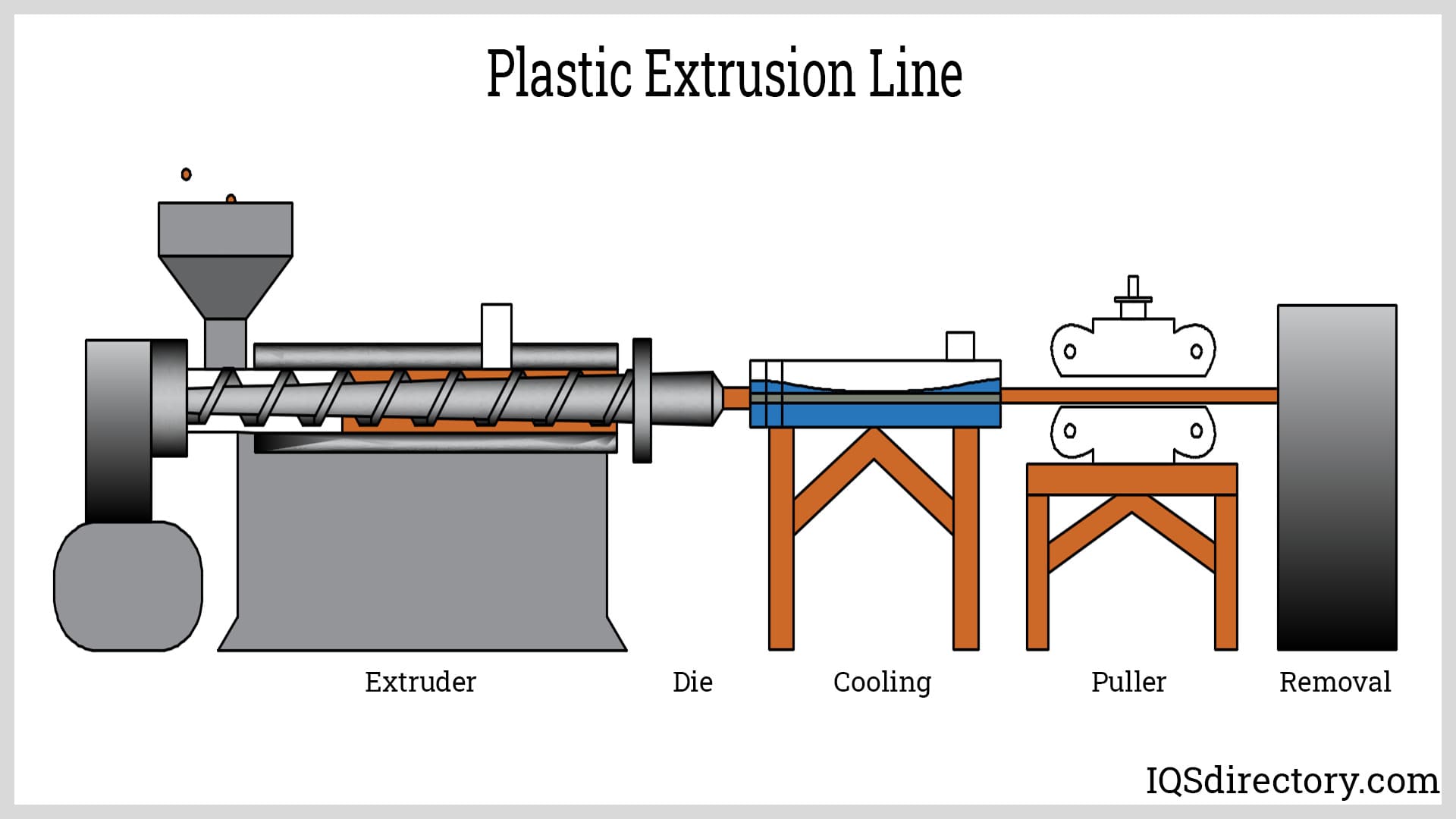
A Deep Dive into Extruder Line Solution
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for extruder line
In the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing, sourcing an efficient and reliable extruder line can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe increasingly demand high-quality plastic products, understanding the intricacies of extruder lines becomes paramount. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, illuminating the various types of extruder lines available, their applications across diverse sectors, and the essential criteria for vetting suppliers.
By delving into factors such as cost, technology advancements, and operational efficiency, this guide equips buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are in Saudi Arabia looking to enhance your production capabilities or in Germany evaluating the latest extrusion technologies, the insights provided here will empower you to navigate the complexities of the global market effectively.
From understanding the key components of extrusion systems to evaluating the benefits of advanced machinery, our aim is to facilitate a seamless procurement process. We highlight the importance of collaboration with experienced suppliers and offer actionable strategies to ensure that your investment in extruder lines yields maximum returns. With this guide, you are not just purchasing machinery; you are making a strategic move towards operational excellence and sustained competitive advantage.
Understanding extruder line Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Screw Extruder | Simple design, widely used, suitable for various thermoplastics | Plastic films, sheets, profiles, and pipes | Pros: Cost-effective, easy maintenance. Cons: Limited mixing capabilities. |
| Twin-Screw Extruder | Enhanced mixing, better temperature control, suitable for complex materials | Compounding, food processing, and specialty applications | Pros: High efficiency, superior material handling. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Co-extrusion Line | Multiple extruders for layered products, customizable output | Multi-layer films, packaging, and specialized sheets | Pros: Versatility in product design, improved barrier properties. Cons: Complexity in setup and operation. |
| Sheet Extrusion Line | Specialized for producing sheets with uniform thickness | Construction materials, packaging, and automotive components | Pros: High-speed production, consistent quality. Cons: Requires precise calibration. |
| Film Extrusion Line | Focused on producing thin films, high output capabilities | Packaging films, agricultural films, and protective wraps | Pros: Efficient for large volumes, customizable thickness. Cons: Limited to thin products. |
What are the Characteristics of a Single-Screw Extruder?
The single-screw extruder is one of the most common types found in the industry, known for its straightforward design and versatility. It consists of a single rotating screw that pushes plastic material through a heated barrel. This type is particularly suited for applications involving thermoplastics, such as films and sheets. When considering a purchase, businesses should evaluate the intended material types and the desired output rates, as this extruder excels in general-purpose applications but may struggle with materials that require extensive mixing.
How Does a Twin-Screw Extruder Differ in Performance?
Twin-screw extruders are characterized by two intermeshing screws that enhance the mixing and processing of materials. They are ideal for applications that involve complex formulations, such as compounding and food processing. The design allows for better temperature control and material feed accuracy, which can significantly improve product quality. B2B buyers should consider the higher upfront costs and the need for specialized training for operators, as these machines often require more sophisticated handling than their single-screw counterparts.
What Advantages Does a Co-extrusion Line Offer?
Co-extrusion lines utilize multiple extruders to create products with distinct layers, allowing for customized properties such as improved barrier performance. This technology is particularly beneficial in packaging applications, where different materials can be combined to enhance functionality. Buyers should assess the complexity of their production needs, as co-extrusion setups can be more intricate and may require additional maintenance and operational expertise.
What Makes a Sheet Extrusion Line Essential for Manufacturers?
Sheet extrusion lines are specifically designed to produce sheets with precise thickness and uniformity. These lines are crucial for industries such as construction and automotive, where consistent material quality is paramount. The ability to achieve high-speed production rates makes them attractive to manufacturers looking to scale operations. However, buyers need to be aware of the calibration requirements to ensure product consistency, which can add to operational complexity.
Why Choose a Film Extrusion Line for High-Volume Production?
Film extrusion lines are tailored for creating thin films and are known for their high output capabilities. These lines are essential in packaging applications, where efficiency and the ability to customize film thickness are critical. While they offer significant advantages in terms of production speed, potential buyers should consider the limitations regarding the types of products that can be produced, as they are primarily focused on thin materials.
Key Industrial Applications of extruder line
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of extruder line | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Packaging | Production of flexible plastic films | High-speed production, reduced material waste | Consider suppliers with advanced temperature control and customizable die heads. |
| Construction Materials | Manufacturing of rigid plastic sheets | Durable, lightweight materials for building | Look for extruders that can handle various polymers and have robust cooling systems. |
| Medical Supplies | Creation of flexible tubing for medical use | High precision, compliance with health standards | Ensure equipment meets strict regulatory requirements and offers high-quality extrusion capabilities. |
| Automotive Components | Production of plastic profiles for interiors | Lightweight, cost-effective materials | Source from manufacturers that provide modular setups for various profile shapes. |
| Consumer Goods | Fabrication of plastic packaging products | Enhanced shelf life, reduced spoilage | Seek suppliers with integrated control systems for consistent quality and efficiency. |
How is the Extruder Line Used in the Packaging Industry?
In the packaging sector, extruder lines are essential for producing flexible plastic films used in food and consumer goods packaging. The extrusion process allows for high-speed production, minimizing waste while ensuring consistent quality. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer advanced temperature control systems and customizable die heads, enabling the processing of various polymer types to meet specific packaging requirements.
What Role Does Extrusion Play in Construction Materials?
Extruder lines are utilized in the construction industry to manufacture rigid plastic sheets that serve as lightweight, durable materials for a variety of building applications. These sheets can be customized in thickness and size, providing versatility in design. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing equipment capable of handling multiple types of polymers and featuring robust cooling systems to maintain material integrity during production.
Why is Extrusion Critical for Medical Supplies?
In the medical field, extruder lines are crucial for producing flexible tubing used in various applications, including IV and respiratory equipment. The precision of the extrusion process ensures that products meet stringent health standards. B2B buyers must ensure that the equipment they invest in complies with regulatory requirements and has capabilities for high-quality extrusion to maintain product safety and reliability.
How is Extrusion Beneficial for Automotive Components?
The automotive industry leverages extruder lines to create plastic profiles used in vehicle interiors, such as trim and moldings. These profiles are lightweight yet durable, contributing to overall vehicle efficiency and aesthetics. Buyers should look for manufacturers that offer modular setups, allowing for the production of various profile shapes while ensuring cost-effectiveness in materials.
What Advantages Does Extrusion Provide for Consumer Goods?
In the consumer goods sector, extruder lines are employed to fabricate plastic packaging products that enhance shelf life and reduce spoilage. The ability to produce consistent and high-quality packaging is vital for maintaining brand integrity. When sourcing extrusion equipment, businesses should seek integrated control systems that facilitate precise adjustments to maintain quality and efficiency throughout the production process.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘extruder line’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Product Quality Leading to Customer Complaints
The Problem: One of the most pressing issues B2B buyers face when investing in an extruder line is the inconsistency in product quality. This can manifest as variations in thickness, texture, or even color of the extruded sheets. Such discrepancies can lead to customer dissatisfaction, increased returns, and a tarnished reputation. For manufacturers producing plastic sheets for sectors like packaging or construction, maintaining strict quality standards is critical. Even minor variations can lead to significant financial losses and strained client relationships.

Illustrative image related to extruder line
The Solution: To address quality consistency, buyers should prioritize investing in high-precision equipment that features advanced temperature control and automated thickness monitoring systems. When sourcing an extruder line, look for models that allow for real-time adjustments based on feedback from integrated sensors. Additionally, implementing a robust quality control process, including periodic audits and sample testing, can ensure that any deviations from the set standards are detected early. Collaborating with experienced suppliers who provide comprehensive training on equipment usage can also enhance the team’s ability to monitor and maintain product quality effectively.
Scenario 2: High Operational Costs Due to Inefficient Equipment
The Problem: Many companies experience rising operational costs due to outdated or inefficient extrusion technology. Inefficient machines consume excessive energy, require frequent maintenance, and have slower production rates, all of which can erode profit margins. For buyers in regions with high energy costs, such as parts of Europe and the Middle East, this issue becomes even more pronounced. As the demand for sustainable practices grows, manufacturers are pressured to find ways to reduce their carbon footprint while remaining competitive.
The Solution: Investing in modern, energy-efficient extrusion lines is the best way to mitigate high operational costs. Look for equipment designed with energy-saving features, such as variable-speed drives and optimized cooling systems. Additionally, conducting a cost-benefit analysis of potential machinery can help determine the ROI of upgrading to newer models. Establish partnerships with suppliers who can assist with financing options or trade-in programs for outdated equipment. Regular maintenance schedules and operator training can also extend the lifespan of the equipment and ensure it operates at peak efficiency.
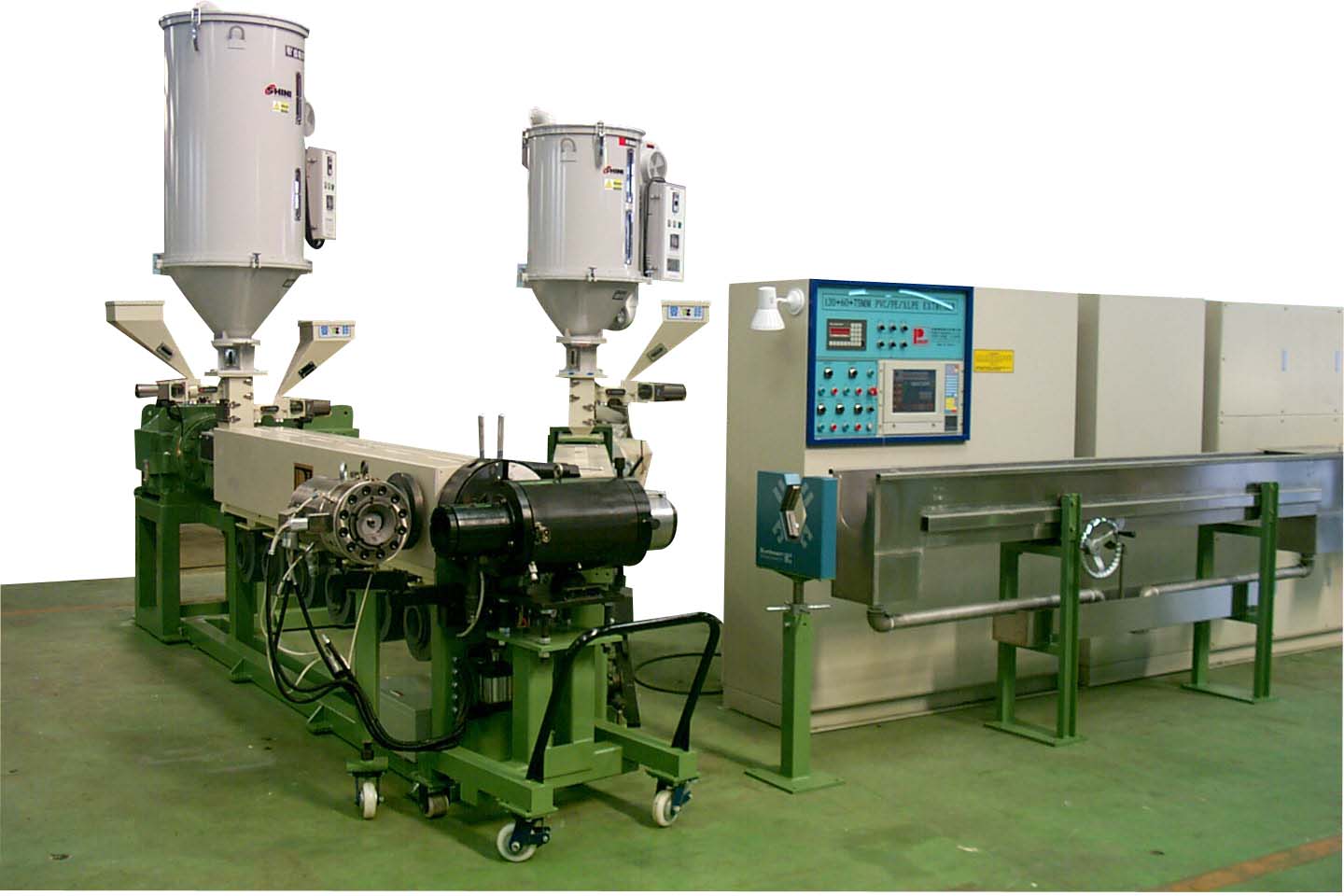
Scenario 3: Downtime Due to Equipment Failures
The Problem: Unexpected equipment failures can lead to significant production downtime, which is detrimental to business operations. For B2B buyers, this scenario can be particularly challenging, as it not only affects immediate productivity but can also result in delayed deliveries and lost contracts. In industries where timely delivery is crucial, such as construction and packaging, even a few hours of downtime can have ripple effects throughout the supply chain.
Illustrative image related to extruder line
The Solution: To minimize downtime, buyers should invest in preventive maintenance programs and consider equipment with advanced diagnostic capabilities. Choosing an extruder line with built-in monitoring systems that can predict failures before they occur can help avert major breakdowns. Additionally, establishing a reliable relationship with a local service provider for quick repairs and maintenance can significantly reduce response times during emergencies. Keeping a stock of critical spare parts on-site can also ensure that minor issues can be resolved swiftly, keeping production lines running smoothly.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for extruder line
What Are the Key Materials Used in Extruder Lines?
When selecting materials for an extruder line, it’s essential to understand the properties, advantages, and limitations of each option. This knowledge helps international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific applications and regional compliance requirements. Below, we analyze four common materials used in extruder lines: Polypropylene (PP), Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), Polystyrene (PS), and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS).
How Does Polypropylene (PP) Perform in Extruder Lines?
Polypropylene is a widely used thermoplastic known for its versatility and resistance to various chemicals. It has a temperature rating of up to 100°C (212°F) and exhibits good impact resistance and tensile strength.

Illustrative image related to extruder line
Pros: PP is lightweight, cost-effective, and has excellent fatigue resistance, making it suitable for applications such as packaging and automotive components. Its low density also contributes to lower shipping costs.
Cons: However, PP can be sensitive to UV radiation, which may lead to degradation if not properly stabilized. Additionally, its processing temperature is relatively lower compared to other materials, which may limit its use in high-temperature applications.
Impact on Application: PP is compatible with a wide range of media, making it suitable for food packaging and medical applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local food safety standards, while European buyers may need to adhere to ASTM or DIN standards for quality assurance.
What Are the Benefits of Using Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)?
Polyethylene Terephthalate is another popular choice, especially in the production of films and sheets. PET has a higher temperature tolerance, typically around 120°C (248°F), and excellent clarity and strength.
Illustrative image related to extruder line
Pros: PET is known for its superior chemical resistance and dimensional stability. Its recyclability is also a significant advantage, aligning with global sustainability trends.
Cons: The primary drawback of PET is its higher cost compared to PP. Additionally, its processing can be more complex, requiring precise temperature control to avoid degradation.
Impact on Application: PET is ideal for applications requiring high clarity and strength, such as beverage bottles and high-performance packaging.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with recycling regulations is crucial, especially in Europe, where PET recycling is heavily promoted. Buyers must also consider local standards for food contact materials.
Why Choose Polystyrene (PS) for Extrusion?
Polystyrene is a cost-effective thermoplastic known for its ease of processing. It typically has a temperature rating of around 70°C (158°F) and offers good clarity.
Pros: PS is lightweight and can be easily molded, making it suitable for various applications, including disposable cutlery and packaging materials.
Cons: Its lower temperature resistance and brittleness can be significant limitations, particularly in applications requiring durability.
Impact on Application: PS is often used in food packaging and consumer products but is less suitable for high-stress environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with food safety regulations is essential for PS applications, particularly in regions like South America and Europe, where standards are stringent.

Illustrative image related to extruder line
What Makes Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) a Strong Candidate?
ABS is a tough, impact-resistant material with a temperature rating of around 100°C (212°F). It is commonly used in applications requiring durability and aesthetic appeal.
Pros: ABS is known for its excellent impact resistance and ease of machining, making it suitable for consumer electronics and automotive parts.
Cons: The main downside is its sensitivity to UV light, which can lead to degradation if not properly treated. Additionally, ABS can be more expensive than other thermoplastics.
Impact on Application: ABS is ideal for applications requiring strength and surface finish, such as housings for electronic devices.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with local regulations regarding the use of ABS in consumer products, especially in Europe and the Middle East.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Extruder Lines
| Material | Typical Use Case for extruder line | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene (PP) | Food packaging, automotive components | Lightweight and cost-effective | Sensitive to UV radiation | Low |
| Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | Beverage bottles, high-performance packaging | Superior chemical resistance and recyclability | Higher cost and complex processing | High |
| Polystyrene (PS) | Disposable cutlery, packaging materials | Easy to process and lightweight | Lower temperature resistance and brittleness | Low |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Consumer electronics, automotive parts | Excellent impact resistance | UV sensitivity and higher cost | Medium |
Selecting the right material for an extruder line is critical for ensuring product performance and compliance with regional standards. By understanding the properties and implications of each material, international B2B buyers can make strategic choices that align with their operational needs and market demands.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for extruder line
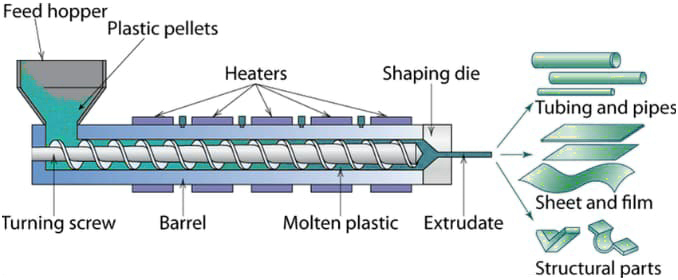
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of an Extruder Line?
The manufacturing process for an extruder line involves several critical stages that ensure the production of high-quality plastic sheets. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, each employing specific techniques to guarantee optimal performance.
How is Material Prepared for Extrusion?
Material preparation is the foundational step in the extrusion process. It involves selecting and blending various polymer resins to achieve the desired characteristics for the final product. The preparation phase may include:
-
Material Sourcing: Suppliers must provide high-quality raw materials, such as polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PET), or polystyrene (PS). Buyers should verify the origin and quality through documentation or certifications.
-
Drying: Many plastics absorb moisture, which can adversely affect the quality of the extrudate. Drying systems remove moisture from the resins before they enter the extruder, ensuring consistent quality and preventing defects.
-
Blending: This stage often involves mixing polymers with additives or colorants. Precision blending equipment ensures that the materials are uniformly mixed to achieve the desired properties.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
The forming stage is where the prepared material is transformed into its final shape. This process typically occurs within the extruder itself, which utilizes specific techniques to achieve consistency:
-
Melting and Homogenizing: The extruder’s screw design plays a critical role in melting the plastic and ensuring thorough mixing. Advanced screw configurations enhance material flow and reduce energy consumption.
-
Die Head Design: The die head shapes the molten plastic into sheets of desired width and thickness. Precision engineering in die design is crucial for maintaining uniformity throughout the production run.
-
Calendering: After exiting the die, the molten sheet enters the calendering section, where it is rolled into its final thickness. Automated thickness control systems monitor and adjust the sheet’s dimensions in real-time.
How is the Assembly Process Conducted?
The assembly phase integrates various components of the extrusion line to ensure smooth operation and high output:
-
Pull Rollers: These components are essential for maintaining consistent tension and drawing the sheet through the extrusion line. Their reliability directly influences production speed and sheet quality.
-
Cooling Systems: Proper cooling is vital to prevent deformation of the extrudate. Integrated cooling systems ensure that the sheet is cooled evenly, preserving dimensional stability before cutting.
-
Cutting and Stacking Systems: Once the sheet is cooled, it is cut to specified lengths and stacked for packaging. Efficient cutting systems contribute to reducing waste and ensuring product uniformity.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Extruder Lines?
Quality assurance is paramount in the extrusion process, particularly for B2B buyers who demand consistent product quality. Various international and industry-specific standards guide the quality control (QC) measures in place.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Adhering to recognized international standards helps ensure that manufacturers meet quality benchmarks. Key standards include:
-
ISO 9001: This certification focuses on quality management systems and is crucial for ensuring that manufacturers maintain consistent quality across their processes.
-
CE Marking: For products intended for the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: For applications in the oil and gas industry, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards ensures that materials can withstand industry-specific conditions.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control in the extrusion process typically involves multiple checkpoints to ensure product integrity:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint verifies the quality of incoming materials against specifications. Buyers should request documentation of material inspections from suppliers.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during production helps identify defects early. This can include real-time measurements of temperature, pressure, and thickness.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): At the end of the production line, finished products undergo thorough testing to ensure they meet predefined specifications. Common tests include dimensional checks, tensile strength, and appearance evaluations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial for mitigating risks.
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Ensure Supplier Compliance?
-
Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the manufacturer’s facilities and processes directly. This can provide insights into the quality management systems in place.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed reports on their quality control procedures, including testing results and any corrective actions taken for defects.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality practices. This is particularly valuable for buyers unfamiliar with local manufacturing standards.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International Buyers?
Quality control nuances may vary based on regional standards and regulations. Buyers should be aware of:
Illustrative image related to extruder line
-
Local Compliance Requirements: Understanding local regulations and standards can help buyers navigate potential challenges in importing products.
-
Cultural Differences in Quality Expectations: Different regions may have varying expectations for product quality and performance. Establishing clear communication with suppliers can help align expectations.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: Quality control can also be impacted by logistics. Ensuring that materials are transported and stored correctly is essential for maintaining quality.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for extruder lines is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on these elements, buyers can ensure they invest in reliable suppliers capable of delivering high-quality products that meet their specifications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘extruder line’
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure an extruder line. The procurement process involves careful consideration of technical specifications, supplier reliability, and long-term operational efficiency. By following this structured approach, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their production needs and strategic goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging suppliers, clearly outline your production requirements. Consider the type of materials you will process, the desired output capacity, and the specific applications of the extruded products.
– Key Details to Specify:
– Material types (e.g., PP, PET, PS)
– Production volume (e.g., kg/hour)
– Sheet dimensions and thickness
Step 2: Research and Shortlist Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers of extruder lines. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in your industry and regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
– Considerations:
– Experience and reputation in the market
– Range of machinery offered, including new and refurbished options
– Customer reviews and testimonials

Illustrative image related to extruder line
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that suppliers hold relevant certifications and adhere to industry standards. This ensures compliance with safety, quality, and environmental regulations, which is critical for operational integrity.
– What to Look For:
– ISO certifications
– Compliance with local and international safety standards
– Evidence of quality control processes
Step 4: Assess Technical Support and Service Offerings
Consider the level of technical support and after-sales services provided by suppliers. Efficient support can significantly impact your production line’s uptime and overall performance.
– Key Services to Evaluate:
– Installation and commissioning support
– Availability of spare parts and maintenance services
– Training programs for operators
Step 5: Request Demonstrations or Trials
Whenever possible, arrange for demonstrations or trials of the extruder line. Observing the equipment in action can provide invaluable insights into its performance and suitability for your specific applications.
– What to Assess During Trials:
– Output quality and consistency
– Ease of operation and maintenance
– Energy efficiency and operational costs
Step 6: Analyze Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Beyond the initial purchase price, evaluate the total cost of ownership, including installation, maintenance, and operational expenses. A thorough TCO analysis helps ensure that your investment is financially viable in the long term.
– Factors to Consider:
– Energy consumption rates
– Maintenance frequency and costs
– Expected lifespan and resale value
Step 7: Finalize Contract Terms
Before finalizing your purchase, ensure that contract terms are clear and protect your interests. Pay attention to warranties, delivery timelines, and payment terms to avoid potential disputes later.
– Key Contract Elements:
– Warranty coverage and duration
– Delivery schedules and penalties for delays
– Payment milestones and financing options
By adhering to this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing an extruder line with confidence, ensuring that their operational needs are met while maximizing return on investment.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for extruder line Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Sourcing an Extruder Line?
When sourcing an extruder line, understanding the intricate cost structure is paramount. The main cost components include:
-
Materials: This encompasses the raw materials used in manufacturing the extruder, such as high-grade steel, specialized alloys for screws and barrels, and various electronic components. The quality and type of materials directly influence the overall cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly based on the region and expertise required. Skilled labor for assembly, quality control, and maintenance can add substantial costs, particularly in regions with higher wage standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and indirect labor that support the production process. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these overheads, impacting the final pricing.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs refer to the expenses associated with molds and fixtures necessary for producing specific parts of the extruder line. Custom tooling can be a significant investment, especially for specialized applications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the extruder meets industry standards and specifications requires rigorous QC processes. This can involve testing materials and components, further adding to costs.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs, especially for international buyers, can significantly affect the total cost. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties should be considered.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a margin to cover risk and profit, which can vary based on market conditions and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Sourcing of Extruder Lines?
Several factors can influence the pricing of extruder lines:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer discounts for higher Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs), making it advantageous for larger operations.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom-built extruders tailored to specific production needs can increase costs. Buyers should assess whether standard models may suffice, which can be more cost-effective.
-
Materials: The choice of materials impacts both the durability and cost of the extruder line. High-performance materials may have a higher upfront cost but can lead to lower maintenance and replacement expenses over time.
-
Quality/Certifications: Extruders that meet specific quality standards or certifications (e.g., ISO) may command higher prices. However, these can ensure reliability and compliance, particularly in regulated markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and geographic location of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their experience and service levels.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers as they define responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. This can significantly affect the total landed cost of the equipment.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers of Extruder Lines?
When negotiating the purchase of an extruder line, consider the following strategies:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Understand market prices and compare multiple suppliers. This knowledge can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Highlight Long-Term Potential: Emphasizing the potential for ongoing business can encourage suppliers to offer better terms, such as reduced pricing or favorable payment terms.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus on the long-term costs associated with the extruder line, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. A higher initial investment may yield lower TCO.
-
Be Open to Alternatives: If budget constraints are an issue, consider alternative models or configurations that may provide a better balance between cost and functionality.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Purchases: For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local regulations that can impact overall costs.
Conclusion: What Should Buyers Keep in Mind?
Sourcing an extruder line involves careful consideration of various cost components and pricing influencers. Buyers should approach negotiations with a clear understanding of their needs and potential costs, while also being mindful of the long-term implications of their purchase decisions. By strategically assessing these factors, B2B buyers can make informed choices that align with their operational goals and budget constraints.
Disclaimer: Prices and costs mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, specific supplier offerings, and buyer negotiations.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing extruder line With Other Solutions
When considering machinery for plastic manufacturing, it’s essential to explore various solutions that can meet production needs effectively. While extruder lines are a popular choice due to their efficiency and versatility, other alternatives may also suit specific applications or operational requirements. This section compares extruder lines with two viable alternatives: injection molding and blow molding.
| Comparison Aspect | Extruder Line | Injection Molding | Blow Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Continuous production of sheets or profiles; high output | Suitable for complex shapes; high precision | Ideal for hollow parts; good for large volumes |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; lower operational costs | Higher initial investment; lower material waste | Moderate investment; cost-effective for large runs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators; setup can be complex | More straightforward for mass production; less training needed | Requires specific molds; setup can be time-consuming |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for optimal performance | Generally low maintenance; molds require periodic checks | Moderate maintenance; molds can wear out over time |
| Best Use Case | Producing sheets, films, and profiles at scale | Manufacturing small, intricate parts with high detail | Creating lightweight containers and packaging |
What are the Pros and Cons of Injection Molding as an Alternative to Extruder Lines?
Injection molding is a widely used method for producing detailed plastic parts. Its strength lies in its ability to create complex shapes with high precision. The technology allows manufacturers to produce large quantities of parts with consistent quality. However, the initial investment in injection molding equipment can be significantly higher than that of an extruder line. Additionally, the process can lead to material waste if not optimized. It is best suited for products that require intricate designs and precise dimensions, making it an excellent choice for industries such as automotive and consumer goods.
How Does Blow Molding Compare to Extruder Lines?
Blow molding specializes in creating hollow plastic parts, such as bottles and containers. This method is particularly advantageous for high-volume production, as it offers faster cycle times compared to extrusion. The costs associated with blow molding are generally moderate, making it an economical choice for manufacturers looking to produce large quantities of similar items. However, blow molding is limited to hollow shapes, which may not be suitable for all applications. Companies in the beverage and packaging industries often find blow molding to be the ideal solution for their needs.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting between an extruder line and its alternatives, B2B buyers should carefully assess their production requirements, budget constraints, and the specific characteristics of the products they intend to manufacture. Factors such as the complexity of the parts, desired production volume, and long-term operational costs should guide their decision-making process. Engaging with experienced suppliers who can provide insights into the latest technologies and tailored solutions will further enhance the selection process, ensuring a choice that aligns with both immediate needs and future growth objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for extruder line
What Are the Key Technical Properties of an Extruder Line?
Understanding the technical properties of an extruder line is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their production processes. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific type of plastic resin used in the extrusion process, such as polypropylene (PP), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), or polystyrene (PS). Each material has distinct properties affecting its melting point, strength, and flexibility. Selecting the appropriate material grade is vital for ensuring product performance and compliance with industry standards, especially for sectors like packaging and construction.
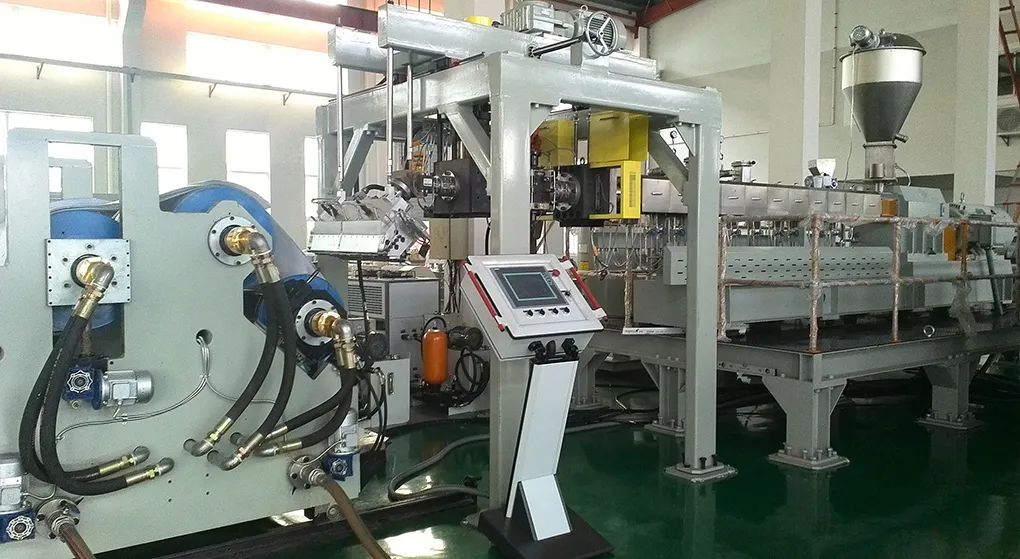

Illustrative image related to extruder line
2. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable variation in dimensions of the extruded product. It is essential for ensuring that the final products meet specific design requirements and fit correctly in their applications. In industries like automotive or aerospace, where precision is critical, adhering to strict tolerance levels can significantly impact product quality and safety.
3. Throughput Rate
Throughput rate is the volume of material processed by the extruder within a specified timeframe, typically measured in kilograms per hour (kg/h). A higher throughput rate indicates more efficient production, enabling manufacturers to meet demand without sacrificing quality. For B2B buyers, understanding throughput helps in assessing the capacity of an extruder line and its suitability for production goals.
4. Screw Design
The screw design of an extruder influences its melting efficiency, mixing capabilities, and material flow. Advanced screw designs can enhance the homogeneity of the extrudate and allow for processing a wider variety of materials. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for companies looking to diversify their product offerings or improve production efficiency.
5. Heating and Cooling Systems
Effective heating and cooling systems are crucial for maintaining the required temperature during the extrusion process. Precision temperature control ensures the proper melting of materials, while efficient cooling systems prevent deformation and guarantee dimensional stability. For B2B buyers, investing in advanced heating and cooling technologies can lead to significant improvements in product quality and operational efficiency.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Extruder Lines?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are several key terms you should know:
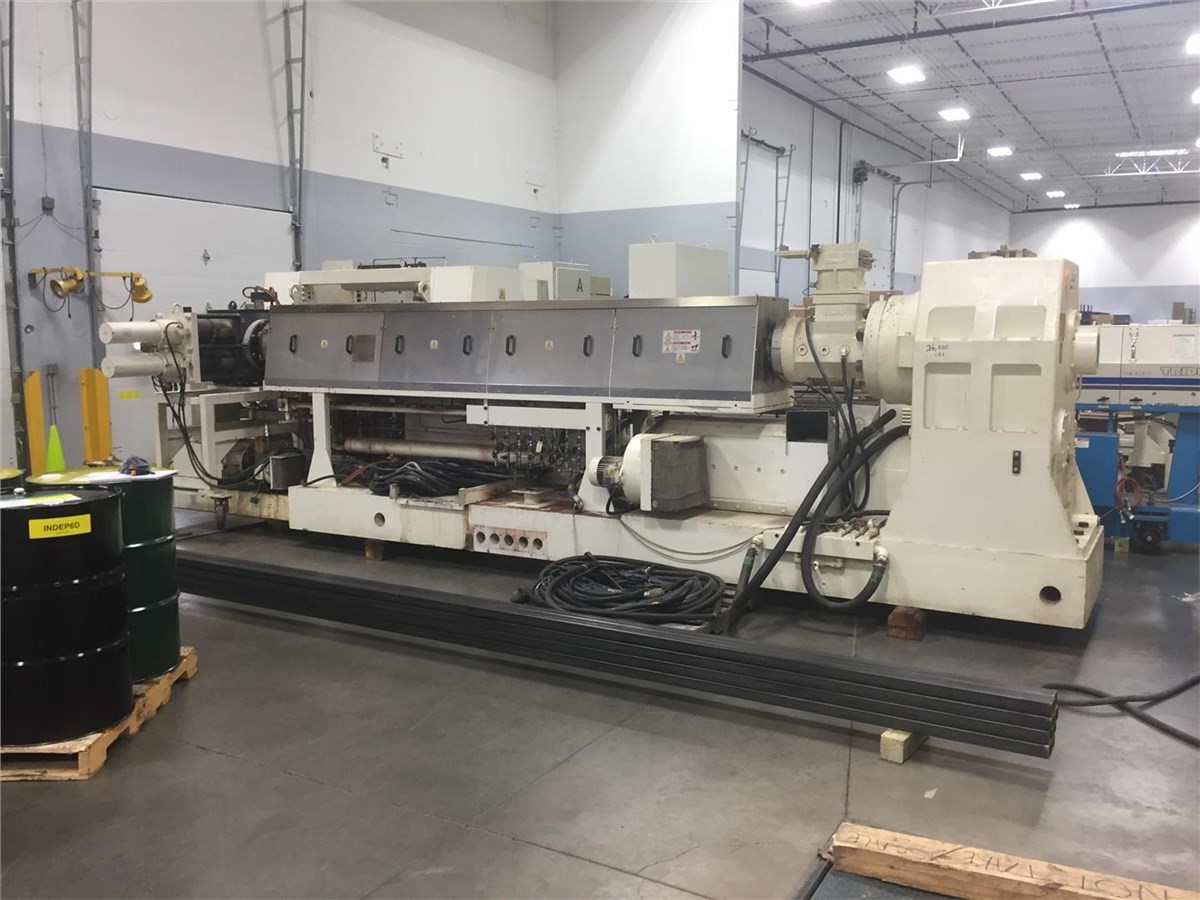

Illustrative image related to extruder line
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of extruder lines, understanding the OEM can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure compatibility with existing machinery.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly important for B2B buyers when negotiating contracts for raw materials or machinery, as it impacts budgeting and inventory management.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process where a company solicits price offers from suppliers for specific products or services. For buyers in the extrusion industry, issuing an RFQ can lead to competitive pricing and better supplier relationships.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms is crucial for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities associated with importing or exporting extruder lines and materials.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. In the extrusion industry, understanding lead times can help companies plan their production schedules and manage customer expectations effectively.
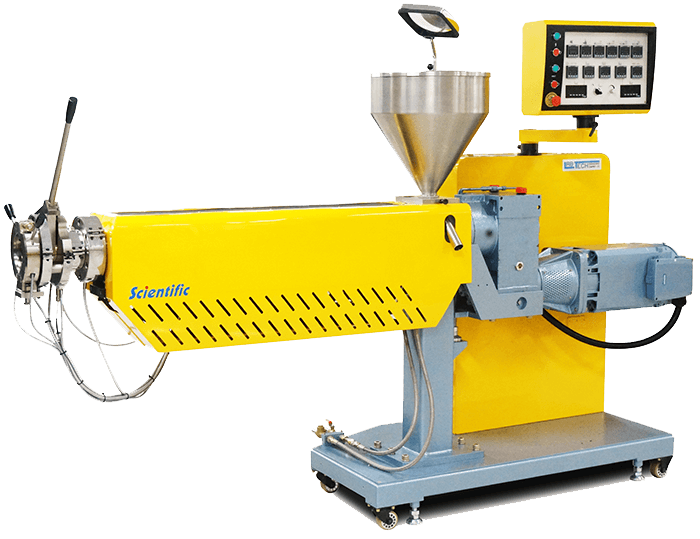

Illustrative image related to extruder line
Incorporating this knowledge of technical properties and trade terminology can significantly enhance decision-making for B2B buyers in the extruder line market. By aligning equipment specifications with business needs and understanding industry jargon, companies can optimize their purchasing processes and improve overall operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the extruder line Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Extruder Line Sector?
The global market for extruder lines is undergoing transformative changes driven by several key factors. First, the increasing demand for sustainable and high-performance materials is shaping the development of extrusion technologies. This demand is particularly pronounced in regions like Europe, where stringent regulations on plastic usage are pushing manufacturers to innovate. Furthermore, the rise of automation and Industry 4.0 technologies is enhancing production efficiency and reducing operational costs, making it an attractive investment for international B2B buyers.
Emerging trends include the integration of advanced materials such as bioplastics and recycled content into the extrusion process. Suppliers are increasingly focusing on offering customizable solutions, allowing businesses to tailor their production lines to specific requirements. In addition, the demand for high-speed production capabilities is fostering the adoption of multi-layer extrusion technology, which provides better material properties and cost-effectiveness.
For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the market dynamics are closely linked to local economic conditions and infrastructure development. As these regions continue to industrialize, the need for high-quality extruded products, including packaging materials and construction components, is expected to rise. Buyers should consider partnerships with established suppliers who can offer not only quality machinery but also technical support and training to optimize production processes.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Extruder Line Sector?
Sustainability has become a critical focus for the extruder line sector, influencing sourcing strategies and operational practices. The environmental impact of plastic production is prompting manufacturers to seek more sustainable solutions, such as using recycled materials or bioplastics. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, including waste reduction and energy efficiency.
Ethical sourcing in the extruder line sector involves ensuring that raw materials are procured responsibly, considering both environmental and social implications. Buyers should look for suppliers who adhere to recognized sustainability certifications, such as ISO 14001 or those that comply with the Global Recycled Standard (GRS). These certifications provide assurance that the materials used in the extrusion process are sourced in a manner that minimizes environmental harm and promotes social responsibility.
Additionally, collaboration with suppliers who invest in sustainable technologies can lead to long-term cost savings and improved product quality. By embracing sustainable sourcing practices, B2B buyers can not only enhance their brand reputation but also meet the growing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products.
What is the Brief Evolution of the Extruder Line Sector and Its Relevance to B2B Buyers?
The extruder line sector has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century, transitioning from simple manual machines to highly sophisticated automated systems. Initially, extrusion was primarily used for creating basic profiles and sheets. However, technological advancements have expanded its applications to include complex products like multi-layer films and specialized tubing.
The introduction of computer-controlled systems in the late 20th century marked a pivotal moment in the industry, allowing for improved precision and efficiency. Today, the integration of smart technologies and real-time monitoring capabilities is redefining production standards and driving innovation. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial, as it highlights the importance of investing in modern, flexible equipment that can adapt to changing market demands and consumer preferences.
As the industry continues to advance, staying informed about historical trends and technological developments will empower buyers to make strategic decisions that align with their operational goals and market opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of extruder line
-
How do I solve the challenges of sourcing a reliable extruder line supplier?
Finding a trustworthy supplier for your extruder line involves several steps. Start by researching potential suppliers through industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms. Verify their reputation by checking customer reviews and testimonials. Engage with previous clients to understand their experiences. Ensure the supplier has a robust after-sales service and support system. Additionally, request a factory visit or virtual tour to assess their manufacturing capabilities and quality control measures. -
What is the best extruder line for producing plastic sheets?
The ideal extruder line for plastic sheet production will depend on your specific needs, such as material type and production volume. Look for a line that features advanced screw design for effective melting and mixing, precise temperature control, and customizable configurations to handle various plastics like PP or PET. Brands like Davis-Standard or KraussMaffei are renowned for their high-quality machines. Consider lines that offer high-speed production, energy efficiency, and integrated cooling systems to ensure consistent product quality. -
How can I ensure the quality of the extruder line I purchase?
To guarantee the quality of your extruder line, conduct thorough due diligence on the supplier. Request detailed specifications and performance metrics for the machinery. It’s beneficial to review certifications and compliance with international standards. Additionally, consider investing in a machine that comes with a warranty and access to technical support. Lastly, arrange for a pre-purchase inspection or test run to verify the equipment’s functionality and output quality before finalizing the purchase. -
What are the common payment terms for international purchases of extruder lines?
Payment terms can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the machinery. Common arrangements include a deposit upfront, often ranging from 30% to 50%, with the balance due upon delivery or installation. For larger orders, consider negotiating payment schedules linked to milestones in production or delivery. Ensure that all terms are clearly outlined in the contract, including currency, payment methods, and any penalties for late payment. -
What customization options are available for extruder lines?
Customization options for extruder lines can include modifications to the extruder size, die head configuration, and cooling systems to suit specific production needs. You may also request features like automated thickness control and enhanced safety mechanisms. Discuss your requirements with the supplier to explore available options and ensure that the machine meets your production goals. Customization can significantly impact efficiency and product quality, making it an essential consideration for your investment. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing an extruder line?
When importing an extruder line, logistics plays a crucial role in ensuring timely delivery and minimizing costs. Consider the mode of transport (sea, air, or land) based on your budget and urgency. Verify customs regulations in your country, as well as any tariffs or duties that may apply. Engage a reliable freight forwarder to handle documentation and shipping arrangements. Finally, plan for installation and setup at your facility, including any necessary training for your staff. -
What should I know about minimum order quantities (MOQ) for extruder lines?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for extruder lines can differ based on the supplier and the type of machinery. Some suppliers may require a specific MOQ to justify production costs, while others may be flexible, especially for customized solutions. It’s essential to clarify these terms during initial discussions. If your production needs are modest, consider suppliers that specialize in refurbished or used equipment, which may have lower MOQs. -
How do I vet suppliers for extruder lines in international markets?
Vetting suppliers for extruder lines involves several key steps. Start by reviewing their company history, including years in operation and industry experience. Check for certifications and compliance with international standards relevant to machinery. Conduct background checks to uncover any potential red flags, such as unresolved complaints. Reach out to existing customers for feedback on their experiences. Finally, consider requesting a trial period or a visit to their facility to evaluate the machinery firsthand and assess their operational standards.
Top 7 Extruder Line Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Arlington Machinery – Key Components of Plastic Sheet Extrusion Lines
Domain: arlingtonmachinery.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Key Components of Plastic Sheet Extrusion Lines: 1. Extruder: Advanced Screw Design, Precision Temperature Control, Customizable Configurations. 2. Die Head: Ensures uniform material flow and consistent sheet dimensions. 3. Calendering and Cooling Section: Automated Thickness Control, Integrated Cooling System. 4. Pull Rollers: Maintain steady tension and constant drawing of the sheet. 5. Cutting …
2. Conair – Auxiliary Equipment for Extrusion Processing
Domain: conairgroup.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Conair offers a range of auxiliary equipment for extrusion processing, including: 1. **Blending**: Gravimetric Batch Blenders, Feeders, and Blending Accessories. 2. **Conveying**: Self-Contained Vacuum Loaders, Compressed Air Material Loaders, Vacuum Pumps/Dust Collectors. 3. **Drying**: Desiccant Dryers, Drying Monitors, Process Heaters. 4. **Extrusion**: Vacuum Sizing Equipment, Cooling Tanks, P…
3. Bausano – Plastic Extrusion Lines and Compounding Machinery
Domain: bausano.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Bausano offers a range of plastic extrusion lines and compounding machinery, including:
1. COMPLETE LINES:
– Pipe Extrusion Lines for standard and special applications
– Profile Extrusion Lines for plastic profiles
– Pelletizing Extrusion Lines for granulation
– WPC Extrusion Lines for wood-plastic composites
– Medical Extrusion Lines for the medical and pharmaceutical industr…
4. Paul Murphy Plastics – Extrusion Lines
Domain: paulmurphyplastics.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Extrusion lines for plastic processing are used to melt and mix polymer resins available in various colors, thicknesses, and types. Key types of extruders mentioned include: 1. Single Screw Extruders – Least expensive, commonly used for manufacturing plastics, suitable for producing high-quality plastic products with minimal effort. 2. Twin Screw Extruders – Used to melt and combine plastic resins…
5. Exelliq – DIGI.LINE & RED.LINE
Domain: exelliq.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Exelliq offers a range of extrusion lines and systems tailored for various needs in the premium, mid, and economy segments. Key products include:
1. DIGI.LINE: Automated extrusion process with real-time optimization for maximum savings.
2. RED.LINE: Focuses on superior profile quality, high productivity, process reliability, and energy savings.
3. RED.LINE wide: Designed for large profiles, pan…
6. Davis-Standard – Blow Molding Extrusion Machinery
Domain: davis-standard.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Davis-Standard offers a comprehensive range of extrusion systems including:
1. **Blow Molding Extrusion Machinery** – Custom-designed for automotive and consumer products, featuring closed-loop hydraulic and electronic controls, state-of-the-art screw design, and spiral head technology for efficient operation.
2. **Elastomer Extrusion Machinery** – Supports global markets for tires, automotive h…
7. Nposk – MC-1102 Cooking/Forming Extruder
Domain: nposk.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Extruder Line includes the MC-1102 Cooking/Forming Extruder (Single Screw Extruder) which kneads raw material under high pressure and cooks it using frictional heat. The extruder features forming nozzles (dies) that create various shapes such as ring and star shapes. The dough is cut into pellets, which can be dried for frying or roasting. Different shapes and sizes are achievable through various …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for extruder line
Why is Strategic Sourcing Essential for Extruder Line Investments?
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing is paramount for businesses looking to invest in extruder lines. By understanding the key components and advanced technologies of these systems, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product quality. The emphasis on high-speed production, energy efficiency, and customizability highlights the value of investing in advanced extrusion technologies that can adapt to varying market demands.
How Can International Buyers Leverage Extruder Line Opportunities?
For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the time is ripe to explore advanced extrusion solutions. Collaborating with experienced suppliers ensures access to the latest innovations, thereby maximizing return on investment. As markets evolve, embracing cutting-edge technology will be crucial for staying ahead of the competition.
What’s Next for Your Business in the Extrusion Sector?
As you consider your next steps in sourcing extruder lines, prioritize partnerships that offer not just equipment, but also expertise and support. Equip your business with the tools necessary to thrive in a dynamic environment. Embrace the future of extrusion processing—invest in high-performance machinery today to secure your competitive edge for tomorrow.
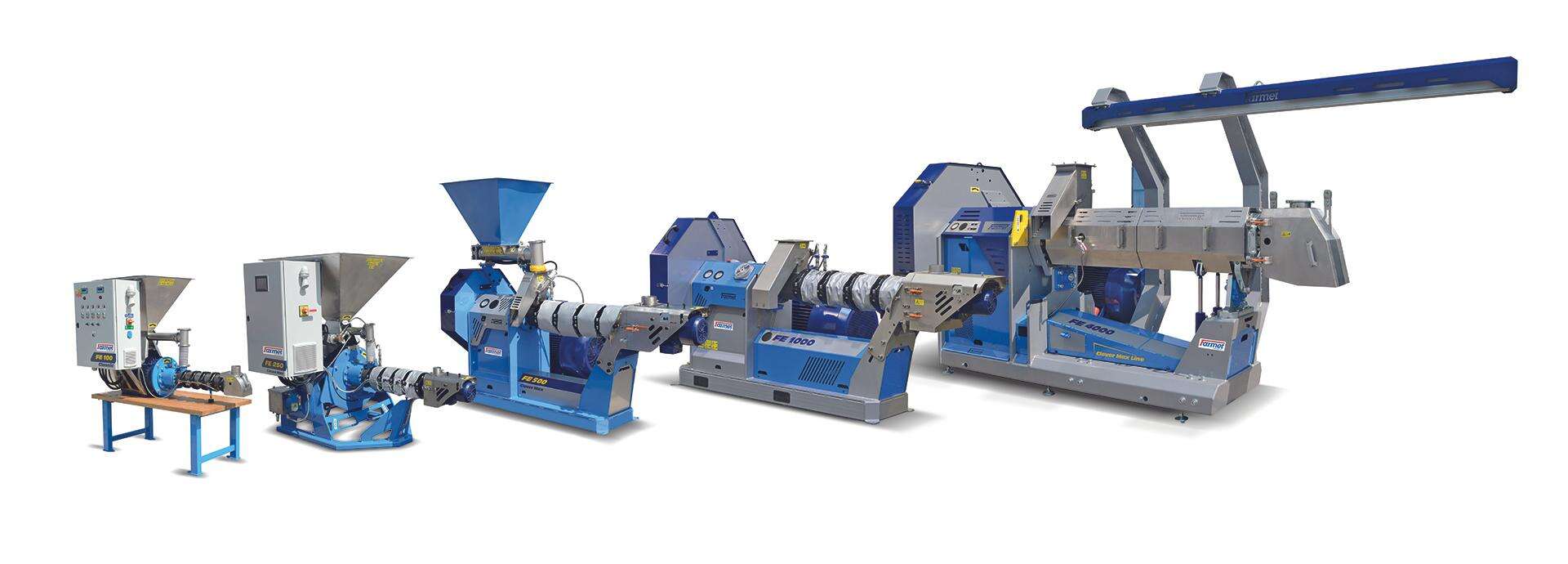

Illustrative image related to extruder line
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.