A B2B Buyer’s Guide to Belt Conveyor Diagram: Price, Quality, and Suppliers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for belt conveyor diagram
In an increasingly competitive global market, sourcing the right belt conveyor systems can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers, particularly when navigating complex diagrams and specifications. Understanding the intricate details of a belt conveyor diagram is essential for making informed purchasing decisions that can enhance operational efficiency and drive profitability. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of belt conveyor systems, their applications across diverse industries, and the key components that influence their performance.
International buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Saudi Arabia—will find invaluable insights on how to vet suppliers effectively, evaluate costs, and assess the suitability of different conveyor systems for their unique operational needs. By equipping decision-makers with a thorough understanding of belt conveyors—from the basic mechanics illustrated in diagrams to advanced applications in material handling—this guide empowers organizations to streamline their procurement processes and enhance productivity.
Whether you are looking to upgrade existing systems or implement new solutions, this resource serves as your go-to reference for navigating the complexities of the global belt conveyor market, ensuring your business remains competitive and poised for growth.
Understanding belt conveyor diagram Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flat Belt Conveyors | Simple structure, uses flat belts for material transport | General manufacturing, packaging | Pros: Versatile and cost-effective. Cons: Limited load capacity and can be prone to wear. |
| Trough Belt Conveyors | Designed with sidewalls to form a trough for bulk materials | Mining, agriculture, and bulk handling | Pros: Reduces spillage, suitable for bulk materials. Cons: More complex design increases maintenance needs. |
| Modular Belt Conveyors | Composed of interlocking plastic segments for flexibility | Food processing, packaging, and assembly | Pros: Easy to clean and customize. Cons: Higher initial cost and may require specialized parts. |
| Inclined Belt Conveyors | Designed for elevation changes, uses a sloped configuration | Warehousing, distribution, and recycling | Pros: Efficient for vertical transport. Cons: Requires careful design to avoid material slippage. |
| Magnetic Belt Conveyors | Incorporates magnets to hold ferrous materials in place | Recycling, metal stamping, and assembly | Pros: Effective for metal parts handling. Cons: Limited to ferrous materials, can be costly. |
What are the Characteristics of Flat Belt Conveyors for B2B Buyers?
Flat belt conveyors are characterized by their straightforward design, utilizing a flat belt to transport items across a level surface. They are widely employed in general manufacturing and packaging industries due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness. When considering a flat belt conveyor, buyers should evaluate the material and thickness of the belt, as these factors influence durability and load capacity. While they are budget-friendly, they may not be suitable for heavy loads or abrasive materials, which could lead to increased wear and higher maintenance costs.
How do Trough Belt Conveyors Benefit Bulk Material Handling?
Trough belt conveyors feature sidewalls that create a trough-like structure, making them ideal for transporting bulk materials such as grains, ores, and aggregates. Their design minimizes spillage and enhances stability, which is crucial in mining and agricultural applications. Buyers should consider the conveyor’s capacity, as well as the material used for the belt, which can affect longevity and resistance to wear. Although they offer significant advantages in bulk handling, their more complex design may lead to higher maintenance requirements.
What Advantages Do Modular Belt Conveyors Offer to B2B Operations?
Modular belt conveyors consist of interlocking plastic segments, providing flexibility and ease of customization. They are particularly advantageous in food processing and packaging industries, where hygiene and adaptability are paramount. Buyers should assess the ease of cleaning, as modular designs facilitate maintenance. While the initial investment may be higher compared to traditional belts, the long-term benefits in terms of durability and operational efficiency often justify the cost, especially in environments requiring frequent sanitation.
In What Scenarios are Inclined Belt Conveyors Most Effective?
Inclined belt conveyors are engineered to transport materials at an angle, making them perfect for applications that require elevation changes, such as in warehousing or recycling operations. Their design must ensure that materials do not slip during transport, which can be a concern for buyers. Evaluating the angle of incline and the belt material is essential for ensuring safe and efficient operation. While they enhance vertical transport efficiency, careful consideration of design and installation is necessary to mitigate potential issues.
How Do Magnetic Belt Conveyors Enhance Material Handling?
Magnetic belt conveyors utilize magnets to securely hold ferrous materials during transport, making them ideal for recycling and metal stamping applications. These systems are beneficial for operations that require precise movement of metal parts, ensuring they remain in place during handling. Buyers should consider the strength of the magnetic field and the types of materials being transported. While they provide efficient solutions for metal handling, their application is limited to ferrous materials, and the initial costs can be higher compared to standard conveyor systems.
Key Industrial Applications of belt conveyor diagram
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of belt conveyor diagram | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mining | Transporting bulk materials from mines | Increases efficiency and reduces labor costs | Durability to withstand harsh environments and heavy loads |
| Agriculture | Grain handling and processing | Streamlines operations and minimizes waste | Material compatibility with various grains and moisture levels |
| Manufacturing | Assembly line operations | Enhances productivity and reduces bottlenecks | Customization options to fit specific layouts and workflows |
| Food Processing | Transporting packaged goods | Maintains hygiene and reduces contamination risks | Compliance with food safety standards and easy cleaning features |
| Logistics and Warehousing | Sorting and distributing packages | Improves speed and accuracy in order fulfillment | Flexibility in design to accommodate varying package sizes |
In the mining industry, belt conveyors are essential for transporting bulk materials like coal, minerals, and aggregates from extraction sites to processing facilities. These systems enhance operational efficiency by minimizing manual handling and reducing the time taken to move materials. Buyers should prioritize sourcing conveyors that are robust enough to withstand harsh mining conditions and capable of handling heavy loads without frequent breakdowns.
In agriculture, belt conveyors facilitate the movement of grains from harvesting equipment to storage facilities or processing plants. They help streamline operations by reducing manual labor and minimizing grain spillage, which can lead to significant losses. When sourcing, buyers should consider the compatibility of conveyor materials with different types of grains and the ability to handle varying moisture levels to ensure optimal performance.
Within the manufacturing sector, belt conveyors are widely used in assembly line operations to transport components efficiently between workstations. This application significantly enhances productivity by reducing bottlenecks and ensuring a smooth workflow. Buyers should look for customization options that allow the conveyor system to be tailored to specific production layouts and operational requirements, ensuring seamless integration into existing processes.
In the food processing industry, belt conveyors are critical for transporting packaged goods while maintaining hygiene standards. These systems help mitigate contamination risks and streamline the movement of products through various processing stages. Buyers must ensure that the conveyors comply with food safety regulations and are designed for easy cleaning to maintain hygiene and prevent cross-contamination.
In logistics and warehousing, belt conveyors are employed for sorting and distributing packages, significantly improving the speed and accuracy of order fulfillment. This application is vital for meeting customer demands in a timely manner. Buyers should focus on sourcing flexible conveyor designs that can accommodate various package sizes and weights, ensuring adaptability in dynamic warehouse environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘belt conveyor diagram’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Understanding Complex Conveyor Systems
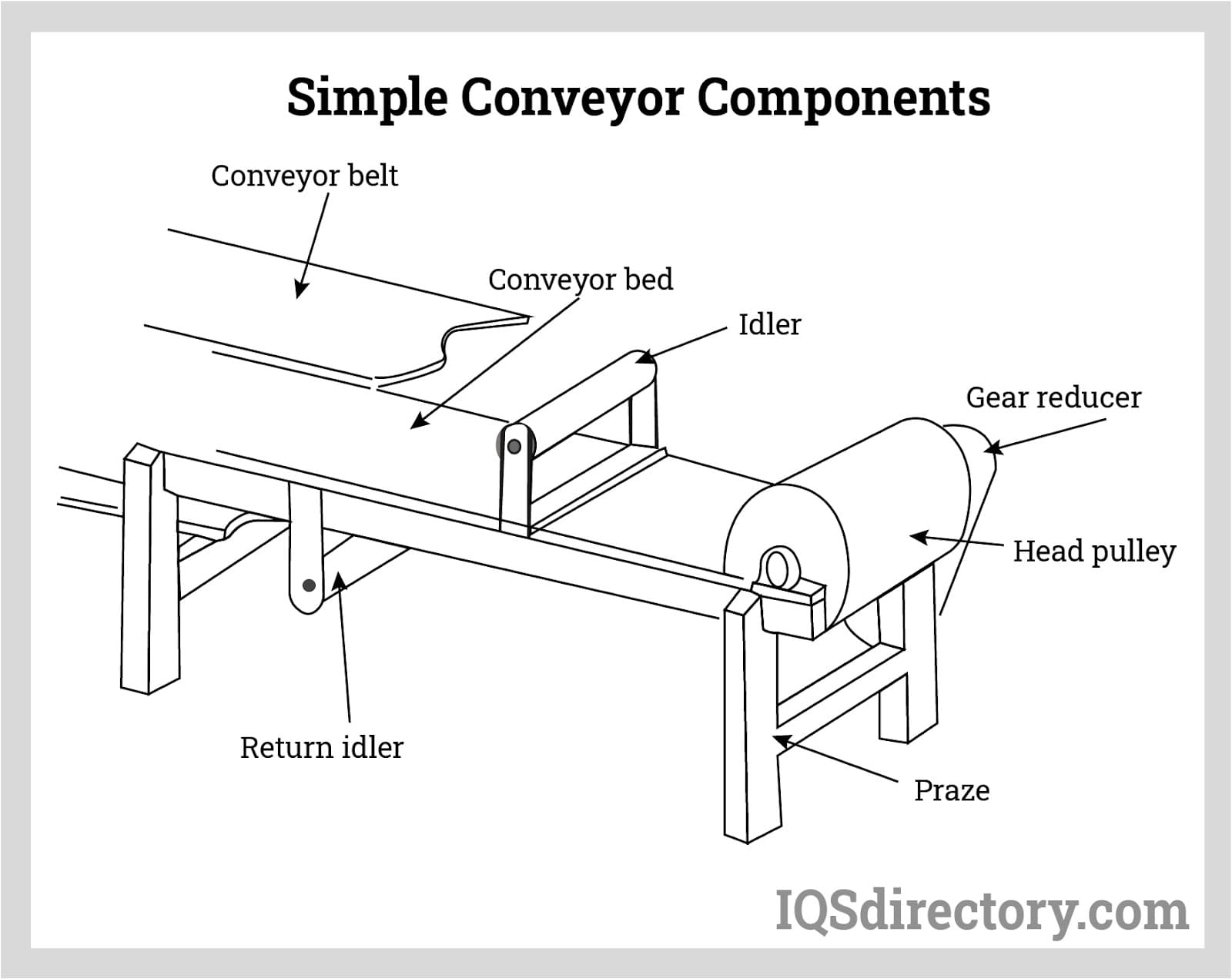
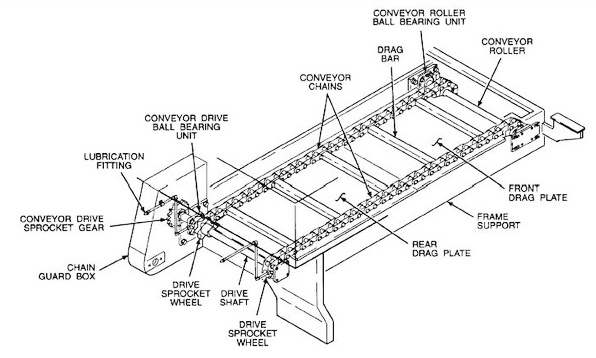
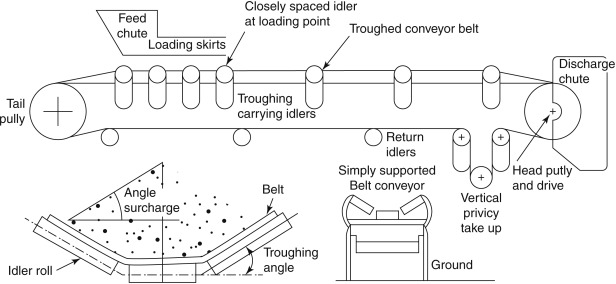
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter challenges when trying to comprehend intricate belt conveyor diagrams that illustrate various components and configurations. These diagrams often include multiple parts such as head pulleys, tail pulleys, idler rollers, and more, which can be overwhelming for those who are not familiar with the technical specifications. This lack of clarity can lead to miscommunication with suppliers and difficulties in specifying the right conveyor system for their unique operational needs.
The Solution: To navigate this complexity, buyers should prioritize a detailed breakdown of each component within the belt conveyor diagram. Engaging with manufacturers who provide clear, annotated diagrams can greatly enhance understanding. Buyers should request training sessions or webinars from suppliers, focusing on how to read and interpret these diagrams effectively. Additionally, utilizing digital tools or software that allow interactive exploration of the conveyor system can provide a hands-on learning experience. This will help ensure that buyers can accurately communicate their requirements and make informed decisions.
Scenario 2: Misalignment Issues Leading to Downtime
The Problem: A common issue faced by B2B buyers is the misalignment of belt conveyors, which can lead to operational inefficiencies and costly downtime. When components are not correctly aligned as depicted in the conveyor diagrams, it results in excessive wear and tear, potential belt slippage, and product spillage. For businesses operating in sectors such as mining or agriculture, where time is money, any downtime can significantly impact profitability.
The Solution: To address alignment issues, buyers should conduct regular inspections and maintenance based on the guidelines provided in the belt conveyor diagrams. Establishing a routine maintenance schedule that includes checking the alignment of pulleys and rollers can prevent misalignment. Furthermore, investing in advanced monitoring technology, such as laser alignment tools, can facilitate precise adjustments. Buyers should also ensure that their installation teams are trained in the specifics of the conveyor diagram to guarantee that the system is set up correctly from the outset.
Scenario 3: Selecting the Right Conveyor Belt Material
The Problem: Selecting the appropriate belt material is a significant pain point for B2B buyers, especially when considering the diverse range of applications and environmental conditions. Many buyers struggle to understand how the material properties—such as tensile strength, resistance to wear, and temperature tolerance—should influence their choice of conveyor belt, as represented in the diagrams. This can lead to premature failure of the belt or inefficiencies in material handling processes.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should engage in thorough research and consultation with manufacturers to understand the characteristics of different belt materials. It’s crucial to analyze the specific requirements of the materials being conveyed, including weight, size, and environmental factors. Buyers can leverage the information provided in conveyor diagrams to match the right belt material with their operational needs. Additionally, conducting a cost-benefit analysis of different belt types can help buyers make informed decisions that balance upfront costs with long-term durability and performance. Seeking samples for testing can also provide firsthand insight into how well a particular belt material meets the operational demands before making a significant investment.
By addressing these common pain points through informed decision-making and proactive strategies, B2B buyers can enhance their operational efficiency and ensure a smoother material handling process.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for belt conveyor diagram
What Are the Key Materials Used in Belt Conveyor Systems?
When selecting materials for belt conveyor systems, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. This analysis focuses on four common materials: rubber, PVC, metal, and fabric. Each material has distinct characteristics that influence performance and suitability for various applications.
How Does Rubber Perform in Belt Conveyor Applications?
Rubber is a widely used material in belt conveyors due to its excellent flexibility and durability. It typically has a high temperature resistance (up to 100°C) and good abrasion resistance, making it suitable for transporting bulk materials like aggregates and grains.
Pros: Rubber belts offer high tensile strength and can handle heavy loads, making them ideal for demanding applications. They also provide good grip, reducing slippage during operation.
Cons: However, rubber can be susceptible to degradation from UV exposure and certain chemicals, which may limit its application in environments with harsh conditions. Additionally, rubber belts can be more expensive than other materials.
Impact on Application: Rubber belts are particularly effective in industries such as mining and agriculture, where they are exposed to heavy loads and abrasive materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM for rubber quality and durability. In regions like Africa and South America, where UV exposure can be intense, selecting UV-resistant rubber is essential.
What Advantages Does PVC Offer for Belt Conveyors?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is another popular choice for belt conveyors, especially in food processing and packaging industries. It is known for its chemical resistance and can withstand temperatures up to 60°C.
Pros: PVC belts are lightweight, cost-effective, and easy to clean, making them suitable for applications that require hygiene, such as food handling.
Cons: However, PVC belts may not be as durable as rubber belts and can suffer from wear and tear under heavy loads. They also have a lower temperature tolerance, which may limit their use in high-heat environments.
Illustrative image related to belt conveyor diagram
Impact on Application: PVC is ideal for applications involving light to moderate loads, particularly in food and pharmaceutical sectors where cleanliness is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with food safety standards such as FDA or EU regulations is critical for buyers in the food industry. Additionally, understanding local PVC regulations is essential in regions like the Middle East and Europe.
Why Choose Metal for Belt Conveyors?
Metal conveyor belts, often made from stainless steel or other alloys, are used in applications requiring high strength and durability. They can handle extreme temperatures (up to 1000°C) and are resistant to corrosion.
Pros: Metal belts are highly durable and can withstand harsh environments, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications in industries like mining and metallurgy.
Cons: The primary drawback is their high cost and weight, which can increase installation and operational expenses. Additionally, metal belts can be noisy during operation.
Impact on Application: Metal belts are ideal for high-temperature processes, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries, where they are used for transporting hot parts.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must consider compliance with international standards like ASTM and DIN for material quality. In regions like Europe, where environmental regulations are stringent, selecting eco-friendly metal options may be beneficial.
What Role Does Fabric Play in Belt Conveyor Systems?
Fabric belts, typically made from polyester or nylon, are versatile and used in various applications. They can handle moderate temperatures (up to 80°C) and offer good flexibility.
Pros: Fabric belts are lightweight and can be manufactured in various widths and lengths, making them easy to customize for specific applications. They also tend to be less expensive than rubber or metal options.
Cons: However, fabric belts generally have lower tensile strength and may not be suitable for heavy loads or abrasive materials. They can also absorb moisture, which can lead to degradation over time.
Illustrative image related to belt conveyor diagram
Impact on Application: Fabric belts are widely used in packaging and light material handling applications, where flexibility and customization are key.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that fabric belts comply with relevant standards like ISO for textile materials. In regions with high humidity, such as parts of Africa and South America, moisture-resistant fabrics may be necessary.
Summary of Material Selection for Belt Conveyors
| Material | Typical Use Case for belt conveyor diagram | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Heavy-duty applications (mining, agriculture) | High durability and grip | Susceptible to UV and chemical degradation | High |
| PVC | Food processing and packaging | Cost-effective and easy to clean | Less durable under heavy loads | Medium |
| Metal | High-temperature and heavy-duty applications | Extremely durable and corrosion-resistant | High cost and noisy operation | High |
| Fabric | Light material handling and packaging | Lightweight and customizable | Lower tensile strength and moisture absorption | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for belt conveyor diagram
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Belt Conveyors?
The manufacturing process of belt conveyors involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets both performance and quality standards. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions.
-
Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing belt conveyors is the selection and preparation of raw materials. Common materials include high-grade steel for the frame, durable rubber or synthetic compounds for the belt, and various polymers for components like idlers and pulleys. The materials undergo cutting, shaping, and pre-treatment processes such as coating or surface treatment to enhance durability and resistance to wear. -
Forming
During the forming stage, the prepared materials are shaped into the necessary components. This includes the fabrication of the frame, which may involve welding or bolting sections together for structural integrity. The belt itself is produced through processes such as extrusion for rubber compounds or weaving for fabric belts. Precision in forming is critical, as it affects the alignment and overall efficiency of the conveyor system. -
Assembly
Once all components are formed, the assembly process begins. This involves integrating various parts, including the belt, pulleys, and idler rollers, into a cohesive unit. Skilled technicians ensure proper alignment and tensioning of the belt, which is vital for smooth operation. Automation technologies, such as robotic arms, may be employed to enhance speed and precision during assembly. -
Finishing
The finishing stage includes applying protective coatings and conducting final adjustments. This may involve painting the frame, applying anti-corrosion treatments, or installing safety features such as guards. Quality checks are conducted at this stage to ensure that all components function as intended before the conveyor is prepared for shipment.
How Is Quality Assurance Ensured in Belt Conveyor Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a fundamental aspect of the belt conveyor manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet international and industry-specific standards. Here are key components of the quality assurance process.
-
International Standards and Compliance
Adhering to international standards such as ISO 9001 is crucial for manufacturers targeting global markets. ISO 9001 outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS) that emphasizes customer satisfaction and continuous improvement. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE mark for compliance with European safety standards or API specifications for oil and gas applications may be necessary, depending on the intended use of the conveyor. -
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) is typically divided into several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery to ensure they meet specified standards. Any subpar materials are rejected, preventing potential issues in the final product.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, QC personnel monitor production processes to identify and rectify defects in real time. This can include checking dimensions, material properties, and assembly accuracy.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, the completed conveyor undergoes comprehensive testing to confirm its functionality and adherence to specifications. This may involve load testing, operational testing, and inspections of safety features. -
Common Testing Methods Used in Quality Assurance
Various testing methods are employed to validate the performance and reliability of belt conveyors. These include:
– Load Testing: Ensuring the conveyor can handle the specified weight without failure.
– Operational Testing: Running the conveyor under normal operating conditions to check for issues like misalignment or excessive wear.
– Material Testing: Conducting tests on raw materials to assess their durability and resistance to environmental factors.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is vital for ensuring product reliability. Here are actionable steps buyers can take:
-
Supplier Audits
Conducting audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. Buyers should request detailed documentation of their QMS, including compliance with ISO standards and any other relevant certifications. -
Requesting Quality Assurance Reports
Buyers should ask suppliers for quality assurance reports that detail the results of their QC processes, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC findings. These reports can offer transparency regarding the supplier’s commitment to quality. -
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s operations. These services can evaluate compliance with international standards, perform random checks on material quality, and validate testing results. -
Understanding Regional Compliance Nuances
Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements that affect quality standards. For instance, manufacturers exporting to Europe must comply with CE marking, while those in the Middle East might need to adhere to local regulatory frameworks. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these nuances to ensure supplier compliance.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for belt conveyors are integral to delivering reliable and effective material handling solutions. By understanding these processes and taking proactive steps to verify supplier quality, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and contribute to their overall success in the marketplace.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘belt conveyor diagram’
To assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring a belt conveyor diagram, this guide outlines essential steps to ensure a successful sourcing process. Whether you’re in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, following this checklist will help streamline your procurement and lead to better operational efficiency.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before you begin sourcing, it’s essential to clearly outline your technical requirements. Consider the materials you will be transporting, the load capacity, and the operational environment (e.g., temperature, humidity). This clarity helps in identifying suppliers who can meet your specific needs.
- Load Characteristics: Specify the type of materials (bulk, packaged, etc.) and their weight.
- Conveyor Length and Width: Determine the dimensions based on your facility layout.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Research potential suppliers in the belt conveyor industry to understand their offerings and market reputation. Look for companies that specialize in your required type of conveyor, as this can significantly influence the performance and longevity of the system.
- Industry Reviews: Read testimonials and case studies to gauge supplier reliability.
- Regional Expertise: Focus on suppliers familiar with your local market conditions and regulations.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website; delve deeper to assess their capabilities.
- Certifications: Verify certifications that indicate compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO).
- Experience: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in similar projects.
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you’ve shortlisted suppliers, request detailed proposals that outline their solutions, pricing, and delivery timelines. This will provide insight into their understanding of your needs and their ability to meet them.
- Cost Breakdown: Ensure the proposal includes a clear breakdown of costs (materials, installation, maintenance).
- Timeline: Confirm estimated delivery and installation timelines to align with your project schedule.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Maintenance
The quality of after-sales support can significantly impact the operational efficiency of your belt conveyor system. Inquire about maintenance services, warranty coverage, and the availability of spare parts.
- Support Availability: Check if they offer 24/7 support or local service teams.
- Training: Ensure they provide training for your staff on system operation and maintenance.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve selected a supplier, negotiate the terms and conditions of the contract. This includes payment terms, warranty agreements, and any service level agreements (SLAs) that define performance expectations.
- Clear Terms: Ensure all agreements are documented to avoid misunderstandings.
- Payment Flexibility: Discuss payment options that align with your financial processes.
Step 7: Finalize the Order and Monitor Progress
After reaching an agreement, finalize your order and maintain regular communication with the supplier. Monitoring progress ensures that the project stays on track and addresses any issues that may arise promptly.
- Regular Updates: Schedule periodic check-ins to review project milestones.
- Quality Control: Establish quality checks at various stages of the production and installation process.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing a belt conveyor diagram more effectively, ensuring they select the right system for their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for belt conveyor diagram Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Belt Conveyor Diagrams?
When sourcing belt conveyor diagrams, several cost components contribute to the overall pricing structure. Understanding these elements can help buyers make informed decisions.
Illustrative image related to belt conveyor diagram
-
Materials: The primary material used in belt conveyors is the belt itself, which can be made from rubber, polymer, or metal. The choice of material influences durability, load capacity, and resistance to wear and tear. High-quality belts are often more expensive but can lead to lower maintenance costs over time.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce required for manufacturing, assembling, and installing the conveyor systems. Skilled labor can command higher wages, especially in regions where expertise is scarce. It’s essential to consider labor costs in the context of local wage standards and availability of skilled workers.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Manufacturing overhead can vary significantly based on the location of the supplier and the scale of operations.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific conveyor designs can add to the initial cost. If a buyer requires unique specifications, the tooling costs may increase. It’s advisable to clarify whether the supplier includes tooling costs in the initial pricing or if they will be charged separately.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing robust QC processes ensures that the conveyor systems meet industry standards and buyer specifications. This may involve additional testing and inspection costs, which should be factored into the pricing.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary based on the distance from the supplier to the buyer, the mode of transport, and any customs duties or tariffs applicable in international shipping. Buyers should consider logistics in relation to their overall budget and timeline.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This can vary depending on the supplier’s market position, reputation, and the level of competition in the sector.
What Price Influencers Should Buyers Consider?
Several factors can influence the pricing of belt conveyor diagrams, making it crucial for buyers to evaluate these aspects when negotiating.
-
Volume/MOQ: The minimum order quantity (MOQ) can significantly impact pricing. Suppliers often offer discounts for bulk purchases, which can lead to substantial cost savings for larger orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific requirements can increase costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their needs to avoid unexpected price hikes later in the process.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and the presence of quality certifications (such as ISO standards) can affect the overall price. High-quality materials often come at a premium but can reduce long-term operational costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier play a critical role in pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms used in the transaction can clarify responsibilities and costs related to shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. This knowledge is crucial for accurate budgeting.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers?
To secure the best pricing for belt conveyor diagrams, consider the following negotiation strategies:
-
Negotiate Based on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Rather than focusing solely on the purchase price, evaluate the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and lifespan. A higher initial investment might lead to lower long-term costs.
-
Leverage Competition: Obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to create a competitive bidding environment. This can provide leverage in negotiations and help achieve better pricing.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, preferential treatment, and insights into future pricing trends.
-
Clarify Payment Terms: Discussing favorable payment terms can also influence overall costs. Options such as extended payment periods or discounts for upfront payments can be beneficial.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be mindful of local economic conditions, currency fluctuations, and trade tariffs, as these factors can significantly influence pricing.
Disclaimer
The prices discussed in this analysis are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and consult with suppliers to obtain accurate pricing tailored to their unique needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing belt conveyor diagram With Other Solutions
In the industrial landscape, the choice of material handling solutions is pivotal for optimizing operations and enhancing productivity. While the belt conveyor diagram illustrates an efficient method for transporting goods, various alternatives exist that may better suit specific operational needs. This section will analyze these alternatives, comparing their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Belt Conveyor Diagram | Bucket Conveyor | Roller Conveyor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High capacity for continuous material flow | Excellent for bulk materials, especially in vertical lifts | Good for diverse load types, but limited to flat surfaces |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment and operational costs | Higher due to complexity and specialized components | Generally lower, but depends on length and configuration |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires significant setup and alignment | Complex installation, especially for vertical systems | Easier to install; modular designs available |
| Maintenance | Moderate; regular inspections needed | High; requires frequent checks on bucket integrity | Low; minimal wear parts, but needs alignment checks |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for continuous and horizontal transport | Best for transporting bulk materials vertically | Suitable for short-distance transport of items on flat surfaces |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Bucket Conveyors?
Bucket conveyors are designed to transport bulk materials vertically and horizontally. They utilize buckets attached to a belt or chain to elevate materials. The primary advantage of bucket conveyors is their ability to handle large volumes of bulk materials efficiently, making them ideal for industries like agriculture and mining. However, they come with higher initial costs and require more maintenance due to the wear and tear on the buckets and chains. Their complexity also means that installation can be more challenging compared to belt conveyors.
How Do Roller Conveyors Compare to Belt Conveyors?
Roller conveyors utilize a series of rollers to facilitate the movement of goods. They are well-suited for transporting items over short distances and are often used in warehouses and distribution centers. One of the main advantages of roller conveyors is their ease of installation and adaptability to various layouts. They also tend to have lower maintenance costs as they have fewer moving parts. However, they are limited to flat surfaces and may not be as efficient for bulk materials compared to belt conveyors.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Material Handling Solution?
Selecting the appropriate material handling solution requires a thorough understanding of your operational needs, budget, and the types of materials being transported. Belt conveyors are ideal for continuous operations and can handle various load types, but alternatives like bucket conveyors and roller conveyors may provide better efficiency or cost-effectiveness depending on your specific use case. B2B buyers should evaluate their unique requirements, including space constraints, load characteristics, and maintenance capabilities, to make an informed decision that aligns with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for belt conveyor diagram
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of Belt Conveyors?
When evaluating belt conveyors, several technical properties are essential for ensuring optimal performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Understanding these specifications can help B2B buyers make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs.
1. Material Grade
The material grade of the conveyor belt significantly influences its strength and durability. Common materials include rubber, PVC, and polyurethane, each offering different levels of resistance to wear, chemicals, and temperature. Selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that the belt can withstand the specific operational environment, thereby minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
2. Tension Rating
Tension rating indicates the maximum load that the conveyor belt can handle without stretching or breaking. It is measured in pounds per inch of width (PIW) or kilonewtons per meter (kN/m). A higher tension rating is critical for applications involving heavy loads, as it ensures the belt maintains its integrity under stress, leading to improved operational efficiency.
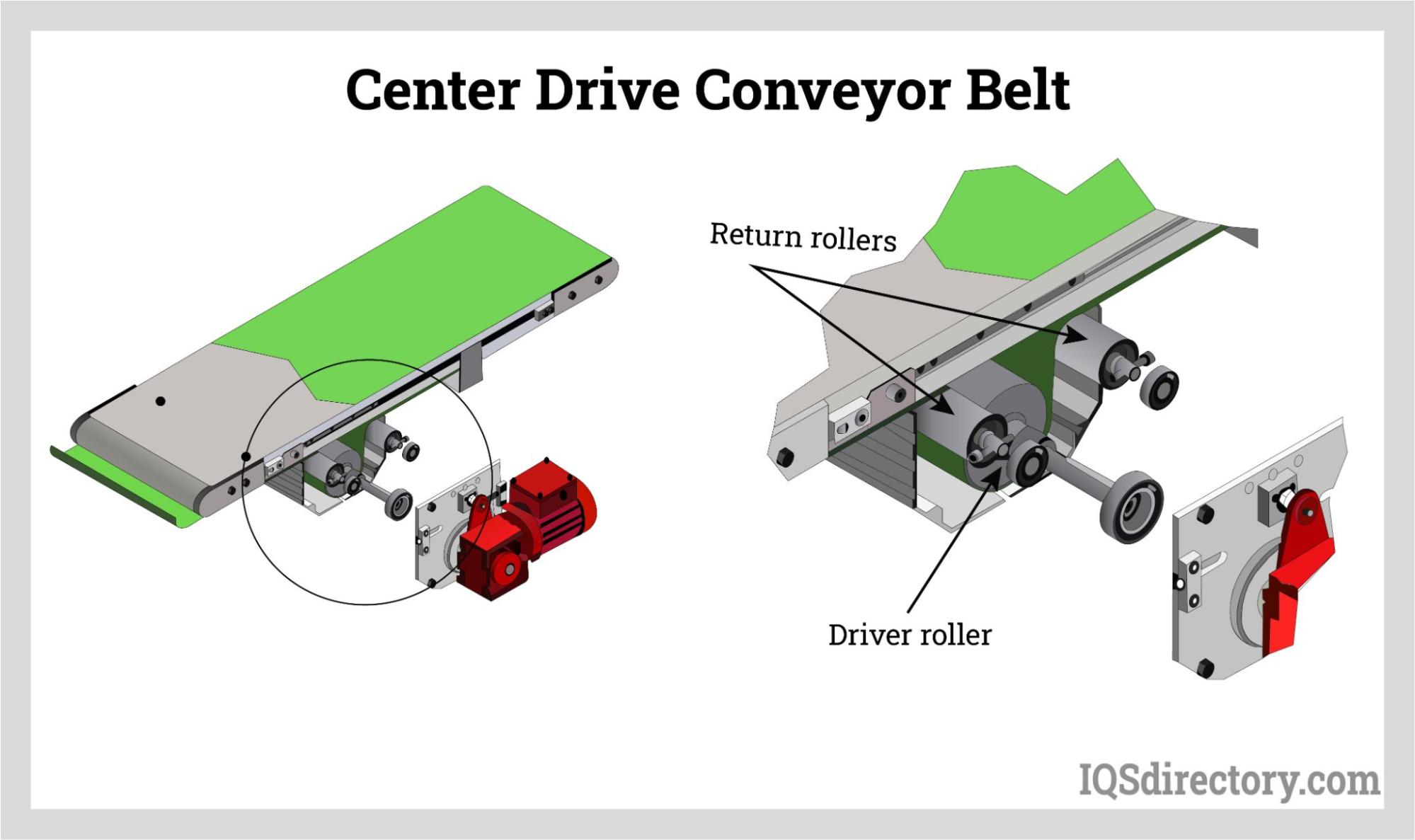
Illustrative image related to belt conveyor diagram
3. Width and Length
The width and length of the conveyor belt are vital specifications that determine its capacity and the types of materials it can transport. Wider belts can carry more material, while length affects the overall layout of the conveyor system. Proper sizing is essential to optimize throughput and prevent bottlenecks in production lines.
4. Belt Thickness
Belt thickness impacts both the durability and flexibility of the conveyor. Thicker belts tend to be more robust and resistant to wear, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. Conversely, thinner belts may be more flexible and easier to install in tight spaces. Selecting the right thickness is crucial for balancing performance and cost-effectiveness.
5. Surface Texture
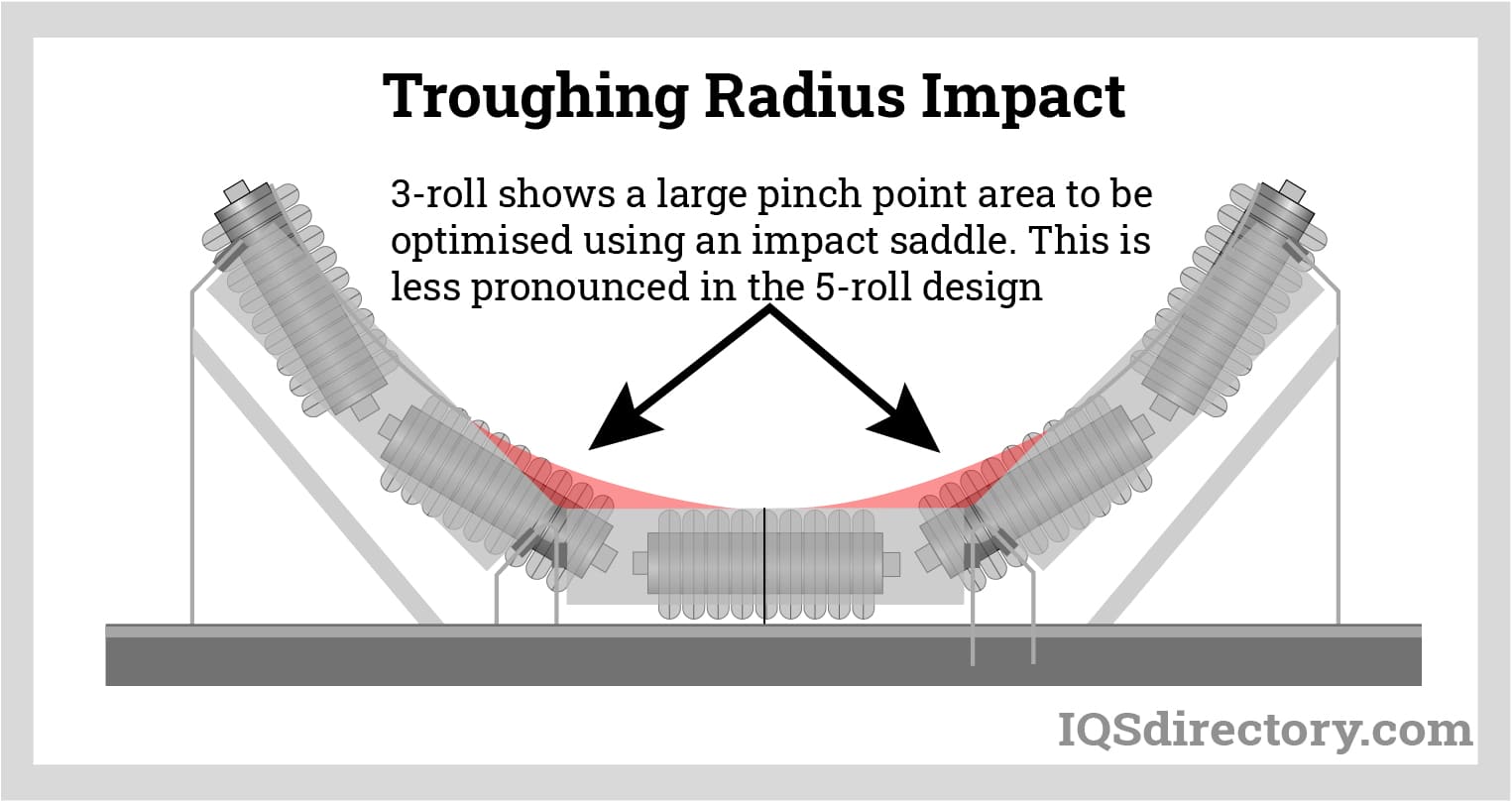
The surface texture of the conveyor belt affects its grip on the transported materials. Textured surfaces can prevent slippage and ensure that materials remain securely in place during transit. This property is particularly important in applications involving inclined or declined transport, where the risk of material rollback is heightened.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Belt Conveyor Industry?
Navigating the belt conveyor industry requires familiarity with specific trade terminology. Understanding these terms can facilitate smoother transactions and communication between suppliers and buyers.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that manufactures products or components that are used in another company’s end products. In the context of belt conveyors, an OEM provides the complete conveyor system or its individual parts, ensuring compatibility and quality assurance.
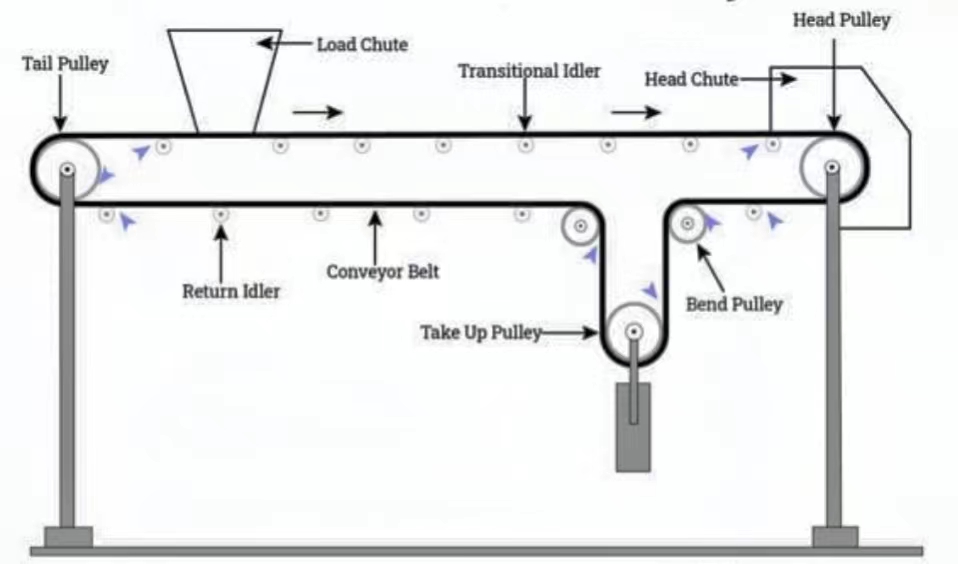
Illustrative image related to belt conveyor diagram
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it helps determine budget constraints and inventory levels. Understanding MOQ can lead to better negotiation strategies and inventory management.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent by potential buyers to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products or services. This process allows buyers to compare costs and evaluate supplier capabilities, ensuring they select the best option for their needs.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. These terms clarify aspects such as shipping, risk transfer, and delivery points. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers engaging in global trade, as they help avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth logistics.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product. Understanding lead times is essential for effective project planning and inventory management. B2B buyers should consider lead times when assessing suppliers to ensure that their operational schedules are met without delays.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and align with their business goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the belt conveyor diagram Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Impacting the Belt Conveyor Diagram Sector?
The global belt conveyor market is witnessing significant growth, driven by increasing automation in various industries, including manufacturing, mining, and logistics. The rise of e-commerce, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, has amplified the demand for efficient material handling systems. International B2B buyers must be aware of emerging technologies such as IoT-enabled conveyors that offer real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime. In the Middle East, investments in infrastructure and industrial sectors further catalyze the need for advanced conveyor solutions.
Additionally, there is a growing trend toward customization, where manufacturers are adapting conveyor systems to meet specific operational needs. This shift is particularly relevant for companies in diverse markets like Brazil and Saudi Arabia, where local conditions and requirements can vary significantly. Buyers should consider suppliers that offer modular designs, allowing for easier upgrades and expansions as business needs evolve.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Belt Conveyor Diagram Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor in sourcing decisions within the belt conveyor sector. As businesses globally strive to reduce their environmental footprint, the demand for eco-friendly materials and processes is on the rise. Conveyor systems made from recycled materials or those that utilize energy-efficient motors are increasingly sought after. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that can demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through certifications such as ISO 14001, which reflects an organization’s adherence to environmental management standards.
Illustrative image related to belt conveyor diagram
Moreover, ethical sourcing practices are gaining traction, particularly in regions with stringent labor laws and environmental regulations. This is crucial for international buyers, as the transparency of supply chains becomes a competitive advantage. Companies that prioritize ethical sourcing not only enhance their brand reputation but also mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions. B2B buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers that provide detailed information about their sourcing practices and material origins, ensuring alignment with their sustainability goals.
What Is the Evolution of the Belt Conveyor System and Its Relevance Today?
The belt conveyor system has evolved significantly since its inception in the late 18th century, initially used for transporting grain and other bulk materials. Over the decades, technological advancements have led to the development of various types of conveyors tailored for specific applications, including belt, roller, and bucket conveyors. This evolution is particularly relevant for B2B buyers today, as the market now offers a wide array of solutions designed to enhance productivity, safety, and efficiency.
Modern belt conveyor systems incorporate features such as advanced materials for durability, automation for improved speed, and integration with smart technologies for enhanced monitoring and control. For international buyers, understanding this evolution is essential for making informed purchasing decisions, ensuring they select systems that not only meet current operational demands but are also adaptable for future advancements. The historical context provides valuable insights into the capabilities and potential of today’s conveyor systems, reinforcing their role as a cornerstone in industrial operations across various sectors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of belt conveyor diagram
-
How do I choose the right belt conveyor system for my industry?
Choosing the right belt conveyor system depends on several factors, including the type of material you need to transport, the distance it must cover, and the required load capacity. Consider the environment in which the conveyor will operate; for instance, if you are in a humid or corrosive setting, a belt made from resistant materials is essential. Additionally, assess your production speed and space constraints, as these will affect the design and layout of the system. Consulting with experienced suppliers can also provide insights tailored to your specific needs. -
What are the key components of a belt conveyor diagram?
A comprehensive belt conveyor diagram typically includes essential components such as the conveyor belt, head and tail pulleys, idler rollers, and drive motors. Understanding the function of each component is crucial for troubleshooting and maintenance. The head pulley drives the belt while the tail pulley provides tension. Idler rollers support the belt and load, ensuring smooth operation. A well-detailed diagram should also illustrate the frame and any additional features, like safety guards or emergency stops, which are vital for operational safety. -
What customization options are available for belt conveyor systems?
Customization options for belt conveyor systems are extensive and can include adjustments in length, width, and material of the conveyor belt. You can also opt for specialized features such as incline/decline configurations, modular designs for easy reconfiguration, or even integrated sensors for automated operations. Many suppliers offer bespoke solutions that cater to specific industry requirements, such as food-grade belts for the food processing industry or heavy-duty systems for mining operations. Always communicate your needs clearly to ensure the solution fits your operational goals. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for belt conveyors?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for belt conveyors can vary significantly among suppliers. Some manufacturers may require a MOQ of one unit, particularly for custom designs, while others may set higher thresholds for bulk orders. It’s advisable to discuss MOQs upfront during negotiations to find a supplier that aligns with your purchasing capacity. Larger orders might also qualify for volume discounts, which can be advantageous for companies looking to scale their operations. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing belt conveyors internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing of belt conveyors often include options such as upfront payments, letters of credit, or installment payments based on milestones. Typically, a 30% deposit is common at the order confirmation, with the remaining balance due before shipment. It’s crucial to clarify these terms in the contract to avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, consider the currency exchange rates and transaction fees that may apply, as these can impact overall costs. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my belt conveyor order?
To ensure quality assurance for your belt conveyor order, start by selecting suppliers with established QA processes and relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001. Request documentation that outlines their QA procedures, including testing methods and inspection protocols. Consider conducting factory audits or requesting samples prior to full production to verify the quality of materials and workmanship. Establishing clear communication channels with the supplier can also facilitate prompt resolution of any quality concerns. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing belt conveyors?
Logistics for importing belt conveyors involve several key considerations, including shipping methods, customs clearance, and local regulations. Determine whether you will use air or sea freight based on urgency and cost. Ensure that all necessary documentation, such as bills of lading and certificates of origin, are in order to facilitate smooth customs processing. Additionally, it’s wise to partner with a logistics provider experienced in handling industrial equipment to navigate any challenges that may arise. -
How do I vet suppliers for belt conveyor systems?
Vetting suppliers for belt conveyor systems involves assessing their industry experience, customer reviews, and certifications. Start by researching potential suppliers online, looking for case studies or testimonials from businesses in your sector. Request references and reach out to previous clients to gauge their satisfaction with the supplier’s products and services. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s facility if possible, to evaluate their manufacturing capabilities and quality control processes firsthand.
Top 6 Belt Conveyor Diagram Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. DPH Engineering – Belt Conveyors
Domain: dphengg.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Belt conveyors are systems that move materials, goods, and people using a belt instead of chains or hydraulics. Key components include: 1. Head Pulley: Drives the belt, located at the discharge end, often with a rough jacket for grip. 2. Tail Pulley: Located at the loading end, provides tension and guides the belt back. 3. Idler Rollers: Support the belt and load, prevent sagging, and clear carryb…
2. Conveyor Systems – E-Learning Presentation
Domain: slideshare.net
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: The document is an e-learning presentation on conveyor belt systems, detailing the types, components, and working principles of conveyors used for bulk material handling. It explains various conveyor types, essential parts like pulleys and idlers, and methods for maintaining and splicing conveyor belts. Additionally, the presentation covers safety devices and maintenance practices to ensure optima…
3. PLOS – Double-Head Driving Belt Conveyor
Domain: plos.figshare.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Schematic diagram of the double-head driving belt conveyor includes the following components: 1. Driving roller 1, 2. Driving roller 2, 3. Tension device, 4. Supporting roller, 5. Conveyor belt, 7. Driving device 2, 8. Driving device 1. This conveyor system is related to power allocation in multi-drive conveyors and involves the selection of conveyor belts, including steel wire core types.
4. Accurate Industrial – Conveyor Belting Solutions
Domain: accurateindustrial.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Conveyor Belting, Lightweight Conveyor Belting, Food Conveyor Belting, General Conveyor Belting, Incline Conveyor Belting, Machine Tapes / Power Transmission Conveyor Belting, Airport / Distribution Conveyor Belting, Heavy Rubber Conveyor Belting, Modular Belting, Modular Plastic Belting, Table Top Conveyor Chains, Wire Belting, Timing / Drive Belts, Timing Belts, Extruded Profiles, Round Belts, E…
5. Pinterest – Conveyor Belt CAD Designs
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Conveyor belt design CAD files available for download, including 2D AutoCAD models. Features include sectional diagrams, dimensions, and sensor placements (misalignment and rotate sensors). Specific designs include a belt conveyor for chicken manure collection with detailed views (top, front, side, and section). Additional resources include technical drawings, installation guides, and various conv…
6. Scribd – Belt Conveyor Components Overview
Domain: scribd.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: The document provides an overview of various components of a typical belt conveyor, including pulleys, idlers, and impact beds, detailing their functions and configurations. It highlights the importance of components like the Tail Pulley, Snub Pulley, and Self-Aligning Idlers in maintaining belt tension and tracking. Additionally, it emphasizes the use of specialized idlers and pulleys for specifi…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for belt conveyor diagram
In navigating the complexities of belt conveyor systems, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical factor for international B2B buyers. Understanding the diverse components, from head pulleys to idler rollers, enables businesses to select systems that enhance operational efficiency while minimizing costs. By prioritizing high-quality materials and innovative designs, companies can not only streamline their production processes but also bolster their competitive edge in the global market.
The value of strategic sourcing extends beyond immediate procurement; it fosters long-term partnerships with suppliers who understand regional challenges and can provide tailored solutions. For businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, investing in reliable conveyor systems is essential for optimizing supply chains and meeting increasing demands.
Illustrative image related to belt conveyor diagram
Looking ahead, the future of belt conveyor systems will likely be shaped by advancements in technology, sustainability, and automation. As you consider your options, seize the opportunity to engage with suppliers who can offer insights into emerging trends and innovations. By making informed sourcing decisions, you position your business for growth and success in an evolving marketplace. Reach out today to explore how the right belt conveyor solutions can transform your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.