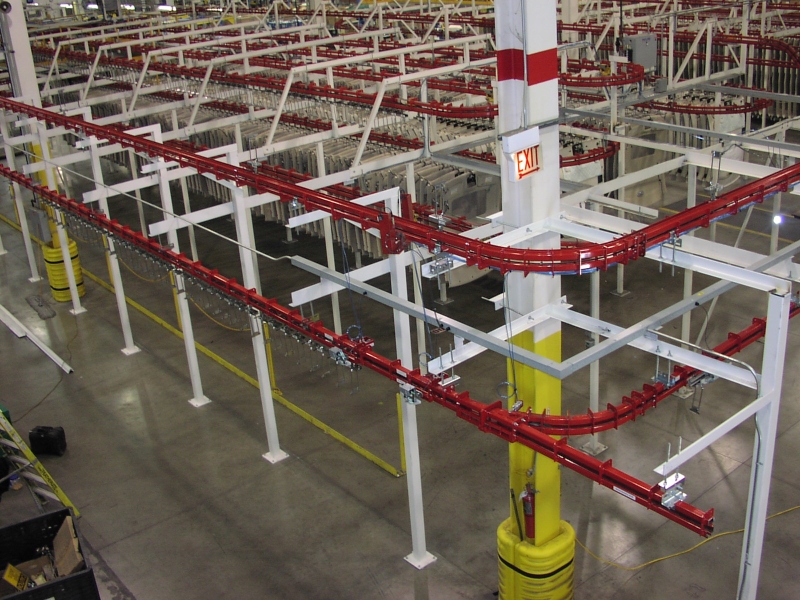
Power And Free Conveyor: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for power and free conveyor
In today’s competitive landscape, international B2B buyers face the pressing challenge of sourcing efficient and adaptable solutions for their material handling needs, particularly when it comes to power and free conveyors. These innovative systems, which combine the benefits of powered and free movement, offer unparalleled flexibility for managing production lines, storage solutions, and assembly processes. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, providing insights into the various types of power and free conveyor systems, their diverse applications, and the critical factors to consider when selecting a supplier.
Navigating the complexities of the global market requires an informed approach, especially for buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where industrial demands differ significantly. We delve into essential aspects such as system design, cost considerations, and supplier vetting processes, empowering you to make educated purchasing decisions. By understanding the intricacies of power and free conveyors, from their modular designs to advanced control systems, you can optimize your operations and enhance productivity.
This guide not only equips you with the knowledge needed to choose the right conveyor solution for your specific requirements but also helps you identify reliable suppliers who can deliver tailored solutions that align with your business goals. Embrace the opportunity to transform your material handling processes and drive operational excellence in your organization.
Understanding power and free conveyor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overhead Power and Free | Twin-track system with a power chain above and free trolleys below | Paint application, assembly lines | Pros: Space-saving, flexible routing; Cons: Higher initial setup cost. |
| Inverted Power and Free | Similar to overhead but designed for floor-mounted applications | Automotive assembly, parts delivery | Pros: Efficient use of floor space; Cons: Limited to specific layouts. |
| Heavy-Duty Power and Free | Built to handle heavier loads (up to 40,000 lbs) | Heavy manufacturing, logistics operations | Pros: High load capacity; Cons: Requires more robust infrastructure. |
| Modular Power and Free | Customizable sections and components for tailored solutions | Custom manufacturing processes | Pros: Flexibility in design; Cons: Complexity in installation and maintenance. |
| Automated Power and Free | Integrated with advanced control systems for automation | High-volume production, warehousing | Pros: Increased efficiency and reduced labor costs; Cons: Higher technology investment. |
What are the characteristics of Overhead Power and Free Conveyors?
Overhead Power and Free conveyors utilize a dual-track system where the power chain runs above and the free trolleys carry the product load below. This configuration allows for efficient space utilization, making it ideal for operations like paint application and assembly lines. Buyers should consider the initial investment and installation complexity, as these systems require careful planning to maximize their benefits.
How do Inverted Power and Free Conveyors function in a B2B environment?
Inverted Power and Free conveyors operate similarly to overhead systems but are mounted to the floor, supporting loads from beneath. This design is particularly effective in automotive assembly and parts delivery, as it allows for seamless integration into existing workflows. When purchasing, businesses should evaluate their layout and ensure that the system aligns with their operational needs.
What sets Heavy-Duty Power and Free Conveyors apart from other types?
Heavy-Duty Power and Free conveyors are engineered to manage substantial loads, ranging from 25 lbs to 40,000 lbs. This makes them suitable for heavy manufacturing and logistics operations where durability and strength are paramount. Buyers must assess their infrastructure capabilities, as these systems may necessitate additional support and maintenance resources.
Why choose Modular Power and Free Conveyors for customized applications?
Modular Power and Free conveyors offer a customizable solution with various sections and components that can be tailored to specific manufacturing processes. This flexibility makes them ideal for businesses that require unique layouts. However, potential buyers should be aware that this customization can lead to increased complexity in installation and ongoing maintenance.
How do Automated Power and Free Conveyors enhance operational efficiency?
Automated Power and Free conveyors incorporate advanced control systems, allowing for seamless integration into high-volume production environments and warehousing operations. They significantly enhance efficiency and reduce labor costs by automating material handling processes. Businesses should consider the upfront technological investment and the potential for long-term savings when evaluating these systems.
Key Industrial Applications of power and free conveyor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Power and Free Conveyor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Parts storage and assembly line sequencing | Increases efficiency by allowing asynchronous operations | Ensure compatibility with existing systems and scalability options. |
| Aerospace | Component painting and curing processes | Reduces cycle time and enhances product quality | Look for systems that accommodate heavy payloads and specific environmental controls. |
| Electronics | Final assembly and testing of electronic components | Enhances flexibility and reduces labor costs | Consider automation integration and the ability to handle delicate components. |
| Food and Beverage | Packaging and labeling processes | Streamlines operations and improves hygiene standards | Evaluate systems for compliance with food safety regulations. |
| Metal Fabrication | Transporting metal parts through various processing stages | Improves workflow and reduces manual handling risks | Assess load capacities and the need for specialized components like lifts or drops. |
How is Power and Free Conveyor Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive sector, power and free conveyors are utilized for parts storage and assembly line sequencing. This application allows for asynchronous operations, meaning that individual carriers can stop and start independently, which enhances flexibility in production processes. By implementing these systems, automotive manufacturers can significantly reduce cycle times and improve throughput. International buyers should focus on sourcing systems that can integrate seamlessly with existing conveyor systems and allow for future scalability as production demands change.
What Role Does Power and Free Conveyor Play in Aerospace?
In aerospace manufacturing, power and free conveyors are essential for component painting and curing processes. These conveyors facilitate the movement of parts through various treatment stations while maintaining precise control over processing times. This capability helps reduce cycle times and ensures that components meet stringent quality standards. Buyers in this sector must prioritize sourcing conveyors that can support heavy payloads and provide necessary environmental controls, such as temperature and humidity regulation, to protect sensitive materials.
How Does Power and Free Conveyor Enhance Electronics Manufacturing?
For the electronics industry, power and free conveyors are used in the final assembly and testing of electronic components. These systems allow for high flexibility, enabling manufacturers to adapt quickly to changes in product design or production volume. The separation of trolleys from the power chain facilitates efficient loading and unloading processes, which can lead to reduced labor costs. Buyers should consider sourcing systems equipped with automation capabilities that can handle delicate components without risk of damage.
In What Ways Does Power and Free Conveyor Benefit Food and Beverage Processing?
In the food and beverage industry, power and free conveyors streamline packaging and labeling processes. By automating these tasks, businesses can enhance operational efficiency while ensuring compliance with stringent hygiene standards. The design of power and free systems allows for easy routing and accumulation of products, which is crucial in high-volume environments. International buyers should evaluate systems for compliance with food safety regulations and ensure they can accommodate specific industry requirements.

Illustrative image related to power and free conveyor
How is Power and Free Conveyor Applied in Metal Fabrication?
Power and free conveyors in metal fabrication are used to transport parts through various processing stages, such as welding, painting, and assembly. These systems significantly improve workflow by reducing manual handling risks and enhancing the overall efficiency of production lines. When sourcing for this application, it is critical to assess load capacities and the availability of specialized components, such as lift and drop sections, to meet the specific needs of the fabrication process.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘power and free conveyor’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inefficient Space Utilization in Manufacturing Facilities
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in manufacturing and assembly environments struggle with optimizing floor space. Traditional conveyor systems often require extensive ground-level infrastructure, limiting the available workspace for other essential operations. This inefficiency can lead to bottlenecks, reduced productivity, and increased operational costs, especially in facilities where space is at a premium. Buyers may also find it challenging to integrate new conveyor systems with existing layouts without incurring significant redesign costs.
The Solution: Power and free conveyors provide a unique solution to this problem by allowing for overhead installation, freeing up valuable floor space. When sourcing a power and free conveyor system, buyers should focus on modular designs that offer flexibility in layout planning. Engage with suppliers who can provide customized solutions, including various track configurations and trolley designs tailored to specific operational needs. It’s also beneficial to conduct a thorough analysis of the production flow before installation. This analysis should include simulations or pilot testing to evaluate how different configurations can maximize space and efficiency. Additionally, leveraging advanced control systems that allow for asynchronous operation can help optimize the flow of materials without congesting the workspace below.
Scenario 2: High Maintenance Costs and Downtime
The Problem: Maintenance costs are a significant concern for B2B buyers operating power and free conveyors. Over time, wear and tear on the components, such as chains, trolleys, and drive units, can lead to unexpected downtime and costly repairs. Buyers often feel overwhelmed by the complexity of maintaining these systems, particularly if they lack in-house expertise or if the conveyor is part of a larger integrated system.
The Solution: To mitigate maintenance costs, it’s crucial to invest in quality components and systems designed for longevity. Buyers should prioritize vendors that offer comprehensive maintenance packages, including routine inspections, lubrication systems, and training for in-house maintenance staff. Implementing a proactive maintenance schedule can greatly reduce the risk of breakdowns. Additionally, selecting power and free conveyor systems with self-lubricating components can further lower maintenance frequency and costs. Investing in a user-friendly control system with monitoring capabilities will enable real-time diagnostics, allowing for timely interventions before minor issues escalate into major problems.
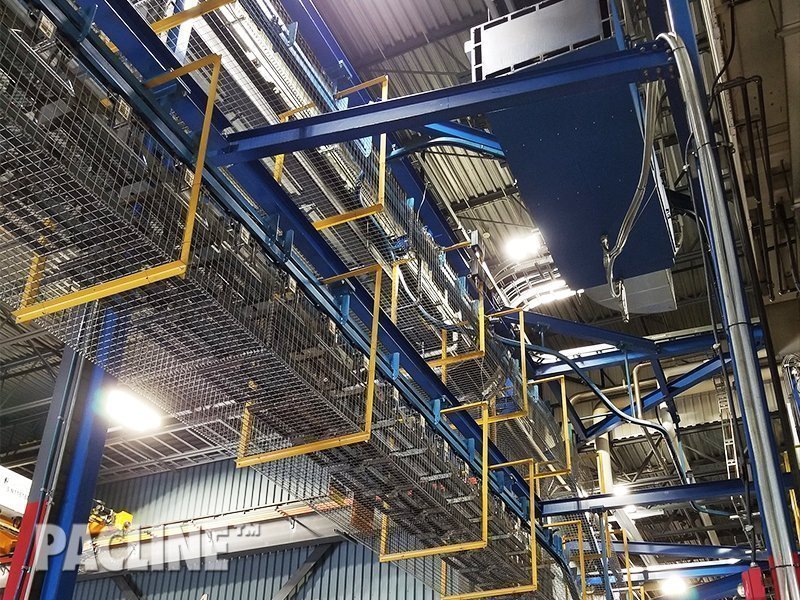

Illustrative image related to power and free conveyor
Scenario 3: Complex Integration with Existing Processes
The Problem: For many B2B buyers, integrating a new power and free conveyor system into existing production lines can be daunting. The need for seamless connectivity with other machinery and processes can complicate installations, leading to delays and increased costs. Buyers may face challenges in ensuring that the new system accommodates varying product sizes, weights, and handling requirements while still aligning with their operational objectives.
The Solution: To effectively integrate a power and free conveyor system, buyers should engage with suppliers who offer a consultative approach during the planning phase. It’s essential to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the existing processes and identify potential integration points. Look for suppliers that can provide tailored solutions, such as customizable trolleys that can accommodate different product specifications and automated controls that allow for easy synchronization with other equipment. Additionally, utilizing simulation software during the design phase can help visualize the entire system and identify any potential integration issues before implementation. Ensuring that the selected conveyor system has the flexibility to adapt to changes in production demands can also alleviate future integration challenges.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for power and free conveyor
What Are the Most Common Materials Used in Power and Free Conveyors?
Power and free conveyors are engineered for flexibility and efficiency, making material selection critical for optimal performance. Below are analyses of four common materials used in the construction of power and free conveyor systems, focusing on their properties, advantages and disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
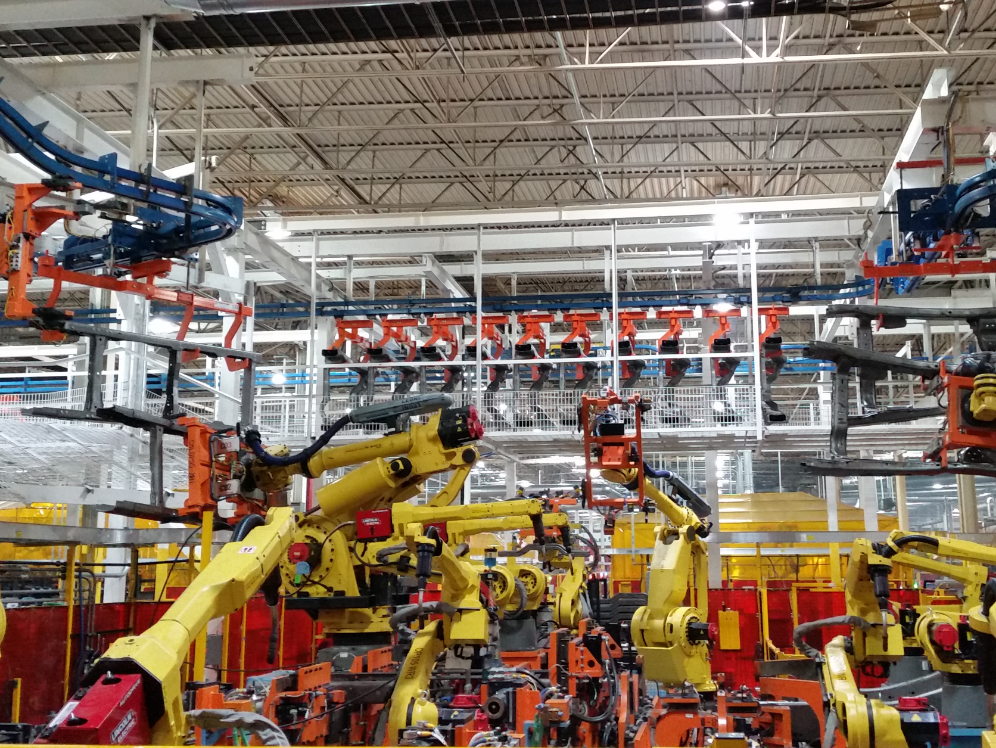

Illustrative image related to power and free conveyor
1. Steel: The Backbone of Conveyor Systems
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, with a typical temperature rating of up to 300°C (572°F).
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its robustness and longevity, which translates into lower replacement costs over time. However, steel is prone to corrosion, which can be a significant drawback in humid or chemically aggressive environments. The manufacturing complexity is moderate, with processes such as welding and machining required.
Impact on Application: Steel is particularly suitable for applications involving heavy loads and high wear, such as automotive assembly lines. However, its susceptibility to rust necessitates protective coatings or regular maintenance.
International Considerations: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should ensure compliance with ASTM or DIN standards for quality assurance. In regions with high humidity, selecting galvanized or stainless steel may be necessary to enhance corrosion resistance.
2. Aluminum: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight yet strong, with a temperature rating of approximately 150°C (302°F). Its natural corrosion resistance makes it suitable for various environments.
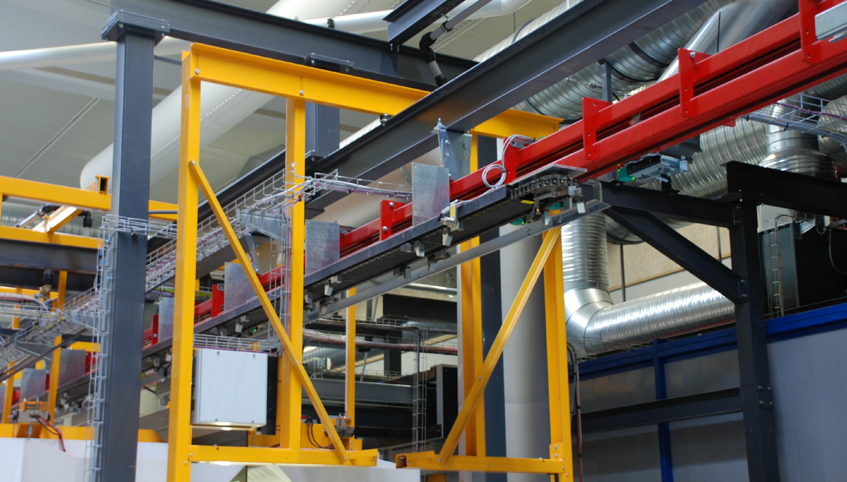

Illustrative image related to power and free conveyor
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which reduces the overall energy consumption of the conveyor system. However, it has a lower load-bearing capacity compared to steel, which may limit its use in heavy-duty applications. The manufacturing process is less complex, allowing for easier customization.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for applications requiring frequent changes in layout or where weight is a concern, such as in packaging and assembly lines. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for environments with moisture or chemicals.
International Considerations: Compliance with JIS standards is essential for buyers in Asia, while European buyers may prefer materials that meet EN standards. Additionally, aluminum’s recyclability aligns with sustainability goals prevalent in many international markets.
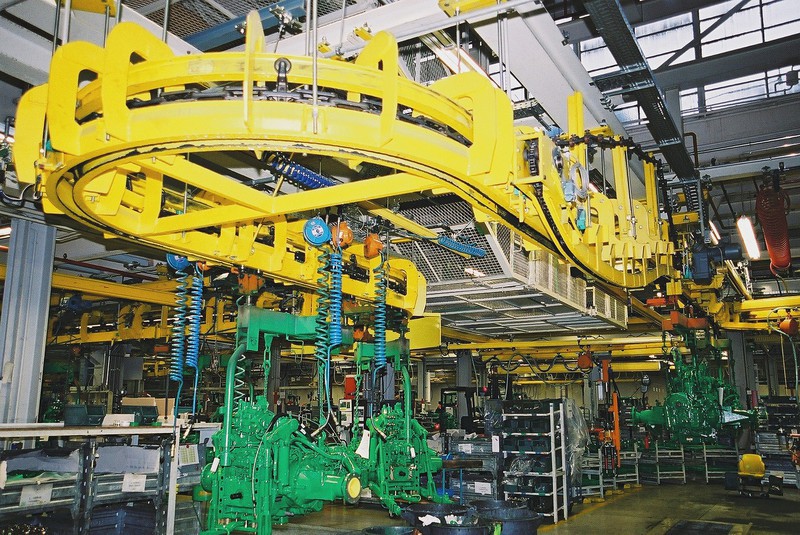

Illustrative image related to power and free conveyor
3. Stainless Steel: The Durable Choice for Harsh Environments
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand temperatures up to 600°C (1112°F), depending on the alloy used.
Pros & Cons: Its durability and resistance to corrosion make stainless steel an excellent choice for food processing and chemical applications. However, it is more expensive than regular steel and aluminum, which can impact budget considerations. The manufacturing complexity is higher due to the need for specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is particularly suited for environments where hygiene and cleanliness are paramount, such as in food and beverage production. Its ability to resist corrosion extends the lifespan of the conveyor system in harsh conditions.
International Considerations: Buyers should be aware of compliance with food safety standards (like FDA or EU regulations) when using stainless steel in food-related applications. Additionally, understanding the specific grade of stainless steel required for different applications is crucial.
4. Plastic: Versatile and Lightweight
Key Properties: Plastic components are lightweight and can operate effectively at temperatures up to 80°C (176°F). They are resistant to a variety of chemicals, making them suitable for specific applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of plastic is its versatility and resistance to corrosion. However, it may not be suitable for heavy loads or high-temperature applications, limiting its use. The manufacturing process can be complex, especially for custom designs.
Impact on Application: Plastic is often used in lighter applications such as packaging and assembly where weight and flexibility are key. Its chemical resistance makes it ideal for handling corrosive materials.
International Considerations: Buyers should ensure that the plastic materials used comply with relevant safety standards, such as REACH in Europe. Understanding the specific chemical compatibility of the plastic with the media being handled is also essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Power and Free Conveyors
| Material | Typical Use Case for Power and Free Conveyor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty applications | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight and flexible layouts | Low weight, energy-efficient | Lower load capacity | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, chemical applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Plastic | Light-duty applications | Versatile and corrosion-resistant | Limited load capacity and temperature range | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling them to make informed decisions based on application requirements and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for power and free conveyor
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Power and Free Conveyors?
The manufacturing process for power and free conveyors involves several critical stages, each contributing to the overall functionality and reliability of the final product. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess the quality and capability of potential suppliers.
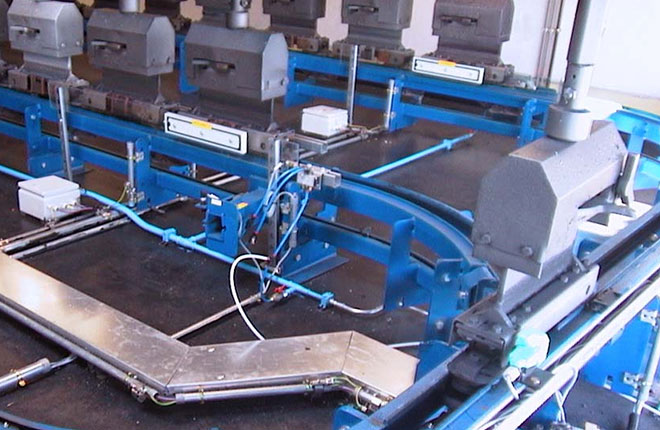

Illustrative image related to power and free conveyor
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used and How Are They Processed?
The first stage involves sourcing and preparing high-quality materials, primarily steel or aluminum for the tracks and trolleys. The choice of material significantly impacts durability, weight capacity, and resistance to environmental factors such as corrosion.
Materials undergo rigorous quality checks upon arrival at the manufacturing facility, ensuring they meet specific standards. Common practices include visual inspections and the use of tools like calipers and gauges to confirm dimensions. This initial quality control (IQC) helps prevent downstream issues during assembly.
How Are the Components Formed During Production?
Following material preparation, the next step is forming the components of the conveyor system. This involves techniques such as cutting, bending, and welding to create the required shapes and sizes of tracks, trolleys, and other components.
Advanced technologies like CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often employed for precision cutting and shaping, which ensures that parts fit together seamlessly. Additionally, the use of automated welding processes enhances consistency and reduces human error, which is crucial for maintaining the structural integrity of the conveyor system.

Illustrative image related to power and free conveyor
What Does the Assembly Process Entail?
Once the components are formed, they are assembled into the final product. This stage typically involves both manual and automated processes, depending on the complexity of the conveyor system.
During assembly, components such as pusher dogs, trolleys, and drive units are integrated into the overall design. Each assembly line should follow specific work instructions to ensure accuracy and consistency. Quality checkpoints, known as in-process quality control (IPQC), are established to monitor the assembly process. These checkpoints verify that components are correctly installed and functioning as intended.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Enhance Quality?
The finishing stage involves applying protective coatings, such as paint or powder coating, which enhance the conveyor’s resistance to wear and environmental damage. This step is essential, particularly for conveyors operating in harsh conditions, such as those found in the automotive or heavy manufacturing industries.
Before final assembly, components undergo a thorough cleaning process to remove any contaminants that could affect coating adhesion. Once the coatings are applied, additional quality checks are performed to ensure uniformity and adherence to specifications.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality assurance is a crucial aspect of the manufacturing process for power and free conveyors, ensuring that the final product meets international and industry-specific standards.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with several key international standards, such as ISO 9001, which governs quality management systems. Compliance with ISO standards indicates that a manufacturer has established processes to ensure consistent product quality and continuous improvement.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in Europe and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for equipment used in oil and gas applications may also be relevant. These certifications reflect adherence to safety and performance guidelines, enhancing buyer confidence.
What Quality Control Checkpoints Are Essential?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Assessing raw materials before they enter the production process.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring assembly and manufacturing at various stages to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting comprehensive testing of the completed conveyor systems to ensure they meet all design specifications and performance criteria.
Common testing methods include load testing, functional testing, and visual inspections to ensure all components operate correctly and meet load capacities.
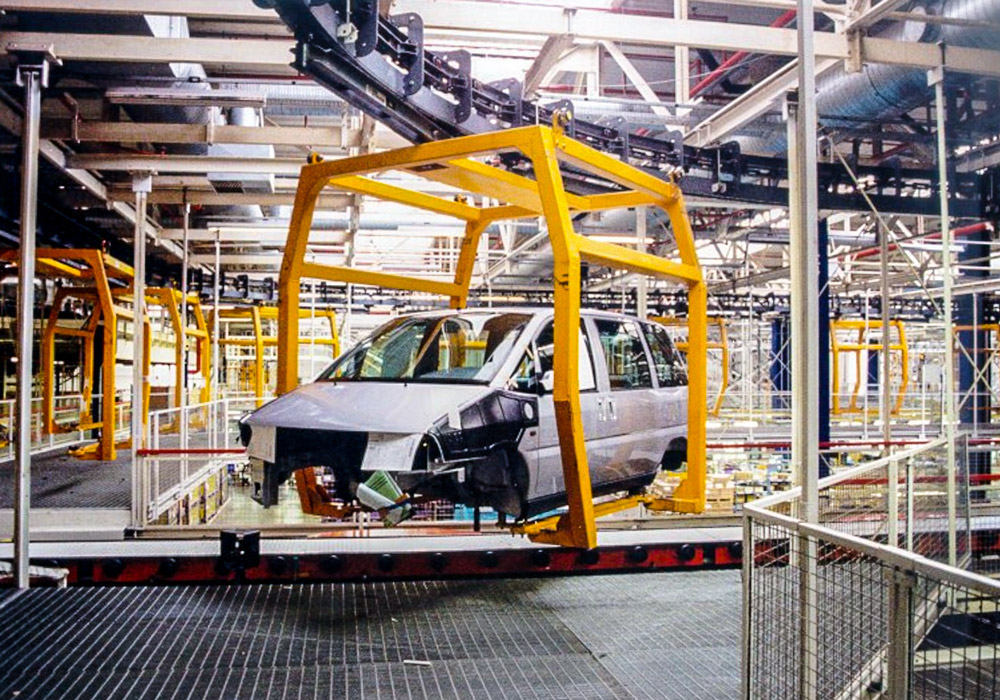

Illustrative image related to power and free conveyor
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Assurance Practices?
B2B buyers need to ensure that their suppliers maintain robust quality assurance practices. Here are some actionable steps to achieve this:
What Are the Best Practices for Conducting Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is a practical approach to verify quality assurance processes. Buyers should request to review the supplier’s quality management system documentation, including ISO certifications and internal audit reports.
On-site visits can provide insights into the manufacturing environment and the effectiveness of quality control measures. During these visits, buyers should evaluate the cleanliness of the facility, the condition of machinery, and the qualifications of the workforce.
How Can Buyers Use Third-Party Inspections to Ensure Quality?
Engaging third-party inspection agencies can further validate a supplier’s quality assurance claims. These agencies can conduct independent assessments at various stages of production, providing impartial reports on material quality, manufacturing processes, and adherence to specifications.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several nuances may impact quality assurance:
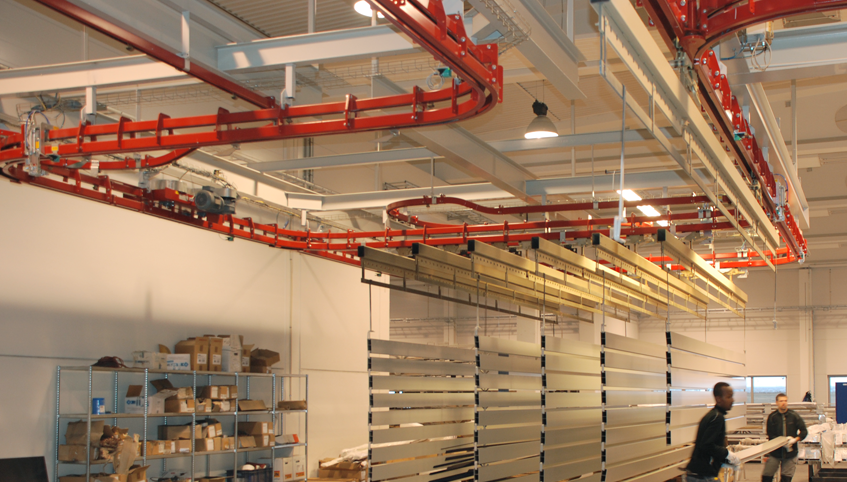

Illustrative image related to power and free conveyor
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that products meet local regulations and standards in the buyer’s country.
- Cultural Differences: Be aware of potential differences in manufacturing practices and quality expectations across different regions.
- Logistical Challenges: Assess how transportation and shipping can impact product quality upon delivery, including potential for damage during transit.
Understanding these factors can help buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for power and free conveyors, ultimately leading to successful procurement and operational efficiency.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘power and free conveyor’
This guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in procuring power and free conveyors, a versatile solution for automated material handling. By following this step-by-step checklist, you can ensure that your selection process is thorough, efficient, and tailored to your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline your technical requirements. Consider factors such as load capacity, conveyor layout, and the types of products you will be handling. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure the system is tailored to your operational needs.
- Load Capacity: Identify the weight range of products to be transported, as power and free conveyors can handle varying loads from light to heavy-duty applications.
- Layout Requirements: Determine whether you need an overhead or inverted configuration based on your facility’s space and workflow.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers in the market. Look for companies with a proven track record in manufacturing power and free conveyors and those that can customize solutions for your specific application.
- Industry Experience: Choose suppliers that have experience in your industry, as they will better understand your unique challenges.
- Client Testimonials: Seek out reviews and case studies to gauge customer satisfaction and the supplier’s ability to deliver on promises.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers possess the necessary certifications and compliance with international standards. This step is crucial for quality assurance and safety in operations.
- Quality Management Systems: Look for ISO certifications, which indicate adherence to quality standards.
- Safety Compliance: Verify compliance with safety regulations relevant to your industry, such as ATEX for explosive environments or high-temperature standards for curing processes.
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed proposals that outline their approach to your project. This should include technical specifications, timelines, and pricing.
- Customization Options: Ensure the proposal addresses your specific needs, including any custom components or integration with existing systems.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate not just the initial costs but also the long-term operational costs, including maintenance and energy consumption.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Maintenance Services
Consider the level of after-sales support and maintenance services offered by the supplier. Effective support can significantly impact the longevity and efficiency of your conveyor system.
- Warranty and Service Agreements: Check what warranties are provided and whether service agreements are available to ensure ongoing support.
- Training Programs: Inquire if the supplier offers training for your staff on system operation and maintenance, which can minimize downtime.
Step 6: Conduct Site Visits and Product Demonstrations
If possible, visit the supplier’s facility to see their systems in action. A demonstration of the power and free conveyor can provide valuable insights into its performance and suitability for your needs.
- Real-World Applications: Observe how the conveyor operates with products similar to yours.
- System Flexibility: Evaluate the ease of adjustments and modifications during the demonstration to understand the system’s adaptability.
Step 7: Finalize the Contract and Payment Terms
After selecting a supplier, carefully review and finalize the contract. Ensure that all terms, including delivery schedules, payment terms, and conditions for changes, are clearly defined.
- Clear Milestones: Establish clear project milestones to track progress.
- Payment Structures: Understand the payment terms, including deposits and final payments, to ensure they align with your budgetary constraints.
By following this checklist, you can navigate the procurement process for power and free conveyors with confidence, ensuring that you choose a solution that meets your operational requirements and supports your business goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for power and free conveyor Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Power and Free Conveyor Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of power and free conveyors is essential for B2B buyers seeking to optimize their procurement processes. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts the cost. High-quality steel or aluminum tracks and components may be more expensive upfront but can enhance durability and longevity. Customization options, such as specialized coatings for corrosion resistance, also affect material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the conveyor system and the location of manufacturing. Skilled labor may be required for assembly, particularly for customized systems or unique configurations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation associated with production. Suppliers often factor these into the final pricing, which can vary based on their operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling required for specific conveyor configurations can lead to increased costs. Suppliers may require a one-time investment in tooling, which can be amortized over larger orders.
-
Quality Control: Rigorous QC processes ensure reliability and performance but can add to the overall cost. Buyers should consider suppliers with established certifications, as these can indicate higher quality assurance standards.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs depend on the shipping method, distance, and weight of the conveyor system. International shipping may involve additional tariffs and duties, which can further influence the total cost.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins can vary based on market competition, exclusivity of technology, and service levels. Understanding these factors can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Power and Free Conveyor Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of power and free conveyors, making it crucial for buyers to evaluate their specific needs and circumstances.
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often offer better pricing for bulk orders or higher minimum order quantities (MOQs). Buyers should assess their requirements to leverage potential discounts.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs tailored to specific operational needs can increase costs. Buyers must balance the necessity for customization against budget constraints.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO) may command a premium. However, investing in quality can reduce maintenance costs and downtime in the long run.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and experience can impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer better reliability and service, justifying a higher price.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of sale, including delivery responsibilities and risk transfer, is crucial for international transactions. Incoterms can affect the overall cost structure and should be clearly negotiated.
What Negotiation Strategies Can Buyers Use for Cost-Efficiency?
Effective negotiation strategies are vital for achieving cost-efficiency in power and free conveyor sourcing.
-
Leverage Volume: Buyers should consolidate orders to increase volume, thereby negotiating lower prices based on higher quantities.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Engaging with multiple suppliers can create competitive pressure, often leading to better pricing and terms.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on the purchase price, buyers should evaluate the TCO, which includes installation, maintenance, and operational costs over the conveyor’s lifespan. This holistic view can justify a higher upfront investment if long-term savings are evident.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of currency fluctuations, local market conditions, and the impact of tariffs. These factors can significantly influence final costs and should be factored into negotiations.
Conclusion and Disclaimer
While this analysis provides valuable insights into the cost structure and pricing factors associated with power and free conveyors, it is essential to note that prices can vary widely based on specific project requirements and market conditions. Always consult multiple suppliers and consider obtaining quotes tailored to your unique needs to ensure the best value for your investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing power and free conveyor With Other Solutions
Introduction: What Are the Alternatives to Power and Free Conveyors?
In the realm of material handling solutions, power and free conveyors stand out for their flexibility and efficiency. However, various alternatives exist that may better suit specific operational needs. Understanding these alternatives allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions when selecting the right conveyor system for their manufacturing or assembly processes.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Power And Free Conveyor | Tow Conveyor | Belt Conveyor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High flexibility with asynchronous operation | Good for continuous flow, less flexibility | Efficient for bulk material handling |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment; long-term savings | Lower initial costs; moderate operating costs | Low initial costs; high maintenance over time |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires custom engineering; moderate complexity | Easier to install; less customization needed | Generally straightforward installation |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance of tracks and components | Lower maintenance needs; fewer moving parts | Regular belt replacements; moderate upkeep |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for complex manufacturing processes requiring part sorting | Suitable for assembly lines with consistent product flow | Best for transporting bulk materials over long distances |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Tow Conveyor: What Are Its Advantages and Disadvantages?
Tow conveyors operate on a similar principle to power and free systems but are more straightforward. They move loads along a fixed path using a towline. The main advantage of tow conveyors is their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation, making them suitable for assembly lines that require consistent flow without the need for complex sorting. However, they lack the flexibility of power and free systems, limiting their use in environments that require frequent changes in product routing or handling.
Belt Conveyor: What Makes It a Common Choice?
Belt conveyors are one of the most commonly used material handling solutions, particularly in bulk material transport. They are characterized by their simplicity and low initial costs, which make them appealing for many operations. However, they are less versatile than power and free conveyors, especially in scenarios requiring product sorting or accumulation. Maintenance can also be a concern, as belts can wear out and require replacement, potentially leading to downtime.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Conveyor Solution?
Selecting the appropriate conveyor system involves evaluating your specific operational needs, including the type of materials being handled, the required flexibility, and budget constraints. Power and free conveyors excel in environments demanding high flexibility and custom solutions, while tow and belt conveyors offer cost-effective options for more straightforward applications. By carefully considering the unique requirements of your operations, B2B buyers can make a well-informed decision that optimizes efficiency and productivity in their material handling processes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for power and free conveyor
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Power and Free Conveyors?
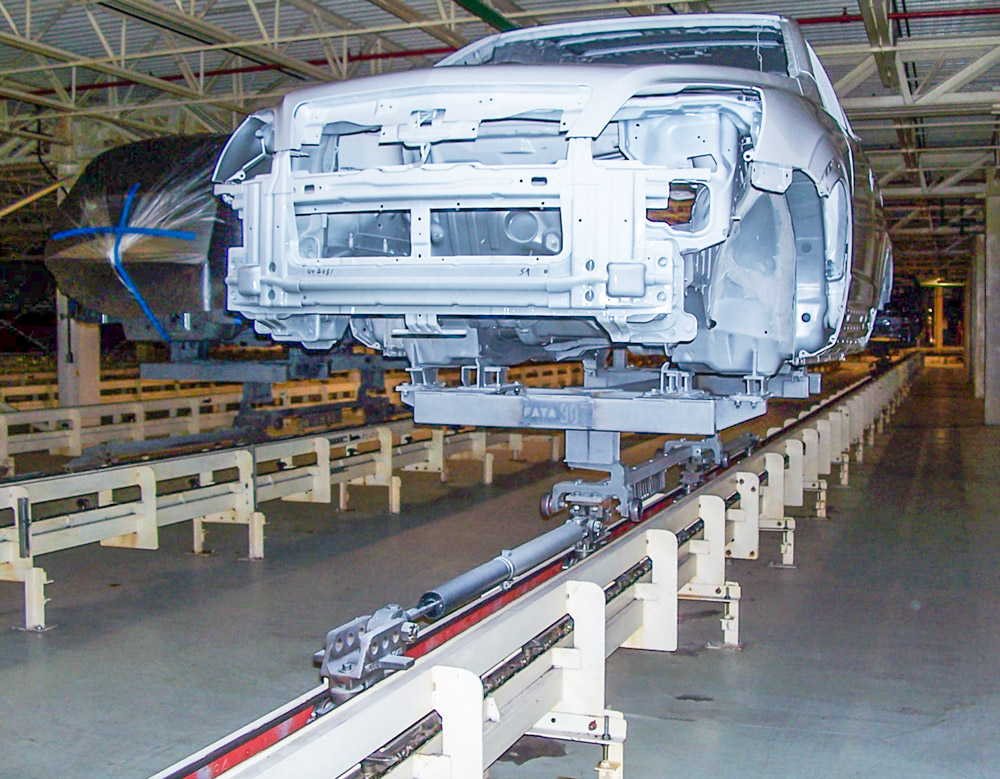
1. Load Capacity
Load capacity refers to the maximum weight that the conveyor system can safely transport. Power and free conveyors can typically handle loads ranging from 25 lbs to 40,000 lbs, depending on the design and application. Understanding load capacity is critical for B2B buyers, as it ensures that the conveyor can accommodate the specific weight requirements of their products without risking damage or operational failure.
Illustrative image related to power and free conveyor
2. Track Configuration
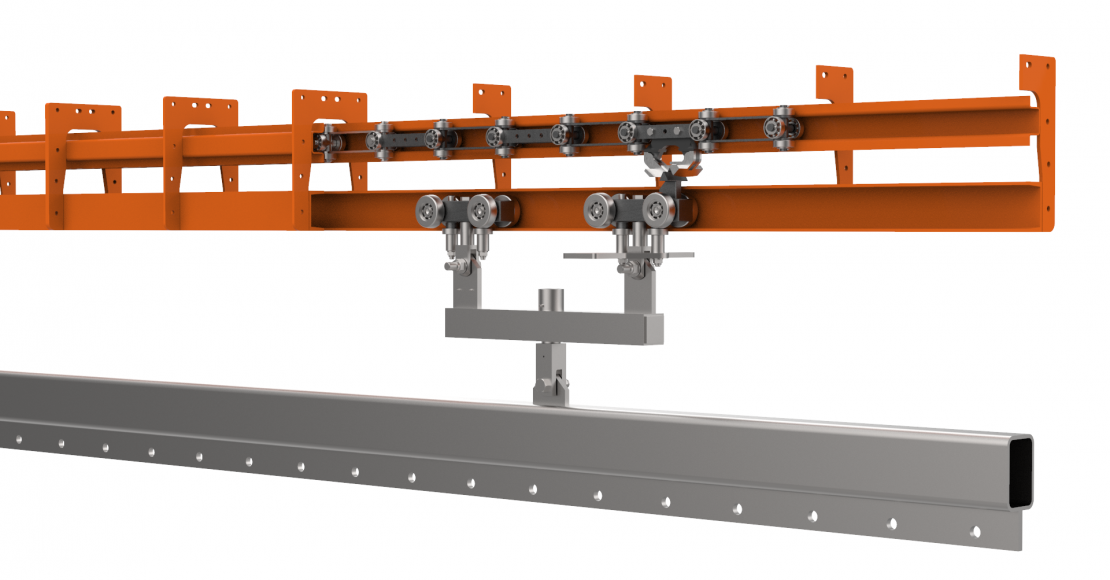
Power and free conveyors utilize a twin-track system—one for the powered chain and another for free-moving trolleys. This configuration allows for flexibility in layout design, enabling businesses to optimize their production space. B2B buyers should consider the track design that best suits their operational needs, as it affects the flow of materials and overall efficiency.
3. Drive Mechanism
The drive mechanism is the system responsible for moving the powered chain. Common types include caterpillar drives and screw drive units, each with different operational characteristics. The choice of drive mechanism impacts energy efficiency, maintenance needs, and overall system performance. Buyers should evaluate these aspects to align with their operational goals and budget constraints.
4. Control System
An advanced control system, often featuring a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) and a user-friendly interface, is essential for managing the operation of power and free conveyors. This system allows for real-time monitoring and control of various conveyor functions, enhancing automation and reducing manual intervention. For B2B buyers, investing in a sophisticated control system can lead to increased productivity and reduced downtime.
5. Material Grade and Durability
The materials used in the construction of power and free conveyors can significantly affect their longevity and performance. High-grade steel or specialized alloys are often used to ensure durability under heavy loads and harsh conditions. Buyers must consider the material quality to prevent premature wear and tear, which can lead to costly repairs and disruptions in production.
What Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Understand for Power and Free Conveyors?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of power and free conveyors, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and gauge the quality of components used in their systems.

Illustrative image related to power and free conveyor
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. For buyers, being aware of MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, as it affects purchasing decisions and can influence cash flow, particularly for companies operating on tight budgets or those just starting.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that solicits price quotes from suppliers for specific goods or services. When sourcing power and free conveyors, B2B buyers should use RFQs to ensure they receive competitive pricing and to clarify specifications, which helps streamline the procurement process.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs, risk management, and delivery responsibilities, ensuring smoother transactions in the global marketplace.
Illustrative image related to power and free conveyor
5. Turnkey Solution
A turnkey solution refers to a system that is delivered complete and ready for immediate use. This term is particularly relevant for power and free conveyors, as many suppliers offer turnkey installations that save buyers time and resources, allowing them to focus on their core operations.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies is essential for B2B buyers looking to invest in power and free conveyor systems. By grasping these concepts, companies can make informed decisions that optimize their operational efficiency and align with their strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the power and free conveyor Sector
What Are the Current Trends Driving the Power and Free Conveyor Market?
The power and free conveyor market is currently witnessing dynamic growth driven by several global factors. The rise of automation in manufacturing processes is a significant catalyst, as industries seek to improve efficiency and reduce operational costs. This has led to increased demand for flexible conveyor systems that can adapt to varying production needs. Furthermore, the need for customized solutions tailored to specific applications—such as assembly lines, paint shops, and logistics—has become prominent among international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Emerging technologies such as IoT-enabled systems and advanced control mechanisms are reshaping sourcing trends. These innovations allow for real-time monitoring and control, enhancing operational efficiency. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can offer integrated solutions that include automated controls and advanced analytics capabilities, which facilitate predictive maintenance and reduce downtime. Additionally, as global supply chains become more interconnected, the emphasis on sourcing from reputable manufacturers with proven track records is intensifying, ensuring quality and reliability.
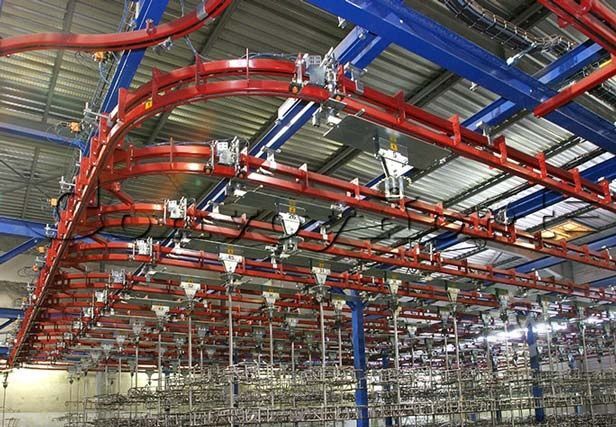

Illustrative image related to power and free conveyor
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Power and Free Conveyor Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal consideration in the procurement of power and free conveyors. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting buyers to seek suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices. This includes the use of recyclable materials and energy-efficient technologies in the production of conveyor systems.
Ethical sourcing is equally crucial, with many companies adopting stringent supplier evaluation criteria to ensure compliance with social and environmental standards. Buyers are increasingly favoring suppliers with green certifications, such as ISO 14001, which indicates a commitment to minimizing environmental footprints. Incorporating sustainable practices not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Moreover, as regulatory pressures around environmental sustainability rise globally, companies that proactively adopt sustainable practices in their conveyor systems are more likely to gain a competitive advantage. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers from regions like Europe, where regulatory frameworks increasingly favor sustainable manufacturing practices.
What Is the Evolution of Power and Free Conveyor Systems in B2B Context?
The power and free conveyor system has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially developed as a solution to enhance efficiency in material handling, these systems have transformed with advancements in technology and changing market demands. The early designs focused on basic functionality, primarily facilitating the movement of materials along a fixed path.
Over the decades, innovations in automation and control technologies have led to the development of modular and customizable systems that cater to diverse industrial applications. Modern power and free conveyors now incorporate advanced features such as asynchronous operation, allowing individual carriers to stop and start independently, thus enhancing flexibility in production lines. This evolution reflects the growing need for adaptive manufacturing solutions that can meet the demands of an increasingly complex global market.
As the industry continues to innovate, the focus on integrating smart technologies will likely shape the future of power and free conveyors, making them an essential component for B2B buyers seeking to optimize their operations and remain competitive in the global marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of power and free conveyor
-
How do I determine the right specifications for a Power and Free conveyor system?
To identify the appropriate specifications for a Power and Free conveyor, begin by assessing your operational needs, including load capacity, speed, and product dimensions. Consider the layout of your facility to optimize the design for space efficiency and workflow. Additionally, consult with suppliers who can provide insights based on similar applications and industry standards. Customization options, such as track configurations and drive systems, should also be discussed to ensure the system aligns with your specific production processes. -
What are the key advantages of using a Power and Free conveyor system in my operation?
Power and Free conveyors offer numerous advantages, including flexibility in processing, efficient space utilization, and the ability to handle varying load sizes. The asynchronous operation allows individual carriers to stop or move at different speeds, enhancing line efficiency and reducing bottlenecks. Moreover, these systems can be tailored to fit specific manufacturing processes, such as painting, assembly, or buffering, making them versatile for various industries. -
What customization options are available for Power and Free conveyor systems?
Customization options for Power and Free conveyors include track layout, carrier design, and control systems. Suppliers can engineer systems to accommodate specific product dimensions and handling requirements, including specialized trolleys for unique loads. Additionally, features like automated stop stations, pneumatic switches, and lubrication units can be integrated based on operational needs. Discussing your requirements with manufacturers will help ensure that the system is tailored to your production processes. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for a Power and Free conveyor system?
Minimum order quantities for Power and Free conveyor systems can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and the complexity of the system. Generally, MOQs may range from a single unit for standard configurations to larger quantities for custom solutions. It’s essential to communicate your specific needs to suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and negotiate terms that align with your production requirements. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing Power and Free conveyors internationally?
Payment terms for international procurement of Power and Free conveyors typically include options like upfront deposits, milestone payments, or net payment terms upon delivery. Many suppliers may request a 30% deposit upon order confirmation, with the balance due prior to shipment or upon installation. It is advisable to clarify payment terms during negotiations to avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction process. -
How can I effectively vet suppliers for Power and Free conveyor systems?
To vet suppliers, research their industry reputation, experience, and customer testimonials. Request case studies or references from previous clients to evaluate their ability to deliver high-quality systems on time. Additionally, consider their certifications, manufacturing capabilities, and after-sales support. Engaging in direct conversations with potential suppliers can also provide insight into their responsiveness and willingness to meet your specific needs. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing Power and Free conveyors?
Logistics for importing Power and Free conveyors involve assessing shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Ensure that your supplier provides clear shipping documentation and complies with international shipping standards. It’s also crucial to plan for installation and commissioning timelines, as well as any training required for your staff. Collaborating with experienced logistics partners can help streamline the import process and mitigate potential delays. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for my Power and Free conveyor system?
Quality assurance can be ensured by establishing clear specifications and standards with your supplier before production begins. Request detailed documentation of testing and inspection processes, including certifications for materials used. Additionally, consider arranging for third-party inspections during manufacturing and prior to shipment. Post-installation, regular maintenance schedules and performance evaluations can further guarantee the long-term reliability of the conveyor system.
Top 6 Power And Free Conveyor Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Ultimation – Power and Free Conveyor Systems
Domain: ultimationinc.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Power and Free Conveyor Systems are designed for transporting parts along assembly lines, allowing for automatic stopping and starting of individual loads without halting the entire production line. They can handle loads from 5 pounds to 20,000 pounds and are suitable for demanding industrial environments. Key features include variable chain speeds, high-speed indexing, on-line storage, and adapta…
2. ASI – Power & Free Conveyors
Domain: asi.com
Registered: 1989 (36 years)
Introduction: Power & Free Conveyors: Available in 3, 4, & 6 in. sizes, designed for overhead and inverted applications. Features include:
– Enclosed Track (Autoflex)
– Versatile material handling solution for various product sizes and shapes
– Capabilities: multiple lane selectivity, automated loading/unloading, accumulation of product carriers, tailored modular design
– 3″ Power & Free: 3500# chain pull c…
3. Daifuku – Power & Free Conveyor
Domain: daifuku.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: The Power & Free Conveyor is a chain conveyor system designed for transporting loads along a set path with the ability to stop at predetermined positions. Key features include:
– High flexibility to convey loads at various speeds suitable for processes like painting, assembly, branching, storage, and final assembly.
– Basic structure consists of a power line driving an X-type forged chain and a fr…
4. Webb-Stiles – Power & Free Conveyor Systems
Domain: webb-stiles.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Power & Free Conveyor Systems by Webb-Stiles are designed for flexibility, control, and complex routing. Key features include:
– Dual-track system allowing independent carrier control with a powered chain on one track and free-trolley carriers on another.
– Ability to stop, accumulate, and divert loads independently, making it ideal for high-throughput assembly lines and robotic integration.
– Sma…
5. Pacline – Power and Free Conveyor
Domain: pacline.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Pacline’s Power and Free Conveyor is a medium-capacity conveyor system designed for various manufacturing processes and assembly applications, including painting, curing, sequencing, and buffer storage. Key components include:
– **Power Drive Unit**: Features either an off-line sprocket or in-line caterpillar drive for reliable service, with compact drive height and four hanging points for easy i…
6. Rapid Industries – Conveyor Systems
Domain: rapidindustries.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Rapid Industries offers a range of conveyor systems designed for various industrial applications. Their products include belt conveyors, roller conveyors, and custom conveyor solutions. The systems are engineered for efficiency, durability, and flexibility, catering to different material handling needs. Rapid Industries emphasizes the importance of quality and reliability in their conveyor systems…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for power and free conveyor
As industries globally navigate the complexities of supply chain management, strategic sourcing of power and free conveyors presents an opportunity to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. These systems offer unparalleled flexibility, allowing for customized layouts that can accommodate diverse manufacturing processes—from assembly to painting and buffering. By leveraging the modular design and advanced automation capabilities of power and free conveyors, businesses can optimize their workflow and increase productivity.
Investing in the right conveyor solutions not only streamlines operations but also positions companies to meet the evolving demands of international markets. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to quality and innovation. Evaluating potential partners based on their engineering capabilities and support services will ensure a successful integration of these systems.
Looking ahead, the demand for efficient material handling solutions will only grow. Now is the time for international buyers to act—embracing strategic sourcing as a key driver for competitiveness in an increasingly globalized marketplace. By doing so, you can secure a robust supply chain that supports sustainable growth and adaptability in the face of change.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to power and free conveyor
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.