A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Grades Of Aluminum Tubing: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for grades of aluminum tubing
In an increasingly interconnected world, sourcing the right grades of aluminum tubing can present significant challenges for international B2B buyers. With diverse applications ranging from aerospace to construction, understanding the nuances of aluminum alloys like 6061, 5052, and 2024 is crucial for making informed decisions. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, addressing the complexities of selecting the appropriate aluminum tubing based on specific application requirements, mechanical properties, and environmental considerations.
As you navigate this global market, you will discover detailed insights into various aluminum grades, their unique characteristics, and the industries they best serve. Additionally, we will explore supplier vetting processes, cost analysis, and logistical considerations that are particularly relevant for buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Nigeria and Germany. By empowering you with this knowledge, our guide aims to streamline your purchasing process and enhance your ability to select high-quality aluminum tubing that meets your operational needs.
Whether you are involved in manufacturing, construction, or any other sector that relies on aluminum products, this guide is designed to facilitate smarter sourcing decisions and ultimately improve your bottom line. Let’s embark on this journey to ensure that your aluminum tubing requirements are met with precision and confidence.
Understanding grades of aluminum tubing Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6061 | Versatile, good corrosion resistance, weldable | Automotive, marine, structural components | Pros: Excellent machinability, good strength-to-weight ratio. Cons: Lower strength compared to some other alloys. |
| 5052 | Highest strength among non-heat-treatable grades | Marine applications, automotive, heavy-duty cooking utensils | Pros: Superior corrosion resistance, good workability. Cons: Less weld-friendly than some alternatives. |
| 2024 | High strength, fatigue resistant, copper-based | Aerospace, transportation, structural components | Pros: Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. Cons: Prone to corrosion; requires protective coatings. |
| 3003 | Commercially pure, good workability, corrosion-resistant | Chemical and food processing, general fabrication | Pros: Excellent forming capabilities, good corrosion resistance. Cons: Lower strength compared to heat-treatable grades. |
| 7075 | One of the highest strength aluminum alloys | Aerospace, military applications, high-stress components | Pros: Excellent strength-to-weight ratio. Cons: More expensive and less corrosion-resistant. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of 6061 Aluminum Tubing for B2B Buyers?
6061 aluminum tubing is renowned for its versatility and excellent corrosion resistance, making it a preferred choice for various applications. This alloy is easily weldable and can be fabricated into intricate shapes, which is particularly beneficial for automotive and marine industries. When considering 6061, buyers should evaluate their specific needs regarding strength and weight, as it offers a good balance but may not be the strongest option available.
How Does 5052 Aluminum Tubing Stand Out in Marine Applications?
5052 aluminum tubing is recognized for its superior strength among non-heat-treatable grades, particularly in marine environments where corrosion resistance is paramount. Its ability to withstand saltwater exposure makes it ideal for shipbuilding and marine components. B2B buyers should consider 5052 for applications requiring durability and resistance to harsh conditions, though they should be mindful of its welding limitations compared to other alloys.
Why Choose 2024 Aluminum Tubing for Aerospace and Transportation?
2024 aluminum tubing is distinguished by its high strength and fatigue resistance, making it particularly suitable for aerospace and transportation applications. This copper-based alloy is often used where a high strength-to-weight ratio is critical. However, B2B buyers should be aware of its susceptibility to corrosion and may need to invest in protective coatings to ensure longevity in demanding environments.

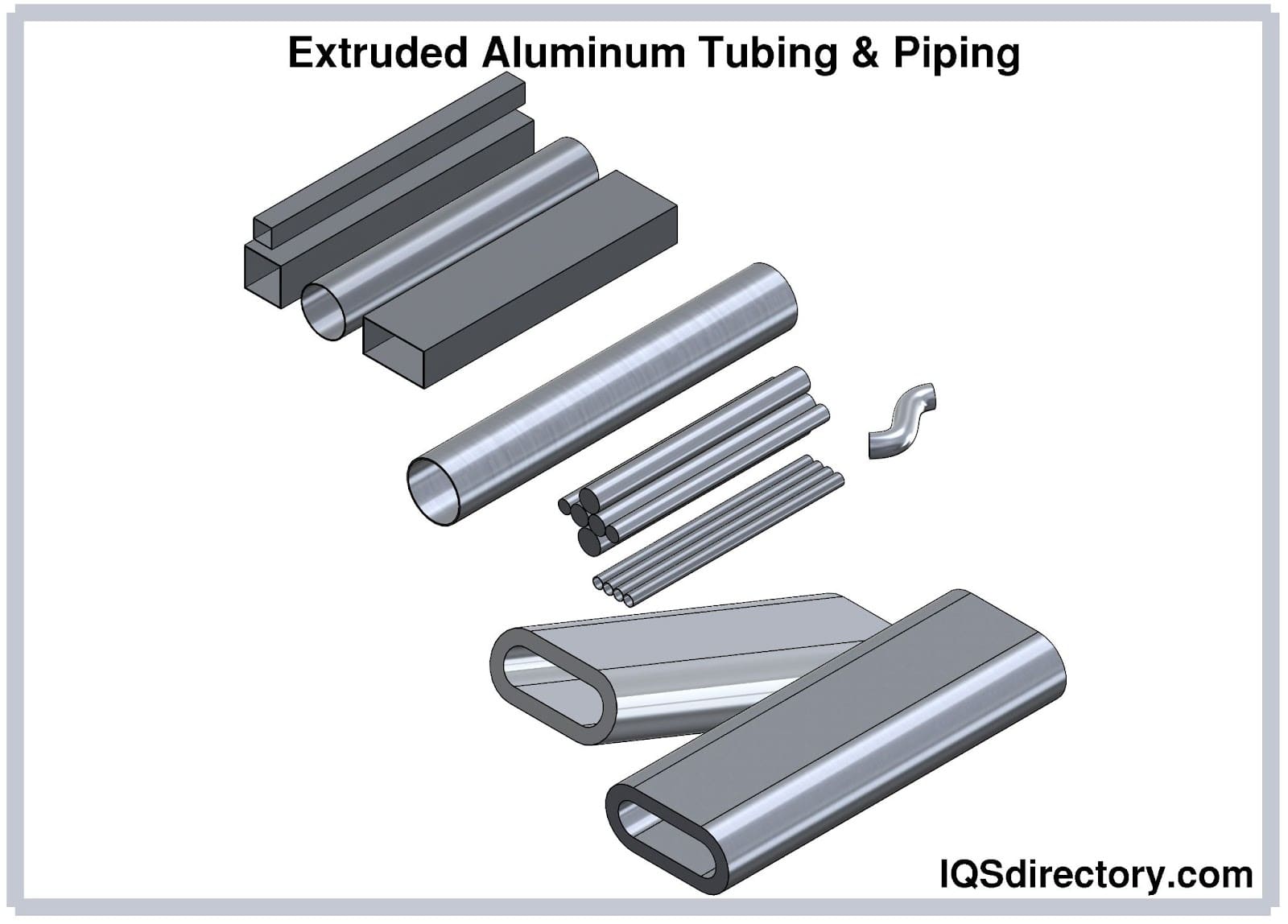
Illustrative image related to grades of aluminum tubing
What are the Key Benefits of 3003 Aluminum Tubing for General Fabrication?
3003 aluminum tubing is a commercially pure alloy that offers excellent workability and corrosion resistance, making it a popular choice in the chemical and food processing industries. Its ability to be deep drawn or spun makes it ideal for complex shapes. Buyers should consider 3003 for applications where aesthetics and ease of fabrication are priorities, although its strength is lower than heat-treatable options.
In What Situations is 7075 Aluminum Tubing the Best Option for B2B Buyers?
7075 aluminum tubing is one of the strongest aluminum alloys available, making it ideal for high-stress applications in aerospace and military sectors. Its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio allows for lighter designs without compromising structural integrity. However, B2B buyers should weigh the higher cost and lower corrosion resistance against their specific needs, especially if the application involves exposure to harsh environments.
Key Industrial Applications of grades of aluminum tubing
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of grades of aluminum tubing | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Structural components for aircraft | High strength-to-weight ratio ensures fuel efficiency and safety | Compliance with stringent aerospace standards and certifications |
| Marine | Boat hulls and fittings | Corrosion resistance enhances durability in harsh environments | Sourcing from suppliers with marine-grade certifications |
| Automotive | Chassis and frame components | Lightweight materials improve fuel efficiency and performance | Need for precision machining and welding capabilities |
| Construction | Architectural frameworks and supports | Provides strength and aesthetic appeal for modern designs | Availability of various shapes and finishes for customization |
| Electronics | Enclosures and heat sinks for electronic devices | Excellent thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance | Ensure compatibility with specific electronic components |
How is Aluminum Tubing Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, grades of aluminum tubing are critical for manufacturing structural components such as fuselages and wing supports. The lightweight nature of aluminum helps enhance fuel efficiency, while its high strength ensures safety and compliance with rigorous aviation standards. Buyers in this sector, especially from regions like Europe and the Middle East, must prioritize suppliers who meet international aerospace certifications and quality standards to ensure reliability and performance.
What Role Does Aluminum Tubing Play in Marine Applications?
Aluminum tubing is extensively used in the marine industry for constructing boat hulls, railings, and fittings due to its exceptional resistance to saltwater corrosion. This durability translates to longer-lasting products, reducing maintenance costs for businesses. For international buyers, especially in South America and Africa, sourcing aluminum from suppliers with marine-grade certifications is essential to ensure compliance with local maritime regulations and standards.
How is Aluminum Tubing Beneficial in Automotive Manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, aluminum tubing is utilized for chassis and frame components, contributing to overall vehicle weight reduction. This leads to improved fuel efficiency and enhanced performance, which are critical factors in today’s competitive automotive market. Buyers in this sector should consider the specific mechanical properties required for their applications, ensuring that suppliers can provide tubing that meets stringent automotive industry standards.
Illustrative image related to grades of aluminum tubing
Why is Aluminum Tubing Important for Construction Projects?
Aluminum tubing plays a significant role in modern construction, particularly for architectural frameworks and structural supports. Its combination of strength and lightweight characteristics allows for innovative designs while maintaining safety and stability. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should seek suppliers that offer a diverse range of profiles and finishes to meet the aesthetic and functional requirements of contemporary construction projects.
How is Aluminum Tubing Used in Electronics?
In the electronics sector, aluminum tubing is commonly used to create enclosures and heat sinks for various devices. Its excellent thermal conductivity helps dissipate heat effectively, ensuring the longevity and performance of electronic components. International buyers, particularly from Africa and South America, must ensure that their suppliers can provide aluminum tubing that meets specific electronic standards and is compatible with their product designs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘grades of aluminum tubing’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding the Right Aluminum Grade for Your Application
The Problem: B2B buyers often face confusion when selecting the appropriate grade of aluminum tubing for their specific applications. With numerous grades available, such as 6061, 5052, and 2024, the nuances in mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and suitability for welding can overwhelm purchasing teams. For instance, a buyer in the aerospace sector may need to choose between 2024 and 6061, where the former offers superior strength but is more prone to corrosion. This indecision can lead to delays in project timelines and increased costs due to miscalculations in material selection.
The Solution: To effectively address this challenge, B2B buyers should start by conducting a comprehensive needs assessment for their projects. This involves evaluating the mechanical requirements, environmental factors, and any specific regulations that may apply to their industry. After gathering this information, consult with suppliers who can provide detailed technical data sheets for each aluminum grade. Engage in discussions to understand the pros and cons of each option. Additionally, consider using sample pieces for testing before making bulk purchases. This hands-on approach not only ensures that the selected grade meets performance criteria but also builds a collaborative relationship with suppliers, facilitating easier adjustments in the future.
Scenario 2: Managing Corrosion Resistance Concerns in Marine Applications
The Problem: In marine applications, corrosion resistance is paramount due to the harsh saltwater environment. Buyers may choose a grade like 5052, known for its excellent resistance to saltwater, but if not properly specified or treated, even this grade can fail prematurely. For example, a company manufacturing marine equipment may encounter significant warranty claims and customer dissatisfaction due to corrosion-related failures, leading to increased operational costs and damage to their reputation.

Illustrative image related to grades of aluminum tubing
The Solution: To mitigate corrosion risks, buyers should not only select the appropriate aluminum grade but also ensure that the tubing is adequately treated or coated. Anodizing or applying a protective coating can enhance the corrosion resistance of aluminum, especially in marine environments. Furthermore, it is crucial to work with suppliers who understand the specific needs of marine applications and can provide guidance on additional treatments. Consider implementing a maintenance plan that includes regular inspections of aluminum components to detect early signs of corrosion and address them proactively. This approach not only extends the lifespan of the materials but also reinforces the company’s commitment to quality and safety.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compliance with International Standards
The Problem: For international buyers, ensuring that the aluminum tubing they source complies with various regional standards can be a significant pain point. Different countries may have specific regulations regarding material properties, certifications, and testing methods. A buyer in South America, for instance, may face challenges when trying to source aluminum tubing that meets both local and European standards, leading to potential project delays and regulatory fines.
The Solution: To navigate this complexity, buyers should familiarize themselves with the relevant standards in both their home country and the countries they wish to export to. Engaging with suppliers who are knowledgeable about international standards is crucial. They can provide documentation and certifications that prove compliance with necessary regulations. Additionally, consider working with a logistics partner who specializes in international trade to ensure that all shipping and customs documentation is in order. This proactive strategy not only streamlines the sourcing process but also mitigates the risk of non-compliance, allowing for smoother operations and market entry.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for grades of aluminum tubing
What Are the Key Properties of Common Aluminum Tubing Grades for B2B Buyers?
When selecting aluminum tubing for industrial applications, understanding the properties of different grades is crucial. Here, we analyze several commonly used grades—6061, 5052, 2024, and 3003—focusing on their key properties, pros and cons, application impacts, and considerations for international buyers.
How Does 6061 Aluminum Tubing Perform in Various Applications?
6061 aluminum is often considered the most versatile aluminum alloy due to its excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. It can withstand moderate to high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for a variety of applications, including structural components and marine fittings. Its weldability and ease of fabrication are significant advantages, allowing for complex shapes and designs.
Illustrative image related to grades of aluminum tubing
Pros: High strength-to-weight ratio, good corrosion resistance, and ease of fabrication make it ideal for diverse applications.
Cons: While it is versatile, it may not be the best choice for applications requiring extreme corrosion resistance, especially in saltwater environments.
Impact on Application: 6061 is compatible with various media, including water and some chemicals, but care should be taken in highly corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential. Buyers from regions like Nigeria and Germany should ensure that suppliers meet local regulatory requirements.
What Advantages Does 5052 Aluminum Tubing Offer?
5052 aluminum is recognized for its high strength and excellent fatigue resistance, particularly in marine environments. This alloy is non-heat-treatable but offers good workability and can be easily formed into intricate shapes.
Pros: Exceptional resistance to saltwater corrosion and high fatigue strength make it suitable for marine applications.
Cons: It is less weldable compared to 6061 and may require specialized techniques for certain applications.
Impact on Application: Ideal for marine and automotive applications, 5052 is suitable for environments exposed to corrosive elements.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions with maritime industries, such as the Middle East and South America, should prioritize suppliers who adhere to marine-grade standards.
Why Choose 2024 Aluminum Tubing for High-Strength Applications?
2024 aluminum is known for its high strength and fatigue resistance, making it a popular choice in aerospace and high-performance applications. However, it is more susceptible to corrosion than other grades, which can be a significant drawback.
Pros: Excellent strength-to-weight ratio and machinability make it ideal for structural components in demanding environments.
Cons: Its lower corrosion resistance means it may require additional protective coatings, increasing overall costs.
Impact on Application: Best suited for applications where strength is critical, but care must be taken in environments with moisture or corrosive substances.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with aerospace industry standards is crucial for buyers in Europe and North America, where strict regulations govern material selection.
How Does 3003 Aluminum Tubing Compare for General Use?
3003 aluminum is one of the most widely used grades due to its good corrosion resistance and workability. It is often employed in applications that do not require high strength but benefit from ease of fabrication.
Pros: Excellent corrosion resistance and good formability make it suitable for a variety of applications, including cooking utensils and chemical equipment.
Cons: Its strength is lower compared to other grades, making it unsuitable for structural applications.

Illustrative image related to grades of aluminum tubing
Impact on Application: Ideal for non-structural applications where corrosion resistance is a priority.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that 3003 meets local standards for food safety and chemical processing, especially in regions like Africa and South America where regulations may vary.
Summary Table of Aluminum Tubing Grades
| Material | Typical Use Case for grades of aluminum tubing | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6061 | Structural components, marine fittings | Versatile with good corrosion resistance | Not ideal for extreme corrosion environments | Medium |
| 5052 | Marine applications, automotive parts | High fatigue strength and corrosion resistance | Less weldable than other grades | Medium |
| 2024 | Aerospace and high-performance applications | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Requires protective coatings for corrosion | High |
| 3003 | Cooking utensils, chemical equipment | Good corrosion resistance and workability | Lower strength limits structural use | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of aluminum tubing grades, facilitating informed decision-making for international B2B buyers. Understanding these materials’ properties and applications will help ensure optimal performance in various industrial contexts.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for grades of aluminum tubing
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Aluminum Tubing?
The manufacturing process of aluminum tubing involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications for various applications. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing aluminum tubing for their projects.
Material Preparation: How Is Aluminum Prepared for Tubing?
The first step in manufacturing aluminum tubing is material preparation. This involves selecting the appropriate aluminum alloy based on the desired properties such as strength, corrosion resistance, and workability. Common grades like 6061, 5052, and 2024 are often chosen for their specific attributes relevant to the intended application.
Illustrative image related to grades of aluminum tubing
Once the alloy is selected, it is typically delivered in the form of large sheets or coils. These materials undergo initial inspections to verify their composition and quality before moving on to the forming stage. Suppliers often use spectrometers to analyze the alloy’s chemical composition, ensuring it aligns with industry standards.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Aluminum Tubing?
The forming stage is where the aluminum material is shaped into tubing. Several techniques can be employed, including extrusion, roll forming, and bending.
-
Extrusion: This is the most common method for producing aluminum tubing. In this process, heated aluminum billets are forced through a die to create a continuous length of tubing with a specific cross-sectional shape. This method allows for complex profiles and is highly efficient.
-
Roll Forming: In this technique, sheets of aluminum are passed through a series of rollers that progressively shape the material into a tubular form. This method is ideal for producing longer lengths of tubing and is often used for structural applications.
-
Bending: For applications that require specific angles or curves, bending techniques can be applied. This can be done using hydraulic or mechanical benders, which ensure uniformity in the curvature of the tubing.
After forming, the tubing is often cut to the desired lengths, and any additional fabrication, such as drilling or machining, can be performed.
Assembly and Finishing: How Are Tubing Components Joined and Treated?
Following the forming stage, aluminum tubing may require assembly, particularly for applications where multiple components are joined. Techniques such as welding, brazing, or mechanical fastening are employed depending on the design requirements and the aluminum grade being used.
Finishing processes are also essential to enhance the tubing’s appearance and performance. Common finishing techniques include:
- Anodizing: This electrochemical process increases corrosion resistance and allows for dyeing in various colors.
- Powder Coating: A dry finishing process that provides a durable, decorative finish to the tubing.
- Polishing: Enhancing the surface finish to achieve a reflective quality.
These finishing processes not only improve aesthetics but also ensure that the tubing can withstand environmental factors, particularly for applications in marine or industrial settings.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Aluminum Tubing Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the aluminum tubing manufacturing process. It ensures that products meet international standards and customer specifications, thereby reducing the risk of failure in end-use applications.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For aluminum tubing, adherence to international standards is essential. Key certifications include:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS), emphasizing customer satisfaction and continual improvement.
- CE Marking: Particularly relevant in Europe, CE marking indicates that a product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Specification: For industries like oil and gas, API standards ensure that products meet rigorous safety and performance criteria.
Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are compliant with these standards as part of their due diligence.

Illustrative image related to grades of aluminum tubing
What Are the Checkpoints in Quality Control?
Quality control (QC) involves systematic checks throughout the manufacturing process to ensure product integrity. Common QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to verify compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring occurs during the manufacturing stages to identify and correct defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of finished products, including dimensional checks, surface quality, and mechanical properties.
Testing methods may include non-destructive testing (NDT), tensile strength tests, and corrosion resistance evaluations, ensuring that the tubing meets the required performance criteria.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers need to take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures employed by their suppliers. Here are several actionable strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers’ manufacturing processes can provide insights into their quality control practices. This includes reviewing documentation related to their QMS, production capabilities, and compliance with international standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality assurance reports, including test results and certifications for the materials used. This transparency is vital for building trust and ensuring product quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. These inspections can verify compliance with international standards and ensure that products meet the specified requirements.
What Are the Unique QC Considerations for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of several unique QC considerations:
-
Customs Regulations: Understanding the customs requirements for importing aluminum tubing is essential. Different regions may have specific regulations that affect the acceptance of products based on their quality certifications.
-
Cultural and Communication Barriers: Effective communication with suppliers across different countries can pose challenges. Establishing clear expectations and maintaining open lines of communication can mitigate misunderstandings related to quality standards.
-
Logistics and Shipping: The transportation of aluminum tubing can introduce risks, such as damage during transit. Buyers should ensure that suppliers implement robust packaging and handling procedures to protect the product.
By being proactive in understanding manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing aluminum tubing, ensuring that they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.

Illustrative image related to grades of aluminum tubing
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘grades of aluminum tubing’
To successfully procure aluminum tubing for your specific needs, it is essential to follow a structured approach that ensures you make informed decisions. This guide provides a clear checklist that will help B2B buyers navigate the complexities of sourcing the right grades of aluminum tubing.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by identifying the specific requirements of your project. This includes understanding the mechanical properties needed, such as tensile strength, weight, and corrosion resistance. Clearly outlining these specifications will help you narrow down the suitable aluminum grades, such as 6061 for versatile applications or 5052 for marine environments.
Step 2: Research Available Aluminum Grades
Familiarize yourself with the different grades of aluminum tubing and their unique properties. For example, 6061 is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and workability, while 2024 offers high strength but lower corrosion resistance. Understanding these characteristics will guide you in selecting the right grade that matches your project’s demands.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers within your industry or region. It’s crucial to ensure that the suppliers have a solid track record in delivering the required quality and service.

Illustrative image related to grades of aluminum tubing
- Look for suppliers with experience in your specific application area.
- Check online reviews and testimonials to gauge customer satisfaction.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001, which guarantees quality management systems. Compliance with international standards is crucial for ensuring that the aluminum tubing meets specific safety and performance criteria, especially in regulated industries like aerospace or automotive.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the aluminum tubing you intend to purchase. Conduct tests to verify that the material meets your technical specifications, including strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability. This step can prevent costly mistakes and ensure that the product performs as expected in your application.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Discuss pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms with your chosen supplier. Ensure that you have a clear understanding of the minimum order quantities and shipping costs. A well-negotiated agreement can provide you with better pricing and service guarantees, which are essential for maintaining your budget and project schedule.

Illustrative image related to grades of aluminum tubing
Step 7: Establish a Quality Control Process
Implement a quality control process for incoming materials. This may include inspecting the aluminum tubing upon delivery and conducting regular checks during fabrication. Having a robust quality assurance strategy will help mitigate risks associated with defects and ensure the longevity and performance of your final products.
By following this step-by-step checklist, you can streamline your procurement process, ensuring that you select the right grade of aluminum tubing that aligns with your project requirements and operational goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for grades of aluminum tubing Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Aluminum Tubing Grades?
When sourcing aluminum tubing, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margins.
-
Materials: The choice of aluminum grade significantly impacts material costs. Grades such as 6061 and 5052 are popular due to their versatility and strength, but they may vary in price based on market demand and alloy composition. Specialty grades like 2024 or 7075, which are used in high-performance applications, generally command a premium.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on the manufacturing location. Countries with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing, but this can sometimes come at the expense of quality. Conversely, suppliers in regions with higher labor costs, such as Western Europe, may provide superior craftsmanship and consistency.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Established suppliers often have streamlined operations that can reduce these costs, allowing for more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront investment but is necessary for producing specialized shapes or sizes. Buyers should weigh the initial tooling costs against long-term savings in production efficiency and material waste.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures product reliability, especially in critical applications. While this can increase costs, it ultimately leads to fewer defects and returns, providing long-term savings.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on distance, method, and Incoterms. Understanding the implications of terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can help buyers manage these costs effectively.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. This margin can fluctuate based on the supplier’s market position, the level of customization required, and the buyer’s negotiation skills.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Aluminum Tubing Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing beyond the basic cost structure:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should consider minimum order quantities (MOQ) and the potential for bulk discounts.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs due to the need for specialized tooling or processes. Buyers should clarify their requirements upfront to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Different grades come with varying levels of certification. For instance, certifications for aerospace applications may increase costs but ensure compliance with industry standards.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and their geographic location can affect pricing. Long-term relationships may yield better prices and terms.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of shipping terms is essential for managing total costs. For example, CIF includes shipping and insurance, while FOB places more responsibility on the buyer for logistics, which can impact overall pricing strategies.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Aluminum Tubing Prices?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation and cost management strategies are vital:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate payment terms and delivery schedules. Flexible terms can lead to better cash flow management.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not only the purchase price but also associated costs such as shipping, duties, and potential tariffs. A lower upfront cost may not always translate to savings in TCO.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of seasonal price fluctuations in raw materials. Timing your purchases can lead to significant savings.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a good relationship with suppliers can result in better pricing and service. Consider long-term partnerships for consistent supply and potential discounts.
-
Request Samples: Before committing to a large order, request samples to evaluate quality and suitability for your applications.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of cost components, price influencers, and effective negotiation strategies will empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing aluminum tubing.

Illustrative image related to grades of aluminum tubing
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing grades of aluminum tubing With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Grades of Aluminum Tubing for B2B Applications
In the industrial landscape, selecting the right material for tubing and structural components is crucial for meeting performance, durability, and cost requirements. While grades of aluminum tubing—such as 6061, 5052, and 2024—are popular choices due to their unique properties, it’s essential to consider alternative materials and technologies that might offer better solutions for specific applications. This analysis will compare aluminum tubing with carbon steel and fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP), two viable alternatives.
| Comparison Aspect | Grades of Aluminum Tubing | Carbon Steel | Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength-to-weight ratio; excellent corrosion resistance | Strong but heavier; rust-prone without treatment | Lightweight; good tensile strength; resistant to many chemicals |
| Cost | Generally higher than steel but lower than high-end composites | Lower initial cost; higher maintenance due to corrosion | Higher upfront cost but lower long-term maintenance |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to machine and fabricate; versatile | Commonly available and easy to work with | Requires specialized skills for fabrication and installation |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to corrosion resistance | Regular maintenance needed to prevent rust | Minimal maintenance; resistant to environmental degradation |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, automotive, marine applications | Construction, industrial piping, automotive frames | Chemical processing, marine applications, infrastructure exposed to corrosive environments |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Carbon Steel Compared to Aluminum Tubing?
Carbon steel is a widely used alternative due to its lower initial cost and high strength. It is ideal for applications where weight is not a primary concern. However, carbon steel is significantly heavier than aluminum and is prone to rust unless properly treated with coatings or galvanization. This necessitates regular maintenance to ensure longevity, making it less suitable for applications in harsh environments. Its availability and ease of fabrication make it a go-to choice for many construction and industrial applications.
How Does Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Compare to Aluminum Tubing?
Fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP) offers a lightweight alternative with good tensile strength and excellent resistance to chemicals and environmental factors. While the initial investment in FRP can be higher than aluminum, it often results in lower maintenance costs due to its durability and resistance to corrosion. However, the fabrication of FRP requires specialized skills and techniques, which may not be as readily available as those for aluminum or steel. FRP is particularly effective in industries such as chemical processing and marine applications, where exposure to harsh conditions is a concern.
How Can B2B Buyers Make the Right Choice Between Aluminum Tubing and Alternatives?
Choosing the right material depends on several factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and the specific environment in which the material will be used. Aluminum tubing is ideal for applications requiring a balance of strength and weight, especially in sectors like aerospace and automotive. In contrast, carbon steel may be more suitable for projects with lower cost expectations and less exposure to corrosive elements. Meanwhile, FRP could be the best option for environments that demand high chemical resistance and minimal maintenance.
Ultimately, B2B buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their project requirements, including mechanical properties, environmental conditions, and cost considerations, to select the most suitable solution for their specific needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for grades of aluminum tubing
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Aluminum Tubing Grades?
Understanding the essential technical specifications of aluminum tubing grades is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are the critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade denotes the specific alloy composition of aluminum tubing, such as 6061, 5052, or 2024. Each grade has distinct mechanical properties, including strength, corrosion resistance, and workability. For instance, 6061 is known for its versatility, making it suitable for various applications, from automotive to marine uses. Selecting the appropriate grade ensures that the tubing meets the specific demands of the project, thereby enhancing performance and longevity.
2. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength measures the maximum amount of tensile (pulling) stress that a material can withstand before failure. This property is critical in applications that require materials to support significant loads, such as structural components in construction or transportation. For example, 7075 aluminum is recognized for its high tensile strength, making it ideal for aerospace applications. Understanding tensile strength helps buyers select materials that will perform safely under expected loads.
3. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance indicates how well aluminum tubing can withstand environmental factors, such as moisture and salt, without deteriorating. This property is particularly important for applications in marine environments or industries exposed to corrosive substances. For instance, 5052 aluminum offers excellent resistance to saltwater corrosion, making it a preferred choice for boat construction. Buyers must prioritize this property to ensure the longevity and safety of their products.
4. Weldability
Weldability refers to how easily a material can be welded without compromising its structural integrity. Certain aluminum grades, such as 6061, are highly weldable, making them suitable for projects that involve extensive fabrication. On the other hand, some grades, like 5052, may present challenges in welding but offer other advantages like strength and corrosion resistance. Understanding weldability is essential for manufacturers to avoid costly rework and ensure product reliability.
5. Tolerance
Tolerance is the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of the aluminum tubing. Accurate tolerances are vital for ensuring that the tubing fits correctly within assemblies, which is crucial in precision engineering and manufacturing. For example, if a component requires exact specifications, knowing the tolerances allows buyers to avoid costly adjustments and ensure compatibility in assembly processes.
What Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know When Sourcing Aluminum Tubing?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiations between buyers and suppliers. Here are some common terms that are essential for B2B transactions:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of aluminum tubing, an OEM might require specific grades or dimensions tailored to their product specifications. Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers identify reliable suppliers who can meet their unique requirements.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it can impact budgeting and inventory management. Knowing the MOQ can assist in negotiating better terms and ensuring that orders align with production needs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request sent by a buyer to suppliers to obtain pricing information for specific products. This process helps in comparing costs and establishing relationships with potential vendors. Crafting a precise RFQ can facilitate better pricing and terms, ensuring that buyers get the best value.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are predefined commercial terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks, which is vital for international procurement, especially for regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. This term is critical for project planning and inventory management. Understanding lead times enables buyers to schedule their production processes effectively and avoid delays.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing aluminum tubing more effectively, ensuring they meet their project requirements and organizational goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the grades of aluminum tubing Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Grades of Aluminum Tubing Sector?
The global aluminum tubing market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand across various sectors such as aerospace, automotive, construction, and marine applications. Notably, the lightweight nature of aluminum, combined with its corrosion resistance, makes it an ideal material for manufacturers looking to enhance efficiency and durability in their products. Key trends include the rising adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies such as 3D printing and automation, which are streamlining production processes and reducing costs. International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly sourcing aluminum tubing from suppliers who can provide tailored solutions that meet specific regulatory and environmental standards.
Emerging markets are playing a pivotal role in this sector, with countries like Nigeria and Brazil expanding their industrial capabilities and infrastructure projects. Moreover, the emphasis on sustainability is influencing sourcing decisions, prompting buyers to seek suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices. The ongoing geopolitical developments and trade agreements also affect the supply chain dynamics, making it essential for buyers to stay informed about market fluctuations and potential risks associated with sourcing from different regions.
How Is Sustainability Influencing the Sourcing of Grades of Aluminum Tubing?
The environmental impact of aluminum production is a growing concern for B2B buyers, prompting a shift toward sustainable sourcing practices. Aluminum is highly recyclable, which significantly reduces its carbon footprint when sourced from recycled materials. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability through certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design). These certifications not only reflect responsible manufacturing practices but also enhance the credibility of suppliers in the eyes of environmentally conscious clients.
Illustrative image related to grades of aluminum tubing
Ethical supply chains are becoming paramount as well. International buyers are keen to ensure that their suppliers uphold fair labor practices and adhere to regulatory compliance, particularly in regions with less stringent enforcement. This focus on ethical sourcing not only fosters goodwill but also mitigates risks associated with reputational damage. As the demand for ‘green’ materials grows, suppliers who can provide aluminum tubing made from sustainably sourced or recycled aluminum are likely to gain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
What Is the Evolution of Aluminum Tubing and Its Relevance to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of aluminum tubing has been marked by technological advancements and an increasing understanding of aluminum’s properties. Initially, the material was primarily used in basic applications; however, innovations in alloy compositions have led to the development of specialized grades that cater to diverse industrial needs. For instance, the introduction of heat-treatable alloys like 6061 and 7075 has expanded the applications of aluminum tubing in high-stress environments such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
Furthermore, the historical context of aluminum sourcing has shifted dramatically. In the past, many buyers relied on local suppliers; today, global supply chains are commonplace. This transition underscores the importance of understanding international market trends, sourcing strategies, and the implications of geopolitical factors on aluminum availability. B2B buyers must remain agile and informed to navigate this evolving landscape effectively, ensuring they leverage the best materials for their specific applications while adhering to sustainability and ethical standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of grades of aluminum tubing
-
How do I select the right grade of aluminum tubing for my application?
Selecting the appropriate grade of aluminum tubing involves assessing your project requirements, including strength, corrosion resistance, and fabrication needs. For example, 6061 aluminum is versatile and easy to weld, making it ideal for a wide range of applications. In contrast, 5052 is more suited for marine environments due to its superior corrosion resistance. Conduct a thorough analysis of your operational conditions and seek advice from suppliers who can provide technical data sheets to make an informed decision. -
What is the best aluminum grade for marine applications?
The best aluminum grade for marine applications is typically 5052. This alloy offers excellent corrosion resistance against saltwater, making it suitable for boat building and marine fittings. Its high fatigue strength ensures durability under harsh conditions. However, 6061 is also a good option for non-exposed components due to its weldability and versatility. Always consider the specific environmental factors and usage conditions when choosing the grade. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for aluminum tubing?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for aluminum tubing can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on the specific grade and form required. Generally, MOQs can range from 100 kg to several tons. It’s advisable to discuss your needs directly with suppliers to find options that align with your project scale. Additionally, consider suppliers who offer flexibility in order sizes, particularly if you are testing new applications or products. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing aluminum tubing internationally?
Payment terms for international aluminum tubing purchases can vary widely, but common practices include letters of credit, wire transfers, and payment upon delivery. Some suppliers may require a deposit upfront, especially for custom orders. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that suit your cash flow while ensuring the supplier’s confidence in fulfilling the order. Always confirm payment terms in writing before finalizing any contracts. -
How can I ensure the quality of aluminum tubing from suppliers?
To ensure quality, always request material certification and test reports from suppliers. Look for reputable suppliers who adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001. Additionally, consider conducting third-party inspections or audits if you are making large investments or sourcing from new suppliers. A well-documented quality assurance process will help mitigate risks associated with material defects. -
What customization options are available for aluminum tubing?
Customization options for aluminum tubing typically include dimensions, wall thickness, and surface finishes (e.g., anodizing or powder coating). Some suppliers may also offer specialized shapes or alloys tailored to specific applications. Discuss your requirements with suppliers to explore available options and ensure that the tubing meets your project specifications. Custom orders may have different lead times, so factor this into your project planning. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing aluminum tubing?
When importing aluminum tubing, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your country. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger shipments. Ensure that you have a clear understanding of import duties and taxes, which can significantly impact total costs. Collaborate with experienced logistics partners who can navigate these complexities and ensure timely delivery. -
What are the common applications for different grades of aluminum tubing?
Different grades of aluminum tubing serve various applications. For instance, 6061 is often used in structural applications and automotive parts due to its weldability and strength. 5052 is favored for marine and food processing applications due to its corrosion resistance. Meanwhile, 2024 is typically used in aerospace applications where high strength is crucial. Understanding these applications will help you select the right grade for your specific needs.
Top 6 Grades Of Aluminum Tubing Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Service Steel – Aluminum Tubing Types
Domain: servicesteel.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Types of Aluminum Tubing: 6061, 5052, 2024. 6061: Versatile, excellent corrosion resistance, ideal for welding, used in machine parts, frames, marine fittings. 5052: Strongest non-heat-treatable grade, high fatigue strength, used in marine applications, aircraft, transportation, electronics. 2024: High strength, good machinability, used in aircraft, structural components, prone to corrosion unless…
2. Metal Supermarkets – Aluminum Grades and Alloys
Domain: metalsupermarkets.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Aluminum Grades: 1100, 2011, 2014, 2024, 3003, 5052, 6061, 6063, 7075.\n\n- Alloy 1100: Commercially pure aluminum, soft, ductile, excellent workability, good corrosion resistance, used in chemical and food processing.\n- Alloy 2011: High mechanical strength, excellent machining, ideal for automatic lathes, produces fine chips.\n- Alloy 2014: Copper-based, high strength, excellent machining, used …
3. IQS Directory – Aluminum Tubing and Piping
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Aluminum tubing and piping are characterized by their silvery-white appearance, softness, and pliability. They are lightweight, weighing about 30% of copper’s density, and maintain effective electrical and thermal conductivity. Aluminum is often alloyed with elements like copper, manganese, zinc, magnesium, and silicon to enhance its properties. Key differences between piping and tubing include th…
4. Texas Alloys – Aluminum Alloys 6061, 6063, 3003, 5052
Domain: texasalloys.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: This company, Texas Alloys – Aluminum Alloys 6061, 6063, 3003, 5052, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Continental Steel – Aluminum Tubing
Domain: continental-steel.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Aluminum Tubing Types: 6061, 5052, 2024. 6061: Versatile, excellent corrosion resistance, ideal for welding, used in truck racks, furniture, marine fittings. 5052: Strongest non-heat-treatable grade, high fatigue strength, excellent saltwater corrosion resistance, used in marine applications, aircraft, heavy cooking utensils, electronics. 2024: High strength, fatigue resistance, prone to corrosion…
6. TW Metals – Aluminum Tubing Supplier
Domain: twmetals.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Aluminum Tubing Supplier – Rounds, Squares, Rectangular, & Streamline Tubing. Types: Drawn Aluminum Tubing (Grades: 2024, 3003, 5052, 6061, 7075) and Extruded Aluminum Tubing (Grades: 6061, 6063, 7075). Shapes available include rounds, squares, rectangles. Inventory tailored to meet industry requirements, including standard and hard-to-find sizes. Products certified to various specifications inclu…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for grades of aluminum tubing
In navigating the diverse landscape of aluminum tubing grades, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to optimize their supply chains and project outcomes. Understanding the unique properties of aluminum grades such as 6061, 5052, and 2024 is vital for selecting the right material that aligns with specific application requirements. Each grade offers distinct advantages, from the versatility of 6061 for general fabrication to the high strength of 2024 for aerospace applications.
Moreover, engaging with reliable suppliers who understand regional market dynamics in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can enhance procurement efficiency. As global demand for lightweight, corrosion-resistant materials continues to rise, the importance of strategic sourcing becomes even more pronounced. Buyers should leverage local expertise and seek partnerships that facilitate access to quality aluminum tubing products, ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Looking ahead, the aluminum market is poised for growth, fueled by advancements in manufacturing technologies and increased emphasis on sustainable practices. By making informed sourcing decisions today, businesses can position themselves advantageously for tomorrow’s challenges and opportunities. Engage with trusted suppliers now to secure the right aluminum grades for your future projects.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.