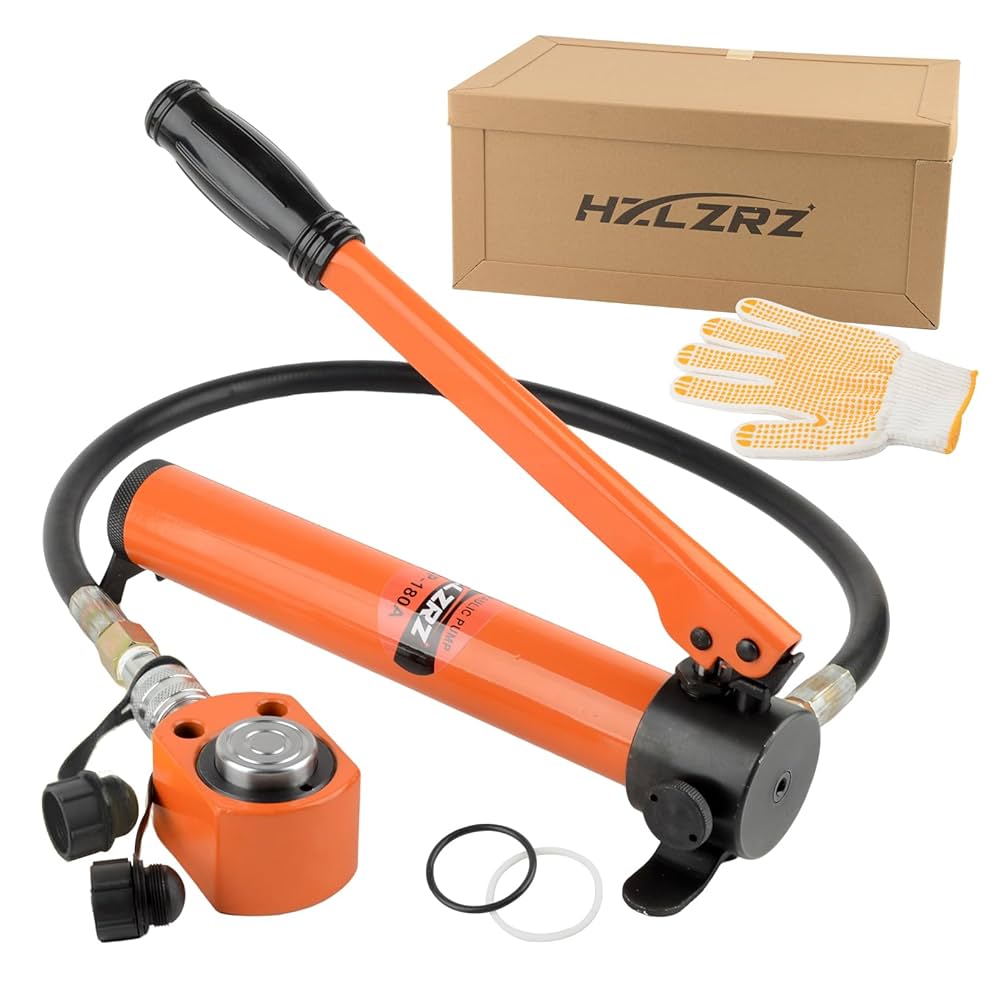
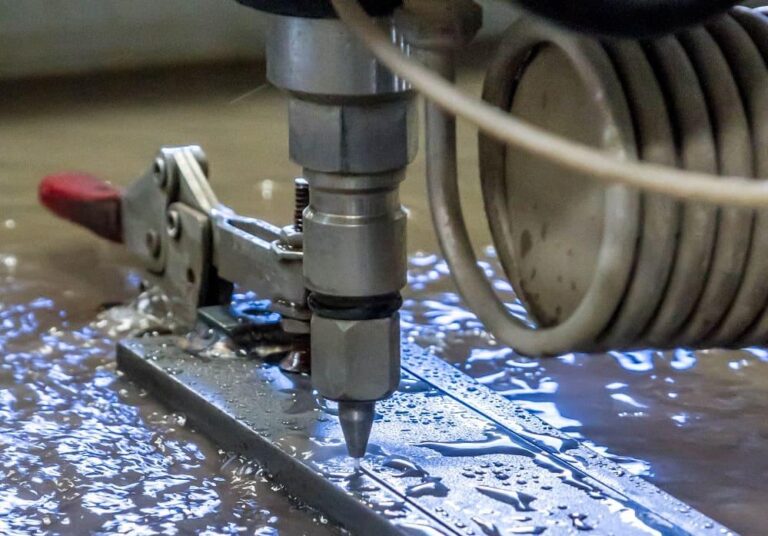
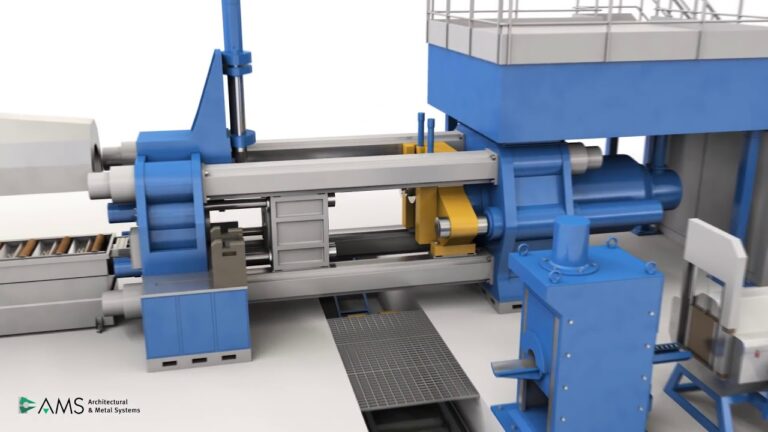
Everything You Need to Know About Pump For Hydraulic Cylinder Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pump for hydraulic cylinder
In an increasingly competitive landscape, sourcing the right pump for hydraulic cylinders can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The diverse range of hydraulic pumps available, from hand-operated models to advanced battery-powered systems, requires a nuanced understanding of specific applications and performance metrics. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of selecting hydraulic pumps, providing insights into various types, applications, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
Buyers will gain a comprehensive overview of hydraulic cylinder and pump sets, including the latest innovations in variable displacement pumps and the advantages of complete kit solutions that streamline operations. Additionally, we delve into cost considerations, enabling businesses to make informed financial decisions that align with their operational needs.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and practical advice, this guide empowers organizations to navigate the global market effectively, ensuring they choose the right hydraulic solutions that enhance productivity and reliability. Whether you are in Vietnam or Brazil, understanding these key elements will facilitate better purchasing decisions, driving long-term success in your hydraulic applications.
Understanding pump for hydraulic cylinder Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hand Pumps | Manual operation, lightweight, portable | Construction, automotive repair | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to use. Cons: Labor-intensive, limited power. |
| Electric Pumps | Powered by electricity, high efficiency | Manufacturing, heavy machinery | Pros: Consistent power, minimal manual effort. Cons: Higher initial cost, requires power source. |
| Air-Driven Pumps | Operates using compressed air, versatile | Industrial applications, assembly lines | Pros: Fast operation, suitable for remote locations. Cons: Dependent on air supply, can be noisy. |
| Piston Pumps | High pressure capability, variable displacement | Hydraulic systems, mobile machinery | Pros: High efficiency, adjustable flow. Cons: Complex design, may require regular maintenance. |
| Battery-Powered Pumps | Cordless, rechargeable, portable | Field operations, emergency services | Pros: Mobility, ease of use in remote areas. Cons: Limited run time, battery replacement costs. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Hand Pumps for Hydraulic Cylinders?
Hand pumps are a popular choice for applications where portability and cost-effectiveness are paramount. They are lightweight and easy to operate manually, making them ideal for smaller tasks or in locations without power access. However, their reliance on human effort can limit their efficiency and suitability for larger operations, where consistent power is necessary.
How Do Electric Pumps Enhance Hydraulic Systems in B2B Applications?
Electric pumps provide a reliable power source for hydraulic systems, ensuring consistent performance and reducing the need for manual labor. They are particularly beneficial in manufacturing and heavy machinery operations, where efficiency and speed are critical. Although they come with a higher upfront cost and require a stable electrical supply, their long-term operational efficiency often justifies the investment.
In What Scenarios Are Air-Driven Pumps Most Effective?
Air-driven pumps are versatile and can be used in various industrial applications, including assembly lines and pneumatic systems. They operate quickly and are ideal for environments where electrical sources are limited. However, their dependence on a compressed air supply can be a drawback, as it may not always be readily available, and they can produce significant noise during operation.
Why Are Piston Pumps Considered a Reliable Choice for High-Pressure Applications?
Piston pumps are known for their ability to deliver high-pressure outputs and adjustable flow rates, making them suitable for hydraulic systems in mobile machinery and industrial applications. Their robust design allows for efficiency and durability, but they can be more complex and may require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
What Advantages Do Battery-Powered Pumps Offer for Remote Operations?
Battery-powered pumps provide unmatched mobility, making them ideal for field operations and emergency services where access to electrical outlets may be limited. They are user-friendly and eliminate the need for cumbersome hoses or cords. However, the limited run time and potential costs associated with battery replacement can be a consideration for B2B buyers looking for long-term solutions.
Key Industrial Applications of pump for hydraulic cylinder
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of pump for hydraulic cylinder | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Lifting and positioning heavy materials | Enhances efficiency and safety on job sites | Ensure compatibility with existing machinery and load capacity. |
| Manufacturing | Precision assembly and automation | Increases production speed and reduces labor costs | Look for pumps with variable speed controls and reliability. |
| Oil & Gas | Wellhead control and maintenance | Improves operational reliability and safety | Consider pumps that can withstand harsh environmental conditions. |
| Agriculture | Equipment operation for planting and harvesting | Boosts productivity and reduces manual labor | Evaluate hydraulic systems for energy efficiency and ease of use. |
| Transportation | Cargo handling and logistics | Enhances throughput and reduces downtime | Focus on sourcing pumps that offer quick response times and durability. |
How Is a Pump for Hydraulic Cylinder Used in Construction Projects?
In the construction industry, pumps for hydraulic cylinders are essential for lifting and positioning heavy materials, such as steel beams and concrete slabs. These pumps enable hydraulic jacks to exert significant force, ensuring safe and precise placement. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-capacity pumps that meet local load requirements and comply with safety standards is crucial. Additionally, robust after-sales support and availability of spare parts should be considered to minimize downtime on job sites.
What Role Does a Pump for Hydraulic Cylinder Play in Manufacturing?
In manufacturing, hydraulic pumps are pivotal for automation and precision assembly tasks. They provide the necessary force for machinery to operate efficiently, significantly increasing production speed while reducing labor costs. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should prioritize sourcing variable volume pumps that can adapt to different operational needs. Reliability and maintenance support are also vital, as any downtime can lead to substantial financial losses in competitive markets.
How Do Pumps for Hydraulic Cylinders Enhance Operations in Oil & Gas?
In the oil and gas sector, pumps for hydraulic cylinders are critical for wellhead control, maintenance, and equipment operation. These pumps ensure that valves and other components function reliably under high-pressure conditions, enhancing safety and operational efficiency. Buyers should focus on sourcing pumps that are designed to withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive environments typical of oil and gas fields, especially in remote locations across Africa and the Middle East.
What Benefits Do Pumps for Hydraulic Cylinders Offer in Agriculture?
In the agricultural sector, hydraulic pumps are used to operate machinery for planting, cultivating, and harvesting crops. They significantly boost productivity by automating tasks that would otherwise require extensive manual labor. International buyers in developing regions should seek pumps that offer energy efficiency and ease of use, as these factors can greatly impact operational costs and labor management in agriculture.

Illustrative image related to pump for hydraulic cylinder
How Are Pumps for Hydraulic Cylinders Utilized in Transportation Logistics?
Pumps for hydraulic cylinders are vital in the transportation industry for cargo handling and logistics operations. They enable the quick and efficient movement of goods, enhancing throughput and reducing operational downtime. Buyers should consider sourcing pumps with quick response times and durability to withstand the rigors of a busy logistics environment, especially in regions like South America where transportation infrastructure may vary.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pump for hydraulic cylinder’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Performance in Hydraulic Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of inconsistent performance from hydraulic pumps, which can result in operational delays and increased costs. For example, a manufacturing company may experience fluctuations in pressure and flow rates, leading to inefficient operation of hydraulic cylinders. This inconsistency can stem from inadequate pump specifications, such as mismatched pump and cylinder sizes or poor-quality components. As a result, the end-users may find themselves grappling with reduced productivity and unexpected downtime.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should conduct thorough assessments of their hydraulic systems before purchasing pumps. This involves understanding the specific requirements of the hydraulic cylinders in use, including load capacities, stroke lengths, and operational speeds. Buyers should consult with suppliers to ensure they are selecting pumps that meet or exceed the required specifications. Additionally, opting for modular hydraulic systems can provide flexibility, allowing for adjustments based on changing operational demands. Regular maintenance and performance monitoring of pumps can also prevent inconsistencies, ensuring optimal performance over time.
Scenario 2: Compatibility Issues with Existing Equipment
The Problem: Another common pain point is the compatibility of new hydraulic pumps with existing equipment. B2B buyers frequently encounter situations where newly acquired pumps do not align with their current hydraulic systems, leading to installation challenges and increased costs. For instance, a construction firm might purchase a pump that does not fit the hydraulic lines or connectors of their existing machinery, resulting in delays and additional modification expenses.
The Solution: To mitigate compatibility issues, buyers should prioritize conducting a comprehensive compatibility analysis before making a purchase. This includes reviewing existing hydraulic schematics and specifications to ensure that any new pump will seamlessly integrate with current systems. Engaging with suppliers who offer customization options can also be beneficial, as they can provide tailored solutions that fit specific equipment requirements. Furthermore, investing in standardized hydraulic components can enhance future compatibility, reducing the likelihood of facing similar issues down the line.
Scenario 3: High Operational Costs Due to Inefficiency
The Problem: High operational costs are a significant concern for businesses utilizing hydraulic systems. B2B buyers may find that their hydraulic pumps consume excessive energy, leading to inflated utility bills and increased wear on components. This inefficiency can arise from outdated technology or poorly designed systems that do not optimize fluid dynamics, ultimately impacting the bottom line.
The Solution: To combat high operational costs, buyers should consider investing in energy-efficient hydraulic pumps, which are designed to reduce energy consumption without sacrificing performance. When sourcing pumps, look for models that feature variable displacement or advanced control systems, as these can significantly enhance efficiency. Additionally, conducting regular system audits can help identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement. Implementing predictive maintenance strategies can further reduce costs by minimizing unexpected breakdowns and extending the lifespan of hydraulic components.

Illustrative image related to pump for hydraulic cylinder
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pump for hydraulic cylinder
When selecting materials for hydraulic pumps used in hydraulic cylinders, it is essential to consider factors such as performance, durability, cost, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of hydraulic pumps, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Cast Iron in Hydraulic Pumps?
Cast iron is a traditional material known for its excellent wear resistance and ability to withstand high pressures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 300°C and can handle pressures exceeding 200 bar. Its inherent corrosion resistance is moderate, making it suitable for various hydraulic fluids, including water-based and oil-based media.
Pros: Cast iron is durable and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for heavy-duty applications. Its machinability allows for complex shapes and designs, which can enhance pump efficiency.

Illustrative image related to pump for hydraulic cylinder
Cons: The primary limitation of cast iron is its brittleness, which can lead to cracking under extreme conditions. Additionally, it is heavier than alternative materials, potentially impacting the overall weight of the hydraulic system.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider the availability of cast iron and its compliance with standards such as ASTM A48. The material’s weight may also influence shipping costs.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Hydraulic Pump Applications?
Aluminum is increasingly favored for hydraulic pumps due to its lightweight nature and good corrosion resistance. It can typically withstand temperatures up to 150°C and pressures around 150 bar, making it suitable for moderate-duty applications.
Pros: The lightweight characteristic of aluminum reduces the overall weight of hydraulic systems, which is beneficial for mobile applications. Additionally, its excellent corrosion resistance extends the lifespan of the pump.
Cons: Aluminum is less durable than cast iron and may not perform well in high-pressure applications. It is also more expensive, which can be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers.

Illustrative image related to pump for hydraulic cylinder
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should ensure that aluminum components meet industry standards such as DIN 1725 for aluminum alloys. The higher cost may be justified in applications where weight savings are critical.
What Are the Benefits of Stainless Steel for Hydraulic Pumps?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications involving aggressive fluids or environments. It can handle temperatures up to 300°C and pressures exceeding 300 bar, providing robust performance.
Pros: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and resistance to corrosion, which reduces maintenance costs over time. Its strength allows for compact designs without compromising safety.
Cons: The main drawback is the high cost of stainless steel, which can significantly impact the overall budget for hydraulic systems. Additionally, machining stainless steel can be more complex and time-consuming.

Illustrative image related to pump for hydraulic cylinder
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the need for compliance with standards such as ASTM A312 for stainless steel pipes. The material’s cost may be a deterrent for buyers in developing regions, but its long-term benefits often outweigh initial expenses.
How Does Composite Material Impact Hydraulic Pump Performance?
Composite materials, often made from a combination of polymers and fibers, are gaining traction in hydraulic pump applications due to their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. They can typically handle temperatures up to 100°C and pressures around 100 bar.
Pros: Composites offer significant weight savings and excellent resistance to chemical corrosion, making them suitable for various hydraulic fluids. They can also be molded into complex shapes, enhancing design flexibility.

Illustrative image related to pump for hydraulic cylinder
Cons: The main limitation is their lower mechanical strength compared to metals, which may restrict their use in high-pressure applications. Additionally, composites can be more expensive to produce.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific chemical compatibility of composite materials with the hydraulic fluids used in their applications. Compliance with standards such as ISO 9001 may also be relevant for ensuring quality.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Hydraulic Pumps
| Material | Typical Use Case for pump for hydraulic cylinder | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Heavy-duty applications requiring high durability | Excellent wear resistance | Brittle under extreme conditions | Low |
| Aluminum | Moderate-duty applications, especially mobile ones | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less durable under high pressure | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | High-pressure and corrosive environments | Exceptional corrosion resistance | High cost and complex machining | High |
| Composite | Lightweight applications with chemical exposure | Significant weight savings | Lower mechanical strength | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on performance requirements, cost considerations, and compliance with international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pump for hydraulic cylinder
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Pumps Used in Hydraulic Cylinders?
Manufacturing pumps for hydraulic cylinders involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets industry standards for performance and durability. The main stages of production include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Hydraulic Pump Manufacturing?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. High-quality materials such as carbon steel, aluminum alloys, and sometimes specialized polymers are selected based on the pump’s intended application and required pressure ratings. Suppliers often provide material certifications to validate the quality and specifications of the raw materials.
Once the materials are chosen, they undergo cutting and machining processes to create components such as housings, pistons, and shafts. Precision machining techniques like CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining are commonly employed to achieve tight tolerances, ensuring that parts fit together seamlessly during assembly.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Pump Manufacturing?
After material preparation, the forming stage begins. This typically includes processes such as casting, forging, and extrusion, depending on the component being produced. For instance, aluminum housings may be die-cast for efficiency, while steel components might be forged for added strength.
Welding and soldering techniques are also employed to join parts together. These methods are crucial for creating the pump body and ensuring that it can withstand high pressures. Advanced techniques like TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding are often used to ensure clean, strong joints that maintain the integrity of the pump.
How Are Hydraulic Pumps Assembled and Finished?
The assembly process is where all the machined and formed components come together. This stage often involves careful alignment and fastening of parts, including seals and gaskets that prevent leaks. Proper assembly is vital for the pump’s performance, as any misalignment can lead to operational failures.
Finishing processes include surface treatments like anodizing, powder coating, or painting to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. These treatments are especially important for pumps used in harsh environments, where exposure to moisture and contaminants can lead to premature failure.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential in Pump Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that every pump meets international standards and customer expectations. The most recognized standard in this regard is ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer has robust processes in place for continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
What International and Industry-Specific Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
In addition to ISO 9001, other certifications may be relevant depending on the application of the hydraulic pump. For example, CE marking is required for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Similarly, pumps used in oil and gas applications may need to meet API (American Petroleum Institute) standards.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Integrated Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically integrated throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. These checkpoints typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications before production begins. Any non-conforming materials are rejected or returned to the supplier.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, operators perform routine checks on dimensions and functionality at various stages. This real-time monitoring helps identify issues before they escalate.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, a comprehensive inspection is conducted to ensure that the completed pump meets all performance standards. Testing may include pressure testing, flow rate testing, and functional tests to validate the pump’s performance under load.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Hydraulic Pumps?
Testing methods vary but typically include:
-
Hydrostatic Testing: This method checks for leaks and ensures the pump can withstand its rated pressure. The pump is filled with water, and pressure is applied to identify any weaknesses.
-
Flow Testing: This assesses the pump’s efficiency by measuring the flow rate at various pressures, ensuring it meets performance specifications.
-
Vibration Analysis: Monitoring vibration levels can help identify mechanical issues that may affect pump longevity and efficiency.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s QC practices is crucial for mitigating risks associated with subpar products. Here are actionable steps to ensure supplier reliability:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of the manufacturing facilities can provide insights into the processes and standards in place. It’s beneficial to have auditors familiar with local regulations and international standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports documenting testing results and compliance with international standards. This transparency fosters trust and accountability.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent third-party inspection services can validate the quality of the products before shipment. These inspectors can perform thorough evaluations based on agreed-upon criteria.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, must navigate diverse regulations and standards. Understanding local market requirements and certifications can be complex, necessitating a proactive approach:
-
Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with specific local regulations regarding hydraulic equipment, as these can vary significantly between countries.
-
Cultural Differences: Building relationships with suppliers may require sensitivity to cultural differences, particularly in negotiation styles and communication preferences.
-
Logistics and Transportation: Consider the implications of logistics on quality assurance. Ensure that transport conditions maintain the integrity of the pump, as improper handling can lead to damage or defects.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices is vital for B2B buyers sourcing hydraulic pumps. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can ensure they procure reliable, high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pump for hydraulic cylinder’
Introduction
Sourcing a pump for hydraulic cylinders requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure that you select a product that meets your operational needs while also aligning with your budget. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist designed for B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Follow these steps to streamline your procurement process and make informed decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining the technical specifications required for your hydraulic pump. Consider factors such as pressure ratings (e.g., PSI), flow rates (GPM), and compatibility with existing hydraulic systems.
– Key Considerations:
– Determine the required displacement and volume of fluid to ensure optimal performance.
– Assess the environmental conditions in which the pump will operate, such as temperature and exposure to contaminants.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers that specialize in hydraulic pumps. Utilize online platforms, industry directories, and trade shows to compile a list of reputable manufacturers and distributors.
– Tip:
– Focus on suppliers with a proven track record in your region and those who understand local market dynamics.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before making a purchase, verify that the suppliers have the necessary certifications and compliance with international standards. This is crucial for ensuring product quality and reliability.
– Important Certifications:
– ISO 9001 for quality management.
– CE marking for compliance with European safety standards.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Whenever possible, request samples or demonstrations of the hydraulic pumps you are considering. This allows you to evaluate the build quality and performance firsthand before committing to a larger order.
– Why This Matters:
– Testing a sample can reveal potential issues and help you make a more informed decision based on actual performance metrics.

Illustrative image related to pump for hydraulic cylinder
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers and compare not just the purchase price but also the total cost of ownership. Consider factors such as maintenance costs, warranty terms, and expected lifespan.
– Cost Breakdown:
– Analyze long-term operational costs, including energy consumption and potential repair expenses.
Step 6: Review Customer Feedback and Case Studies
Look for customer testimonials and case studies related to the pumps you are considering. Understanding the experiences of other businesses can provide valuable insights into the performance and reliability of the product.
– What to Look For:
– Feedback on durability, ease of use, and customer service from the supplier.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase Agreement
Once you have selected a supplier and product, negotiate the terms of the purchase agreement. Pay close attention to delivery timelines, payment terms, and after-sales support.
– Important Considerations:
– Ensure clarity on warranty coverage and service options available after the purchase to avoid future issues.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the sourcing process for hydraulic pumps, making informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pump for hydraulic cylinder Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Pumps for Hydraulic Cylinders?
When sourcing pumps for hydraulic cylinders, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. Key components contributing to the overall cost include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.

Illustrative image related to pump for hydraulic cylinder
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences costs. High-strength alloys or specialized composites for durability will increase material costs. Conversely, opting for standard materials can reduce expenses but may compromise performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can be influenced by local wage rates, skill levels, and labor laws. Automated processes may lower labor costs but require upfront investments in technology.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient operations can minimize overhead, impacting pricing competitiveness.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific designs adds to initial costs but may reduce production time and improve product quality in the long run.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure product reliability and performance, which can increase costs but are essential for maintaining brand reputation and customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs vary significantly based on distance, mode of transport, and volume. International shipping incurs additional tariffs and customs fees, which must be factored into the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin based on their costs and market conditions. Understanding the market landscape can help buyers gauge acceptable margins.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Hydraulic Pumps?
Several factors can influence the pricing of hydraulic pumps, particularly in international markets.
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to discounts due to economies of scale. Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can also dictate pricing structures, with suppliers often more willing to negotiate on larger contracts.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom pumps designed to specific requirements typically come at a premium. Buyers should balance the need for customization against budget constraints.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Premium materials and certifications (e.g., ISO standards) can increase costs. Buyers should assess whether these enhancements are necessary for their application.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and location of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their reliability and quality assurance processes.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can significantly impact total costs. Buyers should be aware of responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs duties, which can vary widely.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Prices in the B2B Pump Market?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation strategies can lead to more favorable pricing.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Understanding market prices and benchmarks for similar products can empower buyers during negotiations. Gathering multiple quotes allows for informed comparisons.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Buyers should consider not just the purchase price but the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational costs, and disposal at the end of the product’s lifecycle. This broader perspective can justify higher upfront costs for more efficient products.
-
Negotiation Flexibility: Being open to different terms, such as longer payment periods or accepting slightly longer lead times, can create opportunities for cost savings.
-
Building Relationships: Establishing strong supplier relationships can lead to better pricing and service. Long-term partnerships often result in more favorable terms and priority during high-demand periods.
What Pricing Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
International buyers must navigate unique pricing challenges, including currency fluctuations and regional market dynamics.
-
Currency Exchange Rates: Fluctuations in currency can impact pricing significantly. Buyers should consider locking in exchange rates or using hedging strategies to mitigate risks.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Understanding local regulations regarding imports can help avoid unexpected costs. Compliance with local safety standards and certifications may be required, adding to the total expense.
-
Cultural Factors: Different regions may have varying expectations regarding negotiation styles, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Being culturally aware can enhance negotiations and foster trust.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of cost components, price influencers, and negotiation strategies is crucial for B2B buyers sourcing hydraulic pumps. By strategically evaluating these factors, buyers can optimize their purchasing decisions and achieve better financial outcomes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pump for hydraulic cylinder With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Hydraulic Power
When considering hydraulic systems, particularly for applications involving hydraulic cylinders, it’s essential to explore various power solutions. While a dedicated pump for hydraulic cylinders is a popular choice, alternative technologies may offer unique benefits tailored to specific operational needs. This analysis compares hydraulic pumps with two viable alternatives: electric linear actuators and pneumatic cylinders, allowing B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and application suitability.

Illustrative image related to pump for hydraulic cylinder
| Comparison Aspect | Pump For Hydraulic Cylinder | Electric Linear Actuator | Pneumatic Cylinder |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High force, continuous operation | Moderate force, variable speed | Quick response, lower force |
| Cost | Medium to high investment | Generally lower initial cost | Low to medium initial cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires setup of hydraulic lines | Simple installation | Easy to install, less complex |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed | Low maintenance | Moderate maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Heavy lifting, industrial applications | Precise positioning, automation | Rapid actuation in light tasks |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Linear Actuators: A Versatile Solution
Electric linear actuators convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, providing a clean and efficient alternative to hydraulic systems. They are particularly effective for applications requiring precise control and positioning, such as robotics and automation. The initial investment tends to be lower than hydraulic systems, and they require minimal maintenance. However, they may not deliver the same level of force as hydraulic pumps, making them less suitable for heavy lifting tasks.
Pneumatic Cylinders: Fast and Efficient for Light-Duty Tasks
Pneumatic cylinders utilize compressed air to create motion, offering rapid actuation and a relatively straightforward installation process. They excel in applications where speed is essential, such as assembly lines and packaging machinery. The cost of pneumatic systems is generally lower, making them attractive for budget-conscious operations. However, they often provide less force compared to hydraulic systems and may require a reliable air supply, which can be a limitation in some environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate power solution for hydraulic cylinders involves weighing the pros and cons of each option against specific operational requirements. For heavy-duty applications requiring high force and continuous operation, hydraulic pumps remain the optimal choice. Conversely, if precision and automation are paramount, electric linear actuators may be preferable. For tasks where speed is critical, pneumatic cylinders could be the ideal fit. B2B buyers should evaluate their unique needs, including budget, application, and maintenance capabilities, to determine the most suitable hydraulic power solution for their operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pump for hydraulic cylinder
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Pumps for Hydraulic Cylinders?
Understanding the technical properties of pumps used in hydraulic cylinders is essential for B2B buyers, particularly when making purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications:

Illustrative image related to pump for hydraulic cylinder
-
Pressure Rating (PSI)
The pressure rating, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI), indicates the maximum pressure the pump can handle. For hydraulic applications, typical ratings range from 1,500 to 10,000 PSI. A higher pressure rating allows for heavier lifting capabilities, making it crucial for industries such as construction and manufacturing where performance under load is vital. -
Flow Rate (GPM)
The flow rate, expressed in gallons per minute (GPM), measures how quickly the pump can deliver hydraulic fluid to the cylinder. This specification impacts the speed of operations; higher flow rates enable faster actuation of hydraulic cylinders. For example, a pump with a flow rate of 5 GPM will fill a cylinder more quickly than one with a 2 GPM rating, directly affecting productivity. -
Power Source
Hydraulic pumps can be powered in various ways, including hand-operated, electric, pneumatic, or battery-powered. Each power source has its advantages depending on the application. Electric pumps are preferred for continuous operations, while hand-operated pumps are suitable for portable and less frequent use. Understanding power source compatibility is critical for ensuring optimal operation in the intended environment. -
Material Composition
The materials used in the construction of the pump influence durability, weight, and corrosion resistance. Common materials include aluminum, cast iron, and stainless steel. For instance, stainless steel pumps are ideal for harsh environments due to their resistance to corrosion, making them a good choice for industries like marine and chemical processing. -
Mounting Configuration
The mounting configuration refers to how the pump is installed, which can vary based on application needs. Common configurations include flange mounting and bracket mounting. The correct configuration ensures that the pump operates efficiently within the hydraulic system and minimizes vibration and wear.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Pumps for Hydraulic Cylinders?
Familiarity with industry terminology can significantly enhance communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common trade terms related to hydraulic pumps:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that manufactures products or components that are used in another company’s end products. In the context of hydraulic pumps, OEM specifications are critical for ensuring compatibility and quality, as they guarantee that the components meet the original design standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for procurement, especially for businesses looking to maintain inventory levels without overcommitting financially. This term helps buyers negotiate terms that align with their operational needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request price quotes from suppliers for specific products. This process helps in comparing prices and terms from various vendors, enabling informed purchasing decisions. An effective RFQ includes detailed specifications to ensure accurate quotes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand their obligations and reduces the risk of unexpected costs. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. In hydraulic pump procurement, lead time can vary based on factors like manufacturing schedules and shipping logistics. Understanding lead time is crucial for project planning and ensuring timely delivery. -
Hydraulic Fluid Compatibility
This term refers to the types of fluids that can be safely used with a pump without causing damage or inefficiency. Different hydraulic fluids have varying chemical properties, and ensuring compatibility is essential for maintaining system integrity and performance.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when selecting pumps for hydraulic cylinders, ultimately improving operational efficiency and reducing costs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pump for hydraulic cylinder Sector
What Are the Key Trends Influencing the Global Pump for Hydraulic Cylinder Market?
The global market for pumps used in hydraulic cylinders is witnessing significant growth, driven by several factors. One of the primary drivers is the ongoing industrialization and urbanization, particularly in emerging economies across Africa, South America, and Southeast Asia, including Vietnam and Brazil. These regions are experiencing a surge in construction and manufacturing activities, necessitating robust hydraulic systems for machinery and equipment.
Furthermore, technological advancements are reshaping the landscape. The integration of smart technologies, such as IoT sensors and automation systems, is enhancing the efficiency and performance of hydraulic pumps. Buyers are increasingly looking for pumps that offer real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities, reducing downtime and increasing operational efficiency.

Illustrative image related to pump for hydraulic cylinder
Another emerging trend is the shift towards customizable hydraulic solutions. B2B buyers are seeking suppliers that can offer tailored pump systems that meet specific operational requirements, such as varying pressure and flow rates. This flexibility is crucial for businesses looking to optimize their hydraulic systems for different applications.
Additionally, the competitive pricing strategy adopted by manufacturers is impacting sourcing decisions. Buyers are now more inclined to compare prices and features across different suppliers, emphasizing the importance of value for money in their procurement processes.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Pump for Hydraulic Cylinder Sector?
As environmental concerns continue to escalate, sustainability has become a pivotal consideration in the sourcing of hydraulic pumps. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using eco-friendly materials and processes. The demand for ‘green’ certifications is on the rise, with buyers looking for products that comply with environmental regulations and standards.
The environmental impact of hydraulic systems is multifaceted, encompassing energy consumption, waste generation, and resource depletion. As a result, companies are seeking pumps designed for energy efficiency, which not only reduce operational costs but also minimize their carbon footprint. Innovations in pump technology, such as variable displacement pumps, are gaining traction for their ability to optimize energy usage based on demand.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is becoming a critical aspect of procurement strategies. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing their supply chains to ensure that materials are sourced responsibly and that manufacturers adhere to ethical labor practices. This focus on transparency not only enhances brand reputation but also fosters long-term partnerships based on shared values.
What Is the Historical Context Behind the Development of Hydraulic Pumps?
The evolution of hydraulic pumps can be traced back to the early 20th century when hydraulic systems began to gain traction in various industrial applications. Initially, these systems were rudimentary, relying on simple mechanical designs. However, as industries expanded, so did the need for more efficient and reliable hydraulic solutions.
The introduction of variable displacement pumps in the 1960s marked a significant advancement, allowing for greater control over flow rates and pressure. This innovation paved the way for more complex hydraulic systems that could meet the demands of modern machinery.
Over the decades, advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques have further refined hydraulic pump technology, leading to the development of pumps that are lighter, more durable, and capable of operating at higher pressures. Today, the integration of digital technologies represents the latest chapter in the evolution of hydraulic pumps, positioning them as critical components in the automation of industrial processes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pump for hydraulic cylinder
-
How do I choose the right pump for my hydraulic cylinder application?
Selecting the right pump involves understanding the specifications and requirements of your hydraulic system. Consider factors such as the required pressure (PSI), flow rate (GPM), and the type of hydraulic fluid used. Additionally, assess the operational environment—whether it will be exposed to extreme temperatures or corrosive substances. Consulting with a knowledgeable supplier or engineer can help ensure you select a pump that meets your operational needs effectively. -
What is the best type of pump for hydraulic cylinders?
The best type of pump depends on your specific application. Common options include gear pumps for lower-pressure applications, piston pumps for high-pressure systems, and vane pumps for moderate pressures. Piston pumps, especially variable displacement models, are often favored for their efficiency and ability to handle varying loads. Evaluate your application’s pressure requirements, flow rates, and any space constraints to determine the most suitable pump type. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for hydraulic pumps?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers, often ranging from a single unit for specialized items to larger batches for standard models. For international buyers, it’s essential to communicate your needs clearly to suppliers. Some manufacturers may offer flexibility on MOQs for established clients or during promotional periods. Always inquire about possible discounts for bulk orders, as this can significantly reduce your per-unit cost. -
How can I ensure the quality of the hydraulic pumps I purchase?
To ensure quality, source pumps from reputable manufacturers with established industry standards. Request certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicate adherence to quality management practices. Conduct thorough supplier vetting by checking references and reviews from previous clients. Additionally, ask for product samples or performance testing data to assess reliability before making a larger commitment. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing hydraulic pumps internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely, but common options include upfront payment, 30/60/90-day net terms, or letters of credit. For international transactions, consider using escrow services to protect your investment. Always clarify payment methods accepted by the supplier, whether bank transfers, credit cards, or trade financing options. Negotiating favorable payment terms can enhance cash flow and mitigate risks associated with international trade. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing hydraulic pumps?
When importing, factor in shipping costs, customs duties, and potential delays at border crossings. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with handling hydraulic equipment to streamline the shipping process. Verify that the supplier provides necessary documentation, such as bills of lading and customs invoices. Additionally, consider insurance options to protect your investment against loss or damage during transit. -
Can I customize hydraulic pumps to fit my specific requirements?
Many manufacturers offer customization options to tailor hydraulic pumps to your specific needs. This may include adjustments to pressure ratings, flow rates, or physical dimensions. Discuss your requirements with the supplier during the initial inquiry phase. Customization may involve additional costs and longer lead times, so it’s crucial to plan accordingly and communicate your needs early in the sourcing process. -
What should I do if I encounter issues with my hydraulic pump after purchase?
If issues arise, first consult the supplier’s warranty and return policy. Most reputable manufacturers provide support for troubleshooting and may offer repairs or replacements for defective products. Document any problems thoroughly, including operational conditions and performance metrics, to facilitate the claims process. Maintaining open communication with the supplier can help resolve issues efficiently and ensure continued operational efficiency.
Top 4 Pump For Hydraulic Cylinder Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Enerpac – Hydraulic Cylinder and Pump Sets
Domain: enerpac.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic Cylinder and Pump Sets, ready-to-use, includes single-acting hydraulic jack (ram), two-speed pump, 6-foot hose, calibrated gauge, gauge adaptor. Available with 5 to 100 ton jacks in general purpose, center hole, and low-height options. Hydraulic pump options: hand, foot, air, and battery-powered models. Free freight on orders over $100. Bonus savings: 3%, 5%, or 8%. Offer ends 29th Augus…
2. Fluidyne & OMFB – Hydraulic Piston Pumps
Domain: baileyhydraulics.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic Piston Pumps available from brands Fluidyne and OMFB. Key specifications include: PSI ratings up to 5800, GPM ratings ranging from 15.7 to 52.3, RPM options from 500 to 3300, and various cubic inch displacements (CID) including 1.10, 1.71, 2.75, 3.66, 4.33, 5.59, and 6.71. Mounting options include 2 bolt A, B, C flanges, ISO 80MM 4B, and SAE-C 4B. Shaft types include straight keyed and s…
3. Hydro-Pack – Hydraulic Piston Hand Pump
Domain: magisterhyd.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Brand: Hydro-Pack, Action: Single Acting, CID: 1.5 and 2.7, Tank Material: Steel, Working Ports: 3/8″ NPTF, Pressure: 3600 PSI, Capacity: 1 QT, 3 QTs, 5 QTs, Piston Action: Double function, Products: Hydraulic piston hand pump 1.5 CID with release knob for single acting cylinder (1 QT tank, $155.00), Hydraulic piston hand pump 1.5 CID with release knob for single acting cylinder (3 QT tank, $160.0…
4. MSC Industrial Supply – Hydraulic Power Units & Pumps
Domain: mscdirect.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: This company, MSC Industrial Supply – Hydraulic Power Units & Pumps, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pump for hydraulic cylinder
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of pumps for hydraulic cylinders offers significant advantages for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the diverse range of hydraulic pump options—from variable volume piston pumps to integrated cylinder and pump sets—enables businesses to select the most efficient solutions tailored to their operational needs.

Illustrative image related to pump for hydraulic cylinder
Key takeaways emphasize the importance of evaluating supplier reliability, product specifications, and pricing structures to ensure optimal performance and value. Moreover, as industries increasingly prioritize sustainability and efficiency, sourcing pumps that minimize energy consumption and maintenance costs will become paramount.
Looking ahead, international buyers should leverage strategic sourcing to foster partnerships with reputable manufacturers and suppliers, ensuring access to innovative technologies and superior customer support. By doing so, businesses can not only enhance their operational capabilities but also position themselves for growth in a competitive landscape. Engage with trusted suppliers today to explore the best hydraulic pump solutions tailored for your specific needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to pump for hydraulic cylinder