Top 5 Valve Plunger Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for valve plunger
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right valve plunger can pose a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With the critical role that valve plungers play in regulating flow and pressure across various applications—from water treatment facilities to industrial machinery—understanding their specifications and functionalities is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of valve plungers, covering various types, their applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting.
As you navigate this guide, you will find detailed insights into the different configurations and materials of valve plungers, enabling you to select the best options that meet your operational needs. Furthermore, we will explore the cost implications associated with sourcing these components and provide strategies for evaluating suppliers to ensure quality and reliability.
By equipping you with the knowledge to assess product specifications and supplier capabilities, this guide empowers B2B buyers to streamline their procurement processes. Whether you’re in Saudi Arabia seeking durable water management solutions or in Brazil looking for precision-engineered components, the insights provided here will help you optimize your sourcing strategy and enhance operational efficiency.
Understanding valve plunger Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Needle Valve | Fine control of flow and pressure; high differential pressure capabilities | Water treatment, power plants, industrial processes | Pros: Precise flow regulation; versatile applications. Cons: Can be more complex to install. |
| Plunger Control Valve | Direct-acting mechanism; compact design; various actuation options | Pneumatic systems, irrigation, manufacturing | Pros: Space-saving; easy maintenance. Cons: Limited flow capacity compared to larger valves. |
| VAG RIKO® Plunger Valve | One-piece body design; handwheel control; robust construction | Water distribution, irrigation systems | Pros: Durable; reliable performance. Cons: Manual operation may not suit all automation needs. |
| Conversion Valve Plunger Kit | Upgraded components for existing systems; compatibility with specific models | Espresso machines, specialty coffee equipment | Pros: Enhances performance; easy upgrade path. Cons: Requires additional components for full functionality. |
| Direct-Acting Plunger Valve | Welded components for leak-tightness; compact size; various seal materials | Fluid control in diverse industries | Pros: High-pressure resistance; customizable. Cons: May require specialized installation knowledge. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Needle Valves?
Needle valves are designed for precise control of flow and pressure, making them ideal for applications requiring fine adjustments. Their construction allows for operation under high differential pressures, which is essential in industries like water treatment and power generation. When purchasing needle valves, B2B buyers should consider the material quality, size range, and whether manual or automated actuation is needed. These valves are versatile but can be complex to install, necessitating skilled personnel for optimal performance.
How Do Plunger Control Valves Stand Out?
Plunger control valves are characterized by their direct-acting mechanism, which allows for quick response times and compact designs. They are often used in pneumatic systems and irrigation applications, where space is at a premium. Buyers should evaluate the actuation options available (manual, electric, hydraulic) and consider the valve’s maintenance requirements. While these valves are user-friendly and easy to maintain, their flow capacity may be limited compared to larger alternatives, which could be a consideration for specific applications.
What Makes the VAG RIKO® Plunger Valve a Reliable Choice?
The VAG RIKO® plunger valve features a robust one-piece body design and manual handwheel control, making it suitable for water distribution and irrigation systems. Its durable construction ensures reliable performance over time, which is crucial for B2B operations relying on consistent water management. Buyers should assess whether the manual operation aligns with their automation goals, as this valve may not be ideal for fully automated systems. However, its reliability and durability are significant advantages for long-term use.
Why Consider Conversion Valve Plunger Kits?
Conversion valve plunger kits are specifically designed to upgrade existing systems, such as espresso machines. These kits often include enhanced components like stainless steel stems and hooks to improve performance. B2B buyers in the specialty coffee sector should consider these kits for their ease of installation and the potential to boost machine efficiency. However, it’s essential to ensure compatibility with existing equipment and account for any additional components required for full functionality.
What are the Benefits of Direct-Acting Plunger Valves?
Direct-acting plunger valves are engineered for high-pressure applications, featuring welded components that enhance leak-tightness and pressure resistance. They are suitable for fluid control across various industries, including manufacturing and chemical processing. B2B buyers should focus on the valve’s size, seal material options, and installation requirements. While these valves offer customization and high performance, they may necessitate specialized installation knowledge, which could impact project timelines and costs.
Key Industrial Applications of valve plunger
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of valve plunger | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Treatment | Flow control in water distribution systems | Enhances efficiency and reliability in water supply | Material durability, pressure ratings, and certifications |
| Oil & Gas | Pressure regulation in pipeline systems | Ensures safety and optimal flow management | Compliance with industry standards and custom sizing |
| Power Generation | Turbine bypass control in hydropower plants | Maximizes energy output and operational stability | Temperature resistance and compatibility with fluids |
| Food & Beverage | Control of liquid flow in processing plants | Maintains product quality and operational efficiency | Hygiene standards and material certifications |
| Chemical Processing | Regulation of reactant flow in chemical reactors | Improves process safety and efficiency | Corrosion resistance and precise control capabilities |
How Are Valve Plungers Utilized in Water Treatment Applications?
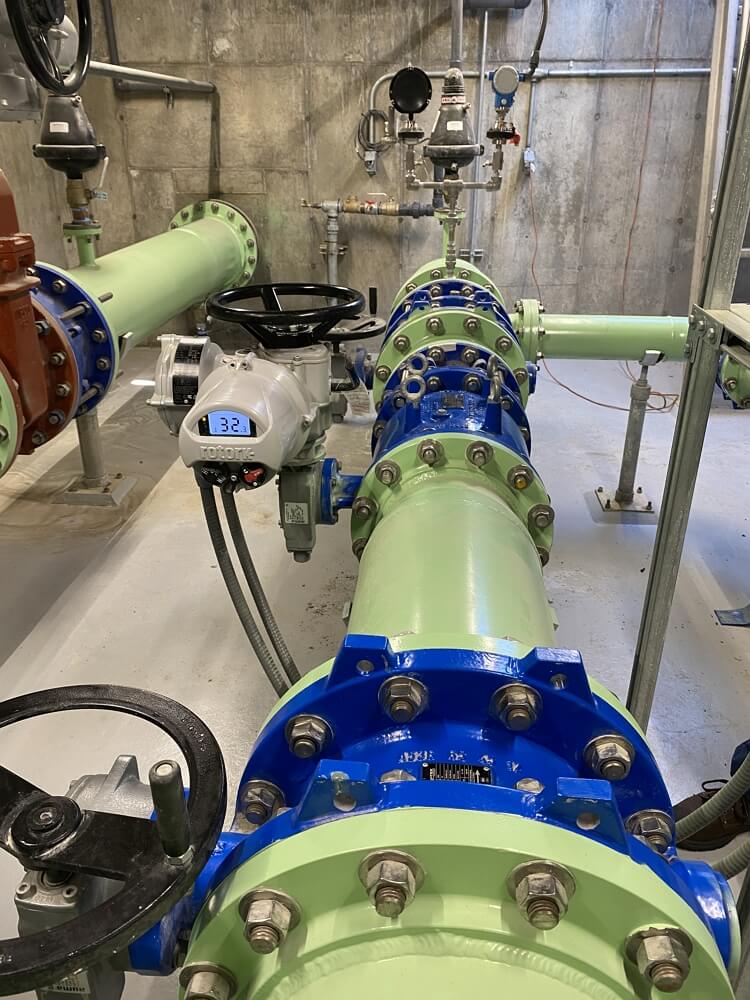
In water treatment facilities, valve plungers play a crucial role in flow control within distribution systems. They regulate the movement of water, ensuring consistent supply and pressure across various points in the network. By using high-quality materials that withstand corrosion and wear, businesses can enhance the reliability of their operations. International buyers should prioritize sourcing valves with appropriate pressure ratings and certifications to comply with local regulations, especially in regions like Africa and South America where infrastructure can be challenging.

Illustrative image related to valve plunger
What Role Do Valve Plungers Play in the Oil & Gas Sector?
In the oil and gas industry, valve plungers are vital for maintaining pressure regulation in pipeline systems. These valves help prevent over-pressurization, which can lead to catastrophic failures. By ensuring safe and efficient flow management, they contribute significantly to operational safety and productivity. B2B buyers must consider factors such as compliance with stringent safety standards and the ability to customize sizes and materials to fit specific pipeline requirements, particularly in the Middle East and Europe where regulations are rigorous.
Why Are Valve Plungers Important for Power Generation?
In power generation, particularly in hydropower facilities, valve plungers are used for turbine bypass control. This application is essential for maximizing energy output while maintaining operational stability. By enabling precise flow control, these valves help manage the hydraulic conditions necessary for efficient turbine performance. Buyers in the energy sector should focus on valves that offer high temperature resistance and compatibility with various fluids to ensure long-term reliability and compliance with environmental standards.
How Do Valve Plungers Enhance Food & Beverage Processing?
In the food and beverage industry, valve plungers are employed to control liquid flow during processing. This application is critical for maintaining product quality and ensuring operational efficiency. The use of hygienic materials that meet food safety standards is paramount, as any contamination can lead to significant losses. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing valves that comply with relevant health regulations, particularly in regions like South America and Europe where consumer safety is heavily regulated.
What Are the Benefits of Valve Plungers in Chemical Processing?
Valve plungers are extensively used in chemical processing to regulate the flow of reactants in reactors. This precise control is crucial for maintaining safety and efficiency in chemical reactions, reducing the risk of hazardous situations. Buyers in this sector must consider valves that offer corrosion resistance and the ability to operate under high pressures, ensuring they meet the specific requirements of the chemicals involved. Sourcing from reputable manufacturers who provide detailed specifications and compliance information is essential for international buyers in this field.

Illustrative image related to valve plunger
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘valve plunger’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Precise Flow Regulation
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter challenges when it comes to controlling water flow and pressure in their industrial applications. For instance, a water treatment facility may struggle with excessive fluctuations in flow rates, leading to inefficiencies, potential damage to equipment, or even compliance issues with regulatory standards. This lack of precise control can stem from using inadequate valve technology, resulting in operational delays and increased costs.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should consider sourcing high-quality plunger valves specifically designed for precise flow regulation. When selecting a valve, it’s crucial to evaluate the specific requirements of the application, including the maximum pressure and flow rates expected. Opting for a needle or plunger valve that can handle higher differential pressures will provide better performance compared to standard diaphragm valves. Additionally, implementing a robust control system that allows for manual or automated actuation can enhance the precision of flow regulation. Buyers should also invest in training for their operational staff to ensure they understand how to optimize the valve settings for their specific needs, thereby reducing variability in flow rates.
Scenario 2: Frequent Valve Maintenance and Failures
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the frequent need for maintenance and repair of valve plungers, which can disrupt operations and incur significant downtime costs. Facilities using older or poorly designed valve systems may find themselves dealing with leaks, corrosion, or other mechanical failures that compromise performance and require immediate attention. This not only affects productivity but also strains maintenance budgets.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, buyers should prioritize sourcing plunger valves made from durable materials that resist corrosion and wear, especially in harsh operating environments. Stainless steel or high-grade plastic options can be effective choices. It’s also advisable to implement a regular maintenance schedule that includes routine inspections and preventative measures, such as replacing seals and checking for wear on moving parts. Establishing a partnership with a reliable supplier who can provide timely replacement parts or even upgraded valve models can also minimize downtime. Furthermore, utilizing modern monitoring technologies, such as pressure sensors, can help predict failures before they occur, allowing for proactive maintenance rather than reactive repairs.
Scenario 3: Compatibility Issues with Existing Systems
The Problem: B2B buyers often face compatibility challenges when integrating new valve plungers into their existing systems. For example, a manufacturing plant looking to upgrade its water delivery system may find that new valves do not fit the existing piping or control mechanisms, leading to increased installation costs and project delays. This incompatibility can stem from differences in valve specifications, such as size, flange types, or actuation methods.
The Solution: To avoid compatibility issues, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their existing infrastructure before selecting new valve plungers. This includes measuring current piping sizes and understanding the types of connections (e.g., flanged, threaded) in use. When sourcing new valves, it’s essential to choose those that offer customizable options or standard sizes that align with existing systems. Engaging with manufacturers who provide comprehensive product documentation and support can greatly aid in ensuring compatibility. Additionally, working with an experienced engineer during the selection and installation process can help identify potential issues early and suggest necessary modifications or additional components needed for a seamless integration. This proactive approach not only streamlines the installation process but also ensures long-term reliability and performance of the valve systems.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for valve plunger
What Are the Key Materials Used in Valve Plungers and Their Properties?
When selecting materials for valve plungers, it’s crucial to consider their performance characteristics, durability, and compatibility with specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of valve plungers: stainless steel, brass, plastic (polymer), and bronze. Each material has its unique properties, advantages, and limitations, which can significantly impact the performance and suitability of the valve in various applications.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Valve Plunger Applications?
Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 800°F (427°C) and can handle pressures exceeding 300 psi, making it suitable for demanding environments such as chemical processing and oil and gas applications.
Pros: Stainless steel’s durability and resistance to rust and corrosion make it ideal for applications involving aggressive media. It also has a long lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, which is higher than other materials. Additionally, manufacturing stainless steel components can be more complex, requiring specialized machining and finishing processes.

Illustrative image related to valve plunger
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with various media, including water, steam, and many chemicals, making it versatile for international applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where quality assurance is critical.
What Advantages Does Brass Offer for Valve Plungers?
Brass is a popular choice for valve plungers due to its good machinability, moderate strength, and excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in water applications. It typically operates effectively at temperatures up to 300°F (149°C) and pressures around 150 psi.
Pros: Brass is generally more affordable than stainless steel and offers good thermal and electrical conductivity, making it suitable for applications that require these properties.
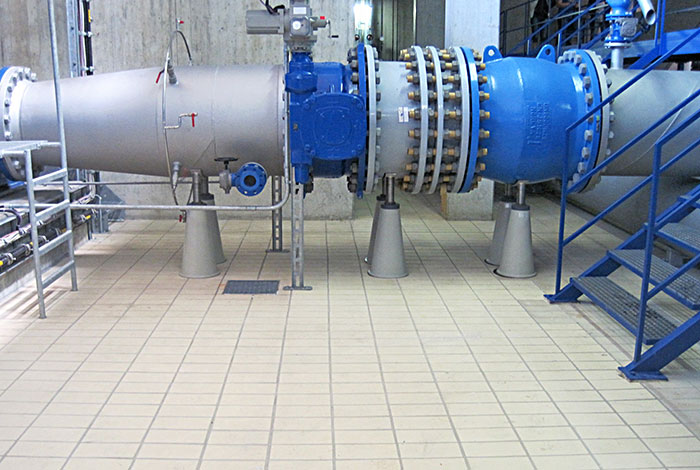

Illustrative image related to valve plunger
Cons: However, brass is less durable than stainless steel and can corrode in certain environments, particularly in the presence of chlorides.
Impact on Application: Brass is commonly used in plumbing and HVAC systems, where water is the primary medium. Its compatibility with potable water makes it a preferred choice in residential and commercial settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure that the brass used complies with local regulations regarding lead content, especially in regions like Europe where strict guidelines are in place.
How Do Plastics (Polymers) Compare in Valve Plunger Manufacturing?
Plastic materials, particularly engineered polymers, are increasingly used for valve plungers due to their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. They can handle temperatures up to 200°F (93°C) and pressures around 100 psi.
Pros: The primary advantage of plastics is their low cost and ease of manufacturing. They can be molded into complex shapes, reducing assembly time and costs.
Cons: Plastics generally have lower strength and temperature resistance compared to metals, limiting their use in high-pressure or high-temperature applications.
Impact on Application: Plastics are ideal for applications involving non-aggressive media, such as water and air, making them suitable for industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with food safety standards and certifications, especially in regions like South America and Europe, where regulations are stringent.
What Role Does Bronze Play in Valve Plunger Applications?
Bronze is another metal option that offers good corrosion resistance and strength, particularly in marine environments. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 400°F (204°C) and can handle pressures similar to brass.
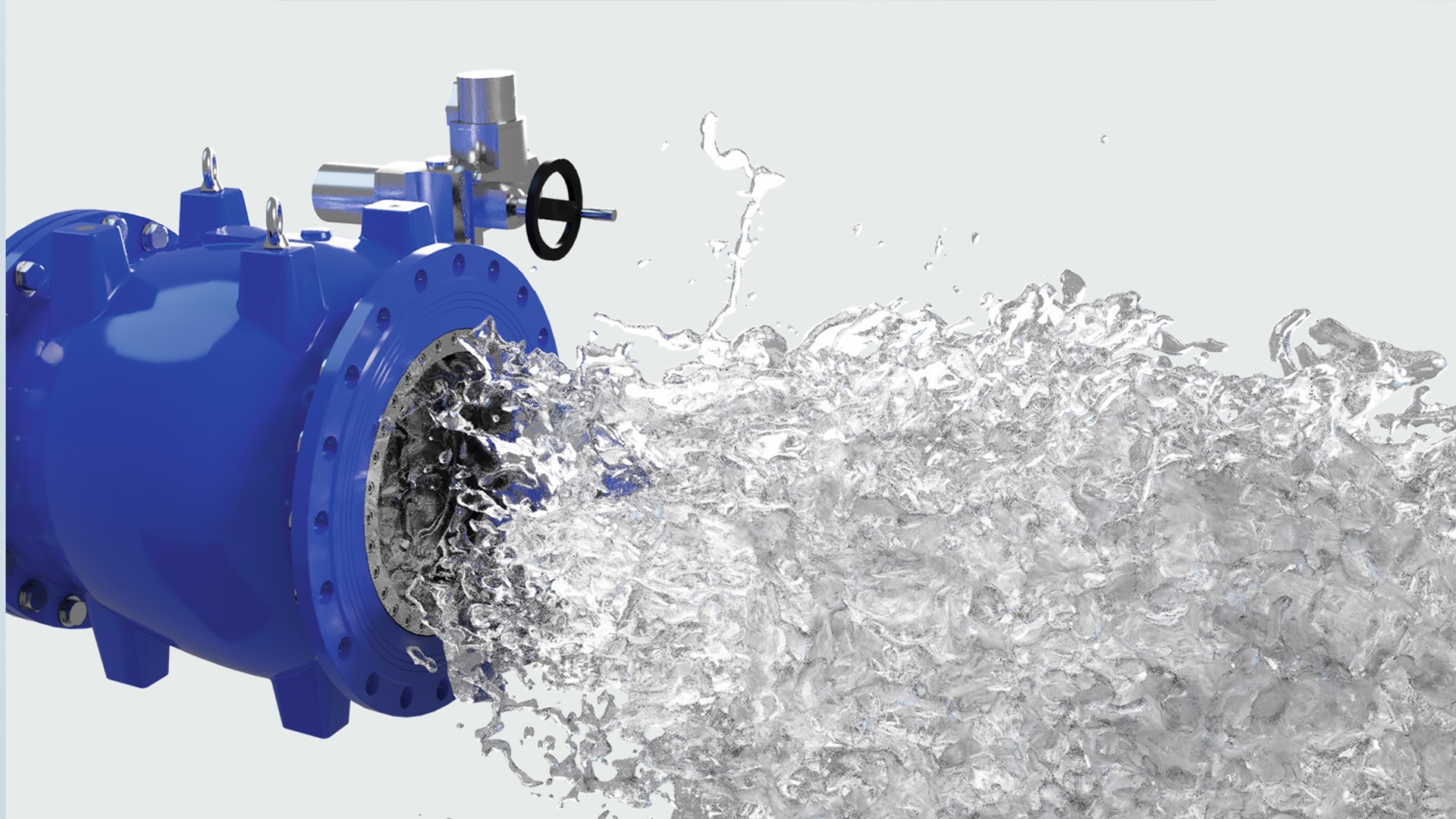

Illustrative image related to valve plunger
Pros: Bronze is highly resistant to corrosion from seawater and other harsh environments, making it ideal for marine applications.
Cons: The main limitation is its cost, which can be higher than brass and some plastics. Additionally, bronze can be heavier than other materials, which may affect installation.
Impact on Application: Bronze is commonly used in applications where exposure to saltwater or other corrosive environments is a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with marine standards and certifications is crucial for buyers in regions like the Middle East and Africa, where marine applications are prevalent.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Valve Plungers
| Material | Typical Use Case for valve plunger | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Chemical processing, oil & gas | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Brass | Plumbing, HVAC systems | Good machinability and affordability | Less durable, susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Plastic | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Low cost and ease of manufacturing | Lower strength and temperature resistance | Low |
| Bronze | Marine applications | High corrosion resistance in seawater | Higher cost, heavier material | Medium |
This material selection guide aims to provide international B2B buyers with actionable insights to make informed decisions when sourcing valve plungers, ensuring compatibility with their specific applications and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for valve plunger
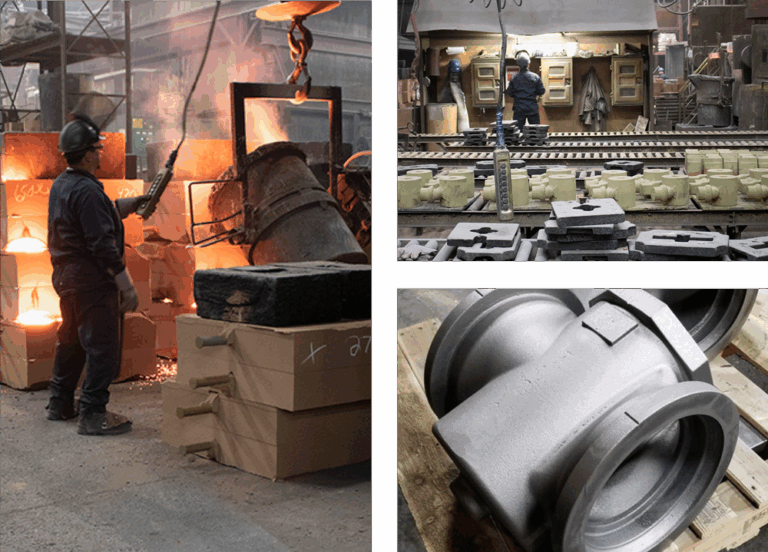
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Valve Plungers?
The manufacturing of valve plungers involves several critical stages, each essential for ensuring that the final product meets the specific requirements of various applications, including water treatment, industrial processes, and fluid control.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Commonly Used?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material selection and preparation. Valve plungers are typically crafted from high-grade materials such as stainless steel, brass, or specialized polymers, depending on the application’s requirements. These materials are chosen for their durability, resistance to corrosion, and ability to withstand high pressures. The preparation stage may involve cutting the raw materials into manageable sizes and conducting initial quality checks to ensure they meet specified standards.
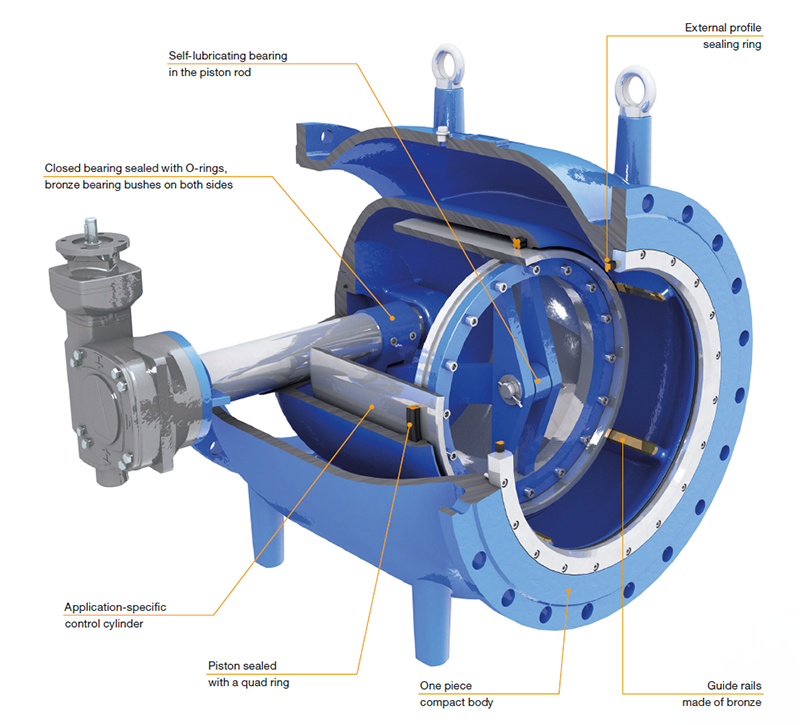
How Are Valve Plungers Formed?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This typically involves machining processes such as turning, milling, and grinding to shape the components of the valve plunger. Advanced techniques like CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining are often employed to achieve precise dimensions and tolerances. In some cases, forming may also include forging or casting, especially for larger components, where the goal is to enhance the mechanical properties of the material.

Illustrative image related to valve plunger
What Does the Assembly Process Entail?
After forming, the assembly of valve plungers takes place. This involves fitting together various components, including the plunger body, seals, and actuators. The assembly process must be conducted in a clean environment to prevent contamination, which could affect performance. Quality assurance checkpoints are integrated at this stage to verify the integrity of seals and the overall assembly, ensuring that the components fit correctly and function as intended.
Which Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used?
The final stage in the manufacturing process is finishing, which enhances the valve plunger’s surface and performance characteristics. This may involve processes such as polishing, coating, or applying protective finishes to improve wear resistance and reduce friction. Finishing also plays a vital role in ensuring that the valve plunger meets aesthetic and functional requirements, such as improved sealing capabilities and reduced leakage.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Valve Plungers?
Quality assurance (QA) is crucial in the manufacturing of valve plungers to ensure that the products not only meet internal standards but also comply with international regulations.
Illustrative image related to valve plunger
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should be familiar with several international standards that govern the quality of valve plungers. ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard for quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers maintain consistent quality in their processes. Other industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for compliance with European safety standards and API standards for the petroleum and natural gas industries are also significant. Understanding these standards helps buyers ensure that they are sourcing products that meet regulatory requirements in their respective markets.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that products meet quality standards at every stage. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, in-process inspections are conducted to monitor the quality of the production process, ensuring that any deviations are promptly addressed.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection checks the finished valve plungers against specifications, ensuring they function correctly and meet all quality standards.
Which Testing Methods Are Commonly Utilized?
Testing methods play a vital role in verifying the performance and reliability of valve plungers. Common methods include:
- Pressure Testing: This ensures that the valve plungers can withstand their rated pressure without leaking.
- Leak Testing: Utilizing techniques such as bubble testing or pressure decay testing helps identify any potential leaks in the assembly.
- Functional Testing: This assesses the operational performance of the valve plunger, ensuring it opens and closes as intended.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is essential to ensure product reliability and compliance with industry standards.
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Assess Supplier QC?
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help buyers assess the quality management systems and manufacturing processes. This may include reviewing production records, quality control measures, and certifications.
-
Request Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for detailed quality reports that outline the results of various tests and inspections performed during the manufacturing process. This transparency helps buyers gauge the reliability of the supplier.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing processes and products. This is particularly important for international transactions where buyers may not have direct oversight.
What Are the QC Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of the nuances in quality control that can vary by region. Factors such as local regulations, cultural differences in manufacturing practices, and varying standards can impact product quality. Buyers should consider these factors when establishing relationships with suppliers and ensure that they align with their own quality expectations and compliance requirements.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for valve plungers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure high-quality products that meet their operational needs and regulatory standards.
Illustrative image related to valve plunger
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘valve plunger’
In the competitive landscape of B2B procurement, sourcing a valve plunger requires careful consideration and strategic planning. This guide outlines essential steps to streamline your sourcing process, ensuring that you select the right products and suppliers to meet your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by outlining the specific requirements for the valve plunger. Consider factors such as size, pressure rating, and material compatibility with the fluids being controlled. Having clear specifications will not only help in identifying suitable products but also facilitate accurate supplier comparisons.
- Key Specifications: Determine the flow rates, pressure ratings (e.g., PN40 or PN100), and dimensions (DN sizes) you require.
- Material Needs: Choose materials that can withstand your operational environment, such as stainless steel for corrosion resistance.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers of valve plungers. Look for companies with a proven track record in your industry and region. Supplier reliability can significantly impact your operations.
- Supplier Background: Review company profiles, product catalogs, and customer testimonials.
- Industry Experience: Prioritize suppliers with experience in your specific application, such as water treatment or industrial automation.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications and comply with industry standards. This is crucial for guaranteeing product quality and safety.
- Certifications to Look For: Check for ISO certifications, CE marking, or other industry-specific credentials.
- Compliance with Regulations: Verify that products meet local and international regulatory requirements, especially if operating in multiple regions.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the valve plungers you are considering. This step allows you to assess product quality and compatibility with your systems.
- Testing for Performance: Evaluate the samples under your operational conditions to ensure they meet performance expectations.
- Fit and Compatibility: Confirm that the samples fit seamlessly with your existing setups or systems.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have identified suitable suppliers and products, enter negotiations to discuss pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Effective negotiation can lead to significant cost savings.
- Cost Considerations: Compare pricing from multiple suppliers to ensure you are getting a competitive rate.
- Payment and Delivery Terms: Clarify terms of payment and expected delivery timelines to avoid any disruptions in your supply chain.
Step 6: Establish a Quality Assurance Process
Implement a quality assurance process to monitor the performance of the valve plungers post-purchase. This is vital for maintaining operational efficiency and minimizing downtime.
- Performance Monitoring: Track the functionality and durability of the valves over time to ensure they meet your specifications.
- Feedback Loop: Maintain open communication with the supplier to address any issues that may arise during use.
Step 7: Review and Optimize Your Sourcing Strategy
After completing your procurement, take time to review the entire sourcing process. Analyze what worked well and what could be improved for future purchases.

Illustrative image related to valve plunger
- Post-Purchase Evaluation: Assess supplier performance, product quality, and overall satisfaction with the procurement process.
- Continuous Improvement: Use insights gained to refine your sourcing strategy, ensuring better outcomes in future purchases.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing valve plungers, ensuring they select the right products from reliable suppliers that meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for valve plunger Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Valve Plunger Manufacturing?
When sourcing valve plungers, it is crucial to understand the underlying cost structure that influences pricing. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost. Common materials such as stainless steel, brass, and specialized alloys can vary in price based on market demand and availability. For instance, high-grade stainless steel may offer corrosion resistance, which is vital for applications in harsh environments but comes at a premium.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is often required for precision machining and assembly, particularly for high-quality valve plungers that demand tight tolerances.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility operations. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead, but investments in advanced technologies may initially raise costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for specific valve designs can be substantial. Custom molds or machining setups may be needed for specialized plungers, which affects the overall pricing structure.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that valve plungers meet international standards and certifications adds to the cost. Quality assurance processes, including testing for pressure resistance and flow accuracy, are essential for maintaining product integrity.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs also play a critical role, especially for international buyers. Shipping costs can vary significantly based on the Incoterms agreed upon in the purchase contract, which governs the responsibilities of buyers and sellers.
-
Margin: Suppliers often build a profit margin into their pricing, which can vary based on market conditions, competition, and the supplier’s business model.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Valve Plunger Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of valve plungers, which buyers should consider:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk orders typically attract lower per-unit pricing due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate favorable terms based on their purchasing power.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized plungers designed for specific applications often come at a higher price due to the additional engineering and manufacturing processes involved. Clear communication of requirements can help avoid unexpected costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The use of premium materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, API) can increase costs but may be necessary for compliance in certain industries. Buyers should weigh the benefits of these certifications against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and location can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge higher prices but offer better service, quality assurance, and support.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon shipping terms can significantly affect total costs. For example, choosing FOB (Free on Board) means the buyer assumes responsibility for shipping once the goods are loaded, potentially increasing logistics costs.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Valve Plunger Prices?
Effective negotiation strategies can help buyers secure favorable pricing:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime. A higher initial investment in quality plungers may lead to lower operational costs over time.
-
Leverage Market Research: Buyers should conduct thorough market research to understand prevailing price ranges and supplier capabilities. This knowledge empowers them to negotiate more effectively.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing long-term relationships can lead to better pricing and preferential treatment. Consistent communication and feedback help build trust, which can be beneficial during negotiations.
-
Explore Alternative Suppliers: Diversifying the supplier base can foster competitive pricing and reduce dependency on a single source. This strategy is particularly relevant for international buyers navigating varying market conditions across regions.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have unique pricing structures due to local economic conditions, tariffs, and import/export regulations. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider these factors when sourcing valve plungers.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost components and price influencers in valve plunger sourcing is essential for international B2B buyers. By leveraging negotiation strategies and maintaining awareness of market dynamics, buyers can optimize their purchasing decisions and achieve better value for their investments.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing valve plunger With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Valve Plungers
When considering valve plungers for flow and pressure regulation, it’s important for B2B buyers to evaluate other available technologies. Each alternative can offer distinct advantages depending on the application, operational environment, and specific requirements of the system in use. This analysis will explore two viable alternatives to valve plungers, comparing them across various critical aspects.

Illustrative image related to valve plunger
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Valve Plunger | Needle Valve | Diaphragm Valve |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision control over flow; suitable for high differential pressures | Excellent for fine flow control; limited by pressure range | Good flow regulation; effective in low-pressure systems |
| Cost | Generally higher due to complex design and materials | Moderate; competitive pricing for basic models | Typically lower; simple design leads to cost-effectiveness |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires careful installation and calibration | Straightforward installation; often user-friendly | Simple installation; minimal setup required |
| Maintenance | May require regular maintenance due to wear | Low maintenance; durable design | Moderate; diaphragm replacement may be necessary |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for water treatment, power plants, and applications requiring fine control | Best for applications needing precise flow regulation, such as laboratories | Suitable for general flow control in various industrial applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Needle Valve
Needle valves are renowned for their ability to provide fine control over flow and pressure. They are particularly effective in applications where precise adjustments are necessary, such as in laboratory settings or specific industrial processes. Their moderate cost and straightforward installation make them an attractive option for many businesses. However, they are limited by their maximum pressure capabilities, which may not be suitable for high-pressure applications.
Diaphragm Valve
Diaphragm valves utilize a flexible diaphragm to control flow, making them ideal for low-pressure systems. Their simple design leads to lower costs, making them accessible for various applications. Additionally, diaphragm valves require minimal maintenance, although users must be prepared for occasional diaphragm replacements. These valves excel in industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing, where hygiene and flow control are paramount. However, they may not offer the same level of precision as valve plungers or needle valves, particularly in high-pressure situations.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between valve plungers and their alternatives, B2B buyers should consider the specific needs of their operations. Factors such as pressure requirements, cost constraints, and maintenance capabilities play crucial roles in the decision-making process. For applications requiring high precision under varying pressure conditions, valve plungers may be the best fit. Conversely, if cost efficiency and ease of installation are priorities, needle or diaphragm valves may provide better value. Ultimately, understanding the unique demands of each application will guide buyers in selecting the most effective solution.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for valve plunger
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Valve Plungers?
Understanding the essential technical properties of valve plungers is critical for B2B buyers involved in industries such as water treatment, manufacturing, and energy. Here are some key specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The choice of material for valve plungers directly impacts their durability and performance. Common materials include stainless steel, brass, and various polymers. Stainless steel is preferred for its corrosion resistance and strength, making it suitable for high-pressure applications. In contrast, brass may be used in lower-pressure environments. Selecting the appropriate material ensures longevity and minimizes maintenance costs.
2. Pressure Rating (PN)
The pressure rating, often denoted as PN (Pressure Nominal), indicates the maximum pressure the valve can handle. For instance, a PN40 valve can withstand pressures up to 40 bar. This specification is crucial for ensuring that the valve can operate safely and effectively within the system’s pressure requirements. Exceeding this rating can lead to valve failure, resulting in costly downtime and repairs.
3. Size and Diameter (DN)
The size of the valve, expressed in nominal diameter (DN), determines the flow capacity. Standard sizes range from DN15 to DN2000, with larger sizes allowing for greater flow rates. Proper sizing is essential for system efficiency and can significantly affect the performance of the fluid control system. Oversized valves can lead to reduced pressure, while undersized valves can cause system strain.
4. Actuation Type
Valve plungers can be actuated manually or through various automated means, such as electrical, hydraulic, or pneumatic systems. The actuation type influences the speed and precision of valve operation. For B2B buyers, understanding actuation options helps in selecting valves that align with operational requirements and automation capabilities.
5. Seal Material
The seal material plays a vital role in ensuring leak-tightness and compatibility with the media being controlled. Common seal materials include rubber, PTFE, and elastomers, each suited for different temperatures and chemical conditions. Selecting the right seal material is essential for maintaining operational efficiency and preventing leaks that could lead to hazardous situations.
6. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions during manufacturing. High tolerance levels ensure a proper fit and function within the system. This is particularly important in high-precision applications, where even minor deviations can lead to operational failures. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance requirements helps in sourcing valves that meet strict engineering standards.
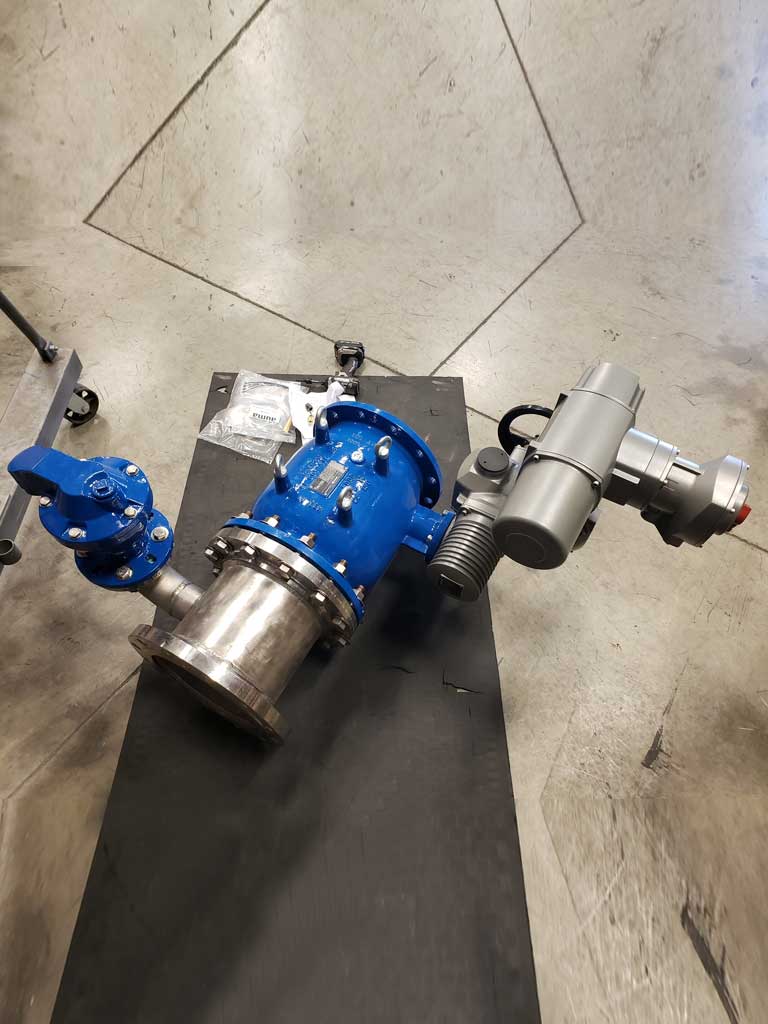

Illustrative image related to valve plunger
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Valve Plungers?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms to know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For buyers, working with OEMs can ensure that they receive high-quality, compatible components for their systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers to manage inventory and budget effectively. It can also impact pricing structures, as larger orders may qualify for discounts.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document requesting price quotes from suppliers for specific products. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ can streamline the procurement process and help in comparing offers from different vendors.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and liabilities, ensuring smoother transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for project planning and inventory management, particularly in industries with tight deadlines.
6. Certification Standards
Certification standards indicate that a product meets specific quality and safety requirements, such as ISO or ANSI certifications. Buyers should verify certifications to ensure compliance with industry regulations and to guarantee product reliability.
These technical properties and trade terminologies equip B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions in the valve plunger market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the valve plunger Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing the Valve Plunger Sector?
The valve plunger market is experiencing notable growth driven by various global factors. One primary driver is the increasing demand for precision flow control in sectors such as water treatment, oil and gas, and manufacturing. As industries strive for greater efficiency and reliability, the need for robust valve systems that can handle higher differential pressures is on the rise. Emerging technologies, such as IoT-enabled valve monitoring systems, are also transforming the landscape by providing real-time data analytics, enhancing operational efficiency, and facilitating predictive maintenance.
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of the regional dynamics that affect sourcing decisions. For instance, in the Middle East, the expansion of infrastructure projects is creating a surge in demand for high-quality plunger valves, while in Africa, the focus on improving water management systems presents significant opportunities. Additionally, sustainability is becoming a critical factor, with buyers increasingly favoring suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices and materials.
Furthermore, the supply chain landscape is evolving with the rise of direct-to-consumer sales models, allowing manufacturers to engage more directly with customers and reduce costs. As a result, B2B buyers must adapt their sourcing strategies to leverage these changes, ensuring they partner with suppliers who can offer both quality and innovation.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Practices Reshaping the Valve Plunger Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become paramount in the valve plunger sector, as businesses recognize their environmental and social responsibilities. The production and disposal of valve components can significantly impact the environment, prompting buyers to seek products that minimize ecological footprints. For instance, valves made from recyclable or biodegradable materials, as well as those produced through energy-efficient processes, are gaining traction.
Ethical supply chains are also essential for B2B buyers aiming to enhance their brand reputation. Sourcing from manufacturers that adhere to fair labor practices and demonstrate transparency in their operations is increasingly vital. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices.
Moreover, the push for ‘green’ certifications is prompting suppliers to innovate in their product offerings. Buyers should look for valve plungers that not only meet performance standards but also contribute to sustainability goals, such as reducing water waste in industrial applications. By prioritizing ethical sourcing, businesses can align their procurement strategies with broader corporate social responsibility objectives, ultimately benefiting both their bottom line and the planet.
What Is the Historical Context of Valve Plunger Development?
The evolution of valve plungers can be traced back to the industrial revolution, which necessitated advancements in flow control technologies. Initially, simple mechanical valves were employed to regulate fluids in various systems. However, as industries expanded, the need for more precise control became evident, leading to the development of needle and plunger valves. These innovations allowed for finer adjustments in flow rates and pressures, significantly improving operational efficiency.
Over the decades, technological advancements have further transformed the valve plunger landscape. The introduction of automated control systems in the late 20th century revolutionized how valves were operated, allowing for remote monitoring and control. Today, the integration of IoT technologies and smart manufacturing principles continues to shape the future of valve plungers, making them more reliable, efficient, and essential in modern industrial applications. For international B2B buyers, understanding this historical context provides valuable insights into the ongoing innovations and trends that are likely to influence their sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of valve plunger
-
How do I select the right valve plunger for my application?
Choosing the appropriate valve plunger involves understanding your specific application needs. Consider factors such as the type of medium (liquid or gas), pressure and temperature conditions, and the required flow control precision. Additionally, evaluate the valve’s material compatibility with the medium, as this can affect performance and longevity. It’s advisable to consult technical data sheets and work closely with suppliers to ensure the selected valve meets all operational requirements. -
What is the best valve plunger for high-pressure applications?
For high-pressure applications, look for plunger valves designed to withstand elevated pressure levels. Needle valves are often recommended due to their ability to manage flow with precision and handle high differential pressures. Select valves with a pressure rating of PN40 or higher, depending on your specific requirements. Ensure the materials used are suitable for the pressure and medium to enhance durability and reliability. -
What are the common applications for valve plungers in industrial settings?
Valve plungers are widely used in various industrial applications, including water treatment, oil and gas, and power generation. They are essential for flow control, pressure regulation, and safely managing the start and stop of pumps and turbines. Additionally, they can be used in chemical processing where precise control over fluid movement is required, making them versatile components in many engineering systems. -
How can I verify the reliability of a valve plunger supplier?
To ensure a supplier’s reliability, conduct thorough research on their reputation within the industry. Check for certifications, compliance with international standards, and customer reviews. Request case studies or references from similar projects to gauge their experience. Additionally, engaging in direct communication can provide insights into their customer service and technical support capabilities, which are vital for long-term partnerships. -
What customization options are available for valve plungers?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for valve plungers to meet specific operational needs. Customizations can include material selection, size variations, and modifications for unique pressure or temperature conditions. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities and lead times for producing custom solutions. This flexibility can enhance the performance of the valve in your particular application. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for valve plungers?
Minimum order quantities for valve plungers can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on the type of valve and customization requirements. Generally, MOQs can range from a few units for standard products to larger quantities for specialized orders. It’s essential to clarify MOQs during negotiations with suppliers to ensure they align with your purchasing needs and production schedules. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing valve plungers internationally?
Payment terms for international transactions can vary widely. Common options include upfront payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery, depending on the supplier’s policies and the buyer’s creditworthiness. Discussing payment terms in advance is crucial to avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction. Be prepared to negotiate terms that are favorable while providing adequate security for the supplier. -
How do I manage logistics for importing valve plungers from overseas suppliers?
Effective logistics management for importing valve plungers involves planning for shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Work with a freight forwarder familiar with your destination country to navigate import duties and tariffs. Ensure all documentation, such as invoices and packing lists, is accurate to facilitate smooth customs clearance. It’s also wise to account for lead times and potential delays in shipping to better align with your project schedules.
Top 5 Valve Plunger Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Flair – Valve Plunger Conversion Kit
Domain: flairespresso.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Valve Plunger Conversion Kit w/ Stem and Hook”, “price”: “$91.00”, “availability”: “In stock”, “weight”: “1.01 lbs”, “components”: [“Conversion valve plunger”, “3-piece hook”, “Stainless steel stem”, “2 hex wrenches”], “note”: “This kit requires a puck screen, which is not included. If you do not have a puck screen, you will need to purchase a different conversion kit.”, “year_in…
2. AVK – Needle Valves
Domain: avkvalves.eu
Introduction: Needle valves, also known as plunger valves, are regulating valves designed for precise control of water flow and pressure. They achieve precision through the fine movement of the shaft, which moves the piston tube to open or close based on control system requirements. Applications include water treatment, distribution, dams, reservoirs, power plants, and industrial uses for flow control, pressure…
3. Avtek – VRX Plunger Control Valves
Domain: avtekvalves.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Product Name: VRX Plunger Control Valves
Key Features:
– Quarter Turn Valve with customizable gear ratio and opening/closing speed.
– Built to last with a ductile iron body, fusion bonded epoxy, and SST internal trim.
– Designed for cavitation control, considering flow, velocity, and pressure for optimal application fit.
– Short lay length for easy retrofitting compared to typical hydraulic contro…
4. Burkert – Type 6012 Plunger Valve
Domain: burkert.com
Introduction: Type 6012 – Plunger valve 3/2 way direct-acting. Available until 6/30/26. Successor type: 7012. Direct-acting, compact small-format valve with diameter up to DN 1.6. Features include a welded stopper and core guide tube for enhanced pressure resistance and leak-tightness, various seal material combinations, Bürkert-specific flange design (SFB) for space-saving arrangement, push-in fittings for fle…
5. VAG – RIKO® Plunger Valve
Domain: vag-group.com
Introduction: VAG RIKO® Plunger Valve: one-piece body, with handwheel; Variants: with electric actuator; Pressure ratings: PN 10/16/25/40; Diameter range: DN 150…2200; Product group: Control Valves; Medium: Water; Features: Externally controlled control valve with annular flow cross-section for continuous regulation of high pressure differences and flow rates; Long service life with non-contact bearings; Wear…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for valve plunger
In the dynamic landscape of valve plunger procurement, strategic sourcing emerges as a crucial component for ensuring operational efficiency and reliability. With applications ranging from water treatment to industrial processing, the precision and control offered by plunger valves are indispensable. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that provide high-quality materials and innovative designs, as these factors directly influence performance and longevity.
Additionally, understanding the specific needs of your application—whether it involves flow regulation, pressure control, or actuation methods—will guide you in selecting the right valve type. Engaging with reputable manufacturers that offer comprehensive support and customization options can significantly enhance your sourcing strategy.
As we look ahead, international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are encouraged to leverage technological advancements and supplier partnerships to optimize their valve systems. By focusing on quality, reliability, and strategic alliances, businesses can ensure they meet the growing demands of their sectors. Now is the time to act—explore your options, evaluate suppliers, and invest in valve plungers that will empower your operations for years to come.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.