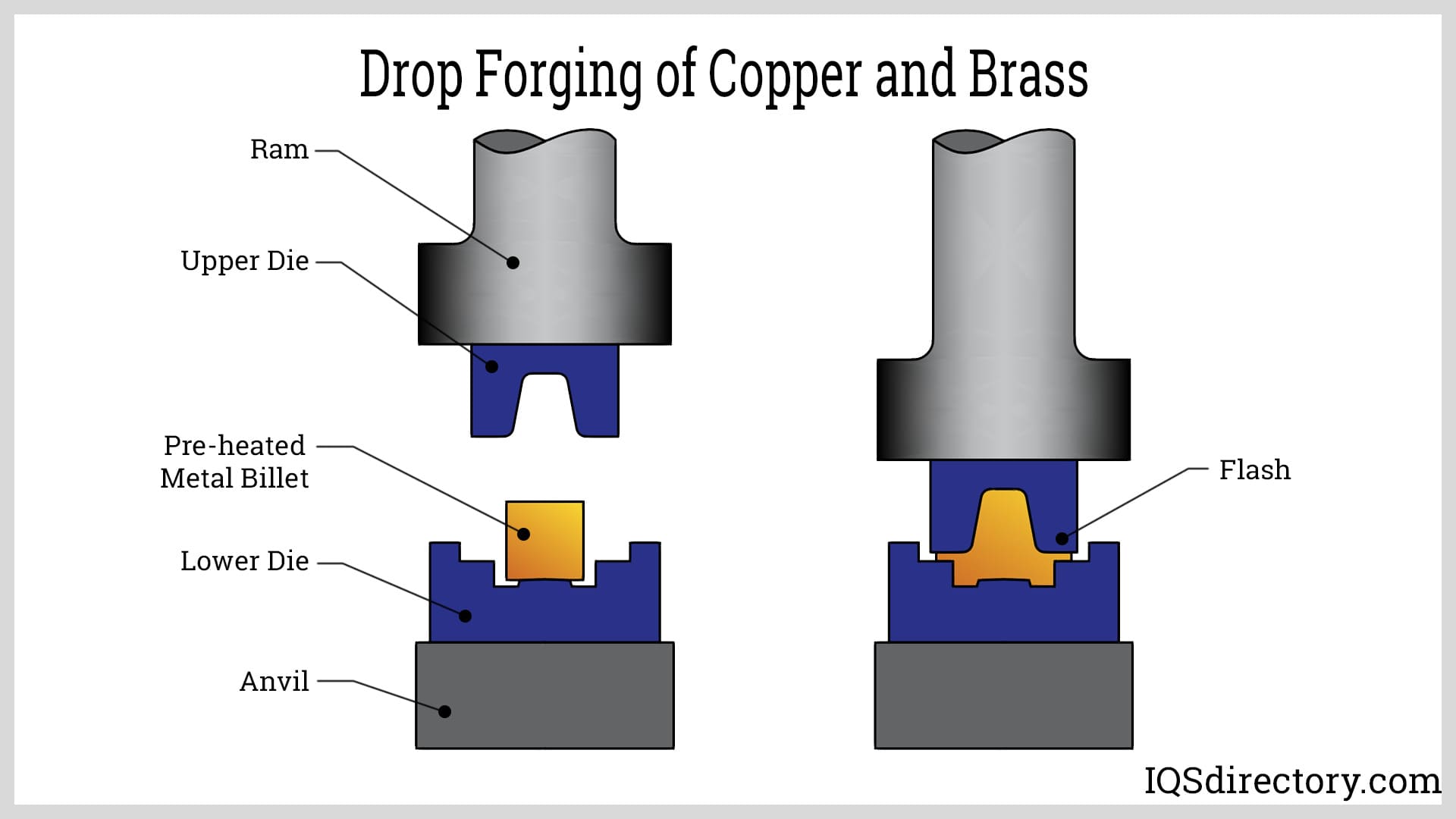
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Copper Forging?
The forming stage involves shaping the heated ingots using a die that corresponds to the desired end product. The die, which is pre-heated, is placed over the ingot, and a hammer or press is used to apply force. This process not only shapes the copper but also alters its internal grain structure, enhancing its mechanical properties.
Common techniques in the forming stage include:
- Open-die forging: Suitable for large parts, this technique allows the metal to flow freely, providing flexibility in shape.
- Closed-die forging: More precise than open-die forging, this method confines the metal within the die, resulting in tighter tolerances and better surface finish.
- Upset forging: This technique increases the diameter of the material by compressing it, often used for creating thicker sections at the ends of components.
How is Assembly Handled in Copper Forging?
In many cases, copper forgings may require assembly with other components to form a complete product. This stage can involve welding, brazing, or mechanical fastening, depending on the application. The assembly process must ensure that the joined parts maintain the integrity and functionality of the final product.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Copper Forging?
Quality assurance is paramount in the copper forging industry to ensure that products meet international standards and customer specifications. Quality control (QC) measures typically include several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should be familiar with relevant international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, which outlines the requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO standards ensures that manufacturers have established processes for consistent quality. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for European markets or API standards for oil and gas applications are essential for ensuring product safety and reliability.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the production stages to monitor and maintain quality. These checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon arrival to verify that they meet specified requirements.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to detect any deviations from quality standards. This may include checking dimensions, material properties, and visual inspections.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the finished product before shipment, ensuring that all specifications are met.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial in establishing trust and ensuring product quality. Here are effective methods for buyers to assess supplier QC:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of the supplier’s manufacturing facilities can provide insights into their quality control processes and adherence to standards.
- Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports can help buyers understand the frequency and results of inspections conducted at various stages of production.
- Third-party Inspections: Engaging third-party quality inspectors can offer an impartial assessment of the supplier’s quality practices and the final products.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Copper Forging Quality Control?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the quality of forged copper products:
- Mechanical Testing: Tests such as tensile strength, hardness, and impact resistance are conducted to evaluate the mechanical properties of the forged parts.
- Non-destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques like ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle testing, and radiographic testing help identify internal defects without damaging the product.
- Chemical Analysis: Verifying the alloy composition through spectrometry ensures that the material meets the specified standards and performs as required in its application.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is vital. Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements and quality expectations.
Buyers should be aware of:
- Local Regulations: Familiarizing themselves with local standards and regulations can help ensure compliance and avoid legal issues.
- Cultural Differences: Cultural attitudes towards quality and manufacturing can vary, influencing communication and expectations between buyers and suppliers.
- Logistical Considerations: The complexities of international shipping and customs can affect product quality. Ensuring that suppliers have robust logistics and handling practices is essential.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in copper forging is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, and stringent quality control practices, buyers can make informed decisions and ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their specifications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘copper forging’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of copper forgings can be complex, especially for international B2B buyers across diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide provides a practical checklist to streamline your sourcing process, ensuring you select the right suppliers and materials for your specific needs.
Illustrative image related to copper forging
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, it’s essential to clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes dimensions, tolerances, alloy types, and any necessary certifications. Precise specifications help avoid misunderstandings and ensure that the forged components meet your application requirements.
- Consider alloy types: Identify whether you need brass, bronze, or a specific copper alloy based on your application.
- Detail tolerances and dimensions: Clearly state the measurements and acceptable deviations to ensure compatibility with your designs.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in copper forging. Look for companies with a solid reputation and experience in your industry.
- Utilize online directories and industry associations: Explore resources like the Copper Development Association or trade shows to find credible suppliers.
- Check for industry experience: Prioritize suppliers with a proven track record in the specific applications relevant to your needs.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Certifications can provide assurance of quality and compliance with international standards. Verify that your potential suppliers possess relevant certifications such as ISO 9001 or other industry-specific accreditations.
- Request documentation: Ask for copies of their certifications and quality control processes.
- Understand compliance: Ensure the supplier adheres to environmental and safety regulations applicable in your region.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before placing a significant order, request samples or prototypes of the copper forgings. This step allows you to evaluate the quality and precision of the supplier’s work.
- Assess material properties: Check for the specific properties you need, such as tensile strength and corrosion resistance.
- Conduct testing: If possible, perform mechanical and thermal tests to validate performance against your specifications.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations to establish favorable terms. Discuss pricing, lead times, minimum order quantities, and payment terms.
- Consider long-term partnerships: Look for suppliers willing to negotiate for future orders, which can lead to better pricing and reliability.
- Be clear about expectations: Ensure that both parties understand delivery schedules and any penalties for delays.
Step 6: Establish Quality Control Measures
Implement quality control measures to ensure that the products you receive meet your specifications. Discuss with your supplier how they manage quality throughout the production process.
- Define inspection criteria: Set clear criteria for inspecting the products upon arrival.
- Plan for audits: If necessary, arrange for periodic audits of the supplier’s processes to maintain quality standards.
Step 7: Finalize the Contract
Before proceeding, finalize a comprehensive contract that outlines all agreed-upon terms, including specifications, pricing, delivery timelines, and penalties for non-compliance.
- Ensure clarity: The contract should be clear and detailed to prevent disputes.
- Legal review: Consider having the contract reviewed by a legal expert familiar with international trade laws to safeguard your interests.
Following this checklist will help you effectively navigate the sourcing process for copper forgings, ensuring that you find reliable suppliers who meet your technical and quality requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for copper forging Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Copper Forging?
When sourcing copper forgings, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is critical for effective budgeting and decision-making. The main cost components include:
Illustrative image related to copper forging
-
Materials: The cost of copper and its alloys, such as brass and bronze, forms the largest part of the overall expenditure. The price of raw materials can fluctuate based on market demand and geopolitical factors, impacting sourcing strategies.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for forging processes, requiring trained personnel to manage machinery and ensure quality. Labor costs can vary significantly based on geographic location, labor laws, and the skill level of the workforce.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead, making it crucial to assess suppliers’ operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: The creation of dies and molds is a capital-intensive aspect of forging. Tooling costs can vary widely based on complexity and the number of units produced. Investing in quality tooling can lead to better outcomes and lower long-term costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the final product meets specific quality standards involves additional costs for inspections and certifications. QC processes are vital for industries where precision is paramount, such as aerospace and medical equipment.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs should be factored in, especially for international shipments. Choosing the right Incoterms can affect the overall logistics expense and risk management.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market conditions and competition. Understanding the market landscape can provide leverage in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors can influence pricing in copper forging:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders typically lead to lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Establishing a Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) can help buyers negotiate better rates.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific tolerances can increase costs due to the additional work required. Buyers should evaluate whether customization is necessary or if standard products can meet their needs.
-
Material Choices: The type of copper alloy selected can significantly impact pricing. Alloys with higher performance characteristics may incur higher costs, but the added value may justify the expense.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that require compliance with international standards or certifications will typically come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the importance of certifications against cost.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and location can influence pricing. Establishing long-term relationships with trusted suppliers can lead to better pricing and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is essential for managing costs associated with shipping and insurance.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs in Copper Forging?
To maximize cost-efficiency in sourcing copper forgings, consider these actionable tips:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Build relationships with suppliers and engage in open negotiations. Understanding their cost structure can provide leverage during discussions, leading to more favorable terms.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the upfront costs but also the long-term implications of maintenance, durability, and potential failures. A lower initial price may lead to higher costs down the line.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to local market conditions and regulations. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should conduct thorough market research to understand these nuances.
-
Leverage Technology: Employing digital tools for procurement and supply chain management can streamline processes and reduce operational costs.
-
Monitor Market Trends: Keeping an eye on market trends, including fluctuations in copper prices and changes in trade regulations, can help buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for copper forging can vary widely based on numerous factors, including geographic location, market conditions, and specific project requirements. It is advisable to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and to consider all cost components thoroughly.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing copper forging With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Manufacturing Solutions
In the competitive landscape of B2B manufacturing, companies often seek optimal solutions that balance performance, cost, and efficiency. While copper forging has established itself as a reliable method for producing high-quality components, other manufacturing techniques may also offer viable alternatives depending on specific project requirements. This analysis will compare copper forging with two notable alternatives: copper casting and metal machining.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Copper Forging | Copper Casting | Metal Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, strength, and ductility | Good dimensional accuracy, but less strength than forging | Excellent precision and surface finish |
| Cost | Moderate initial setup cost; lower long-term cost due to durability | Lower initial cost; higher scrap rates can increase overall costs | High tooling costs; can be expensive for complex shapes |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment and skilled labor | Simpler setup; requires melting and pouring | Relatively straightforward; requires CNC machines and skilled operators |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; durable end products | Moderate; molds can wear out and need replacement | Moderate; machines require regular upkeep |
| Best Use Case | High-stress applications needing strength and durability | Decorative items, complex shapes, or large volumes | Precision parts where tight tolerances are necessary |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What Are the Pros and Cons of Copper Casting?
Copper casting involves pouring molten copper into a mold to create parts. This method allows for complex geometries and is often more cost-effective for producing large volumes of products. However, while casting can achieve good dimensional accuracy, it typically results in parts with lower strength compared to forged components. Additionally, the cooling process can introduce defects like porosity, which may affect the overall durability of the product. Therefore, while casting is ideal for decorative items or applications with less mechanical stress, it may not be suitable for critical structural components.
How Does Metal Machining Compare?
Metal machining, particularly CNC machining, utilizes cutting tools to remove material from a solid block of copper. This method excels in achieving precise dimensions and superior surface finishes, making it a go-to for high-precision applications. However, machining can incur higher material costs due to significant waste and tooling expenses. It is most suitable for projects requiring tight tolerances, such as aerospace or automotive components. The downside is that machining may not be as efficient for high-volume production, where the time-intensive nature of the process can lead to longer lead times and increased costs.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Selecting the right manufacturing method hinges on understanding the specific needs of your project. For applications requiring superior strength and durability, copper forging stands out as the ideal choice, especially in industries like automotive or aerospace. Conversely, if your project emphasizes complex shapes and lower initial costs, copper casting may be more appropriate. Lastly, for precision parts where tolerances are critical, metal machining offers unparalleled accuracy. By carefully evaluating these factors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budget constraints.

Illustrative image related to copper forging
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for copper forging
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Copper Forging?
Understanding the technical properties of copper forgings is vital for B2B buyers to ensure they select the right materials for their applications. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of copper alloys based on their composition and mechanical properties. Common grades include C11000 (electrolytic tough pitch copper) and C36000 (brass). The choice of grade affects the material’s conductivity, strength, and corrosion resistance. For industries like electrical engineering and plumbing, selecting the correct grade can significantly impact product performance and longevity.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance is the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in the forging process. Tight tolerances (e.g., ±0.005 inches) are crucial in applications requiring precision, such as aerospace and electronics. Understanding tolerances helps buyers ensure that forged parts fit correctly and function reliably, minimizing waste and rework costs.
3. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength measures a material’s resistance to being pulled apart. It is a critical property for components subjected to stress, such as those in automotive and industrial applications. A higher tensile strength means better durability and reliability, which can reduce maintenance and replacement costs over time.
4. Ductility
Ductility is the ability of a material to deform under tensile stress without breaking. High ductility in copper forgings allows for complex shapes and designs, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. For manufacturers, ductility can facilitate the production of intricate components while reducing the risk of fracture during processing.
5. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance refers to the material’s ability to withstand degradation due to environmental factors. Copper and its alloys are known for their excellent resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for plumbing and marine applications. B2B buyers must consider this property to ensure the longevity of their products in challenging environments.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Copper Forging?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common trade terms relevant to copper forging:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of copper forging, buyers often deal with OEMs to source custom components. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure they receive high-quality parts that meet their specifications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. It is a critical factor for B2B buyers, especially when considering inventory costs and production schedules. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchases and manage cash flow effectively.

Illustrative image related to copper forging
3. RFQ (Request for Quote)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products or services. For buyers in the copper forging industry, submitting an RFQ allows them to compare offers from different manufacturers, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of standardized trade terms used in international shipping that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions involving copper forgings, as they dictate who bears the costs and risks associated with shipping and delivery.
5. Heat Treatment
Heat treatment refers to processes such as annealing or quenching that enhance the properties of forged copper. Buyers should understand the implications of heat treatment on performance characteristics, as it can significantly affect strength, ductility, and overall material behavior.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing copper forgings, leading to better product outcomes and improved business efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the copper forging Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Copper Forging Sector?
The copper forging market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand in various sectors such as construction, automotive, and electronics. The global push for renewable energy solutions is also propelling the use of copper in applications like electric vehicles and wind turbines. In regions like Africa and South America, the growing infrastructure projects are creating a robust market for copper products, while Europe, particularly Germany, is seeing a rise in precision engineering applications that utilize copper forging for high-performance components.

Illustrative image related to copper forging
Emerging B2B technology trends are reshaping the sourcing landscape. Digital platforms for procurement are streamlining the sourcing process, allowing international buyers to connect directly with manufacturers. This trend is particularly beneficial for buyers in developing regions, providing access to competitive pricing and quality assurance. Furthermore, advancements in manufacturing technologies, such as automation and smart manufacturing, are enhancing the efficiency of copper forging processes, which in turn impacts pricing and lead times.
Another notable trend is the increased focus on customization. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking tailored solutions that meet specific application requirements, which has led to a rise in collaborative partnerships between manufacturers and clients. This dynamic fosters innovation, enabling the development of specialized copper alloys and forging techniques that cater to unique industry needs.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Copper Forging Sector?
Sustainability has become a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the copper forging sector. The environmental impact of copper mining and processing can be significant, leading to a growing demand for ethical sourcing practices. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices, such as responsible mining, reduced carbon footprints, and the use of recycled materials.
Incorporating ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and certifications for sustainable sourcing, is becoming essential for suppliers aiming to attract international buyers. These certifications not only demonstrate a commitment to environmental stewardship but also enhance the credibility of the supplier in competitive markets.
Moreover, the use of recycled copper in forging processes is gaining traction. Recycled copper retains many of the desirable properties of virgin copper while significantly reducing the environmental impact associated with mining. As regulations around sustainability tighten globally, suppliers who adopt environmentally friendly practices will likely find themselves better positioned to meet the demands of conscientious buyers.
What Is the Evolution of Copper Forging and Its Significance for B2B Buyers?
Copper forging has a rich history that dates back thousands of years, making it one of the oldest metalworking processes known to humanity. The process evolved from simple hand tools to sophisticated techniques used in modern manufacturing. Historically, copper’s malleability and conductivity made it a preferred material for various applications, ranging from tools and weapons to decorative items.
In the contemporary context, the evolution of copper forging has been characterized by technological advancements and a deeper understanding of metallurgy. The introduction of precision forging and advanced heat treatment techniques has enabled manufacturers to create high-quality, durable components that meet stringent industry standards. For B2B buyers, this evolution signifies not just a wider range of products but also the potential for greater customization and efficiency in sourcing.
Understanding the historical context of copper forging can provide B2B buyers with insights into the reliability and performance of forged copper products, underscoring their value in modern applications across multiple industries. As the market continues to evolve, the ability to leverage historical knowledge alongside current trends will be crucial for buyers looking to make informed procurement decisions.

Illustrative image related to copper forging
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of copper forging
-
How do I ensure the quality of copper forgings from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of copper forgings, conduct thorough supplier audits that include reviewing certifications, quality control processes, and past performance records. Request samples to evaluate craftsmanship and adherence to specifications. Look for suppliers who use standardized testing methods such as tensile tests and corrosion resistance evaluations. Additionally, consider suppliers who are ISO certified, as this indicates compliance with international quality standards. Establish clear quality expectations in your contracts to safeguard your interests. -
What is the best type of copper alloy for high-temperature applications?
For high-temperature applications, copper-nickel alloys are often the best choice due to their excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion, especially in marine and industrial environments. They maintain strength and durability at elevated temperatures, making them suitable for components in aerospace and power generation. Alternatively, high copper alloys can also perform well, but it’s essential to analyze the specific environmental conditions and load requirements of your application before making a decision. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for copper forging?
Minimum order quantities for copper forging can vary significantly by supplier, product complexity, and customization level. Generally, MOQs range from 100 to 1,000 units, depending on factors such as material costs and production capabilities. For highly specialized or custom parts, some suppliers may accommodate smaller orders, but this could lead to higher per-unit costs. Always discuss MOQs upfront with potential suppliers to align expectations and budget. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing copper forgings internationally?
Payment terms for international copper forging orders often include options such as advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Common practices include a 30% upfront deposit with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 terms depending on your relationship and order size. It’s crucial to negotiate clear payment terms in your contract to avoid misunderstandings and ensure cash flow management. -
How do I vet suppliers for copper forging to mitigate risks?
To mitigate risks when vetting suppliers for copper forging, conduct extensive research on their reputation and reliability. Check online reviews, industry ratings, and request references from previous clients. Evaluate their manufacturing capabilities, including equipment quality and workforce expertise. Additionally, consider visiting their facilities if possible or utilizing third-party auditing services to assess compliance with industry standards. Establishing a strong communication channel can also help you gauge their responsiveness and professionalism. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing copper forgings?
Logistics for importing copper forgings involve several key considerations: choosing the right shipping method (air vs. sea), understanding customs regulations, and coordinating with freight forwarders. Ensure that your supplier provides necessary documentation, such as certificates of origin and compliance. Calculate total landed costs, including shipping, tariffs, and taxes, to avoid budget overruns. Also, factor in lead times for production and shipping to ensure timely delivery aligned with your project timelines. -
Can I customize copper forgings to meet specific project requirements?
Yes, customization of copper forgings is widely available and often encouraged to meet specific project requirements. Most suppliers can accommodate custom dimensions, shapes, and alloy compositions based on your needs. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and consider engaging in a prototyping phase to test designs before full production. Be aware that custom orders may involve higher costs and longer lead times, so plan accordingly to avoid delays. -
What industries commonly use copper forgings, and why?
Copper forgings are commonly used across various industries, including electronics, plumbing, aerospace, automotive, and oil and gas. Their popularity stems from copper’s excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and strength. In electronics, for example, copper connectors and components are vital for performance, while in plumbing, forged copper fittings ensure durability and reliability. Understanding the specific applications and benefits within your industry can help you make informed sourcing decisions.
Top 3 Copper Forging Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Bunty LLC – Custom Copper Forging Services
Domain: buntyllc.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Copper forging services including custom shapes and sizes, high-quality copper materials, precision manufacturing, and applications in various industries such as electrical, plumbing, and automotive.
2. Scot Forge – Copper Forgings
Domain: scotforge.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Copper forgings are known for their durability, lightweight properties, superior heat transfer, electrical conductivity, and corrosion resistance. They are utilized in various industries, particularly in Aerospace, R&D, Marine, and Naval sectors. The advantages of forged copper include its thermal and electrical characteristics, abrasion resistance, and resistance to seawater corrosion. Scot Forge…
3. iForge Iron – Solid Copper Ground Rod
Domain: iforgeiron.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Copper ground rod used for forging; solid copper, not copper clad; safe forging practices discussed; forging temperatures indicated by color changes (dull red to bright red); can be forged hot or cold; caution advised regarding potential harmful dust and fumes; importance of verifying material purity before use.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for copper forging
Copper forging stands out as a highly effective method for producing durable, high-precision components essential across various industries. By leveraging the unique properties of copper and its alloys—such as excellent electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and malleability—businesses can enhance their product offerings while achieving cost efficiencies. Strategic sourcing plays a critical role in optimizing supply chains, ensuring that manufacturers can access high-quality materials while maintaining competitive pricing.
As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate the complexities of sourcing copper forgings, it is vital to partner with reliable suppliers who understand local market dynamics and regulatory requirements. Establishing strong relationships with manufacturers can lead to innovations in product design and improvements in production processes, ultimately driving business growth.
Looking ahead, the demand for copper forgings is set to rise, driven by advancements in technology and an increasing emphasis on sustainability. Companies that proactively engage in strategic sourcing and adapt to market trends will be better positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities. Now is the time to evaluate your sourcing strategies and explore the potential of copper forging to enhance your product line and operational efficiency.

Illustrative image related to copper forging
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to copper forging