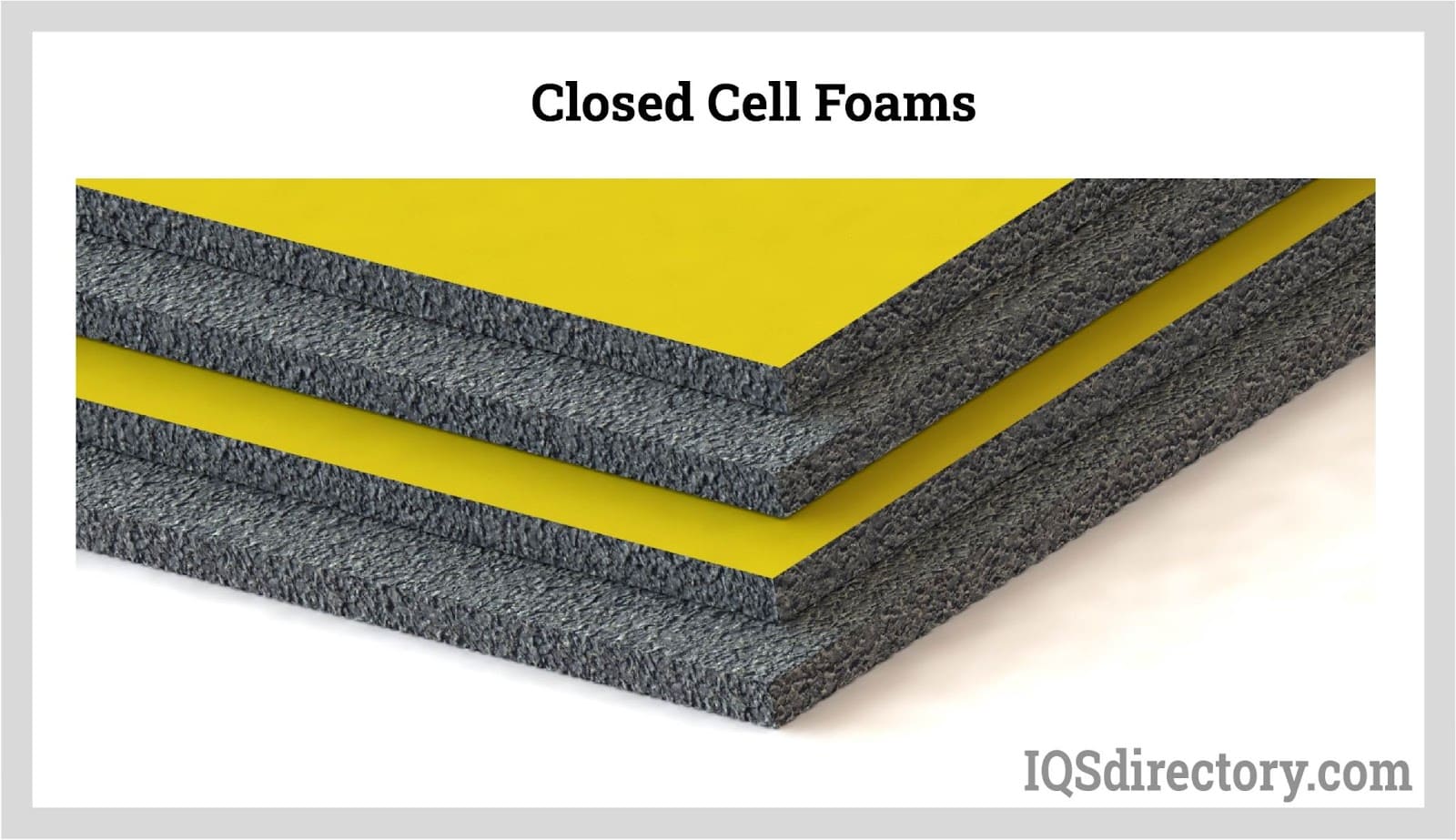
The Definitive Guide to Closed-Cell Polyurethane Foam: Cost, Materials & Top Vendors
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for closed-cell polyurethane foam
Navigating the complex landscape of sourcing closed-cell polyurethane foam can present significant challenges for B2B buyers across diverse global markets. As international businesses strive to find reliable suppliers, the need for high-quality materials that meet specific application requirements becomes paramount. This guide offers a thorough exploration of the various types of closed-cell polyurethane foams, including polyethylene, polystyrene, and neoprene, along with their unique properties and applications.
In addition to detailing material characteristics, this resource emphasizes best practices for supplier vetting, ensuring that buyers can confidently select partners who meet their quality and compliance standards. Understanding cost factors, including pricing structures and shipping logistics, is also crucial for making informed purchasing decisions that align with budgetary constraints.
By providing actionable insights tailored to the needs of buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Vietnam—this guide empowers businesses to navigate the global market with confidence. Whether your focus is on packaging, construction, or specialized industrial applications, you will find essential information that enhances your procurement strategy and optimizes your supply chain. Embrace the opportunity to elevate your sourcing practices with this comprehensive resource.
Understanding closed-cell polyurethane foam Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene Foam | Lightweight, buoyant, water-resistant | Packaging, insulation, arts & crafts | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile; Cons: Limited durability compared to others. |
| Cross-Linked Polyethylene Foam | Enhanced durability, mold and mildew resistant | Flotation devices, industrial applications | Pros: High strength, resistant to chemicals; Cons: Typically higher cost. |
| Polystyrene Foam | Rigid structure, available in various densities | Packaging, storage, construction | Pros: Strong, excellent for structural support; Cons: Less flexible, can be brittle. |
| Neoprene Rubber Foam | Resistant to moisture, bacteria, and chemicals | Athletic equipment, insulation, flooring | Pros: Durable, hygienic; Cons: Can be more expensive than standard foams. |
| Polyurethane Foam Core | Rigid, flame-retardant, high strength-to-weight ratio | Composite structures, transportation packaging | Pros: Excellent for load-bearing; Cons: Limited thermal insulation compared to softer foams. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Polyethylene Foam for B2B Buyers?
Polyethylene foam is a lightweight and buoyant closed-cell foam, making it an excellent choice for various applications such as packaging and insulation. Its water-resistant properties make it suitable for outdoor use, while its cushioning ability is ideal for protecting delicate items during transit. B2B buyers should consider the cost-effectiveness of polyethylene foam, especially for projects requiring large quantities. However, they should also note that it may not provide the same level of durability as some other closed-cell foam types.
How Does Cross-Linked Polyethylene Foam Stand Out in the Market?
Cross-linked polyethylene foam is known for its enhanced durability and resistance to mold, mildew, and chemicals. This makes it a preferred choice for demanding applications, including flotation devices and industrial uses. Its robust nature allows it to withstand harsh conditions, making it suitable for long-term projects. For B2B buyers, the higher upfront cost may be justified by its longevity and performance in challenging environments, providing a solid return on investment.

Illustrative image related to closed-cell polyurethane foam
Why Choose Polystyrene Foam for Structural Applications?
Polystyrene foam is characterized by its rigid structure and varying densities, making it ideal for applications that require strong support, such as packaging and construction. Its inherent strength allows it to be used effectively in storage solutions and as a protective barrier for sensitive items. B2B buyers should consider the specific density required for their project, as this can impact the foam’s performance. However, they should also be aware that its rigidity can make it less suitable for applications requiring flexibility.
What Advantages Does Neoprene Rubber Foam Offer for Specific Industries?
Neoprene rubber foam is highly valued for its resistance to moisture, bacteria, and chemicals, making it ideal for use in athletic equipment, flooring, and insulation in environments where hygiene is critical. Its durability ensures that it can withstand heavy use, making it suitable for industries such as healthcare and sports. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of its hygienic properties against its potentially higher cost compared to standard foams, especially when looking for long-lasting solutions.
How Does Polyurethane Foam Core Provide Structural Integrity?
Polyurethane foam core is a rigid, flame-retardant material that boasts a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it excellent for composite structures and transportation packaging. Its design allows for effective load-bearing capabilities, which is crucial in applications requiring structural integrity. B2B buyers should consider its performance characteristics, particularly in terms of load-bearing and flame resistance, although they should also be mindful that it may not provide the same level of thermal insulation as softer foam variants.
Key Industrial Applications of closed-cell polyurethane foam
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of closed-cell polyurethane foam | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Insulation for walls and roofs | Enhances energy efficiency and reduces heating/cooling costs | Ensure compliance with local building codes and fire safety regulations. |
| Automotive | Soundproofing and vibration dampening | Improves passenger comfort and reduces noise levels | Source materials with high durability and resistance to moisture. |
| Medical | Padding for medical devices and equipment | Provides comfort and protection for patients and medical staff | Look for hypoallergenic options and compliance with health regulations. |
| Packaging | Protective packaging for fragile items | Reduces damage during transportation, lowering costs | Consider variations that offer anti-static properties for electronics. |
| Marine | Buoyancy aids and flotation devices | Ensures safety and performance in aquatic environments | Verify resistance to water absorption and UV degradation. |
How Is Closed-Cell Polyurethane Foam Used in the Construction Industry?
In the construction sector, closed-cell polyurethane foam serves as an effective insulation material for walls and roofs. Its high thermal resistance helps in maintaining indoor temperatures, thereby enhancing energy efficiency and significantly reducing heating and cooling costs. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing foam that complies with local building codes and fire safety regulations is crucial. Additionally, the foam’s lightweight nature simplifies handling and installation, offering further operational efficiencies.
What Role Does Closed-Cell Polyurethane Foam Play in Automotive Applications?
In the automotive industry, closed-cell polyurethane foam is primarily used for soundproofing and vibration dampening in vehicles. This application improves passenger comfort by minimizing noise levels and vibrations from the engine and road. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing materials that exhibit high durability and moisture resistance, as these properties ensure long-lasting performance. Suppliers should also provide detailed specifications to meet the varying demands of different vehicle models and regional standards.
How Is Closed-Cell Polyurethane Foam Beneficial in Medical Equipment?
Closed-cell polyurethane foam is widely utilized in the medical field for padding in devices and equipment, providing essential comfort and protection for both patients and medical staff. Its properties, such as resistance to moisture and easy cleaning, make it ideal for healthcare settings. International buyers must consider sourcing hypoallergenic options that comply with health regulations, particularly in regions with stringent medical device standards. This ensures safety and comfort in critical care environments.

Illustrative image related to closed-cell polyurethane foam
In What Ways Does Closed-Cell Polyurethane Foam Enhance Packaging Solutions?
In packaging, closed-cell polyurethane foam is used to create protective packaging for fragile items, significantly reducing the risk of damage during transportation. This not only lowers costs associated with product returns but also improves customer satisfaction. For businesses in regions like the Middle East and Europe, it’s essential to consider variations of the foam that offer anti-static properties, particularly for electronic goods. Sourcing from reliable suppliers who can provide customized solutions can also enhance overall packaging efficiency.
How Does Closed-Cell Polyurethane Foam Contribute to Marine Safety?
Closed-cell polyurethane foam is crucial in marine applications, particularly for creating buoyancy aids and flotation devices. Its water-resistant properties ensure safety and performance in aquatic environments, making it indispensable for life jackets and other marine safety equipment. International buyers, especially those in coastal regions, should verify the foam’s resistance to water absorption and UV degradation, ensuring long-term reliability. Collaborating with manufacturers who understand marine regulations can further enhance compliance and safety standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘closed-cell polyurethane foam’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Foam for Specific Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often face confusion when selecting closed-cell polyurethane foam for specialized applications, such as in automotive or healthcare settings. With various types available, such as polyethylene and neoprene, each having unique properties, buyers may struggle to understand which foam will meet their specific requirements. This can lead to costly mistakes, such as purchasing the wrong type of foam that fails to provide adequate insulation or protection, thus compromising product quality or safety.
The Solution: To effectively navigate this challenge, buyers should conduct a thorough needs assessment before sourcing closed-cell polyurethane foam. This involves defining the specific application requirements, including environmental conditions (like moisture exposure or temperature fluctuations), mechanical stresses, and any regulatory standards that must be met (e.g., FDA compliance for healthcare applications). Engaging with suppliers who offer technical support can provide invaluable insights. Request product datasheets that outline physical properties such as density, compressive strength, and thermal conductivity. Additionally, consider samples to test in real-world conditions, allowing for a hands-on evaluation of performance prior to bulk purchasing.
Scenario 2: Challenges in Foam Longevity and Durability
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the concern over the longevity and durability of closed-cell polyurethane foam. Industries such as construction and automotive rely on materials that can withstand harsh conditions, including exposure to chemicals, moisture, and physical wear. Buyers often report that certain foams degrade quicker than expected, resulting in replacement costs and potential project delays.

Illustrative image related to closed-cell polyurethane foam
The Solution: To address durability concerns, it is crucial for buyers to prioritize sourcing high-quality closed-cell polyurethane foams with proven longevity. When selecting foam, focus on options that are specifically designed to resist environmental factors, such as UV degradation and chemical exposure. Request information regarding the foam’s resistance to moisture, mold, and mildew, as well as any certifications that ensure its performance over time. Engaging with manufacturers who provide warranties or performance guarantees can also offer peace of mind. Furthermore, consider utilizing coatings or treatments that enhance the foam’s resistance to wear and environmental stressors, extending its lifespan and reliability in demanding applications.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Foam Fabrication and Integration
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter challenges when it comes to fabricating and integrating closed-cell polyurethane foam into their products or systems. Whether it’s for packaging, insulation, or component manufacturing, the complexity of shaping, cutting, or assembling foam can lead to inefficiencies and increased labor costs, particularly if the foam is not easily machinable or requires specialized tools.
The Solution: To streamline the fabrication and integration process, buyers should collaborate closely with foam suppliers who offer customization services. Look for suppliers that provide options for CNC machining, contouring, or pre-cut shapes that align with your specific requirements. Additionally, consider investing in training for your team on best practices for handling and working with closed-cell polyurethane foam, which can include cutting techniques and the use of adhesives for bonding. Explore the use of adhesives specifically formulated for foam applications to ensure a strong bond without compromising the integrity of the material. By enhancing the fabrication capabilities and reducing the learning curve, you can achieve smoother integration into your production line, ultimately saving time and reducing costs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for closed-cell polyurethane foam
What Are the Key Properties of Common Closed-Cell Polyurethane Foam Materials?
Closed-cell polyurethane foam is a versatile material used across various industries. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of different types of closed-cell foams can help B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their specific applications.
Polyethylene Foam: What Makes It a Preferred Choice?
Polyethylene foam is known for its excellent buoyancy, sound dampening, and shock absorption properties. It is resistant to moisture, chemicals, and UV light, making it suitable for outdoor applications. The material is lightweight yet durable, with a density that typically ranges from 2 to 6 pounds per cubic foot (PCF).
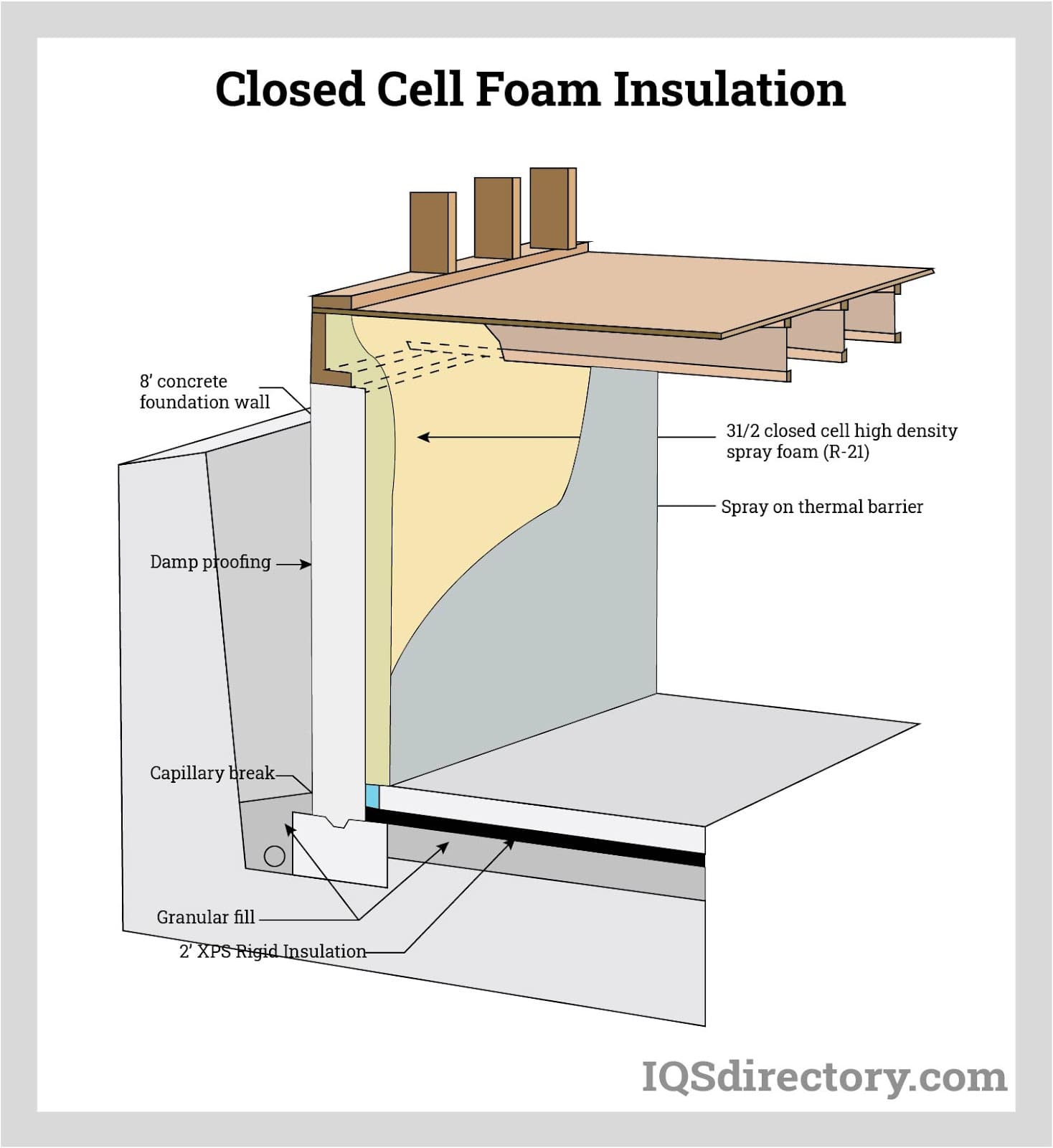
Illustrative image related to closed-cell polyurethane foam
Pros: Its affordability and versatility make it ideal for packaging, insulation, and sports equipment. It can be easily cut into various shapes and sizes, allowing for customization.
Cons: While it is durable, it may not withstand extreme temperatures as effectively as other materials. Additionally, its lower density may not be suitable for high-load applications.
Impact on Application: Polyethylene foam is compatible with a variety of media, including water and certain chemicals, making it suitable for packaging and insulation in diverse environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding material safety and environmental impact. Standards such as ASTM and ISO may apply.

Illustrative image related to closed-cell polyurethane foam
Cross-Linked Polyethylene Foam: Why Choose This Material?
Cross-linked polyethylene foam offers enhanced durability and resistance to water absorption, mold, and mildew. Its structure provides a higher strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for demanding applications in construction and automotive industries.
Pros: This foam is flame-retardant and can withstand higher temperatures compared to standard polyethylene. It also offers excellent thermal insulation properties.
Cons: The manufacturing process for cross-linked polyethylene can be more complex, leading to higher costs. It may also be less flexible than other foam types.

Illustrative image related to closed-cell polyurethane foam
Impact on Application: It is ideal for applications requiring moisture resistance and structural integrity, such as flotation devices and industrial packaging.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with fire safety regulations is crucial, especially in regions like the Middle East where such standards are stringent. Buyers should also consider the availability of the material in local markets.
Polyurethane Foam Core: What Are Its Unique Advantages?
Polyurethane foam core is a rigid, closed-cell material known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to water and chemicals. With a density of around 6 PCF, it is often used in composite structures and applications requiring flame retardation.

Illustrative image related to closed-cell polyurethane foam
Pros: Its versatility allows it to be easily shaped and machined, making it suitable for custom applications. It also exhibits excellent thermal insulation properties.
Cons: The higher density can lead to increased costs, and it may require specialized tools for fabrication.
Impact on Application: Polyurethane foam core is particularly effective for applications involving load-bearing structures and insulation in high-temperature environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that the foam meets local safety and environmental regulations, particularly in Europe where compliance with REACH and RoHS is essential.
Summary Table of Closed-Cell Polyurethane Foam Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for closed-cell polyurethane foam | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene Foam | Packaging, insulation, sports equipment | Affordable and versatile | Lower temperature resistance | Low |
| Cross-Linked Polyethylene Foam | Construction, automotive applications | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Polyurethane Foam Core | Composite structures, insulation | Excellent thermal insulation | Requires specialized fabrication | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the properties and applications of various closed-cell polyurethane foams, enabling B2B buyers to align their material choices with project requirements and regional regulations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for closed-cell polyurethane foam
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Closed-Cell Polyurethane Foam?
The manufacturing process of closed-cell polyurethane foam involves several critical stages, each contributing to the final product’s quality and performance. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers ensure they source high-quality materials suitable for their applications.
1. Material Preparation: What Are the Key Components?
The first stage of manufacturing closed-cell polyurethane foam involves preparing the raw materials. The primary components are polyols and isocyanates, which are combined to create polyurethane. In addition to these, additives such as blowing agents, catalysts, and surfactants are included to enhance properties like density, flexibility, and flame resistance.
To ensure consistency and performance, suppliers must use high-quality raw materials. Buyers should inquire about the source and quality of these components, as the foam’s characteristics largely depend on them.
2. Forming: How Is the Foam Created?
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo a chemical reaction that causes them to expand and form foam. This process typically occurs in a controlled environment where temperature and pressure are meticulously regulated. The mixture is poured into molds or onto a conveyor belt, where it expands into sheets or blocks of foam.
Key techniques in this stage include:
- Batch Processing: Suitable for custom orders, where specific densities and characteristics are required.
- Continuous Processing: Ideal for mass production, offering uniformity and efficiency.
B2B buyers should assess the supplier’s capabilities in both techniques, depending on their volume and customization needs.

Illustrative image related to closed-cell polyurethane foam
3. Assembly: How Are Foam Products Structured?
After forming, the foam may be cut or shaped according to specific requirements. This stage often includes assembling multiple layers or components, especially for applications that require additional strength or insulation properties. Techniques such as lamination and bonding can be employed to combine different foam types or to integrate other materials like fabrics or plastics.
Buyers should verify that suppliers can accommodate their design specifications, including dimensions and material combinations.
4. Finishing: What Enhancements Are Applied?
The final stage involves finishing processes that improve the foam’s performance or aesthetic appeal. This can include surface treatments, coatings, or treatments for fire resistance. Additionally, finishing may involve cutting the foam to precise dimensions or adding features such as adhesive backing.

Illustrative image related to closed-cell polyurethane foam
In this stage, B2B buyers should confirm the quality and durability of any finishes applied, as these can significantly affect the foam’s lifespan and suitability for various applications.
What Are the Quality Control (QC) Standards for Closed-Cell Polyurethane Foam?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of closed-cell polyurethane foam, ensuring that the final products meet international and industry-specific standards.
1. What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Several international standards apply to the manufacturing of polyurethane foam, including:
- ISO 9001: This quality management standard outlines requirements for a quality management system, ensuring that suppliers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: Indicates that the product complies with European safety, health, and environmental protection standards, which is crucial for buyers in Europe.
- API Standards: For applications in the oil and gas industry, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may be necessary.
Understanding these standards allows B2B buyers to evaluate the credibility of their suppliers.
2. What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, samples are taken to monitor the foam’s properties and ensure consistency.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished products undergo rigorous testing for physical properties, density, and any additional characteristics required by the buyer.
Buyers should request information about these checkpoints and the criteria used to evaluate quality.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed for Quality Assurance?
Several testing methods are commonly used to assess the quality and performance of closed-cell polyurethane foam:
- Density Testing: Determines the weight of the foam per cubic foot, which is crucial for ensuring it meets application requirements.
- Compression Testing: Evaluates the foam’s ability to withstand compressive forces, ensuring it performs effectively in its intended application.
- Water Absorption Testing: Measures how much water the foam can absorb, which is essential for applications requiring water resistance.
- Flame Retardancy Testing: Assesses how well the foam resists ignition and burning, critical for safety in many applications.
B2B buyers should ensure that suppliers provide detailed reports on these testing methods, including any certifications obtained.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
To ensure the reliability of their suppliers, B2B buyers should engage in several verification practices:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting site visits or audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing process and quality control measures in place.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of quality tests and compliance with international standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors can provide unbiased evaluations of the supplier’s quality control practices.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification:
- Regional Regulations: Different regions may have varying regulations regarding material safety, environmental impact, and product certifications. It’s essential for buyers to understand these differences to avoid compliance issues.
- Cultural Differences: Communication styles and business practices vary across cultures, impacting negotiations and quality expectations. Buyers should take the time to understand their supplier’s cultural context to foster better relationships.
By being informed about the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for closed-cell polyurethane foam, B2B buyers can make educated decisions that align with their project requirements and ensure the reliability of their supply chain.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘closed-cell polyurethane foam’
Introduction
Sourcing closed-cell polyurethane foam requires a strategic approach to ensure you acquire the right material for your specific application. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the procurement process efficiently, ensuring that the chosen foam meets technical requirements while aligning with business objectives.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, it’s essential to clearly define your technical requirements. Consider factors such as density, thickness, flame retardancy, and chemical resistance based on the intended use of the foam. For example, if the foam will be exposed to moisture, prioritize closed-cell varieties that offer superior water resistance.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers of closed-cell polyurethane foam. Look for companies with a proven track record in your industry, focusing on their experience and product range. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online reviews to gather insights into their reliability and quality.

Illustrative image related to closed-cell polyurethane foam
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications that validate their product quality and safety standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management or specific environmental certifications can indicate a commitment to excellence. Additionally, inquire about compliance with local regulations, especially if the foam will be used in sensitive applications like healthcare or food service.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples to evaluate the foam’s performance in real-world conditions. Testing samples allows you to assess properties such as durability, flexibility, and water resistance. This step is crucial for ensuring that the foam meets your specific application needs and expectations.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, engage in negotiations to secure favorable pricing and terms. Consider factors such as minimum order quantities, lead times, and payment terms. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can lead to better pricing and service in the long run, especially for repeat orders.
Illustrative image related to closed-cell polyurethane foam
Step 6: Verify Production Capabilities
Assess the supplier’s production capabilities to ensure they can meet your order requirements consistently. Inquire about their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and capacity for customization. Understanding their capabilities will help you gauge their ability to deliver on time and to specification.
Step 7: Establish a Clear Communication Plan
Effective communication is vital throughout the sourcing process. Establish a clear plan that outlines points of contact, preferred communication channels, and timelines for updates. This will help facilitate a smooth transaction and ensure that both parties are aligned on expectations and requirements.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and successfully procure closed-cell polyurethane foam that meets their operational needs and enhances product performance.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for closed-cell polyurethane foam Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Closed-Cell Polyurethane Foam?
When sourcing closed-cell polyurethane foam, understanding the cost structure is critical for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as polyurethane and additives, typically constitutes a significant portion of the overall expense. Prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, availability, and the quality of the materials used.
-
Labor: Labor costs are tied to the production process, including cutting, shaping, and assembling the foam. Labor rates can vary widely by region and are influenced by local wage standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative costs. Efficient production processes can help mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: For custom projects, tooling costs can be substantial. This refers to the expense of creating molds and other equipment necessary for specific foam shapes or sizes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality through testing and inspections is essential, especially for applications in regulated industries. QC costs can vary based on the complexity of the tests required.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are influenced by the foam’s weight, volume, and destination. International shipping can add layers of complexity, including customs duties and taxes.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their operational costs and profit, which varies based on market demand and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Closed-Cell Polyurethane Foam?
Several factors can influence the pricing of closed-cell polyurethane foam, especially for international buyers:

Illustrative image related to closed-cell polyurethane foam
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often yield better pricing due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to negotiate favorable terms.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications, such as density, thickness, and additional properties like flame retardancy, can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the necessity of these features against their budget.
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly affects pricing. Higher-quality or specialty materials will generally command a premium.
-
Quality and Certifications: Foams with certifications (e.g., fire resistance, environmental compliance) may have higher costs. Buyers should confirm the required certifications for their specific applications.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, reputation, and production capabilities can impact pricing. Building a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better terms and pricing.
-
Incoterms: Understanding international shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is crucial for calculating total costs. These terms dictate who is responsible for shipping costs and risks, which can significantly affect the overall price.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs for International Sourcing?
International B2B buyers should adopt strategic approaches to optimize their sourcing of closed-cell polyurethane foam:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders. Leverage your volume commitments to secure better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Analyze the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes not only the purchase price but also logistics, handling, and potential waste. TCO can reveal hidden costs that may influence the choice of supplier.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations, especially in emerging markets like Africa and South America. Understanding local market conditions can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Quality Assurance: Invest in quality assessments to avoid issues that could lead to additional costs down the line. A focus on quality can prevent future expenses related to returns or compliance failures.
-
Local Market Insights: Familiarize yourself with local regulations and market dynamics in your target regions (e.g., Brazil, Vietnam). This knowledge can aid in navigating sourcing complexities and achieving cost savings.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for closed-cell polyurethane foam can vary widely based on multiple factors, including market fluctuations, supplier pricing strategies, and specific buyer requirements. The figures provided in this analysis are indicative and should be confirmed with suppliers during the sourcing process.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing closed-cell polyurethane foam With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Closed-Cell Polyurethane Foam
When selecting materials for insulation, packaging, or structural support, closed-cell polyurethane foam is a popular choice due to its durability and water resistance. However, various alternatives may better suit specific applications or budget constraints. This analysis compares closed-cell polyurethane foam with two viable alternatives: cross-linked polyethylene foam and polystyrene foam.
| Comparison Aspect | Closed-Cell Polyurethane Foam | Cross-Linked Polyethylene Foam | Polystyrene Foam |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength-to-weight ratio; excellent insulation and moisture resistance | Good insulation; resistant to mold and mildew | Rigid; excellent for packaging but less insulating |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate | Low to moderate |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precise cutting and shaping | Easy to cut and shape | Simple to work with |
| Maintenance | Minimal, durable against wear | Low, resistant to deterioration | Low, but can be damaged by UV exposure |
| Best Use Case | Structural applications, flotation devices | Automotive, healthcare, and packaging | Packaging, construction, and insulation |
Understanding Cross-Linked Polyethylene Foam: Advantages and Disadvantages
Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) foam is a strong contender in the foam market. It offers excellent moisture resistance and is naturally resistant to mold and mildew. This makes it suitable for applications in healthcare and automotive industries where cleanliness and durability are paramount. XLPE is easy to work with, allowing for straightforward cutting and shaping, which can reduce labor costs. However, it may not match the strength-to-weight ratio of closed-cell polyurethane foam, limiting its use in more demanding structural applications.
Evaluating Polystyrene Foam: Benefits and Drawbacks
Polystyrene foam is one of the most cost-effective options available, making it attractive for budget-conscious projects. It is widely used for packaging and construction insulation due to its rigidity and lightweight nature. While it provides decent thermal insulation, it lacks the moisture resistance and durability of closed-cell polyurethane foam. Additionally, polystyrene can be more susceptible to UV damage, which may lead to degradation over time, making it less suitable for long-term applications in outdoor environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
Choosing the right foam solution depends on the specific requirements of your project. Closed-cell polyurethane foam excels in performance, especially for structural applications requiring strength and moisture resistance. If budget constraints are a primary concern, polystyrene foam may be the best option, particularly for packaging. Cross-linked polyethylene foam offers a balanced solution for those seeking durability and resistance to contaminants without the higher price point of polyurethane. By evaluating the performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance needs of each option, B2B buyers can make informed decisions tailored to their unique project requirements.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for closed-cell polyurethane foam
What are the Key Technical Properties of Closed-Cell Polyurethane Foam?
Closed-cell polyurethane foam is recognized for its unique properties, making it suitable for various applications across multiple industries. Here are some critical specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
-
Density
Density is a crucial metric in determining the foam’s strength and application suitability. Closed-cell polyurethane foam typically ranges from 1 to 8 pounds per cubic foot (PCF). Higher density foams provide greater durability and mechanical strength, making them ideal for load-bearing applications, while lower density options can be more suitable for insulation and cushioning. -
Compressive Strength
This property measures the foam’s ability to withstand axial loads without permanent deformation. Compressive strength values can vary widely, but a typical range for closed-cell polyurethane foam is between 100 to 300 psi. High compressive strength is essential for applications in construction and automotive sectors, where structural integrity is paramount. -
Water Absorption
Closed-cell foams inherently resist water absorption due to their cellular structure. Water absorption rates typically fall below 0.2 lbs/ft², making them suitable for outdoor applications or environments where moisture resistance is critical. This property enhances the foam’s longevity and performance in wet conditions, such as in marine applications. -
Flame Retardancy
Many closed-cell polyurethane foams are formulated to be flame retardant, which is essential for safety in various applications, particularly in aerospace, automotive, and construction. Flame retardant foams can significantly reduce the risk of fire hazards and meet specific industry standards, making them a preferred choice for safety-conscious buyers. -
Thermal Conductivity
The thermal conductivity of closed-cell polyurethane foam typically ranges from 0.20 to 0.25 BTUin/ft²°F*h. This low thermal conductivity indicates excellent insulation properties, making it ideal for energy-efficient buildings and refrigeration applications. Buyers should consider this property to ensure compliance with energy regulations. -
Chemical Resistance
Closed-cell polyurethane foams exhibit varying degrees of resistance to chemicals and solvents, depending on their formulation. This resistance is crucial for applications in industries like automotive and chemical processing, where exposure to harsh substances is common. Ensuring chemical compatibility can extend the foam’s life and maintain performance standards.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Understand?
In the realm of closed-cell polyurethane foam, specific jargon and trade terms are vital for clear communication and effective transactions. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking for custom solutions or specific product integrations. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest order amount a supplier will accept. Knowing the MOQ can help buyers plan their inventory and budget effectively. For closed-cell polyurethane foam, MOQs can vary significantly based on foam type and supplier. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process used by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It typically includes specifications, quantities, and delivery requirements. Submitting a well-structured RFQ can streamline the procurement process and ensure competitive pricing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers engaged in cross-border transactions, as they help clarify who bears the risk at various stages of the shipment. -
Custom Fabrication
This term refers to the process of creating tailored products to meet specific requirements. For closed-cell polyurethane foam, custom fabrication may involve cutting, shaping, or combining different foam types to suit unique applications, which can enhance product performance. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the duration from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is crucial for B2B buyers to manage project timelines and inventory levels effectively, especially when dealing with custom orders or large quantities.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing closed-cell polyurethane foam for their projects.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the closed-cell polyurethane foam Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Affecting Closed-Cell Polyurethane Foam?
The closed-cell polyurethane foam market is experiencing robust growth, driven by a range of global factors. Increased demand for lightweight and durable materials in sectors such as automotive, construction, and packaging is propelling market expansion. The shift toward energy-efficient and environmentally friendly products has also influenced purchasing decisions, particularly in regions like Europe, where stringent regulations exist. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce and the need for protective packaging solutions have created new opportunities for closed-cell foam suppliers, especially in emerging markets across Africa and South America.
International B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging technology in their sourcing strategies. E-procurement platforms and digital marketplaces are simplifying supplier discovery and streamlining the purchasing process. Moreover, advancements in manufacturing technologies, such as 3D printing and CNC machining, are enabling custom solutions tailored to specific applications, enhancing product offerings for buyers. As buyers become more aware of the benefits of closed-cell foams, including moisture resistance and structural integrity, the competition among suppliers intensifies, encouraging innovation and improved service delivery.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Closed-Cell Polyurethane Foam Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a central focus in the closed-cell polyurethane foam sector, as businesses recognize the environmental impact of their materials. The production of traditional foams often involves harmful chemicals and processes that can contribute to pollution. In response, many manufacturers are adopting eco-friendly practices, such as using CFC-free, flame-retardant materials and sourcing raw materials from sustainable suppliers.
Ethical supply chains are also gaining traction among B2B buyers. Companies are increasingly seeking suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with environmental regulations and social responsibility standards. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and GREENGUARD for low chemical emissions are becoming important factors in supplier selection. Buyers who prioritize sustainability not only reduce their ecological footprint but also enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
What Is the Historical Context of Closed-Cell Polyurethane Foam in B2B Markets?
The history of closed-cell polyurethane foam dates back to the mid-20th century when innovations in polymer chemistry enabled the development of versatile foam materials. Initially used in packaging and insulation, closed-cell foams have evolved to meet the diverse needs of various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and healthcare. The introduction of environmentally friendly formulations in the 1980s marked a significant turning point, as manufacturers began to phase out harmful substances like CFCs.
As technology advanced, the applications for closed-cell polyurethane foam expanded, driven by its unique properties such as lightweight, buoyancy, and resistance to moisture. This evolution has positioned closed-cell polyurethane foam as a critical material in contemporary manufacturing processes, making it a key consideration for international B2B buyers looking for reliable and innovative solutions.

Illustrative image related to closed-cell polyurethane foam
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of closed-cell polyurethane foam
-
How do I choose the right closed-cell polyurethane foam for my application?
Selecting the appropriate closed-cell polyurethane foam depends on your specific requirements, including density, rigidity, and intended use. Consider factors such as moisture resistance, thermal insulation, and sound absorption. For applications in harsh environments, opt for foams with enhanced durability and chemical resistance. It is also beneficial to consult with suppliers who can provide technical specifications and recommend products based on your project’s demands. -
What are the key properties of closed-cell polyurethane foam?
Closed-cell polyurethane foam is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent moisture resistance, and flame retardancy. Its closed-cell structure prevents water absorption, making it suitable for outdoor applications. Additionally, it provides good thermal insulation and sound dampening properties. The foam is also resistant to chemicals and fungi, ensuring longevity in various environments, from automotive to construction sectors. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for closed-cell polyurethane foam?
The minimum order quantity can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of foam required. Generally, MOQs range from small quantities for sample orders to larger volumes for bulk purchases. It’s advisable to communicate directly with suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your project needs and budget constraints, especially if you are looking for custom dimensions or specifications. -
How can I verify the quality of closed-cell polyurethane foam from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of closed-cell polyurethane foam, request certifications and test reports from suppliers. Look for compliance with international standards such as ISO or ASTM, which indicate reliable manufacturing processes. Additionally, consider asking for samples to conduct your own tests on properties like density, tensile strength, and thermal insulation. Engaging in direct communication with the supplier can also provide insights into their quality control measures. -
What customization options are available for closed-cell polyurethane foam?
Many suppliers offer customization options, including varying densities, thicknesses, and shapes. You can also request specific treatments, such as flame retardancy or anti-static properties. CNC machining and contouring services may be available to tailor the foam to your project specifications. Discuss your exact requirements with suppliers to explore available customization options and any associated costs. -
What are the typical payment terms for purchasing closed-cell polyurethane foam internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region but often include options such as advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. For international transactions, suppliers may require partial upfront payments, especially for custom orders. It is essential to clarify payment terms, including currency and potential fees, during negotiations to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions. -
How does shipping logistics work for closed-cell polyurethane foam orders?
Shipping logistics for closed-cell polyurethane foam typically involve coordination between the supplier and the buyer. Factors such as order size, destination, and shipping method (air or sea freight) will influence delivery times and costs. Ensure that the supplier provides detailed shipping information, including packaging requirements to maintain foam integrity during transport. It’s also wise to inquire about customs documentation and import regulations specific to your country. -
Are there specific regulations or compliance standards for closed-cell polyurethane foam?
Yes, closed-cell polyurethane foam may be subject to various regulations depending on its intended use and the region of sale. For instance, in Europe, compliance with REACH and RoHS directives may be necessary, while in the U.S., certain foams must meet ASTM standards. If the foam is used in food or medical applications, ensure it meets FDA regulations. Always confirm with your supplier about compliance to avoid legal issues and ensure product safety.
Top 6 Closed-Cell Polyurethane Foam Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. US Composites – Marine Polyurethane Foam
Domain: uscomposites.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Urethane Foam: Expanding Marine Polyurethane Foam, 2 Part Liquid. Available in densities: 2LB, 3LB, 4LB, 8LB, and 16LB. This closed cell, pourable foam resists water absorption and can be laminated over with polyester, epoxy, or vinyl ester resin. Ideal working temperature is 75-80 degrees F. Working time before foaming: approx. 45 seconds; Time before full expansion: approx. 5 minutes. Shelf life…
2. Bottom Paint Store – Liquid Urethane Foam Kit
Domain: bottompaintstore.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Liquid Urethane Foam Kit, 8LB Density, Closed Cell
3. FoamOrder – Closed Cell Foam Types Comparison
Domain: foamorder.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Closed Cell Foam is a type of foam with tightly pressed closed cells, making it water-resistant and providing higher density and pressure resistance. It comes in various forms including EVA Foam, Polyethylene Foam (Cross-Poly), Flotex Foam, and Volara Foam.
**Comparison of Closed Cell Foam Types:**
1. **EVA Foam**:
– Size: Sheet (40×80), custom cut
– Thickness: 1/8″, 1/4″, 1/2″, 3/4″, 1″,…
4. Energy Efficient Solutions – Open-Cell vs. Closed-Cell Polyurethane Spray Foam
Domain: energyefficientsolutions.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Open-Cell vs. Closed-Cell Polyurethane spray foam is categorized into two types: open-cell and closed-cell, each with distinct advantages and disadvantages based on application requirements. Closed-cell polyurethane spray foam is highly efficient, with R-values around 6.0 per inch, making it one of the most effective insulating materials available. It incorporates an insulating gas retained within…
5. Profoam – JM Corbond IV 2# HFO Closed Cell Spray Foam
Domain: profoam.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: JM Corbond IV 2# HFO Closed Cell Spray Polyurethane Foam is a next generation HFO blown, two component, Class 1 rated, medium density SPF insulation system. It is designed for insulating commercial, residential, and industrial buildings. The foam is produced with low Global Warming Potential (GWP) and has an Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP) of zero. It offers high yield, superior thermal and moistu…
6. IQS Directory – Closed Cell Foam Solutions
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Closed cell foam is characterized by tightly packed and enclosed cells, making it durable and resistant to water and moisture. It is available in various forms, including:
1. Polyethylene Foam – Resists water absorption and stains, suitable for packaging, arts and crafts, offering sound dampening and shock absorption.
2. Polyethylene Rolls – Available in rolls for automotive, healthcare, and rec…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for closed-cell polyurethane foam
In summary, the strategic sourcing of closed-cell polyurethane foam offers numerous advantages for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This versatile material, known for its durability, water resistance, and flame retardant properties, serves a wide range of applications, from packaging to construction and healthcare. By selecting the right type of closed-cell foam—such as polyethylene or cross-linked variants—businesses can enhance product performance while ensuring compliance with safety standards.
Leveraging strategic sourcing not only optimizes cost-efficiency but also fosters strong supplier relationships, critical for navigating the complexities of international trade. As markets evolve and demand for high-quality materials increases, staying informed about the latest innovations and applications in closed-cell polyurethane foam will be essential.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers are encouraged to explore collaborative partnerships with reputable suppliers who can provide tailored solutions to meet specific project needs. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your product offerings and operational efficiency by integrating high-quality closed-cell polyurethane foam into your supply chain today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to closed-cell polyurethane foam
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.