Top 7 3/3 Way Solenoid Valve Suppliers (And How to Choose)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 3/3 way solenoid valve
In today’s competitive global marketplace, sourcing the right 3/3 way solenoid valve can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers, especially when considering factors such as application requirements, supplier reliability, and cost-effectiveness. These valves play a crucial role in various industries, from automotive to food processing, by controlling the flow of fluids with precision and efficiency. As international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including Brazil and Nigeria) seek to optimize their operations, understanding the nuances of 3/3 way solenoid valves becomes imperative.
This comprehensive guide aims to empower B2B buyers by providing an in-depth exploration of 3/3 way solenoid valves. We will cover various types, their applications across different industries, and essential criteria for supplier vetting. Additionally, we will delve into cost considerations and best practices for installation and maintenance, ensuring that you make informed purchasing decisions. By the end of this guide, you will be equipped with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of the global market for solenoid valves, enabling you to select the right solutions that meet your operational needs while maximizing efficiency and reliability. With this information at your fingertips, you can confidently engage with suppliers and enhance your procurement strategies.
Understanding 3/3 way solenoid valve Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normally Closed (NC) | Exhaust port open when de-energized; directs flow when energized. | HVAC systems, chemical processing, automotive | Pros: Prevents fluid buildup; reliable in critical applications. Cons: Limited flow direction options. |
| Normally Open (NO) | Exhaust port closed when de-energized; allows flow when energized. | Irrigation systems, pneumatic controls | Pros: Ideal for applications requiring immediate flow. Cons: Risk of uncontrolled fluid flow when power is lost. |
| 3-Position (Tandem Center) | Offers three distinct positions: advance, hold, and return. | Hydraulic systems, machinery control | Pros: Versatile control for complex systems; enhances safety. Cons: More complex installation and maintenance. |
| Body Ported Valve | Integrated piping for compact installation; suitable for high flow. | Industrial automation, robotics | Pros: Space-saving design; high flow capacity. Cons: May require specialized fittings. |
| Pilot Operated Valve | Uses pilot pressure to control larger flows; energy-efficient. | Oil and gas, water treatment | Pros: Handles high pressure with lower energy usage. Cons: Potentially more complex in design and operation. |
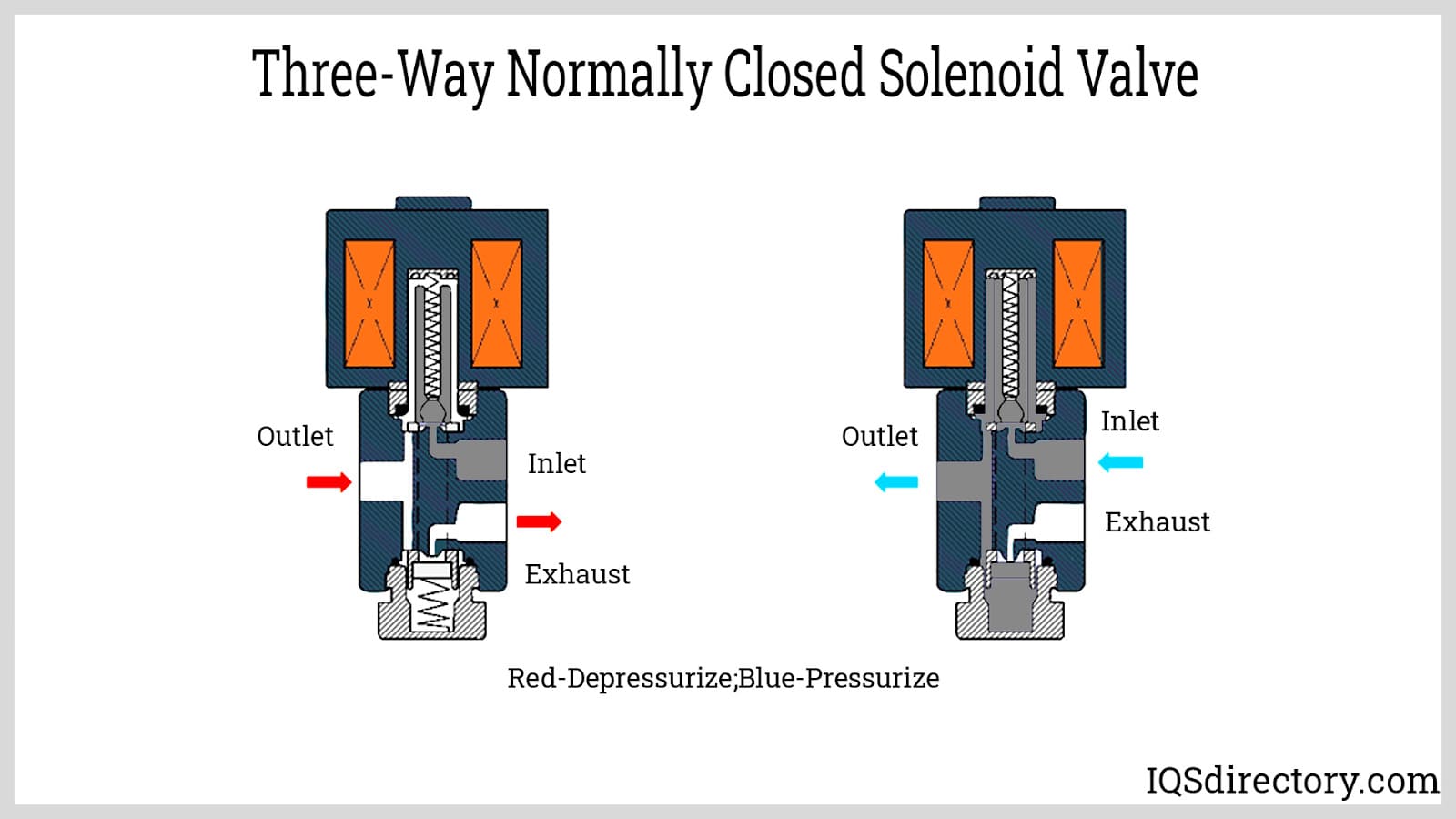
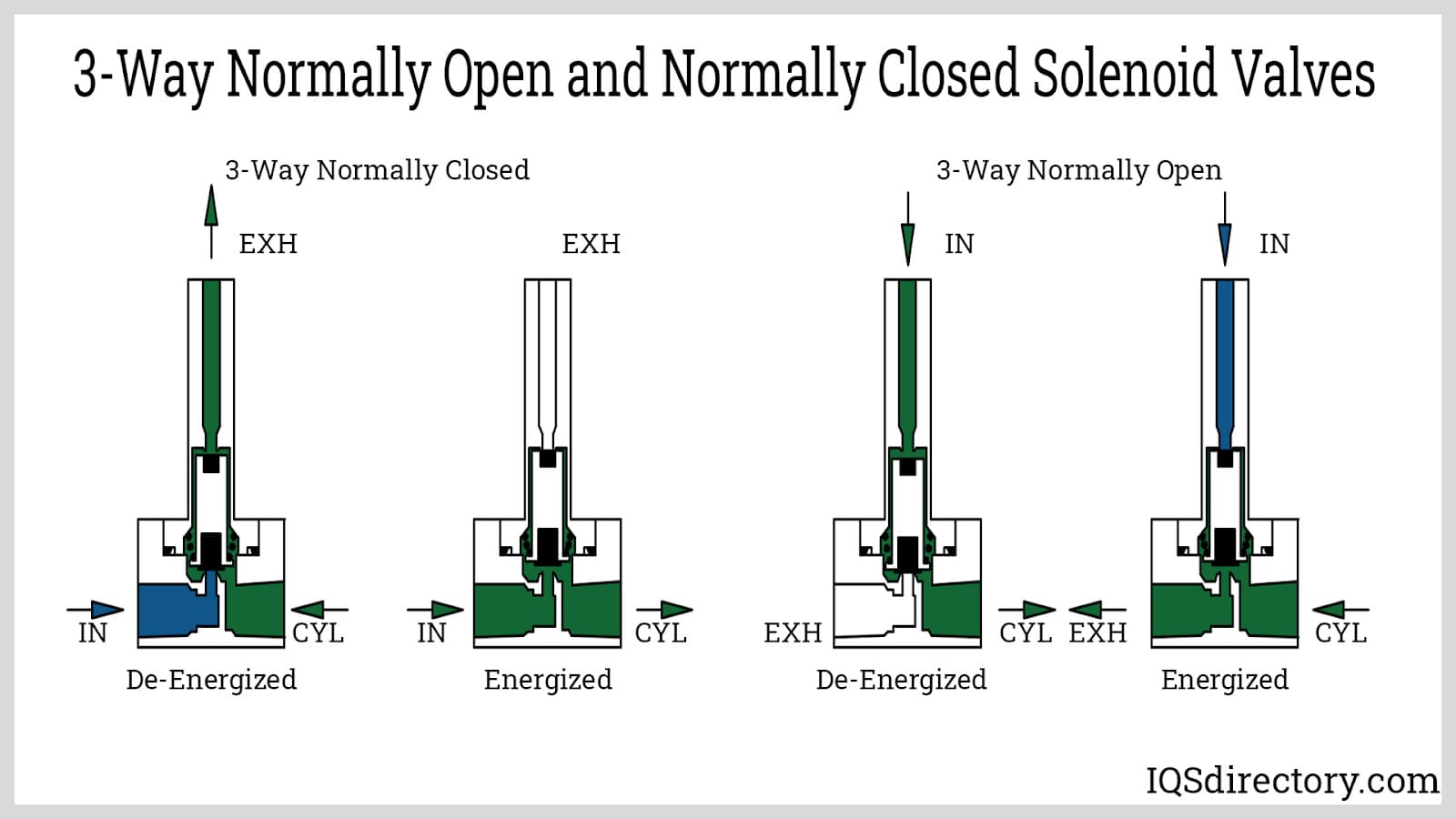
What are the characteristics and suitability of Normally Closed (NC) 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves?
Normally Closed (NC) 3/3 way solenoid valves maintain the exhaust port open when de-energized, allowing for pressure release. They are widely used in HVAC systems and chemical processing, where controlling the flow of media is crucial to prevent damage from pressure buildup. Buyers should consider the valve’s compatibility with the fluid type and ensure it meets the pressure and temperature specifications of their application. The reliability of NC valves in critical systems often outweighs their limitations in flow direction options.
How do Normally Open (NO) 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves differ in functionality?
Normally Open (NO) valves keep the exhaust port closed when de-energized, permitting fluid flow when energized. This design is particularly beneficial in irrigation systems and pneumatic controls where immediate flow is necessary. However, buyers must be aware of the risk of uncontrolled fluid flow in case of power loss, making it essential to evaluate the application’s safety measures. The immediate responsiveness of NO valves can significantly enhance operational efficiency in time-sensitive applications.
What advantages do 3-Position (Tandem Center) 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves provide?
3-Position (Tandem Center) valves offer three distinct operational states: advance, hold, and return. This versatility is crucial in hydraulic systems and machinery control, providing enhanced safety and control in complex applications. Buyers should consider the additional complexity in installation and maintenance, as these valves often require more intricate setups. The capability to maintain pressure without continuous power makes them a valuable choice for applications where load stability is paramount.
Why choose Body Ported Valves for industrial applications?
Body ported valves integrate piping directly into the valve body, allowing for a compact installation that is ideal for high flow applications in industrial automation and robotics. Their space-saving design can be a significant advantage in environments with limited space. However, buyers should assess the need for specialized fittings, which may increase initial costs. The high flow capacity of body ported valves makes them suitable for demanding applications requiring efficient media control.
What makes Pilot Operated Valves a preferred choice in high-pressure scenarios?
Pilot operated valves utilize pilot pressure to manage larger flow volumes, making them an energy-efficient choice for applications in the oil and gas or water treatment sectors. Their ability to handle high pressures while consuming less energy is a key selling point for B2B buyers. However, the complexity of design and operation may require specialized knowledge for installation and maintenance. Understanding the operational environment and pressure requirements is critical when selecting pilot operated valves for specific applications.
Key Industrial Applications of 3/3 way solenoid valve
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 3/3 way solenoid valve | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| HVAC | Temperature control in heating and cooling systems | Enhances energy efficiency and precision in climate control | Ensure compatibility with specific HVAC systems and energy ratings |
| Agriculture | Automated irrigation systems | Optimizes water usage and reduces labor costs | Look for durability in harsh environments and compatibility with various media |
| Automotive | Coolant flow management in engine systems | Improves engine efficiency and performance | Consider pressure ratings and material compatibility with fluids |
| Chemical Processing | Flow control for mixing and transferring chemicals | Ensures safety and precision in chemical handling | Verify chemical compatibility and compliance with industry standards |
| Food and Beverage | Automation in food processing and packaging | Enhances productivity and maintains hygiene standards | Source valves with certifications for food safety and hygiene |
How Are 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves Utilized in HVAC Systems?
In HVAC applications, 3/3 way solenoid valves play a crucial role in managing the flow of hot and cold water, allowing for rapid switching to achieve desired temperatures. This flexibility enhances energy efficiency, as it ensures that systems operate optimally based on real-time demand. Buyers in this sector should prioritize valves that are compatible with their specific HVAC configurations and ensure they meet energy efficiency standards relevant to their region.
What Role Do 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves Play in Agriculture?
In the agricultural sector, 3/3 way solenoid valves are integral to automated irrigation systems, allowing for the precise control of water flow to various areas of a farm. This automation not only optimizes water usage, reducing waste, but also lowers labor costs associated with manual irrigation methods. Buyers should consider the valve’s durability, especially in harsh environmental conditions, and ensure compatibility with the specific types of fluids used in their irrigation systems.
How Are 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves Used in the Automotive Industry?
In automotive applications, these valves manage coolant flow within engine systems, ensuring that temperature control is maintained for optimal engine performance. By allowing for precise control over coolant flow, they help prevent overheating and improve fuel efficiency. Buyers should focus on sourcing valves that can withstand high-pressure environments and are compatible with the specific fluids used in their vehicles to ensure reliable performance.
What Are the Applications of 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves in Chemical Processing?
In chemical processing, 3/3 way solenoid valves are essential for controlling the flow of various chemicals, enabling safe and efficient mixing and transferring. They help mitigate risks associated with pressure build-up and ensure accurate dosing of chemicals. Buyers must verify that the valves are compatible with the chemicals being handled and compliant with industry safety standards, which is particularly important for international buyers operating in diverse regulatory environments.
How Do 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves Benefit the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, 3/3 way solenoid valves facilitate automation in processing and packaging lines, contributing to enhanced productivity and adherence to hygiene standards. These valves enable precise control over the flow of liquids, ensuring that products are processed efficiently without contamination. Buyers should prioritize sourcing valves that meet food safety certifications and can handle the specific media involved in their operations, ensuring compliance with health regulations across different markets.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘3/3 way solenoid valve’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Fluid Control in Automated Systems
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face challenges with inconsistent fluid control in automated systems. In industries such as food processing or chemical manufacturing, precise flow management is crucial. A malfunctioning or improperly specified 3/3 way solenoid valve can lead to irregular fluid flow, resulting in production delays, wasted resources, and potential safety hazards. For example, if a valve fails to open or close correctly, it may disrupt the intended flow path, causing contamination or pressure buildup that could damage sensitive equipment.
The Solution:
To mitigate this issue, buyers should prioritize selecting high-quality 3/3 way solenoid valves specifically designed for their application’s fluid characteristics. It’s essential to evaluate the valve’s compatibility with the media being controlled, considering factors like viscosity, temperature, and pressure. Buyers should consult manufacturers’ chemical compatibility databases and seek guidance from technical support teams to ensure they select the right materials. Additionally, implementing regular maintenance schedules and monitoring systems can help detect issues early, ensuring consistent performance and reducing downtime.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Installation and Integration
The Problem:
Many buyers encounter significant hurdles during the installation and integration of 3/3 way solenoid valves into existing systems. This can stem from a lack of clear technical specifications or compatibility issues with other components. In regions with limited technical support, such as parts of Africa or South America, the absence of local expertise can exacerbate these difficulties, leading to improper installation and functionality concerns.
Illustrative image related to 3/3 way solenoid valve
The Solution:
To streamline the installation process, buyers should choose solenoid valves that come with comprehensive installation guides and customer support. Engaging with suppliers who offer on-site installation assistance or training can also be invaluable. Furthermore, before purchasing, it’s advisable to verify compatibility with existing systems by requesting detailed technical specifications and possibly a demo or trial unit. This proactive approach allows for adjustments before full-scale implementation, ensuring a smoother integration process.
Scenario 3: Costly Operational Inefficiencies
The Problem:
Operational inefficiencies related to energy consumption are a common pain point for buyers of 3/3 way solenoid valves. Many manufacturers are under pressure to reduce operational costs while maintaining efficiency. However, if the solenoid valves in use are not energy-efficient, they can significantly increase operational expenses due to higher electricity bills and maintenance costs. This is especially critical in industries where profit margins are slim, such as agriculture and manufacturing.
The Solution:
Buyers should focus on sourcing energy-efficient solenoid valves that are designed for low power consumption. Understanding the power requirements of different valve types is crucial; opting for models that utilize pulse width modulation (PWM) or low-voltage options can reduce energy costs. Additionally, implementing smart control systems that optimize valve operation based on real-time demand can lead to substantial savings. Regularly reviewing operational data can help identify inefficiencies, allowing businesses to make informed decisions about upgrades or replacements that enhance overall energy efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 3/3 way solenoid valve
What Are the Key Materials Used in 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves?
When selecting materials for 3/3 way solenoid valves, it is essential to consider their properties and how they align with specific application requirements. Here, we analyze four common materials used in these valves: brass, stainless steel, plastic, and aluminum. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly impact performance, durability, and suitability for various media.
How Does Brass Perform in 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves?
Brass is a popular choice for solenoid valves due to its excellent corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 180°C and can handle pressures of around 10 bar. The advantages of brass include its durability and resistance to wear, making it suitable for applications involving water, air, and gas. However, brass can be more expensive than plastic and may not be ideal for highly corrosive environments, such as those involving saltwater or aggressive chemicals. For international buyers, brass valves often comply with ASTM standards, making them a reliable choice in markets like Europe and the Middle East.
What Are the Benefits of Stainless Steel for Solenoid Valves?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments. It can withstand temperatures up to 300°C and pressures exceeding 20 bar, making it suitable for demanding applications, including chemical processing and food industries. The primary advantage of stainless steel is its longevity, which can lead to lower maintenance costs over time. However, the manufacturing complexity and higher cost of stainless steel can be prohibitive for some buyers. Compliance with international standards such as DIN and JIS is crucial for buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where quality assurance is paramount.
How Do Plastics Compare in Terms of Cost and Application?
Plastic materials, such as polyamide and polycarbonate, offer a lightweight and cost-effective alternative to metals. They are generally suitable for lower pressure and temperature applications, typically rated up to 80°C and 6 bar. The main advantage of plastic solenoid valves is their resistance to corrosion and chemical attack, making them ideal for applications involving aggressive fluids. However, plastics may not provide the same level of durability and mechanical strength as metals, which can limit their use in high-stress environments. For international buyers, ensuring that plastic materials meet relevant compliance standards is crucial, especially in regulated industries.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Solenoid Valve Manufacturing?
Aluminum is another viable option for solenoid valves, known for its lightweight and good strength-to-weight ratio. It can handle temperatures up to 150°C and pressures around 10 bar. The advantages of aluminum include its resistance to corrosion and ease of machining, which can lower manufacturing costs. However, aluminum may not be as durable as brass or stainless steel in high-stress applications. For buyers in regions like Brazil and Nigeria, aluminum valves should meet local standards to ensure compatibility with specific media and environmental conditions.
Summary of Material Selection for 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves
| Material | Typical Use Case for 3/3 Way Solenoid Valve | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | Water, air, and gas applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, not suitable for aggressive chemicals | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Chemical processing, food industry | Exceptional strength and durability | High manufacturing complexity and cost | High |
| Plastic | Aggressive fluid applications | Lightweight and cost-effective | Limited durability and pressure rating | Low |
| Aluminum | General industrial applications | Lightweight and easy to machine | Less durable than brass or stainless steel | Medium |
In conclusion, the choice of material for 3/3 way solenoid valves is critical for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Each material has its unique advantages and limitations, which should be carefully considered based on the specific application and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 3/3 way solenoid valve
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves?
The manufacturing process of 3/3 way solenoid valves involves several critical stages, ensuring that the final product meets high standards of performance and reliability. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves?
Material preparation begins with sourcing high-quality materials, typically brass, stainless steel, or plastic, depending on the application and environmental conditions. Suppliers must ensure that materials meet specific standards for corrosion resistance and strength. This stage may involve various tests to verify the material’s properties, such as tensile strength and ductility. Proper documentation should be maintained to trace material origins, which is vital for compliance with international standards.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
During the forming stage, techniques such as machining, stamping, and molding are employed to create the valve components. Precision machining is critical for parts like the valve body and solenoid, ensuring tight tolerances that facilitate optimal sealing and operation. Advanced CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are commonly used to achieve the required precision. Additionally, forming processes must align with environmental regulations, especially for buyers in regions with stringent manufacturing laws.
How Are 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves Assembled?
The assembly stage involves combining the formed components into a complete valve. This process typically follows a systematic approach, often utilizing automated assembly lines to enhance efficiency and reduce human error. Key components such as the solenoid coil, plunger, and valve body are meticulously assembled, with particular attention paid to the alignment and sealing of parts. Quality checks are integrated at this stage to ensure that each assembly meets the design specifications.
What Finishing Processes Are Critical for 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves?
Finishing processes include surface treatments such as plating, anodizing, or painting, which enhance the durability and corrosion resistance of the valve. These treatments are especially important for valves used in harsh environments, such as those in the chemical processing or automotive industries. Final inspections are conducted to ensure that the surface finish meets industry standards, and any defects are addressed before the product moves to packaging.
What International Standards Guide Quality Assurance for 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves?
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of 3/3 way solenoid valves is guided by several international standards. ISO 9001 is a fundamental standard that outlines the criteria for a quality management system, focusing on consistent quality and customer satisfaction. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, compliance with CE marking requirements is crucial for products sold within the European Union, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Established?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically established throughout the manufacturing process. These typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint examines the raw materials and components before they enter production. Suppliers must provide certification and test results to validate that materials meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular inspections are performed to monitor the quality of components and assembly. This helps in identifying defects early, reducing waste and rework.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before packaging, a comprehensive final inspection is conducted. This includes functional testing of the valves, ensuring they operate correctly under specified conditions.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves?
Testing methods for 3/3 way solenoid valves include:
-
Pressure Testing: Valves are subjected to pressure tests to ensure they can withstand operational pressures without leaking.
-
Functional Testing: This involves operating the valve under simulated conditions to ensure it responds correctly to electrical signals and that the flow paths function as intended.
-
Leak Testing: Using methods such as helium leak detection, manufacturers can identify any potential leaks that may compromise the valve’s performance.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control measures of their suppliers:
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of the supplier’s manufacturing facilities can help assess compliance with quality standards and identify areas for improvement.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports that outline the QC processes, test results, and certifications can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance, especially for international transactions where local compliance may differ.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local regulations and compliance requirements is essential. Different markets may have varying standards for materials and safety, which can affect product acceptance. It’s crucial for buyers to establish clear communication with suppliers regarding these requirements and ensure that all products are certified accordingly.
Additionally, buyers should be aware of the potential for cultural differences in business practices, which can influence the reliability of quality assurance processes. Engaging with suppliers who have a proven track record in international trade can help mitigate these risks and ensure a smoother procurement process.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with 3/3 way solenoid valves, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure reliable and high-quality products for their applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘3/3 way solenoid valve’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of a 3/3 way solenoid valve requires careful consideration of various technical and supplier-related factors. This checklist aims to guide international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, through a structured process to ensure they secure the right product for their applications.
Illustrative image related to 3/3 way solenoid valve
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your technical requirements is essential before sourcing a 3/3 way solenoid valve. Consider the flow rate, pressure and temperature ranges, and the type of media (air, water, chemicals) that will be controlled. Each application may demand different specifications, so documenting these details helps in narrowing down the options.
- Flow Rate: Ensure the valve can handle the expected volume of media.
- Pressure and Temperature: Verify that the valve’s ratings match your system’s operational conditions.
Step 2: Research Available Valve Types
Familiarize yourself with the different types of 3/3 way solenoid valves available on the market. Options may include normally closed, normally open, and 3-position valves, each serving distinct functions in fluid control. Understanding these variations will help you select a valve that aligns with your specific operational needs.
- Configuration Options: Assess whether a 3-position valve is necessary for your application.
- Material Compatibility: Ensure the valve material is suitable for the type of media being used.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. This step ensures that the supplier has a proven track record and can meet your quality and service expectations.
- Certifications: Look for ISO certifications or industry-specific standards that the supplier complies with.
- Customer Reviews: Analyze feedback from previous customers to gauge reliability and support.
Step 4: Request Samples or Prototypes
Where possible, request samples or prototypes of the valves you are considering. Testing a sample allows you to verify the valve’s performance in your specific application environment before making a bulk purchase. This step can save time and costs associated with returns or failures.
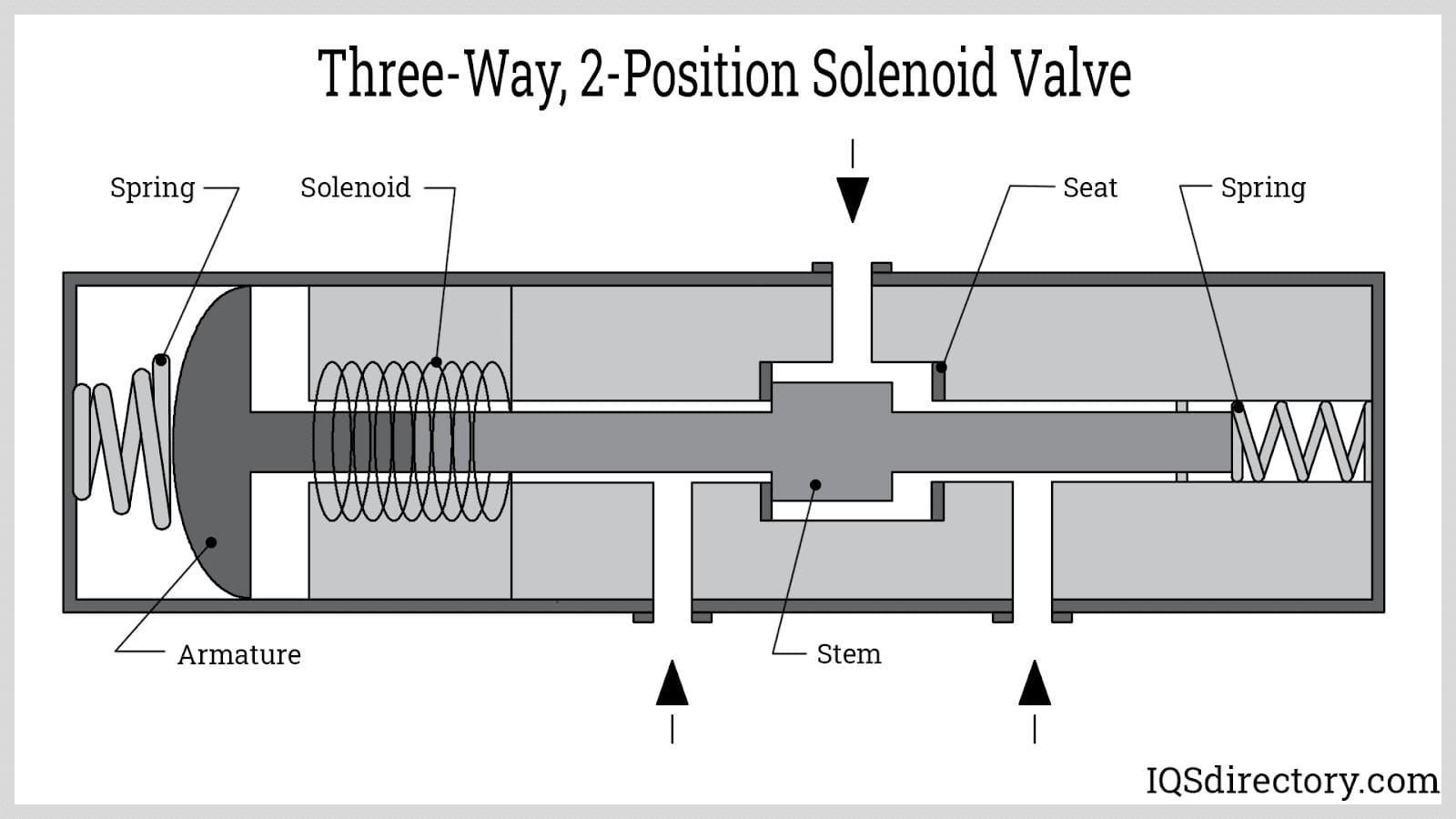
Illustrative image related to 3/3 way solenoid valve
- Performance Testing: Assess the valve’s functionality under actual operating conditions.
- Installation Compatibility: Ensure the sample fits seamlessly into your existing system.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers and products, compare pricing and terms. Look beyond the initial purchase price; consider factors such as warranty, after-sales service, and shipping costs. Understanding the total cost of ownership will help you make a more informed decision.
- Bulk Purchase Discounts: Inquire about pricing structures for larger orders.
- Payment Terms: Clarify payment options, including deposits and credit terms.
Step 6: Verify Technical Support and Warranty
Ensure that the supplier offers robust technical support and a comprehensive warranty for their products. A responsive support team can assist with installation, troubleshooting, and maintenance, which is vital for minimizing downtime.
- Warranty Coverage: Understand what is covered under the warranty and for how long.
- Support Availability: Check if technical assistance is available locally or during your operational hours.
Step 7: Finalize and Place Your Order
Once you’ve completed the previous steps and feel confident in your choice, finalize the order. Confirm the specifications, delivery timeline, and any additional services. Clear communication at this stage helps ensure a smooth procurement process.
- Order Confirmation: Double-check that all details match your requirements.
- Follow-Up: Stay in contact with the supplier to track the order status and address any potential issues promptly.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process for 3/3 way solenoid valves, ensuring they select the right product for their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 3/3 way solenoid valve Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Sourcing 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves?
When sourcing 3/3 way solenoid valves, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Brass, stainless steel, and plastic are common materials used in solenoid valves. Each material has varying costs, durability, and suitability for specific applications, which can affect pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary depending on the region of production. In regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of South America and Africa, manufacturers may offer more competitive pricing. However, skilled labor is essential for ensuring quality, especially for custom valve solutions.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory maintenance, utilities, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower overhead costs, which can be passed on to buyers.
-
Tooling: The initial setup costs for molds and dies used in production can be significant, especially for custom valves. These costs are amortized over production runs, making it crucial to consider order volume.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in quality control is critical to ensure the reliability and performance of solenoid valves. Certifications such as ISO and industry-specific standards can add to costs but are essential for maintaining product integrity.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary based on the shipping method and distance. International buyers should account for additional costs associated with customs, tariffs, and insurance, which can significantly influence total expenses.
-
Margin: Supplier margins vary based on market competition, brand reputation, and relationship with buyers. Understanding the markup can help in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Affect 3/3 Way Solenoid Valve Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of 3/3 way solenoid valves, making it essential for buyers to consider these when sourcing.
-
Volume/MOQ: Manufacturers often have a minimum order quantity (MOQ) that can affect pricing. Bulk orders typically lead to cost savings per unit, while smaller orders may incur higher prices.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom valves tailored to specific requirements will generally be more expensive than standard models. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unnecessary costs.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects performance but also costs. Premium materials designed for high-pressure applications will result in higher prices, while standard materials may offer cost savings.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards or have specific certifications are typically priced higher due to the additional testing and validation processes involved.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer entrants may offer lower prices to capture market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping (Incoterms) is crucial for international buyers. These terms define responsibilities for shipping costs, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly impact the total cost.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves?
To maximize value when sourcing 3/3 way solenoid valves, buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in negotiations to secure better pricing, especially for larger orders. Building a long-term relationship can also lead to discounts and favorable terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs. Lower upfront costs may not always translate to overall savings.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations and international shipping complexities, which can affect pricing.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Conduct thorough research on multiple suppliers to compare pricing, quality, and service. Request samples when possible to evaluate performance before committing to larger orders.
-
Stay Updated on Market Trends: Understanding current market trends and technological advancements can help buyers make informed decisions and capitalize on new opportunities.
By considering these factors, international B2B buyers can make strategic decisions that optimize their sourcing of 3/3 way solenoid valves while managing costs effectively.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 3/3 way solenoid valve With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves
In the realm of fluid control systems, 3/3 way solenoid valves serve as a popular choice due to their versatility and efficiency. However, various alternative technologies can also effectively manage fluid flow. This section explores these alternatives, comparing their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance requirements, and best use cases.

Illustrative image related to 3/3 way solenoid valve
Comparison of 3/3 Way Solenoid Valve with Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | 3/3 Way Solenoid Valve | Pneumatic Actuator | Manual Ball Valve |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Fast actuation, precise control | Moderate response time, suitable for high flow | Reliable but slower operation |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost, low operational cost | Higher initial cost, variable operational costs | Low initial cost, no ongoing energy costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy installation, minimal wiring | More complex setup requiring compressed air | Simple to install, no power required |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, occasional cleaning needed | Moderate maintenance for air lines | Low maintenance, infrequent replacement |
| Best Use Case | HVAC, automotive, chemical processing | High-flow applications, automation systems | Simple on/off applications, low-pressure systems |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Pneumatic Actuators
Pneumatic actuators utilize compressed air to produce mechanical motion, offering a reliable solution for high-flow applications. They excel in environments where speed and force are crucial, making them suitable for automation systems. However, they come with a higher initial investment and require a dedicated air supply, complicating installation. Maintenance involves regular checks of air lines and filters, which can add to operational costs over time.
Manual Ball Valves
Manual ball valves are a straightforward and cost-effective alternative. They are designed for simple on/off control, making them ideal for low-pressure systems. With no reliance on electricity or compressed air, they are easy to install and maintain. However, their operation is manual, which can slow down processes that require quick adjustments. For applications where flow regulation is not frequently needed, they present a viable solution at a lower cost.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution
When selecting the appropriate fluid control solution, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific application requirements, budget constraints, and operational efficiency goals. While 3/3 way solenoid valves offer fast and reliable performance in diverse applications, alternatives like pneumatic actuators and manual ball valves can provide significant benefits in specific contexts. Understanding the trade-offs between performance, cost, and maintenance will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and long-term objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 3/3 way solenoid valve
Understanding the key technical properties and terminology associated with 3/3 way solenoid valves is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when making informed purchasing decisions. This section provides valuable insights into essential specifications and commonly used trade terms.
What Are the Critical Technical Specifications of 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves?
-
Material Grade
The material of construction significantly impacts the valve’s durability and suitability for various applications. Common materials include brass, stainless steel, and plastic. Brass valves offer good corrosion resistance and are suitable for water and air applications, while stainless steel is preferred for chemical processing due to its robustness against harsh environments. -
Pressure Rating
This specification indicates the maximum pressure the valve can safely handle, typically measured in psi (pounds per square inch) or bar. Understanding the pressure rating is vital for ensuring that the valve operates effectively within the system’s requirements, preventing leaks or failures that could disrupt operations. -
Flow Rate
The flow rate, measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per minute (LPM), determines how quickly the fluid can pass through the valve. A higher flow rate means better efficiency in systems like HVAC or irrigation, allowing for optimal performance in applications requiring quick media transfer. -
Operating Voltage
Most solenoid valves operate on specific voltages, commonly 12V, 24V, or 110V AC/DC. Selecting the right voltage is crucial for compatibility with existing electrical systems. Misalignment can lead to malfunctions or even damage to the valve. -
Temperature Range
The operating temperature range indicates the conditions under which the valve can function effectively. Valves designed for high-temperature applications are essential in industries like automotive and chemical processing, where extreme temperatures are common. -
Actuation Type
Solenoid valves can be normally open (NO) or normally closed (NC), affecting how they control fluid flow. Understanding the actuation type is crucial for application-specific setups, ensuring that the valve responds correctly to electrical signals.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce components that are used in the manufacturing of other products. In the context of solenoid valves, OEMs may provide customized valves tailored to specific industry needs, emphasizing the importance of selecting reputable manufacturers for quality assurance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQs is essential for B2B buyers, as it can influence inventory management and overall procurement strategies, especially for smaller businesses or those with lower usage rates. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. For buyers, submitting an RFQ for 3/3 way solenoid valves can streamline the purchasing process, allowing for better comparisons and negotiations. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are internationally recognized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery obligations, which is crucial when importing valves from international suppliers. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the products. Knowing the lead time for 3/3 way solenoid valves is important for planning and ensuring that projects remain on schedule, especially in industries where timely installation is critical. -
Certification Standards
Many industries require products to meet specific certification standards (e.g., ISO, CE) to ensure safety and performance. Buyers should verify that solenoid valves comply with relevant standards to mitigate risks and ensure product reliability.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms can empower B2B buyers to make well-informed decisions when selecting 3/3 way solenoid valves, enhancing operational efficiency and project success.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 3/3 way solenoid valve Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the 3/3 Way Solenoid Valve Sector?
The global market for 3/3 way solenoid valves is experiencing significant growth, driven by various industrial applications in sectors such as automotive, HVAC, chemical processing, and food production. Key trends indicate a rising demand for automation and smart technologies, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As industries increasingly adopt Industry 4.0 principles, the integration of IoT devices with solenoid valves is becoming commonplace, enhancing real-time monitoring and control capabilities.
International buyers are also witnessing a shift towards energy-efficient solutions, with manufacturers focusing on designs that reduce power consumption while maintaining performance. The versatility of 3/3 way solenoid valves allows for configurations that adapt to specific media types, whether gas, liquid, or vacuum, making them a preferred choice for many applications. Furthermore, as manufacturing processes become more complex, the need for valves with quick response times and reliability is paramount.
Additionally, regulatory standards are evolving, emphasizing the need for compliance with safety and environmental guidelines. Buyers must stay informed about these changes to ensure their sourcing strategies align with market demands and regulatory requirements.

Illustrative image related to 3/3 way solenoid valve
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the 3/3 Way Solenoid Valve Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are increasingly critical in the manufacturing of 3/3 way solenoid valves. The environmental impact of valve production—ranging from resource extraction to manufacturing processes—necessitates a focus on reducing carbon footprints and promoting eco-friendly practices. Manufacturers are adopting sustainable materials and technologies, such as recyclable metals and energy-efficient production methods, which not only minimize environmental damage but also appeal to a growing base of environmentally conscious buyers.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing their suppliers’ practices, seeking certifications that demonstrate a commitment to responsible sourcing. Green certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, can enhance a company’s reputation and marketability.
Furthermore, companies that prioritize sustainability often find themselves at a competitive advantage, as they can tap into markets that are willing to pay a premium for environmentally friendly products. By aligning sourcing strategies with sustainability goals, international buyers can contribute to a healthier planet while meeting the demands of their end customers.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of 3/3 Way Solenoid Valves?
The evolution of 3/3 way solenoid valves dates back to the early 20th century, during which the principles of electromagnetism were harnessed for fluid control applications. Initially, these valves were mechanical, requiring manual operation, which limited their efficiency and precision. The introduction of solenoid technology revolutionized the industry, enabling remote operation and automation.
As industries grew and the demand for precision control increased, the designs of 3/3 way solenoid valves evolved to include features such as faster response times, improved durability, and the capability to handle a wider variety of fluids and gases. This evolution has been influenced by advancements in materials science, allowing for the development of valves that can withstand harsher environments and operate under higher pressures.
Today, the ongoing integration of digital technologies and IoT capabilities into solenoid valve design is setting the stage for the next phase of innovation, making these valves not just components of fluid control systems but integral parts of smart manufacturing processes. As a result, the future of 3/3 way solenoid valves looks promising, with continuous improvements in functionality and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 3/3 way solenoid valve
-
How do I select the right 3/3 way solenoid valve for my application?
Selecting the right 3/3 way solenoid valve involves understanding your specific application needs. Key factors include the type of media (liquid, gas, or vacuum), flow rate, pressure, and temperature requirements. Additionally, consider the electrical specifications such as voltage and frequency. It’s advisable to consult a chemical compatibility database if you are handling various fluids. Ensuring the valve’s material is suitable for your application will also prevent premature failure and enhance durability. -
What are the common applications for 3/3 way solenoid valves?
3/3 way solenoid valves are versatile and used in numerous applications, including HVAC systems for temperature control, irrigation systems for automated water distribution, and the automotive industry for regulating coolant flow. They are also prominent in chemical processing, where they manage the flow of various chemicals efficiently. Understanding your specific application will help you leverage the full potential of these valves. -
What customization options are available for 3/3 way solenoid valves?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for 3/3 way solenoid valves to meet specific operational needs. Customizations can include variations in port sizes, materials (like brass or stainless steel), and electrical configurations. Additionally, you can request specific features like manual overrides or different actuator types. It’s essential to communicate your requirements clearly to the supplier to ensure the valve meets your operational standards. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for 3/3 way solenoid valves?
The minimum order quantity for 3/3 way solenoid valves can vary significantly by manufacturer and product specifications. Generally, MOQs can range from as low as 10 units for standard products to several hundred for specialized or customized valves. When sourcing from international suppliers, inquire about their MOQs upfront to avoid any surprises during the procurement process. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing 3/3 way solenoid valves internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of 3/3 way solenoid valves typically include options like upfront payment, net 30, or letter of credit, depending on the supplier’s policies. It’s crucial to clarify these terms before finalizing your order to ensure alignment with your financial processes. Additionally, consider currency exchange rates and potential transaction fees that may arise in international dealings. -
How can I ensure the quality of 3/3 way solenoid valves from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of 3/3 way solenoid valves, conduct thorough supplier vetting. Look for manufacturers with certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Request product samples and technical specifications to assess their performance. Additionally, consider suppliers with a robust warranty and return policy, as this reflects their confidence in product quality. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing 3/3 way solenoid valves?
Logistics considerations for importing 3/3 way solenoid valves include shipping methods, customs duties, and lead times. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with your region’s import regulations. It’s also essential to account for potential delays in customs clearance and to ensure that all necessary documentation, such as invoices and certificates of origin, is in order to facilitate a smooth import process. -
What is the typical lead time for 3/3 way solenoid valves from order to delivery?
Lead times for 3/3 way solenoid valves can vary based on the supplier, customization requirements, and order quantity. Standard lead times range from 2 to 6 weeks for off-the-shelf products, while customized orders may take longer, often up to 12 weeks or more. Always confirm lead times with your supplier at the outset to ensure your project timelines are met effectively.
Top 7 3/3 Way Solenoid Valve Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Electric Solenoid Valves – 3 Way Solenoid Valves
Domain: electricsolenoidvalves.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: 3 Way Solenoid Valves are used for controlling the flow of water, air, vacuum, or other low viscosity fluids. They have three ports: an inlet port, an outlet port, and an exhaust port. The exhaust port vents or releases pressure or fluid, preventing buildup. Key features include flexibility in configuration, energy efficiency, reliability, versatility for various applications (HVAC, irrigation, au…
2. Pneumadyne – 3-Way 3-Position Valves
Domain: pneumadyne.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: 3-Way 3-Position Valves are dual function products that contain two valves in one body with a common input and common exhaust. They can be used as independent 3-way valves or as a 4-way (5/3) with an Open Center. Common applications include pneumatic pilot control for hydraulic valves and controlling the motion of air motors. Features include anodized and electroless nickel plating for corrosion a…
3. McMaster – Three-Way Solenoid Valves
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Three-Way Solenoid Valves, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
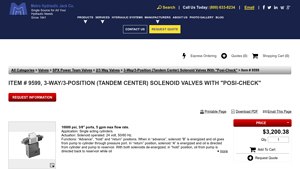
4. Metro Hydraulic – 3-Way/3-Position Solenoid Valve
Domain: metrohydraulic.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: {“Item Number”: “9599”, “Type”: “3-Way/3-Position (Tandem Center) Solenoid Valve”, “Posi-Check Feature”: true, “Pressure Rating”: “10000 psi”, “Max Flow Rate”: “5 GPM”, “Port Size”: “3/8 inches”, “Functions”: [“Advance”, “Hold”, “Return”], “Actuation”: “Solenoid operated”, “Voltage”: “24 V”, “Frequency”: “50/60 Hz”, “Weight”: “14.0 lbs”, “Shipping Weight”: “14.6 lbs”, “Application”: “Single Acting…
5. SMC – VEX3 3 Port Valve
Domain: smcusa.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: VEX3, 3 Port 3 Position Valve, Body Ported
6. Solenoid Solutions Inc – 3-Way Normally Open Solenoid Valves
Domain: solenoidsolutionsinc.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
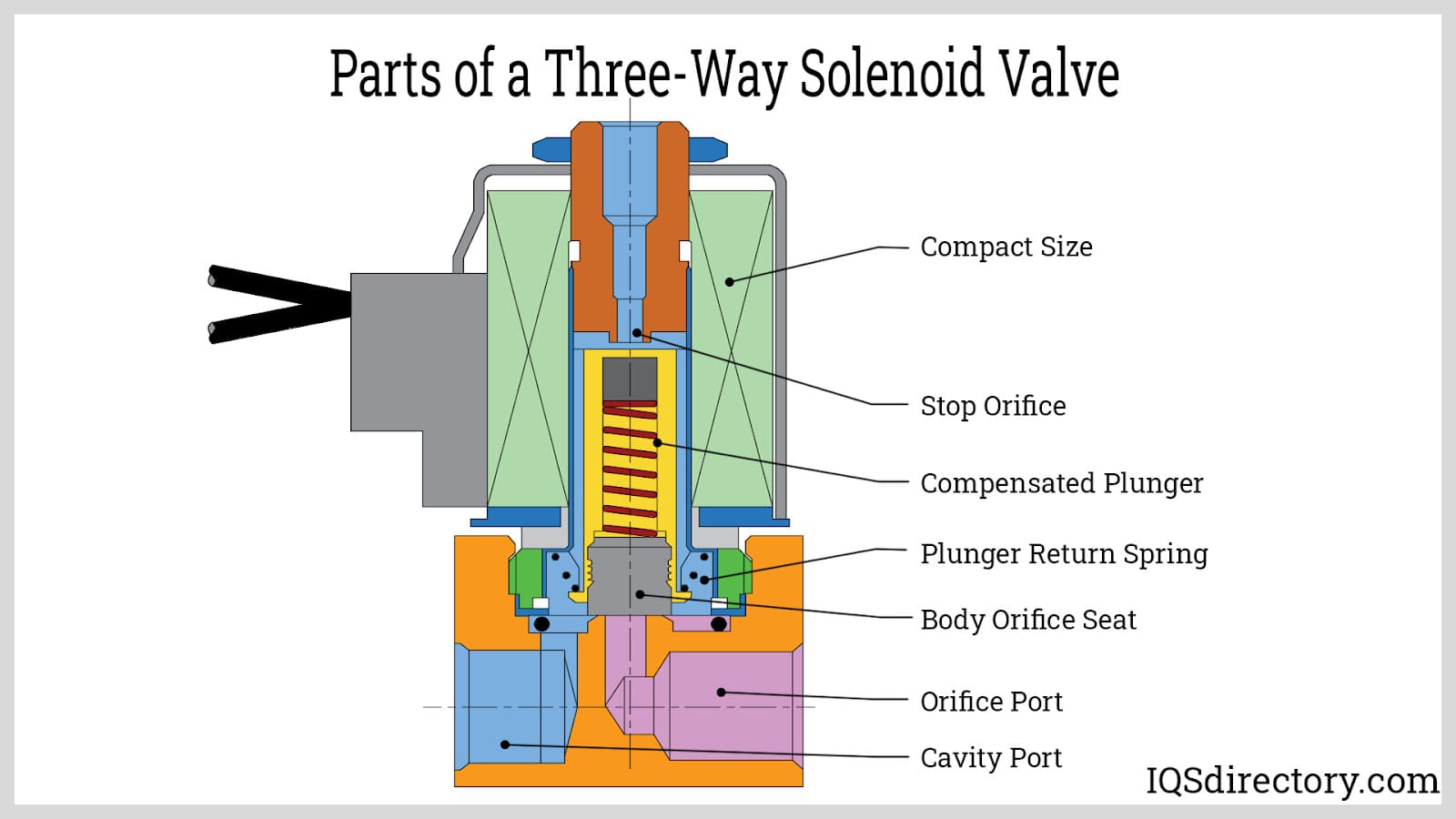
Introduction: Different Types of 3-Way Valves include: 1. 3-way Normally Open Solenoid Valves: – 3 pipe connections (cavity port, body orifice port, stop port) – 2 orifices (body orifice and stop orifice) – Power off: plunger raised, seals stop orifice, opens body orifice. – Power on: plunger down, seals body orifice, opens stop orifice. 2. 3-way Normally Closed Solenoid Valves: – 3 pipe connections (cavity por…
7. Emerson – Three-Way Solenoid Valves
Domain: emerson.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, Emerson – Three-Way Solenoid Valves, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 3/3 way solenoid valve
In the evolving landscape of industrial automation, the strategic sourcing of 3/3 way solenoid valves offers significant advantages to businesses across various sectors. These valves, renowned for their versatility, reliability, and energy efficiency, are integral to applications ranging from HVAC systems to chemical processing. By understanding the unique requirements of your operations—such as flow rates, pressure specifications, and the types of media being controlled—B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance system performance and reduce operational costs.
Investing in high-quality solenoid valves not only mitigates the risk of system malfunctions but also streamlines maintenance processes, ultimately leading to increased productivity. As international markets, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, continue to expand, now is the time for buyers to leverage strategic sourcing to secure the best products at competitive prices.
Looking ahead, businesses that prioritize robust supplier relationships and adopt innovative sourcing strategies will be well-positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities. Engage with reputable manufacturers and distributors to explore how 3/3 way solenoid valves can drive efficiency in your operations. The future of fluid control is promising—make sure your organization is part of it.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.