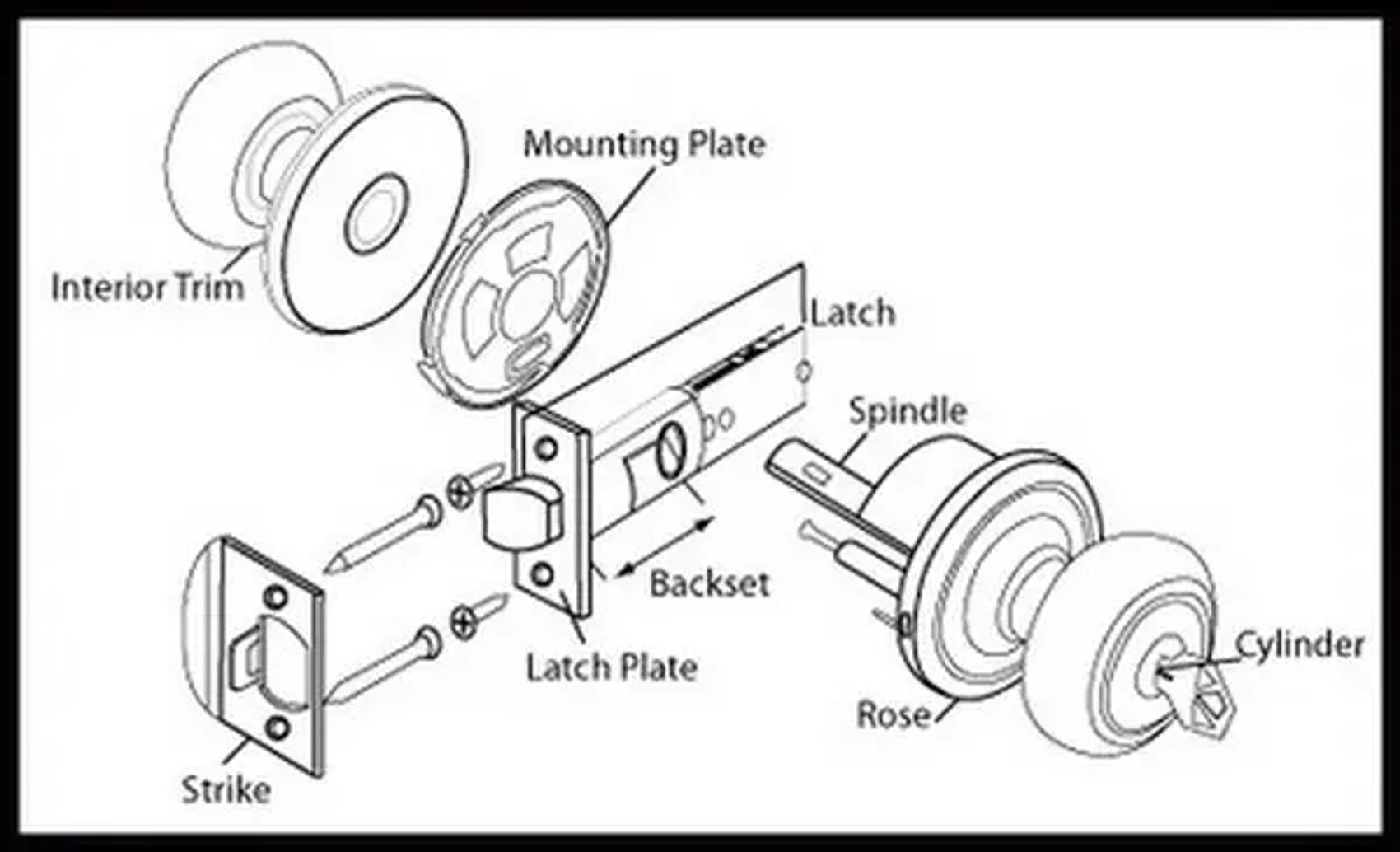
Door Lock Anatomy: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for door lock anatomy
In an increasingly interconnected world, B2B buyers face the challenge of sourcing high-quality door lock anatomy components that meet both security standards and local regulations. Understanding the intricate parts of door locks, from cylinders to bolts and strike plates, is crucial for selecting the right products for various applications, whether for commercial buildings or residential complexes. This comprehensive guide delves into the anatomy of door locks, covering essential components, their functions, and the types of locks available in the global market.
By navigating through this resource, international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Nigeria—will gain valuable insights into supplier vetting, cost considerations, and the latest advancements in lock technology. The guide not only aims to enhance security but also empowers buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their specific needs and market demands.
With a focus on practical applications and expert recommendations, this guide serves as a vital tool for companies looking to enhance their security solutions while ensuring compliance with industry standards. As you explore the anatomy of door locks, you will be better equipped to select the most effective and reliable options for your projects, ensuring peace of mind for your clients and stakeholders.
Understanding door lock anatomy Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deadbolt | High security, requires a key or thumb turn | Commercial buildings, high-security areas | Pros: Superior security; Cons: More complex installation. |
| Cylinder Lock | Versatile, uses interchangeable cylinders | Residential properties, offices | Pros: Easy to rekey; Cons: Vulnerable to picking. |
| Smart Lock | Keyless entry, integrates with smart home systems | Tech-savvy businesses, hotels | Pros: Convenient access control; Cons: Dependent on power/internet. |
| Mortise Lock | Built into the door, offers high security | High-end residential and commercial | Pros: Durable and aesthetically pleasing; Cons: Requires professional installation. |
| Padlock | Portable, versatile for various applications | Warehouses, temporary storage | Pros: Easy to transport; Cons: Limited security compared to fixed locks. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Deadbolt Locks?
Deadbolt locks are known for their robust security features, often found in both residential and commercial settings. They are either single or double-cylinder, requiring a key from either side or just one side, respectively. Their resistance to forced entry makes them ideal for high-security areas. B2B buyers should consider the installation complexity and compatibility with existing doors, as deadbolts may require specific door preparation.
How Do Cylinder Locks Provide Versatility?
Cylinder locks are widely used due to their adaptability and ease of rekeying. They consist of a cylinder that can be replaced without changing the entire lock, making them ideal for properties that undergo frequent tenant changes, such as rental units and office spaces. Buyers should evaluate the level of security needed, as while they are convenient, they can be susceptible to lock picking and bumping.
What Innovations Do Smart Locks Offer Businesses?
Smart locks represent a modern solution to access control, allowing for keyless entry and remote management via smartphones or integrated security systems. They are particularly suitable for businesses that prioritize convenience and technology, such as hotels and coworking spaces. However, buyers must assess the reliability of the technology, as dependence on power or internet connectivity can pose risks in critical situations.
Why Are Mortise Locks Preferred for High-End Applications?
Mortise locks are embedded within the door, providing a seamless appearance and superior security. They are often used in upscale residential properties and commercial buildings that require a higher level of aesthetic and functional quality. B2B buyers should be aware that mortise locks often necessitate professional installation and may have a higher upfront cost, but their durability and security features can justify the investment.
What Advantages Do Padlocks Offer in Various Settings?
Padlocks are portable and versatile, making them suitable for temporary storage solutions, warehouses, and outdoor applications. They come in various sizes and security levels, allowing businesses to choose locks that fit their specific needs. However, while they offer ease of use and transport, buyers should consider the security limitations of padlocks compared to more permanent locking solutions, especially in high-risk environments.
Key Industrial Applications of door lock anatomy
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of door lock anatomy | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial Real Estate | Access control systems for office buildings | Enhances security and tenant trust, reduces liability | Durability, compliance with local regulations, scalability |
| Hospitality | Locking mechanisms in hotel room doors | Increases guest safety and satisfaction | Aesthetic appeal, ease of use, integration with smart systems |
| Healthcare | Secure access to patient rooms and medication storage | Protects sensitive information and medications | Compliance with health regulations, reliability, ease of maintenance |
| Education | Lock systems for classrooms and dormitories | Ensures safety for students and staff | Cost-effectiveness, compatibility with existing systems, ease of installation |
| Retail | Security locks for storefronts and display cases | Reduces theft, enhances customer confidence | Versatility, resistance to tampering, warranty and support services |
How is Door Lock Anatomy Utilized in Commercial Real Estate?
In commercial real estate, door lock anatomy plays a crucial role in access control systems for office buildings. Various lock types, including electronic and mechanical systems, are employed to manage who can enter specific areas, enhancing security and tenant trust. With increasing concerns over workplace safety, businesses must consider durable locks that comply with local regulations and can be scaled as tenant needs change. Buyers should focus on the longevity of materials and ease of integration with existing security systems.
What Role Does Door Lock Anatomy Play in the Hospitality Sector?
In the hospitality industry, the locking mechanisms used in hotel room doors are vital for ensuring guest safety and satisfaction. Key card systems and electronic locks provide guests with a seamless experience while maintaining high security levels. For international buyers, factors like aesthetic appeal and compatibility with smart technologies are essential. Suppliers must offer locks that not only meet safety standards but also enhance the overall guest experience through ease of use and reliability.
How is Door Lock Anatomy Critical in Healthcare Facilities?
Healthcare facilities require robust door lock systems to secure patient rooms and medication storage areas, protecting sensitive information and pharmaceuticals. The anatomy of these locks must comply with strict health regulations, ensuring they are tamper-proof and reliable. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing locks that are easy to maintain, provide high security, and are designed for frequent use. The ability to integrate with electronic health record systems may also be a consideration for modern healthcare environments.
Why is Door Lock Anatomy Important in Educational Institutions?
In educational institutions, door lock systems are essential for securing classrooms and dormitories, ensuring safety for students and staff. The anatomy of these locks must be user-friendly, allowing for quick access during emergencies while being cost-effective for budget-conscious educational bodies. Buyers should consider compatibility with existing infrastructure and the ease of installation, as well as the potential need for future upgrades to enhance security measures as technology evolves.
How Does Door Lock Anatomy Enhance Security in Retail Environments?
Retail environments utilize various security locks for storefronts and display cases to minimize theft and bolster customer confidence. The anatomy of these locks must be versatile and resistant to tampering, ensuring that products are secure while still being accessible to customers. When sourcing for this application, retailers should consider warranty and support services, as well as the lock’s ability to integrate with broader security systems, such as surveillance cameras and alarms, to create a comprehensive security solution.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘door lock anatomy’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding Complex Lock Mechanisms
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially in industries like construction and property management, encounter difficulties when dealing with various door lock types. The anatomy of locks can vary significantly between models and manufacturers, leading to confusion during installation or maintenance. For instance, a buyer may purchase a deadbolt system but struggle with the specifics of its components—such as the cylinder, strike plate, and bolt—causing delays in project timelines and potential security vulnerabilities.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should invest in comprehensive training for their teams on the specific door lock mechanisms they will be handling. This can include workshops or online courses focused on the anatomy of various locks, ensuring that employees can accurately identify and understand the function of each component. Additionally, sourcing detailed product manuals and installation guides from manufacturers can provide essential insights into the specific assembly and operation of the locks. Establishing a standardized checklist for installation processes can further streamline operations and enhance security measures.
Scenario 2: Sourcing Quality Components for Diverse Needs
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in sourcing high-quality door lock components that meet their specific security needs, especially when operating in multiple regions with varying security standards. In markets like Africa or South America, where local regulations may differ from those in Europe, the risk of selecting subpar or incompatible products increases. This can lead to increased costs due to frequent replacements or security breaches.
The Solution: To address this pain point, buyers should conduct thorough market research and establish relationships with reputable suppliers who understand the nuances of different regional security requirements. Creating a procurement strategy that emphasizes quality over cost can also help ensure that the components sourced are reliable and compliant with local standards. Engaging in partnerships with manufacturers who offer customization options can allow businesses to tailor their lock solutions to meet specific security challenges in their markets, ensuring both safety and compliance.
Scenario 3: Troubleshooting Common Lock Issues
The Problem: It’s not uncommon for B2B buyers, particularly in facility management, to encounter everyday issues with door locks, such as jamming, difficulty in turning the key, or misalignment with the strike plate. These problems can lead to operational disruptions and increased maintenance costs, especially in environments with high foot traffic where security is paramount.
The Solution: Establishing a preventive maintenance program is crucial for mitigating these issues. Buyers should train their maintenance staff to recognize early signs of lock malfunctions, such as unusual sounds or resistance when locking or unlocking doors. Implementing routine inspections of door locks can help identify and address issues before they escalate. Additionally, investing in higher-quality locks with robust components can reduce the likelihood of these problems occurring. When issues do arise, having a reliable locksmith service on speed dial can ensure quick resolutions, minimizing downtime and maintaining security integrity across facilities.

Illustrative image related to door lock anatomy
Strategic Material Selection Guide for door lock anatomy
What Are the Key Materials Used in Door Lock Anatomy?
When selecting materials for door lock anatomy, it is crucial to consider the properties that will affect performance, durability, and security. Here, we analyze four common materials used in door locks: brass, stainless steel, zinc alloy, and plastic. Each material has unique characteristics that influence its suitability for various applications.
How Does Brass Perform in Door Lock Applications?
Brass is a traditional material widely used in the manufacturing of door locks due to its excellent corrosion resistance and durability. It can withstand a wide range of temperatures, making it suitable for various climates. Brass locks are often favored for their aesthetic appeal, as they can be polished to a bright finish.
Pros: Brass is highly durable and resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications. Its malleability allows for intricate designs, enhancing its aesthetic value.
Cons: The primary drawback of brass is its cost, which can be higher than other materials. Additionally, it may tarnish over time if not properly maintained.
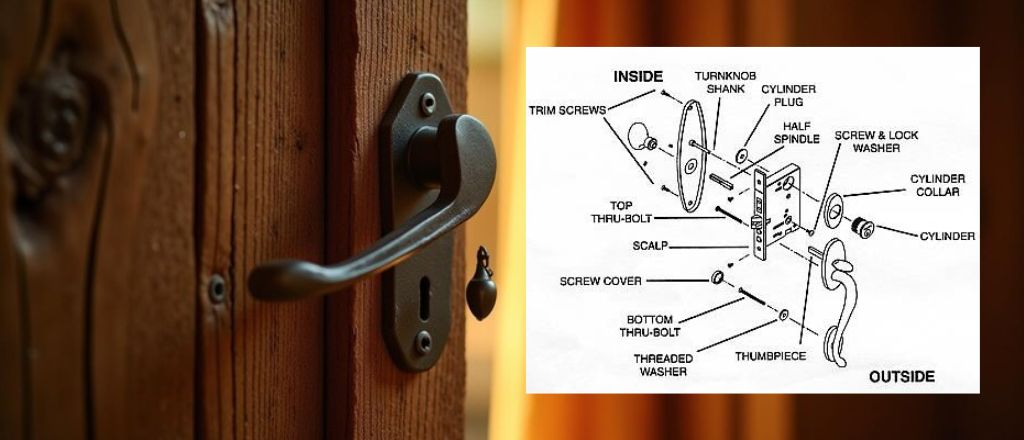
Illustrative image related to door lock anatomy
Impact on Application: Brass locks are compatible with various media, including residential and commercial settings. However, they may not be suitable for environments with extreme humidity or exposure to harsh chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and EN is essential for brass locks. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local preferences for aesthetics and durability.
What Are the Advantages of Stainless Steel in Door Locks?
Stainless steel is another popular choice due to its exceptional strength and resistance to corrosion and rust. It can withstand high pressures and temperatures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros: The durability of stainless steel makes it ideal for high-security locks. Its resistance to environmental factors ensures longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements.

Illustrative image related to door lock anatomy
Cons: Stainless steel can be more expensive than other materials, and its manufacturing process is more complex, which can lead to higher production costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel locks are particularly effective in industrial and commercial settings where security is paramount. They are also suitable for coastal areas due to their corrosion resistance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that stainless steel locks meet local standards, such as DIN and JIS, especially in Europe and the Middle East, where stringent regulations may apply.
Illustrative image related to door lock anatomy
How Does Zinc Alloy Compare for Door Lock Manufacturing?
Zinc alloy is often used in the production of door locks due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. It is lightweight and can be molded into various shapes, allowing for diverse design options.
Pros: The primary advantage of zinc alloy is its low cost and versatility in design. It is suitable for producing decorative locks that do not require high security.
Cons: Zinc alloy is less durable than brass or stainless steel and may corrode over time, particularly in humid environments.
Impact on Application: Zinc alloy locks are best suited for low-security applications, such as interior doors or decorative purposes. They may not be ideal for external doors exposed to harsh weather.

Illustrative image related to door lock anatomy
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify the alloy’s compliance with local standards, especially in regions with high humidity, such as parts of Africa and South America.
What Role Does Plastic Play in Door Lock Design?
Plastic is increasingly used in door lock manufacturing, particularly for internal components. It is lightweight, cost-effective, and can be produced in various colors and designs.
Pros: The main advantage of plastic is its low cost and ease of production. It can be molded into complex shapes, making it suitable for innovative designs.
Cons: Plastic is generally less durable and secure than metal options, making it unsuitable for high-security applications.
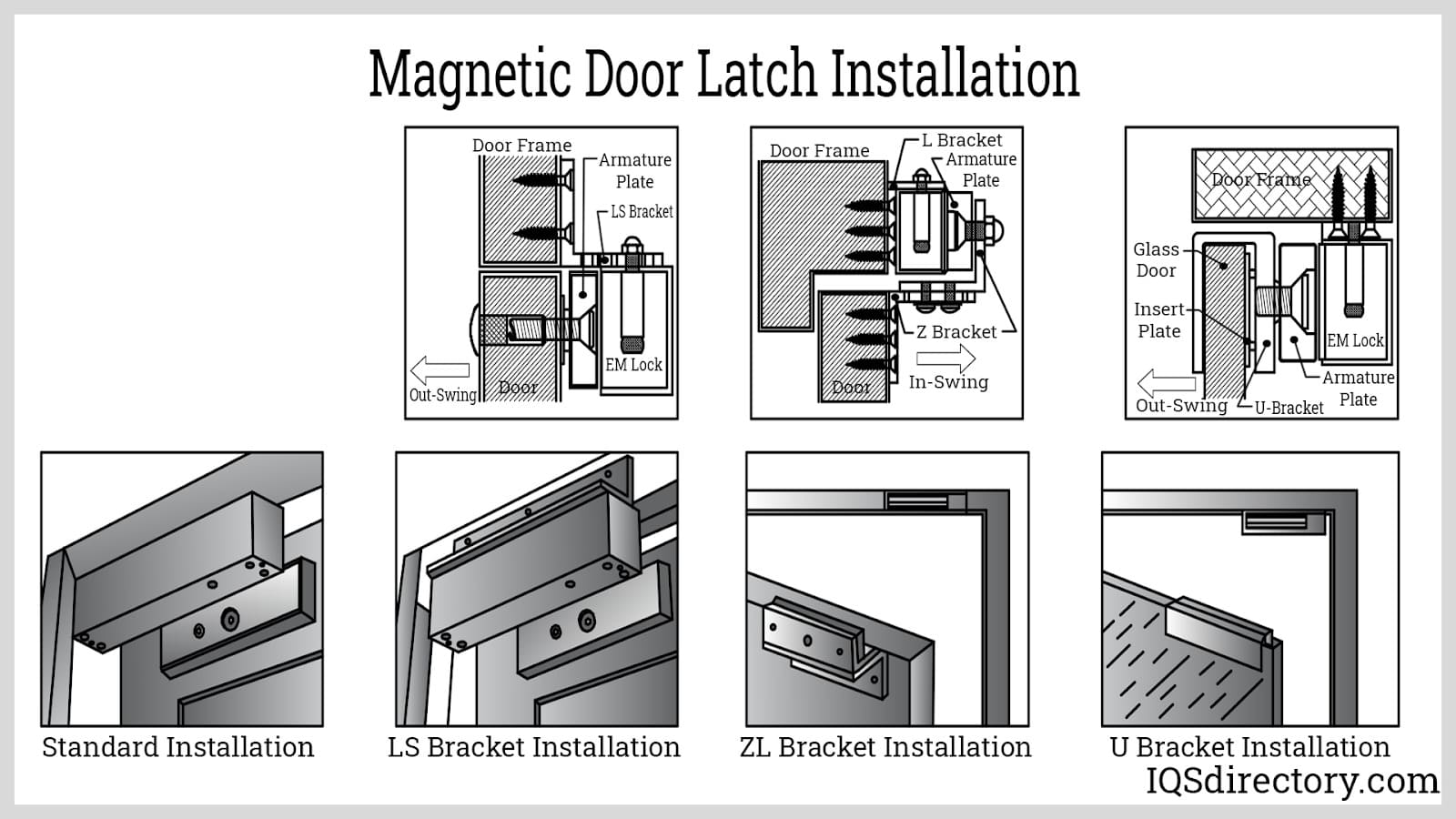
Illustrative image related to door lock anatomy
Impact on Application: Plastic locks are ideal for low-security applications, such as cabinet locks or internal doors. However, they should not be used in outdoor settings or areas prone to tampering.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the quality of the plastic used and ensure it meets safety standards relevant to their region.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Door Lock Anatomy
| Material | Typical Use Case for Door Lock Anatomy | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | Residential and decorative locks | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and maintenance required | High |
| Stainless Steel | Industrial and high-security locks | Exceptional strength and durability | More expensive and complex to manufacture | High |
| Zinc Alloy | Low-security and decorative applications | Cost-effective and versatile design | Less durable and prone to corrosion | Low |
| Plastic | Internal components and low-security locks | Lightweight and easy to produce | Less durable and secure | Low |
This comprehensive analysis provides B2B buyers with the insights necessary to make informed decisions regarding material selection for door lock anatomy, ensuring optimal performance and compliance with regional standards.
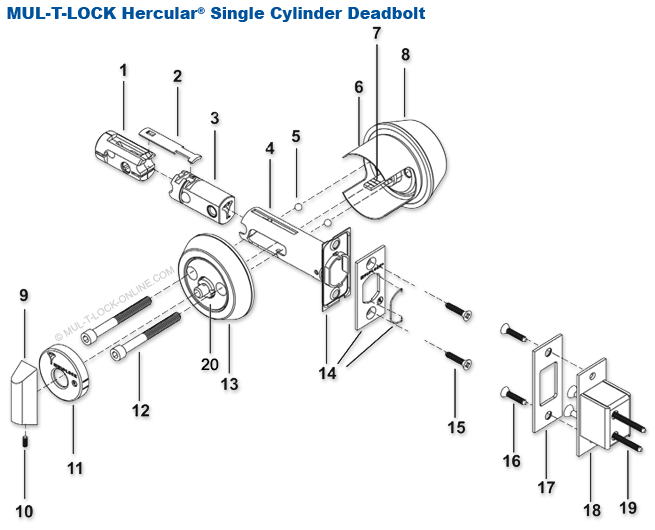
Illustrative image related to door lock anatomy
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for door lock anatomy
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Door Locks?
Manufacturing door locks involves a series of stages that ensure the final product meets the necessary security standards and functional requirements. The process typically consists of material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Door Lock Manufacturing?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This involves selecting high-quality materials, commonly steel, brass, or zinc alloys, which are chosen for their durability and resistance to wear. The materials are then cut into specified dimensions, followed by processes like heat treatment to enhance strength. Quality assurance begins at this stage, as the raw materials must meet specified standards to prevent defects in the final product.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Door Lock Production?
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo various forming techniques. These may include machining, forging, and stamping.
-
Machining: This is used for precision parts like cylinders and bolts, where exact dimensions are critical. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often employed to ensure accuracy.
-
Forging: This process involves shaping the metal using compressive forces, which enhances its structural integrity. Forged locks generally offer greater strength and resistance against tampering.
-
Stamping: This technique is utilized for producing flat components such as strike plates and faceplates. It is efficient for high-volume production and ensures uniformity across components.
How Are Door Locks Assembled?
The assembly stage is where all individual components come together. This includes integrating the cylinder, latch, bolts, and various plates. Each lock is meticulously assembled to ensure that all parts fit properly and function as intended. Assembly often involves both automated processes and skilled labor, particularly for complex locking mechanisms.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Door Locks?
Finishing is the final stage of manufacturing, which includes surface treatments like plating, painting, or powder coating. These processes not only enhance the lock’s aesthetic appeal but also provide corrosion resistance. Quality checks at this stage include visual inspections and tests for durability, ensuring that the finish meets the desired specifications.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Door Lock Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, particularly for products that play a crucial role in security. A robust QA system can significantly reduce defects and enhance customer satisfaction.

Illustrative image related to door lock anatomy
What International Standards Are Relevant for Door Lock Quality Assurance?
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems. Compliance with these standards indicates that a manufacturer adheres to globally recognized quality practices. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for locks used in specific industrial applications may apply.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is implemented at various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, periodic checks are conducted to monitor processes and detect any deviations from quality standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, a comprehensive inspection is performed on the final product. This includes functional tests, dimensional checks, and visual inspections to ensure that the locks operate smoothly and meet all design specifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Lock Quality?
Testing methods for door locks include:
-
Functional Testing: Ensuring that the lock operates smoothly, including testing the key insertion, turning mechanisms, and latch operations.
-
Durability Testing: Subjecting locks to stress tests that simulate wear and tear over time, checking for resistance to tampering and environmental factors.
-
Salt Spray Testing: This method assesses corrosion resistance by exposing the locks to a saline mist for an extended period.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential.
What Should B2B Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits and Reports?
Buyers should request detailed reports from suppliers, which should include:
-
Quality Management System Documentation: Evidence of adherence to international standards like ISO 9001.
-
Quality Control Reports: Documentation of QC checks, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC results.
-
Test Certificates: Results from functional and durability tests, as well as any certifications obtained through third-party testing agencies.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Trust in Supplier Quality?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an impartial evaluation of a supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures. These inspections typically involve:
-
Site Audits: Verifying that manufacturing facilities adhere to the required standards and practices.
-
Sample Testing: Conducting independent tests on samples to ensure they meet specified criteria.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various quality control nuances, particularly when sourcing from different regions.
-
Understanding Local Standards: Different regions may have unique regulations and standards, such as the EN (European Norms) for the European market, which may differ from standards in Africa or South America.
-
Cultural and Operational Differences: Recognizing that quality assurance practices may vary based on local business cultures and operational capabilities is crucial. B2B buyers should be prepared to engage in dialogue with suppliers to understand their specific quality measures.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: International shipments may introduce additional quality risks. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust logistics and handling procedures to protect product integrity during transit.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols is vital for B2B buyers in the door lock industry. By focusing on these elements, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their security offerings and ensure customer satisfaction.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘door lock anatomy’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide provides B2B buyers with a step-by-step checklist for procuring door lock components. Understanding the anatomy of door locks is crucial for selecting the right products that ensure security and functionality. This guide aims to streamline the sourcing process, helping you make informed decisions that align with your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your sourcing process. Consider the types of locks needed, such as deadbolts, latch bolts, or smart locks, and their intended applications. This clarity ensures that you procure products that meet the security requirements of your specific projects.
- Key Considerations:
- Material (e.g., brass, stainless steel)
- Security rating (e.g., ANSI/BHMA grades)
- Functionality (e.g., electronic vs. mechanical)
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Stay informed about current trends and innovations in door lock technology. Understanding market developments can help you identify high-demand products that may enhance your offering. This knowledge also enables you to recognize potential competitive advantages.
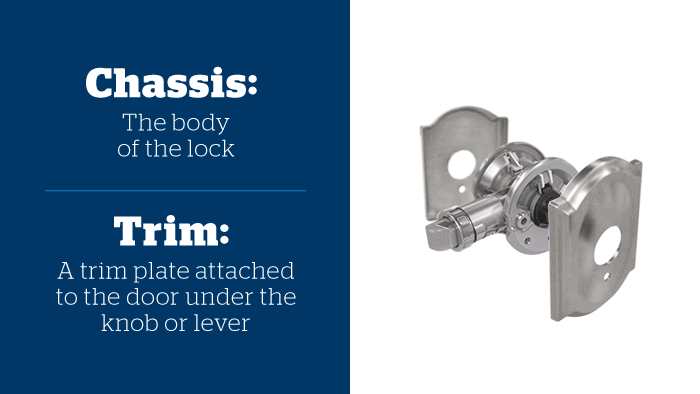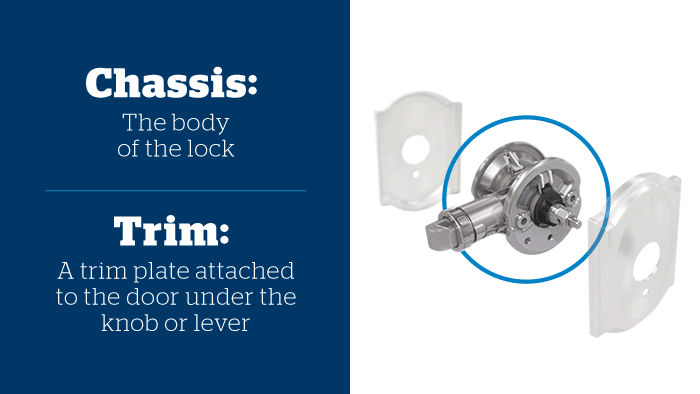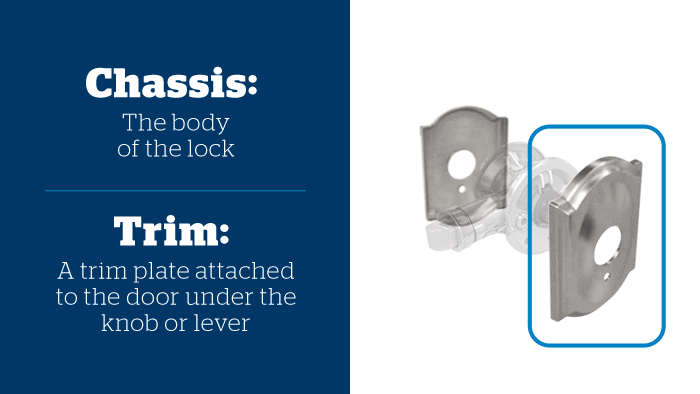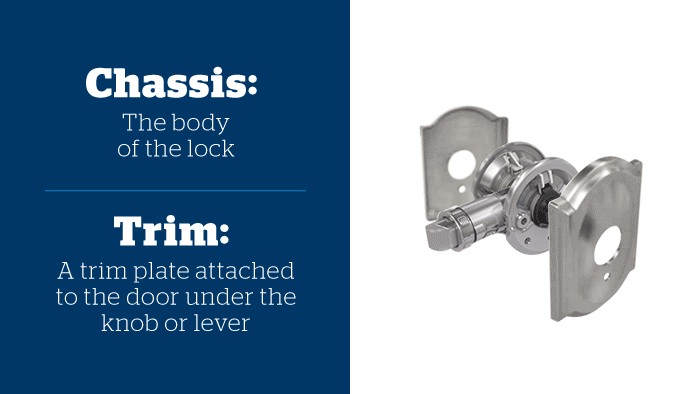
Illustrative image related to door lock anatomy
- Focus Areas:
- Rise of smart locks and IoT integration
- Emerging security technologies (e.g., biometrics)
- Industry standards and certifications
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies to assess their capabilities. Additionally, look for references from other businesses in your industry to gauge supplier reliability and quality.
- What to Assess:
- Years of experience and expertise in the market
- Customer reviews and testimonials
- Product warranty and service offerings
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers hold relevant certifications that demonstrate their commitment to quality and safety. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or ANSI/BHMA can provide assurance that the products meet established industry standards.
- Why This Matters:
- Reduces risks associated with subpar products
- Enhances your credibility when reselling or using these locks
- Helps in compliance with local regulations in your market
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the door lock components. Testing these samples will help you evaluate their functionality, durability, and overall quality. This step is essential to ensure that the products meet your technical specifications and performance expectations.
- Testing Considerations:
- Ease of installation and operation
- Resistance to tampering and wear
- Compatibility with existing door hardware
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a supplier, negotiate the terms and conditions of your purchase. Discuss pricing, minimum order quantities, lead times, and payment terms to ensure a mutually beneficial agreement. Effective negotiation can lead to significant cost savings and improved supply chain efficiency.
- Key Points to Address:
- Bulk purchasing discounts
- Return policies and warranties
- Shipping and handling arrangements
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship
Building a long-term relationship with your suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority support, and access to new products. Regular communication and feedback will foster trust and collaboration, enhancing your overall procurement process.
- Strategies for Engagement:
- Schedule regular check-ins to discuss needs and feedback
- Collaborate on product development or customization
- Participate in supplier-led training or workshops
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process for door lock components, ensuring that they make well-informed decisions that enhance their security offerings.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for door lock anatomy Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Door Lock Manufacturing?
When sourcing door locks, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary components influencing the cost include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects the cost. Common materials include brass, steel, and zinc alloys, with higher-grade materials generally leading to higher prices. Additionally, specialized materials for enhanced security features can further elevate costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and are influenced by local wage standards. Skilled labor for assembly, machining, and quality assurance can add to overall expenses, especially if the manufacturing process involves intricate components.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and indirect labor. Efficient operations can reduce these overhead costs, impacting the final price of the door locks.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for molds and machinery can be substantial, particularly for customized or high-precision components. These costs are often amortized over production volumes, influencing pricing strategies.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that door locks meet safety and performance standards is critical. The costs associated with quality inspections, certifications, and compliance testing can contribute significantly to overall expenses.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs are vital, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties can affect the total cost significantly.
-
Margin: Profit margins can vary depending on the competitive landscape and the value-added services provided by suppliers. Premium suppliers may justify higher margins through enhanced quality or customer service.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Door Lock Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of door locks, particularly for international B2B buyers.
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can affect pricing significantly. Bulk orders often lead to discounts, making it essential for buyers to assess their needs against potential savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized locks designed for specific applications may incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of tailored solutions against standard offerings.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Locks with higher-quality materials or industry certifications (e.g., ANSI/BHMA) typically command higher prices. Buyers should consider the long-term value of investing in certified products.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer better warranties or support, justifying higher costs.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate who bears shipping costs and risks, influencing overall pricing.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Door Lock Sourcing?
B2B buyers should adopt strategic approaches to maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing door locks.
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing, especially when dealing with larger orders. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases or long-term contracts.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, replacement, and potential security risks associated with lower-quality locks. A higher upfront cost may be justified by lower long-term expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: International buyers should be mindful of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local market conditions. These factors can significantly affect the total cost of sourcing.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to new products. Trust and reliability often translate into better deals.
In conclusion, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and price influencers is essential for B2B buyers in the door lock market. By leveraging strategic negotiation and focusing on the total cost of ownership, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their security needs and budgetary constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing door lock anatomy With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternative Security Solutions
In the realm of security, particularly for commercial and residential properties, the anatomy of door locks plays a critical role in safeguarding assets. However, several alternative solutions exist that can provide similar or enhanced levels of security. By comparing these alternatives to traditional door lock anatomy, B2B buyers can make informed decisions tailored to their unique security needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Door Lock Anatomy | Smart Lock Technology | Biometric Security Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable mechanical security | Remote access and monitoring | High-security, unique user access |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Higher upfront cost | Premium pricing due to technology |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward installation | Requires Wi-Fi and app setup | Complex installation and setup |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Regular software updates needed | Low, but hardware may require replacement |
| Best Use Case | Traditional security in homes/offices | Modern businesses with tech-savvy clients | High-security environments needing strict access control |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Smart Lock Technology
Smart locks represent a significant evolution in locking mechanisms, integrating digital technologies with traditional locking systems. They allow users to control access remotely via smartphones, providing the convenience of keyless entry and the ability to monitor who enters and exits. However, their reliance on technology can be a double-edged sword; they are vulnerable to hacking and require a reliable power source and internet connection. For businesses operating in tech-centric environments, smart locks offer a blend of convenience and security but come with higher initial costs and require regular updates to maintain security integrity.
Biometric Security Systems
Biometric systems, which use unique physical characteristics (like fingerprints or facial recognition) for access control, provide an advanced layer of security. They eliminate the risk of lost keys or forgotten codes, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive areas. While highly effective, the complexity of installation and higher costs can be significant barriers for some organizations. Additionally, biometric systems require maintenance to ensure sensors remain functional and effective. They are ideal for high-security environments, such as data centers or financial institutions, where security cannot be compromised.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Security Solution
Selecting the right security solution involves evaluating specific needs, budget constraints, and the environment in which the system will be implemented. Traditional door lock anatomy offers a reliable and cost-effective solution for many businesses, particularly those prioritizing simplicity and low maintenance. In contrast, smart locks and biometric systems cater to organizations seeking modern, tech-savvy solutions with enhanced monitoring capabilities. By carefully analyzing the pros and cons of each alternative, B2B buyers can choose a solution that best aligns with their operational requirements and security objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for door lock anatomy
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Door Locks for B2B Buyers?
Understanding the technical properties of door locks is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential specifications that define the quality and functionality of door locks:
-
Material Grade
The material grade refers to the type of materials used in manufacturing door locks, which can include brass, stainless steel, or zinc alloy. Higher-grade materials typically offer better durability, corrosion resistance, and security. For B2B buyers, selecting locks made from superior materials can minimize maintenance costs and enhance the longevity of the product. -
Lock Tolerance
Tolerance is the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In the context of door locks, it dictates how well the components fit together, impacting the lock’s functionality and security. Lower tolerances generally indicate higher quality, reducing the risk of tampering. Buyers should prioritize locks with precise tolerances to ensure effective operation and enhanced security. -
Bolt Throw Distance
The bolt throw distance is the measurement of how far the bolt extends into the door frame when locked. A longer bolt throw typically provides better security, as it makes forced entry more difficult. For B2B buyers, considering this specification is vital for applications that require enhanced security measures, such as commercial buildings or high-risk environments. -
Cycle Rating
Cycle rating indicates how many times a lock can be operated before it may fail. It is an important measure of durability, especially for high-traffic areas. B2B buyers should consider locks with a high cycle rating to ensure they withstand frequent use without compromising security or functionality. -
Security Rating
Security ratings are often defined by industry standards, such as ANSI/BHMA (American National Standards Institute/Builders Hardware Manufacturers Association) ratings. These ratings assess the lock’s resistance to various forms of attack, including picking, drilling, and forced entry. For B2B buyers, understanding the security rating is essential for selecting locks that meet the specific safety requirements of their projects.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know in Door Lock Procurement?
Navigating the procurement process for door locks involves understanding specific industry jargon. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of door locks, purchasing from an OEM can ensure high-quality components that meet specific requirements. B2B buyers often seek OEM partnerships to maintain consistency in quality across their product offerings. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers, as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs to avoid excess inventory or stock shortages. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that invites suppliers to submit bids for providing specific products or services. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ can streamline the procurement process, enabling them to compare pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, thus facilitating informed decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery responsibilities, which is critical for budgeting and logistics planning. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is received. Understanding lead times is essential for B2B buyers to plan inventory effectively and meet project timelines. Buyers should communicate clearly with suppliers about expected lead times to avoid disruptions in their supply chain.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when procuring door locks, ultimately enhancing their security measures and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the door lock anatomy Sector
What Are the Key Drivers and Trends Shaping the Door Lock Anatomy Market?
The door lock anatomy sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by various global factors. An increasing focus on security, particularly in emerging markets like Nigeria and Brazil, is propelling demand for sophisticated locking systems. This surge is complemented by advancements in smart technology, where locks can now integrate with home automation systems, providing enhanced security and convenience. International buyers are particularly interested in products that combine traditional mechanical systems with digital features, catering to a growing consumer preference for smart home devices.
Another notable trend is the rise of e-commerce platforms that facilitate direct sourcing from manufacturers. This change allows B2B buyers to access a broader range of products, including innovative locking mechanisms that may not be available in local markets. Moreover, the proliferation of online reviews and product ratings helps buyers make informed decisions based on quality and reliability.
As the global economy recovers from recent disruptions, regional market dynamics are shifting. In Africa and South America, urbanization is driving infrastructure development, which in turn increases the demand for secure locking solutions. Conversely, European markets are seeing a trend toward premium products that emphasize aesthetic appeal alongside functionality. B2B buyers are therefore advised to stay informed about regional preferences and technological advancements to make strategic sourcing decisions.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Door Lock Sector?
Sustainability has become a critical consideration in the door lock anatomy sector, affecting how products are sourced and manufactured. The environmental impact of traditional manufacturing processes has led to a heightened demand for ethically sourced materials and ‘green’ certifications. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices, such as using recycled metals and non-toxic finishes in their products.
Ethical supply chains are vital for businesses aiming to enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles. By sourcing from manufacturers that adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental regulations, companies can mitigate risks associated with reputational damage. Moreover, certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) are becoming essential for B2B buyers who want to ensure their products align with sustainable practices.

Illustrative image related to door lock anatomy
Additionally, the push for energy-efficient locking systems, such as those that minimize energy consumption in smart locks, reflects a growing trend toward sustainability. B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint, as this not only meets consumer demand but also contributes to long-term business viability.
What Is the Historical Context of Door Lock Technology?
The evolution of door lock technology dates back thousands of years, with the earliest known locks made from wood and used by ancient Egyptians. Over time, advancements in metallurgy led to the development of more secure and durable locking mechanisms, such as the pin tumbler lock in the 19th century, which remains a foundational design in modern locks.
In the late 20th century, the introduction of electronic locks marked a significant shift, paving the way for the integration of smart technology in locking systems. Today, the market is characterized by a blend of traditional and digital solutions, reflecting the diverse needs of consumers and businesses alike. Understanding this historical context can help B2B buyers appreciate the value of innovation in current products, allowing them to make informed decisions about sourcing the most effective and secure locking solutions for their needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of door lock anatomy
-
How do I solve issues with my door locks not functioning properly?
If your door locks are malfunctioning, first inspect the visible components such as the handle, latch, and strike plate for any signs of wear or misalignment. Lubricate the lock mechanism with a graphite or silicone-based lubricant to eliminate sticking. If the problem persists, consider disassembling the lock to check for internal issues like broken pins or springs. For complex problems, it may be wise to consult a professional locksmith to ensure a proper diagnosis and repair. -
What is the best type of door lock for commercial properties?
For commercial properties, deadbolts and smart locks are often the best choices. Deadbolts provide superior security as they extend deeper into the door frame, making forced entry more difficult. Smart locks offer advanced features such as keyless entry, remote access, and audit trails, which enhance security and convenience. Consider the specific security needs of your property and the level of access control required when selecting the right lock type. -
How can I vet potential suppliers for door locks?
Vetting suppliers involves several key steps: first, research the supplier’s reputation by checking online reviews and industry ratings. Request references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and product quality. Additionally, assess their compliance with international standards and certifications relevant to door locks. Finally, consider visiting their facilities or arranging a video call to discuss their production capabilities and commitment to quality assurance. -
What customization options are available for door locks?
Many manufacturers offer customization options such as different finishes, sizes, and security features tailored to specific needs. You can often request branded key cylinders or unique key profiles for enhanced security. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore their customization capabilities and lead times, ensuring that the final product aligns with your brand identity and operational needs. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for door locks?
MOQs can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the type of door locks being sourced. Generally, larger manufacturers may require MOQs ranging from 100 to 500 units, while smaller suppliers might accommodate orders as low as 50 units. Always confirm the MOQ with the supplier before placing an order to ensure it fits your inventory strategy and budget constraints. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing door locks internationally?
Payment terms for international transactions can vary widely among suppliers. Common terms include a deposit (typically 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or trade financing options. Ensure that you clearly understand the payment terms and negotiate favorable conditions that align with your cash flow and risk management strategies. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when purchasing door locks?
To ensure quality assurance, request certifications from the supplier that demonstrate compliance with relevant international standards, such as ISO 9001. Implement a quality control process that includes inspecting samples before bulk orders and conducting random checks upon delivery. Establish a clear return policy for defective products and maintain open communication with the supplier to address any quality concerns promptly. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing door locks?
When importing door locks, consider factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your destination country. Choose a reliable logistics partner experienced in handling hardware imports to navigate potential challenges. Ensure that all necessary documentation, such as invoices and packing lists, is accurate to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Additionally, factor in potential tariffs and duties that may apply to your order to avoid unexpected costs.
Top 4 Door Lock Anatomy Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Hardware Hut – Door Lock Latches
Domain: hardwarehut.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Door Lock Latches and Latchbolts | Shop Door Lock Parts | 110 items available | Categories include: Door Hardware, Door Locks (Commercial), Deadbolts, Door Closers, Exit Devices, Door Hinges, Electric Strikes, Door Stops, Door Bottoms, Thresholds, Weatherstripping, Door Lock Filler, Strike Plates, Protectors, Door Kick Plates, Door Flush & Surface Bolts, ADA Door Signs, Door Pulls & Push Plates, D…
2. Barry Bros – Security Solutions
Domain: barrybros.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Barry Bros Security offers a variety of lock and security solutions including: 1. Lock Installations 2. Lock Repairs & Replacements 3. Emergency Exit Compliance 4. Multi Point Locking Systems 5. Key Duplication and Repairs 6. Master Suited Locks & Keys 7. Antique Locks & Keys 8. Insurance Graded Security & Domestic Safes 9. Fire Resistant Safes 10. Electronic Locking Systems 11. Access Control Sys…
3. Chicago Locksmiths – Door Lock Parts
Domain: chicagolocksmiths.net
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Door Lock Parts: Cylinder, Bolt, Box; Deadbolt Parts: Bolt, Thumb Latch, Turnpiece, Keyhole; Strike Plate, Rosette.
4. Express Locksmiths – Anatomy of Door Locks
Domain: expresslocksmithshouston.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: The Anatomy Of Door Locks includes traditional and electronic locks. Key components of a door lock are: 1. Cylinder: The part where the key is inserted, engaging spring-loaded pins to lock the cylinder. 2. Bolt: Also known as the latch, it extends from the door into the frame to hold it closed. 3. Box: Holds the bolt in place when locked. 4. Key Parts: Bit (blade) and bow. 5. Deadbolt Parts: Actua…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for door lock anatomy
In summary, understanding the anatomy of door locks is critical for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance security in various applications. By familiarizing themselves with key components such as cylinders, bolts, and strike plates, businesses can make informed decisions that improve safety and operational efficiency. Moreover, strategic sourcing of high-quality lock systems not only ensures reliability but also fosters long-term partnerships with manufacturers who prioritize innovation and security.
As buyers from diverse regions including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe evaluate their options, it is essential to consider the unique security challenges and regulatory requirements of each market. Engaging with suppliers who offer tailored solutions can lead to significant cost savings and enhanced security protocols.
Looking ahead, the evolving landscape of door security technology presents opportunities for innovation and integration, such as smart locks and advanced locking mechanisms. We encourage B2B buyers to explore these advancements and leverage strategic sourcing to position themselves competitively in their respective markets. Embrace the future of security solutions to ensure your business remains secure and prosperous.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.