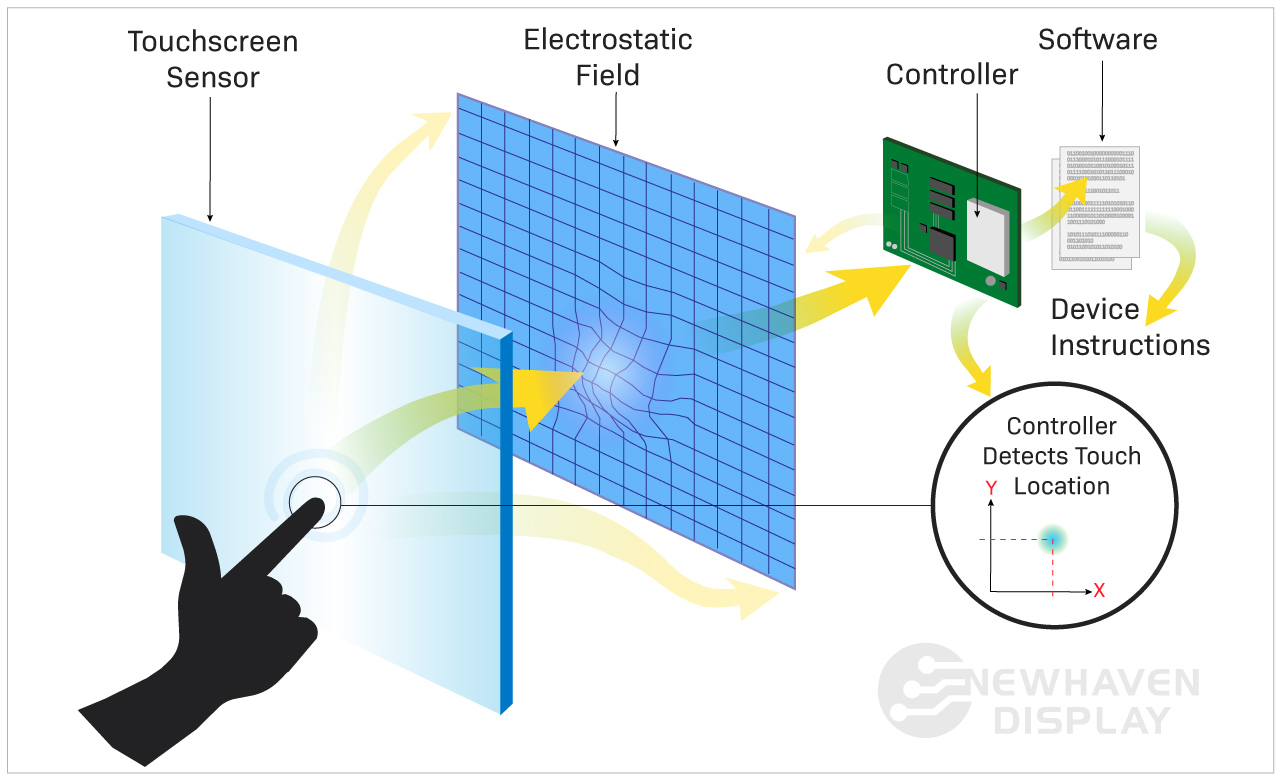
Touch Screen Diagram Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for touch screen diagram
In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, sourcing the right touch screen diagram can be a pivotal challenge for B2B buyers aiming to enhance user interaction and operational efficiency. As touch screens become increasingly integral to devices across various sectors—from retail kiosks to industrial equipment—understanding the diverse types and their applications is essential. This guide delves into the intricacies of touch screen technology, covering essential aspects such as resistive and capacitive screens, projected capacitive (P-Cap) systems, and emerging technologies like infrared and optical imaging.
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, will find actionable insights into supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and market trends. By equipping decision-makers with a comprehensive understanding of touch screen functionalities and their specific applications, this guide empowers organizations to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are looking to upgrade existing systems or implement new technologies, the insights provided herein will facilitate strategic sourcing and enhance your competitive edge in the global market.
Understanding touch screen diagram Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistive Touchscreen | Operates on pressure; consists of two flexible layers | Industrial equipment, kiosks, ATMs | Pros: Cost-effective, durable, works with gloves. Cons: Lower clarity, requires pressure to register. |
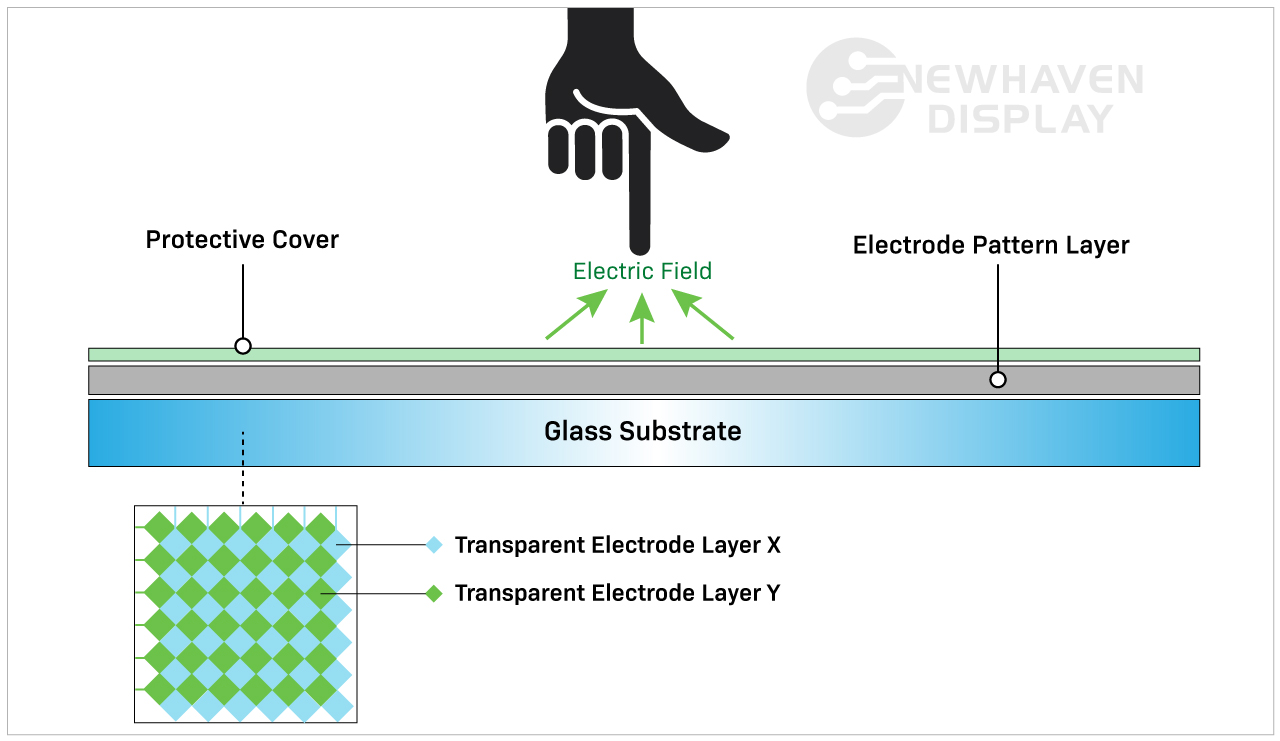
| Capacitive Touchscreen | Utilizes electrical conductivity; supports multi-touch gestures | Smartphones, tablets, interactive displays | Pros: High sensitivity, excellent clarity, multi-touch support. Cons: More expensive, less effective with gloves. |
| Projected Capacitive (P-Cap) | Advanced capacitive technology; detects touch through the glass layer | Retail displays, medical devices | Pros: High durability, supports gestures, responsive. Cons: Higher cost, can be affected by water. |
| Infrared Touchscreen | Uses infrared light to detect touch; no physical contact needed | Interactive kiosks, gaming systems | Pros: No wear and tear, works with any object. Cons: Sensitive to ambient light, can be costly. |
| Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) | Utilizes ultrasonic waves; offers high clarity and sensitivity | High-end retail, ATMs, gaming consoles | Pros: Excellent image quality, multi-touch capability. Cons: Susceptible to dirt and scratches, requires maintenance. |
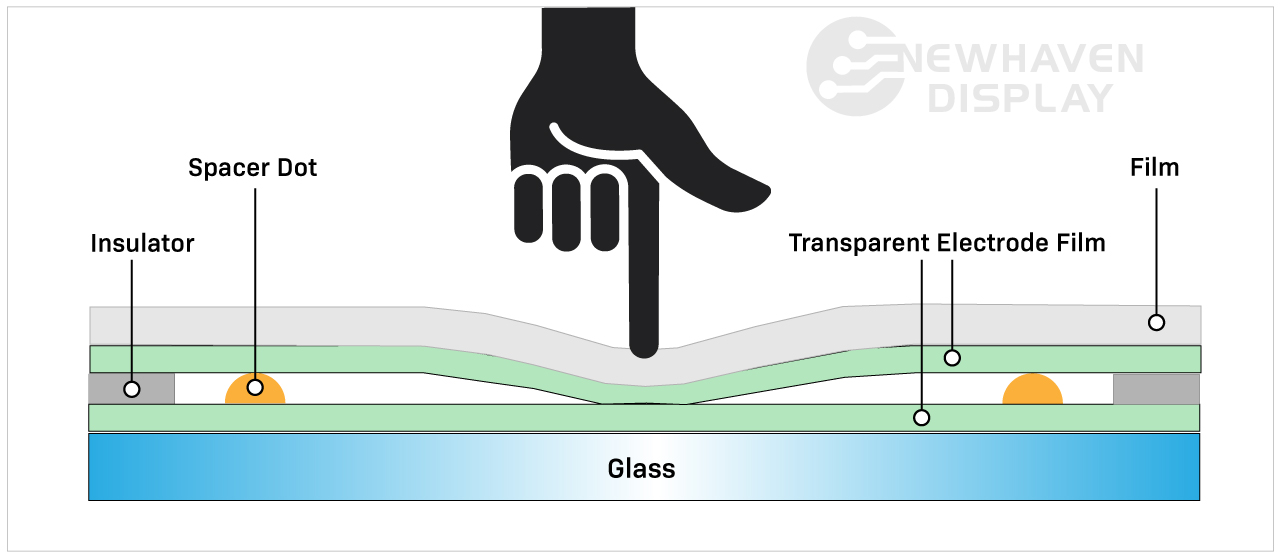
What Are the Characteristics and Suitability of Resistive Touchscreens?
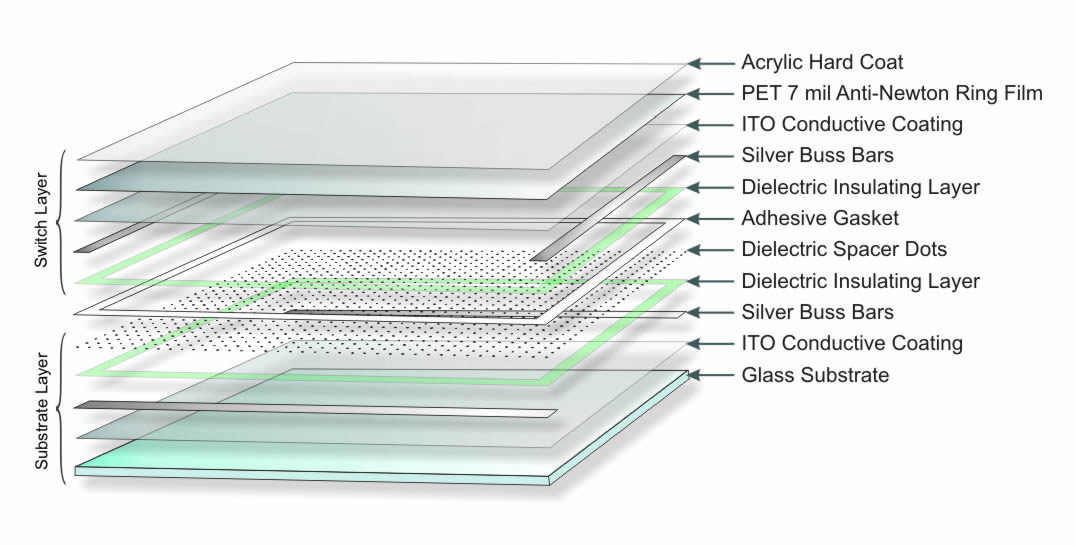
Resistive touchscreens are characterized by their reliance on pressure to register touch inputs. They consist of two layers, which, when pressed together, create a contact point that registers the touch. This technology is particularly suitable for environments where durability and cost-effectiveness are paramount, such as industrial equipment, kiosks, and ATMs. When considering B2B purchases, buyers should evaluate the operational environment, as resistive screens can handle harsh conditions but may not provide the clarity needed for high-resolution applications.
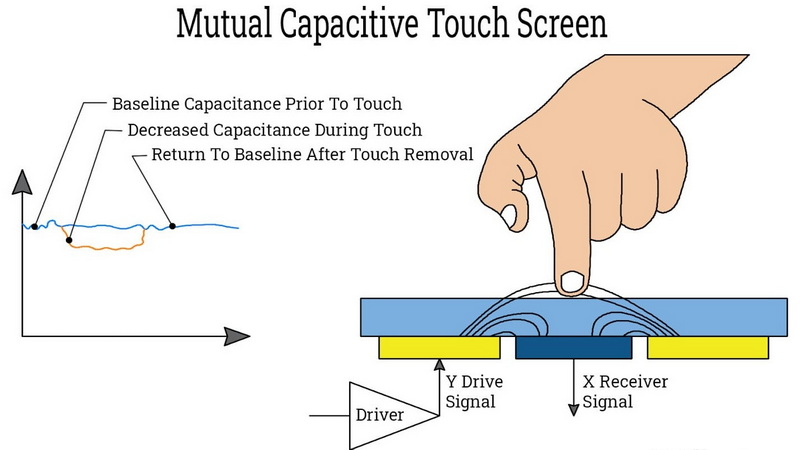
How Do Capacitive Touchscreens Stand Out in B2B Applications?
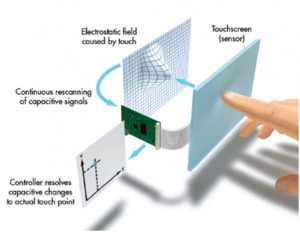
Capacitive touchscreens detect touch through the electrical properties of the human body, allowing for a more responsive and intuitive interaction. They are commonly used in smartphones, tablets, and interactive displays due to their high sensitivity and ability to support multi-touch gestures. For B2B buyers, the clarity and responsiveness of capacitive screens make them ideal for customer-facing applications, but the higher price point and reduced functionality with gloves must be considered, especially in industrial settings.
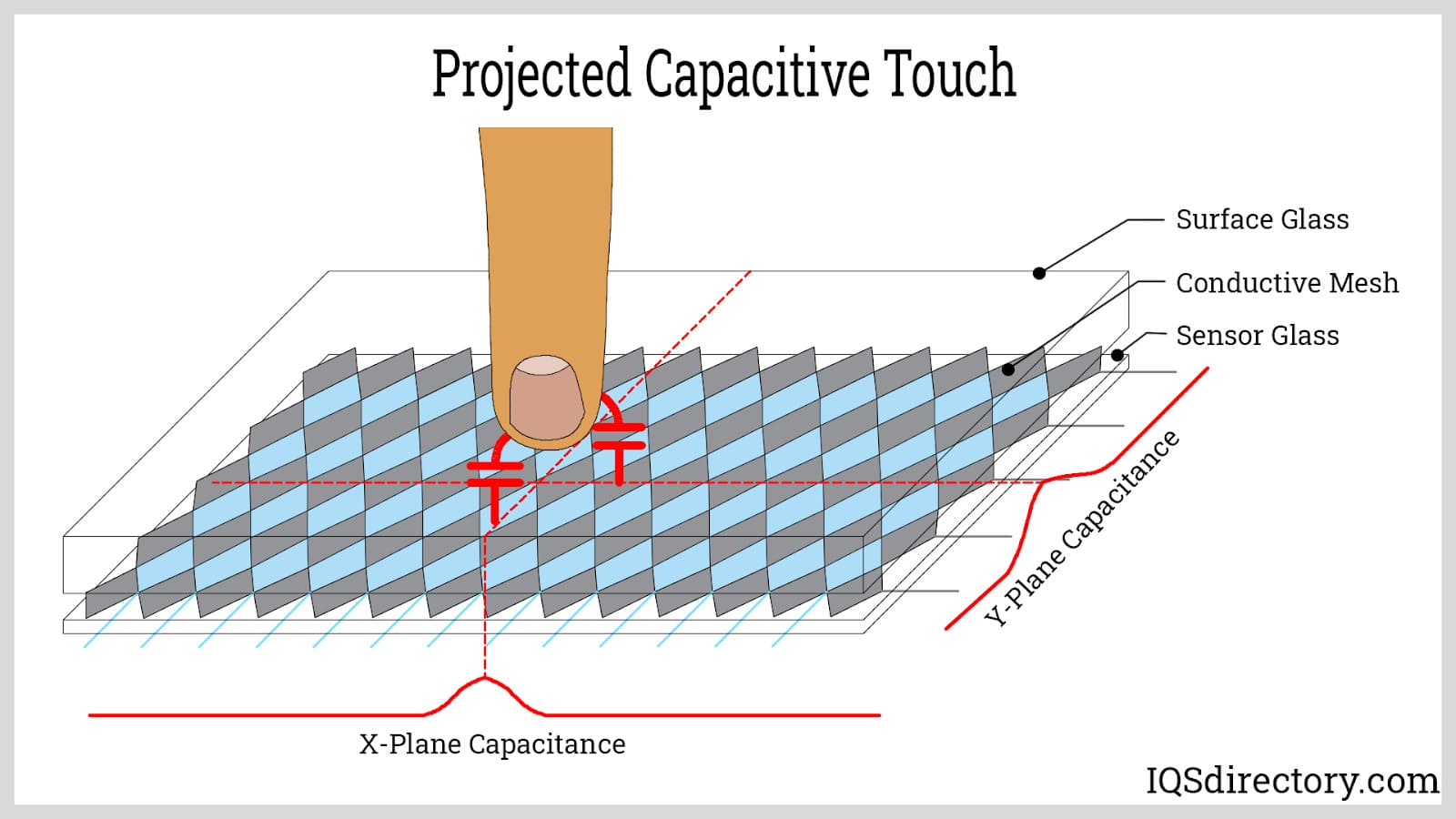
Why Choose Projected Capacitive (P-Cap) Touchscreens for Your Business?
Projected capacitive (P-Cap) touchscreens represent an advanced form of capacitive technology, allowing for touch detection through a glass surface. This technology is highly durable and supports a variety of gestures, making it suitable for applications in retail displays and medical devices. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of high durability and responsiveness against the potential for higher costs and sensitivity to water, which can affect performance in certain environments.
Illustrative image related to touch screen diagram
What Are the Advantages of Infrared Touchscreens in Interactive Solutions?
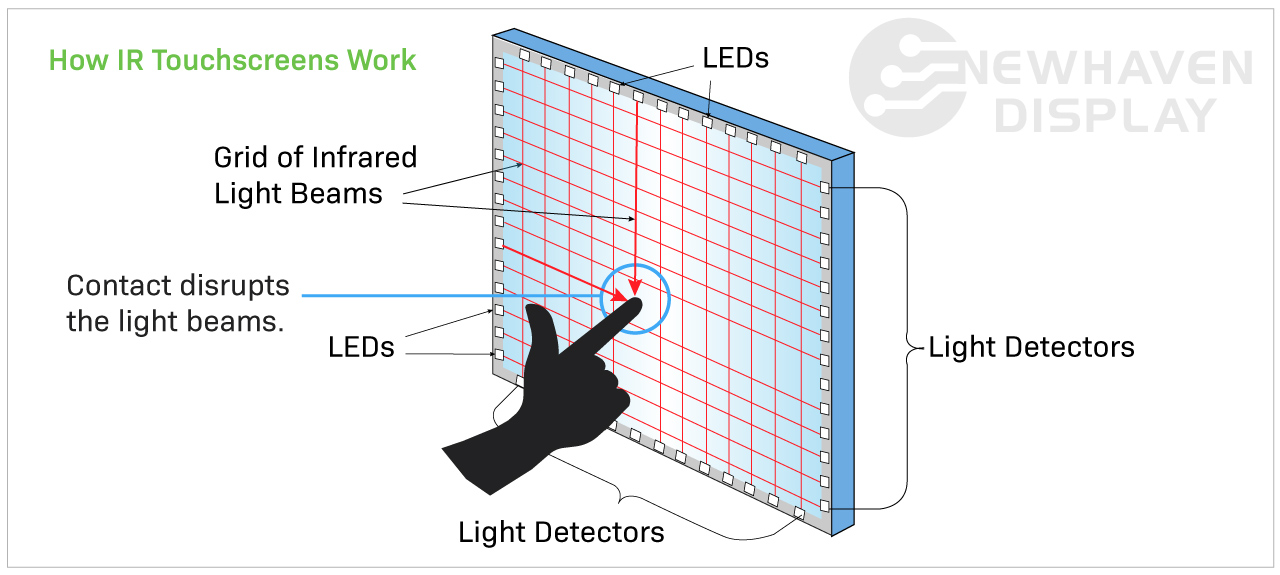
Infrared touchscreens operate by detecting interruptions in infrared light beams, allowing for touch detection without the need for physical contact. This feature makes them ideal for interactive kiosks and gaming systems, where durability and ease of use are critical. For B2B buyers, the lack of wear and tear is a significant advantage; however, sensitivity to ambient light and the potential for higher costs are important considerations when selecting this technology.
How Do Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) Touchscreens Enhance User Experience?
Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) touchscreens utilize ultrasonic waves to detect touch, providing high clarity and sensitivity. They are commonly found in high-end retail environments and gaming consoles due to their excellent image quality and ability to support multi-touch gestures. B2B buyers should note that while SAW screens offer superior performance, they are susceptible to dirt and scratches, necessitating maintenance in environments where cleanliness is a concern.
Key Industrial Applications of touch screen diagram
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of touch screen diagram | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Patient Management Systems | Improves patient engagement and data accuracy | Compliance with health regulations, durability, and ease of cleaning |
| Retail | Self-Service Kiosks | Enhances customer experience and reduces wait times | User-friendly interface design and robust software support |
| Manufacturing | Equipment Control Panels | Streamlines operations and reduces downtime | Customization options and compatibility with existing systems |
| Transportation | Ticketing and Information Systems | Increases operational efficiency and user satisfaction | Weather resistance and high visibility in various lighting conditions |
| Education | Interactive Learning Tools | Facilitates engaging learning experiences | Multi-touch capability and durable design for frequent use |
How is Touch Screen Technology Used in Healthcare Applications?
In the healthcare sector, touch screen diagrams are pivotal for patient management systems, enabling medical staff to interact seamlessly with electronic health records. These systems enhance patient engagement by allowing easy access to personal health information and treatment plans. Additionally, touch screens can facilitate better data accuracy and streamline workflows. B2B buyers in this sector must consider compliance with health regulations, durability for frequent cleaning, and responsiveness to touch in various conditions.
What Role Do Touch Screens Play in Retail Environments?
In retail, touch screen diagrams are integral to self-service kiosks, where customers can place orders or check in without human assistance. This technology not only enhances the customer experience by reducing wait times but also allows businesses to allocate staff more efficiently. Buyers in the retail sector should prioritize user-friendly interface designs and robust software support to ensure seamless operations and customer satisfaction.
Illustrative image related to touch screen diagram
How Can Manufacturing Benefit from Touch Screen Control Panels?
Manufacturers utilize touch screen diagrams for equipment control panels, which streamline operations by allowing operators to monitor and control machinery with ease. This technology reduces downtime and enhances productivity through intuitive interfaces that facilitate quick adjustments and real-time monitoring. B2B buyers must focus on customization options to fit specific industrial needs and ensure compatibility with existing systems to maximize investment.
In What Ways Are Touch Screens Enhancing Transportation Systems?
In transportation, touch screen diagrams are commonly used in ticketing and information systems, providing users with an efficient way to purchase tickets and access travel information. This technology increases operational efficiency and enhances user satisfaction by minimizing queues and facilitating easy navigation. Buyers in this sector should consider sourcing touch screens that are weather-resistant and provide high visibility in diverse lighting conditions to ensure reliable performance.
How Do Touch Screens Transform Educational Tools?
Touch screen diagrams are revolutionizing educational tools by offering interactive learning experiences that engage students more effectively than traditional methods. These systems allow for multi-touch capabilities, enabling collaborative learning and hands-on interaction with educational content. For B2B buyers in education, it is crucial to consider the durability of the devices, as they will be subject to frequent use, and the need for intuitive designs that accommodate diverse learning styles.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘touch screen diagram’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex Touch Screen Diagrams for Technical Integration
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to interpret complex touch screen diagrams, which can hinder the integration of touch screen technology into their existing systems. This issue is particularly pronounced when dealing with multiple components, such as controllers and software interfaces. Without a clear understanding of how these elements interact, businesses may face delays in project timelines, increased costs, and potential system failures. The confusion can lead to miscommunication among teams, ultimately impacting the product development cycle.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, it is essential to source high-quality, detailed touch screen diagrams that include annotations and specifications for each component. Buyers should collaborate closely with manufacturers to obtain customized diagrams that reflect their specific application requirements. Additionally, investing in training sessions or workshops can empower teams to decode these diagrams effectively. This not only enhances comprehension but also fosters collaboration between technical and non-technical staff. Regularly reviewing these diagrams during project meetings can ensure all stakeholders are aligned and can address any uncertainties in real-time.
Scenario 2: Selecting the Right Touch Screen Technology for Diverse Environments
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face difficulties in selecting the appropriate touch screen technology that suits diverse environmental conditions, such as outdoor settings or industrial applications. For instance, a resistive touch screen may be ideal for environments where users wear gloves, but it might lack the clarity needed for detailed visual tasks. This mismatch can lead to operational inefficiencies, user frustration, and ultimately, decreased productivity.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their operational environment and user needs before choosing a touch screen technology. Leveraging touch screen diagrams that clearly illustrate the specifications and functionalities of various technologies—such as capacitive, resistive, and SAW—can aid in making informed decisions. It is advisable to create a decision matrix that considers factors like environmental exposure, user interaction style, and clarity requirements. Engaging with suppliers who can provide real-world examples of similar implementations can also offer valuable insights and build confidence in the chosen solution.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Effective Touch Screen Maintenance and Troubleshooting
The Problem: After installation, many B2B buyers encounter challenges in maintaining touch screens and troubleshooting issues due to a lack of clear guidelines. Problems such as unresponsive screens, inaccuracies in touch detection, or software glitches can significantly disrupt business operations. Without proper maintenance protocols or understanding of the system’s design as outlined in touch screen diagrams, businesses risk prolonged downtimes and increased repair costs.
The Solution: To address this pain point, it is crucial to develop a comprehensive maintenance plan that includes regular inspections and clear troubleshooting protocols based on the touch screen diagrams. Buyers should work with manufacturers to receive detailed documentation that outlines common issues, their causes, and step-by-step solutions. Creating a dedicated maintenance team trained to understand these diagrams and perform routine checks can also enhance system reliability. Additionally, establishing a feedback loop with end-users can provide insights into usability issues that may not be immediately apparent, ensuring that the touch screens function optimally over time.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for touch screen diagram
What Are the Key Materials Used in Touch Screen Diagrams?
When selecting materials for touch screen diagrams, it is essential to consider properties that influence performance, durability, and cost. Here, we analyze four common materials used in touch screen applications: glass, plastic, indium tin oxide (ITO), and polycarbonate. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly impact the functionality and suitability of touch screens in various environments.
How Does Glass Perform as a Material for Touch Screens?
Glass is a popular choice for touch screens due to its excellent optical clarity and scratch resistance. It typically has a high-temperature rating, making it suitable for devices used in various environments. However, glass can be brittle and susceptible to shattering upon impact, which may limit its use in rugged applications. Additionally, while glass offers superior durability, its weight can increase manufacturing complexity and shipping costs.
For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, the availability of tempered glass that complies with safety standards (such as ASTM or EN standards) is crucial. This ensures that the glass can withstand environmental stresses while providing a safe user experience.
What Advantages Does Plastic Offer for Touch Screen Applications?
Plastic, particularly acrylic or polycarbonate, is lightweight and shatter-resistant, making it an attractive option for portable devices. It can be molded into various shapes and sizes, which simplifies manufacturing processes and reduces costs. However, plastic is generally less scratch-resistant than glass and may yellow over time when exposed to UV light, which could affect the longevity of the touch screen.
For B2B buyers in the Middle East and Europe, it is essential to consider the specific grades of plastic that meet relevant industry standards for durability and safety. The cost-effectiveness of plastic can be appealing, but potential buyers should weigh its long-term performance against initial savings.
Why Is Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) Important in Touch Screen Manufacturing?
Indium tin oxide (ITO) is a critical material used for the conductive layer in touch screens, particularly capacitive types. ITO offers excellent electrical conductivity and transparency, which is vital for touch sensitivity and display quality. However, ITO is relatively expensive and can be challenging to source, especially in regions with limited access to raw materials.
Illustrative image related to touch screen diagram
International buyers should be aware of the supply chain dynamics surrounding ITO, including potential fluctuations in pricing and availability. Compliance with international trade regulations and standards is also crucial, as sourcing ITO may involve navigating complex supply chains.
What Role Does Polycarbonate Play in Touch Screen Design?
Polycarbonate is another plastic material used in touch screens, known for its high impact resistance and optical clarity. It is often used in applications where durability is paramount, such as in industrial or outdoor settings. However, polycarbonate can be more expensive than other plastics and may require additional coatings to enhance scratch resistance.
For buyers in emerging markets, such as Brazil and Vietnam, the choice of polycarbonate may depend on balancing cost with performance requirements. Understanding local market preferences and standards can help in selecting the most suitable material for specific applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Touch Screen Diagrams
| Material | Typical Use Case for touch screen diagram | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass | Smartphones, tablets, high-end kiosks | Excellent optical clarity and scratch resistance | Brittle and heavy | High |
| Plastic | Portable devices, consumer electronics | Lightweight and shatter-resistant | Less scratch-resistant, may yellow | Medium |
| Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) | Capacitive touch screens | High electrical conductivity and transparency | Expensive and challenging to source | High |
| Polycarbonate | Industrial touch screens, outdoor devices | High impact resistance and clarity | More costly, requires coatings | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide equips B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties and implications of various materials used in touch screens. Understanding these factors can help in making informed decisions that align with product performance and market demands.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for touch screen diagram
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Touch Screens?
The manufacturing of touch screens involves several critical stages that ensure both functionality and quality. Understanding these stages is vital for B2B buyers looking to source reliable touch screen products.
How Is Material Prepared for Touch Screen Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the initial stage in touch screen manufacturing. This process involves selecting high-quality raw materials, such as glass substrates, conductive coatings (like indium tin oxide), and adhesive materials. The glass is typically cut to size and thoroughly cleaned to remove any contaminants that could affect the touch screen’s performance.
Advanced techniques, such as chemical treatments, are often employed to enhance the surface properties of the glass, making it more durable and responsive to touch. This stage sets the foundation for the entire manufacturing process, as the quality of materials directly impacts the final product’s performance.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Touch Screens?
The forming stage involves applying various techniques to create the touch-sensitive layers of the screen. This typically includes:
-
Coating: The glass surface is coated with a conductive material, which is essential for touch detection. This layer must be uniform to ensure consistent touch sensitivity across the screen.
-
Layering: For multi-touch functionality, manufacturers may incorporate multiple layers, including protective layers, touch sensors, and display elements.
-
Laminating: In some cases, a lamination process is used to bond these layers together. This not only enhances durability but also improves optical clarity, which is crucial for user experience.
These processes are often performed under controlled environments to prevent contamination and ensure precision.
How Is Assembly Conducted in Touch Screen Manufacturing?
The assembly stage is where all components come together to form the final product. This involves:
-
Component Integration: The touch sensor is integrated with the display module, ensuring that all connections are secure.
-
Wiring: Proper wiring is crucial for the responsiveness of the touch screen. Manufacturers use automated systems to solder connections, minimizing human error.
-
Encapsulation: The assembled unit is then encapsulated to protect against environmental factors like dust and moisture. This step is particularly important for touch screens intended for outdoor or industrial applications.
What Are the Finishing Touches in Touch Screen Manufacturing?
Finishing processes are essential to ensure that the touch screens meet aesthetic and functional standards. This includes:
-
Testing: Each unit undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets performance standards. This may involve checking touch sensitivity, clarity, and response time.
-
Quality Control: Final inspections are conducted to identify any defects or inconsistencies. This includes visual inspections as well as functional tests.
-
Packaging: Proper packaging is crucial for protecting touch screens during transportation. Manufacturers often use anti-static materials to prevent damage from electrical discharges.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Touch Screen Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of touch screen manufacturing, ensuring that products meet international and industry-specific standards.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Touch Screen Quality Control?
Many manufacturers adhere to international standards like ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. This certification demonstrates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement. Additionally, industry-specific standards such as CE marking for products sold in Europe and compliance with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) are often required.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that any issues are identified and addressed promptly. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials for quality and conformity to specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular checks are made to assess the quality of the forming, assembly, and finishing processes. This helps catch defects early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the touch screens are assembled, they undergo comprehensive testing to ensure they meet all functional and aesthetic criteria before being packaged for shipment.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Common testing methods include:
- Functional Testing: Verifying that touch sensitivity and responsiveness meet specified criteria.
- Environmental Testing: Assessing how the touch screen performs under various environmental conditions, including temperature and humidity extremes.
- Durability Testing: Evaluating how the screen withstands physical stress, such as impacts or scratches.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must be proactive in verifying the quality assurance processes of their suppliers. Here are effective methods to ensure compliance and quality:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control practices, and adherence to international standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for detailed quality reports that outline testing results and any certifications achieved by the manufacturer.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes and the quality of the products being manufactured.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing touch screens internationally, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers should be aware of several nuances:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements, such as CE marking in Europe or specific certifications in Africa and South America. Understanding these regulations is crucial for compliance.
-
Cultural Considerations: Communication styles and business practices can vary significantly across cultures. Building strong relationships with suppliers can help navigate these differences effectively.
-
Logistical Challenges: International shipping may introduce delays or additional quality risks. Buyers should factor in logistics when establishing quality control measures, ensuring that products remain protected during transit.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures that underpin touch screen production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they source high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘touch screen diagram’
To successfully procure touch screen diagrams for your business needs, it’s essential to follow a structured approach. This guide outlines the critical steps that B2B buyers should take to ensure they select the right products and suppliers for their specific applications.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by clearly outlining your requirements for the touch screen diagrams. This includes understanding the type of touchscreen technology (e.g., resistive, capacitive) you need based on your application. Additionally, consider factors such as size, resolution, and compatibility with existing systems. A well-defined specification will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and avoid potential mismatches.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Stay informed about the latest advancements in touchscreen technology. Understanding current trends can help you identify the most suitable options for your business. Look for innovations in user interface design, durability, and responsiveness that align with your industry needs. This knowledge will empower you to make informed decisions and gain a competitive edge.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough evaluations. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies from suppliers. Seek references from businesses in similar industries or regions to assess reliability. This step ensures you partner with suppliers who have a proven track record of delivering quality products and services.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Confirm that potential suppliers adhere to relevant industry standards and certifications. This includes ISO certifications, CE marking, or RoHS compliance, which can indicate product quality and safety. Suppliers who meet these standards are more likely to provide reliable and compliant products that meet your regulatory requirements.
Illustrative image related to touch screen diagram
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request samples of the touch screen diagrams. Testing samples allows you to evaluate the quality, responsiveness, and usability of the products. Pay close attention to how well the touch screens perform under various conditions, such as different lighting and environmental factors.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Engage in discussions with suppliers about pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Ensure that you understand the total cost of ownership, including warranty and support services. Clear negotiation of terms will help establish a solid foundation for a long-term partnership and avoid misunderstandings down the line.
Step 7: Finalize Your Order and Monitor Delivery
After selecting a supplier and negotiating terms, finalize your order. Keep track of the delivery process to ensure that timelines are met and products arrive in good condition. Maintaining communication with the supplier throughout this process will help address any potential issues promptly.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively source touch screen diagrams that meet their technical and business needs, ensuring a successful procurement process.
Illustrative image related to touch screen diagram
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for touch screen diagram Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of touch screen diagrams is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis will outline the primary cost components, price influencers, and provide actionable tips for buyers to navigate this complex procurement landscape.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Touch Screen Diagram Sourcing?
The cost structure for sourcing touch screen diagrams consists of several critical components:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. Touch screens can be made from various substrates (glass, plastic) and coatings (anti-glare, anti-fingerprint). Higher-quality materials typically incur a premium.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the region and the level of skill required for assembly and testing. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing but could compromise on quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom designs. Buyers should consider these costs when evaluating suppliers, as they can influence the overall price significantly.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure product reliability and adherence to specifications, which can increase costs. However, investing in quality control can reduce long-term costs associated with defects and returns.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight and insurance, can add to the final price. Buyers should account for the logistics implications of sourcing from different regions, considering factors like distance, customs duties, and local regulations.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. Understanding the standard margins in the industry can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Touch Screen Diagram Costs?
Several factors influence the final pricing of touch screen diagrams:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs and consider ordering in bulk to achieve better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized touch screen diagrams tailored to specific applications or designs will typically incur higher costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the added expense.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., CE, ISO) can increase costs but also enhance product reliability and marketability. Buyers in regulated markets should prioritize certified products.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and location can greatly impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium but often provide better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, insurance, and risk. This knowledge can help buyers negotiate better terms and avoid unexpected charges.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers should consider the following strategies to maximize cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiate Terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate on pricing, especially for large orders. Suppliers may offer discounts for volume purchases or long-term contracts.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider logistics, maintenance, and potential warranty costs to understand the full financial impact.
-
Research Market Pricing: Familiarize yourself with market rates for touch screen diagrams in your specific region. This knowledge will empower you during negotiations.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, improved service, and preferential treatment during supply shortages.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Sourcing from local suppliers can minimize logistics costs and reduce lead times, providing a competitive edge in time-sensitive markets.
Conclusion
While the pricing structure for touch screen diagrams can be complex, understanding the cost components and price influencers enables B2B buyers to make informed decisions. By leveraging strategic negotiation and considering total cost implications, buyers can optimize their sourcing strategies and ensure sustainable procurement practices. Always remember to request indicative prices and clarify all terms before finalizing agreements to avoid potential discrepancies in costs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing touch screen diagram With Other Solutions
Exploring Viable Alternatives to Touch Screen Diagrams
In the realm of user interface design and interaction, touch screen diagrams have become a popular choice due to their intuitive nature and versatility. However, various alternative solutions exist that can serve similar purposes, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific operational requirements and constraints.
| Comparison Aspect | Touch Screen Diagram | Voice Recognition | Gesture Control |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High sensitivity; excellent for multitouch scenarios | Moderate; accuracy can vary with accents and ambient noise | High; can be very intuitive but may struggle with complex commands |
| Cost | Moderate; costs include hardware and software integration | Low to moderate; primarily software-based with minimal hardware | Moderate; requires specific hardware but less than touch screens |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires integration with existing systems | Quick to deploy; minimal training required | May need extensive setup; user training essential |
| Maintenance | Moderate; hardware can wear over time | Low; software updates needed | Moderate; hardware and software may require regular updates |
| Best Use Case | Retail, kiosks, and mobile devices | Customer service, smart home devices | Gaming, automotive interfaces, and smart TVs |
Analyzing Alternative Solutions to Touch Screen Diagrams
Voice Recognition
Voice recognition technology allows users to interact with devices through spoken commands. This solution is increasingly popular in environments where hands-free operation is beneficial.
Pros:
– Cost-effective: Primarily software-based, making it cheaper to implement than touch screens.
– Ease of Use: Allows for quick deployment with minimal training required for users.
Cons:
– Accuracy Variability: Performance can be affected by background noise and user accents, potentially leading to misinterpretations.
– Limited Functionality: While useful for simple commands, it may struggle with complex tasks that require nuanced input.
Gesture Control
Gesture control technology enables users to interact with devices through physical movements, often detected by cameras or sensors. This method is gaining traction in various applications, from gaming to smart home technology.
Pros:
– Intuitive Interaction: Users can engage with technology in a natural way, often enhancing user experience.
– Dynamic Control: Offers a wide range of commands that can be executed through gestures.
Cons:
– Setup Complexity: Requires specific hardware and can be more challenging to implement than touch screens.
– User Training: Effective use may necessitate training, particularly for users unfamiliar with gesture-based interfaces.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between touch screen diagrams and their alternatives, consider the specific context of use. Evaluate factors such as the environment, user demographics, and the nature of tasks to be performed. For instance, if your application is in a noisy setting, voice recognition may not be optimal. Conversely, for environments requiring direct user interaction, touch screens may provide the most straightforward solution. Each technology presents unique advantages and limitations, so aligning your choice with your operational goals and user needs is essential for maximizing effectiveness and enhancing user satisfaction.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for touch screen diagram
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Touch Screens?
When evaluating touch screens for B2B applications, understanding critical technical properties is essential. These specifications not only influence the performance and durability of touch screens but also determine their suitability for various environments and applications.
1. Material Grade
The material used in touch screens significantly impacts their durability and functionality. Common materials include glass and plastic, with advanced options like Gorilla Glass offering enhanced scratch resistance. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade ensures the product can withstand the rigors of its intended use, whether in industrial settings or consumer electronics.
Illustrative image related to touch screen diagram
2. Touch Sensitivity
This property refers to the screen’s responsiveness to touch inputs. It is measured in terms of how much pressure is needed to register a touch. Higher sensitivity allows for lighter touches, which can improve user experience in applications where speed and accuracy are critical. In a B2B context, ensuring appropriate touch sensitivity can reduce user fatigue and increase productivity.
3. Resolution
Resolution determines the clarity and detail of the display. Measured in pixels per inch (PPI), higher resolutions provide sharper images and text. For B2B applications, particularly in fields like design or healthcare, high-resolution touch screens can enhance visual communication and data interpretation, ultimately leading to better decision-making.
4. Operating Temperature Range
The operating temperature range indicates the environments in which a touch screen can function effectively. This property is crucial for industries such as manufacturing or outdoor applications where temperatures can fluctuate significantly. Understanding this range helps buyers ensure that touch screens will perform reliably under expected conditions.
5. Durability Rating (IP Rating)
The Ingress Protection (IP) rating assesses how well a touch screen resists dust and moisture. An IP rating of IP65, for instance, indicates that the device is dust-tight and can withstand water jets. For B2B buyers, especially in sectors like logistics or food service, choosing touch screens with appropriate durability ratings minimizes maintenance costs and extends product lifespan.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Touch Screens?
In the B2B landscape, familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms that buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products or components that are sold by another company under its brand. In the touch screen industry, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure product quality.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B transactions, knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, as it can significantly impact purchasing decisions.
Illustrative image related to touch screen diagram
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document soliciting price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. This process is important for B2B buyers to compare pricing and terms, ensuring they receive the best value for their investment.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery terms, which are essential for successful cross-border transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. In industries that rely on timely deliveries, understanding lead times can aid in effective supply chain management, helping businesses meet customer demands without delays.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting touch screens for their specific applications, ensuring they achieve the best performance and value.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the touch screen diagram Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers for Touch Screen Technology in B2B?
The global touch screen market is driven by the increasing demand for intuitive user interfaces across various sectors, including retail, healthcare, and transportation. As businesses strive to enhance customer experience and streamline operations, the adoption of touch screen technology is becoming critical. Key trends include the shift towards capacitive touch technology, which provides a more responsive and clear interface, particularly in mobile devices. Additionally, the growing integration of touch screens in kiosks, ATMs, and smart appliances is reshaping consumer interaction, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where mobile technology is rapidly advancing.
International B2B buyers should also be aware of the shift towards multi-touch capabilities, which allow for more complex interactions and improved usability. Emerging markets are particularly focused on affordability and functionality, leading to increased interest in resistive touch technology for applications that require durability and cost-effectiveness. Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the demand for touchless technology solutions, prompting manufacturers to explore innovations such as infrared and surface acoustic wave (SAW) touch screens to meet hygiene standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Ensure Sustainability in Touch Screen Sourcing?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of supply chain management in the touch screen sector. As environmental concerns rise, B2B buyers are prioritizing suppliers who adopt sustainable practices. The environmental impact of touch screen production, from raw material extraction to waste management, necessitates a focus on ethical sourcing. Buyers should look for suppliers that utilize recycled materials and implement energy-efficient manufacturing processes.
Certifications such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) indicate compliance with environmental standards, ensuring that products are safe for both consumers and the environment. Additionally, the use of eco-friendly materials, such as biodegradable plastics and low-impact adhesives, can further enhance the sustainability profile of touch screens. By prioritizing suppliers with green certifications, B2B buyers can not only mitigate environmental impact but also improve their brand reputation in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
Illustrative image related to touch screen diagram
What Has Been the Evolution of Touch Screen Technology Relevant to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of touch screen technology dates back to the 1960s, with significant advancements that have shaped its current state. Initially, touch screens were primarily used in specialized applications, such as control panels. The introduction of resistive touch screens in the 1970s paved the way for broader consumer applications, including ATMs and kiosks. The late 2000s marked a turning point with the advent of capacitive touch screens, which offered superior responsiveness and clarity, becoming the standard for smartphones and tablets.
This historical context is crucial for B2B buyers as it highlights the rapid technological advancements that have increased touch screen functionality and reliability. Understanding the trajectory of touch screen development can inform purchasing decisions, especially when considering future-proofing investments in technology that aligns with ongoing trends in user experience and interaction design.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of touch screen diagram
-
How do I select the right type of touchscreen for my business needs?
Choosing the appropriate touchscreen technology depends on your specific application. For environments requiring durability and resistance to elements, resistive touchscreens may be preferable due to their ruggedness and ability to work with gloves or styluses. Capacitive touchscreens offer superior clarity and multi-touch capabilities, making them ideal for interactive displays. Assess your usage context, whether industrial, retail, or medical, to determine which technology aligns best with your operational requirements. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for touch screen diagrams?
When evaluating suppliers, consider their industry experience, reputation, and manufacturing capabilities. Verify certifications that ensure quality standards, such as ISO 9001, and request samples to assess product quality firsthand. Additionally, check customer reviews and ask for references to gauge reliability and service quality. An established supplier should also provide clear communication regarding timelines, pricing, and support for customization needs. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for touch screen diagrams?
Minimum order quantities for touch screens can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the specific technology. Generally, MOQs may range from 100 to 1,000 units, especially for customized designs. For bulk orders, suppliers might offer flexibility on MOQs. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements upfront to negotiate terms that suit your purchasing needs and budget. -
What payment terms are typically offered by suppliers of touch screens?
Payment terms vary by supplier, with common options including upfront payments, net 30, or net 60 days. For international buyers, suppliers may require a letter of credit or secure payment methods like PayPal or escrow services to mitigate risks. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing contracts and consider negotiating terms that align with your cash flow needs. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for touch screen products?
To ensure quality assurance, request a detailed QA process from your supplier, which should include inspections at various production stages. It’s beneficial to establish acceptance criteria for performance, durability, and aesthetic qualities. Consider having third-party inspections or audits conducted to validate compliance with international standards, particularly if sourcing from different regions. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing touch screens?
Logistics considerations include shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your destination country. Determine whether your supplier can handle shipping arrangements or if you need to engage a freight forwarder. Be aware of potential tariffs, taxes, and import duties, as these can affect your overall cost. Ensure that packaging is robust to protect the screens during transit. -
Can touch screens be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for touch screens, including size, shape, and technology type. You can also specify features such as screen sensitivity, anti-glare coatings, or specific touch gestures. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers early in the negotiation process to ensure they can meet your needs and provide a timeline for production. -
What are the current trends in touch screen technology that I should be aware of?
Current trends in touch screen technology include advancements in multi-touch capabilities, improved durability with scratch-resistant materials, and the integration of haptic feedback for enhanced user experience. Additionally, there’s a growing trend towards incorporating artificial intelligence for gesture recognition and touchless interfaces. Staying updated on these trends can help your business leverage the latest technology to improve user engagement and operational efficiency.
Top 4 Touch Screen Diagram Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Winmate – Touch Screen Technologies
Domain: winmate.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Touch Screen technologies available include IntelliTouch Surface Wave, SecureTouch Surface Wave, SAW Touch, CarrollTouch, Infrared, 5 Wire Resistive Touch, and Projected Capacitive Resistive Touch. IntelliTouch Surface Wave Touch Technology features a pure glass construction for superior optical performance and scratch resistance, widely used in kiosks and office automation. It operates using piez…
2. Pyroelectro – Simple Touch Screen Interface Schematic
Domain: pyroelectro.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Schematic for a Simple Touch Screen Interface featuring a 16×2 LCD, 18F452 microcontroller, and a Touch Screen. The schematic includes a +5v power regulator circuit with a bypass capacitor. The touch screen has 6 connections: 2 to an Analog to Digital converter on the PIC and 4 to PORTD pins RD0 – RD3 for power and ground. The LCD display uses a 4-bit interface with 2 line configuration, where POR…
3. Crestron – Touch Screen Control Flow Diagram
Domain: docs.crestron.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: The text discusses a simplified touch screen control flow diagram that illustrates the relationship of pages and page flips. It emphasizes the importance of creating a similar diagram during system design to help programmers visualize the entire system and simplify the task of specifying controls on each screen.
4. Reshine – Capacitive Touch Screen
Domain: reshine-display.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Capacitive Touch Screen
Product Keyword: Capacitive Touch Screen
Product Model: 11.6-21.5, 2.4-4.0, 4.3-6.0, 7.0-10.4
Product Summary: Capacitive touch screens utilize the electrical properties of the human body for touch detection, offering high sensitivity, multi-touch support, and durability.
Product Description: Capacitive touch screens consist of a glass substrate, a transparent…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for touch screen diagram
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, the strategic sourcing of touch screen technologies presents significant opportunities for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the nuances of various touchscreen types—such as resistive, capacitive, and projected capacitive—enables organizations to select the most suitable solutions tailored to their specific applications, whether in consumer electronics, industrial automation, or healthcare.
Investing in high-quality touch screen solutions not only enhances user experience but also drives operational efficiency and innovation. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, businesses can leverage competitive pricing, ensure consistent supply chains, and improve product quality, ultimately maximizing return on investment.
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced touch technologies is set to grow, driven by trends such as increased automation, digital transformation, and the Internet of Things (IoT). B2B buyers are encouraged to stay informed about emerging technologies and market trends to capitalize on opportunities that align with their business goals. Engaging with reliable suppliers and fostering long-term partnerships will be crucial for navigating this dynamic landscape and achieving sustained growth.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.