Cold Heading Equipment Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cold heading equipment
In the fast-paced world of manufacturing, sourcing reliable cold heading equipment can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers, particularly those navigating the diverse landscapes of Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With increasing global demand for high-quality fasteners and components, the need for efficient and durable cold heading machines is more critical than ever. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of the cold heading equipment market, providing comprehensive insights into various types of machines, their applications, and key considerations for supplier vetting.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the latest advancements in cold forming technology, highlight the benefits of different machine configurations, and outline the essential factors influencing cost and performance. By equipping international buyers with actionable information, we empower you to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance your production capabilities and drive business growth. Whether you’re in Nigeria or Vietnam, understanding the nuances of cold heading machinery will enable you to select equipment that meets your specific operational needs while optimizing efficiency and quality.
By delving into critical aspects such as automation options, maintenance requirements, and supplier reliability, this guide serves as a valuable resource for businesses aiming to thrive in the competitive global market. Prepare to elevate your procurement strategy and discover how the right cold heading equipment can transform your manufacturing processes.
Understanding cold heading equipment Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cold Header Machines | High tonnage capacity (up to 75 tons), suitable for high-volume production, easy maintenance | Fasteners, automotive parts, agricultural components | Pros: High productivity, low operational costs; Cons: Initial investment can be significant. |
| Thread Rolling Machines | Specialized for creating threads with high precision and speed | Manufacturing of screws, bolts, and nuts | Pros: Efficient for threaded components; Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Bearing Headers | Capable of forming ball, tapered, and cylindrical rollers at high speeds | Bearing production for automotive and industrial applications | Pros: High speed and quality; Cons: Complex setup may require specialized training. |
| CNC Radial Crimpers | Offers precision forming with programmable features and quick-change capabilities | Aerospace and automotive precision components | Pros: Versatile and efficient; Cons: Higher cost due to advanced technology. |
| Custom Cold Forming Machines | Tailored solutions for specific production needs, often integrating multiple processes | Specialized parts across various industries | Pros: Flexibility in design; Cons: Longer lead times for development. |
What Are Cold Header Machines and Their Applications?
Cold header machines are designed for high-volume production, offering tonnage capacities of up to 75 tons. These machines excel in creating a wide range of components, such as fasteners and automotive parts, through a process that minimizes waste and maximizes efficiency. Buyers should consider the machine’s maintenance ease and the potential for automation, which can streamline operations and reduce labor costs. However, the initial investment can be substantial, making it essential to evaluate long-term production needs and cost savings.
How Do Thread Rolling Machines Enhance Production Efficiency?
Thread rolling machines focus on creating threads with precision, making them indispensable in the fastener industry. They operate at high speeds, which enhances productivity while maintaining quality. These machines are particularly suitable for manufacturing screws, bolts, and nuts, where consistency is crucial. Buyers should assess the machine’s capabilities in terms of thread size and material compatibility. While thread rolling machines are efficient, their application scope may be limited compared to more versatile equipment.
What Are the Advantages of Bearing Headers in Manufacturing?
Bearing headers are specialized machines that form various types of rollers, including ball and tapered designs, at exceptional speeds. These machines are crucial in producing bearings for automotive and industrial applications, where precision and speed are paramount. When considering a bearing header, businesses should evaluate the machine’s speed and output quality. However, the setup complexity may require specialized training, which could impact the overall operational efficiency.

Illustrative image related to cold heading equipment
Why Choose CNC Radial Crimpers for Precision Operations?
CNC radial crimpers are engineered for precision cold forming, particularly in the aerospace and automotive sectors. Their programmable features allow for intricate designs and quick adjustments, enhancing versatility and efficiency in production. Buyers should consider the machine’s ability to handle various materials and the potential for automation. While the initial costs are higher due to advanced technology, the long-term benefits of increased precision and reduced waste can justify the investment.
How Do Custom Cold Forming Machines Meet Unique Production Needs?
Custom cold forming machines offer tailored solutions that can integrate multiple processes, catering to specific production requirements across various industries. These machines are ideal for manufacturers looking to produce specialized parts that standard equipment cannot accommodate. When investing in custom machinery, businesses should weigh the flexibility and unique capabilities against the longer lead times and potential costs involved in development. The ability to meet precise specifications can significantly enhance product quality and competitiveness in the market.
Key Industrial Applications of cold heading equipment
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cold heading equipment | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of fasteners and brackets | High-volume production with reduced waste | Look for precision machinery with minimal downtime and easy maintenance. |
| Construction | Fabrication of structural components | Increased strength and reliability of parts | Ensure compatibility with local materials and compliance with regional standards. |
| Aerospace | Manufacturing of precision components | Enhanced safety and performance of aircraft | Seek advanced technology for high-tolerance parts and support for complex designs. |
| Electronics | Creation of connectors and housings | Improved efficiency and reduced assembly costs | Focus on equipment that offers automation options for high-speed production. |
| Agricultural Equipment | Fabrication of pins and linkage components | Durable and efficient components for machinery | Prioritize suppliers with a strong service and support network in your region. |
How is Cold Heading Equipment Used in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, cold heading equipment is crucial for producing fasteners and brackets that are integral to vehicle assembly. This equipment allows manufacturers to create high volumes of components with minimal waste and high precision, addressing the industry’s demand for both efficiency and quality. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing machines that offer easy maintenance and support is vital, as this reduces downtime and operational disruptions.

Illustrative image related to cold heading equipment
What Role Does Cold Heading Equipment Play in Construction?
Cold heading is widely used in the construction sector for fabricating structural components such as bolts, nuts, and anchors. The process ensures that parts have enhanced strength and reliability, which is critical for safety in construction projects. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should consider sourcing equipment that is compatible with local materials and adheres to regional building standards, ensuring compliance and quality assurance in their projects.
Why is Cold Heading Equipment Important in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In aerospace manufacturing, cold heading equipment is employed to create precision components that meet stringent safety and performance standards. The ability to produce complex shapes from high-strength materials is essential, as these parts often operate under extreme conditions. International buyers, especially in regions with emerging aerospace markets, should seek advanced machinery that supports high tolerances and offers robust technical support to navigate the complexities of aerospace design.
How Does Cold Heading Equipment Benefit the Electronics Industry?
The electronics industry utilizes cold heading equipment to manufacture connectors and housings that require high precision and efficiency. This technology allows for the rapid production of intricate parts, significantly reducing assembly costs and improving overall product reliability. Buyers in Africa and Vietnam should focus on equipment that incorporates automation features, as this enhances production speed and ensures consistent quality across large batches.
What Applications of Cold Heading Equipment Exist in Agricultural Equipment?
Cold heading equipment is essential in the agricultural sector for producing durable pins and linkage components used in machinery. The equipment’s ability to create strong, reliable parts is vital for the performance of agricultural tools and vehicles. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who have a strong service network and can provide ongoing support, as this ensures that equipment remains operational in the demanding environments typical of agricultural applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cold heading equipment’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Quality of Cold-Headed Parts
The Problem: One major challenge faced by B2B buyers in the cold heading equipment sector is the inconsistency in the quality of the parts produced. This inconsistency often stems from outdated machinery or inadequate tooling, resulting in defects that can lead to costly rework or scrapped materials. Buyers may find that their current equipment struggles with tolerances, leading to variations in dimensions and strength of the fasteners produced. This is particularly critical in industries like automotive and aerospace, where precision is non-negotiable.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should invest in advanced cold heading machinery that features precise tooling and automation capabilities. When sourcing equipment, it’s essential to request detailed specifications and performance data from suppliers. Buyers should prioritize machines that offer adaptive technology, such as automatic die adjustments and real-time quality monitoring systems. This approach ensures that the equipment can maintain tight tolerances and consistently produce high-quality components. Additionally, regular maintenance and training for operators can greatly enhance the equipment’s performance and prolong its lifespan, ultimately leading to better consistency in production.
Scenario 2: High Operational Costs Due to Inefficiencies
The Problem: Many B2B buyers experience high operational costs associated with inefficient cold heading processes. Inefficiencies can arise from manual operations, outdated machinery, or suboptimal production workflows. These factors lead to increased labor costs, higher energy consumption, and longer lead times, negatively impacting the overall profitability of the manufacturing operation. This is especially pressing for companies in competitive markets where cost control is vital.
The Solution: To combat operational inefficiencies, businesses should consider upgrading to fully automated cold heading systems that integrate seamlessly with other manufacturing processes. When evaluating new equipment, focus on models that are designed for easy automation and can handle a variety of materials and shapes. Implementing a lean manufacturing approach can also help streamline operations; this includes analyzing workflows and eliminating non-value-added steps. Investing in training for operators to maximize the use of automation technology is crucial. Moreover, collaborating with equipment suppliers for tailored solutions can lead to improvements in productivity, thereby reducing costs over time.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Sourcing Customized Solutions
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to find cold heading equipment that meets their specific production needs, particularly when it comes to custom parts. Many suppliers provide standard models that may not align with unique requirements, leading to additional costs and time delays. This challenge can be exacerbated in regions with limited access to specialized manufacturing technology, such as parts of Africa and South America.
The Solution: To effectively source customized cold heading solutions, buyers should engage with suppliers that offer comprehensive consultation services. A detailed initial design consultation can help identify precise requirements and allow for the development of tailored machinery. Buyers should look for manufacturers that have a proven track record of customizing equipment, as well as those who are willing to collaborate on design and engineering aspects. Additionally, forming partnerships with local distributors can facilitate better access to tailored solutions, providing ongoing support and maintenance services that are critical for ensuring the longevity of specialized equipment. Engaging in industry networks and forums can also provide insights and recommendations for reputable suppliers who can deliver on custom needs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cold heading equipment
What Are the Key Properties of Steel in Cold Heading Equipment?
Steel is the most commonly used material in cold heading applications due to its excellent mechanical properties. It offers high tensile strength, making it suitable for producing components that must withstand significant stress. Steel’s temperature and pressure ratings are generally high, allowing for versatility in various industrial applications. Additionally, it can be treated for enhanced corrosion resistance, which is crucial for components exposed to harsh environments.
Pros and Cons of Using Steel
The durability of steel is one of its most significant advantages, providing long-lasting performance in demanding applications. However, the cost of high-grade steel can be relatively high, which may impact the overall production cost. Manufacturing complexity can also arise from the need for precise tooling and heat treatment processes. For international buyers, compliance with standards such as ASTM or DIN is essential, particularly when exporting to regions with strict quality regulations.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Cold Heading Applications?
Aluminum is increasingly popular in cold heading due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. It is particularly useful in applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries. Aluminum typically has a lower melting point than steel, which can simplify the manufacturing process.
Pros and Cons of Using Aluminum
The primary advantage of aluminum is its low density, which allows for the production of lighter components without sacrificing strength. However, aluminum may not be suitable for high-stress applications due to its lower tensile strength compared to steel. Additionally, the cost of aluminum can vary significantly based on market conditions, which may influence budgeting for international projects. Buyers in emerging markets should consider local availability and potential import tariffs.
What Are the Benefits of Using Brass in Cold Heading Equipment?
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, is known for its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. It is often used in applications requiring good electrical conductivity, such as electrical connectors and fittings. Brass can also be cold-headed to create intricate shapes without compromising its structural integrity.
Pros and Cons of Using Brass
One of the key advantages of brass is its resistance to corrosion and tarnishing, making it ideal for outdoor applications. However, brass is generally more expensive than steel and aluminum, which can be a limiting factor for large-scale production. Moreover, the manufacturing process for brass can be more complex, requiring specialized tooling. International buyers should be aware of the specific standards for brass components, as these can vary significantly across regions.
How Does Stainless Steel Compare in Cold Heading Equipment?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance and durability, making it a preferred choice for many cold heading applications, especially in industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals. Its ability to maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions makes it suitable for high-performance components.
Pros and Cons of Using Stainless Steel
The primary advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and resistance to corrosion, which reduces the need for frequent replacements. However, the cost of stainless steel is typically higher than that of carbon steel and aluminum, which can impact budget considerations. The manufacturing complexity is also notable, as stainless steel requires specific tooling and processes to achieve desired shapes. For international buyers, adherence to standards such as ASTM A240 or EN 10088 is crucial for ensuring product quality.
Summary Table of Strategic Material Selection for Cold Heading Equipment
| Material | Typical Use Case for cold heading equipment | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Fasteners, automotive parts | High tensile strength | Higher cost for high grades | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, lightweight fittings | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength than steel | Medium |
| Brass | Electrical connectors, plumbing fittings | Excellent machinability | Higher cost than steel and aluminum | High |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, medical devices | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers in various regions, helping them make informed decisions based on application requirements and material properties.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cold heading equipment
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Cold Heading Equipment?
The manufacturing process for cold heading equipment involves several critical stages that ensure high-quality production. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to invest in efficient machinery.
-
Material Preparation
The first step involves selecting the appropriate raw materials, typically wire or rod stock made from various metals, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloys. The material must meet specific mechanical properties to ensure optimal performance during cold heading. Proper handling and storage of materials are crucial to prevent contamination or deformation before processing. Additionally, cutting the wire or rod to the correct length is vital, as this directly influences the final product’s dimensions. -
Forming Process
The heart of cold heading equipment lies in its forming capabilities. This process typically employs a series of dies and punches to shape the raw material without the application of heat. Key techniques include:
- Heading: The primary operation where the material is shaped into a specific form through a series of strikes from a punch.
- Thread Rolling: This technique creates threads on the fasteners using a set of rolling dies, ensuring precision and enhancing the part’s strength.
- Secondary Operations: These may include trimming, piercing, and bending, which further refine the component’s shape and features.
Advanced machinery often integrates automation and control systems to enhance precision and reduce cycle times, thereby improving overall productivity.
-
Assembly
Once formed, components may undergo assembly processes if they are part of multi-part products. This can involve the integration of various fasteners or elements that require precise alignment. Automated assembly systems are increasingly used to enhance efficiency and accuracy during this stage. -
Finishing
The finishing stage involves surface treatments to improve the component’s performance and aesthetics. Common techniques include coating (e.g., galvanizing, anodizing), polishing, and heat treatment to enhance corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. Quality at this stage is crucial, as it influences the longevity and reliability of the final product.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Cold Heading Equipment Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the production of cold heading equipment, ensuring that every component meets stringent industry standards and customer expectations.
-
International and Industry-Specific Standards
Adhering to international standards such as ISO 9001 is essential for manufacturers targeting global markets. This certification indicates a commitment to consistent quality management practices. Additionally, industry-specific standards like CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in Europe and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for oil and gas applications further define quality benchmarks that manufacturers must meet. -
Quality Control Checkpoints
Effective QA processes typically involve several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing cycle:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial phase checks the raw materials for compliance with specifications before they enter production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify defects early. This may involve measuring dimensions, material properties, and process parameters.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, the finished components undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet the required standards. This may include dimensional checks, mechanical testing, and performance evaluations.
- Common Testing Methods
Various testing methods are employed to ensure quality, including:
- Tensile Testing: Determines the material’s strength and ductility.
- Hardness Testing: Assesses the material’s resistance to deformation.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic or magnetic particle testing help identify internal flaws without damaging the components.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial to ensure a reliable partnership.
-
Audits and Inspections
Conducting supplier audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturer’s quality management systems firsthand. This process can include reviewing documentation, observing production practices, and evaluating the effectiveness of quality checkpoints. -
Quality Reports
Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s performance metrics, defect rates, and compliance with industry standards. These reports should be transparent and regularly updated to reflect the latest quality assessments. -
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality practices. These inspections can be particularly valuable when dealing with international suppliers, ensuring adherence to global standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate specific nuances when it comes to quality control in cold heading equipment manufacturing:
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences
Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality and the regulatory environment in different regions is vital. For instance, suppliers in Europe may have more stringent quality controls compared to those in other regions. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and quality expectations. -
Communication and Language Barriers
Effective communication is essential for ensuring that quality expectations are clearly understood. Language barriers can lead to misinterpretations of quality standards, so it’s beneficial for buyers to work with suppliers who have experience in international trade and can communicate effectively in the buyer’s preferred language. -
Logistical Considerations
Quality control does not end with production; it extends to logistics and shipping. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have quality processes in place for handling and transporting equipment, as improper handling can compromise the quality of the final products upon arrival.
By understanding the intricacies of manufacturing processes and quality assurance for cold heading equipment, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and establish successful partnerships with suppliers across the globe.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cold heading equipment’
Introduction
When sourcing cold heading equipment, it’s essential to approach the process with a structured strategy to ensure you choose the right machinery for your manufacturing needs. This guide provides a comprehensive checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the complexities of procurement, ensuring that you make informed decisions that enhance productivity and efficiency.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, outline your specific needs regarding cold heading equipment. Consider factors such as the types of parts you will manufacture, the materials you will use, and production volumes. Having clear specifications will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure that you select equipment that meets your operational requirements.
Illustrative image related to cold heading equipment
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable manufacturers and suppliers of cold heading machinery. Look for companies with a proven track record in the industry and positive customer reviews. Pay attention to their experience in international markets, especially those relevant to your region, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
It’s crucial to verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications and comply with international quality standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 indicate a commitment to quality management and can assure you of the reliability of their equipment. Additionally, check for compliance with local regulations and standards applicable in your country or region.
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed proposals that include technical specifications, pricing, and delivery timelines. Analyze these proposals to ensure they align with your defined requirements. Look for transparency in pricing and terms to avoid unexpected costs later in the procurement process.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Maintenance Services
Strong after-sales support is vital for the long-term success of your cold heading operations. Inquire about the maintenance services offered by suppliers, including warranty terms, availability of spare parts, and technical support. A supplier that provides robust after-sales support can help minimize downtime and maintain production efficiency.
Step 6: Arrange for Equipment Demonstrations
If possible, arrange for demonstrations of the cold heading equipment before finalizing your purchase. Observing the machinery in action will give you insight into its performance, ease of operation, and maintenance requirements. This step can also provide an opportunity to ask questions directly to the supplier’s technical team.

Illustrative image related to cold heading equipment
Step 7: Finalize the Contract with Clear Terms
After selecting a supplier, ensure that the contract clearly outlines all terms and conditions, including delivery schedules, payment terms, and warranty details. Be diligent in reviewing the contract to protect your interests and establish a strong foundation for a successful business relationship.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the sourcing process for cold heading equipment, ensuring that they invest in machinery that will enhance their production capabilities and meet their business goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cold heading equipment Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Cold Heading Equipment?
When analyzing the costs associated with cold heading equipment, several components play a crucial role in determining the overall price structure.
-
Materials: The primary materials for cold heading machinery include high-grade steel and alloys that ensure durability and performance. Fluctuations in raw material prices can significantly impact the cost. For international buyers, sourcing materials locally can mitigate some shipping costs and tariffs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both the workforce needed for manufacturing and ongoing maintenance. Skilled technicians are often required for assembly and setup, which can vary by region. For instance, labor costs may be lower in countries like Vietnam compared to Europe, influencing the final pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these overhead costs, ultimately benefiting buyers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling is often required for specific applications, which adds to the cost. Buyers should consider the longevity and versatility of tooling options, as these can affect both immediate and long-term expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are essential to ensure that machinery meets industry standards. The investment in quality checks can increase upfront costs but often leads to lower failure rates and reduced maintenance expenses over time.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary significantly based on the supplier’s location and the buyer’s destination. Understanding the best Incoterms for your purchase can help manage these logistics costs effectively.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on their market positioning, brand reputation, and after-sales support offerings. Buyers should evaluate not just the base price but also the total value delivered, including warranty and service agreements.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Cold Heading Equipment Pricing?
Several factors influence the pricing of cold heading equipment, which buyers must consider when sourcing machinery.
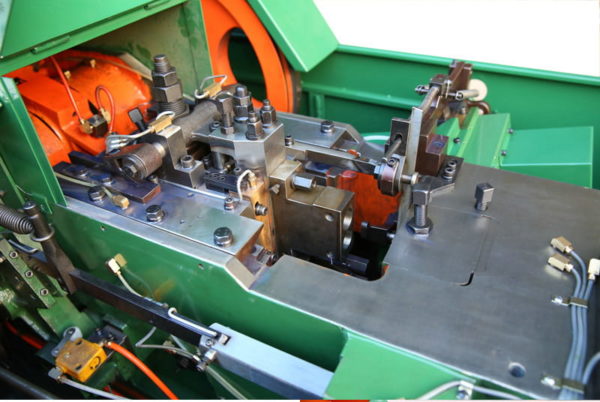

Illustrative image related to cold heading equipment
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often have minimum order quantities (MOQs) that can affect pricing. Purchasing in larger volumes typically results in lower per-unit costs, making it advantageous for companies with high production needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom machines tailored to specific applications can lead to higher costs. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against their budget and production requirements.
-
Quality and Certifications: Equipment that meets international quality standards or certifications may carry a premium price. However, investing in certified machinery can lead to greater reliability and compliance in international markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their expertise and service, but this can translate into better support and lower risk.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects shipping responsibilities and costs. Buyers should negotiate terms that minimize their risk while ensuring timely delivery.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers in Cold Heading Equipment?
To achieve favorable pricing on cold heading equipment, consider the following negotiation strategies:
-
Research and Benchmark: Gather data on industry pricing and competitor offerings. This information can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Highlight Volume Purchases: If your company plans to purchase multiple units or has the potential for repeat orders, use this as leverage to negotiate better terms.
-
Ask for Discounts: Don’t hesitate to ask for discounts based on quantity, early payment, or long-term partnership agreements.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): When assessing offers, consider not only the purchase price but also the costs associated with maintenance, operation, and potential downtime.
-
Cultural Sensitivity: Understand the cultural dynamics in regions like Africa and the Middle East, where relationship-building can be key to successful negotiations.
What Should International Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Pricing Nuances?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges. Currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and regional economic conditions can all impact the final price. Buyers should also be aware of local regulations and standards that may affect machinery compatibility and operation.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for cold heading equipment can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. This analysis provides a general framework for understanding costs and pricing but should not be considered definitive. Always seek detailed quotes from suppliers and conduct thorough due diligence to ensure the best possible investment for your business.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cold heading equipment With Other Solutions
When evaluating production methods for metal fasteners and components, it is essential to consider various options beyond cold heading equipment. Cold heading is a prevalent process for manufacturing high-strength parts but may not always be the best fit for every application. Here, we explore viable alternatives that can achieve similar results, offering insights into their performance, cost, and usability.
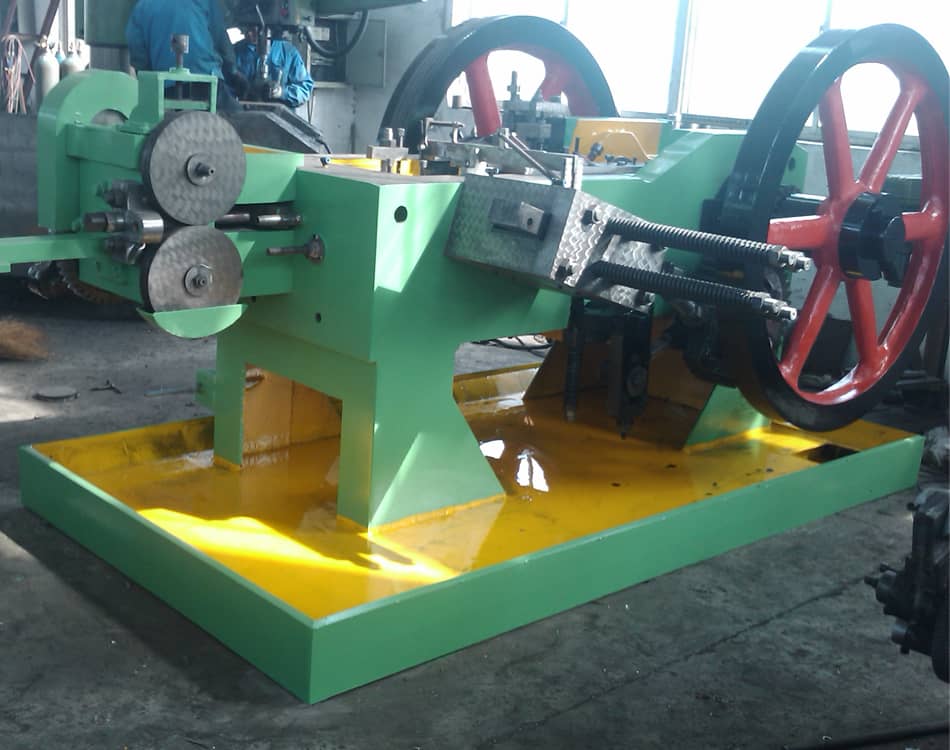

Illustrative image related to cold heading equipment
| Comparison Aspect | Cold Heading Equipment | Alternative 1: Forging Equipment | Alternative 2: Machining Processes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-speed, efficient, and precise; ideal for mass production. | Excellent strength and durability; suitable for complex shapes. | Versatile, precise, but typically slower and more costly for mass production. |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; lower operational costs with volume production. | Higher initial investment; cost-effective for large batches. | Lower initial costs but higher per-part costs; efficiency decreases with volume. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized training for setup and operation; relatively straightforward for mass production. | Complex setup and tooling; requires skilled labor for operation. | Easier to set up; widely understood process but may require extensive programming for CNC machines. |
| Maintenance | Generally low; modern machines are designed for easy maintenance. | Moderate; requires regular maintenance to ensure equipment longevity. | High; CNC machines often require frequent calibration and maintenance. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for producing large quantities of standardized fasteners. | Best for producing high-strength, custom-shaped components in lower volumes. | Suitable for producing intricate components with tight tolerances across varied volumes. |
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Forging Equipment?
Forging equipment is a robust alternative to cold heading, particularly for applications requiring high strength and durability. This method involves shaping metal using compressive forces, which can produce complex shapes and improve the material’s grain structure, resulting in enhanced mechanical properties. However, the initial investment for forging equipment can be significant, and the complexity of setup may require skilled labor. It is most effective for lower volume production of custom parts where strength is paramount.
How Does Machining Compare to Cold Heading in Terms of Application?
Machining processes, such as CNC machining, offer a high degree of precision and flexibility, allowing manufacturers to create intricate components from a variety of materials. This method is particularly beneficial for producing parts with complex geometries that cannot be easily formed through cold heading or forging. While the initial setup costs for machining can be lower, the per-part costs tend to rise with production volume, making it less suitable for mass production compared to cold heading. Additionally, the time required for machining can hinder throughput, especially in high-demand environments.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Production Method?
When selecting the right production method, B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific requirements, including the desired strength, complexity of parts, production volume, and budget constraints. Cold heading equipment excels in high-volume, standardized production scenarios, while forging offers superior strength for custom parts in lower volumes. Machining provides unmatched versatility for intricate designs but may not be cost-effective for large-scale manufacturing. By evaluating these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cold heading equipment
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Cold Heading Equipment?
When evaluating cold heading equipment, understanding the technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade refers to the type of metal used in production, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, or alloy steel. Each material grade has unique properties that affect the strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability of the final product. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade is essential to ensure that the components meet industry standards and application requirements, especially in sectors like automotive or aerospace.

Illustrative image related to cold heading equipment
2. Tonnage Capacity
Tonnage capacity indicates the maximum force the cold header can apply to deform the material. Machines can vary widely in tonnage, often ranging from 10 to 75 tons or more. For manufacturers, understanding tonnage is vital for determining the machine’s suitability for specific applications and ensuring it can handle the volume of production required. Higher tonnage often translates to the ability to work with thicker materials or create more complex shapes.
3. Precision Tolerance
Precision tolerance is the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in the produced parts. This specification is critical for applications where components must fit together precisely, such as in machinery or automotive assemblies. For B2B buyers, knowing the tolerance capabilities helps ensure that the cold heading equipment will produce parts that meet their quality standards and reduce the need for costly rework or adjustments.
4. Cycle Time
Cycle time is the total time taken to produce one part, encompassing all stages of the cold heading process. Shorter cycle times can significantly enhance productivity, enabling manufacturers to meet tight deadlines and improve their overall output. Understanding cycle time is essential for B2B buyers as it directly impacts operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
5. Automation Capabilities
Automation capabilities refer to the extent to which a cold header can be automated, including features like programmable controls and integration with other machinery. Advanced automation can reduce labor costs, increase production rates, and improve consistency in part quality. For buyers, evaluating automation options can lead to significant long-term savings and operational advantages.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Cold Heading Equipment?
In addition to technical properties, familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are several key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of cold heading equipment, it’s important for buyers to understand who the OEM is, as this can affect warranties, service, and support.
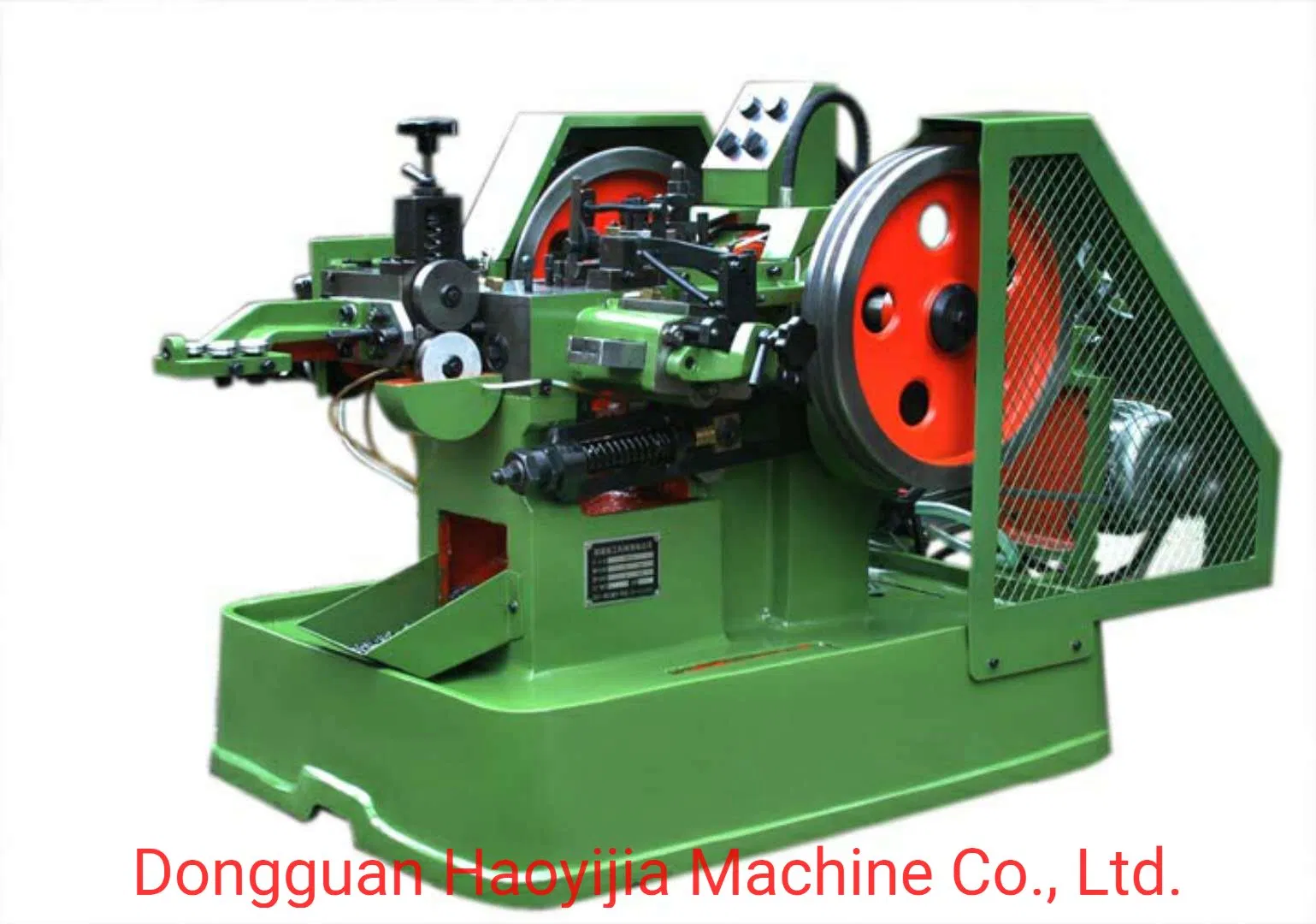

Illustrative image related to cold heading equipment
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for B2B buyers to consider, as it can influence inventory management and cash flow. Understanding MOQs helps companies plan their purchases more effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. This process is essential for obtaining competitive bids and ensuring that buyers can compare offers from multiple vendors.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery obligations.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead time is crucial for B2B buyers to manage production schedules and inventory effectively.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of cold heading equipment procurement with greater confidence and clarity.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cold heading equipment Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Cold Heading Equipment?
The global cold heading equipment market is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing demand for high-precision fasteners across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction. As international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to enhance their manufacturing capabilities, they are gravitating toward advanced cold forming technologies that offer higher efficiency and reduced waste. Key trends include the integration of automation and Industry 4.0 technologies, which enable real-time monitoring and optimization of production processes. This shift not only improves productivity but also enhances the precision of the components produced.
Additionally, the demand for customization is on the rise, with manufacturers increasingly offering tailored solutions that meet specific client needs. Equipment that supports rapid changeover and flexibility in production is highly sought after, enabling businesses to respond quickly to market fluctuations. Moreover, the emphasis on supply chain resilience has led to a growing interest in local sourcing and partnerships with regional suppliers, particularly in emerging markets where logistics challenges can affect lead times.
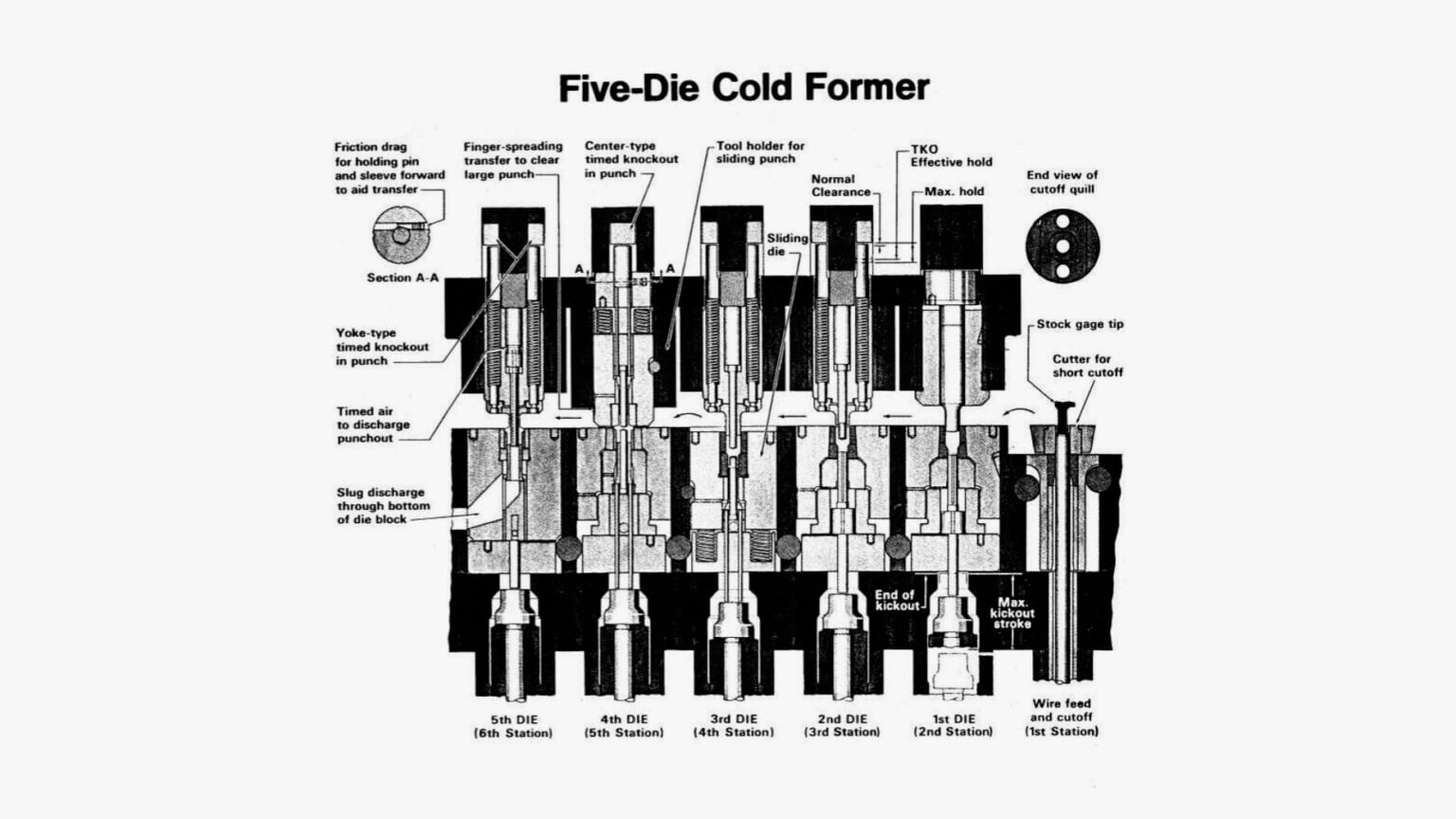
Illustrative image related to cold heading equipment
How Is Sustainability Influencing the Sourcing of Cold Heading Equipment?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor in the sourcing of cold heading equipment. As environmental regulations tighten globally, international buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing and reduced environmental impact. This includes the use of green certifications and materials, which signify compliance with sustainable practices. For instance, equipment manufacturers are adopting energy-efficient technologies and materials that minimize carbon footprints during production.
Furthermore, companies are recognizing that ethical supply chains can enhance their brand reputation and customer loyalty. Buyers are now more likely to engage with suppliers who provide transparency about their sourcing practices and environmental impact. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions like Europe, where consumers and businesses alike are advocating for responsible manufacturing processes. In response, many equipment manufacturers are investing in sustainable production methods, such as recycling scrap metal and reducing waste during the cold forming process.
What Is the Historical Evolution of Cold Heading Technology?
Cold heading technology has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially, the process was limited to simple fasteners and components, but advancements in machinery and tooling have expanded its capabilities dramatically. The introduction of sophisticated multi-die presses and automation in the 1950s marked a turning point, allowing manufacturers to produce complex shapes with greater precision and efficiency.
As industries grew more demanding, the technology adapted to meet these needs, incorporating features that enhance speed and accuracy. Today, modern cold heading equipment is characterized by its versatility, enabling the production of a wide range of components from various materials. The ongoing innovation in this sector reflects a commitment to improving productivity while addressing the challenges posed by global competition and evolving customer expectations.
In conclusion, as B2B buyers navigate the cold heading equipment landscape, understanding these market dynamics, sustainability imperatives, and the historical context will be crucial for making informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational goals and values.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cold heading equipment
-
How do I choose the right cold heading machine for my production needs?
Selecting the right cold heading machine involves assessing your production volume, the types of parts you need to manufacture, and your budget. Start by evaluating the tonnage required for your specific applications; machines typically range from 30 to 75 tons, with higher capacities available for custom needs. Consider features such as automation options, ease of maintenance, and compatibility with existing tooling. Consulting with manufacturers can provide insights into which machine best suits your requirements and will enhance your overall productivity. -
What are the key benefits of investing in cold heading equipment?
Investing in cold heading equipment offers several advantages, including increased production efficiency, reduced material waste, and improved part strength and consistency. This process allows for the creation of complex shapes from wire or rod at room temperature, which enhances the mechanical properties of the finished product. Moreover, cold heading can significantly lower production costs over time due to its high-speed capabilities and minimal scrap rates, making it an attractive option for manufacturers in competitive markets. -
What customization options are available for cold heading machines?
Most suppliers offer a range of customization options to meet specific production needs. These may include modifications to the machine’s tonnage, tooling configurations, and integration with automation systems. Additionally, some manufacturers provide tailored solutions for unique part designs or production processes. Engaging in a design consultation with the supplier can help clarify your requirements and ensure that the machinery is optimized for your specific applications. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for cold heading equipment?
Minimum order quantities for cold heading equipment can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the machinery. Generally, for standard machines, MOQs may start at one unit, while custom solutions could require larger orders. It’s essential to discuss your needs with potential suppliers early in the negotiation process to understand their MOQ policies and how they align with your production goals. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing cold heading machines?
Payment terms for cold heading equipment can vary widely among suppliers. Common practices include a deposit upon order placement, followed by a balance payment upon delivery or installation. Some manufacturers may offer financing options or payment plans, especially for larger investments. Always ensure to discuss and negotiate terms clearly before finalizing the purchase to avoid any misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure the quality of the cold heading equipment I am purchasing?
To ensure quality, it is crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Look for manufacturers with a solid reputation, positive customer reviews, and certifications that demonstrate compliance with international standards. Request samples or case studies of previous work to evaluate the performance of their equipment. Additionally, inquire about warranties, after-sales support, and the availability of spare parts, as these factors can indicate the reliability of the equipment. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing cold heading machines?
When importing cold heading machines, logistics play a critical role in ensuring timely delivery and operational readiness. Consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that may apply in your country. Work closely with your supplier and a logistics provider experienced in heavy machinery to plan for transportation, handling, and installation. It’s also advisable to factor in lead times for production and shipping to avoid delays in your manufacturing schedule. -
What support services are available after purchasing cold heading equipment?
Most reputable suppliers offer a range of support services post-purchase, including installation assistance, operator training, and maintenance services. Ensure that the supplier provides a comprehensive service package, including access to spare parts and technical support. Some manufacturers also offer ongoing process development assistance to optimize your production efficiency. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can facilitate better support and resources as your production needs evolve.
Top 7 Cold Heading Equipment Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Overton Industries – Cold Header Machines
Domain: overtonind.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Cold Header Machines from Overton Industries offer turnkey productivity and are designed for efficient, cost-effective manufacturing of large quantities. Key features include:
– Available in multiple tonnages, standard up to 75 tons with custom options available.
– Capable of producing various parts such as exhaust hanger brackets, agricultural pins, and linkage components.
– Easy to automate a…
2. SACMA – KSP12 Header
Domain: fastenershows.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: 1. SACMA KSP12: A fully re-designed 1D2B header with thread rolling, suitable for producing screws (self-tapping and metric) from diameter 3mm to 8mm. 2. Kinefac RP-10 CNC KINECRIMP: A high precision radial forming machine for cold-form crimping operations, capable of creating hexagonal, square, and rectangular shapes. It has a 10-ton force capacity, can handle nut sizes from M4 to M18, and featur…
3. Cold Headed Parts – Fasteners & Automotive Components
Domain: coldheadedparts.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Cold headed parts are metal parts formed using cold working processes, specifically featuring an enlarged section on one end. They are produced through cold heading, a specialized technique within cold forming. Key examples include fasteners (screws, bolts, rivets), automotive parts (clips, brackets, pins), construction components (steel studs, joists), and electronics (connector pins, terminals)….
4. TFG USA – Cold Heading Solutions
Domain: tfgusa.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Cold heading is a high-speed metal forming process that shapes parts at room temperature without the need for heat. It is primarily used for forming the heads on fasteners like bolts, screws, rivets, and nails. Key advantages include minimal waste, faster production, stronger parts due to work hardening, reduced costs, and simplification of multi-piece assemblies. Cold heading supports sustainable…
5. Hariton Machinery – Progressive & Multi Die Headers
Domain: haritonmachinery.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Progressive & Multi Die Headers available from various manufacturers including AJAX, AMADA, ASAHI, and more. Types include: 2 Die 2 Blow, 2 Die 3 Blow, 2 Die 4 Blow, 3 Die Progressive, 4 Die Progressive, and 5 Die Progressive Headers. Specific models listed include National-Formax Model FX-32M, National Machinery Formax Model FX22M, National FORMAX Model FX33M, Jern Yao Model JBF-24B4S, Asahi Suna…
6. Ningbo Anchors – High Speed Cold Heading Machines
Domain: anchor-fasteners.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: High Speed Cold Heading Machine – Bolt Nut Making Machine, Cold Forging Machine, Screw production machine, Progressive stamping press and mold, Screw heading machine, Thread rolling machine, Nut tapping machine. Manufacturer: Ningbo Anchors Precision Machinery Co., Ltd, China.
7. TruForm Equipment – Advanced Cold Forming & Fastener Solutions
Domain: truformequipment.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: {“categories”: [“Cold Forming Equipment”, “High-Speed Sorting Equipment”, “Aerospace Fastener Manufacturing Equipment”, “Thread & Form Rolling Equipment”, “Feeding & Assembly Systems”, “Nut Crimping Equipment”, “Packaging Equipment”, “Tapping Equipment”, “Mist & Smoke Collection Equipment”, “Friction Welding Equipment”, “Pointing Equipment”, “Recycling & Reclamation Equipment”], “products”: [{“nam…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cold heading equipment
As the demand for precision-engineered components continues to surge globally, strategic sourcing of cold heading equipment has emerged as a critical factor for businesses looking to enhance productivity and operational efficiency. Key takeaways highlight the importance of investing in advanced machinery, such as customizable cold header machines that accommodate various tonnages and integrate seamlessly with existing production lines. The ability to automate processes not only reduces labor costs but also improves consistency and quality, making it essential for suppliers to partner with reputable manufacturers that offer robust support services.
For international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local market needs and aligning them with cutting-edge technology is vital for sustainable growth. Engaging in strategic sourcing allows companies to leverage high-performance machinery tailored to their specific production requirements, ultimately enhancing their competitive edge.
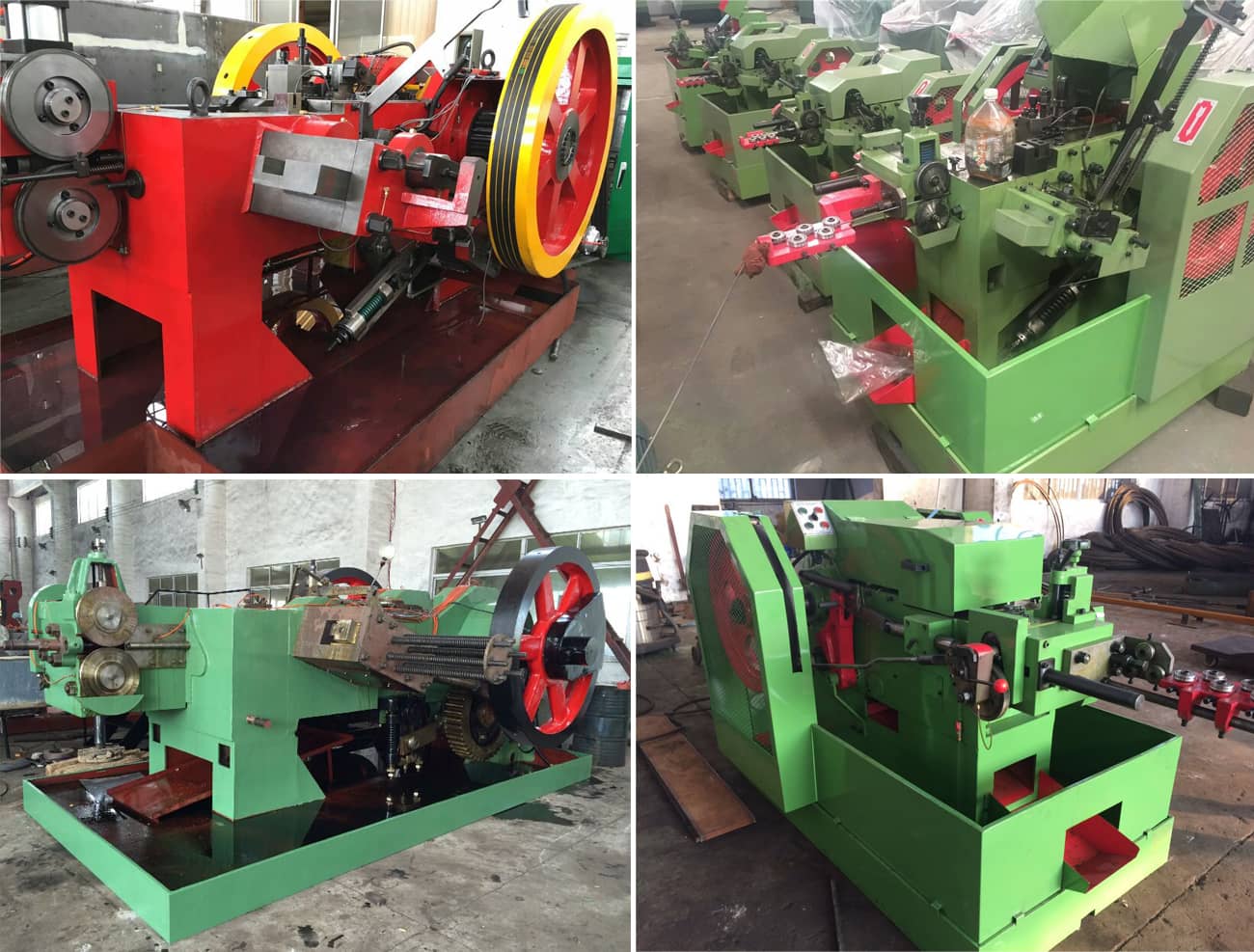

Illustrative image related to cold heading equipment
Looking ahead, the landscape of cold heading technology is ripe for innovation. Buyers are encouraged to explore the latest advancements and consider partnerships with manufacturers who prioritize customer support and process development. By doing so, companies can position themselves for success in a rapidly evolving market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.