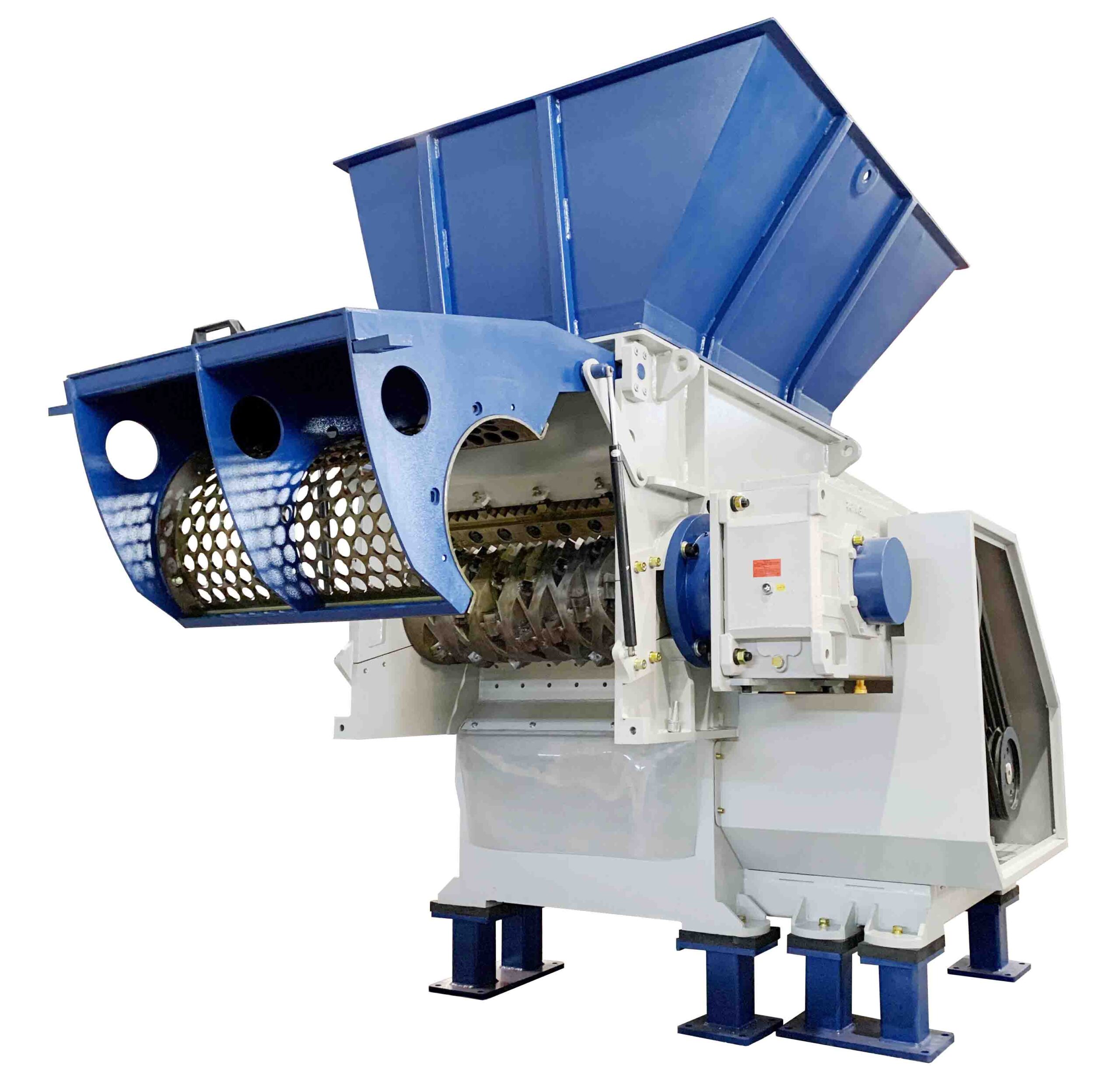
Plastic Shredder Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for plastic shredder
Navigating the complexities of sourcing a plastic shredder can be daunting for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Africa and South America, as well as established regions such as Europe and the Middle East. With the global emphasis on sustainability and efficient waste management, the demand for high-quality plastic shredders is on the rise. This guide aims to demystify the process, offering insights into various types of shredders, their applications in recycling and manufacturing, and strategies for effective supplier vetting.
Understanding the nuances of different plastic shredders—ranging from compact models suitable for small businesses to industrial-grade machines for large-scale operations—is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. We will explore the costs associated with these machines, highlighting factors such as energy efficiency, maintenance requirements, and potential ROI. Additionally, this guide will provide actionable tips for evaluating suppliers, ensuring that you partner with reputable manufacturers who can meet your specific operational needs.
By leveraging this comprehensive resource, buyers from diverse regions—including Germany, Saudi Arabia, and beyond—will be empowered to make strategic decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and contribute to a more sustainable future. Embrace the opportunity to streamline your procurement process and align your operations with global best practices in plastic recycling and waste management.
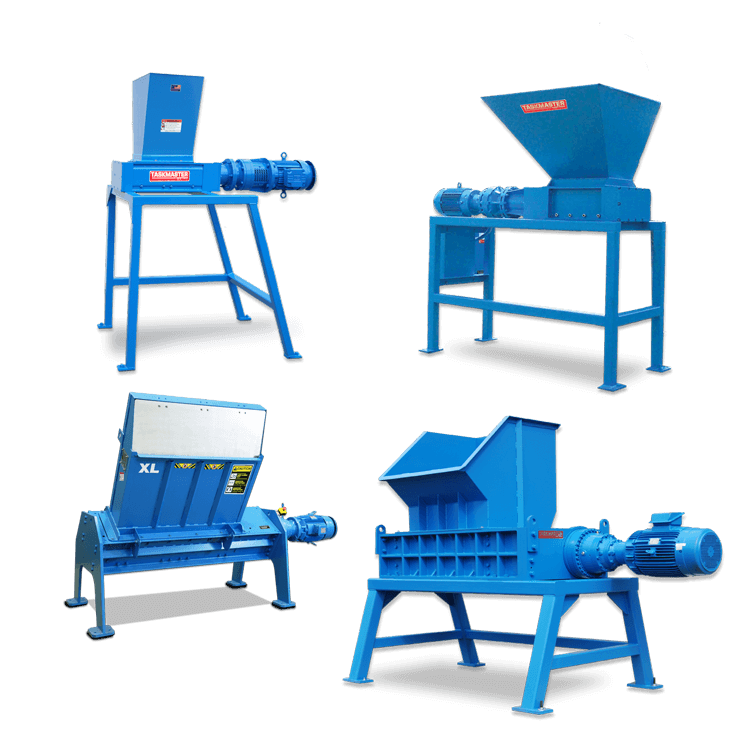
Understanding plastic shredder Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Shaft Shredder | Features a single rotor with fixed knives; ideal for continuous operation. | Recycling facilities, manufacturing waste | Pros: Efficient for bulky materials; Cons: Limited to lower throughput. |
| Double Shaft Shredder | Utilizes two counter-rotating shafts for shredding; highly versatile. | Industrial waste management, e-waste recycling | Pros: High throughput; Cons: More complex maintenance. |
| Granulator | Designed for smaller particle sizes; typically follows shredding. | Plastic recycling, 3D printing industries | Pros: Produces uniform granules; Cons: May require additional equipment. |
| Mobile Shredder | Compact, portable units designed for on-site operations. | Construction sites, remote recycling | Pros: Flexibility and convenience; Cons: Limited capacity compared to stationary models. |
| Heavy-Duty Shredder | Built for heavy materials with robust construction; suitable for tough applications. | Demolition, metal recycling | Pros: Can handle tough materials; Cons: Higher initial investment. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of a Single Shaft Shredder?
Single shaft shredders are characterized by their straightforward design, featuring a single rotor equipped with fixed knives. They are particularly suited for processing large volumes of bulky materials, such as plastic crates and pallets. For B2B buyers, this type of shredder is ideal for recycling facilities and manufacturers looking to streamline waste management. However, while they are efficient for continuous operation, their throughput may be limited compared to other types.
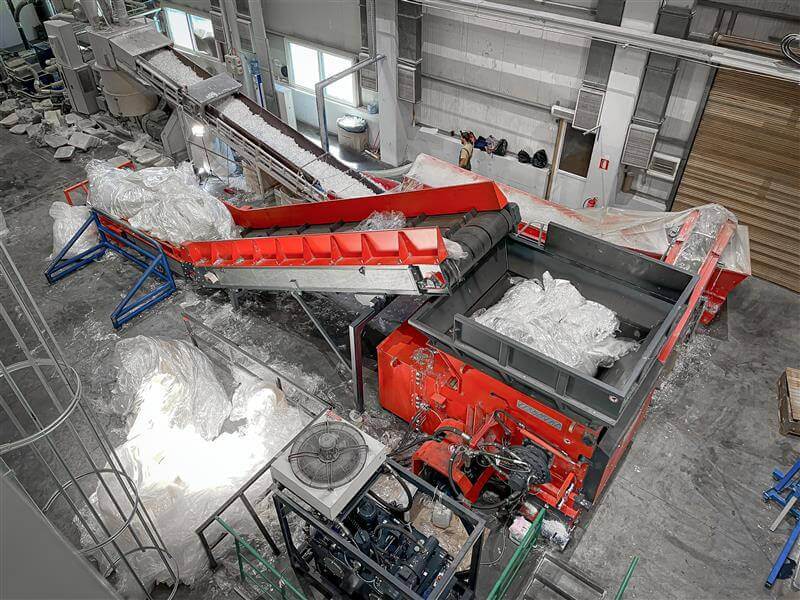
How Does a Double Shaft Shredder Provide Versatility?
Double shaft shredders are recognized for their two counter-rotating shafts, which enhance shredding efficiency and versatility. They excel in managing a diverse range of materials, including industrial waste and e-waste, making them a popular choice in waste management sectors. For B2B buyers, the high throughput and adaptability to various materials are significant advantages, although the complexity of maintenance can be a drawback.

Illustrative image related to plastic shredder
What Role Does a Granulator Play in Plastic Recycling?
Granulators are specialized shredders designed to produce smaller, uniform particle sizes, ideal for recycling processes and 3D printing applications. They are often used in conjunction with other shredding equipment to create granules from shredded plastic. B2B buyers should consider granulators for operations that require consistent granule size, but they may need to invest in additional machinery to achieve optimal results.
Why Choose a Mobile Shredder for On-Site Operations?
Mobile shredders are compact and designed for portability, making them suitable for on-site operations such as construction sites or remote recycling initiatives. Their flexibility allows businesses to address shredding needs directly where waste is generated, thus reducing transport costs. However, B2B buyers should be aware that mobile shredders may have a lower capacity than stationary models, which could impact efficiency for larger projects.
What Are the Advantages of a Heavy-Duty Shredder?
Heavy-duty shredders are engineered to handle tough materials, featuring robust construction that allows them to shred items like metals and dense plastics. They are commonly used in demolition and metal recycling industries. For B2B buyers, these shredders offer the advantage of durability and the ability to process challenging materials; however, they typically require a higher initial investment, which should be factored into the purchasing decision.
Key Industrial Applications of plastic shredder
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Plastic Shredder | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recycling Industry | Shredding post-consumer plastic waste | Reduces waste volume, increases recycling efficiency | Machine capacity, blade durability, energy consumption |
| Manufacturing | Recycling production scrap | Minimizes material costs, promotes sustainability | Material compatibility, maintenance requirements, throughput |
| Construction | Processing plastic packaging waste | Enhances waste management, supports eco-friendly practices | Size of shredded material, machine mobility, reliability |
| Automotive | Shredding end-of-life vehicle plastics | Facilitates material recovery, lowers disposal costs | Compliance with recycling regulations, machine robustness |
| 3D Printing | Recycling failed prints and filament remnants | Reduces costs, enables continuous production cycles | Precision of shredding, compatibility with specific plastics |
How is Plastic Shredder Used in the Recycling Industry?
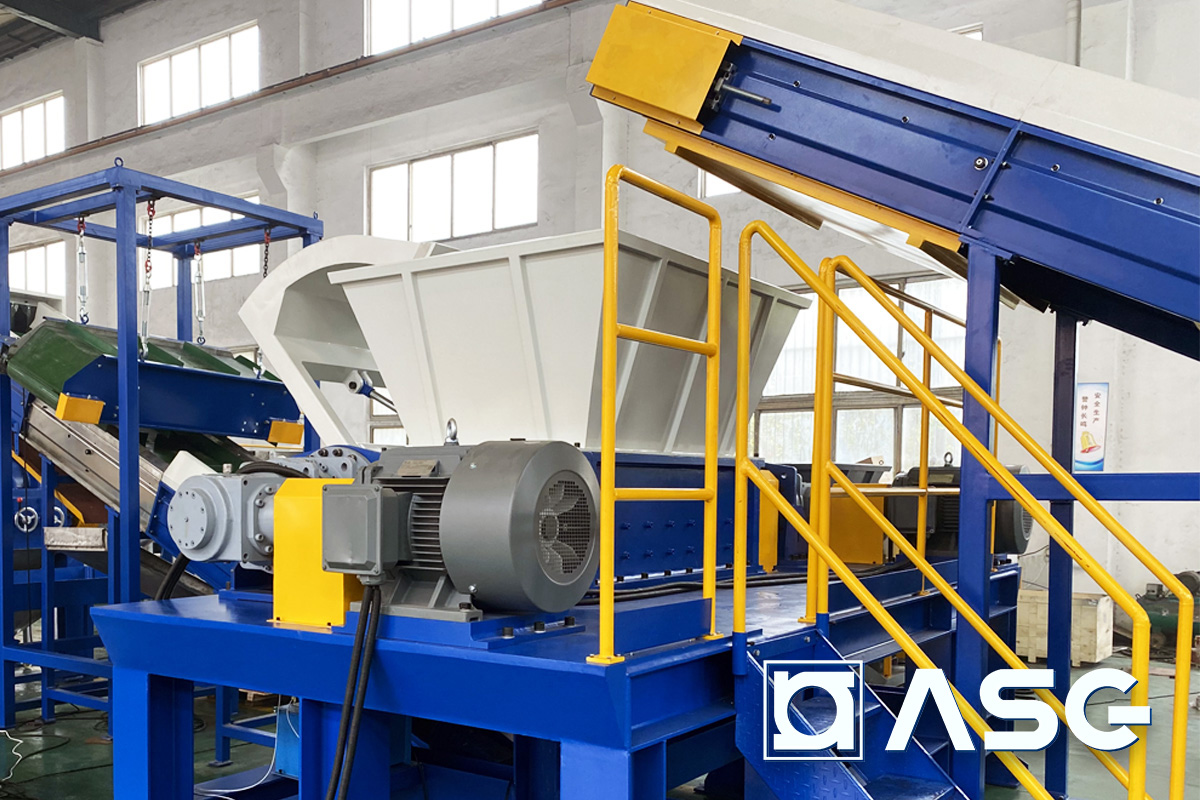
In the recycling industry, plastic shredders are crucial for processing post-consumer plastic waste. They break down large plastic items into smaller, manageable pieces, significantly reducing their volume. This shredding process enables easier transportation and sorting, improving overall recycling efficiency. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing shredders that can handle diverse types of plastics while ensuring durability and low energy consumption is essential.
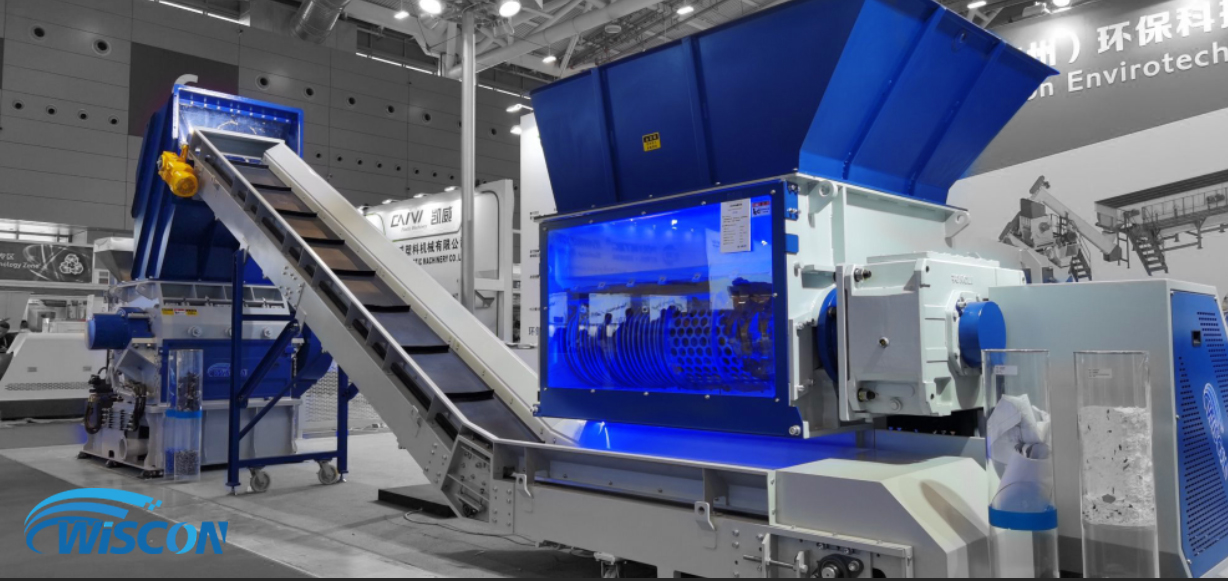
What Role Does Plastic Shredder Play in Manufacturing?
Manufacturers often generate plastic scrap during production, which can be recycled using plastic shredders. By shredding this scrap into reusable flakes, businesses can minimize material costs and adhere to sustainability practices. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should consider shredders with high throughput and compatibility with various plastic types to maximize their recycling efforts and reduce waste.

Illustrative image related to plastic shredder
How is Plastic Shredder Beneficial in Construction?
In the construction sector, plastic shredders are used to process plastic packaging waste generated on job sites. This not only enhances waste management practices but also supports eco-friendly initiatives by diverting waste from landfills. When sourcing shredders, businesses should look for models that can efficiently handle bulky materials while being portable enough for on-site use, particularly in developing regions.
How Does Plastic Shredder Support the Automotive Industry?
The automotive industry utilizes plastic shredders to process end-of-life vehicle plastics, facilitating material recovery and reducing disposal costs. Shredded plastics can be recycled into new products, contributing to a circular economy. Buyers must ensure that shredders comply with local recycling regulations and are robust enough to handle various plastic compositions, particularly in regions with stringent environmental standards.
Why is Plastic Shredder Important for 3D Printing?
In the 3D printing sector, plastic shredders are employed to recycle failed prints and filament remnants. This process allows businesses to convert waste into reusable filament, reducing costs and promoting sustainability. Buyers should prioritize shredders that offer precision shredding capabilities to maintain the quality of the recycled material, particularly in regions where 3D printing is rapidly expanding.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘plastic shredder’ & Their Solutions
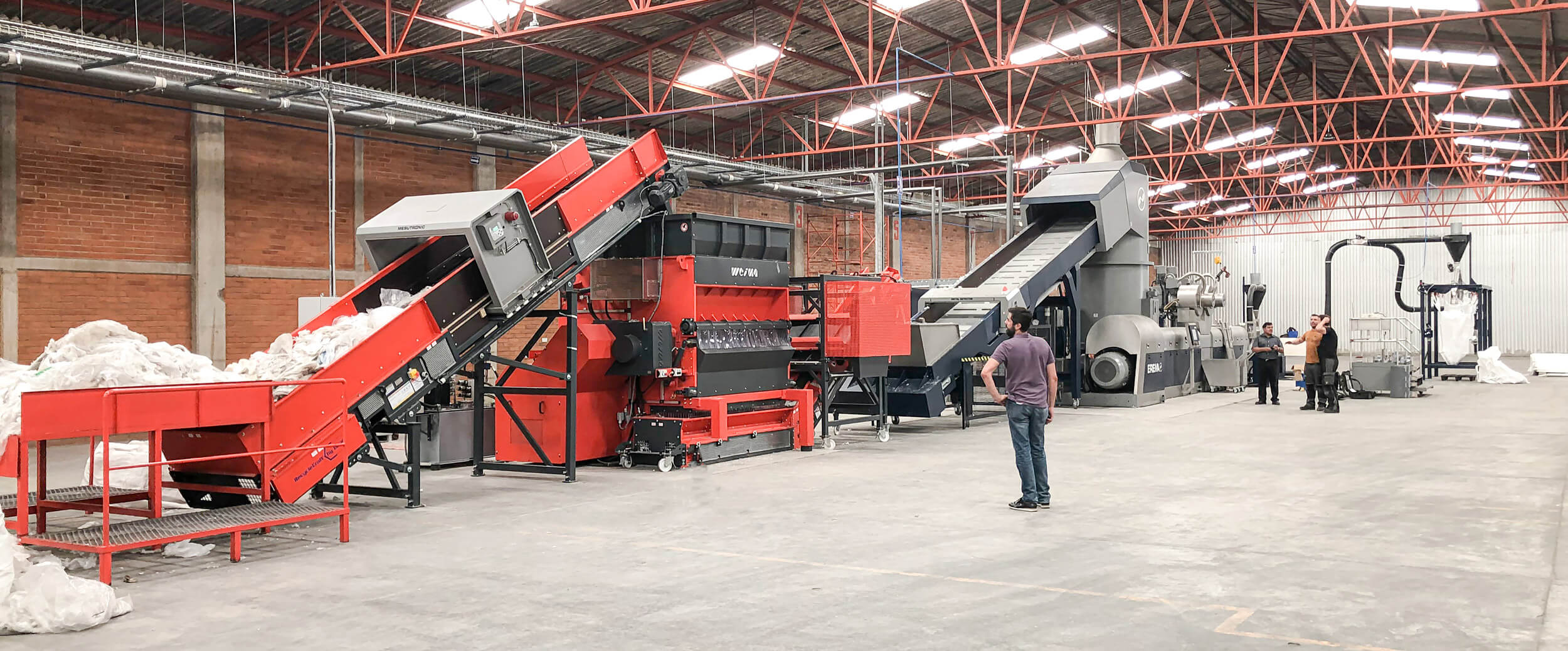
Scenario 1: Inefficient Waste Processing and High Operational Costs
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly those in manufacturing and recycling sectors, face challenges with inefficient waste processing systems. Traditional plastic shredders often struggle to handle diverse plastic types, resulting in bottlenecks that can lead to increased operational costs. For instance, if a company primarily processes PET and HDPE plastics but lacks a shredder capable of efficiently handling mixed plastics, they may experience downtime and increased labor costs as workers manually separate materials or wait for the machine to catch up.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should consider investing in high-capacity, multi-material plastic shredders that are designed to handle various types of plastics simultaneously. When sourcing shredders, it’s crucial to assess the machine’s specifications, including its motor power, cutting technology, and throughput capacity. Look for models that feature adjustable cutting sizes and robust blades that can easily handle tougher materials. Additionally, ensuring that the shredder is equipped with a reliable feeding system can help maintain consistent operation and reduce downtime. Buyers should also engage with suppliers who provide comprehensive after-sales support, including maintenance services and readily available spare parts, to minimize disruptions in their processing operations.

Illustrative image related to plastic shredder
Scenario 2: Safety Concerns and Compliance with Regulations
The Problem: In many regions, including Europe and the Middle East, businesses are increasingly held accountable for workplace safety and environmental compliance. A common pain point arises when companies invest in plastic shredders that do not meet safety regulations or have inadequate safety features, leading to potential accidents and legal issues. For example, inadequate guarding around moving parts can expose operators to serious injuries, while failing to manage noise pollution can result in complaints or fines.
The Solution: Buyers must prioritize safety features when selecting a plastic shredder. This includes looking for machines that are equipped with emergency stop buttons, safety interlocks, and sound-dampening technology. Additionally, it’s advisable to consult with local safety regulations to ensure compliance. Buyers can also implement training programs for operators to educate them about safe handling practices and the proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE). Regular maintenance checks should be scheduled to ensure all safety features are functional, and companies should keep detailed records of compliance to demonstrate adherence to regulations during audits.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Finding the Right Replacement Parts
The Problem: A frequent issue for B2B buyers is the challenge of sourcing replacement parts for their plastic shredders, especially when dealing with older or less common models. This can lead to prolonged downtime and operational delays, as businesses often find it difficult to locate specific parts or face exorbitant shipping costs for international orders. For instance, a company that relies heavily on a single shredder for processing plastic waste may find itself at a standstill when a crucial component fails, impacting productivity and revenue.
The Solution: To mitigate this problem, businesses should proactively source shredders from reputable manufacturers that offer extensive support for parts availability. When purchasing a shredder, buyers should inquire about the longevity of parts supply and whether the manufacturer provides a comprehensive parts catalog. Establishing a relationship with suppliers who are committed to long-term support can also be beneficial. Furthermore, companies can maintain a small inventory of critical spare parts based on their operational needs to avoid unexpected downtimes. Implementing a scheduled maintenance program can help identify potential issues before they lead to equipment failure, ensuring continuous operation and efficiency.

Illustrative image related to plastic shredder
Strategic Material Selection Guide for plastic shredder
What Are the Key Materials for Plastic Shredders?
When selecting materials for plastic shredders, it is essential to consider properties that directly influence performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of plastic shredders, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Steel Perform in Plastic Shredder Applications?
Key Properties: Steel, particularly high-carbon or tool steel, exhibits excellent hardness and tensile strength. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros & Cons: The durability of steel ensures a long lifespan for shredder components, reducing the need for frequent replacements. However, the manufacturing complexity can be high due to the need for precision machining. Additionally, steel is susceptible to corrosion unless treated, which can impact its longevity in humid or wet environments.
Impact on Application: Steel components are compatible with a wide range of plastics, including tougher materials like PET and HDPE. However, the risk of corrosion necessitates careful consideration of the operating environment.

Illustrative image related to plastic shredder
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions such as Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local standards for material quality and safety. In Europe, adherence to ASTM and DIN standards is crucial for market acceptance.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Plastic Shredder Design?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its corrosion resistance and high strength-to-weight ratio. It performs well in environments exposed to moisture and chemicals.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to rust and corrosion, making it ideal for regions with high humidity or where the shredded material may contain contaminants. However, it is more expensive than regular steel, which can increase the overall manufacturing cost.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel’s compatibility with various plastics, including those with chemical additives, makes it suitable for diverse shredding applications. Its durability ensures consistent performance over time.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe may prefer stainless steel due to stringent regulations on material safety and environmental impact. Understanding local compliance requirements is essential for successful procurement.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Plastic Shredders?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and offers good corrosion resistance. It has moderate strength and can be anodized for enhanced durability.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum reduces the overall weight of the shredder, making it easier to transport and install. However, its lower strength compared to steel means it may not be suitable for heavy-duty applications, limiting its use to lighter plastics.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly effective for shredding softer plastics, such as polystyrene and PVC. Its lower strength may lead to wear and tear when handling tougher materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions like South America, where logistics can be challenging, the lightweight properties of aluminum may be advantageous. However, buyers should consider the trade-off between weight and durability when making purchasing decisions.
What About Composite Materials in Plastic Shredder Manufacturing?
Key Properties: Composite materials, such as fiberglass-reinforced plastics, offer a unique combination of strength, lightweight, and corrosion resistance.

Illustrative image related to plastic shredder
Pros & Cons: Composites can be engineered to meet specific performance criteria, making them versatile for various applications. However, they can be more expensive to manufacture and may require specialized processing techniques.
Impact on Application: Composites are suitable for shredding a wide range of plastics, providing flexibility in design and performance. Their resistance to corrosion makes them ideal for humid environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: In markets like Germany, where innovation and advanced materials are prioritized, composites may align well with buyer preferences for cutting-edge technology. Understanding the local market demand for advanced materials can enhance procurement strategies.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Plastic Shredders
| Material | Typical Use Case for plastic shredder | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty shredders for tough plastics | High durability and strength | Susceptible to corrosion | High |
| Stainless Steel | Shredders in humid or chemical-rich environments | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost compared to regular steel | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight shredders for soft plastics | Reduced weight for easy transport | Lower strength limits application | Medium |
| Composite Materials | Versatile applications for various plastics | Customizable performance | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
By carefully evaluating these materials, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements in their respective regions.

Illustrative image related to plastic shredder
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for plastic shredder
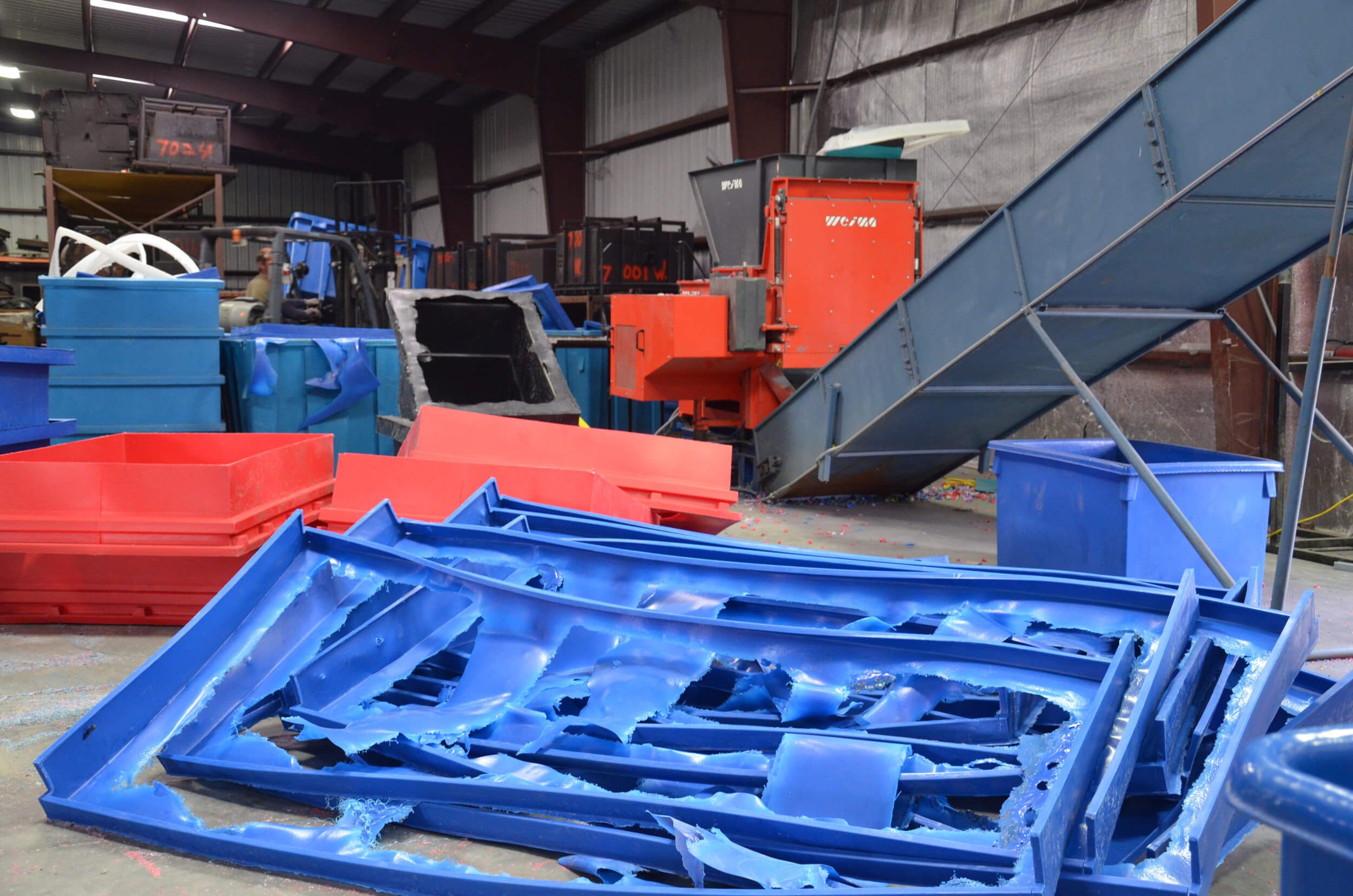
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Plastic Shredders?
The manufacturing process of plastic shredders typically involves several critical stages, each requiring specialized techniques and materials. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers who are looking for quality and reliability in their sourcing decisions.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used and How Are They Processed?
The first stage in manufacturing a plastic shredder involves selecting high-quality raw materials. Common materials include high-grade steel for the blades and chassis, as well as durable plastics for non-load-bearing components.
Once materials are sourced, they undergo a preparation process that includes cutting, shaping, and treating the metals to enhance durability and resistance to wear. Techniques such as laser cutting and CNC machining are often employed to achieve precise specifications that ensure optimal performance of the shredder.
Additionally, suppliers may use heat treatment processes to enhance the hardness of the steel components, which is crucial for maintaining the effectiveness of the shredding blades over time.
How Is the Forming Process Executed in Plastic Shredder Manufacturing?
The forming stage involves creating the various components of the plastic shredder. This typically includes the housing, blades, and any electronic components.
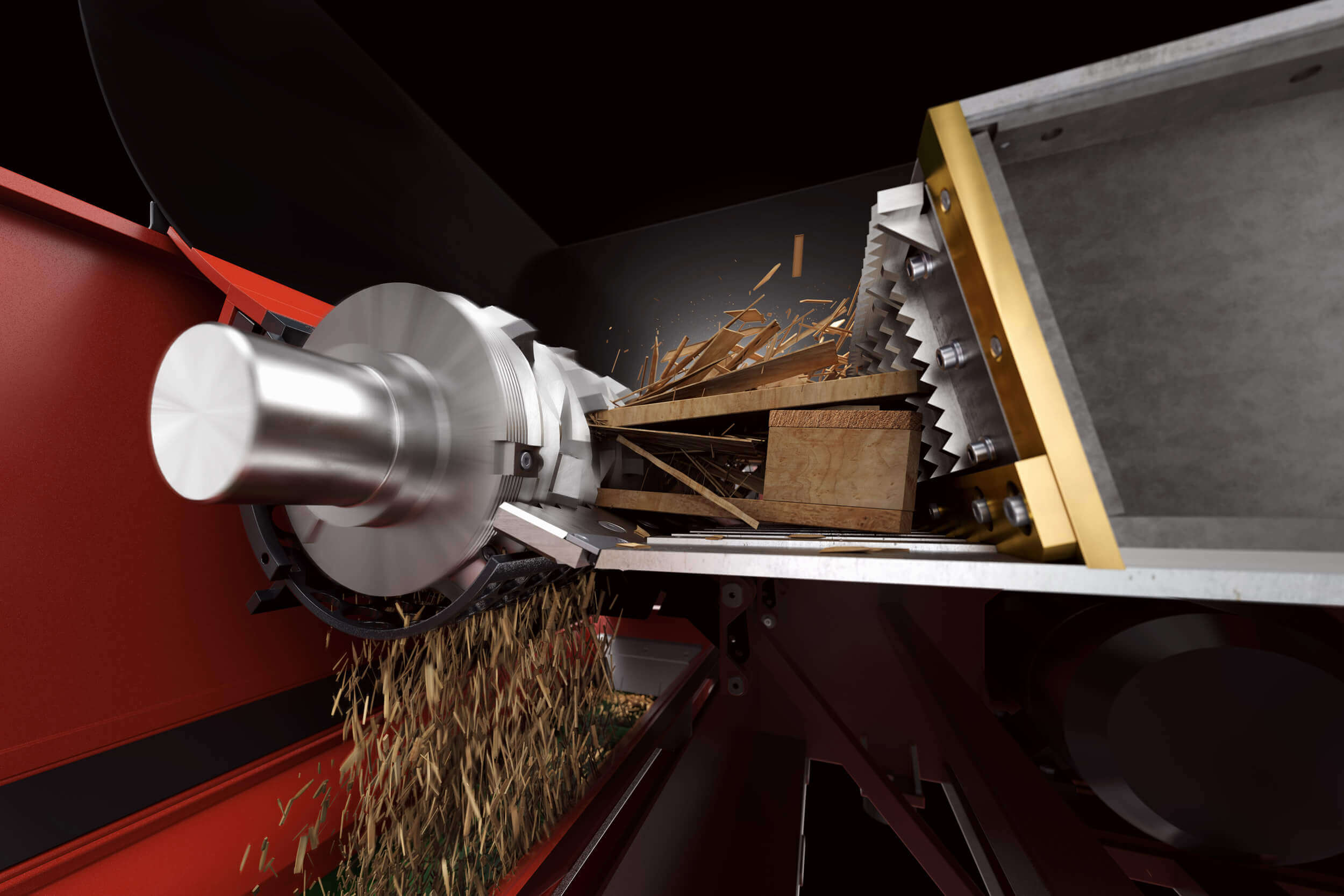

Illustrative image related to plastic shredder
Manufacturers utilize processes such as injection molding for plastic parts and stamping or forging for metal components. For instance, the blades may be forged from high-carbon steel to provide the necessary strength and cutting capability.
Quality control begins at this stage, where initial inspections ensure that components meet design specifications before moving to the assembly phase. This is critical to prevent issues later in the production process.
What Assembly Techniques Are Commonly Used in Plastic Shredder Production?
In the assembly phase, all prepared components are brought together to create the final product. This process often involves both manual labor and automated systems.
Key assembly techniques include the use of precision fasteners, welding, and bonding for securing components. The assembly line is typically organized to facilitate a smooth workflow, ensuring that each component is installed correctly and efficiently.
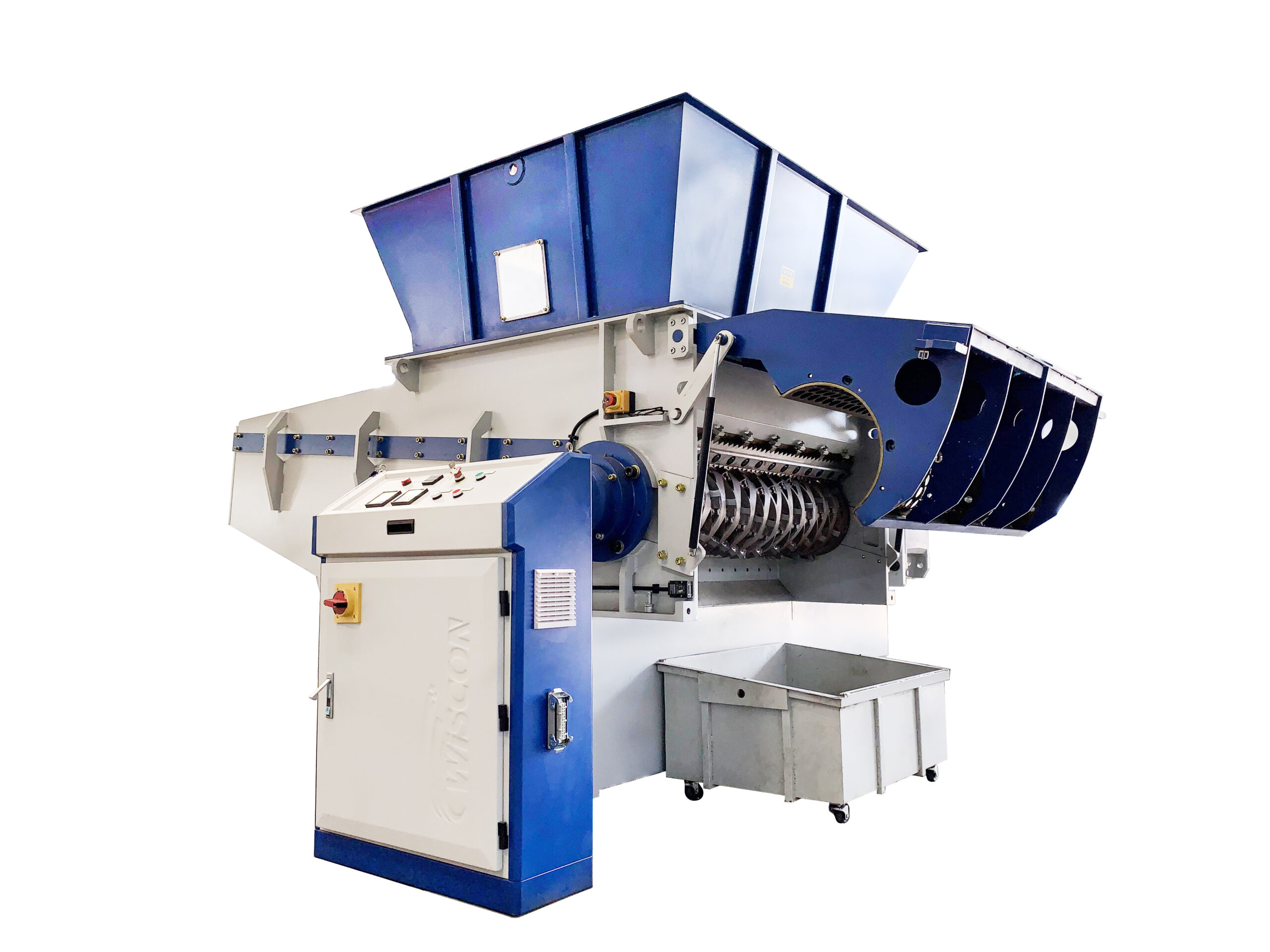

Illustrative image related to plastic shredder
During this phase, manufacturers may implement real-time quality checks to catch any defects or misalignments early on, reducing the likelihood of costly rework later in the production process.
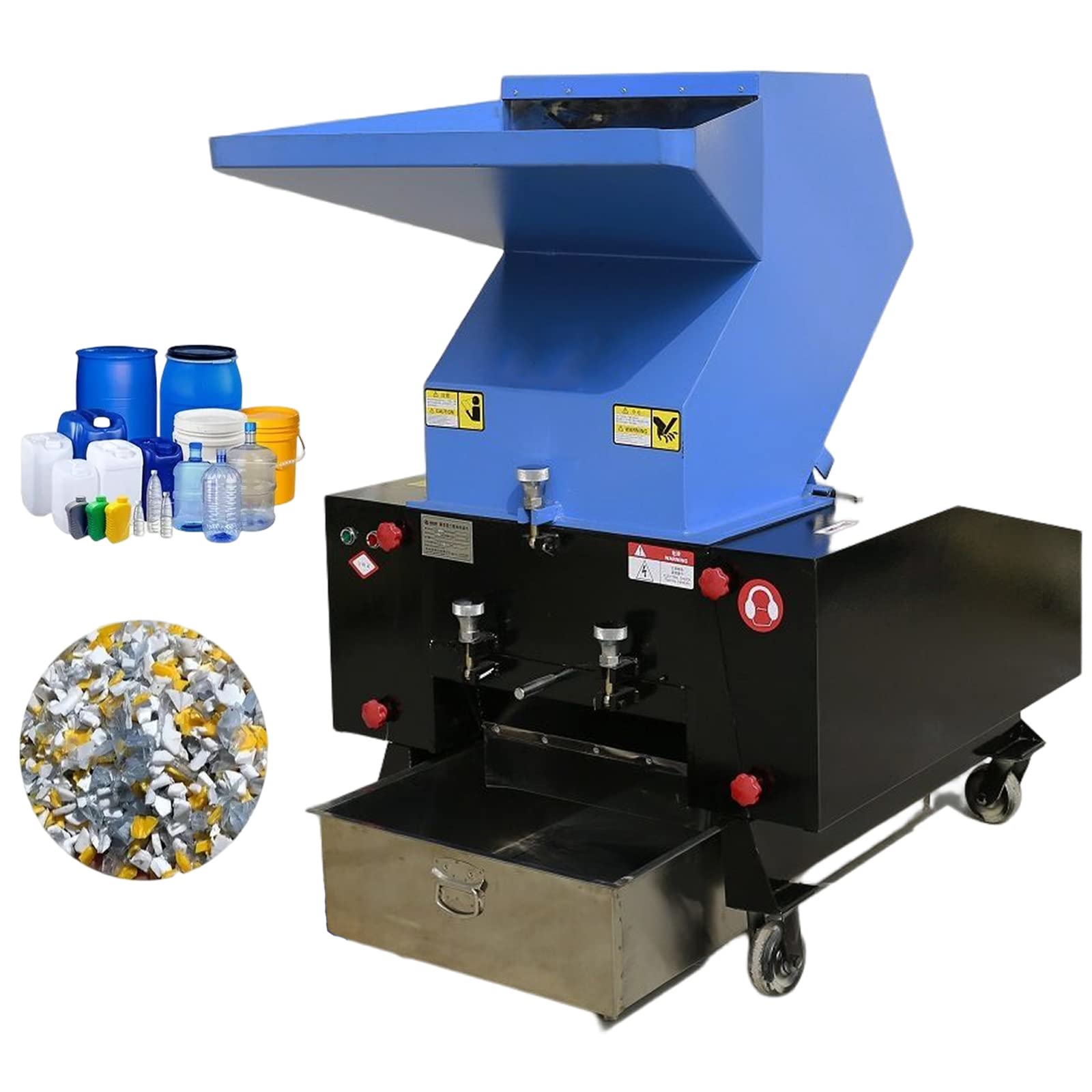
What Finishing Processes Ensure Quality and Durability in Plastic Shredders?
Finishing processes are crucial for enhancing the appearance and longevity of plastic shredders. This stage may include surface treatments such as powder coating, anodizing, or galvanizing to protect against corrosion and wear.
Manufacturers may also apply noise-dampening materials to minimize operational noise, a significant consideration for many industrial buyers.
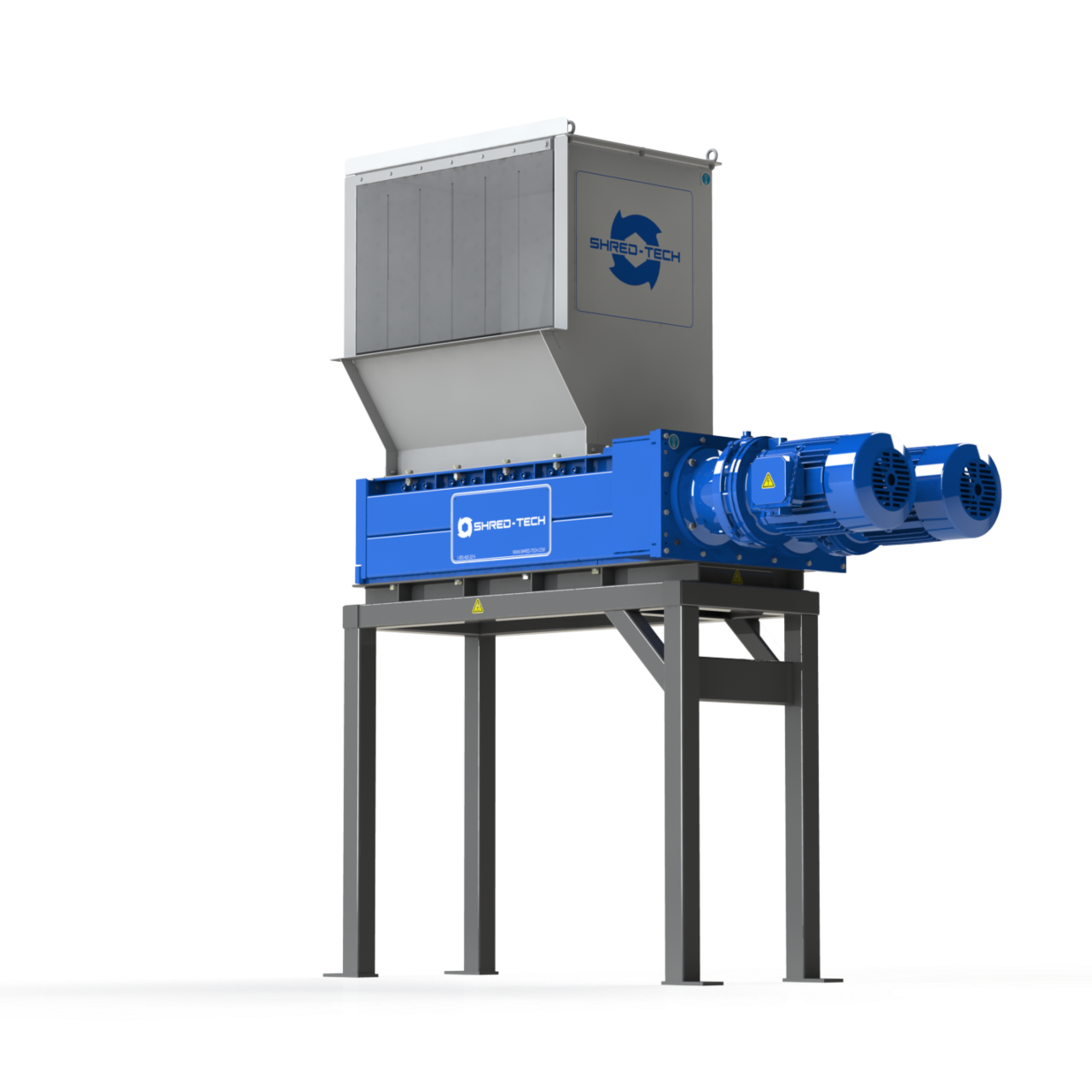
Illustrative image related to plastic shredder
Final inspections are conducted to ensure that the shredder meets all aesthetic and functional specifications. This includes thorough testing of the shredding mechanism and electrical components to confirm they operate smoothly under load.
What International Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Plastic Shredder Manufacturers?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of plastic shredder manufacturing, particularly for international B2B buyers. Adhering to recognized international standards can assure buyers of the product’s reliability and performance.
Which Quality Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Key international quality standards include ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems, and CE marking, which indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Additionally, industry-specific standards such as API (American Petroleum Institute) may apply for shredders used in certain sectors, ensuring that equipment meets rigorous operational criteria.
Buyers should verify that manufacturers are certified by these standards, as this often reflects a commitment to quality and continuous improvement in manufacturing processes.
What Quality Control Checkpoints Should Be Implemented During Production?
Quality control should encompass several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet required specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular checks are conducted to monitor the quality of components and assemblies.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This stage involves comprehensive testing of the finished product to ensure it meets all functional and safety standards before shipping.
Each of these checkpoints is essential for identifying and rectifying potential issues early, thus ensuring that only high-quality products reach the market.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers.
What Steps Can Be Taken to Ensure Supplier Compliance?
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. This can include reviewing their facilities, equipment, and quality control systems.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for quality control reports that detail the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC processes. These documents can help assess the reliability of the supplier’s quality assurance practices.
-
Engaging Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of verification. These independent organizations can perform audits and testing to ensure compliance with international standards.
-
Certifications and Documentation: Buyers should ensure that suppliers possess relevant certifications and maintain proper documentation of their quality control processes, including traceability of materials and components.
What Are the Quality Assurance Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing plastic shredders internationally, buyers must be aware of specific nuances that may affect quality assurance.
How Do Regulatory Differences Impact Quality Assurance?
Regulatory environments can vary significantly across regions. For example, European standards may differ from those in the Middle East or South America.
B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with the specific regulatory requirements applicable to their market. This includes understanding any local certifications that may be necessary for compliance, as well as potential tariffs and trade regulations that could affect the supply chain.
What Should Buyers Consider Regarding After-Sales Support and Warranty?
After-sales support is an essential consideration for B2B buyers. It’s important to inquire about warranty terms and the availability of spare parts, as well as the manufacturer’s capability to provide ongoing support and service.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance standards for plastic shredders can empower B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can ensure they source reliable, high-quality equipment that meets their operational needs.

Illustrative image related to plastic shredder
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘plastic shredder’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in navigating the complexities of procuring plastic shredders. Given the growing demand for efficient recycling solutions across industries, it is essential to approach the sourcing process with a strategic mindset. This checklist will help you make informed decisions, ensuring you choose the right equipment to meet your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical requirements is the first step in sourcing a plastic shredder. Consider factors such as the type of plastic you will be shredding, desired output size, and processing capacity. This will help narrow down your options and ensure the machinery aligns with your production goals.
- Types of Plastics: Identify whether you will process rigid plastics, films, or other materials.
- Output Size: Determine the flake size required for your end product, as this affects the shredder’s design.
Step 2: Research Market Options
Conduct thorough market research to identify potential suppliers and models. Look for manufacturers known for reliability and innovation in shredding technology. Investigate online marketplaces, industry directories, and trade shows to gather information.
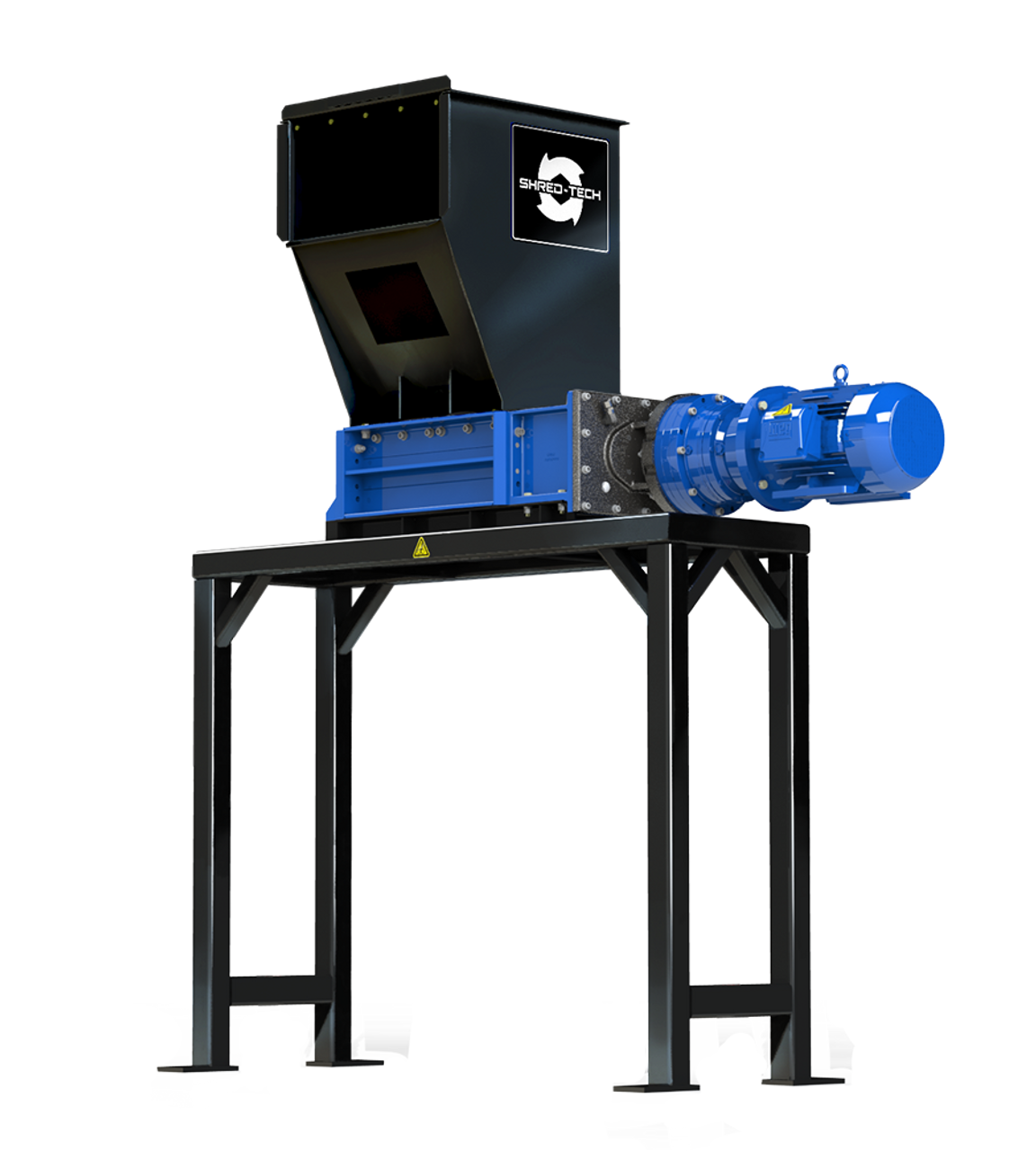
Illustrative image related to plastic shredder
- Supplier Reputation: Focus on established brands with positive reviews and case studies.
- Technology Trends: Stay informed about advancements in shredding technology that can enhance efficiency.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. This step ensures you are dealing with reputable manufacturers capable of delivering quality machinery.
- Quality Assurance: Inquire about certifications and quality control processes.
- Customer Support: Evaluate the level of technical support and after-sales service provided by the supplier.
Step 4: Compare Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers, but don’t focus solely on the initial purchase price. Calculate the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and energy consumption over time.
- Initial Costs vs. Long-term Value: Understand how different models perform in terms of durability and efficiency.
- Hidden Costs: Be aware of potential shipping fees, installation costs, and spare parts pricing.
Step 5: Verify Compliance with Local Regulations
Ensure that the plastic shredder complies with local and international regulations related to safety, emissions, and waste management. This is particularly crucial for buyers in regions with stringent environmental laws.
- Certifications: Look for compliance certifications such as CE marking for European markets or other relevant standards.
- Local Regulations: Consult with local authorities or industry experts to confirm adherence to specific regulations.
Step 6: Request Demonstrations or Trials
Whenever possible, request a demonstration or trial of the plastic shredder. This hands-on experience allows you to assess the machine’s performance, ease of use, and suitability for your specific applications.
- Performance Evaluation: Observe the shredder in action to evaluate speed, efficiency, and output quality.
- User Experience: Consider the machine’s operability and maintenance requirements during the trial.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase and Negotiate Terms
Once you have selected a supplier, it’s time to finalize the purchase. Negotiate terms that align with your budget and operational needs, including payment terms, warranty, and service agreements.

Illustrative image related to plastic shredder
- Contract Clarity: Ensure all terms are clearly defined in the purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings.
- After-Sales Support: Confirm the availability of ongoing support and maintenance services.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the sourcing process for plastic shredders, making informed decisions that align with their business goals and sustainability efforts.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for plastic shredder Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Plastic Shredders?
When sourcing plastic shredders, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The type of materials used for the shredder significantly impacts cost. High-quality steel and durable plastics are common, with prices fluctuating based on global commodity markets. Buyers should consider sourcing from regions with lower raw material costs to enhance their price competitiveness.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely by region. Countries with lower wage structures may offer more competitive pricing but may compromise on quality. It’s essential to evaluate the skill level of laborers involved in the production process, as this directly affects the durability and reliability of the shredder.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses factory utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative costs. Manufacturers often calculate overhead as a percentage of direct costs. Understanding this helps buyers gauge the overall pricing strategy of suppliers.
-
Tooling: The initial setup costs for specialized machinery can be substantial, particularly for custom or high-capacity shredders. This cost is often amortized over larger production runs, making it essential for buyers to understand minimum order quantities (MOQs) to optimize costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the shredder meets international standards requires investment in QC processes. Certifications like ISO or CE can add to the cost but provide assurance of quality, which is particularly valuable for buyers in regulated markets.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the supplier’s location and the buyer’s destination. Understanding Incoterms is vital here, as they dictate who bears the costs and risks during transportation.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing. This can vary based on the supplier’s brand reputation, market demand, and the competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Plastic Shredder Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of plastic shredders, crucial for B2B buyers to consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers are often willing to negotiate better pricing structures for bulk orders, which can lower the overall cost per unit.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized shredders designed for specific types of plastic or production capacities can be more expensive due to the additional engineering and materials required. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unnecessary costs.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: The quality of materials and compliance with industry standards can impact the price. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who provide certifications, as these can mitigate risks associated with inferior products.
-
Supplier Factors: Relationships with suppliers can affect pricing. Long-term partnerships may yield better terms, while new buyers might face higher initial costs. It’s advisable to conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers with a track record of reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping can drastically affect costs. For instance, opting for Delivered Duty Paid (DDP) can simplify logistics for buyers but may come with higher upfront costs. Clear communication about responsibilities in the shipping process can help avoid unexpected expenses.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help Buyers Achieve Cost-Efficiency?
To maximize cost-efficiency in sourcing plastic shredders, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Before negotiations, conduct market research to understand typical pricing and features available. This empowers buyers during discussions and helps establish realistic expectations.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building a rapport with suppliers can lead to better terms. Regular communication and transparency about your business needs can foster trust, potentially leading to improved pricing.
-
Negotiate for Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus not only on the purchase price but also on the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, energy consumption, and operational costs. Suppliers who provide energy-efficient models may justify a higher upfront cost through lower operational expenses.
-
Consider Payment Terms: Flexibility in payment terms can influence pricing. Offering upfront payments may provide leverage for discounts, while longer payment terms might be preferable for cash flow management.
-
Evaluate Shipping Options: Analyze different shipping options and their associated costs. Consolidating shipments or using regional suppliers can significantly reduce logistics expenses.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the intricate cost structure and pricing influences of plastic shredders is essential for international B2B buyers. By strategically navigating these components, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their purchasing efficiency while ensuring quality and reliability in their shredding solutions. Always consider the dynamic nature of pricing and maintain a flexible approach to negotiations to achieve the best outcomes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing plastic shredder With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Plastic Shredders
In the quest for efficient plastic waste management, businesses often seek solutions that balance performance, cost, and operational efficiency. While plastic shredders are a popular choice, various alternative methods and technologies can also effectively process plastic waste. This section will explore these alternatives, providing a comparative analysis that aids B2B buyers in making informed decisions.
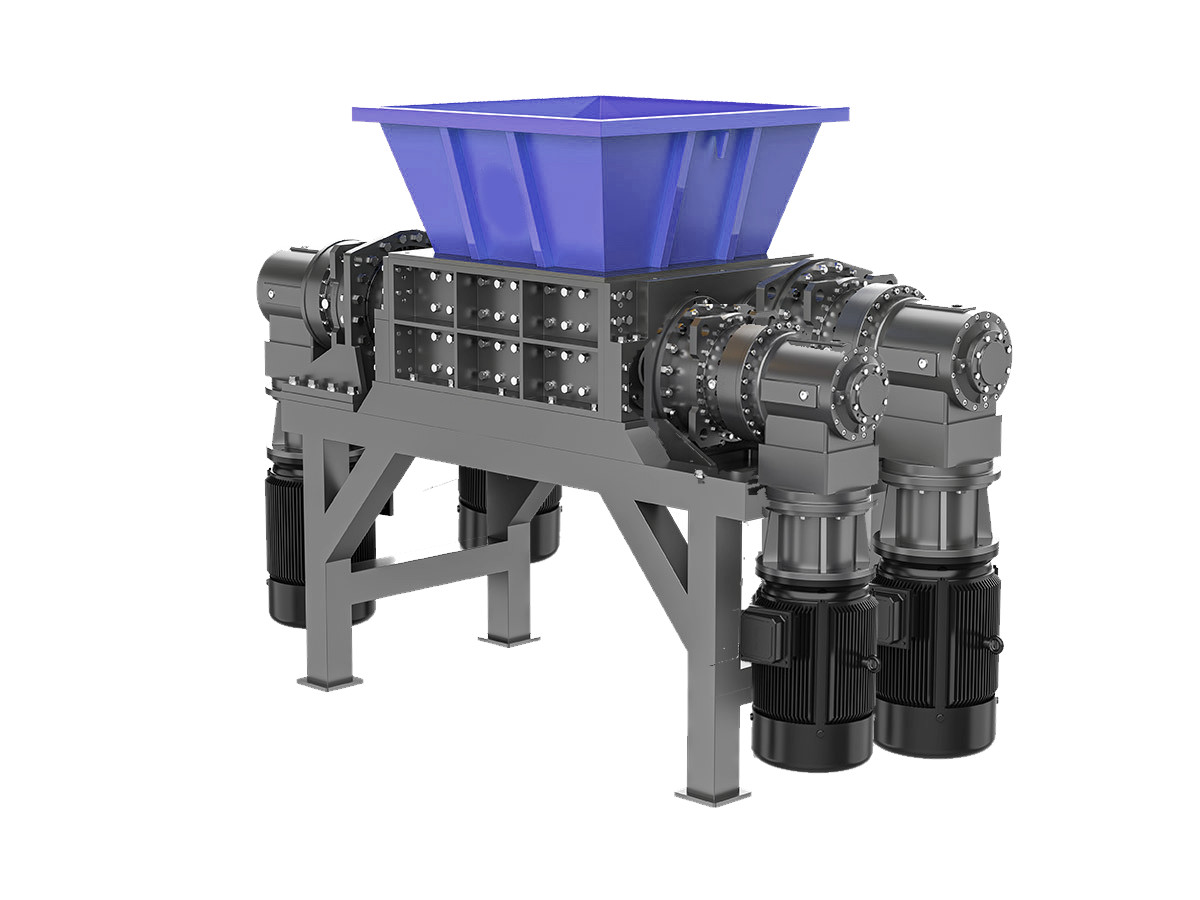

Illustrative image related to plastic shredder
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Plastic Shredder | Granulator | Manual Recycling Techniques |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High throughput, uniform size | High-quality output, versatile | Variable, highly dependent on skill |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Higher initial investment | Low-cost, but labor-intensive |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires setup and training | Requires technical expertise | Simple tools, minimal setup |
| Maintenance | Moderate upkeep | High maintenance needed | Minimal maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Large-scale recycling operations | Versatile for mixed plastics | Small-scale or artisanal projects |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Granulator
Granulators are machines designed to reduce plastic waste into smaller pieces, providing a fine output that can be used for various applications. They typically offer high performance and versatility, capable of processing different types of plastics, including rigid and flexible materials. However, the initial investment for a granulator is generally higher than that for a plastic shredder. Additionally, they require more technical expertise for setup and maintenance, making them less accessible for smaller businesses. Granulators excel in large-scale operations where the quality of the output is crucial, such as in the production of recycled plastic products.
Manual Recycling Techniques
Manual recycling techniques encompass a range of low-cost methods that individuals or small businesses can employ to process plastic waste. This can include using simple tools to cut, melt, or reshape plastic materials. While these methods are cost-effective and require minimal investment, they are highly dependent on the skill and experience of the operator. The performance can vary significantly, making it less reliable for consistent results. These techniques are ideal for small-scale operations or artisanal projects, where the focus is on craftsmanship rather than high throughput. However, the labor-intensive nature can be a drawback for businesses looking to scale their operations.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a solution for plastic waste management, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and desired output quality. Plastic shredders provide a robust solution for large-scale recycling operations, offering high performance and uniformity. In contrast, granulators may be better suited for businesses requiring versatility and high-quality outputs, albeit at a higher cost. Meanwhile, manual recycling techniques present an accessible option for smaller enterprises focused on artisanal production. Evaluating these factors will empower buyers to choose the most suitable method for their unique operational context.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for plastic shredder
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Plastic Shredders?
Understanding the technical specifications of plastic shredders is crucial for B2B buyers looking to invest in equipment that meets their operational needs. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material grade of the shredder’s components, especially the blades and housing, is critical. High-quality steel or hardened alloys are preferred for durability and resistance to wear. This is important for maintaining performance and reducing replacement costs, making it essential for buyers to assess the longevity of the shredder. -
Flake Size
Flake size refers to the dimensions of the shredded plastic pieces. Common specifications include small (0-7 mm) and medium (0-10 mm). The desired flake size impacts the downstream processing methods, such as extrusion or injection molding. Buyers should choose a shredder that aligns with their recycling process to maximize efficiency. -
Power Rating
The power rating, measured in kilowatts (kW), indicates the motor’s capability to handle different types of plastics. A higher power rating typically translates to better performance, particularly for tougher materials. For B2B buyers, understanding the power requirements is essential for ensuring compatibility with existing electrical systems and assessing operational costs. -
Throughput Capacity
This specification denotes the amount of material the shredder can process in a given time frame, usually expressed in kilograms per hour (kg/h). High throughput is vital for businesses that handle large volumes of plastic waste, ensuring that operations remain efficient and cost-effective. -
Voltage and Frequency
Different regions operate on varying voltage levels (e.g., 110V, 220V) and frequencies (50 Hz, 60 Hz). Buyers must ensure that the shredder’s electrical specifications match their local standards to avoid operational issues. This is particularly important for international buyers who may face compatibility challenges. -
Safety Features
Safety features such as emergency stop buttons, protective covers, and automatic shut-off mechanisms are essential for preventing accidents. Investing in shredders with robust safety features can protect workers and reduce liability, making this a critical aspect for responsible B2B purchasing.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Plastic Shredder Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology helps facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are some common terms used in the plastic shredder market:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another company. In the context of plastic shredders, buyers often source OEM parts for maintenance or upgrades, ensuring compatibility and performance consistency. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers, especially those looking to manage inventory costs effectively. Low MOQs may be beneficial for smaller companies or startups. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent by buyers to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. This is an essential step in the procurement process, enabling buyers to compare offers and negotiate better deals. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand their obligations and avoid unexpected costs. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO encompasses all costs associated with purchasing and operating a shredder, including initial purchase price, maintenance, energy consumption, and disposal costs. This holistic view is vital for B2B buyers to assess the long-term financial impact of their investment. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the duration from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for operational planning, especially in industries where timely waste processing is critical.
By grasping these technical specifications and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when investing in plastic shredders, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the plastic shredder Sector
What Are the Key Trends Influencing the Global Plastic Shredder Market?
The plastic shredder market is experiencing significant transformations driven by various global factors. An increasing emphasis on sustainability and recycling is reshaping consumer and industrial behaviors, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Countries are instituting stricter regulations on plastic waste management, prompting businesses to invest in efficient shredding technologies. This shift not only aids in compliance but also enhances corporate responsibility narratives.
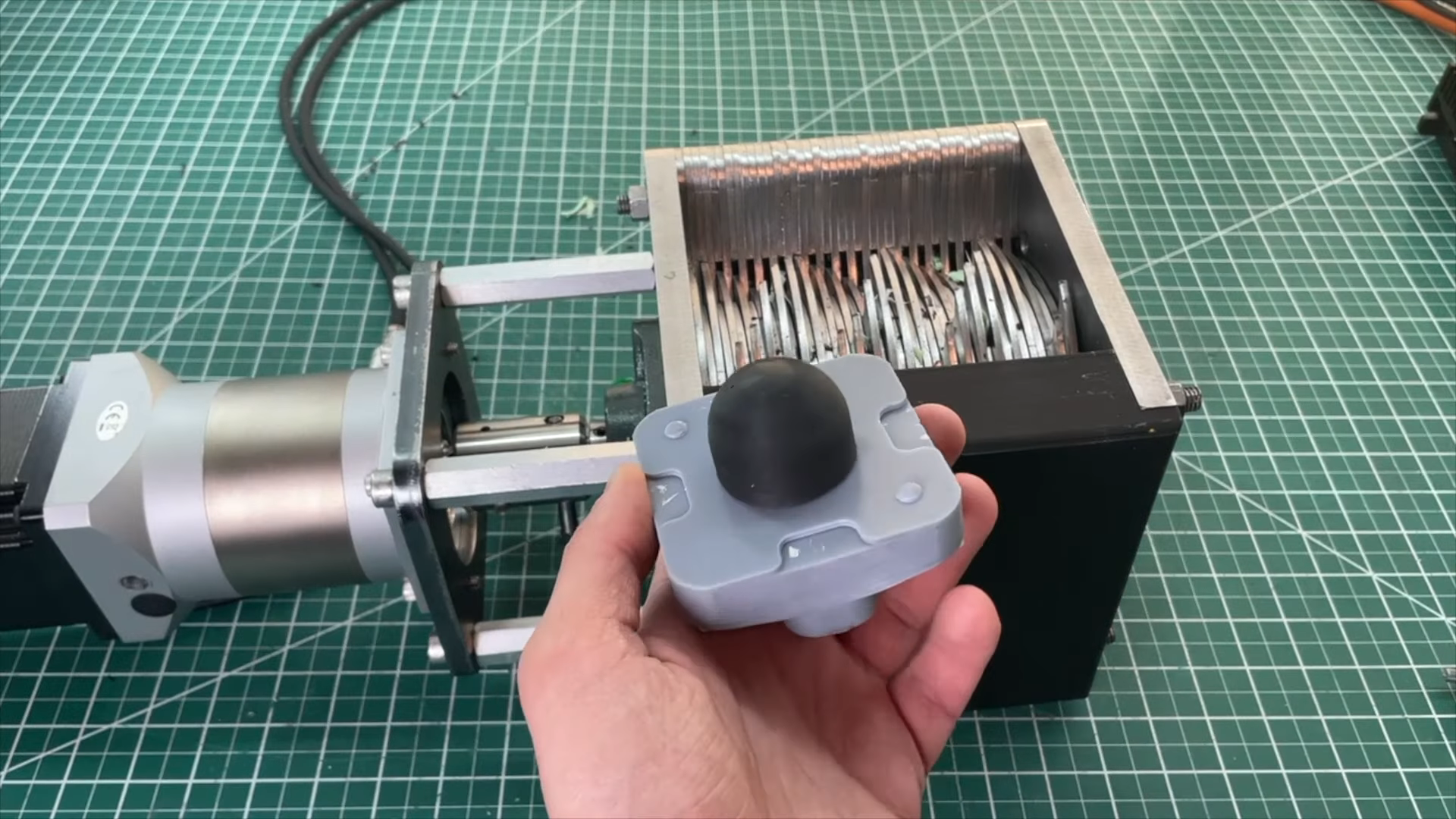

Illustrative image related to plastic shredder
Emerging technologies such as IoT-enabled shredders are gaining traction, allowing for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. These innovations help businesses optimize operational efficiency and reduce downtime, which is crucial for B2B buyers looking for reliability in their machinery. Furthermore, the trend toward modular and customizable shredders is on the rise. Companies are increasingly seeking solutions that can be tailored to specific waste types and operational requirements, making them more versatile and cost-effective over time.
The competitive landscape is also evolving, with new entrants offering affordable, DIY shredding solutions alongside established manufacturers. This diversification allows international buyers to choose from a broader range of options, accommodating varying budgets and specifications. As the market continues to grow, understanding these dynamics will be essential for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Plastic Shredders?
Sustainability has become a central theme in the procurement of plastic shredders. The environmental impact of plastic waste is prompting organizations to prioritize equipment that not only processes materials efficiently but also aligns with eco-friendly practices. Buyers are increasingly looking for shredders that minimize energy consumption and are made from recyclable or sustainably sourced materials.
Ethical sourcing is critical, as companies face pressure to ensure their supply chains are transparent and responsible. This includes verifying that components are sourced from suppliers that adhere to environmental and labor standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems or adherence to the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) can serve as benchmarks for potential suppliers.
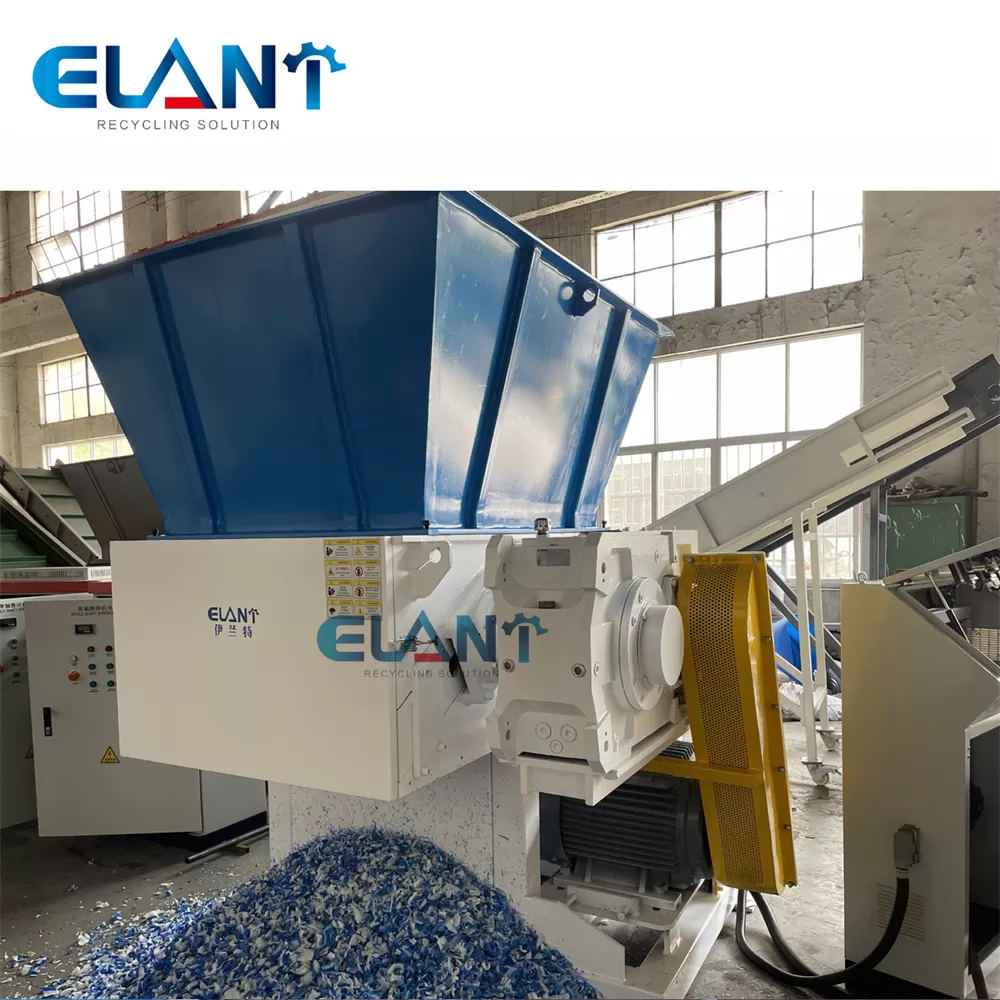

Illustrative image related to plastic shredder
Moreover, the demand for ‘green’ certifications for shredding equipment is on the rise. These certifications indicate that the machinery is designed with a focus on reducing carbon footprints and promoting recycling. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through their manufacturing processes, materials, and operational practices.
What Is the Historical Context of Plastic Shredders in the B2B Market?
The evolution of plastic shredders can be traced back to the early days of waste management technology. Initially, these machines were simple mechanical devices designed for basic shredding tasks. Over time, as awareness of environmental issues grew and recycling became a necessity, the technology advanced significantly.
In the late 20th century, the introduction of electric and hydraulic systems transformed shredders into more efficient and powerful machines capable of handling a variety of materials. The advent of computer-controlled systems in the 21st century further enhanced performance, allowing for precise operations and improved safety features.
Today, plastic shredders are integral to waste management strategies, not only in industrial settings but also in smaller-scale operations, such as community recycling programs. The ongoing advancements in technology and materials continue to influence their design and functionality, making them indispensable tools for businesses committed to sustainability and efficiency in waste processing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of plastic shredder
-
How do I select the right plastic shredder for my business needs?
Choosing the right plastic shredder involves assessing your specific processing requirements. Consider the type of plastic waste you will be shredding, the desired particle size, and the volume of material to be processed. Additionally, evaluate the shredder’s power, efficiency, and durability. Research various models, read reviews, and consult with suppliers to understand which machine aligns best with your operational goals and budget. -
What are the key features to look for in a plastic shredder?
Key features to consider include the shredder’s blade configuration, motor power, and safety mechanisms. Look for adjustable settings that allow you to customize shred size, as well as ease of maintenance and parts availability. Additionally, consider the machine’s energy efficiency and noise levels, especially if it will be used in a workplace setting. A robust warranty and reliable customer support from the manufacturer are also essential. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for plastic shredders?
Minimum order quantities for plastic shredders can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the specific model. Some suppliers may offer single units, while others might require bulk orders. It’s crucial to communicate with potential suppliers to clarify their MOQ policies, especially if you are looking to negotiate pricing or explore customization options. Understanding the MOQ can help you plan your procurement budget effectively. -
How can I verify the credibility of a plastic shredder supplier?
To verify a supplier’s credibility, conduct thorough research by checking their business licenses, certifications, and customer reviews. Request references from previous clients and inquire about their experience with the supplier. Additionally, consider their industry reputation, years of operation, and whether they participate in relevant trade shows or associations. Engaging in direct communication can also provide insights into their professionalism and responsiveness. -
What payment terms are typically available when purchasing plastic shredders?
Payment terms for plastic shredders can differ among suppliers but often include options like advance payment, net 30/60 days, or payment upon delivery. Some manufacturers may offer financing options or installment plans, especially for larger orders. It’s essential to discuss and negotiate payment terms upfront to ensure they align with your cash flow and budgeting needs. -
What is the typical lead time for shipping plastic shredders internationally?
Lead times for international shipping of plastic shredders depend on several factors, including the supplier’s location, production capacity, and shipping method. Generally, lead times can range from a few weeks to several months. It’s advisable to request a shipping timeline from your supplier and factor in customs clearance and potential delays. Establishing clear communication regarding delivery expectations is crucial for effective planning. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for my plastic shredder?
Quality assurance can be ensured by selecting suppliers who adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO certifications. Request detailed specifications and test reports for the shredders you are considering. Additionally, it may be beneficial to conduct a factory audit or request a sample unit to evaluate performance before making a bulk purchase. Establishing a clear agreement on quality expectations in your purchase contract can further safeguard your investment. -
What are the options for customizing plastic shredders?
Customization options for plastic shredders can include variations in blade design, size specifications, and additional features such as automated controls or safety enhancements. Many manufacturers are open to tailoring their products to meet specific operational needs. When discussing customization, provide detailed requirements and be prepared to collaborate closely with the supplier. This may involve additional costs and extended lead times, so plan accordingly.
Top 4 Plastic Shredder Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Instructables – $50 Plastic Shredder
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: $50 Plastic Shredder / Grinder / Recycler; Designed for DIY community and 3D printing enthusiasts; Utilizes a cross-cut paper shredder mechanism; Requires a powerful motor and metal gear drive; Recommended shredder: AmazonBasics 12-Sheet Cross-Cut Shredder; Additional tools needed: PH screwdriver, basic electrical tools, saw or drill; Project completion time: approximately 48 hours; Key steps incl…
2. WEIMA – WLK 800 & WLK 15 Shredders
Domain: weima.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: WEIMA offers a range of industrial plastic shredders and granulators designed for efficient plastic recycling. Key products include: 1. WLK 800 Single-shaft shredder – Economical compact machine with conveyor belt cut-out. 2. WLK 15 Single-shaft shredder – Best all-around with lift-up screen basket. 3. WLK 18 J Single-shaft shredder – Highly productive with a 500 mm rotor diameter. 4. WKS 2200 Sin…
3. Shred-Tech® – High-Torque Plastic Shredders
Domain: shred-tech.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Shred-Tech® offers a range of high-torque dual- and four-shaft plastic shredders designed for plastic recycling. These shredders can handle various plastic materials including large molded items, purgings, engineered plastics, and film, reducing them to reusable scraps for further granulation. Key models include: ST-15, ST-25, ST-35, ST-50, ST-75, ST-100, ST-300, ST-400, ST-480, ST-700, ST-1200, a…
4. Sustainable Design – Shredder Mini V2
Domain: sustainabledesign.studio
Introduction: {“name”: “Shredder Mini V2”, “price”: “from £200.00”, “description”: “The new Shredder Mini V2 boasts a refined design to serve as an efficient, cost-effective solution for small-scale plastic recycling. Suitable for workshops, schools, or on-the-go use.”, “configurations”: [“Box Only”, “Box with Table Mount”, “Box with Painted Table Mount”], “key_features”: {“High-Quality Construction”: “Made wit…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for plastic shredder
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of plastic shredders is critical for businesses looking to enhance their recycling capabilities and reduce operational costs. By understanding the diverse range of machines available—from DIY solutions to advanced commercial models—international buyers can make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs. Key considerations include the shredder’s capacity, efficiency, and adaptability to different types of plastics, which are essential for maximizing return on investment.
Moreover, sourcing from reliable manufacturers not only ensures quality but also fosters long-term partnerships that can lead to better pricing and service agreements. As global demand for sustainable practices continues to rise, the importance of integrating efficient plastic shredding solutions into operational frameworks cannot be overstated.
Looking ahead, businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are encouraged to explore the latest innovations in plastic shredding technology. By investing in these solutions today, companies can position themselves as leaders in sustainability and environmental stewardship. Now is the time to take action—evaluate your sourcing strategy and unlock the potential of plastic shredders to transform waste into valuable resources.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
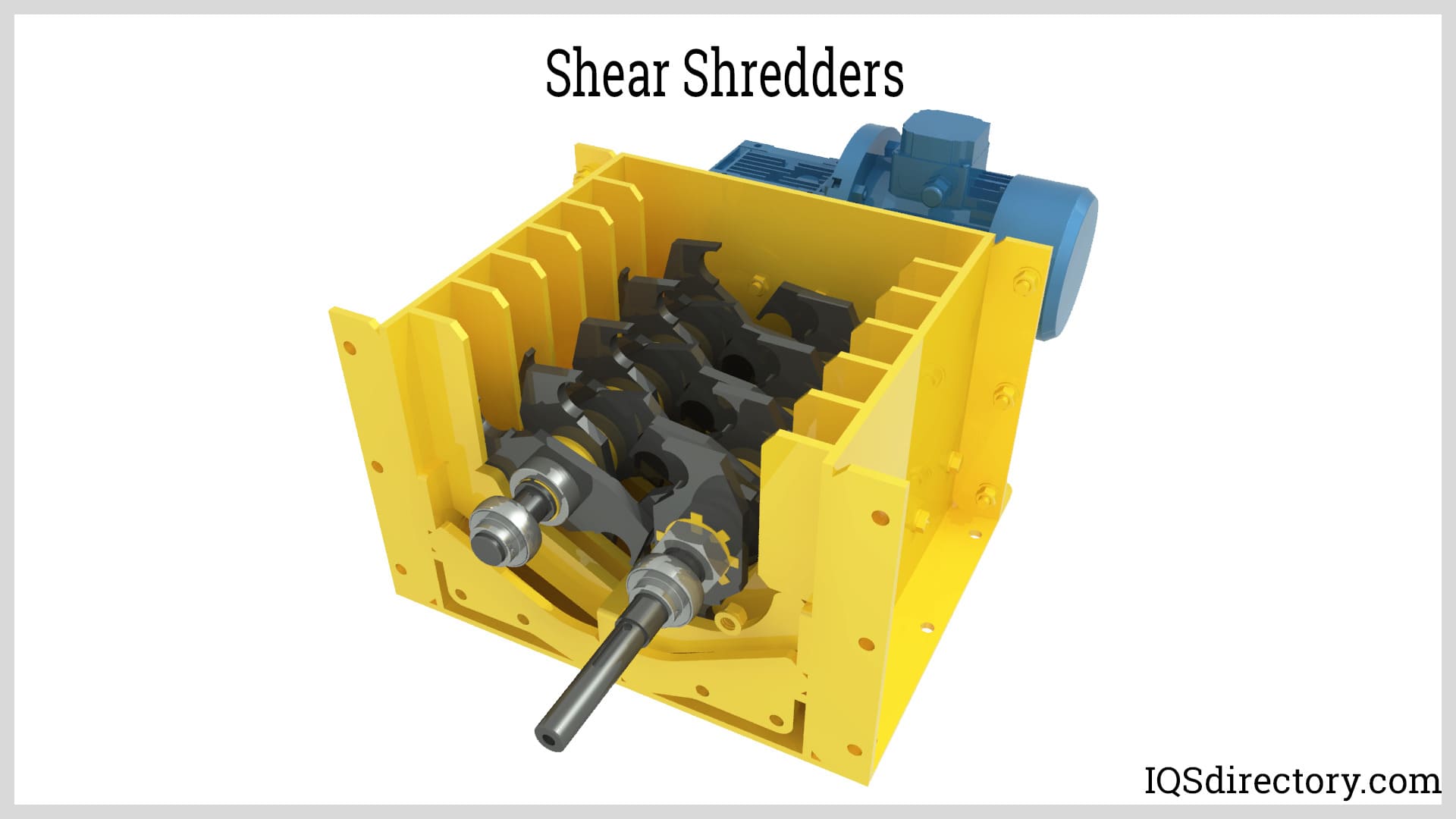

Illustrative image related to plastic shredder
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.