The Definitive Guide to Heating Filament: Cost, Materials & Top Vendors
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for heating filament
In an increasingly competitive global market, sourcing high-quality heating filament presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Whether you are in the industrial sector, manufacturing small appliances, or providing heating solutions for specialized applications, understanding the nuances of heating filaments is crucial. This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of various heating filament types, their applications, and critical considerations for supplier vetting and cost analysis.
By delving into the specifics of heating elements—from ceramic and cartridge heaters to flexible and infrared options—this resource equips international buyers with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions. Furthermore, the guide emphasizes the importance of aligning with suppliers who not only provide quality products but also understand regional market dynamics.
With actionable insights and expert recommendations, this guide empowers B2B buyers to navigate the complexities of sourcing heating filaments effectively. It addresses the unique challenges faced by companies in Brazil, Vietnam, and beyond, ensuring that you can leverage the best solutions tailored to your operational needs. Ultimately, this guide serves as a vital tool for optimizing your supply chain and enhancing your product offerings in a globalized marketplace.
Understanding heating filament Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open Coil | Simple design, high surface area for heat distribution | Space heaters, hair dryers | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to manufacture. Cons: Less efficient in confined spaces. |
| Cartridge Heater | Cylindrical, provides precise heating | Industrial ovens, machinery | Pros: High precision, compact design. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Flexible Heaters | Adaptable, can conform to various shapes | Medical devices, automotive applications | Pros: Lightweight, customizable. Cons: Higher cost than rigid options. |
| Band Heaters | Clamps onto objects for external heating | Plastic molding, pipeline heating | Pros: Efficient for targeted heating. Cons: Requires secure mounting. |
| Infrared Heaters | Uses electromagnetic waves for heating | Drying processes, heating large spaces | Pros: Fast heating, energy-efficient. Cons: Limited penetration in dense materials. |
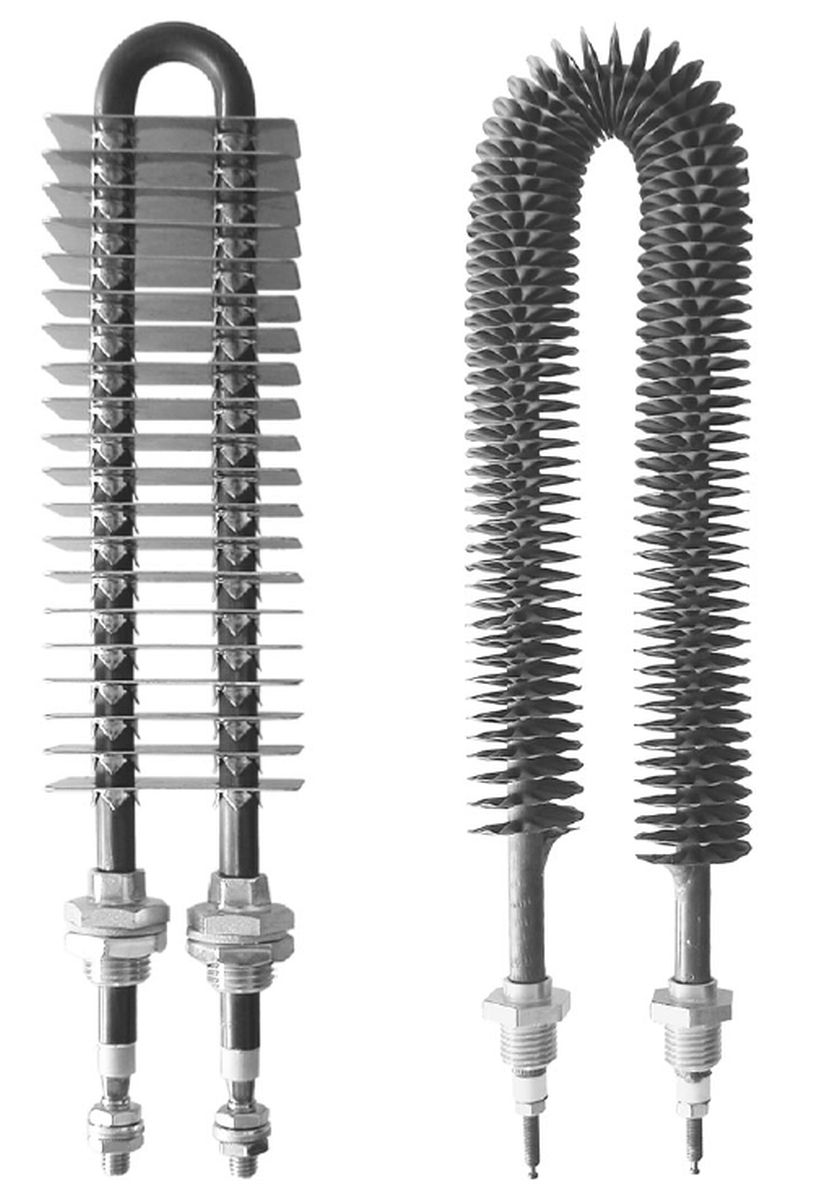
What Are the Characteristics of Open Coil Heating Elements?
Open coil heating elements feature a straightforward design that maximizes the surface area available for heat distribution. This type is widely utilized in applications such as space heaters and hair dryers due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. However, buyers should be mindful that open coil heaters may not be as efficient in confined spaces, leading to uneven heating in certain configurations. When considering open coil elements, assess the specific heating requirements and spatial constraints of your application to determine suitability.
How Do Cartridge Heaters Provide Precise Heating?
Cartridge heaters are cylindrical devices designed to deliver precise heating to various forms of materials and machinery. They are particularly effective in industrial ovens and equipment requiring consistent heat distribution. Their compact size allows for easy integration into existing systems, making them ideal for B2B applications. While cartridge heaters offer high precision, they are limited to specific applications and may not be the best choice for broader heating needs. Buyers should evaluate their operational requirements and compatibility with existing equipment when selecting cartridge heaters.
Illustrative image related to heating filament
Why Choose Flexible Heaters for Custom Applications?
Flexible heaters are designed to conform to various shapes and surfaces, making them ideal for applications in medical devices and automotive components. These heaters are lightweight and highly customizable, allowing for unique configurations that meet specific heating requirements. However, they typically come at a higher cost compared to rigid options. When considering flexible heaters, it is essential to analyze the balance between customization needs and budget constraints, as well as the potential benefits of reduced weight and improved thermal performance.
What Are the Advantages of Using Band Heaters?
Band heaters provide external heating by clamping directly onto the objects needing heat, making them efficient for applications such as plastic molding and pipeline heating. Their targeted heating approach allows for rapid temperature adjustments, essential in processes requiring precise thermal management. However, the effectiveness of band heaters hinges on secure mounting, which may add complexity to installation. B2B buyers should evaluate the ease of installation and the specific heating requirements of their applications to determine the best fit.
How Do Infrared Heaters Enhance Energy Efficiency?
Infrared heaters utilize electromagnetic waves to generate heat, providing rapid heating for large spaces and drying processes. Their ability to heat objects directly rather than the surrounding air makes them energy-efficient and effective for various industrial applications. However, infrared heaters may have limited penetration capabilities in dense materials, which can restrict their effectiveness in some scenarios. Buyers should consider the specific heating environment and the materials involved when opting for infrared heating solutions, ensuring alignment with operational goals.
Key Industrial Applications of heating filament
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Heating Filament | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Industrial Ovens and Furnaces | Efficient cooking and baking processes, improving product quality | Temperature control, durability under high heat, compliance with food safety standards |
| Medical Equipment | Autoclaves for Sterilization | Reliable sterilization of medical instruments, ensuring patient safety | Resistance to corrosion, precise temperature regulation, and compliance with health regulations |
| Plastics and Materials | Plastic Molding and Extrusion Machines | Enhanced material flow and shaping, reducing cycle times | Customization for specific molding requirements, thermal efficiency, and compatibility with various polymers |
| HVAC Systems | Duct Heaters and Unit Heaters | Improved energy efficiency and comfort in climate control systems | Sizing, watt density, and material compatibility for specific environmental conditions |
| Electronics | Flexible Heaters for Circuit Boards | Effective heat management in compact designs, preventing overheating | Size constraints, heat distribution efficiency, and reliability under varying conditions |
How is Heating Filament Utilized in Food Processing?
In the food processing industry, heating filaments are crucial for industrial ovens and furnaces, where they provide consistent and efficient heat for cooking and baking. They help maintain precise temperatures, which is essential for product quality and safety. Buyers must consider the materials’ ability to withstand high temperatures and the need for compliance with food safety standards. This is particularly important for international buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where regulations may vary significantly.
What Role Does Heating Filament Play in Medical Equipment?
Heating filaments are integral to medical autoclaves, which sterilize instruments through high-temperature steam. The reliability of these heating elements is vital to ensure thorough sterilization, thus safeguarding patient health. Buyers in the medical sector need to prioritize materials that resist corrosion and offer precise temperature control. This is especially critical for international markets, where healthcare standards can differ, necessitating compliance with local regulations.
How is Heating Filament Applied in Plastics and Materials?
In the plastics and materials sector, heating filaments are utilized in molding and extrusion machines to facilitate the heating of raw materials. This ensures optimal flow and shaping, which reduces cycle times and enhances product quality. For B2B buyers, sourcing considerations include the customization of heating elements to meet specific molding requirements, as well as ensuring thermal efficiency compatible with various polymers. This is particularly relevant for manufacturers in emerging markets such as Brazil and Vietnam.
What Benefits Does Heating Filament Provide in HVAC Systems?
Heating filaments are employed in HVAC systems, specifically in duct and unit heaters, to improve energy efficiency and occupant comfort. They ensure consistent heating across environments, which is essential for maintaining optimal conditions in commercial and residential spaces. Buyers should focus on the sizing and watt density of the heating elements to match their specific environmental conditions. International buyers, particularly in the Middle East, may need to consider the local climate’s impact on heating requirements.
How is Heating Filament Utilized in Electronics?
In the electronics industry, heating filaments are essential for flexible heaters used in circuit boards. They manage heat effectively in compact designs, preventing overheating and ensuring device longevity. Buyers in this sector must consider size constraints and the efficiency of heat distribution. Reliability under varying conditions is also crucial, especially for international buyers in regions with diverse climates, such as Europe and Africa, where environmental factors can influence product performance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘heating filament’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Sourcing High-Quality Heating Filament for Diverse Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with sourcing heating filaments that meet specific performance requirements for various applications, including industrial ovens, medical devices, or consumer appliances. This challenge is compounded by the variability in manufacturing quality, material composition, and thermal efficiency of the filaments available in the market. Buyers may find themselves receiving subpar products that lead to operational inefficiencies, increased costs, and ultimately, customer dissatisfaction.
The Solution: To effectively source high-quality heating filaments, buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer transparent manufacturing processes and detailed product specifications. Start by requesting samples to evaluate the filament’s performance in real-world conditions. Look for suppliers who provide comprehensive data sheets that outline thermal conductivity, electrical resistance, and material composition. It is also beneficial to partner with manufacturers that allow for customization, enabling the heating elements to be tailored to specific operational needs. Establishing a strong relationship with a reliable supplier can facilitate better communication, ensuring that any adjustments in design or function can be quickly addressed. Lastly, consider conducting periodic quality audits of your suppliers to maintain consistent standards.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Heat Distribution Challenges in Complex Equipment
The Problem: In industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics, achieving uniform heat distribution is crucial for product quality. Buyers often encounter issues where heating filaments fail to provide consistent heat across the entire surface area of the equipment, leading to hot spots or insufficient heating. This uneven heat distribution can cause material warping, product defects, and costly rework, resulting in significant downtime and loss of revenue.
The Solution: To mitigate heat distribution challenges, buyers should consider advanced heating filament designs such as flexible heaters or custom-configured heating elements that can adapt to complex geometries. Engaging with manufacturers who specialize in custom solutions allows for the development of heating filaments that can be precisely placed according to the specific needs of the equipment. Additionally, using thermal simulation software during the design phase can help predict heat distribution patterns, enabling adjustments before production. Implementing temperature sensors in critical areas can also provide real-time feedback, allowing for adjustments to be made dynamically. Regularly reviewing the heating system’s performance and making data-driven decisions will enhance overall efficiency and reliability.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compliance with International Safety Standards
The Problem: International B2B buyers face the challenge of ensuring that heating filaments comply with varying safety and performance standards across different regions. Non-compliance can lead to product recalls, legal repercussions, and damage to brand reputation. As regulations differ widely in regions such as Europe, Africa, and South America, buyers must navigate a complex landscape of certifications and compliance requirements.
Illustrative image related to heating filament
The Solution: To ensure compliance with international safety standards, buyers should work closely with suppliers who have a proven track record of adhering to relevant certifications such as UL, CE, and ISO. Buyers should request documentation that verifies compliance with local regulations and international standards. It is also advisable to stay informed about the regulatory landscape in target markets, as laws and standards may evolve. Establishing a compliance checklist tailored to the regions in which the products will be sold can streamline this process. Additionally, engaging legal counsel or compliance experts familiar with the specific requirements of each market can help navigate any complexities and ensure all products meet the necessary regulations before they reach the market. Regular training for the procurement and engineering teams on compliance issues will also enhance overall awareness and mitigate risks.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for heating filament
What are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Heating Filaments?
When selecting materials for heating filaments, it is essential to consider their key properties, which directly influence product performance. Common materials include Kanthal, Nichrome, Copper, and Stainless Steel, each with distinct characteristics that cater to various applications.
Kanthal: A Versatile Heating Element Material
Key Properties: Kanthal is an iron-chromium-aluminum alloy known for its high-temperature resistance, capable of withstanding temperatures up to 1400°C (2552°F). It exhibits excellent oxidation resistance, making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
Pros & Cons: The durability of Kanthal is one of its significant advantages, as it maintains performance over extended periods. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, and its manufacturing complexity may increase costs. It is particularly well-suited for industrial furnaces and heating elements in high-temperature environments.
Illustrative image related to heating filament
Impact on Application: Kanthal’s compatibility with various media, including air and inert gases, makes it a preferred choice for applications requiring consistent heat without degradation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial when sourcing Kanthal. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that suppliers provide certifications for material quality and performance.
Nichrome: The Industry Standard for Heating Elements
Key Properties: Nichrome, an alloy of nickel and chromium, is renowned for its excellent electrical resistance and ability to operate at temperatures up to 1200°C (2192°F). It also offers good corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various heating applications.
Pros & Cons: One of Nichrome’s key advantages is its cost-effectiveness, as it provides a good balance between performance and price. However, it may not be as durable as Kanthal at extremely high temperatures, and its oxidation can be an issue in certain environments.
Impact on Application: Nichrome is widely used in applications ranging from household appliances to industrial heating systems. Its compatibility with air and other gases makes it versatile across different sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding electrical components and ensure that Nichrome products meet the necessary safety standards. This is particularly important in regions like the Middle East, where compliance can vary significantly.

Illustrative image related to heating filament
Copper: A Conductive Option for Low-Temperature Applications
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, making it suitable for low-temperature heating applications. However, it has a lower melting point (around 1085°C or 1985°F) compared to Kanthal and Nichrome.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its affordability and ease of manufacturing, allowing for quick production runs. However, its susceptibility to corrosion and lower temperature resistance limits its application scope.
Impact on Application: Copper is ideal for heating elements in small appliances and low-power applications. However, its use in high-temperature environments is limited due to its lower melting point.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the corrosion resistance of copper in their specific environments, especially in humid or corrosive atmospheres common in regions like Brazil and Vietnam. Ensuring that the copper used meets local standards is essential.
Stainless Steel: A Robust Alternative for Diverse Applications
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and strength, withstanding temperatures up to 800°C (1472°F). It is less conductive than copper but offers a good balance of durability and performance.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel makes it suitable for various applications, including food processing and medical equipment. However, its higher cost and lower thermal conductivity compared to copper can be disadvantages.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is commonly used in environments where corrosion resistance is critical, such as in food and pharmaceutical industries. Its ability to maintain structural integrity at moderate temperatures makes it a versatile choice.
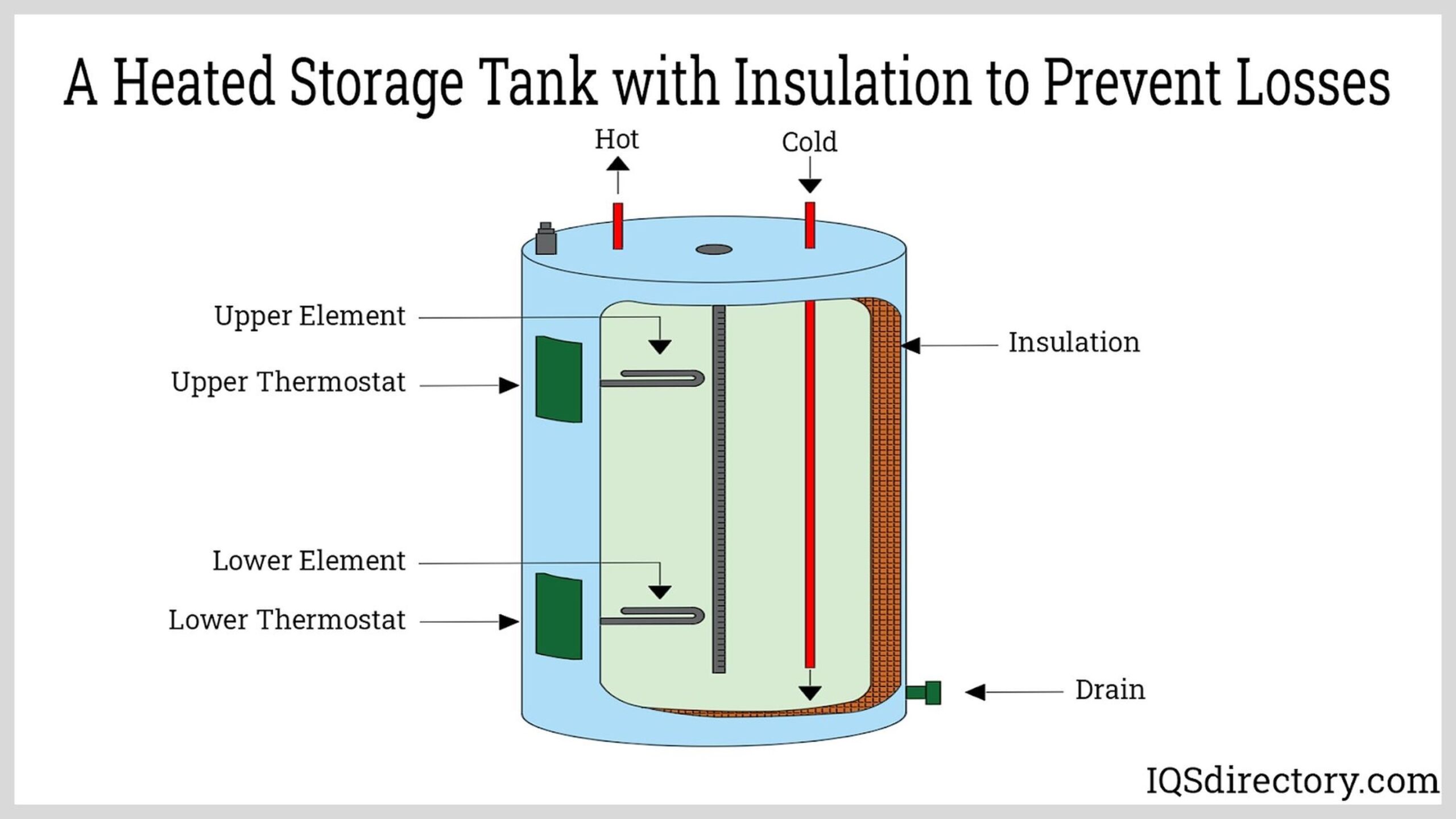
Illustrative image related to heating filament
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with food safety and medical equipment standards is vital for buyers in these sectors. International standards such as ISO and ASTM should be verified to ensure product suitability.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Heating Filaments
| Material | Typical Use Case for heating filament | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kanthal | Industrial furnaces, high-temperature applications | High-temperature resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Nichrome | Household appliances, industrial heating | Cost-effective, good performance | Less durable at extreme temperatures | Medium |
| Copper | Low-power appliances, heating coils | Excellent conductivity, affordable | Corrosion susceptibility, low melting point | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, medical equipment | Corrosion resistance, durability | Higher cost, lower thermal conductivity | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of common heating filament materials, enabling informed purchasing decisions tailored to their specific applications and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for heating filament
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Heating Filaments?
The manufacturing of heating filaments is a meticulous process that involves several key stages, each crucial for ensuring the final product’s performance and reliability. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation
The process begins with the selection of appropriate materials, typically high-resistance alloys such as nickel-chromium or kanthal. These materials must be carefully sourced to meet specific electrical and thermal properties. Suppliers often conduct material inspections to ensure compliance with international standards. This stage may also involve cutting the materials into predetermined lengths and diameters to facilitate efficient processing. -
Forming
During the forming stage, the prepared materials are shaped into the desired configuration. Techniques such as coiling, bending, and twisting are employed to create the filament’s structure. Advanced machinery is utilized to ensure precision in forming, which is essential for achieving uniform heat distribution. This stage may also involve the creation of customized shapes to meet specific application requirements. -
Assembly
The assembly process incorporates various components, including terminals and insulation materials. Depending on the design, techniques such as crimping, soldering, or welding are applied to secure connections. This stage is critical as it ensures that the heating element can withstand operational stresses and maintain electrical integrity over time. -
Finishing
The final stage involves applying protective coatings and conducting surface treatments to enhance durability and performance. Finishing techniques may include anodizing, powder coating, or applying heat-resistant insulations. These treatments not only protect the filament but also contribute to its efficiency in heat generation.
What Quality Assurance Measures Should B2B Buyers Expect?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing of heating filaments, as it directly impacts product reliability and safety. Buyers should look for suppliers who implement comprehensive QA processes aligned with international standards.
-
International Standards Compliance
Suppliers should adhere to ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with CE marking is also essential for products sold within the European market, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. For specific applications, certifications from organizations like API (American Petroleum Institute) may also be relevant. -
Quality Control Checkpoints
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet required specifications. This is crucial to prevent defects in the final product.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, regular inspections and tests are conducted to monitor processes and identify potential issues early. This can include checking dimensional accuracy and resistance values.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): After the product is assembled, a comprehensive final inspection is conducted. This includes performance testing under operational conditions to verify that the heating element meets the specified standards. -
Common Testing Methods
Various testing methods are employed to ensure product quality, including:
– Electrical Testing: Measures resistance, insulation resistance, and dielectric strength.
– Thermal Testing: Assesses temperature uniformity and heating efficiency.
– Mechanical Testing: Evaluates the durability of connections and overall structural integrity.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control practices is crucial in ensuring product reliability.
-
Supplier Audits
Conducting on-site audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols. During these audits, buyers can assess the supplier’s adherence to international standards and their QA methodologies. -
Requesting Quality Reports
Buyers should request detailed quality reports that outline testing results, compliance certifications, and any non-conformance incidents. These documents are essential for understanding the supplier’s commitment to quality. -
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s operations. These inspections can be scheduled at various points in the manufacturing process to ensure ongoing compliance with quality standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate several nuances in quality control, particularly when sourcing heating filaments from diverse regions.
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences
Understanding regional regulations and cultural practices is essential. For instance, compliance with local safety standards in Africa or South America may differ significantly from those in Europe. Buyers should be well-versed in these regulations to ensure that products meet necessary safety requirements. -
Language Barriers
Language differences can pose challenges in understanding technical documentation and compliance reports. Buyers should ensure that communication channels are clear and that documentation is available in a language that is easily understood. -
Supply Chain Transparency
Maintaining transparency throughout the supply chain is crucial for ensuring quality. Buyers should establish clear lines of communication with suppliers regarding material sourcing, manufacturing practices, and quality assurance processes. This transparency can help mitigate risks associated with sourcing from international suppliers.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for heating filaments are complex but vital for ensuring product reliability and performance. By understanding the main stages of production, the necessary quality control measures, and how to verify supplier practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operations and meet their specific heating needs. As the global market continues to evolve, staying informed about these processes is essential for maintaining a competitive edge.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘heating filament’
Introduction
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure heating filaments. Sourcing the right heating filament is critical for ensuring product efficiency, reliability, and compliance with industry standards. This step-by-step approach will help you navigate the procurement process effectively, ensuring you select a supplier that meets your technical requirements and business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline your technical requirements for the heating filament. This includes specifications like power rating, operating temperature range, and material composition.
– Consider the application: Different applications may require specific types of heating filaments (e.g., for industrial ovens or household appliances).
– Assess performance needs: Determine if you need rapid heating, high durability, or resistance to specific chemicals.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in heating filaments. Look for companies that have a strong track record in your industry and are known for quality products.
– Utilize online directories: Websites like IQS Directory and industry-specific platforms can help you find reputable manufacturers.
– Review product offerings: Make sure the suppliers offer a range of heating elements that can cater to your specific needs.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers have the necessary certifications and compliance with industry standards. This is crucial for ensuring product quality and safety.
– Request documentation: Ask for certifications such as ISO 9001, UL, or CE, which indicate adherence to quality management and safety standards.
– Check for specific industry compliance: Depending on your region, ensure the suppliers comply with local regulations, especially if you are sourcing from international markets.
Step 4: Assess Customization Capabilities
In many cases, standard heating filaments may not meet your specific application needs. Evaluate suppliers’ ability to customize products based on your requirements.
– Discuss technical capabilities: Inquire about the types of customization available, such as size, shape, and material variations.
– Review past projects: Ask for examples of previous custom projects to gauge their capability and flexibility in meeting unique specifications.
Step 5: Request Samples and Quotes
Once you have narrowed down your list of suppliers, request samples and quotes to better understand the product quality and pricing.
– Evaluate performance: Testing samples will allow you to assess the heating efficiency, durability, and overall performance of the filaments.
– Compare pricing: Analyze quotes to ensure they align with your budget while considering the quality and specifications.
Step 6: Check References and Reviews
Before finalizing your supplier choice, contact references and review online testimonials. This step is essential for gaining insights into the supplier’s reliability and service quality.
– Engage with past clients: Ask about their experience with the supplier, focusing on product quality, delivery times, and customer service.
– Look for industry-specific feedback: Reviews from clients in similar industries can provide valuable insights into how well the supplier meets specific needs.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Terms
Once you have selected a supplier, negotiate and finalize the contract terms. Pay close attention to aspects such as delivery timelines, payment terms, and warranty provisions.
– Ensure clarity: Make sure all specifications and expectations are clearly outlined in the contract to avoid misunderstandings.
– Establish communication protocols: Set up regular check-ins to ensure that both parties are aligned throughout the production and delivery process.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the procurement of heating filaments, ensuring that they select the best suppliers for their specific needs and applications.

Illustrative image related to heating filament
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for heating filament Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Heating Filament Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of heating filaments is essential for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of resistance alloys used directly impacts the cost. Common materials like nickel-chromium or iron-chromium alloys vary in price based on market demand and availability. Additionally, the choice between standard and specialized materials affects overall expenses.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce involved in the manufacturing process, including skilled technicians for fabrication and assembly. In regions with varying labor costs, such as Africa and South America, sourcing from local manufacturers can lead to significant savings.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility operations. Efficient production methods and technology integration can reduce overhead costs, making it crucial for suppliers to adopt lean manufacturing principles.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for custom designs can be substantial. Buyers seeking unique specifications should factor in these costs, as they can significantly affect the total upfront expenditure.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC measures ensures product reliability but adds to the cost. Certifications such as ISO or CE may also be required, influencing the price based on compliance needs.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, especially for international buyers, can vary widely based on the chosen Incoterms. Factors such as distance, mode of transportation, and customs duties play critical roles in total logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover risks and ensure business sustainability. This margin can fluctuate based on competitive pressures and market conditions.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Heating Filament Costs?
Several factors influence pricing in the heating filament market:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk orders generally lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to maximize cost-efficiency, particularly when sourcing from international suppliers.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs can significantly increase costs. Buyers should balance the need for tailored products with budget constraints and consider whether standard options meet their needs.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications often command premium prices. However, investing in quality can lead to reduced failure rates and lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) in the long run.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record of quality and service, while new entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can greatly affect total costs. Understanding whether costs are included (CIF, DDP) or need to be managed separately (FOB) is crucial for international buyers to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Heating Filament Procurement?
International B2B buyers should consider the following strategies to enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiate Pricing: Always negotiate pricing and payment terms with suppliers. Understanding market conditions and having multiple quotes can strengthen your bargaining position.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not just the initial purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, replacement, and energy efficiency of heating filaments.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have distinct pricing structures influenced by local market dynamics, tariffs, and shipping costs. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should conduct thorough market research to understand these nuances.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and insights into market trends.
-
Request Samples: Before committing to large orders, request samples to assess quality and performance. This can prevent costly mistakes and ensure the products meet your specific requirements.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market fluctuations, supplier agreements, and specific project requirements. It is recommended to obtain tailored quotes from multiple suppliers for accurate budgeting and decision-making.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing heating filament With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Heating Solutions to Heating Filament
In the realm of industrial heating solutions, it is essential for B2B buyers to evaluate various technologies that can fulfill their heating needs. Heating filaments are widely used due to their effectiveness, but alternatives such as electric resistance heaters and infrared heating systems offer distinct advantages. Understanding these alternatives can help businesses make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and application suitability.
| Comparison Aspect | Heating Filament | Electric Resistance Heaters | Infrared Heating Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency for localized heating | Reliable and uniform heat distribution | Quick heat-up time, targeted heating |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; long lifespan | Low to moderate cost; energy-efficient | Higher initial investment; savings on energy bills |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation; requires electrical knowledge | Easy to install; various configurations available | Requires specialized installation; may need reflective surfaces |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; occasional checks required | Generally low; periodic inspection recommended | Minimal; occasional cleaning of infrared panels |
| Best Use Case | Small appliances, industrial applications | Industrial ovens, HVAC systems | Warehouses, outdoor heating, and rapid heating applications |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Electric Resistance Heaters?
Electric resistance heaters utilize resistive heating elements to generate heat, providing a reliable and uniform heat distribution. They are particularly effective in applications where consistent temperature control is critical, such as industrial ovens or HVAC systems. The initial investment is generally low to moderate, making them an attractive option for many businesses. However, while they are energy-efficient, they may not offer the localized heating benefits that heating filaments provide. Additionally, their performance can be affected by the resistance of the material being heated, which could lead to inefficiencies in certain applications.
How Do Infrared Heating Systems Compare?
Infrared heating systems are designed to provide quick heat-up times and targeted heating, making them ideal for situations where immediate warmth is necessary, such as in warehouses or outdoor environments. They work by emitting infrared radiation that directly warms objects and people in their line of sight, bypassing the air. While the initial investment in infrared systems can be higher, they often result in energy savings over time due to their efficiency. The need for specialized installation and reflective surfaces can add complexity, which may deter some buyers. However, their effectiveness in reducing energy costs and providing rapid heating solutions can make them a worthwhile investment.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Heating Solution?
Choosing the appropriate heating solution requires a thorough assessment of your specific needs and operational context. Consider the performance requirements, budget constraints, and the installation and maintenance capabilities of your team. For localized heating needs in small appliances or specialized industrial applications, heating filaments may be the best choice. Conversely, for larger-scale operations requiring uniform heat distribution, electric resistance heaters could be more suitable. If your operations demand rapid heating capabilities or outdoor applications, infrared heating systems might be the ideal solution. By evaluating these factors, B2B buyers can select a heating solution that aligns with their operational goals and budgetary considerations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for heating filament
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Heating Filament?
When sourcing heating filament, understanding its technical properties is essential for ensuring optimal performance in your applications. Below are several critical specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
Heating filaments are typically made from various resistance alloys such as nichrome, kanthal, or copper. The material grade affects not only the filament’s resistance but also its durability and thermal efficiency. Nichrome, for example, is favored for its high-temperature resistance and oxidation resistance, making it suitable for industrial applications. Selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that the filament can withstand the operational conditions without degrading.
2. Resistance Value
The resistance value, measured in ohms, is a crucial specification that dictates how much current the filament will draw at a given voltage. This value influences the heating efficiency and energy consumption of the system. A lower resistance filament may provide quicker heating but can also lead to increased energy costs. Understanding resistance values helps buyers optimize their heating systems for both performance and cost-efficiency.
3. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from the specified resistance value and is usually expressed as a percentage. Tight tolerances are critical in applications where precise heating is required, such as in medical devices or industrial ovens. Specifying the correct tolerance ensures that the heating element will perform consistently and reliably, reducing the risk of overheating or inadequate heating.
4. Watt Density
Watt density, measured in watts per square inch, indicates how much power is applied to a given area of the heating element. High watt density can lead to faster heating but may also risk overheating if not managed properly. Understanding watt density is essential for selecting a heating filament that meets the specific thermal requirements of your application while ensuring safety and longevity.
5. Operating Temperature Range
The operating temperature range specifies the minimum and maximum temperatures at which the heating filament can function effectively. This property is vital for applications that involve extreme conditions, such as industrial furnaces or heating in outdoor environments. Buyers should ensure that the filament selected can operate within the required temperature range for their specific application.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Heating Filament Procurement?
Familiarity with trade terminology is essential for efficient communication and transaction processes in the B2B heating filament market. Here are some commonly used terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that manufactures products that are sold by another company under its brand name. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking to source heating filaments tailored for specific applications or integrated into larger systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly important for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cost-efficiency. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses assess whether a supplier aligns with their purchasing strategy.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It typically includes specifications, quantities, and other requirements. For buyers, issuing an RFQ can streamline the procurement process and ensure competitive pricing.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery obligations, ensuring clarity in contracts and negotiations.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to its delivery. This term is critical for supply chain management and planning. Buyers should consider lead time when selecting suppliers to ensure they can meet their project timelines without delays.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing heating filament, ensuring that they meet their operational needs efficiently and effectively.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the heating filament Sector
What Are the Key Trends and Market Dynamics in the Heating Filament Sector?
The heating filament sector is experiencing significant transformation, driven by globalization, technological advancements, and evolving customer demands. One of the most notable trends is the increased focus on customization. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking tailored solutions to meet specific application needs, whether in industrial ovens, small appliances, or medical equipment. This trend is particularly relevant in regions such as Africa and South America, where diverse industrial applications require versatile heating solutions.
Another key driver is the integration of smart technology into heating systems. The rise of IoT (Internet of Things) in manufacturing has led to the development of heating elements that can be monitored and controlled remotely. This is particularly advantageous for European and Middle Eastern markets, where energy efficiency and operational optimization are paramount. B2B buyers are looking for heating elements that not only provide high performance but also enhance the overall energy efficiency of their operations.
Moreover, supply chain dynamics are shifting due to the need for shorter lead times and more reliable sourcing options. As manufacturers and distributors adapt to these demands, buyers are encouraged to develop relationships with suppliers who prioritize quality and responsiveness. This is crucial in regions like Brazil and Vietnam, where local sourcing can significantly reduce shipping costs and lead times.
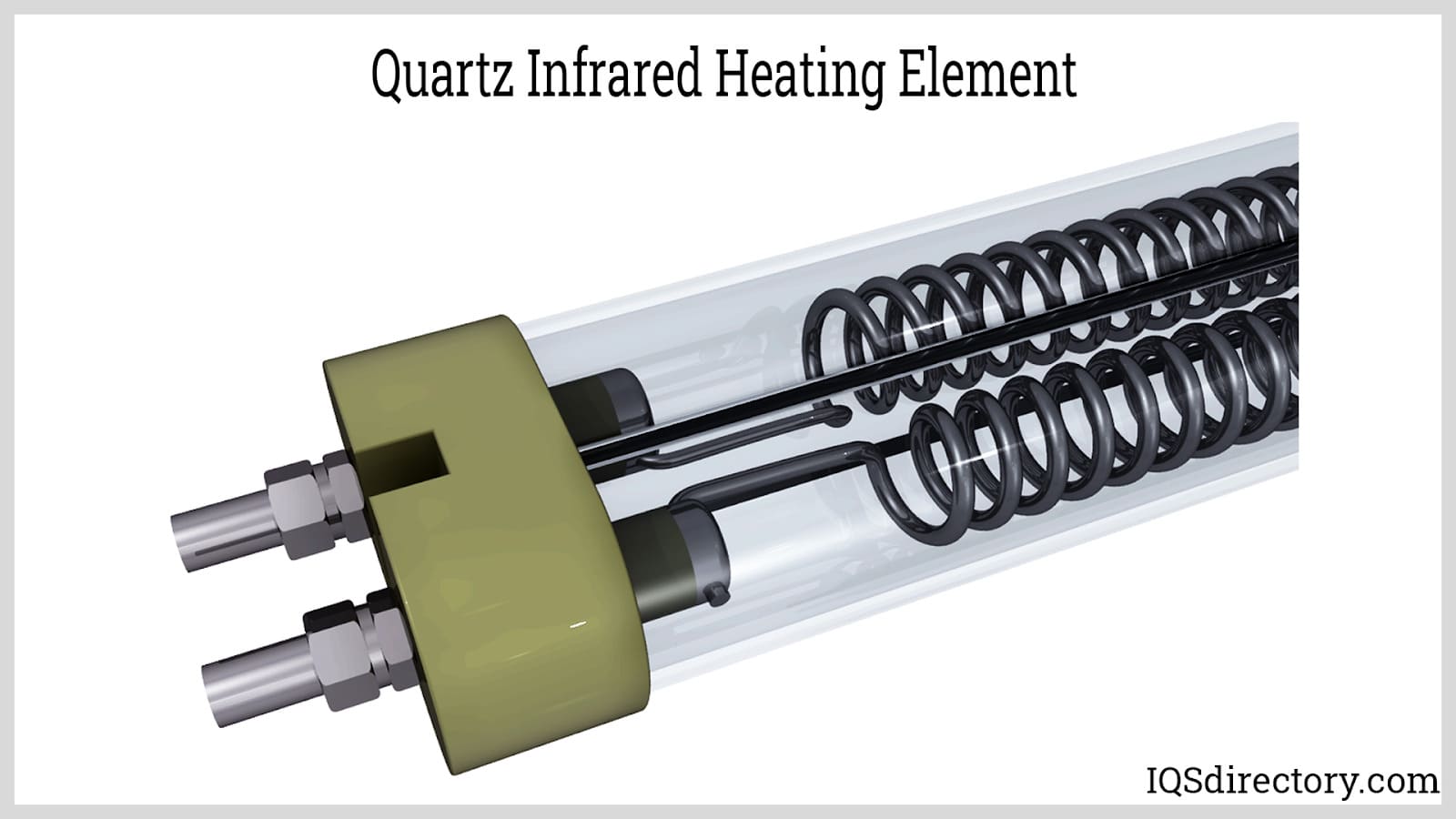
Illustrative image related to heating filament
How Does Sustainability Influence Sourcing Decisions for Heating Filaments?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the heating filament sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the materials used in heating elements is under increasing scrutiny. Companies are now more inclined to partner with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through ethical sourcing practices and environmentally friendly materials.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly aware of the implications of their sourcing decisions, opting for suppliers who can provide transparency regarding the origins of their materials and the sustainability of their production processes. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) are becoming essential criteria for evaluation.
Additionally, green materials, such as those derived from renewable resources or with lower carbon footprints, are gaining traction. B2B buyers are actively seeking suppliers who offer eco-friendly heating solutions, which not only align with corporate sustainability goals but also appeal to environmentally conscious end-users.
How Has the Heating Filament Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the heating filament sector can be traced back to the early days of electric heating, where simple resistance wires were the primary means of generating heat. Over the decades, advancements in materials science and engineering have led to the development of a wide variety of heating elements, including flexible heaters and ceramic-based options.
The introduction of advanced manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing and precision coiling, has further transformed the landscape, allowing for more complex designs and greater efficiency. These innovations have paved the way for customized solutions that cater to specific industrial needs, making heating filaments integral to numerous applications today.
In conclusion, the heating filament sector is poised for continued growth as international B2B buyers increasingly prioritize customization, sustainability, and technological integration in their sourcing strategies. As the market evolves, understanding these dynamics will be crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of heating filament
1. How do I select the right heating filament for my application?
Choosing the appropriate heating filament involves considering several factors such as the application temperature range, the environment (e.g., moisture, chemical exposure), and the specific heating requirements (e.g., rapid heating or consistent temperature). Evaluate your project’s specifications and consult with manufacturers to ensure compatibility with your equipment. It’s also important to review the thermal properties of different filament materials, such as nickel-chromium or copper, to ensure optimal performance for your specific use case.
2. What are the customization options available for heating filaments?
Most manufacturers offer extensive customization options for heating filaments, including variations in length, gauge, and configuration. You can specify terminal types, winding styles, and power ratings based on your unique application needs. Some suppliers also provide prototyping services, allowing you to test the heating element before committing to a larger order. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to see how they can tailor their products to meet your specifications effectively.
3. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for heating filaments?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for heating filaments can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and the specific product line. Typically, MOQs can range from small quantities for custom orders to larger volumes for standard products. When sourcing from suppliers, inquire about their MOQ policies and consider the implications for your inventory management. Some manufacturers may offer more flexibility for first-time buyers or larger projects, so it’s beneficial to negotiate based on your needs.

Illustrative image related to heating filament
4. How can I ensure the quality of heating filaments from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of heating filaments, look for suppliers with established certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicate adherence to quality management standards. Request product samples and documentation detailing the material specifications and manufacturing processes. Additionally, consider suppliers that offer warranties or guarantees on their products. Engaging in thorough supplier vetting, including customer reviews and case studies, can also provide insights into the reliability and quality of the heating elements.
5. What payment terms should I expect when purchasing heating filaments?
Payment terms for heating filaments can differ widely between suppliers and regions. Common terms include payment in advance, net 30, or net 60 days upon receipt of goods. It’s crucial to clarify these terms before finalizing an order. Some suppliers may also offer financing options or discounts for bulk purchases. Be sure to discuss payment methods, such as wire transfers or letters of credit, especially for international transactions, to ensure a smooth purchasing process.
6. What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when importing heating filaments?
When importing heating filaments, consider shipping costs, customs duties, and delivery timelines. Ensure that the supplier can provide appropriate documentation, including invoices and certificates of origin, to facilitate customs clearance. It’s advisable to work with a logistics partner experienced in international trade to navigate potential challenges. Additionally, check the supplier’s shipping options, such as air freight for urgent needs or sea freight for cost-effective bulk orders.
7. How do I address potential compatibility issues with my existing equipment?
To address compatibility issues, conduct a thorough analysis of your current equipment and its specifications. Consult with both your engineering team and potential suppliers to identify any discrepancies in voltage, wattage, or physical dimensions. Suppliers often have technical support teams that can assist in evaluating compatibility and suggesting modifications if necessary. Additionally, reviewing case studies or testimonials from other clients in similar industries can provide valuable insights into successful integrations.

Illustrative image related to heating filament
8. What are the common applications for heating filaments in various industries?
Heating filaments are widely used across multiple industries, including manufacturing, food processing, and healthcare. Common applications include heating elements for industrial ovens, medical autoclaves, and HVAC systems. They are also utilized in consumer appliances like hair dryers and heating pads. Understanding the specific application requirements, such as temperature control and environmental conditions, will help you choose the right filament for optimal performance in your industry.
Top 2 Heating Filament Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Heating Elements
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Heating elements are components designed to convert electrical energy into heat through Joule heating. Key properties include: 1. Resistivity: Essential for efficient heat production and energy consumption. 2. Oxidation Resistance: Important for longevity, especially in metals and ceramics. 3. Temperature Coefficient of Resistance (TCR): A lower TCR is preferred for stable heating output. 4. Mecha…
2. Hudson Reed – 1000 Plug-In Watt Electric Heating Element
Domain: usa.hudsonreed.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: {‘name’: ‘1000 Plug-In Watt Electric Heating Element’, ‘sku’: ‘CHE1000W’, ‘price’: ‘$209.95’, ‘features’: [‘Easy plug-in installation’, ‘Element Cable Length: 35.4″ includes plug’, ‘Made from ABS Plastic & Stainless Steel’, ‘Ingress Protection Rating: IP67’, ‘UL Approved’], ‘style’: ‘Modern’, ‘finish’: ‘Chrome’, ‘power’: ‘1000W’, ‘warranty’: ‘2 Years’, ‘shipping_info’: ‘Free shipping to any addres…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for heating filament
As the demand for efficient heating solutions continues to grow across diverse industries, the strategic sourcing of heating filaments stands as a critical component for international buyers. Key takeaways emphasize the importance of understanding the various types of heating elements and their applications, as well as the value of customization to meet specific operational needs. By leveraging quality materials and advanced technologies, businesses can not only enhance performance but also reduce lead times and costs, thereby driving profitability.
For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic partnerships with manufacturers that prioritize innovation and customer collaboration are essential. Engaging with suppliers who offer tailored solutions—ranging from small appliances to industrial applications—can significantly impact your product quality and market competitiveness.
Looking ahead, the heating filament market is poised for growth, driven by advancements in materials and technology. Now is the time for international buyers to evaluate their sourcing strategies and align with manufacturers who can deliver not just products, but comprehensive solutions that foster long-term success. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your supply chain and position your business for a sustainable future in the heating elements sector.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.