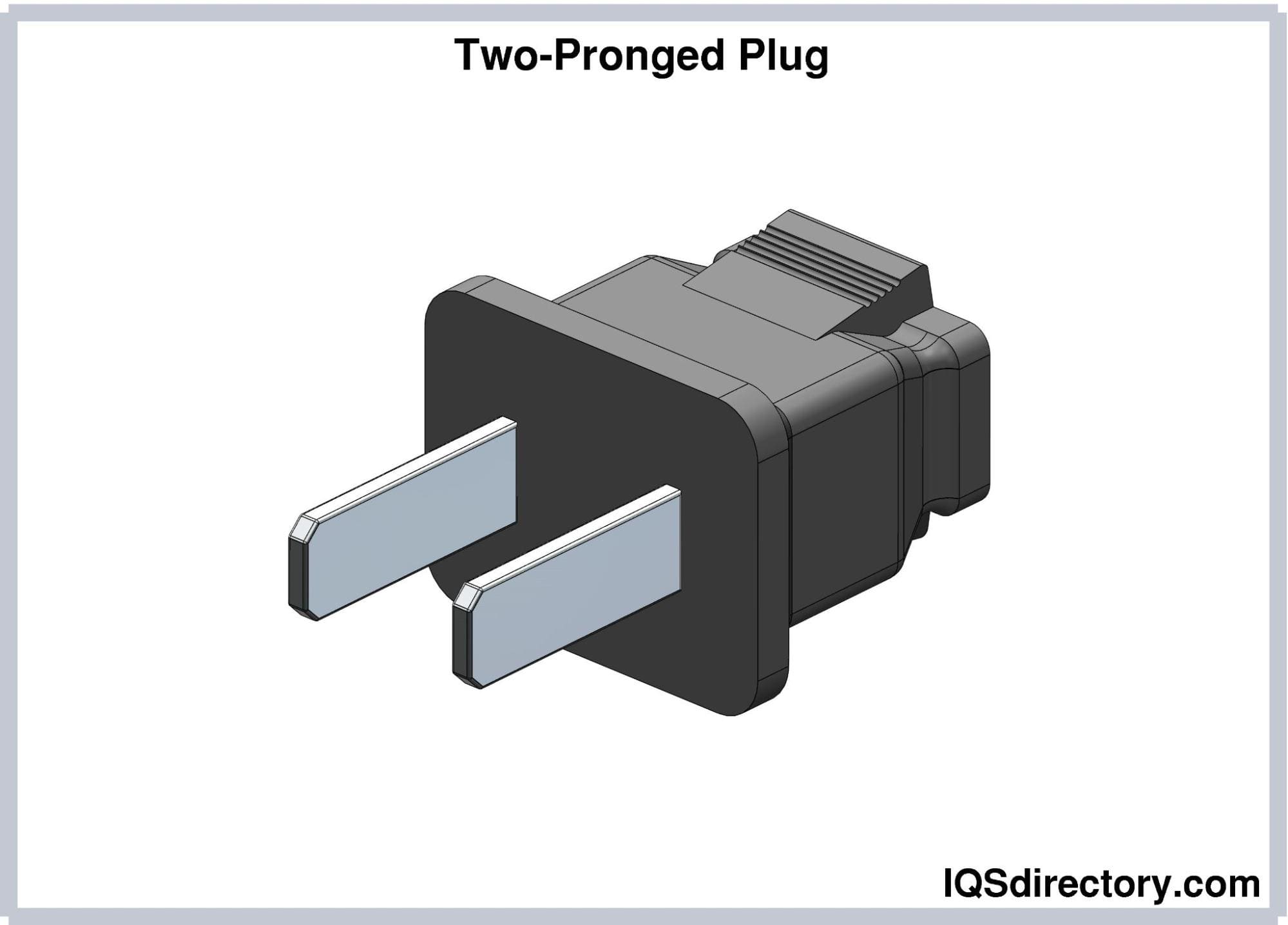
Is Your Two Pronged Plugs Are Designed For Home Use Sourcing Strategy Flawed? Read…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for two pronged plugs are designed for home use
In today’s global marketplace, sourcing reliable two-pronged plugs designed for home use presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers. With varying standards and safety regulations across regions, understanding the nuances of these electrical components is crucial for ensuring compliance and functionality in residential applications. This guide delves into the essential aspects of two-pronged plugs, including their types, applications, and the importance of proper supplier vetting, ensuring that you make informed purchasing decisions tailored to your market needs.
International buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—like Germany and Nigeria—will benefit from a comprehensive analysis of the cost implications and quality assurance practices that govern the manufacturing and distribution of two-pronged plugs. By navigating through the intricacies of voltage compatibility, material quality, and safety standards, you will be equipped to select products that not only meet local regulations but also enhance customer satisfaction and safety in residential environments.
This guide aims to empower you with the knowledge necessary to streamline your procurement process, mitigate risks associated with substandard products, and ultimately foster a safer electrical infrastructure in homes around the world. As the demand for reliable electrical solutions continues to rise, being well-informed will position your business advantageously in this competitive landscape.
Understanding two pronged plugs are designed for home use Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEMA 1-15 | Flat parallel blades, ungrounded | Residential appliances, lamps | Pros: Cost-effective, simple design. Cons: Lacks grounding, less safe. |
| Type C (Europlug) | Two round pins, compatible with Type E and F | Small appliances, travel chargers | Pros: Widely used in Europe, versatile. Cons: May require adapters in some regions. |
| BS 1363 (UK Plug) | Three rectangular prongs, includes fuse | Home appliances, power tools | Pros: Enhanced safety, built-in fuse. Cons: Bulkier design may not fit all sockets. |
| Type I (Australian Plug) | Two flat pins in a V-shape, with a grounding pin | Electronics, power strips | Pros: Safe grounding, commonly used in Australia. Cons: Limited compatibility outside Australia. |
| Type B (NEMA 5-15) | Two flat parallel blades and a round grounding pin | Heavy-duty appliances, industrial equipment | Pros: Grounding enhances safety, robust design. Cons: More expensive than ungrounded types. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of NEMA 1-15 Plugs?
NEMA 1-15 plugs are characterized by their flat parallel blades and lack of grounding. Commonly found in older residential buildings, these plugs are primarily used for low-power devices like lamps and small appliances. While they are cost-effective and easy to use, the absence of a grounding mechanism raises safety concerns, particularly in regions prone to electrical surges. B2B buyers should consider the risks associated with using ungrounded plugs, especially in commercial settings where safety standards are paramount.
How Does the Type C Europlug Stand Out in the Market?
The Type C Europlug features two round pins and is known for its compatibility with various European socket types, such as Type E and F. This versatility makes it ideal for small appliances and travel chargers. Its widespread acceptance across Europe allows for seamless integration into various electrical systems. However, buyers should be mindful of potential adapter needs when utilizing this plug in regions with different socket designs, which can complicate international business operations.
Why Is the BS 1363 Plug a Preferred Choice in the UK?
The BS 1363 plug is distinguished by its three rectangular prongs and built-in fuse, which enhances safety by preventing overloads. It is the standard plug for home appliances and power tools in the UK, making it essential for businesses operating in this market. While its bulkier design may not fit all sockets, its safety features make it a reliable choice for electrical installations. B2B buyers should evaluate the balance between safety and compatibility when considering this plug type for their operations.
What Advantages Does the Type I Australian Plug Offer?
The Type I plug is characterized by its two flat pins arranged in a V-shape, along with a grounding pin. It is commonly used in Australia and is suitable for a range of electronics and power strips. The grounding feature enhances safety, making it a preferred option for businesses in sectors where electrical safety is critical. However, B2B buyers should note that this plug may not be compatible with sockets in other regions, necessitating additional investments in adapters or converters.
How Do Type B (NEMA 5-15) Plugs Enhance Safety for Industrial Applications?
Type B plugs, also known as NEMA 5-15, feature two flat parallel blades and a round grounding pin, providing a robust design suitable for heavy-duty appliances and industrial equipment. Their grounding capability significantly reduces the risk of electrical shocks and equipment damage, making them an optimal choice for businesses that prioritize safety. While they may come at a higher cost compared to ungrounded options, the investment is justified by the added protection they offer. B2B buyers should assess their specific electrical needs and safety requirements when selecting plug types for industrial applications.
Key Industrial Applications of two pronged plugs are designed for home use
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of two pronged plugs are designed for home use | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residential Construction | Used in older homes for basic electrical needs | Cost-effective solution for existing infrastructure | Compliance with local electrical standards and safety regulations |
| Hospitality | Powering appliances in budget hotels and motels | Affordable option for temporary or transient lodging | Durability and reliability in high-usage environments |
| Retail | Connecting point-of-sale systems and display lighting | Enhances customer experience and operational efficiency | Compatibility with existing electrical systems |
| Education | Powering classroom equipment and educational tools | Supports learning environments with minimal costs | Safety certifications and ease of installation |
| Manufacturing | Used in low-power machinery and equipment | Provides flexibility in equipment setup and maintenance | Availability of bulk purchasing options and quality assurance |
How Are Two-Pronged Plugs Utilized in Residential Construction?
In the residential construction sector, two-pronged plugs are often found in older homes that have not undergone electrical upgrades. These plugs serve basic electrical needs, allowing homeowners to connect small appliances without the necessity for grounding. However, this application presents challenges, as two-pronged outlets lack the safety features of modern three-prong systems. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider the age of the infrastructure when sourcing these plugs, ensuring compliance with local safety standards to mitigate risks of electrical hazards.

Illustrative image related to two pronged plugs are designed for home use
What Role Do Two-Pronged Plugs Play in the Hospitality Industry?
In the hospitality industry, particularly in budget hotels and motels, two-pronged plugs are frequently used to power essential appliances such as lamps, televisions, and small kitchen devices. This application allows for a cost-effective solution that meets the basic electrical needs of transient guests. However, businesses should prioritize sourcing high-quality plugs that can withstand frequent usage and comply with local electrical codes. International buyers must also consider the varying electrical standards in their regions to avoid compatibility issues.
How Are Two-Pronged Plugs Applied in Retail Settings?
Retail environments utilize two-pronged plugs primarily for connecting point-of-sale systems, display lighting, and other low-power devices. This application enhances the customer shopping experience while maintaining operational efficiency. Retailers looking to source these plugs should ensure that they meet the necessary electrical safety certifications and are compatible with existing systems. Additionally, they should consider the aesthetic aspects, as the appearance of plugs and cords can impact the overall store design.
In What Ways Do Educational Institutions Use Two-Pronged Plugs?
Educational institutions often rely on two-pronged plugs to power classroom equipment and educational tools, such as projectors and audio-visual devices. These plugs provide a budget-friendly option for schools operating under tight financial constraints. However, it is crucial for educational buyers to prioritize safety and reliability, particularly in high-traffic areas. When sourcing these plugs, institutions should look for products that are easy to install and comply with safety regulations to ensure a safe learning environment.
What Are the Applications of Two-Pronged Plugs in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, two-pronged plugs are commonly used to power low-power machinery and equipment. This application offers flexibility in setting up workstations and allows for easy maintenance and replacement. Businesses sourcing these plugs should consider bulk purchasing options to reduce costs and ensure quality assurance. It’s essential to verify that the plugs meet the specific power requirements of the equipment used, especially in regions with varying electrical standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘two pronged plugs are designed for home use’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Outdated Electrical Infrastructure Challenges
The Problem:
Many businesses and property managers are faced with older buildings that still utilize two-prong plugs. This situation presents a significant challenge, as two-prong outlets lack grounding, making them less safe for modern electrical appliances. The absence of grounding can lead to increased risks of electrical shocks, fires, and damage to sensitive electronics. This concern is especially pertinent in regions where electrical standards are evolving, and businesses must comply with safety regulations.

Illustrative image related to two pronged plugs are designed for home use
The Solution:
To address this problem, B2B buyers should prioritize a comprehensive electrical assessment of their facilities. Engaging with licensed electricians to evaluate the existing electrical infrastructure is crucial. When sourcing two-pronged plugs, opt for those that meet or exceed international safety standards. Additionally, consider investing in a phased upgrade plan to replace two-prong outlets with three-prong alternatives. This not only enhances safety but also improves the overall functionality of the electrical system, thereby protecting valuable equipment and ensuring compliance with local regulations.
Scenario 2: Compatibility Issues with Modern Devices
The Problem:
As technology advances, many businesses are increasingly reliant on devices that require three-prong plugs for optimal performance. However, the presence of two-prong outlets can create compatibility issues, leading to frustrations when trying to connect essential equipment. This can disrupt daily operations, particularly in industries that depend heavily on electronic devices for productivity and efficiency.
The Solution:
B2B buyers should consider investing in high-quality adapters or converters that allow two-prong plugs to connect to three-prong outlets. However, it’s essential to ensure that these adapters are certified and designed for safe use with the specific devices in question. For a more permanent solution, businesses should plan for an upgrade of their electrical systems to include three-prong outlets. This proactive approach not only alleviates compatibility issues but also signals to clients and employees that the business prioritizes safety and modernity in its operations.
Scenario 3: Limited Safety Awareness Among Employees
The Problem:
In many organizations, employees may not be fully aware of the safety hazards associated with using two-prong plugs. This lack of awareness can lead to improper usage, such as overloading outlets or using damaged plugs, which can increase the risk of accidents. Moreover, without proper training, employees may inadvertently jeopardize their safety and the safety of the workplace environment.
The Solution:
To mitigate this issue, B2B buyers should implement a comprehensive training program focused on electrical safety and the specific risks associated with two-prong plugs. This program should include guidelines on safe usage, recognizing faulty equipment, and the importance of using grounded outlets. Additionally, consider providing visual reminders or posters in common areas to reinforce safety protocols. By fostering a culture of safety awareness, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of electrical accidents and ensure a safer working environment for all employees.

Illustrative image related to two pronged plugs are designed for home use
Strategic Material Selection Guide for two pronged plugs are designed for home use
What Are the Common Materials for Two-Pronged Plugs Designed for Home Use?
When selecting materials for two-pronged plugs intended for home use, it is crucial to consider the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material. This analysis will focus on four common materials: thermoplastic, thermoset plastic, metal (typically copper), and rubber. Each material has unique characteristics that can influence performance, safety, and compliance with international standards.
How Does Thermoplastic Perform in Two-Pronged Plugs?
Key Properties: Thermoplastic materials, such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or nylon, are known for their excellent electrical insulation properties and temperature resistance, typically ranging from -40°C to 85°C. They can withstand moderate mechanical stress and are resistant to moisture.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of thermoplastics is their low cost and ease of manufacturing, allowing for mass production. However, they may not be as durable as other materials and can degrade under prolonged exposure to UV light or extreme temperatures. This can affect the longevity of the plugs in varying climates.
Impact on Application: Thermoplastics are suitable for residential applications where electrical safety and insulation are paramount. However, they may not be ideal for environments with extreme temperatures or high humidity.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa or South America should ensure that thermoplastic materials comply with local electrical safety standards, such as IEC or ANSI, to avoid potential hazards.
What Are the Benefits of Using Thermoset Plastics?
Key Properties: Thermoset plastics, such as epoxy or phenolic resins, are characterized by their high thermal stability and resistance to deformation under heat. They typically have a temperature rating of up to 150°C and excellent electrical insulation properties.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of thermoset plastics is their durability and resistance to chemicals and heat, making them suitable for high-performance applications. However, they are generally more expensive and complex to manufacture, which can increase the overall cost of the plugs.
Impact on Application: Thermoset plastics are ideal for plugs that may be exposed to higher temperatures or corrosive environments, ensuring long-term reliability.

Illustrative image related to two pronged plugs are designed for home use
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe, particularly Germany, should look for compliance with DIN standards, as thermoset materials are often preferred for their robustness in industrial applications.
Why Is Metal (Copper) Essential in Two-Pronged Plugs?
Key Properties: Copper is widely used in electrical contacts due to its excellent conductivity, with a resistivity of approximately 1.68 µΩ·m. It can handle high current loads and has a melting point of around 1,085°C, making it suitable for high-performance applications.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which ensures efficient power transfer. However, copper is susceptible to corrosion, which can lead to electrical failures over time. Coating with materials like tin can mitigate this issue but adds to manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Copper is essential for the internal wiring and contacts of two-pronged plugs, ensuring they can handle the electrical load safely.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that copper components meet ASTM standards for electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, especially in humid climates like those found in parts of Africa.
How Does Rubber Contribute to Electrical Safety?
Key Properties: Rubber materials, particularly silicone rubber, offer excellent insulation properties and flexibility. They can operate effectively within a temperature range of -60°C to 200°C, making them suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons: The flexibility and insulating properties of rubber provide excellent protection against electrical shocks. However, rubber can wear down over time, especially in outdoor applications, and may require periodic replacement.
Impact on Application: Rubber is often used in the outer casing of plugs to enhance safety and prevent electrical shock, especially in homes with children or pets.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international safety standards, such as IEC 60884, is crucial for rubber components to ensure they meet electrical safety requirements.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Two-Pronged Plugs
| Material | Typical Use Case for two pronged plugs are designed for home use | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastic | Insulation and casing for standard plugs | Low cost and easy to manufacture | Less durable, can degrade in UV exposure | Low |
| Thermoset Plastic | High-performance plugs in extreme conditions | High durability and thermal stability | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Metal (Copper) | Internal wiring and contacts for efficient power transfer | Superior electrical conductivity | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Rubber | Outer casing for safety and insulation | Excellent shock protection | Can wear down over time | Medium |
This comprehensive analysis provides a clear understanding of the material options available for two-pronged plugs, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for two pronged plugs are designed for home use
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Two-Pronged Plugs for Home Use?
The manufacturing of two-pronged plugs involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets safety and performance standards.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used for Two-Pronged Plugs?
The manufacturing process begins with material selection. Two-pronged plugs are typically made from high-quality thermoplastics or thermosetting plastics for the body, which provide durability and electrical insulation. Copper or brass is commonly used for the prongs due to their excellent conductivity. The choice of materials is crucial, as they directly influence the plug’s performance, safety, and longevity.
How Are Two-Pronged Plugs Formed?
The next stage is forming, which involves shaping the selected materials into the desired components. This may include injection molding for the plastic housing and stamping or forging for the prongs. Advanced techniques such as die-casting can also be employed for precision. The forming process must ensure that the components are uniform in size and free from defects, as these factors can affect the plug’s overall functionality.
What Does the Assembly Process Look Like?
Once the individual components are prepared, they are assembled. This process involves inserting the prongs into the plastic housing, ensuring they are securely fitted to prevent any movement that could lead to electrical hazards. Automated assembly lines are often utilized to enhance efficiency and precision. Quality checks during assembly are essential to identify any misalignments or defects before the plugs move on to the finishing stage.
How Is the Finishing Process Performed?
The finishing stage includes surface treatment and the application of any necessary labels or certifications. This may involve coating the prongs with a layer of nickel or tin to prevent corrosion and improve conductivity. The plugs are then tested for visual defects, and any necessary markings, such as safety certifications, are applied. A polished finish not only enhances the aesthetic appeal but also contributes to the plug’s overall durability.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Two-Pronged Plugs?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of electrical components, particularly for products like two-pronged plugs that must meet strict safety standards.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Consider?
B2B buyers should look for compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers maintain consistent quality throughout the production process. Additionally, certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) signify that the plugs meet European safety and environmental standards, while UL (Underwriters Laboratories) certification is crucial in North America. For buyers in Africa and South America, local standards may also apply, necessitating an understanding of regional compliance requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): This ongoing assessment occurs during the manufacturing stages. Regular inspections help identify issues early, minimizing waste and ensuring product integrity.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, plugs undergo rigorous testing to verify they meet all specifications. This includes electrical testing for insulation resistance and functionality.
How Can Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of the manufacturing facilities can provide insights into the supplier’s production practices and adherence to quality standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to share documentation of their QC processes, including testing results and compliance certificates.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspection Services: Utilizing independent inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing process and product quality.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Two-Pronged Plugs?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure that two-pronged plugs are safe and reliable:
-
Electrical Testing: This includes measuring voltage, current, and resistance to ensure the plug operates within safe limits.
-
Mechanical Testing: Tests such as pull force and insertion force are conducted to assess the durability of the prongs and the integrity of the connection.
-
Environmental Testing: Plugs may be subjected to temperature and humidity tests to evaluate their performance under various conditions.
What Quality Control Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances when sourcing two-pronged plugs.
How Do Regional Standards Impact Quality Assurance?
Different regions may have specific safety and quality standards. For example, European buyers must ensure CE compliance, while buyers in the Middle East may require specific local certifications. Understanding these requirements is essential to avoid non-compliance issues that could lead to product recalls or legal complications.
What Role Do Certifications Play in Global Trade?
Certifications not only serve as proof of compliance but also enhance the credibility of manufacturers in the global marketplace. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with recognized certifications, as these can facilitate smoother trade and improve market acceptance.
How Can Buyers Navigate Language and Cultural Barriers?
Effective communication is crucial when dealing with international suppliers. B2B buyers should consider working with local representatives or consultants who understand the regional market dynamics and can bridge any language or cultural gaps. This can significantly enhance the purchasing experience and lead to better supplier relationships.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for two-pronged plugs is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material selection, production techniques, and stringent quality control measures, buyers can ensure they source high-quality, compliant products. Additionally, being aware of international standards and regional requirements will help navigate the complexities of global trade, ensuring safety and reliability in electrical components.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘two pronged plugs are designed for home use’
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure two-pronged plugs designed for home use. Understanding the nuances of sourcing these electrical components is essential for ensuring safety, compliance, and functionality in residential settings. Follow these steps to streamline your procurement process effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial to ensure that the two-pronged plugs meet your operational needs. Consider factors such as voltage, current ratings, and compatibility with existing electrical systems. This step helps prevent costly errors and ensures that you procure plugs that are suitable for your target markets.
- Voltage and Current Ratings: Ensure the plugs are rated for the appropriate voltage (typically 110-120V or 220-240V) and current levels to suit your applications.
- Material Quality: Look for plugs made from durable materials that can withstand wear and tear, particularly in high-use environments.
Step 2: Research Compliance Standards
Two-pronged plugs must comply with various international safety standards and regulations. Familiarize yourself with the specific requirements in your target regions, such as CE marking in Europe or IEC standards. Compliance not only guarantees safety but also enhances the credibility of your products.
- Safety Certifications: Ensure the plugs have certifications from recognized testing organizations relevant to your market.
- Regional Regulations: Be aware of any regional variations in standards that may affect your product’s acceptance.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ascertain their reliability and reputation in the market. Request detailed company profiles, product samples, and references from other businesses that have worked with them.
- Supplier History: Look into how long they have been in the business and their experience with two-pronged plugs.
- Customer Feedback: Seek testimonials or case studies from previous clients to gauge satisfaction and reliability.
Step 4: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Cost is a significant factor in any procurement decision. However, it is essential to balance price with quality and service. Request quotes from multiple suppliers and evaluate their payment terms to find the best fit for your budget and cash flow.
- Bulk Purchase Discounts: Inquire about pricing models for large orders to maximize savings.
- Payment Flexibility: Look for suppliers that offer favorable payment terms, such as extended payment periods or installment plans.
Step 5: Review Logistics and Delivery Options
Understanding the logistics involved in shipping and delivery is vital for timely project completion. Ensure that the supplier can meet your delivery timelines and has a robust logistics strategy to minimize delays.
- Shipping Methods: Discuss available shipping options and their associated costs, including express delivery if needed.
- Customs and Import Regulations: Be aware of any customs regulations in your country that might affect delivery times or costs.
Step 6: Plan for After-Sales Support
After-sales support can significantly influence your overall satisfaction with the supplier. Ensure that they offer reliable customer service for any issues that may arise post-purchase, such as product defects or compliance queries.
- Warranty and Returns Policy: Understand the warranty period and the process for returning faulty products.
- Technical Support: Verify if the supplier provides technical assistance or troubleshooting support for their products.
By following this checklist, you can ensure a smooth and effective procurement process for two-pronged plugs, leading to successful outcomes for your business and clients.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for two pronged plugs are designed for home use Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Two-Pronged Plugs?
When sourcing two-pronged plugs designed for home use, it is essential to understand the various cost components that contribute to the overall pricing. The primary elements include:
Illustrative image related to two pronged plugs are designed for home use
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials—such as plastic, copper, and metal components—plays a significant role. The quality and source of these materials can vary widely, affecting the final price. High-quality materials may be more expensive but can lead to better durability and safety.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages paid to workers involved in manufacturing the plugs. This includes assembly line workers, quality control personnel, and engineers. Labor rates can vary greatly depending on the country of manufacture and the level of automation used in the production process.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with running the production facility, such as utilities, maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, thus lowering the overall price.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in molds and machinery required for producing two-pronged plugs can be substantial. These costs are typically amortized over the production volume, making them a crucial factor in pricing, especially for low-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that products meet safety and performance standards is vital, particularly in the electrical industry. QC processes incur costs, but they help mitigate risks associated with defective products, which can lead to costly recalls or safety incidents.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs are critical in the pricing structure. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and the terms of delivery (Incoterms) can significantly affect the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically mark up their prices to ensure profitability. The margin can vary based on market conditions, competition, and demand.
What Influences the Pricing of Two-Pronged Plugs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of two-pronged plugs, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can greatly affect pricing. Larger orders often lead to economies of scale, reducing the per-unit cost. Buyers should negotiate for better pricing based on anticipated volume.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific certifications (e.g., CE, UL) can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and internationally recognized certifications can raise costs but are essential for safety and compliance, especially in regions with stringent electrical standards.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their products due to their proven track record, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The terms of trade (Incoterms) dictate who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms is crucial for calculating the total landed cost of the plugs.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Pricing?
To ensure cost-efficiency when sourcing two-pronged plugs, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Building a strong relationship can lead to better terms and discounts.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate the total cost, including shipping, duties, and potential warranty or service costs. A lower initial price may not always equate to a better deal in the long run.
-
Be Aware of Regional Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to local regulations, tariffs, and market conditions. Buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of these factors when sourcing.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Conduct thorough research to compare multiple suppliers. Look for reviews, certifications, and past performance to ensure you are getting the best value.
-
Understand Market Trends: Stay informed about market trends and fluctuations in material costs. This knowledge can empower buyers to make timely purchasing decisions.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure, pricing influencers, and negotiation strategies is essential for international B2B buyers looking to source two-pronged plugs effectively. By leveraging these insights, buyers can optimize their procurement processes and ensure that they receive quality products at competitive prices.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing two pronged plugs are designed for home use With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Two-Pronged Plugs for Home Use
In the realm of electrical solutions, particularly for residential applications, the choice of plug types can significantly impact safety, efficiency, and functionality. While two-pronged plugs have been a longstanding standard, evolving technologies and designs present viable alternatives that enhance user experience and safety. This analysis compares two-pronged plugs designed for home use with three-pronged plugs and smart plugs, focusing on key performance metrics that matter to B2B buyers.
| Comparison Aspect | Two Pronged Plugs Are Designed For Home Use | Three Pronged Plugs | Smart Plugs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Basic functionality; limited safety features | Enhanced safety with grounding; supports higher loads | Remote control, automation, energy monitoring |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Moderate cost increase | Higher initial cost, potential savings in energy use |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation | Requires grounding; may need electrical upgrades | Easy installation; requires Wi-Fi setup |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance but lacks upgrade options | Moderate; may require periodic checks | Low; software updates needed occasionally |
| Best Use Case | Older homes or low-power appliances | Modern homes, high-power appliances | Smart homes, energy-conscious users |
Exploring Three-Pronged Plugs as an Alternative
Three-pronged plugs are designed with an additional grounding wire, providing enhanced safety features compared to their two-pronged counterparts. This grounding wire helps mitigate risks associated with electrical shocks and equipment damage, making them the preferred choice for modern electrical systems. Although the initial installation cost may be higher, the long-term safety and reliability they offer justify the investment. Moreover, three-prong outlets are better suited for high-power devices, ensuring that electrical systems can handle increased loads without risk.
The Advantages of Smart Plugs for Modern Homes
Smart plugs represent a significant advancement in home electrical technology, allowing users to control devices remotely via smartphone applications. They typically feature energy monitoring capabilities, which can lead to cost savings by optimizing power consumption. While the initial purchase price of smart plugs is higher than traditional options, the benefits of automation and remote management can greatly enhance operational efficiency. However, they do require a Wi-Fi connection and may involve occasional software updates, which could be a consideration for less tech-savvy users.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When evaluating the best electrical solution for home use, B2B buyers should consider their specific requirements, including safety, cost, and ease of integration. Two-pronged plugs may serve as a budget-friendly option in older homes, but they lack the safety features that modern electrical standards demand. On the other hand, three-pronged plugs provide a balanced approach between safety and cost, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. For those looking to embrace smart technology, smart plugs offer advanced features that can lead to long-term savings and enhanced convenience. Ultimately, the choice will depend on the specific needs of the end-user, the existing electrical infrastructure, and the commitment to safety and efficiency in their operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for two pronged plugs are designed for home use
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Two-Pronged Plugs for Home Use?
When considering two-pronged plugs designed for home use, several technical properties are crucial for ensuring safety, compatibility, and functionality. Understanding these specifications can help B2B buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
1. Material Grade
Two-pronged plugs are typically made from thermoplastic or thermoset materials, which offer durability and electrical insulation. The material grade affects not only the plug’s longevity but also its resistance to heat and environmental factors. For B2B buyers, selecting plugs made from higher-grade materials can reduce the risk of failures, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and safety.
2. Current Rating (Amperage)
The current rating indicates the maximum amount of electrical current the plug can safely handle, usually measured in amperes (A). Common ratings for household two-pronged plugs range from 10A to 15A. This specification is critical for ensuring that the plug can support the devices it will be used with, preventing overheating and potential electrical fires. Buyers should match the current rating with the intended application to ensure safety and compliance with local electrical codes.
3. Voltage Rating
Voltage rating defines the maximum voltage that the plug can safely handle, typically expressed in volts (V). In many regions, two-pronged plugs are designed for 120V or 240V applications. Understanding the voltage rating is essential for B2B buyers to ensure that the plugs are suitable for the electrical systems in the target markets, as mismatches can lead to equipment damage or safety hazards.
4. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels refer to the acceptable range of variation in dimensions and electrical properties of the plugs. For example, the spacing between prongs and the diameter of the prongs must adhere to strict tolerances to ensure proper fit and functionality in outlets. For B2B buyers, ensuring that the plugs meet these tolerance levels is vital for product compatibility and reliability.
5. Safety Certifications
Safety certifications, such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or CE (Conformité Européenne), indicate that the plugs meet specific safety standards. These certifications are particularly important in international trade, as they assure buyers of product safety and compliance with local regulations. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing plugs with recognized safety certifications to mitigate liability risks and enhance marketability.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Two-Pronged Plugs?
Familiarity with industry-specific jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some key terms relevant to two-pronged plugs:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of two-pronged plugs, buyers may source from OEMs that specialize in electrical components, ensuring quality and compatibility with existing products.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for buyers to manage inventory costs effectively. For two-pronged plugs, MOQs can vary significantly between suppliers, influencing purchasing decisions based on budget and demand.

Illustrative image related to two pronged plugs are designed for home use
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document used by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products. By submitting an RFQ for two-pronged plugs, buyers can compare pricing, specifications, and terms from multiple vendors, allowing for more informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers involved in importing two-pronged plugs, as they dictate cost allocation and risk management throughout the shipping process.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time from the placement of an order until it is fulfilled. In the context of two-pronged plugs, lead times can impact supply chain efficiency and inventory management. Buyers should consider lead times when planning orders to ensure they meet market demands promptly.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing two-pronged plugs effectively, ensuring they meet safety standards and market demands while optimizing their procurement processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the two pronged plugs are designed for home use Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Trends in the Two-Pronged Plug Sector?
The global market for two-pronged plugs designed for home use is experiencing dynamic shifts, driven largely by safety regulations and technological advancements. As countries modernize their electrical standards, the demand for safer, more reliable electrical outlets is on the rise. In regions such as Africa and South America, older infrastructure still relies heavily on two-prong outlets, presenting a unique market opportunity for suppliers who can provide upgraded solutions that meet local safety standards. In contrast, Europe, particularly Germany, is moving towards more stringent safety regulations, often favoring three-pronged outlets, which creates a demand for retrofitting older homes.
Emerging technologies are also influencing sourcing trends. Smart home integration is becoming a key consideration for B2B buyers, as the connectivity of devices requires robust electrical systems. This trend encourages manufacturers to innovate, developing two-prong plugs that can integrate with smart home technologies while ensuring compliance with international safety standards. Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated digital transformation in supply chains, prompting businesses to seek out suppliers who can provide reliable e-commerce platforms and logistics solutions.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Two-Pronged Plug Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are increasingly important in the two-pronged plug market. Environmental concerns surrounding plastic waste and energy consumption are prompting manufacturers to adopt greener practices. Using recyclable materials and reducing energy consumption during production are significant steps that can appeal to environmentally conscious buyers.
Ethical supply chains are also vital, especially for international B2B buyers. Suppliers who demonstrate compliance with labor laws and ethical sourcing practices can build stronger relationships with clients in regions sensitive to these issues. Certifications such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and ISO 14001 (Environmental Management Systems) are becoming essential for manufacturers looking to enhance their credibility in the global market. Buyers are more likely to partner with suppliers who can provide these credentials, ensuring that the products they source are safe and environmentally friendly.
Illustrative image related to two pronged plugs are designed for home use
What is the Historical Context of Two-Pronged Plugs in the Electrical Market?
The evolution of two-pronged plugs dates back to the early 20th century when electrical systems were first being standardized. Initially, these plugs provided a simple solution for powering devices but lacked grounding, making them less safe than contemporary designs. As electrical safety standards evolved, three-pronged outlets emerged, incorporating grounding wires that greatly reduced the risk of electrical hazards.
In many regions, particularly in developing countries, two-pronged plugs remain prevalent due to legacy infrastructure. However, as awareness of electrical safety grows and modernization efforts accelerate, there is a clear trend towards upgrading these systems. This historical context highlights the importance of understanding local regulations and the potential for innovation in the two-pronged plug market, providing B2B buyers with insights into the future of electrical safety and technology integration.
In summary, the two-pronged plug market is poised for growth driven by safety, sustainability, and technological advancement, making it a critical focus for international B2B buyers looking to enhance their offerings in the home electrical sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of two pronged plugs are designed for home use
-
How do I ensure the safety of two-pronged plugs for home use?
To ensure safety, verify that the two-pronged plugs comply with international safety standards such as IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) or UL (Underwriters Laboratories). Regularly inspect the plugs for any signs of wear or damage, and ensure they are used in compatible outlets. Consider educating end-users about the limitations of two-pronged plugs, including their lack of grounding, to mitigate risks of electrical hazards. Collaborating with reputable suppliers who prioritize quality assurance can also enhance safety. -
What is the best way to select a supplier for two-pronged plugs?
When selecting a supplier, assess their reputation in the industry by reviewing customer testimonials and seeking references from other businesses. Verify their compliance with international safety standards and certifications. Additionally, evaluate their production capabilities, delivery timelines, and responsiveness to inquiries. Engaging in direct communication and requesting product samples can further aid in determining the supplier’s reliability and quality. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for two-pronged plugs?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among manufacturers and suppliers. Typically, MOQs range from 1,000 to 10,000 units depending on the supplier’s production capabilities and your customization needs. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements directly with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms. Some suppliers may offer flexibility in MOQs for first-time orders or ongoing partnerships, so it’s worth exploring different options. -
Can I customize two-pronged plugs to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for two-pronged plugs, including variations in color, material, and design features. Customization can also extend to branding, such as incorporating your logo or specific packaging requirements. Engage with suppliers early in the procurement process to discuss your needs and ensure they can accommodate your specifications within their production capabilities. -
What are the payment terms typically offered by suppliers of two-pronged plugs?
Payment terms vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include a deposit upfront (usually 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or after inspection. Some suppliers may offer favorable terms like net 30 or net 60 days for established clients. It’s essential to discuss payment options during negotiations and ensure they align with your financial capabilities and cash flow management. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for two-pronged plugs?
To ensure quality assurance, request certifications such as ISO 9001 from suppliers, which indicates adherence to quality management systems. Conduct regular audits and inspections of the manufacturing process and finished products. Establish clear quality standards and specifications in your purchase agreements and consider implementing a third-party inspection service to evaluate product quality before shipment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing two-pronged plugs internationally?
When sourcing internationally, consider factors such as shipping costs, lead times, and customs regulations in both the exporting and importing countries. Ensure the supplier can provide necessary documentation for customs clearance. It’s also beneficial to work with logistics partners who have experience in handling electronic components to mitigate risks of delays or damage during transit. -
How do I handle disputes or issues with suppliers of two-pronged plugs?
To effectively manage disputes, establish clear communication channels and maintain a written record of all correspondence. Refer to the terms outlined in your contract, including warranties and return policies. If issues arise, engage in direct discussions with the supplier to resolve the matter amicably. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as alternative dispute resolution methods to avoid legal proceedings.
Top 3 Two Pronged Plugs Are Designed For Home Use Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. HowStuffWorks – Electrical Safety Explained
Domain: electronics.howstuffworks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Two-pronged plugs have two vertical slots (neutral and hot) and do not provide grounding, while three-pronged plugs include a ground prong for safety against electric shock. The left slot is neutral (larger), the right is hot, and the round hole is ground. Three-prong plugs are used for appliances with metal cases to prevent electric shock if a wire comes loose. Existing two-prong outlets are lega…
2. Teague Electric – Outlet Upgrade Services
Domain: teagueelectric.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Teague Electric offers outlet upgrade services, specifically focusing on replacing outdated two-prong outlets with modern three-prong outlets to enhance safety and compliance with current electrical codes. The upgrade process includes inspecting existing wiring, running a ground wire if necessary, and installing Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlets as an alternative when grounding is im…
3. Reddit – Electrical Outlet Safety
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Electrical outlets with only 2 holes and no grounding wire are typically not considered safe for large appliances. The discussion mentions the use of adapters that allow 3-pronged appliances to connect to these 2-prong outlets, but safety concerns arise due to the lack of grounding. The original wiring from the 1940s likely does not include a ground, making the use of these adapters potentially un…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for two pronged plugs are designed for home use
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of two-pronged plugs for home use presents both challenges and opportunities for international B2B buyers. As electrical safety standards evolve, the importance of understanding the differences between two-prong and three-prong outlets becomes paramount. Two-pronged plugs, while still prevalent in older homes, may pose significant safety risks, including potential electrocution and equipment damage.
For buyers, sourcing high-quality three-prong alternatives not only meets modern safety standards but also enhances the overall functionality of electrical systems in residential settings. This transition is essential for ensuring compliance with evolving regulations across regions, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where diverse market needs exist.
By prioritizing strategic sourcing and aligning with manufacturers that emphasize safety and innovation, buyers can secure reliable products that resonate with contemporary consumer expectations. As we look ahead, the demand for safer, more efficient electrical solutions will only grow. Thus, now is the time to engage with trustworthy suppliers and invest in the future of home electrical systems. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your product offerings and ensure safety in the homes of your customers.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.